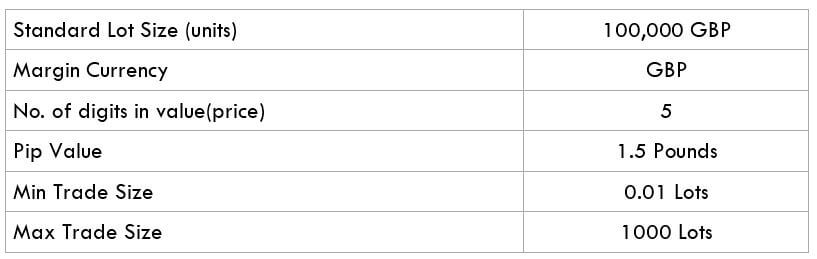
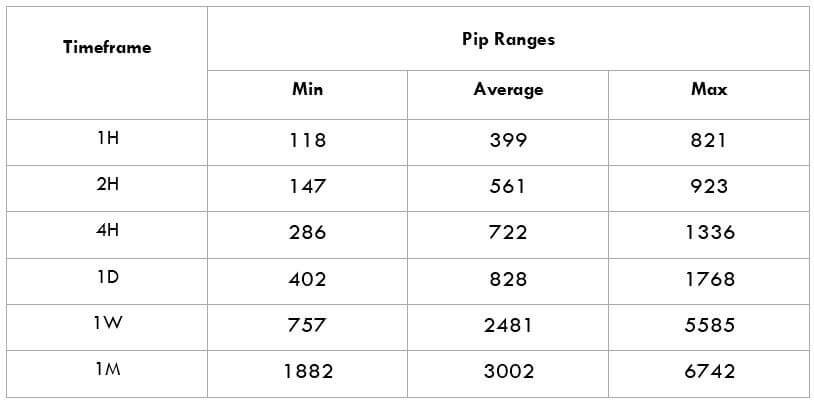
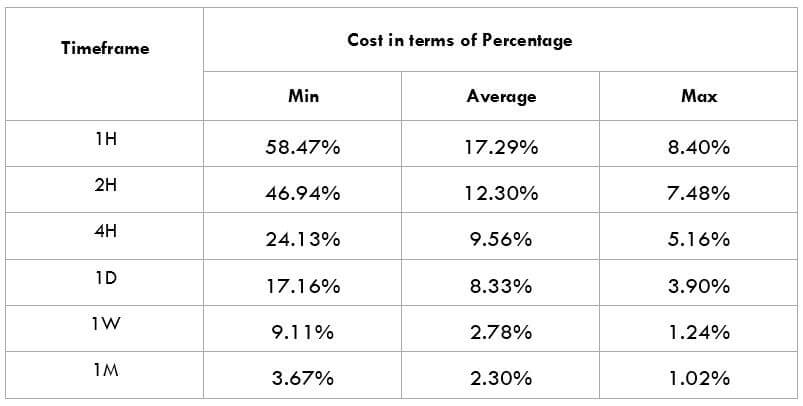
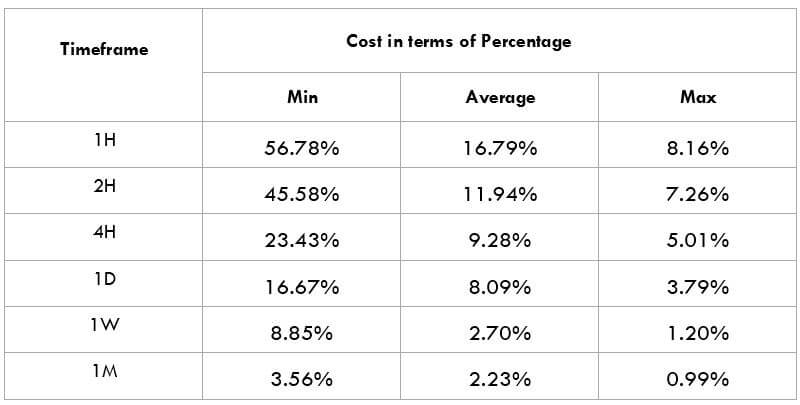
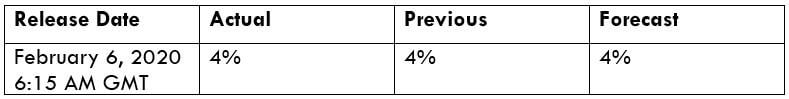
What is the Income Tax?
An Income Tax is a percentage of our income that the government takes in the form of taxes. Income Tax is paid by individuals and entities depending on the level of earning and gains during a financial year. In most of the countries, a single income tax does not usually apply to the entire income, but rather various rates apply to different portions of the “taxable income.” The different tax rates and the income levels at which they apply vary widely.
Types of Income which attracts Tax
Income Tax is a direct tax that is levied on the income and other types of earnings of an individual in a financial year. Below are some types of incomes and taxation rules.
Income from Salary: This includes basic salary, taxable allowances, and profit in lieu of salary, pension received by the person who himself has retired from the service. They all fall under the category of taxable income.
Income from business/profession: This includes presumptive incomes from business and professions that individuals do in their capacity and maybe their part-time work. This is also added to the taxable income after adjustment of the allowed deductions.
Income from properties: A taxable person may also own one or more house properties. These properties can be self-occupied or rented out or even vacant. The rules of Income Tax state that rent from house properties is to be treated for the purpose of calculation of taxable income. An income tax assessee can, however, claim certain deductions for house maintenance in certain areas.
Capital Gains: They are the gains that one makes from selling capital assets like Gold, house properties, stocks, mutual funds, securities, etc. Although capital gains are a part income tax, they are not added to taxable income, as they are taxed at different rates.
Economics and Income Tax
Tax plays a major role in maintaining a balance between people, businesses, and governments, which broadly represents the economic activity of a country. Here are two ways in which changes to Income Tax affects the economic activity and well being of people.
Tax Incentives
By granting incentives, taxes can affect both supply and demand in an economy. Reducing marginal tax rates on wages can motivate workers to work more. Expanding the income tax credit can bring more low-skilled workers into the labor force. Reducing Tax rates can also encourage to employed persons to invest in stocks and bonds, which improves the capital flow of companies.
Budget Deficit
Large Tax cuts can slow economic growth by increasing budget deficits. When the economy is operating at its potential, a sudden reduction in tax rates may provoke the government to borrow capital from foreign investors and institutions. They will also divert some funds allocated to private investment, reducing productive capacity relative to what it could have been. Either way, deficits increase and thus reduce well-being.
The Economic Reports
The Income-tax rates are announced every year by the Finance Ministry during a press release, which puts out all the slabs and tax brackets based on the income level. This is usually the Central Government tax rate, but there is also a yearly announcement made by all the states, which impose income taxes in the same way the federal government does. In some countries, a single tax rate is applicable to everyone, regardless of the income level. This is called a “flat tax.”
Analyzing The Data
Investors, when analyzing a currency Fundamentally, give extreme importance to the Capital Gains tax of that country. Income Tax is not a major concern for investors when taking a position in the market. But a major deviation from the standard Income Tax rates catches the attention of investors. However, if the Federal government has been maintaining a fixed rate over the years without any major changes, there is no reason to worry, as they fell, the economy is stable. However, an increase in Capital Gains tax is not taken well by the institutional investors, which changes their stance on the economy and the currency, mostly to negative.
Impact on the currency
A study conducted by economists examined the impact of taxes on the real exchange rates through their effects on economic activity. Their report says that an increase in the capital interest tax rate leads to depreciation in the currency, while an increase in the wage or consumption tax leads to a real domestic currency appreciation. This hypothesis is supported by the data estimations of annual data from 10 OECD countries over 17 years.
A marginal increase in Income Tax is considered to be good for the economy as it increases the revenue of government organizations, but a substantial increase in tax rate can have a reverse effect on the economy, and this will be unbearable for salaried persons.
Source of information on Income Tax rates
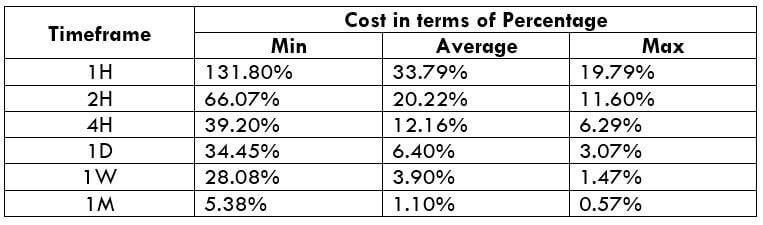
Income Tax rates are available on the official website of the finance department of the country, where one can also find the rates for previous years as well (of more than 30 years). Using this information, a trader can analyze the trend in the Income Tax rates over the years. Here is a list of major countries of the world with their Income Tax rates.
Links to Income Tax information sources
GBP (Sterling) | USD | EUR | CHF | CAD | NZD | JPY
Income Taxes is a compulsory contribution to state revenue, levied by the government on workers’ income and business profits. This gives the ability to the government to provide basic safety and community systems for the public. This ensures freedom and basic living standards that citizens expect. Therefore, it is the duty of citizens to timely file Income Tax returns and be a responsible civilian.
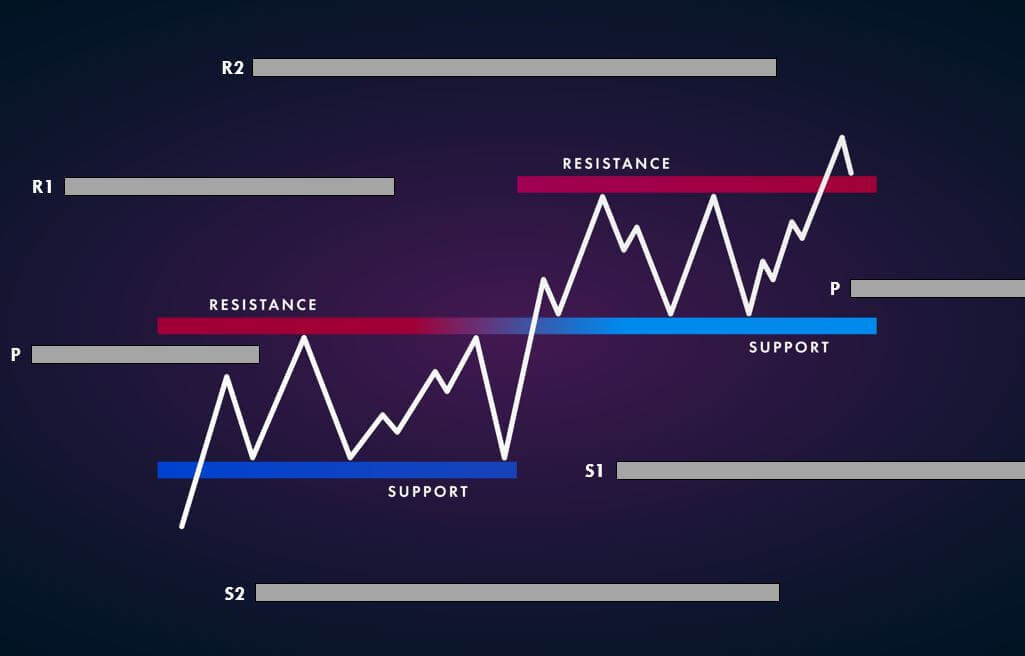
Impact of the Income Tax news release on the price chart
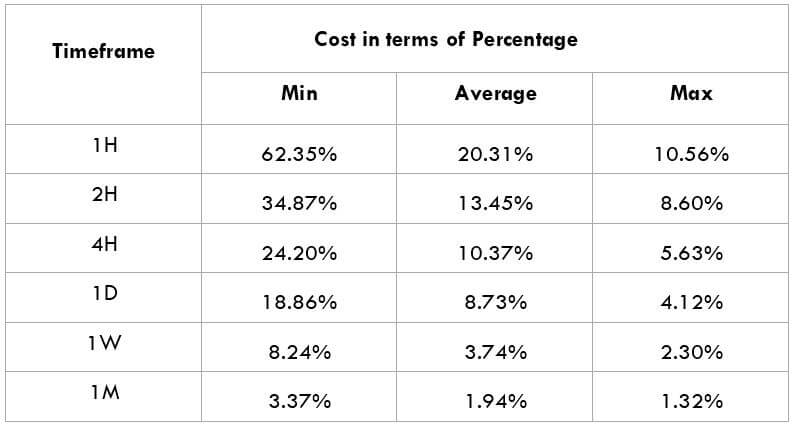
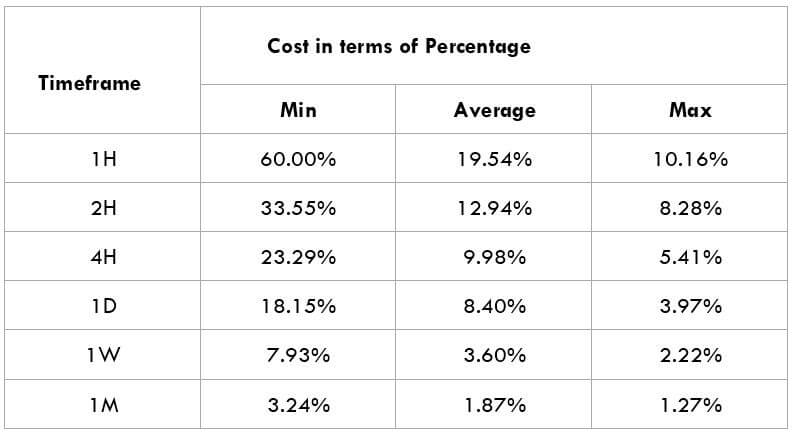
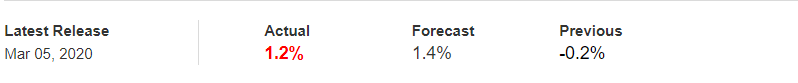
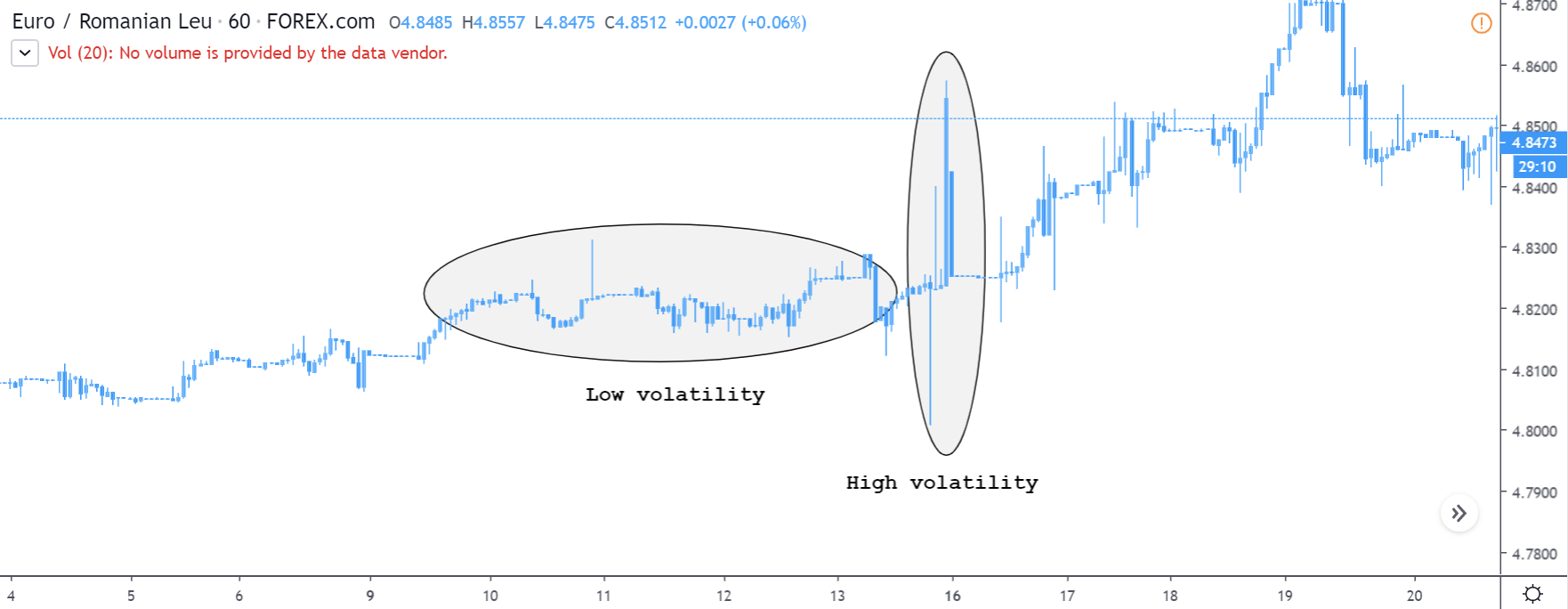
After having a clear understanding of the Income Tax and its role in the economy, we will now extend our discussion and study the impact of the same on the value of a currency. Investors and traders mainly consider the Capital Gains tax rates, which is also a form of Income Tax. Any major changes to the Capital Gains tax cause extreme volatility in the currency pair and a change in the outlook for that currency. Thus, the income tax alone is not explicitly taken into account by traders.

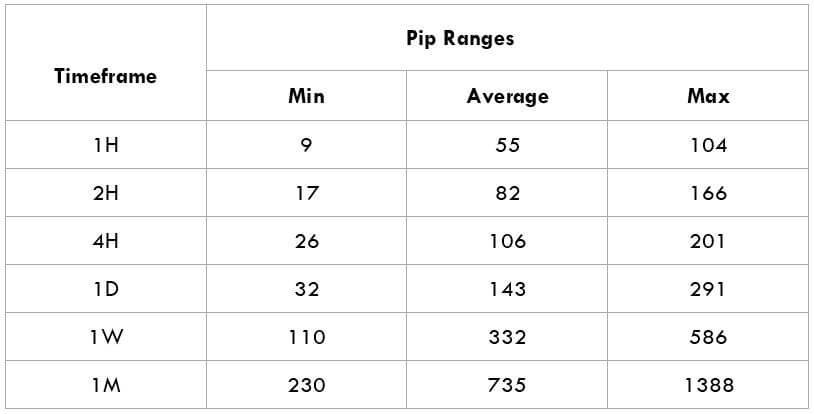
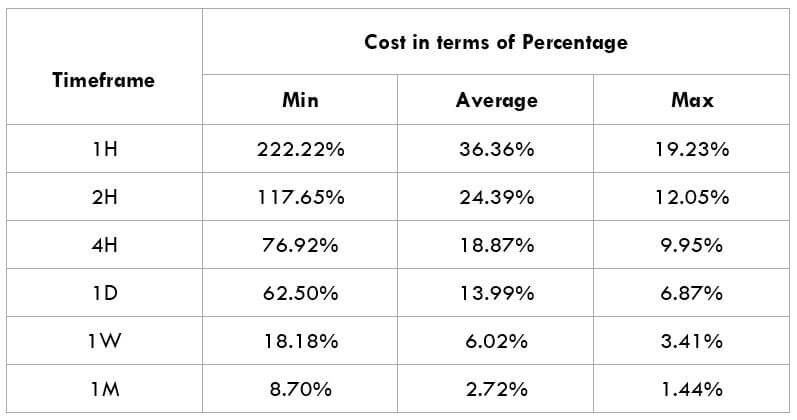
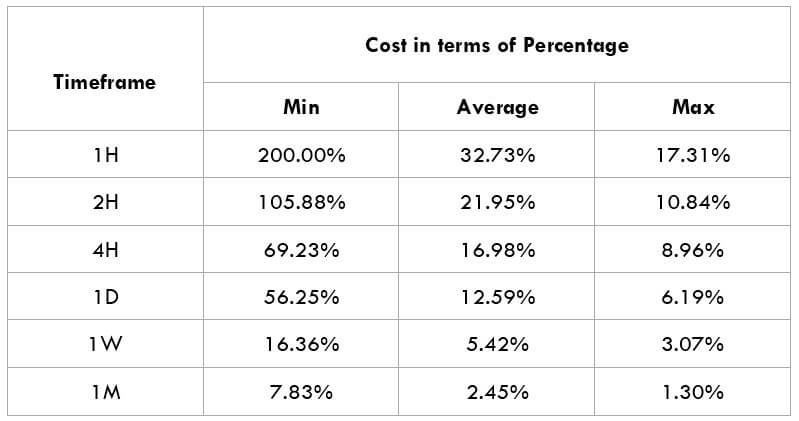
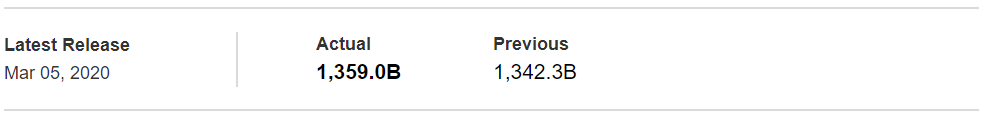
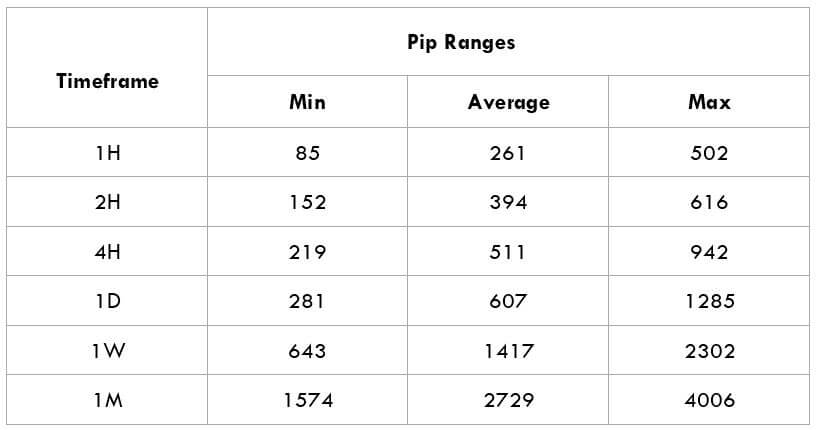
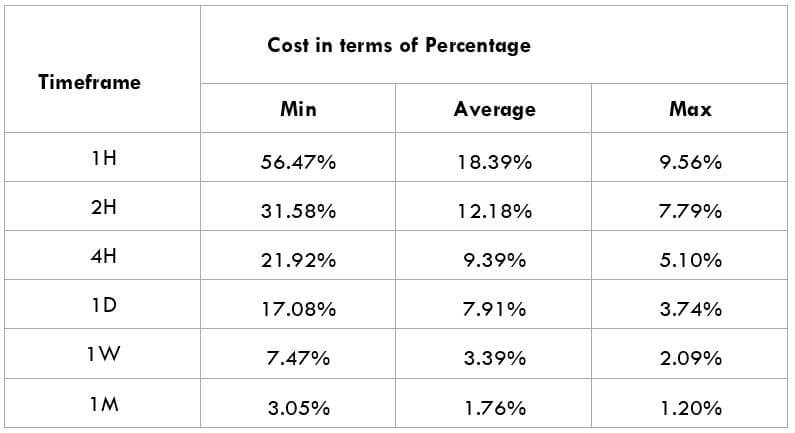
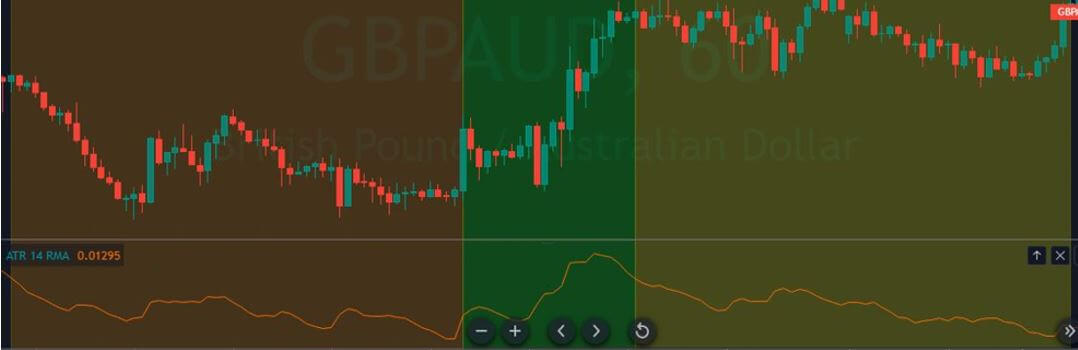
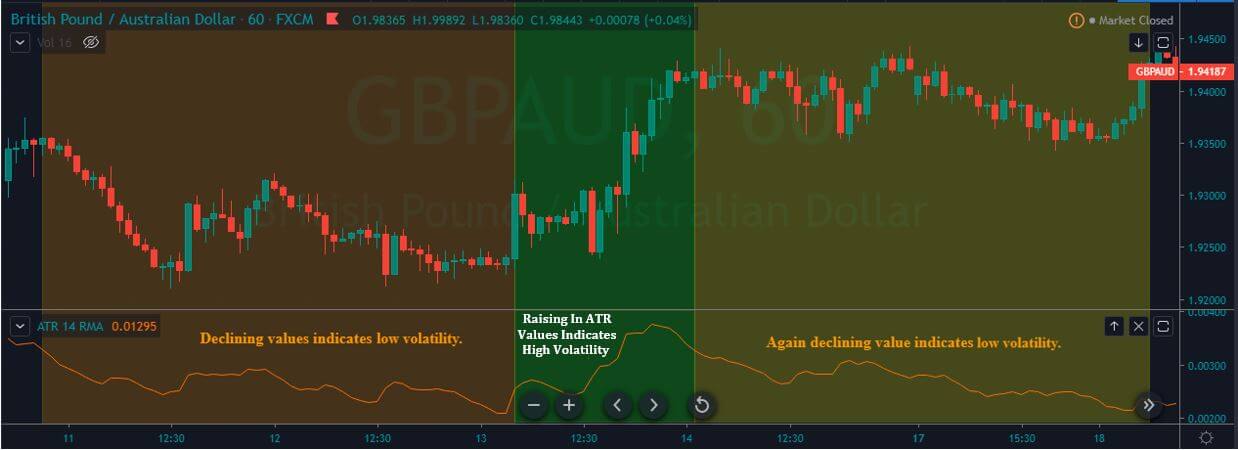
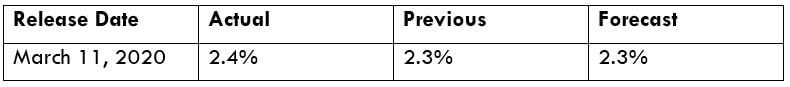
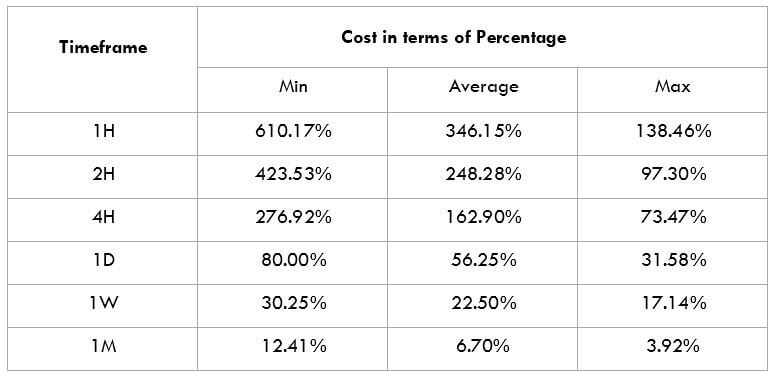
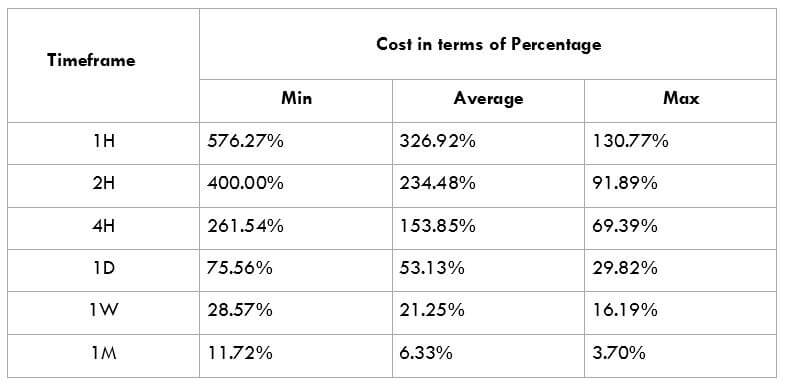
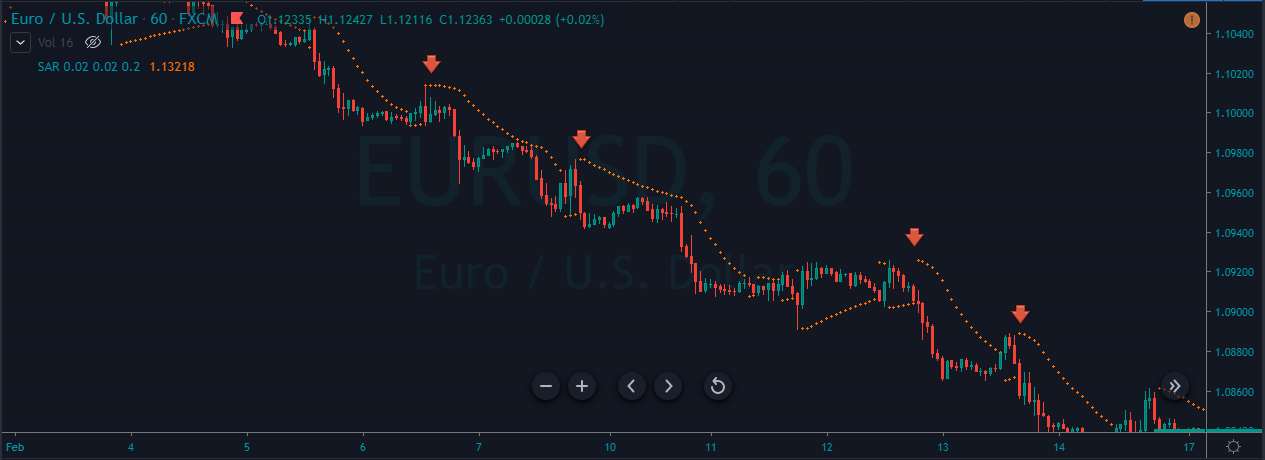
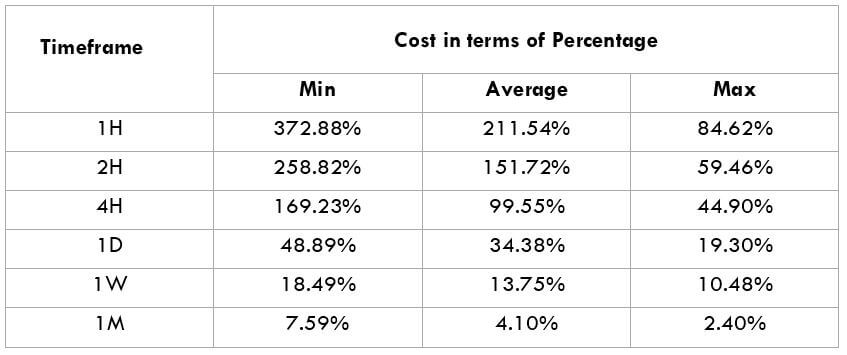
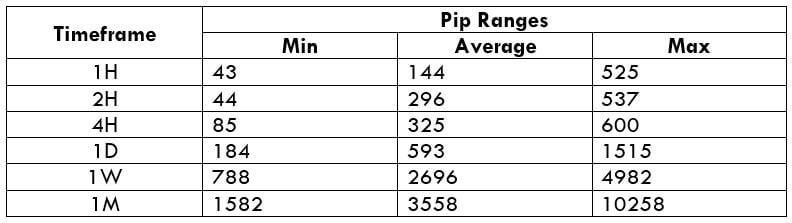
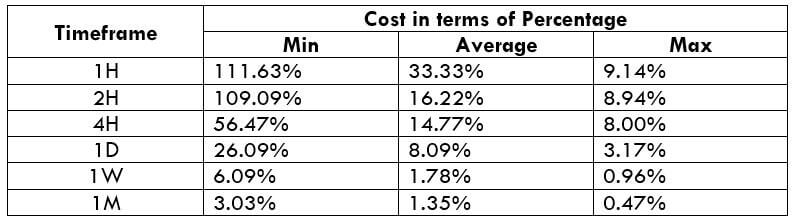
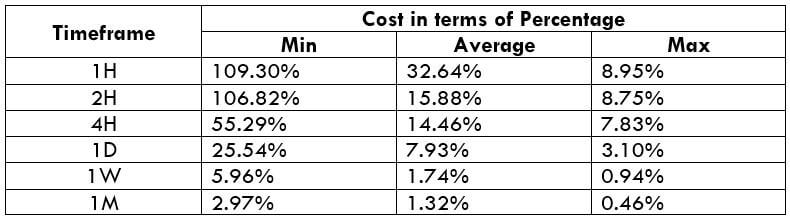
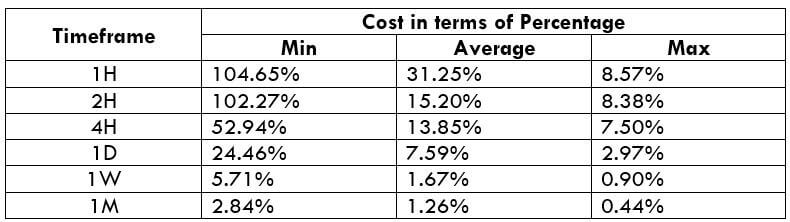
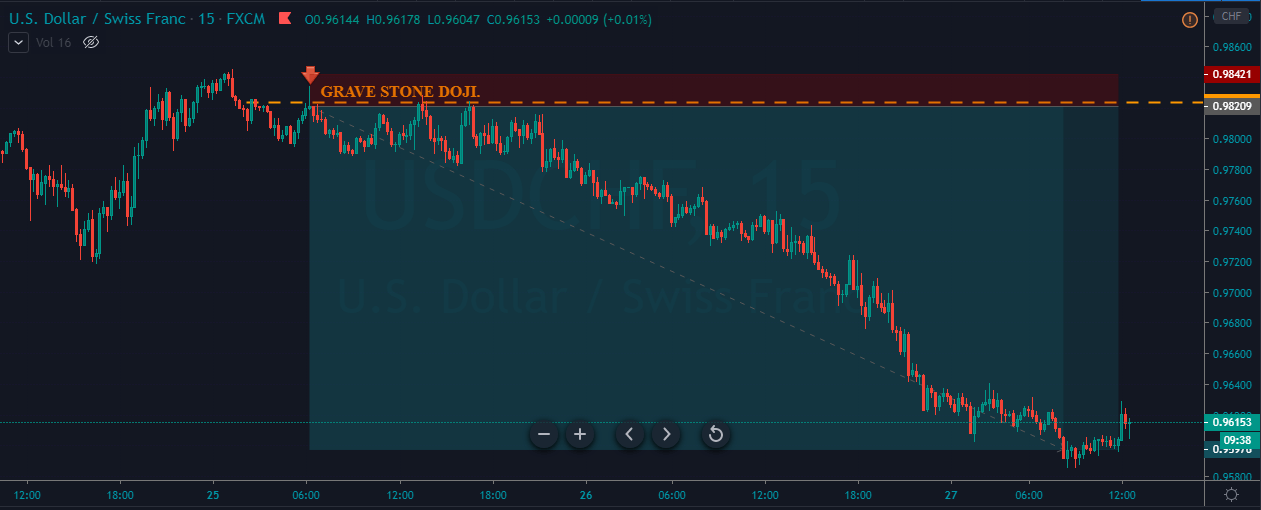
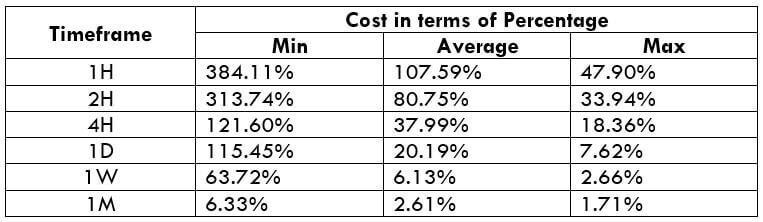
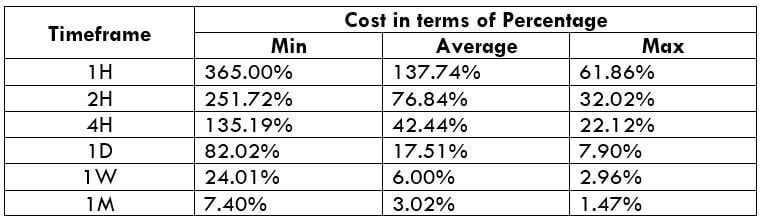
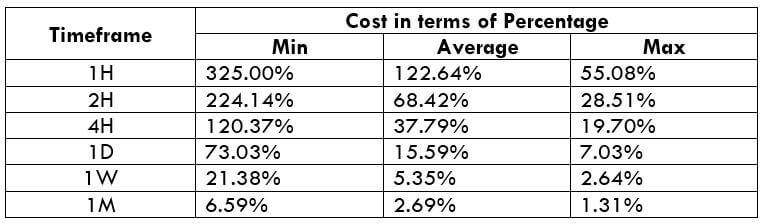
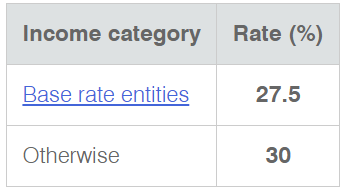
In the upcoming sections, we will analyze the change in volatility in the currency pair due to the announcement of Income Tax rates. The above image shows the Federal Tax rates of Canada for 2020, where we can see the percentage of income that will be levied as Income Tax on individuals of the country. This is also known as ‘Tax Bracket.’ The maximum Income Tax rate stood at 33%, and this rate has been maintained from the past four years. This data is published by the Canada Revenue Agency, where one can find other tax rates as well.
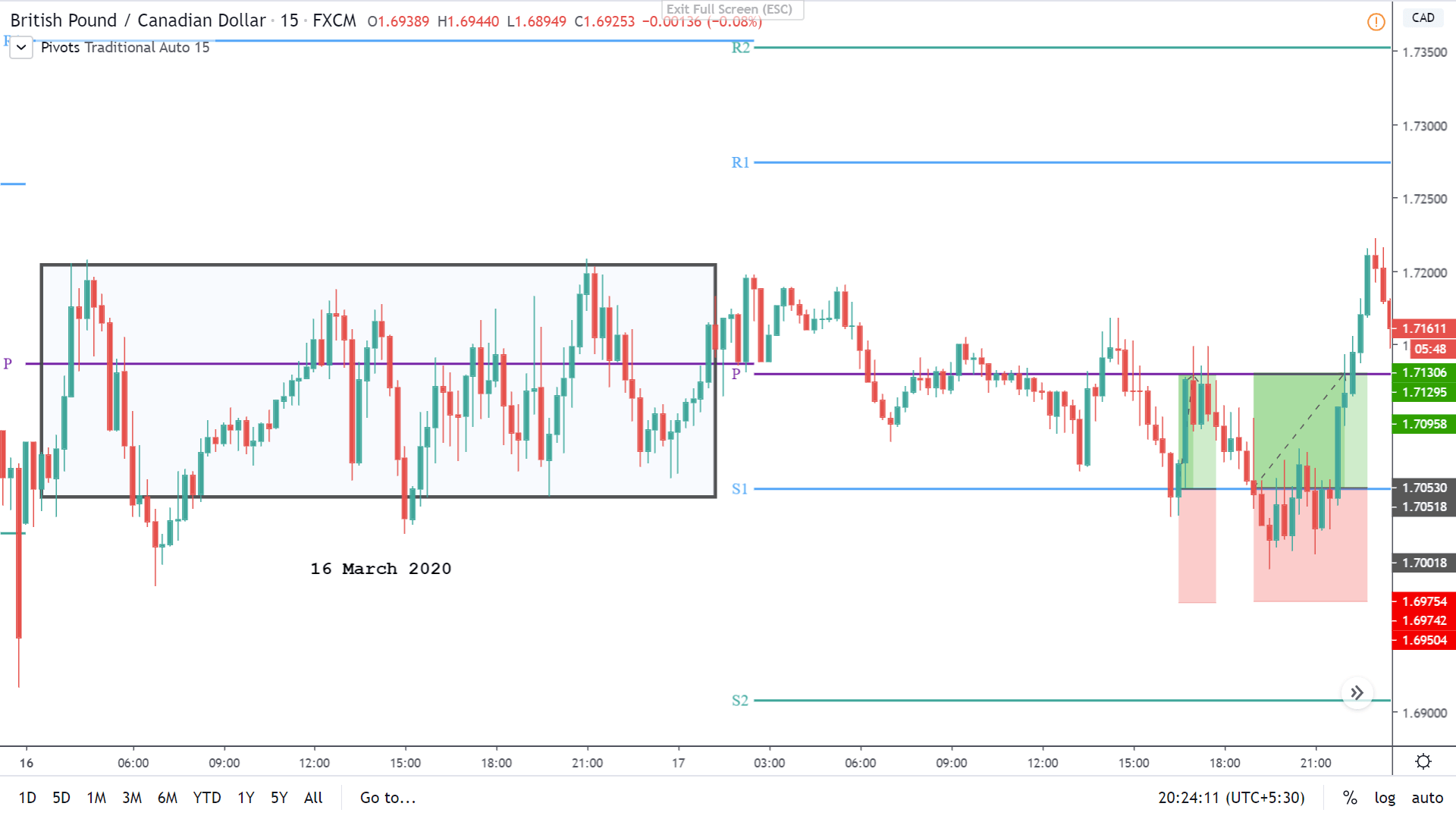
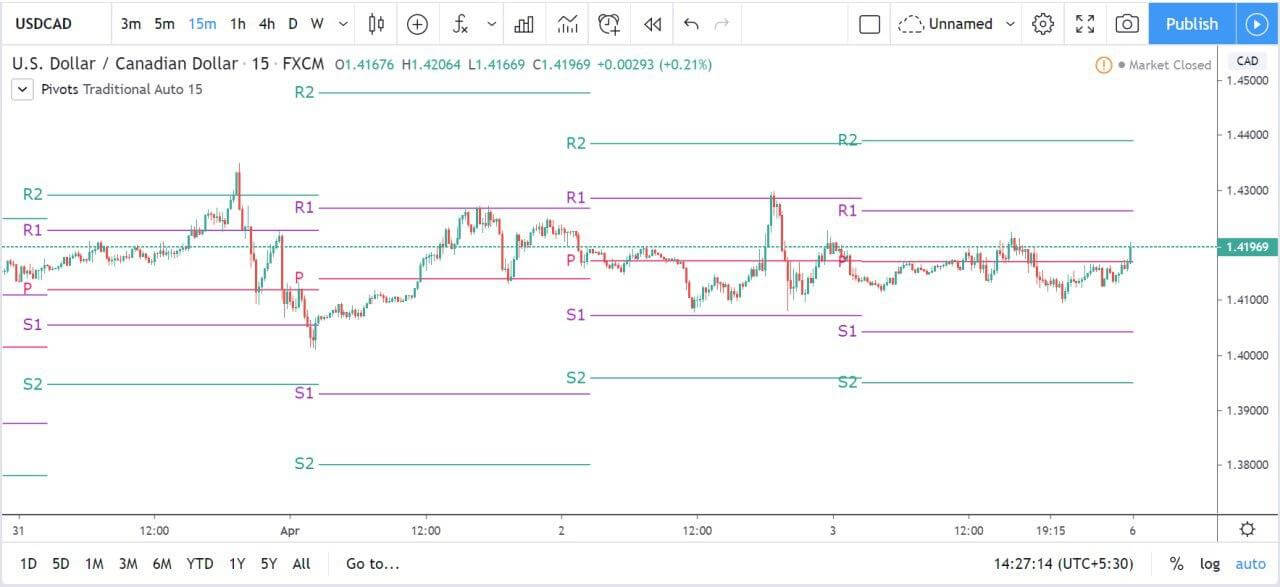
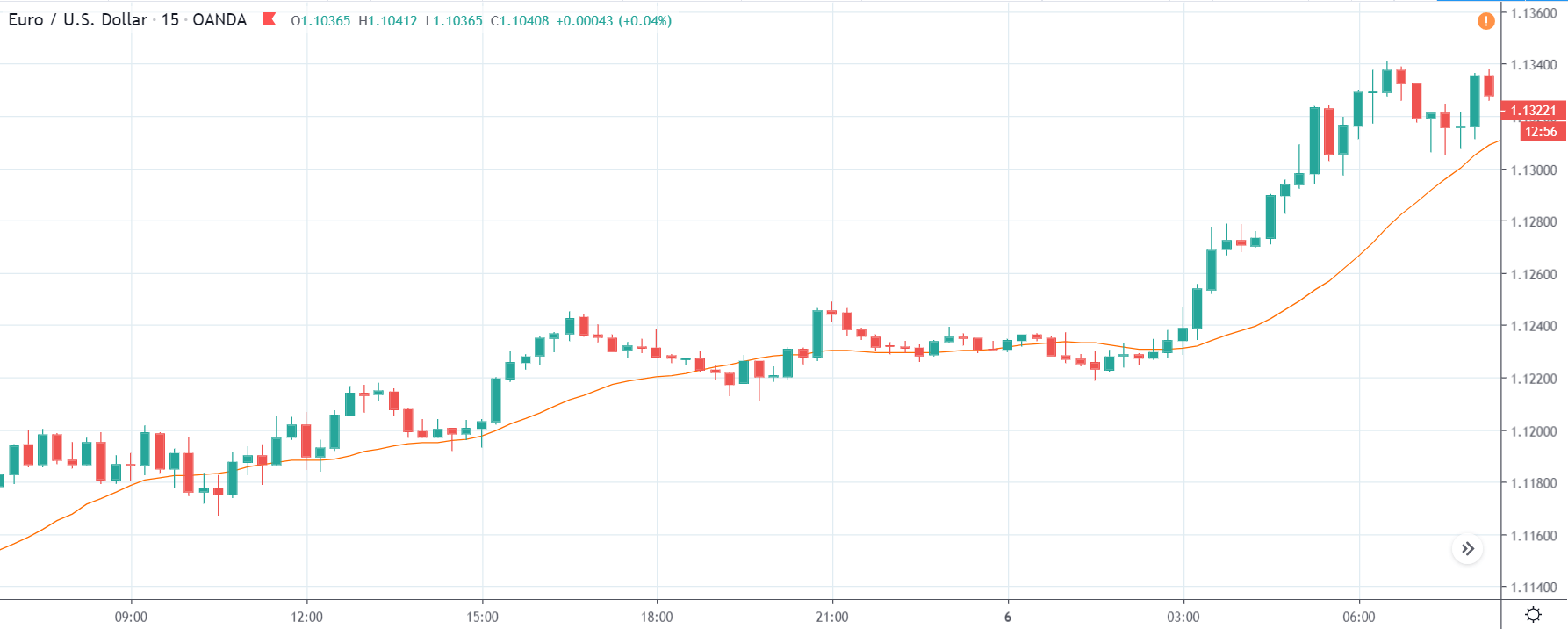
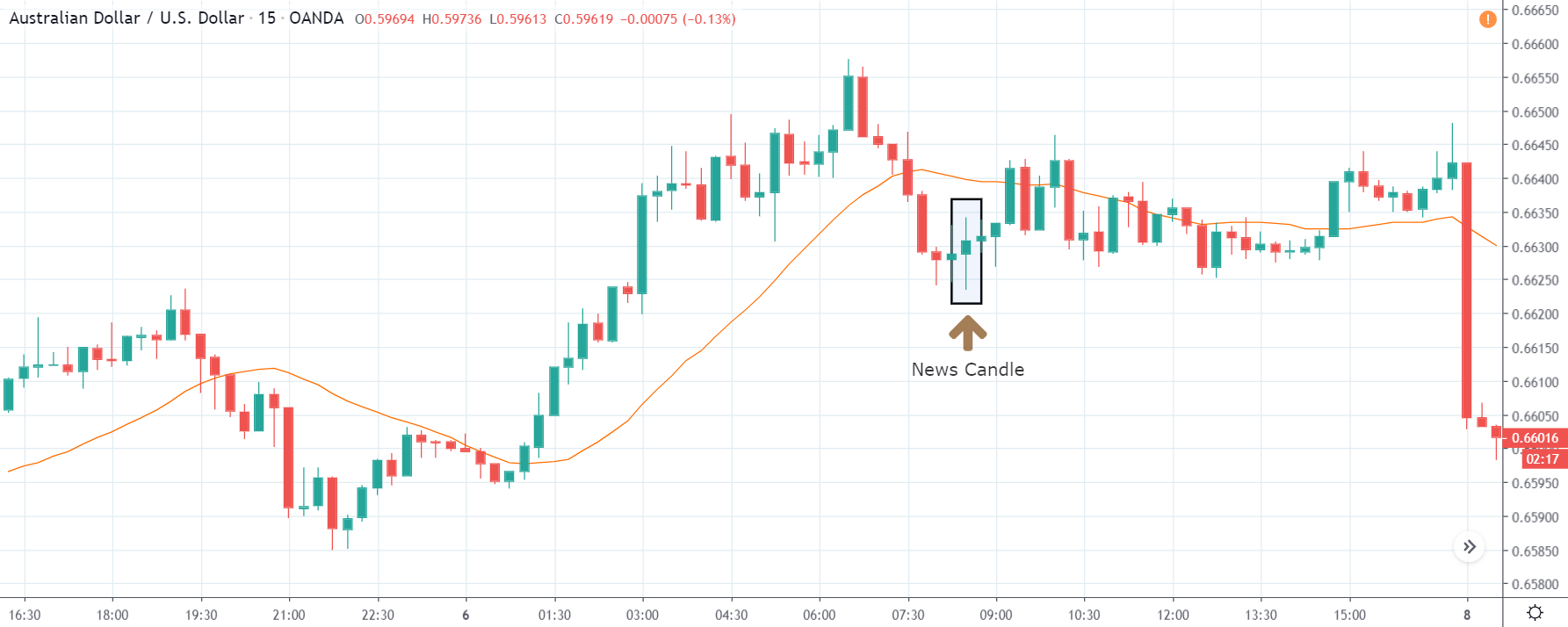
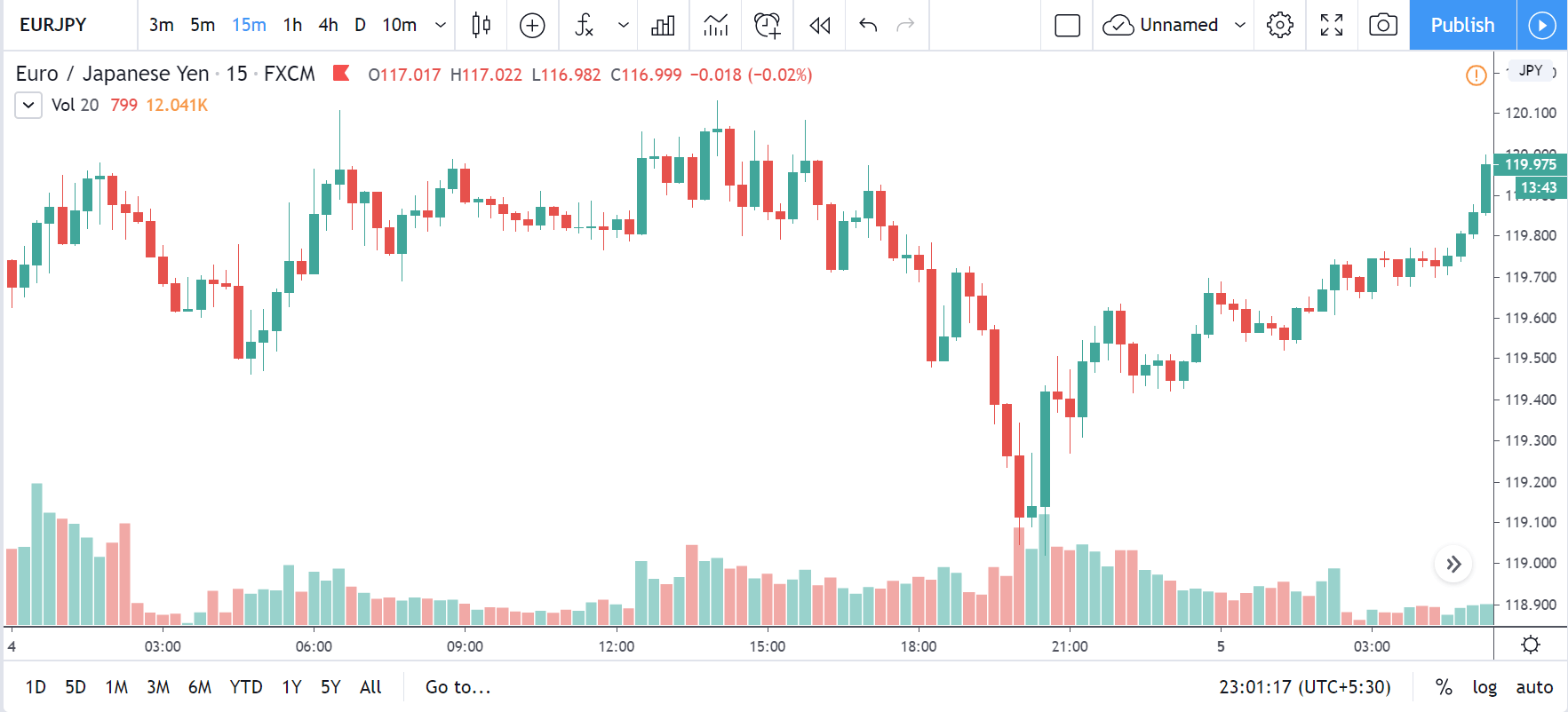
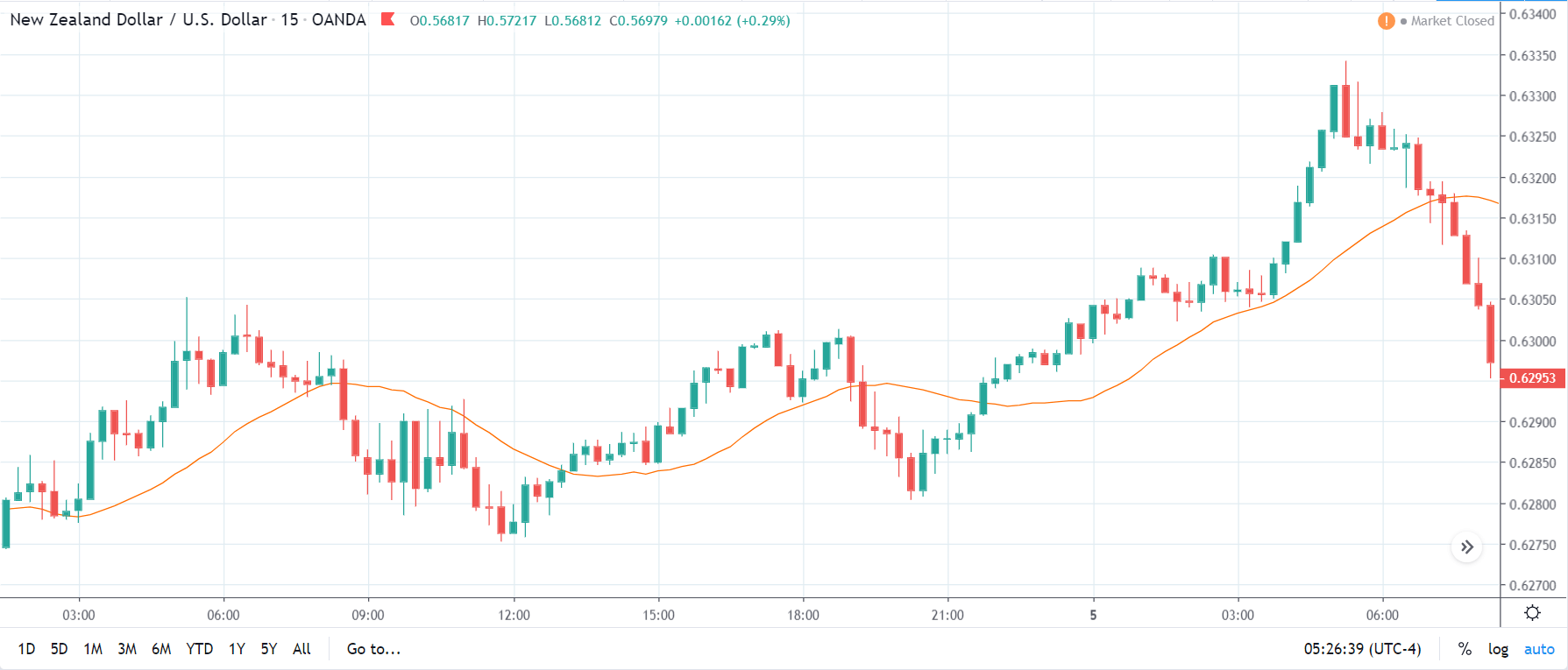
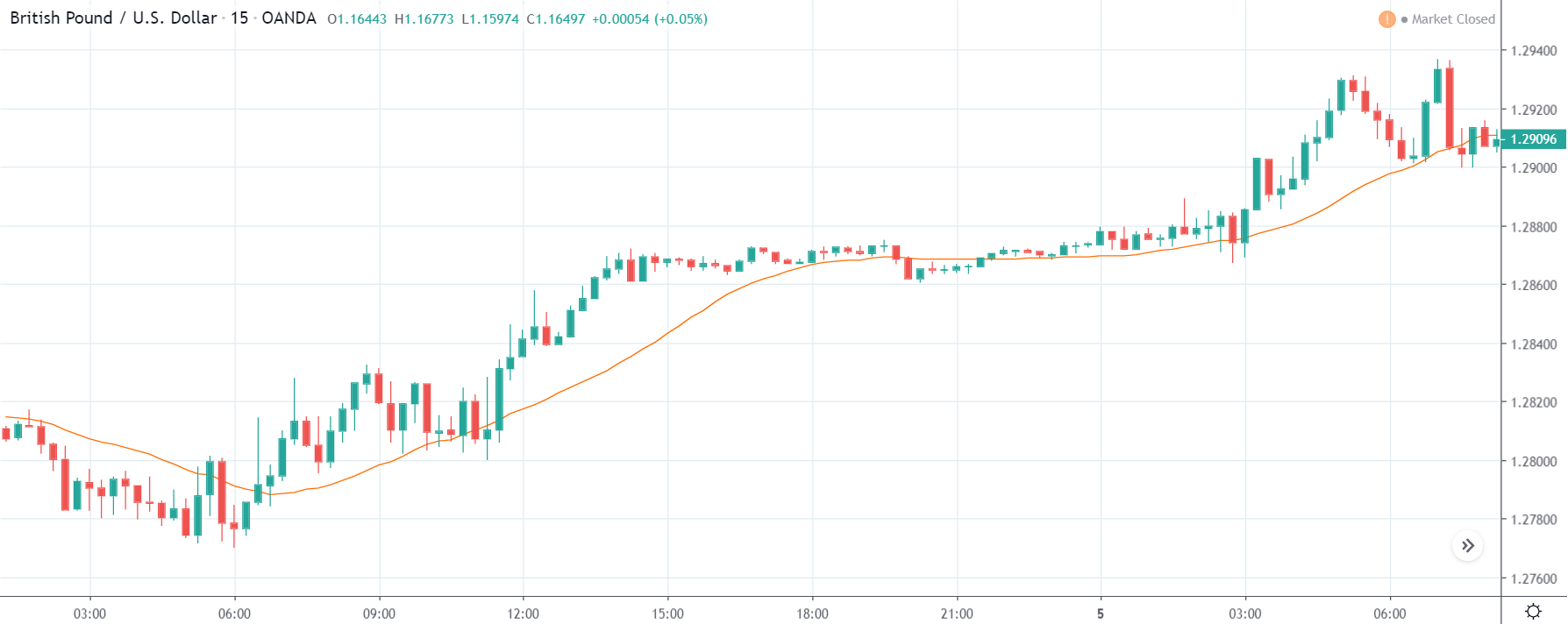
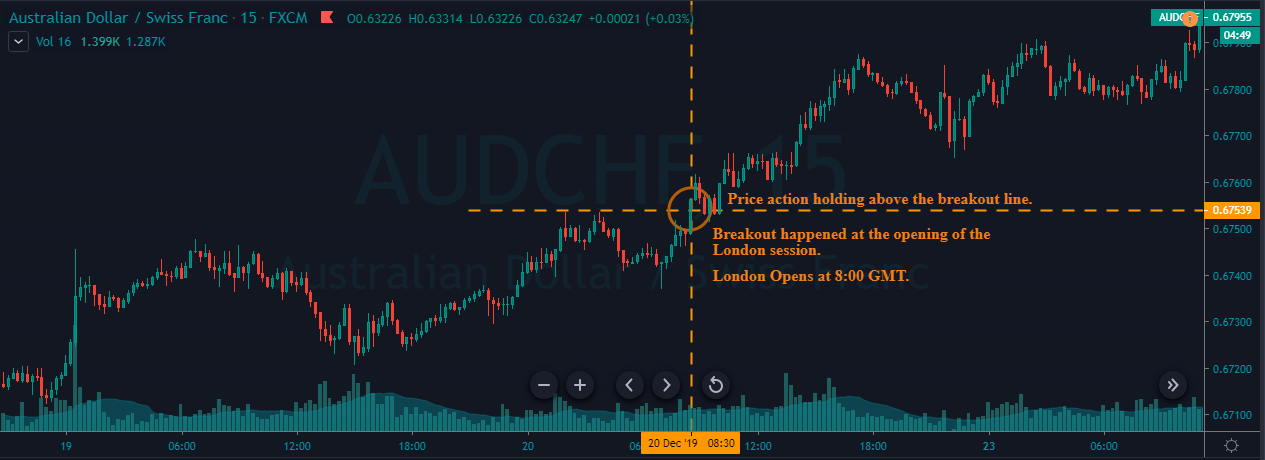
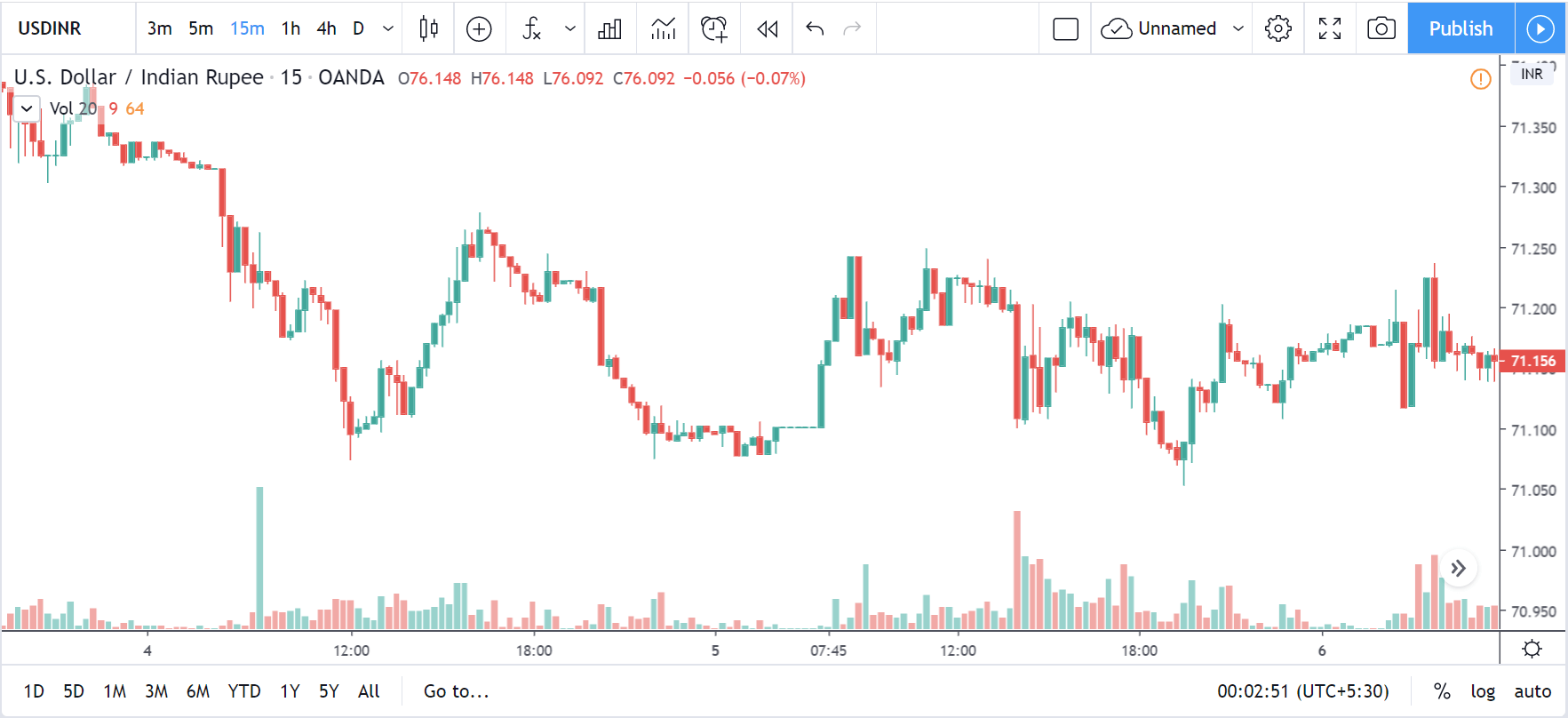
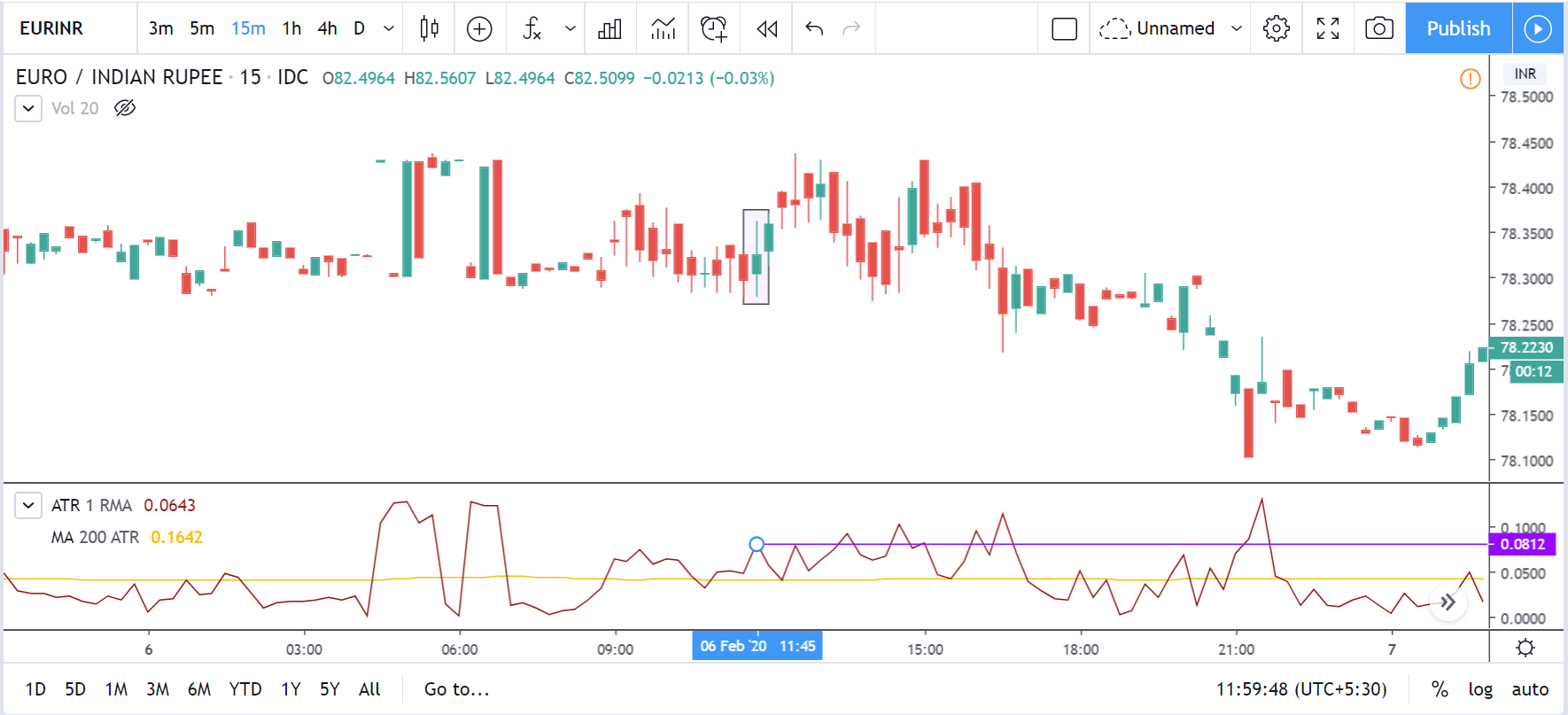
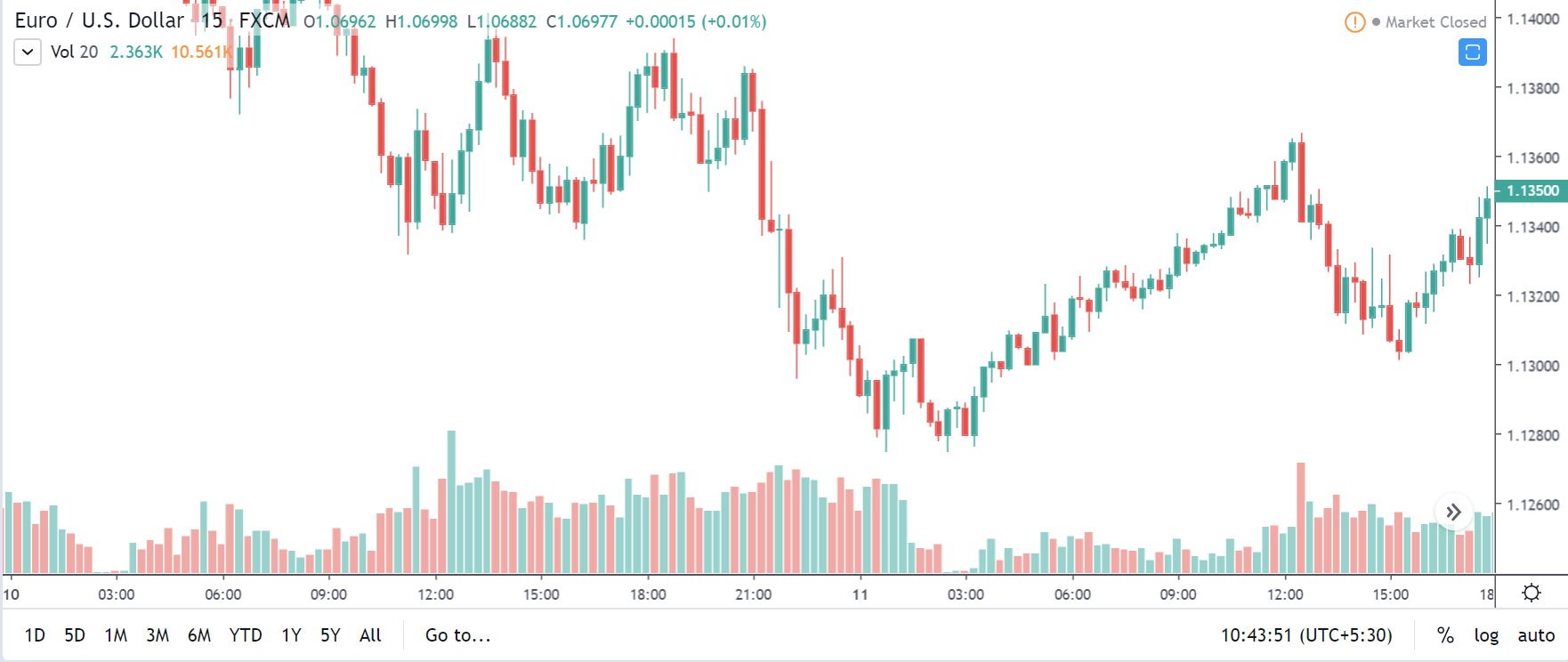
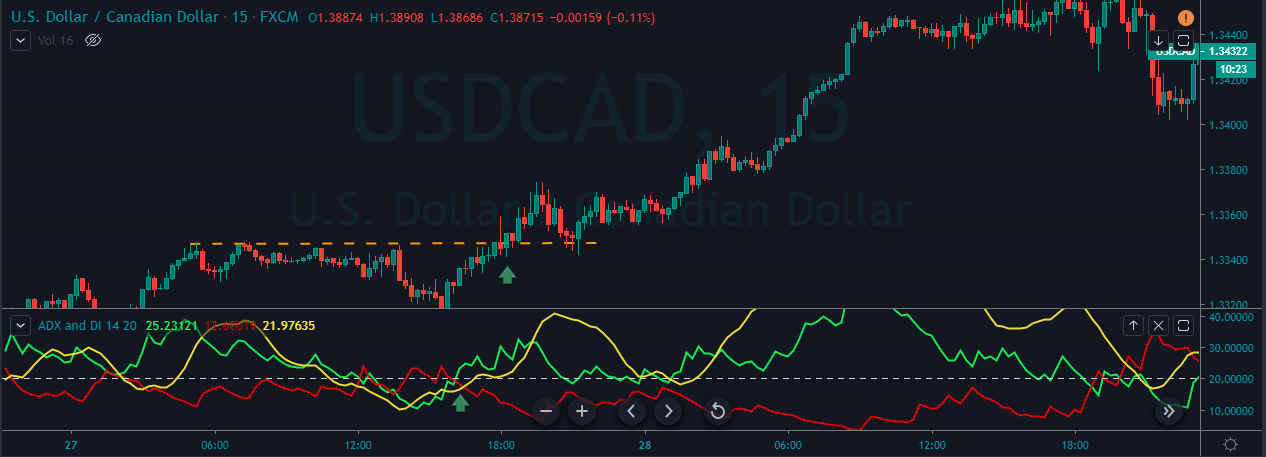
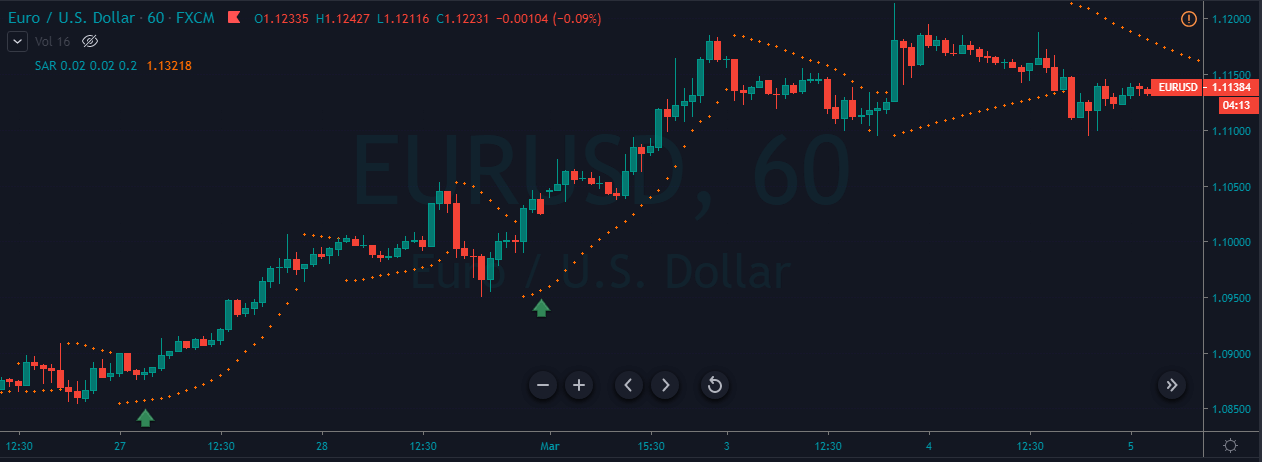
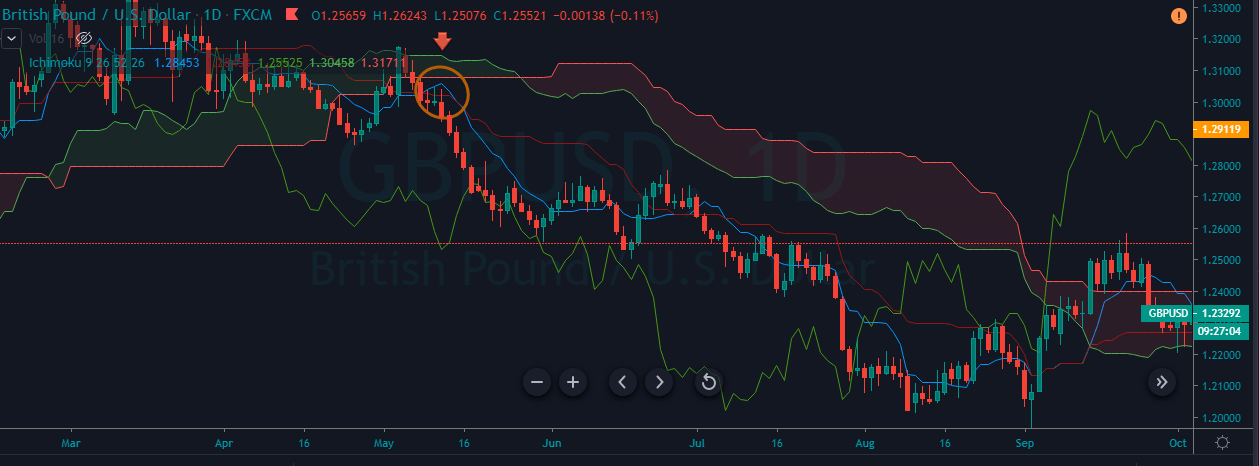
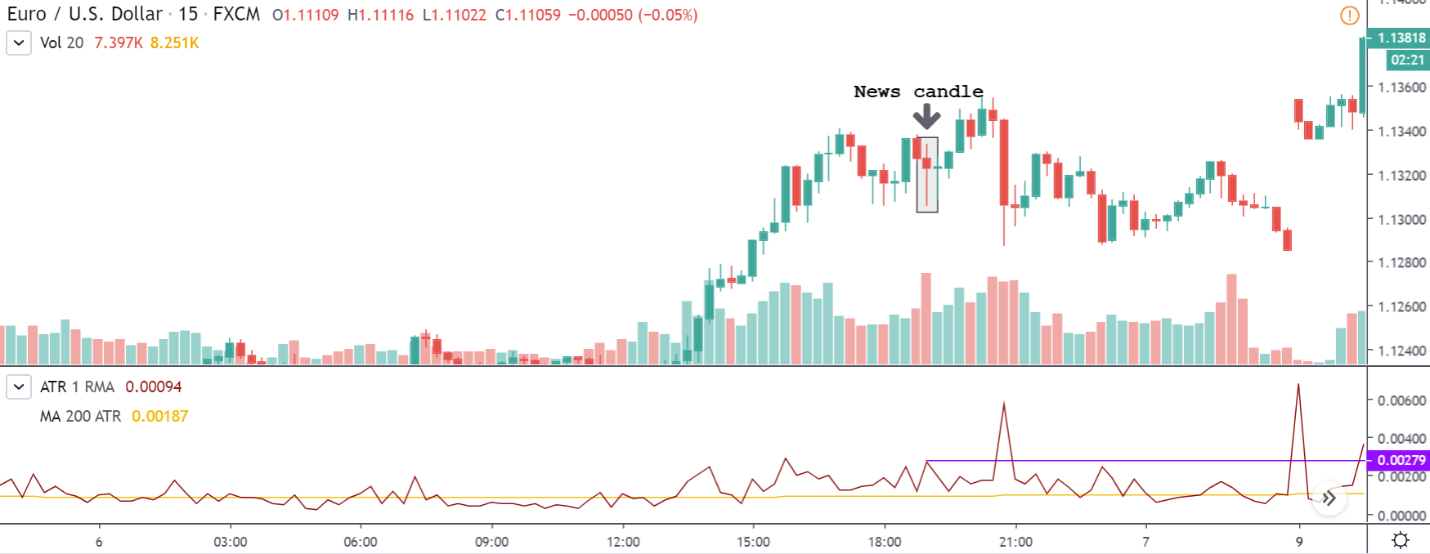
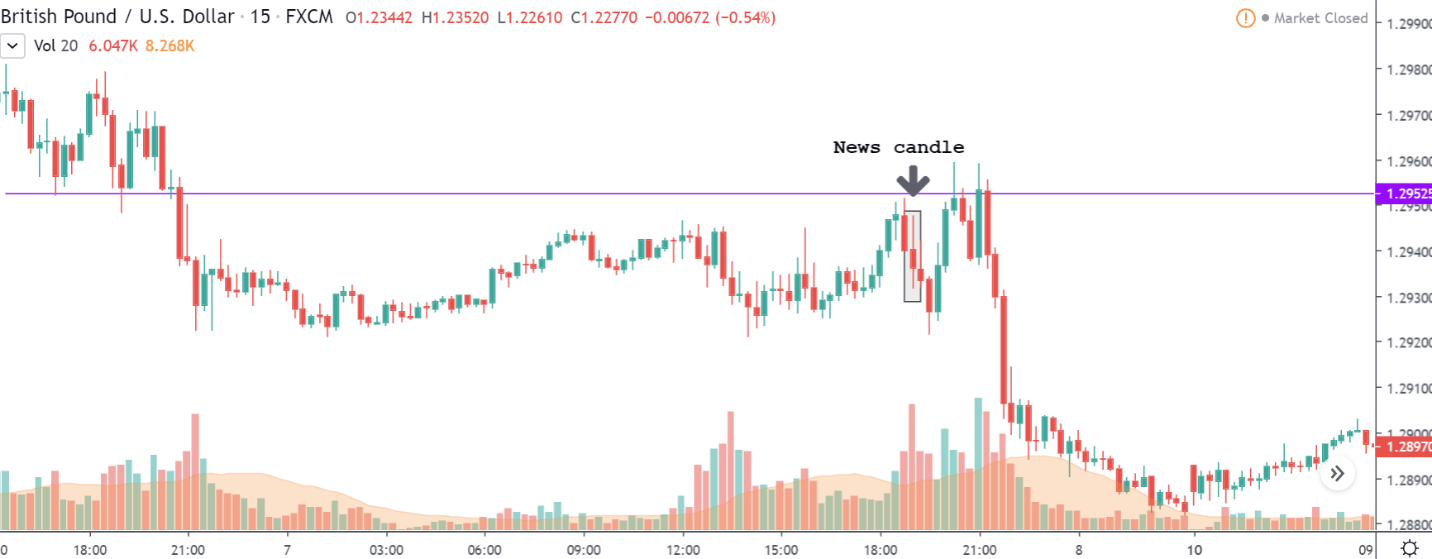
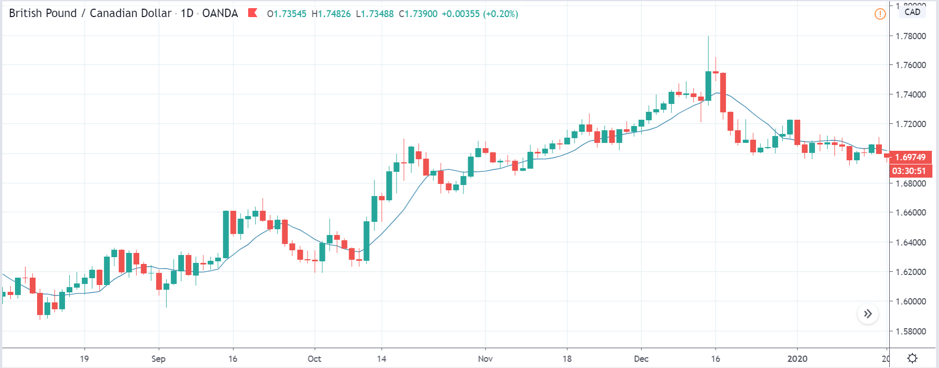
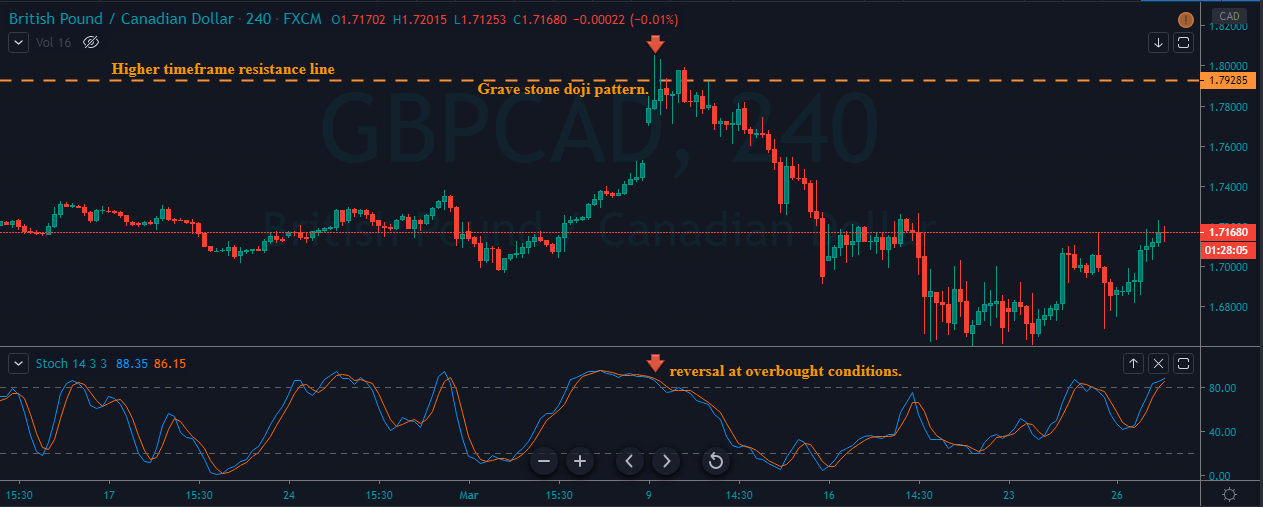
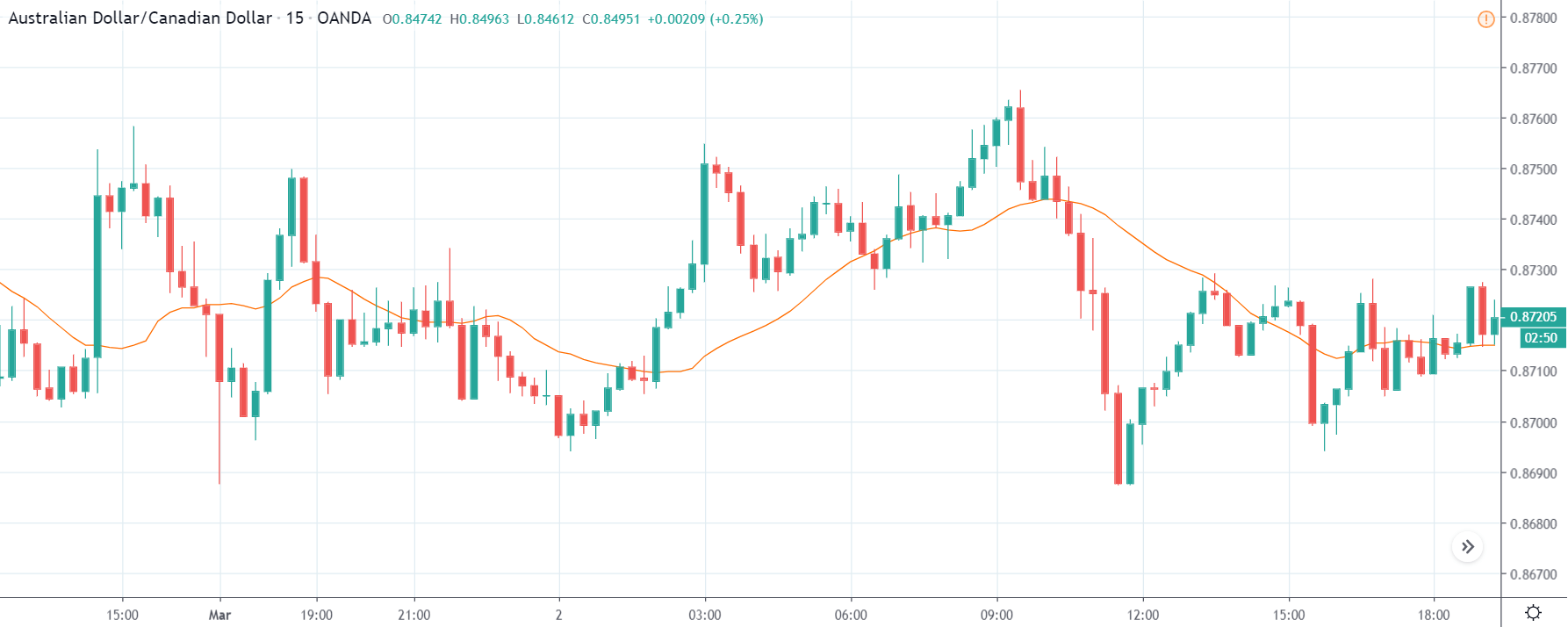
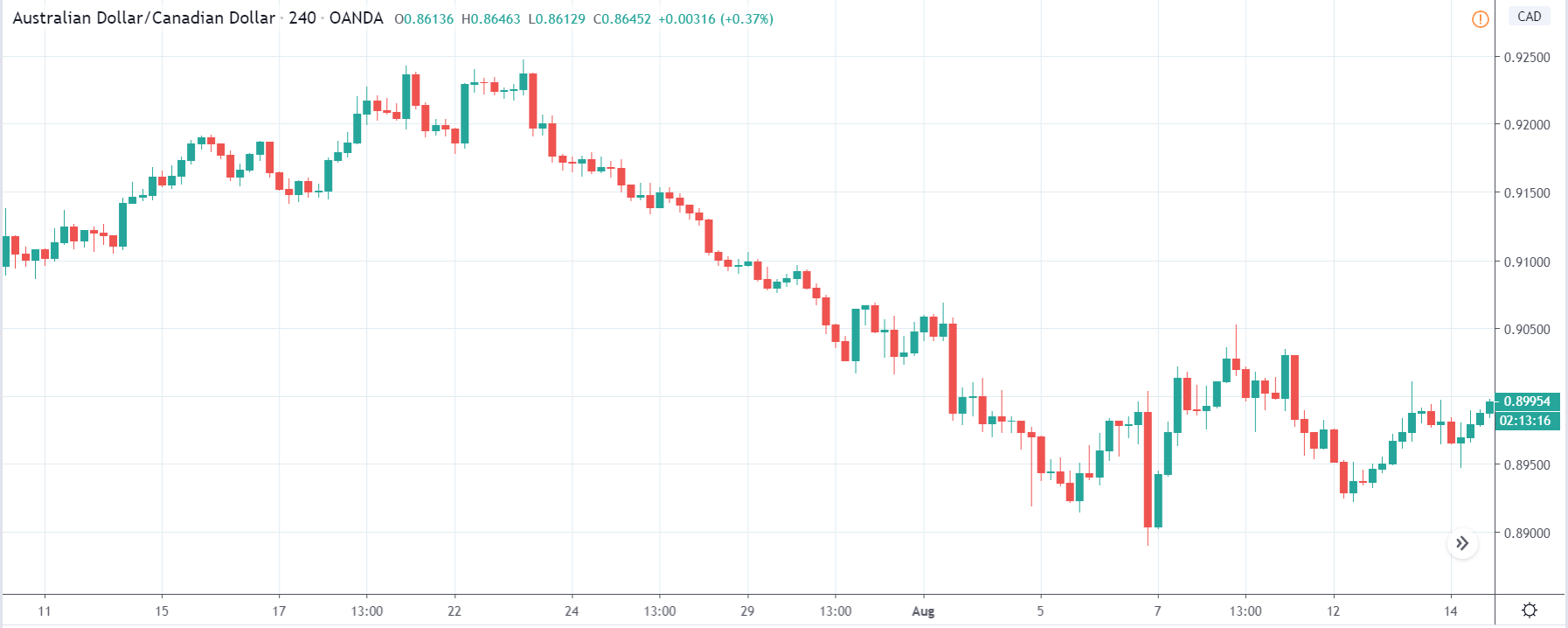
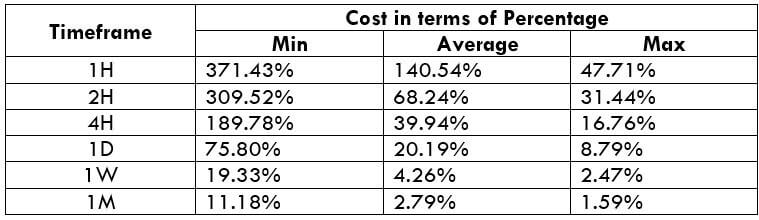
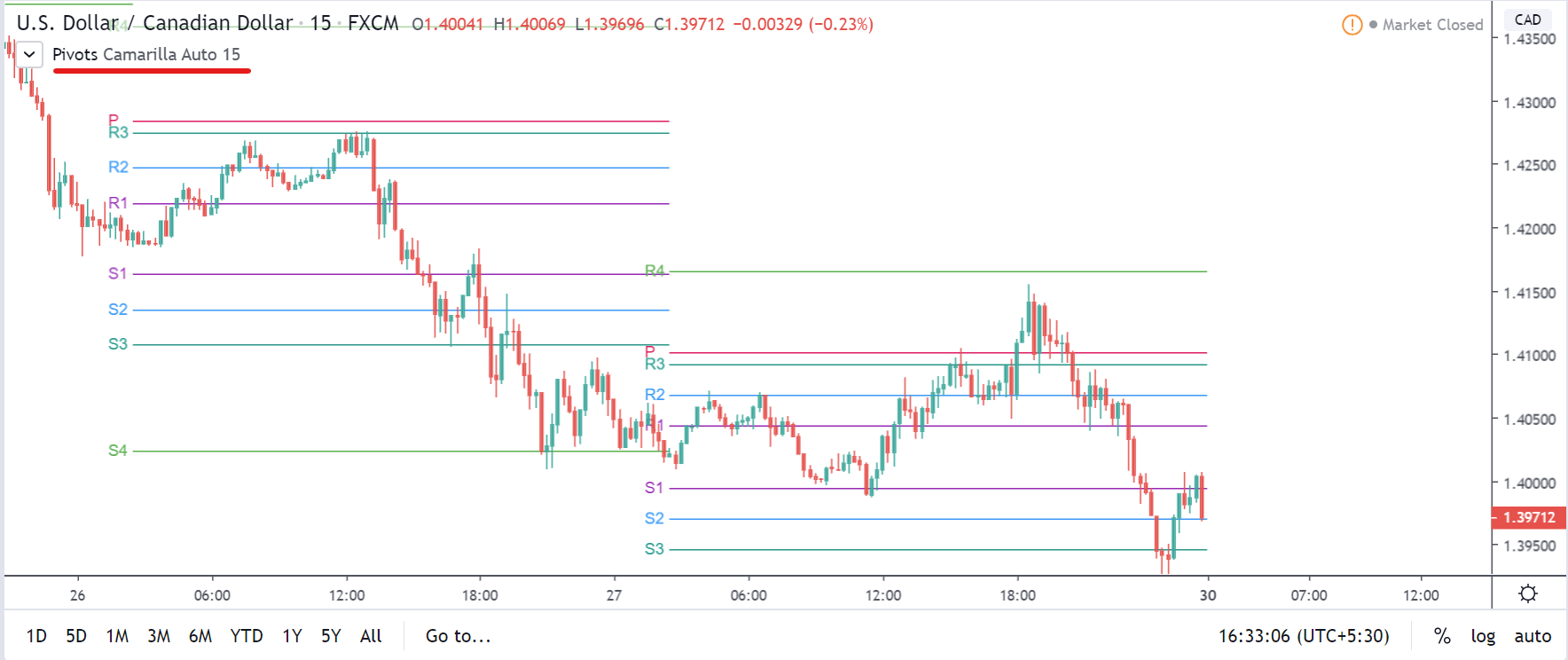
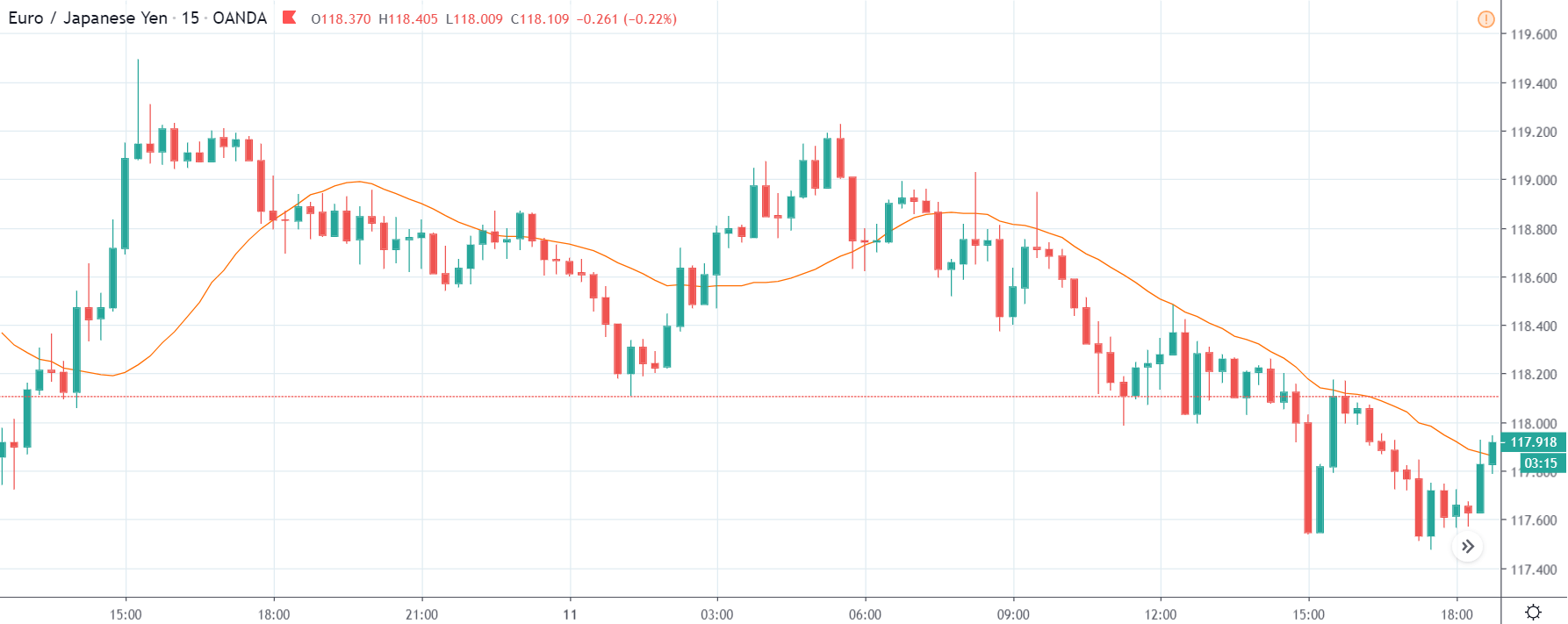
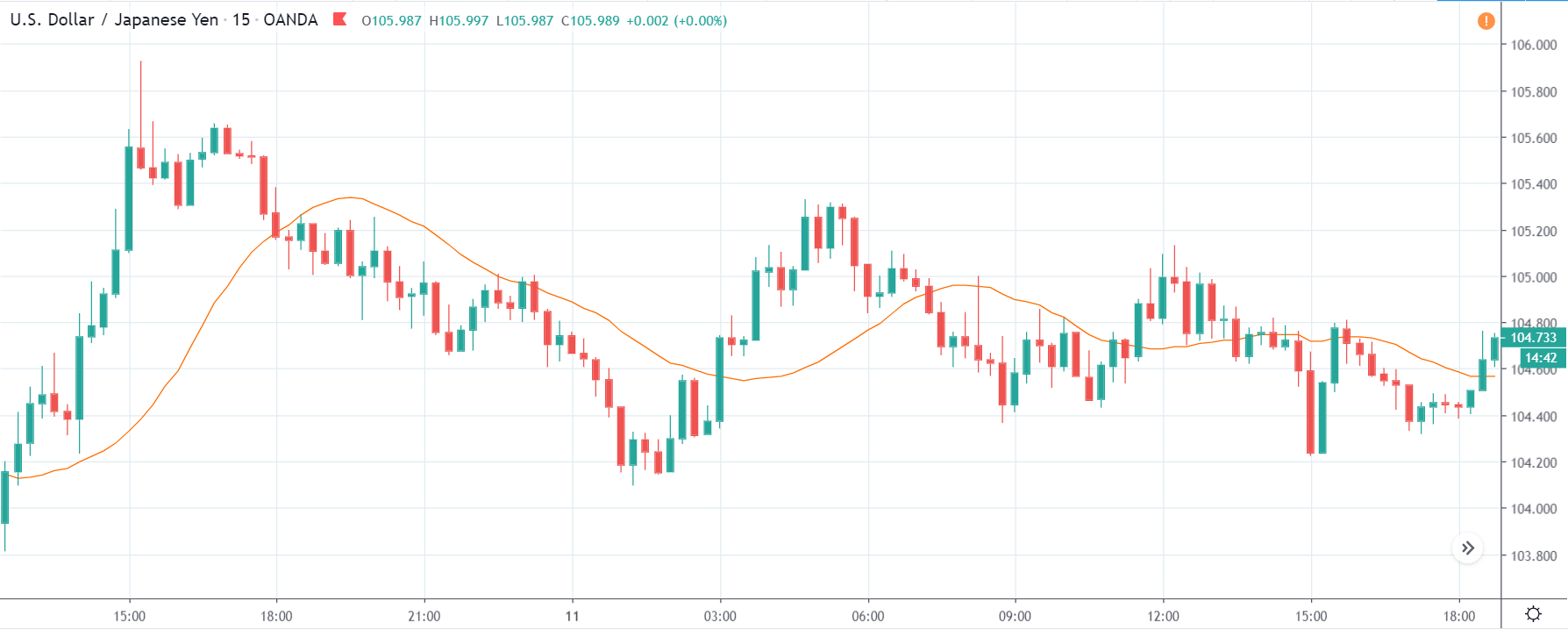
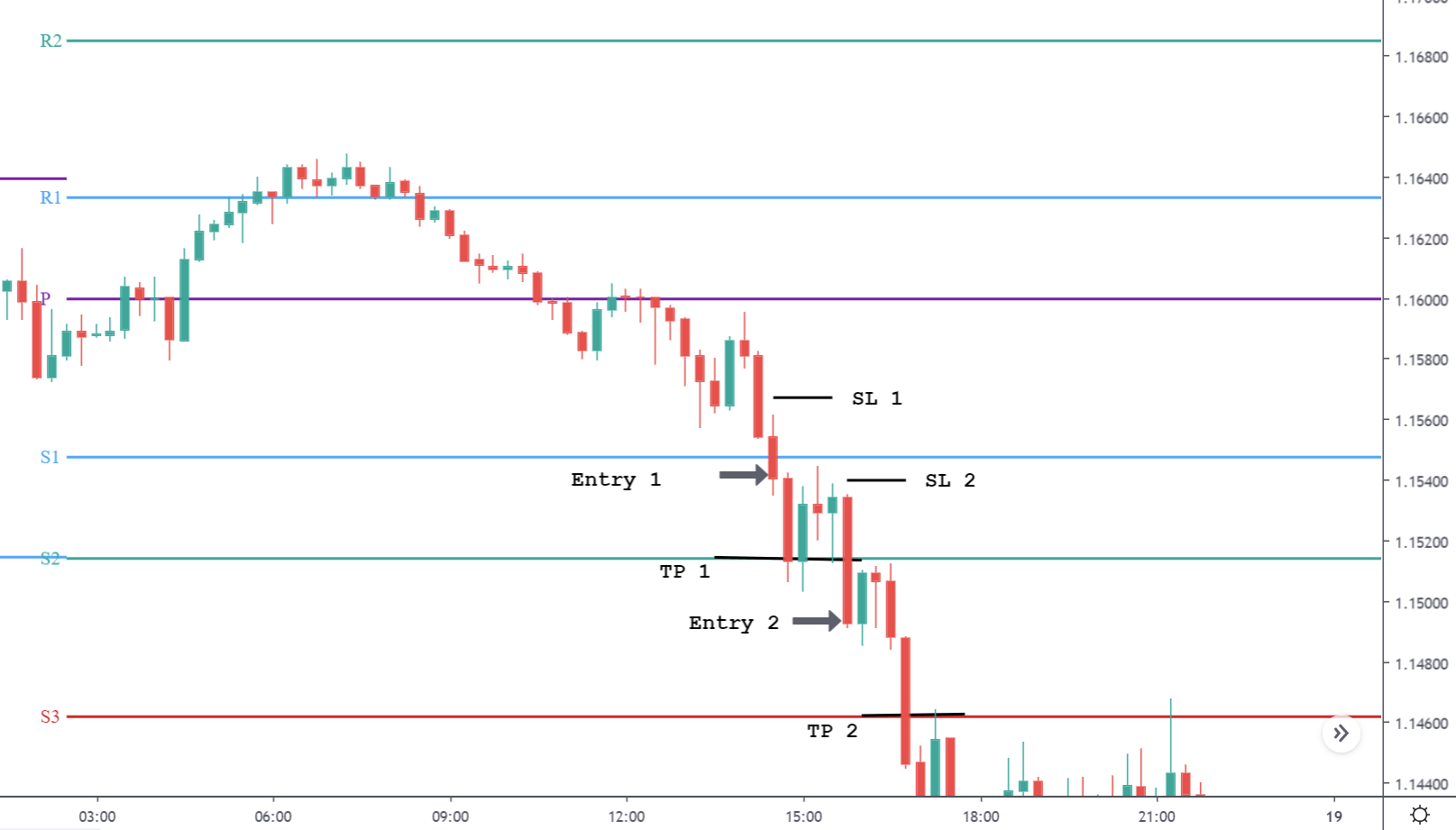
GBP/CAD | Before The Announcement
We start our discussion with the GBP/CAD currency pair, where the above image shows the behavior of the chart before the news announcement. Price action suggests that the price seems to be retracing the big uptrend and is at a key ‘support’ level. If the Income Tax rate announcement comes out to be negative for the Canadian economy and not per expectations, one can take a ‘buy’ trade in the above pair. Whereas positive data might not result in a trend reversal as the overall trend is up.
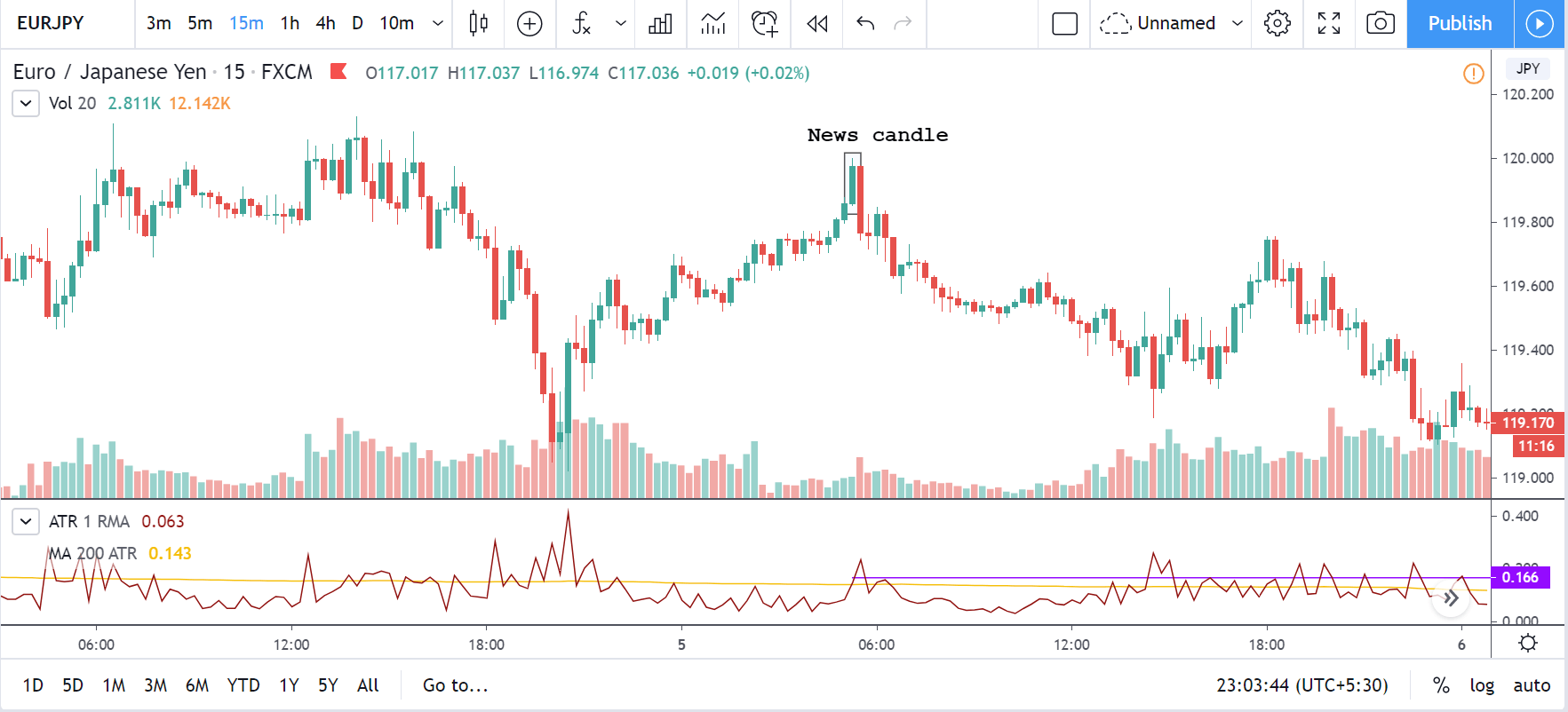
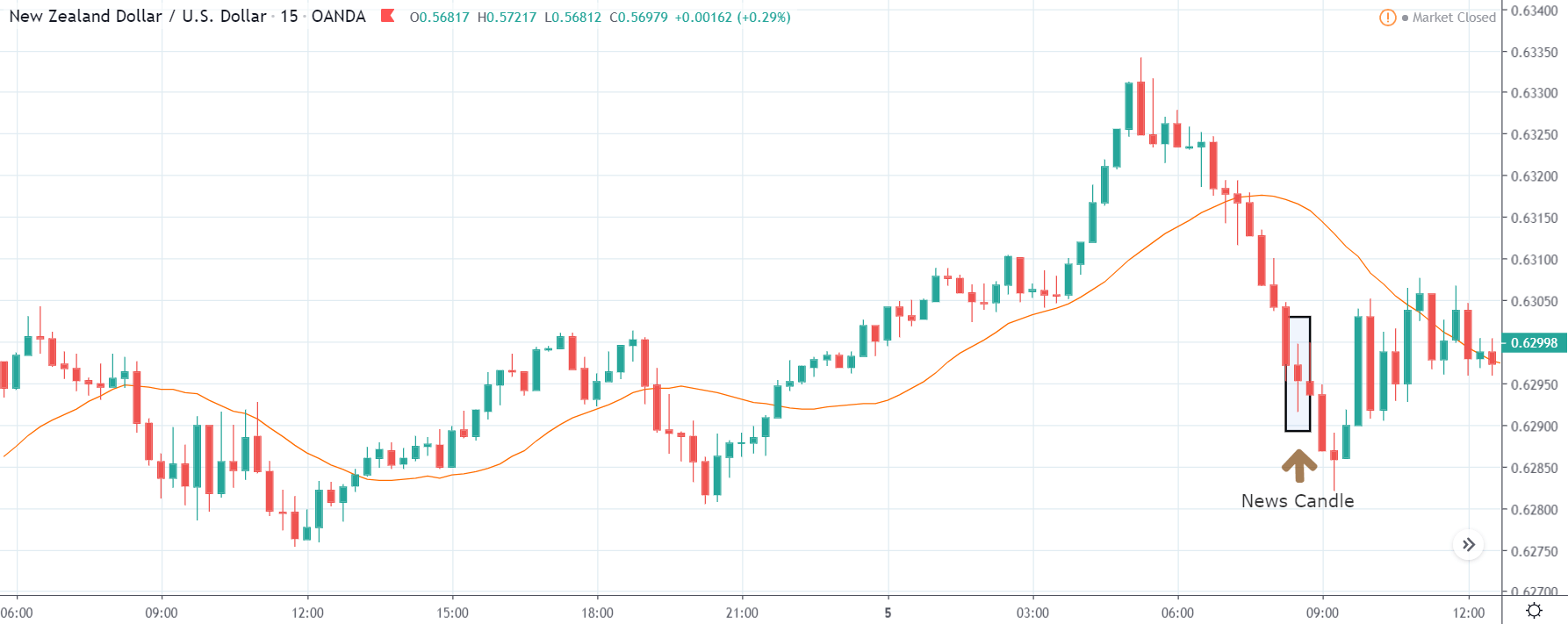
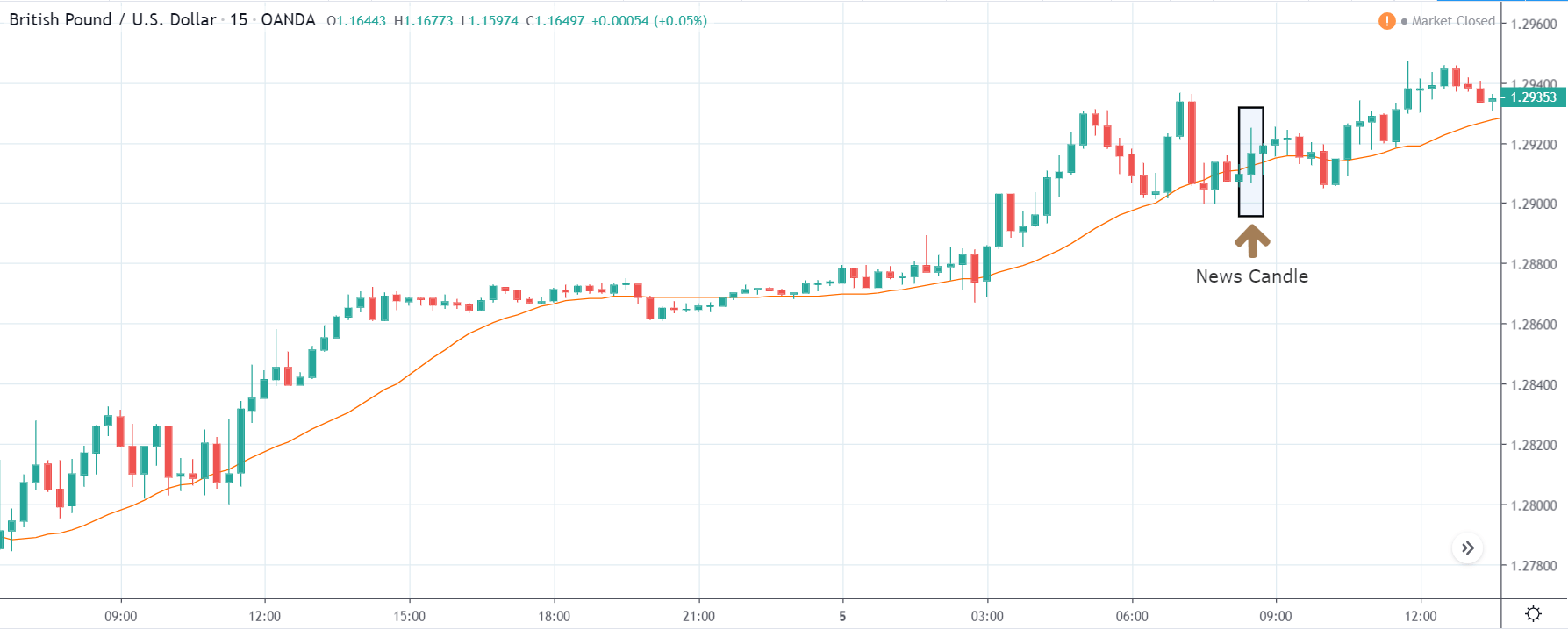
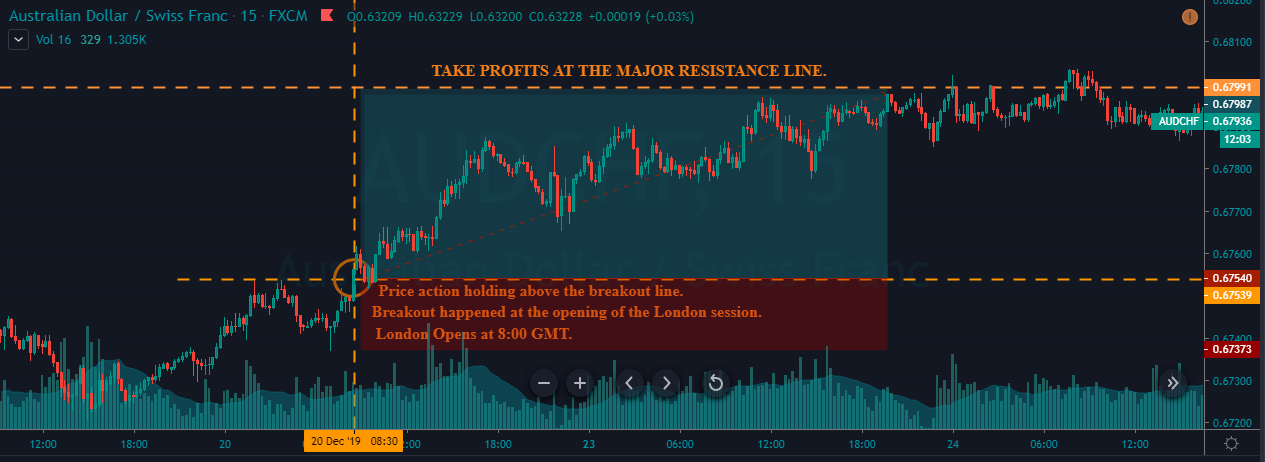
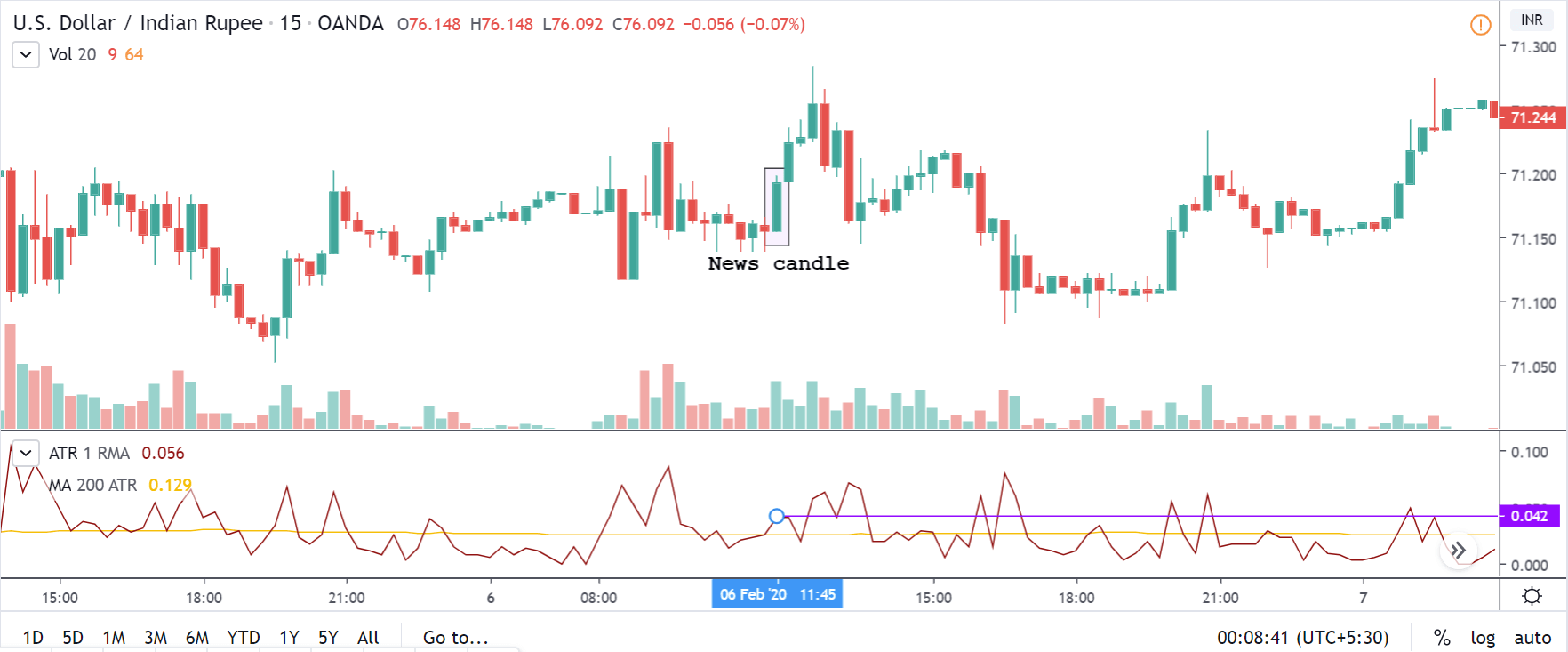
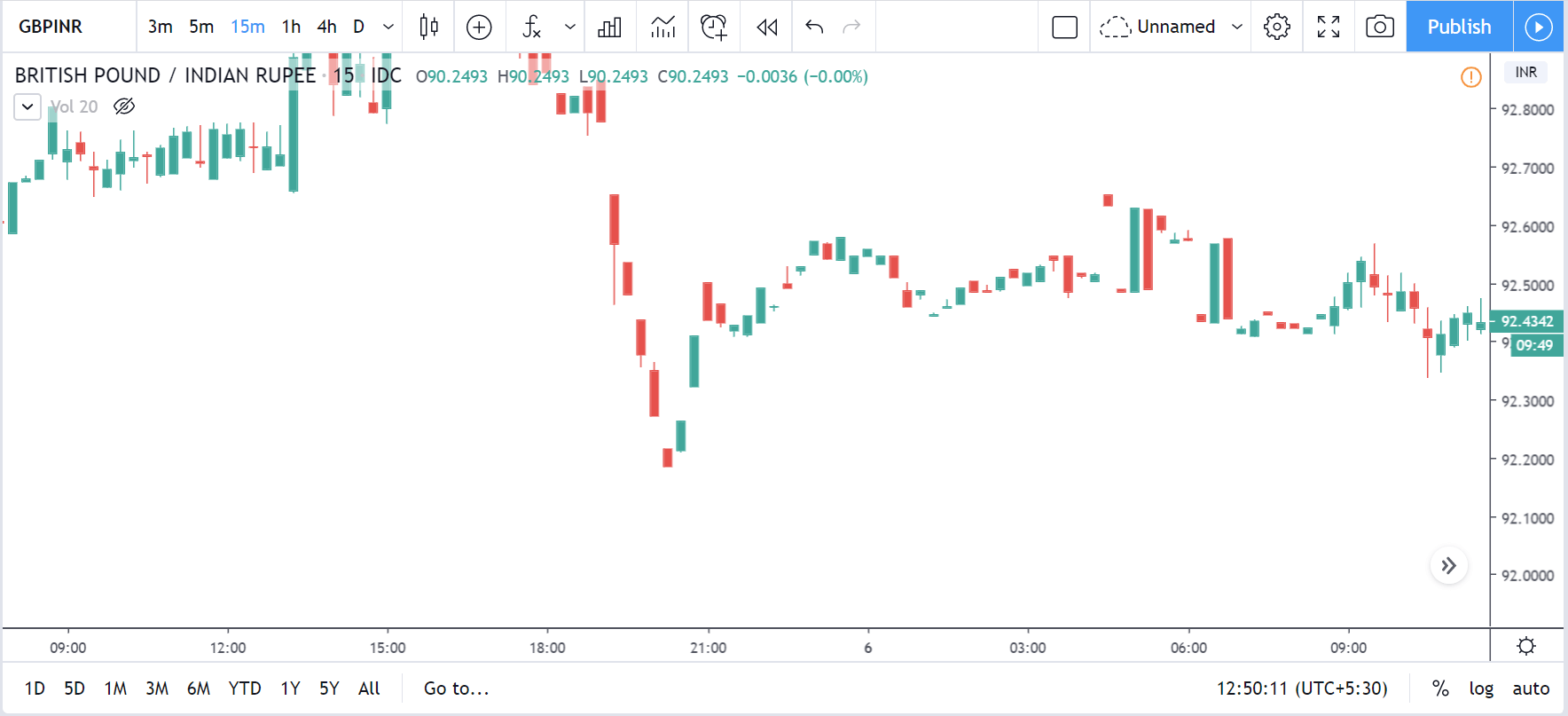
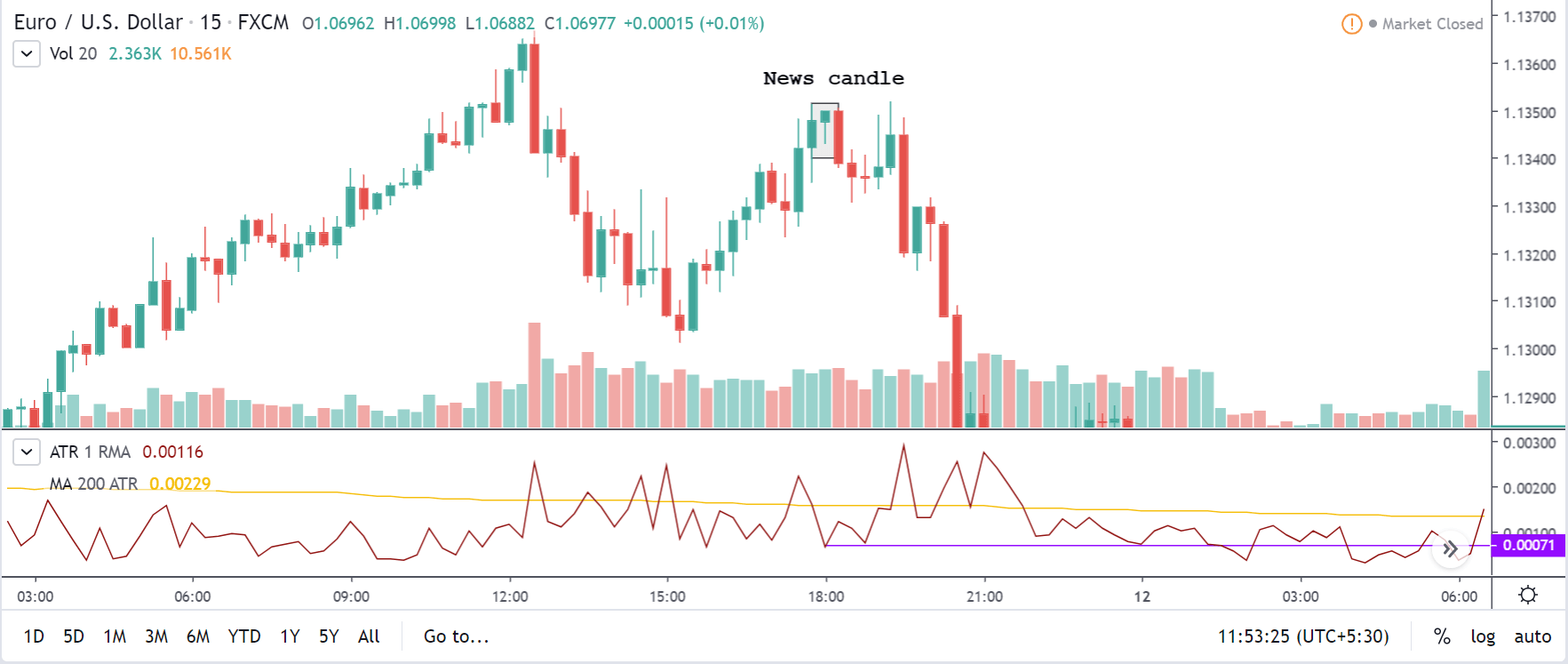
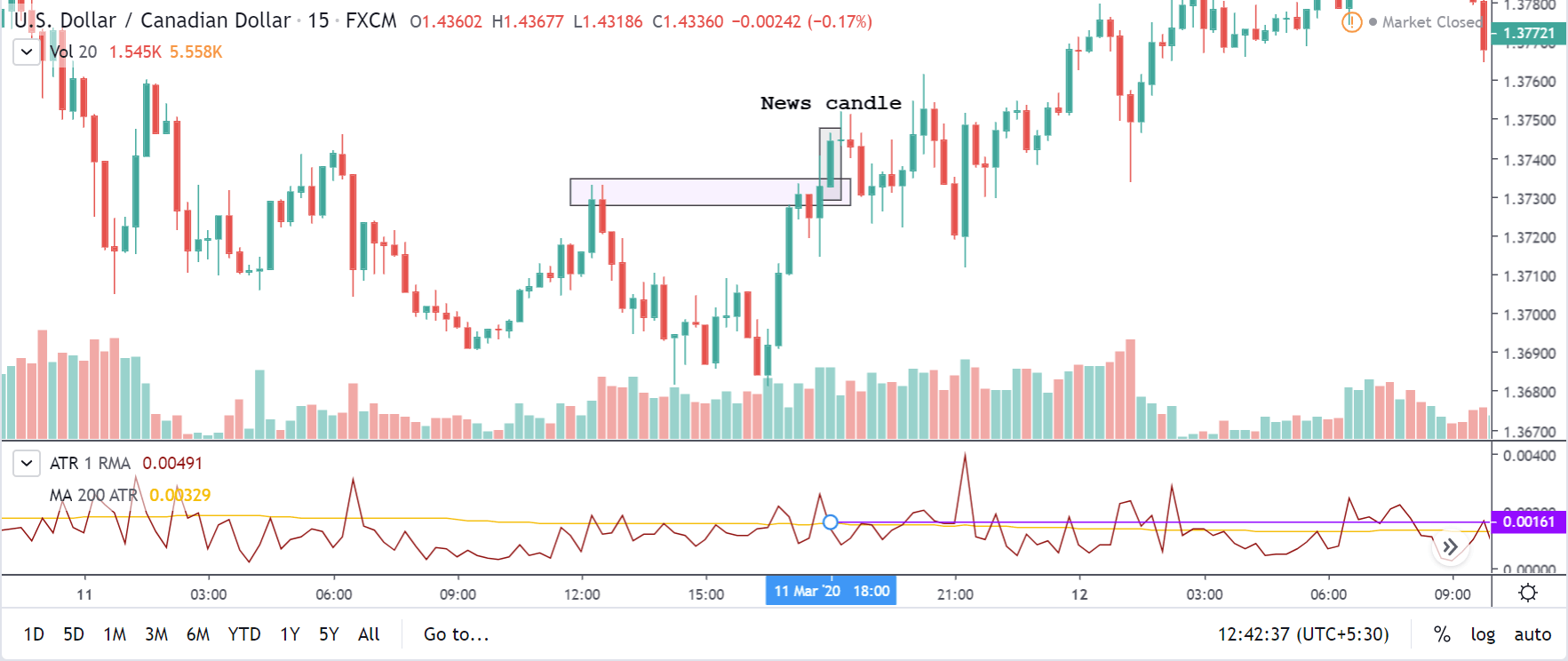
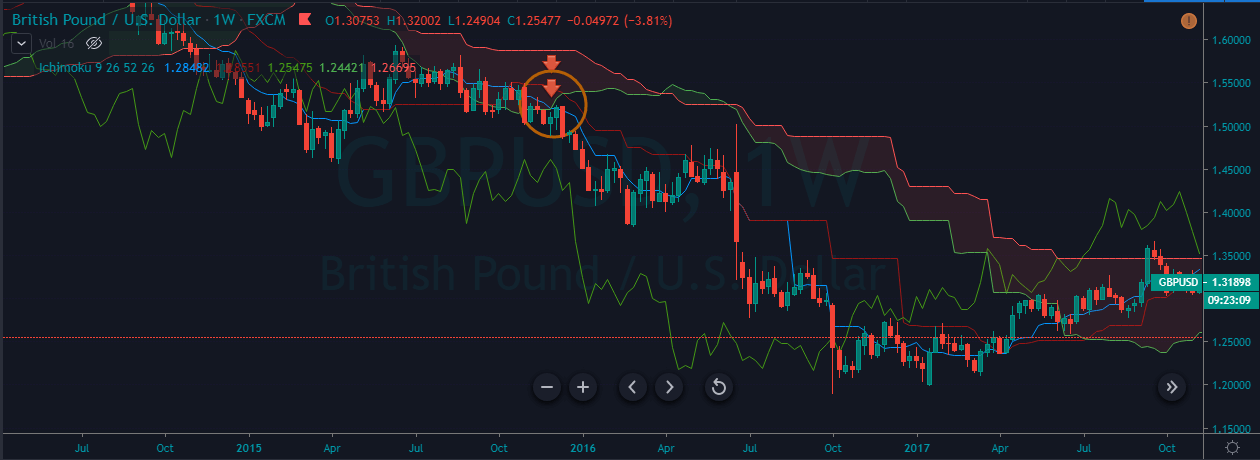
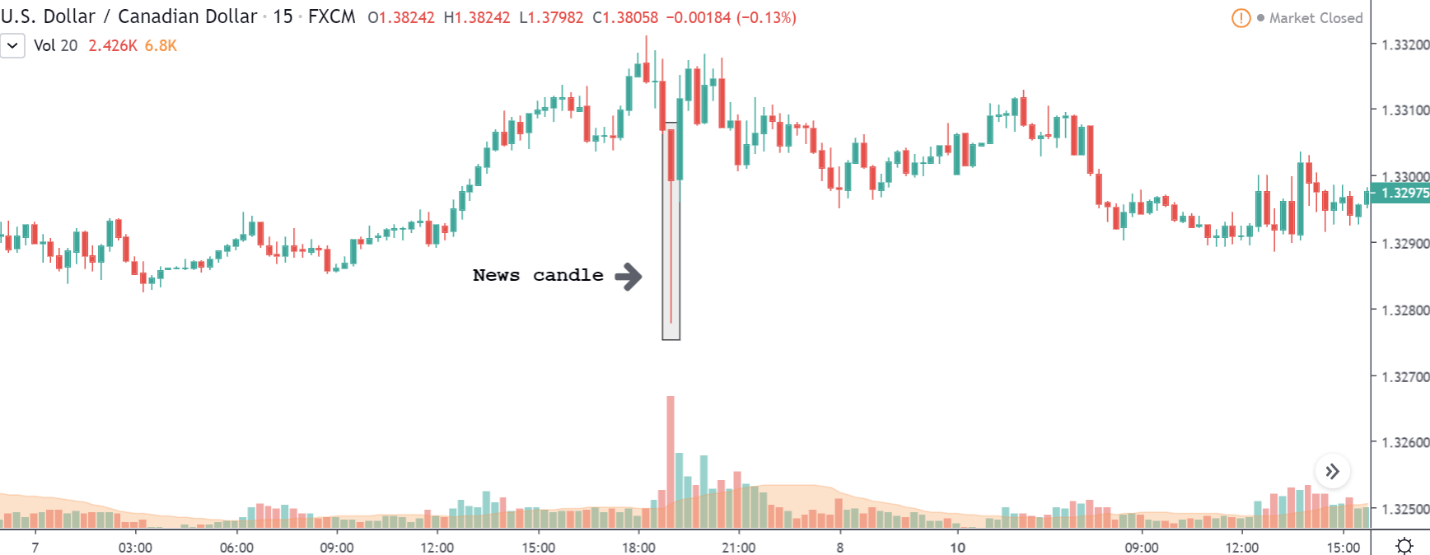
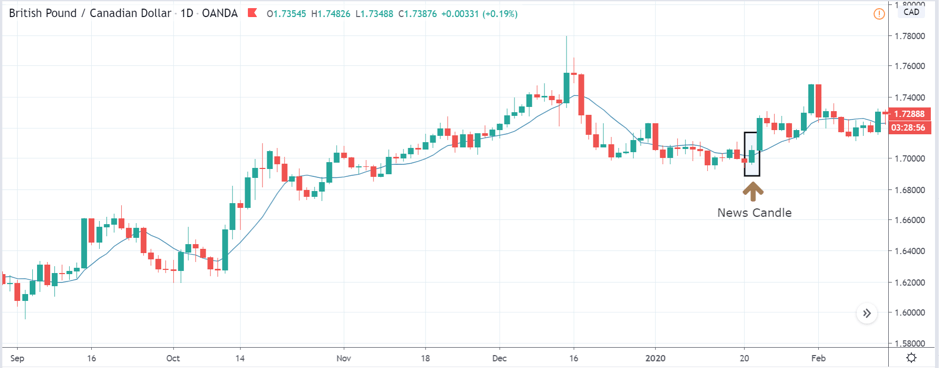
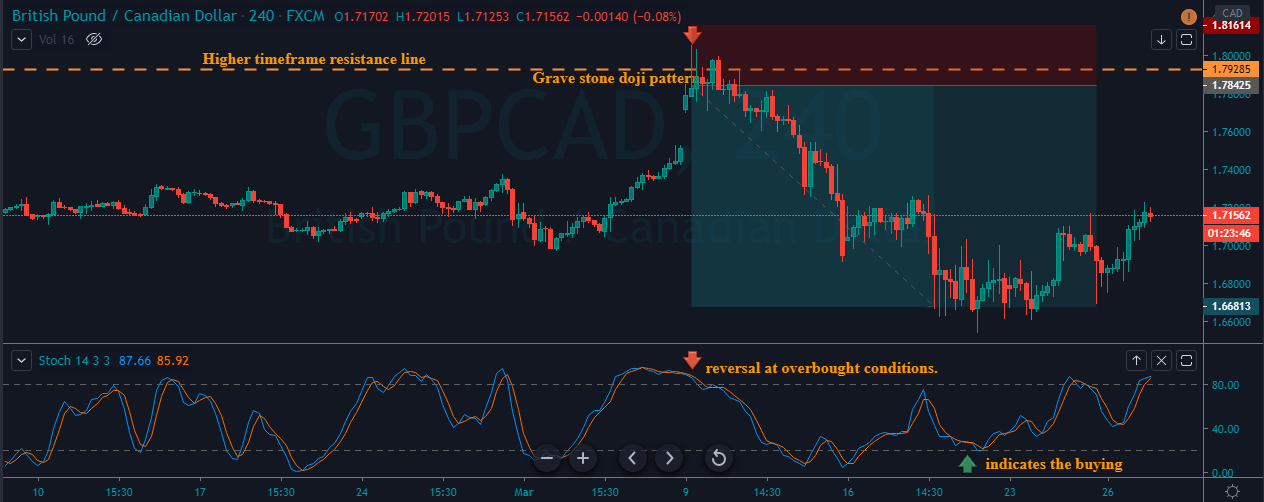
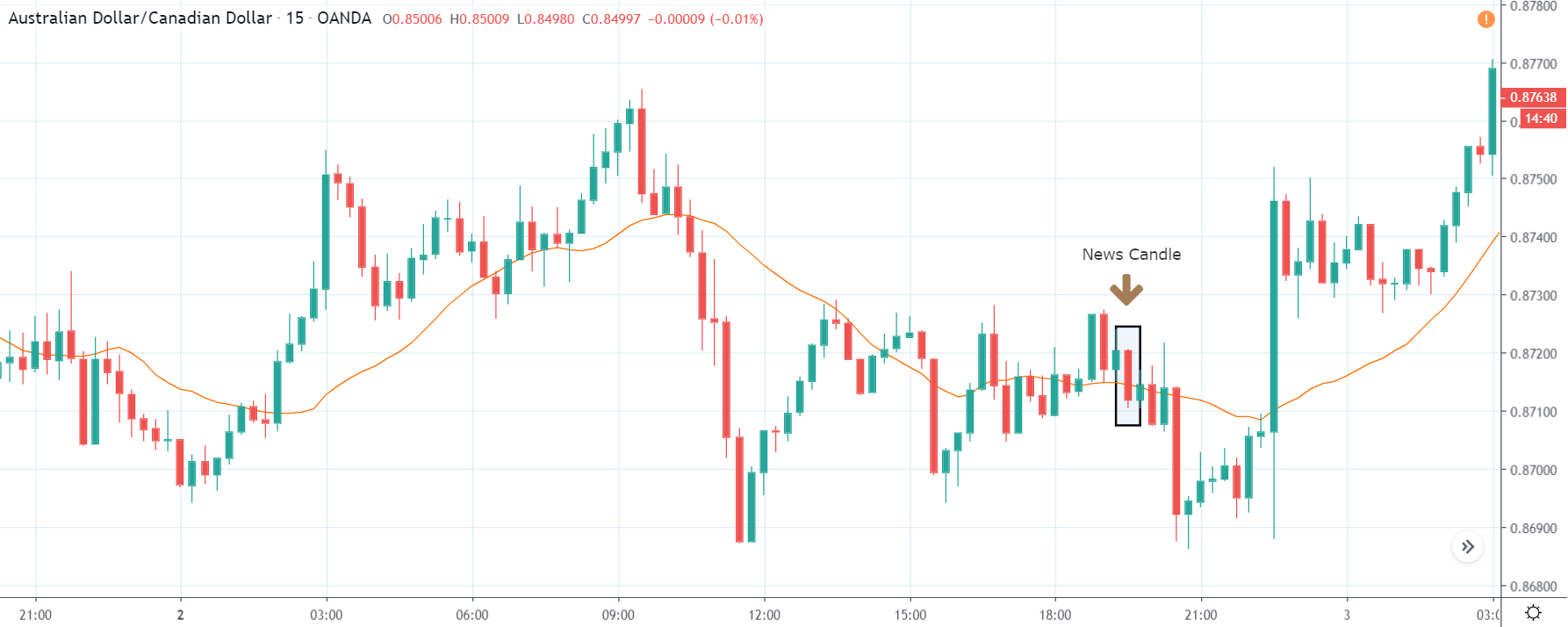
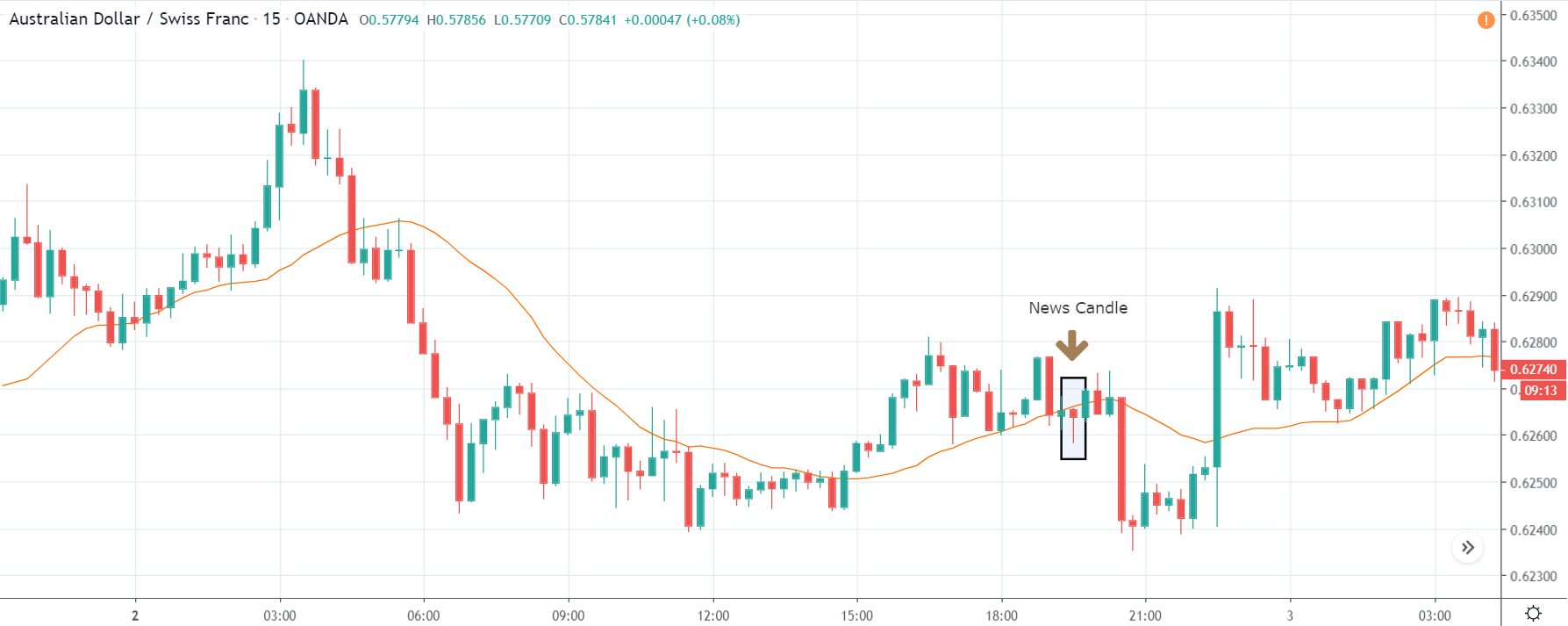
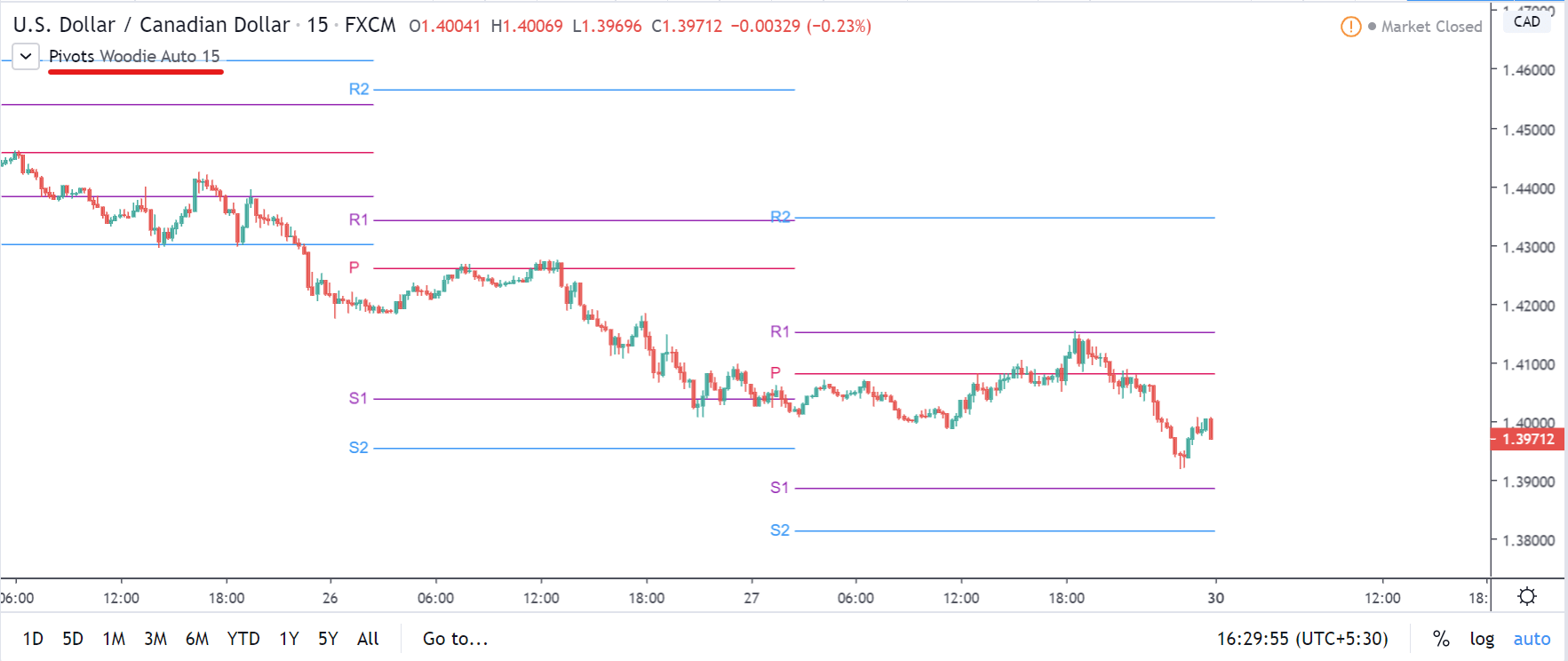
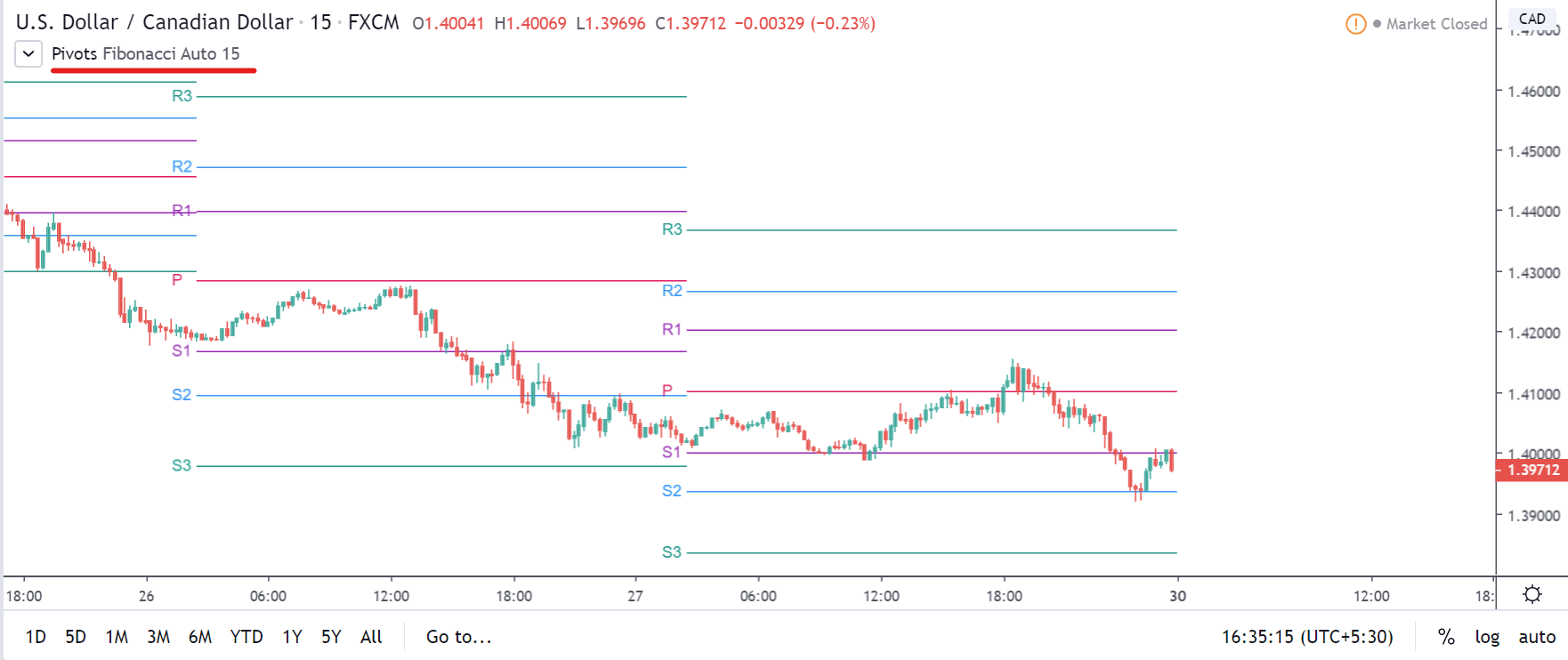
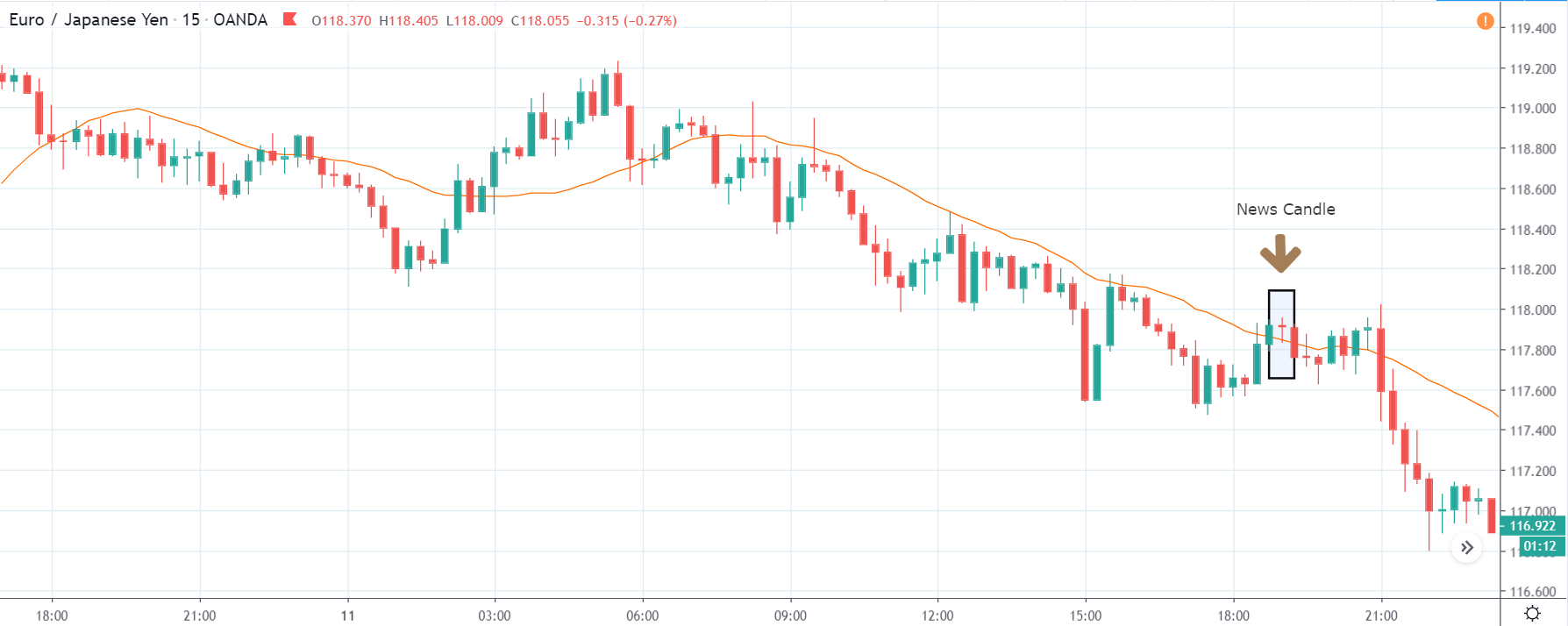
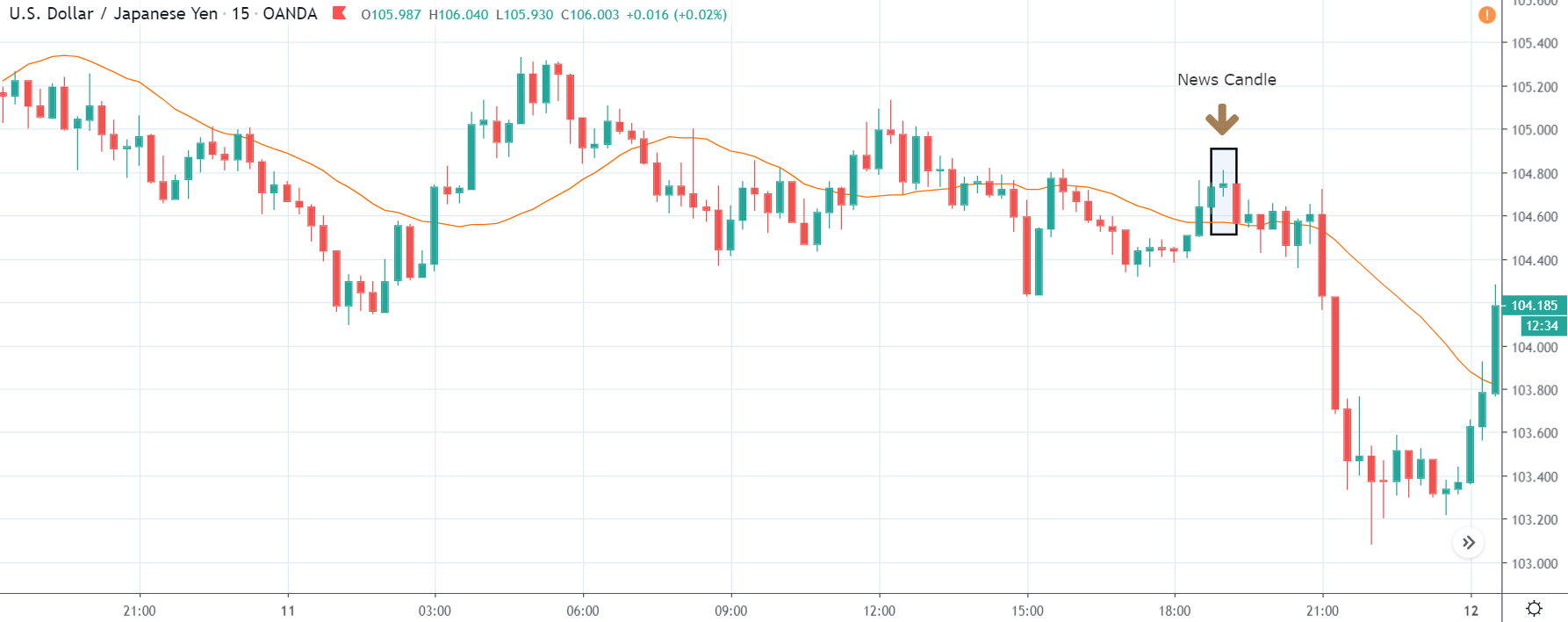
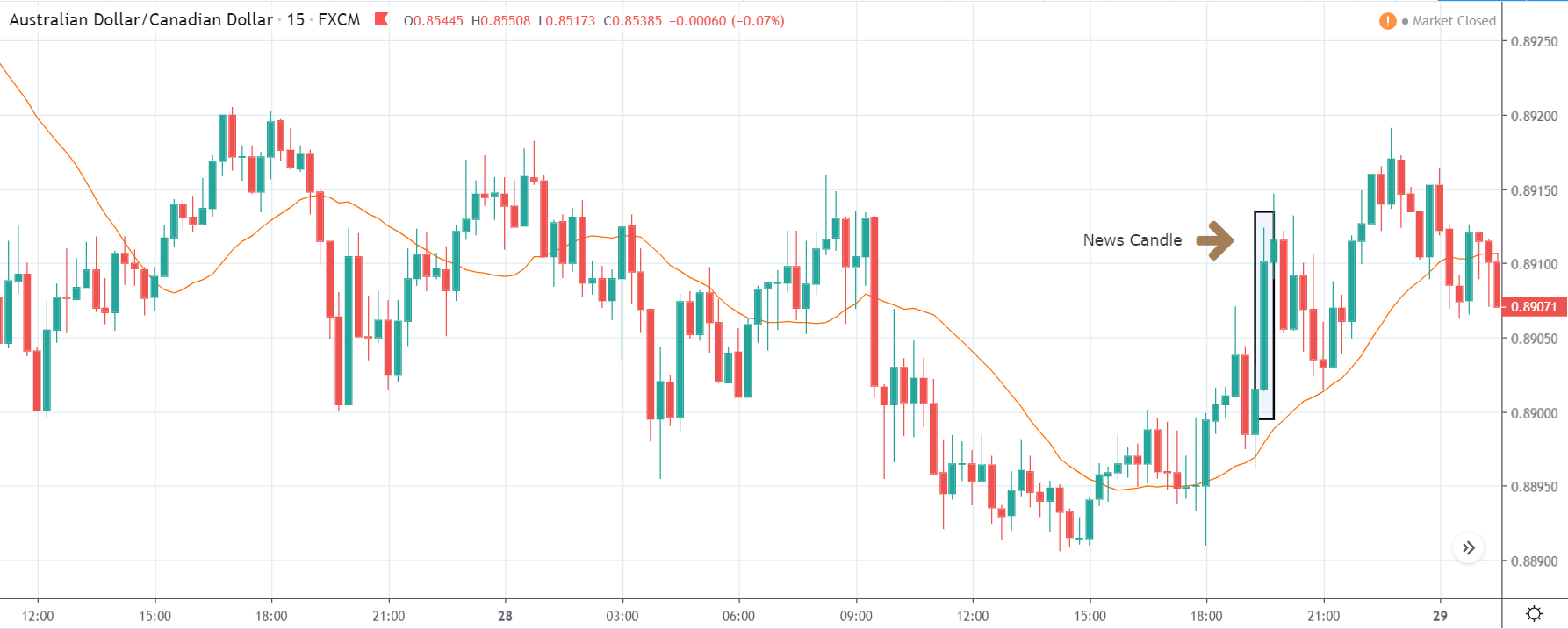
GBP/CAD | After The Announcement
After the announcement, we see that the price moves higher, and it closes with a fair amount of bullishness. The increase in volatility to the upside is a sign of continuation of the trend, and this shows that the data was not very positive for the Canadian dollar. The bullish ‘news candle’ indicates a weakness in the currency where traders find the data to be negative for the economy. As the market moves higher, once can go ‘long’ in the market with a stop loss below the ‘news candle’ and ‘take profit’ at the recent ‘high.’
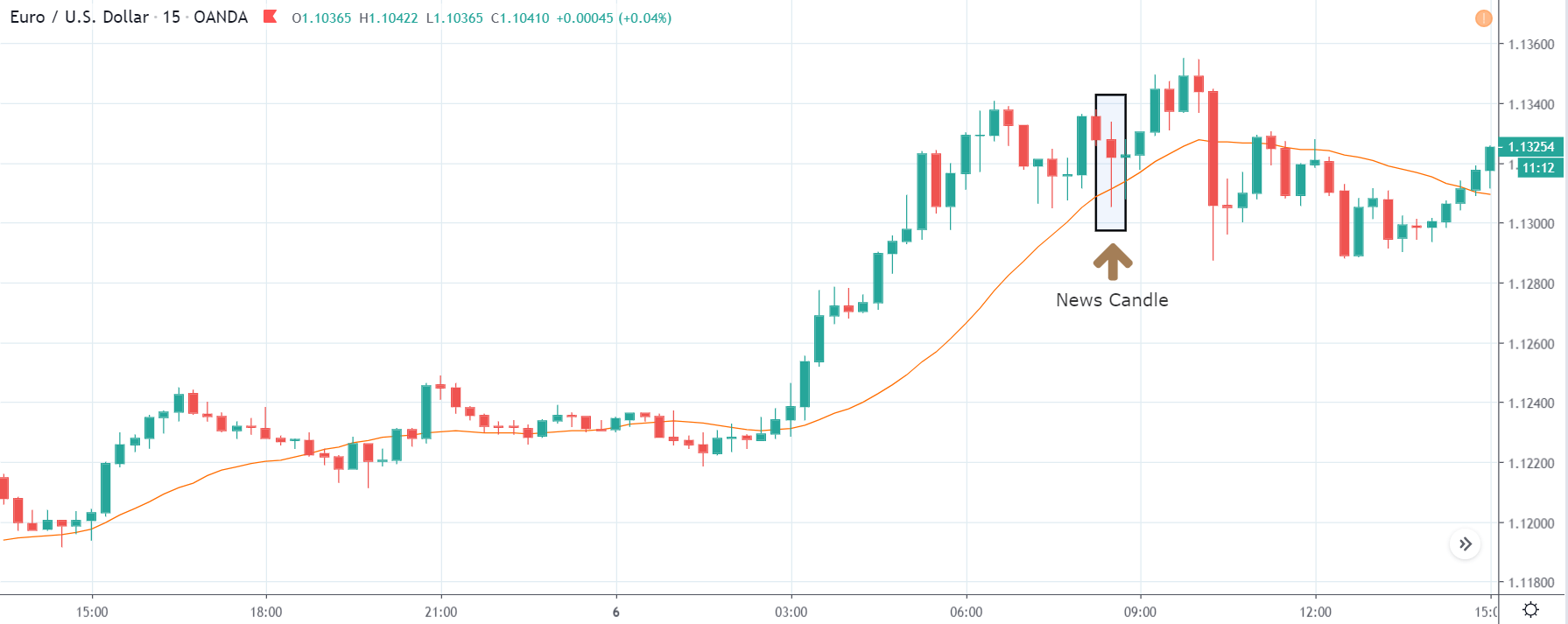
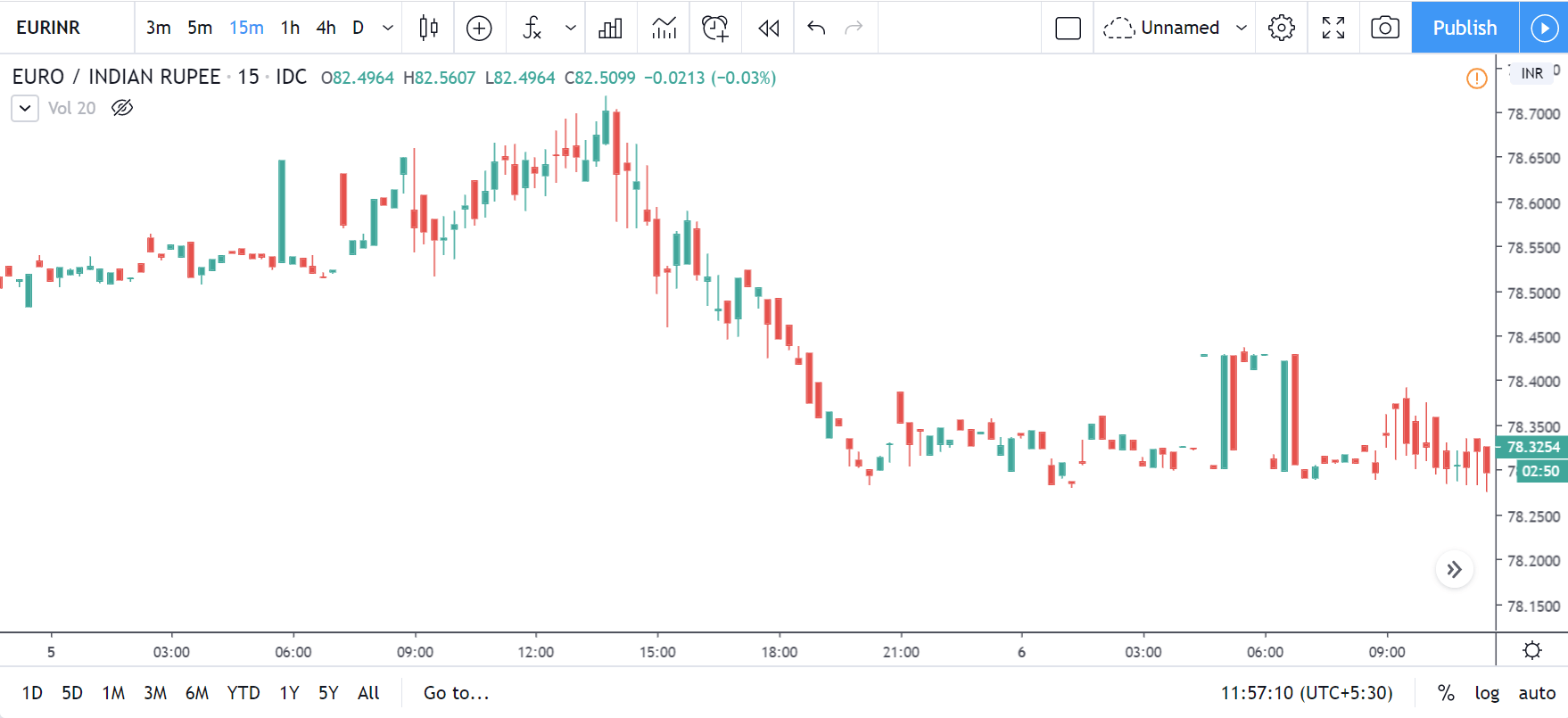
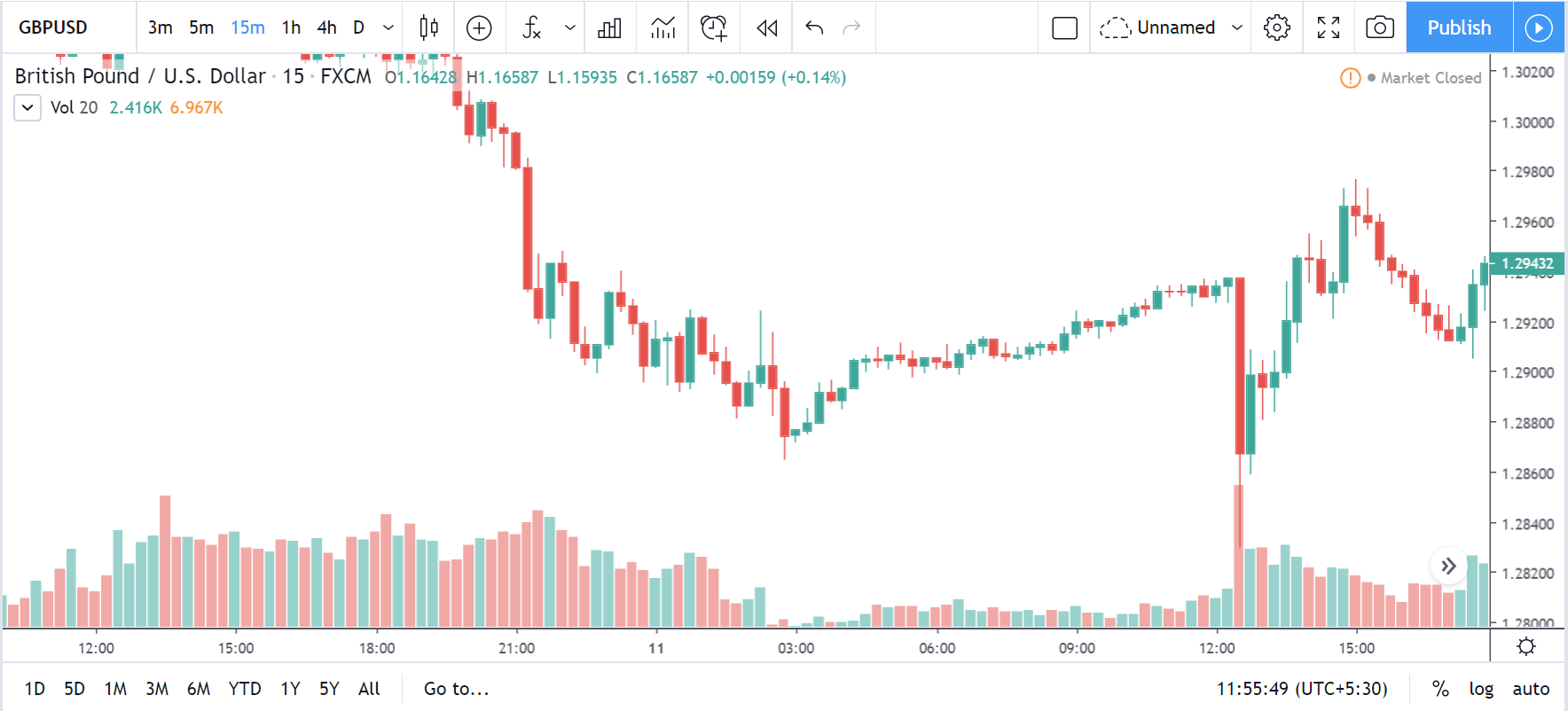
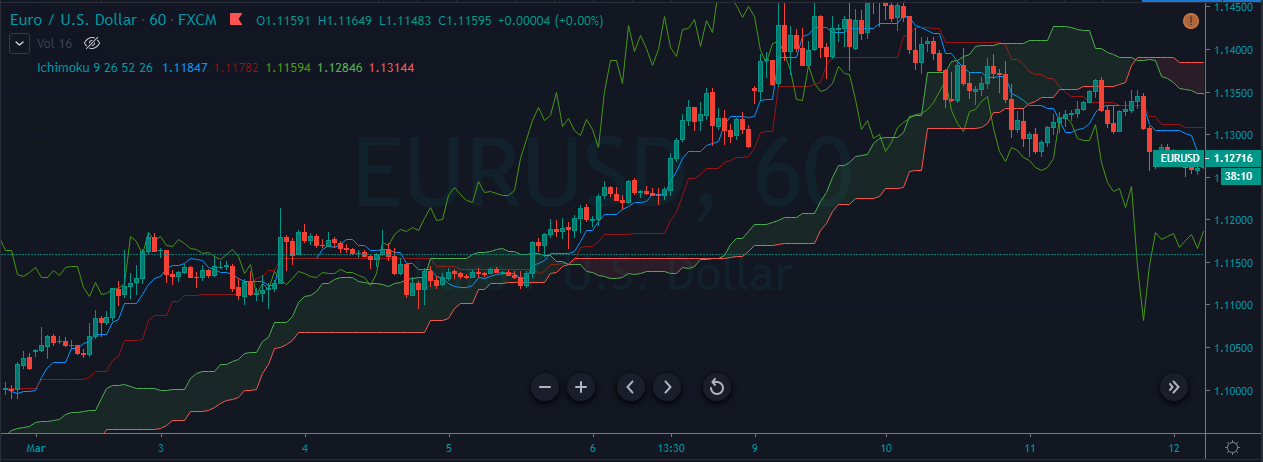
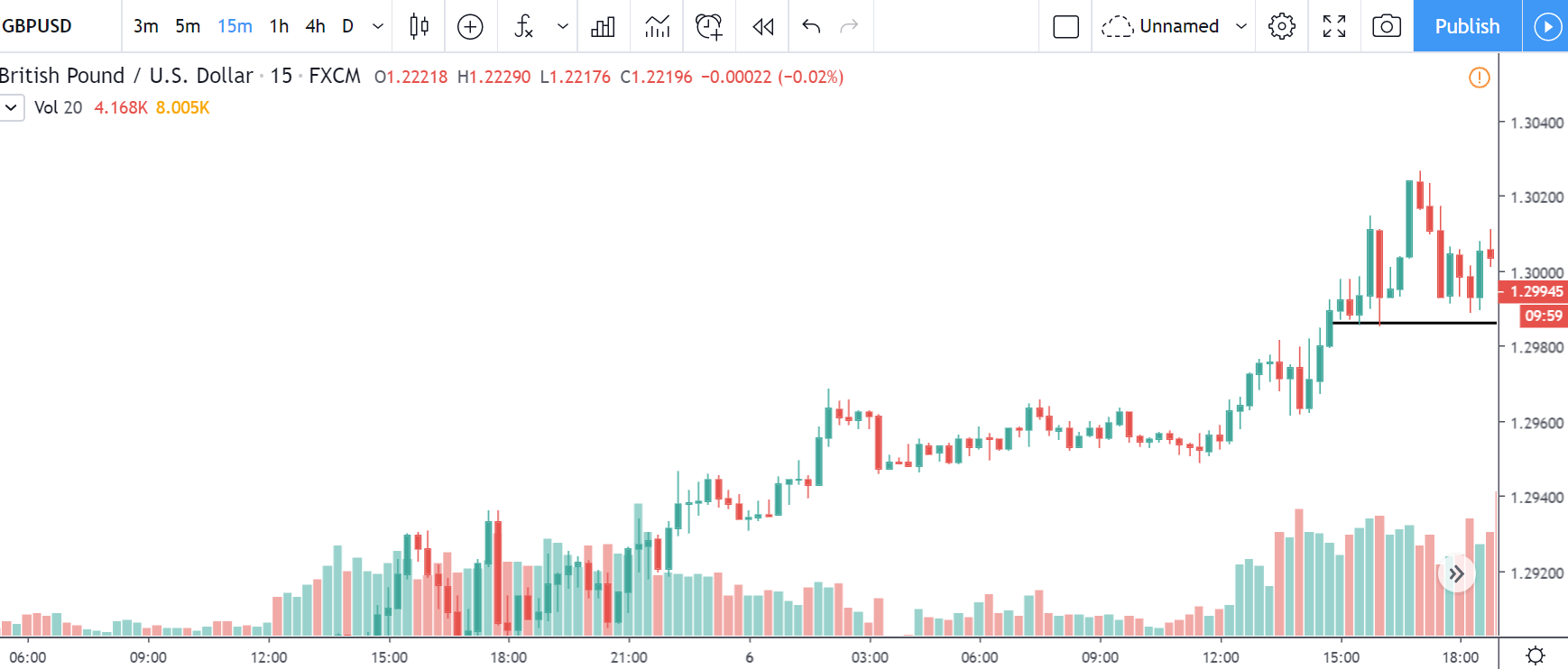
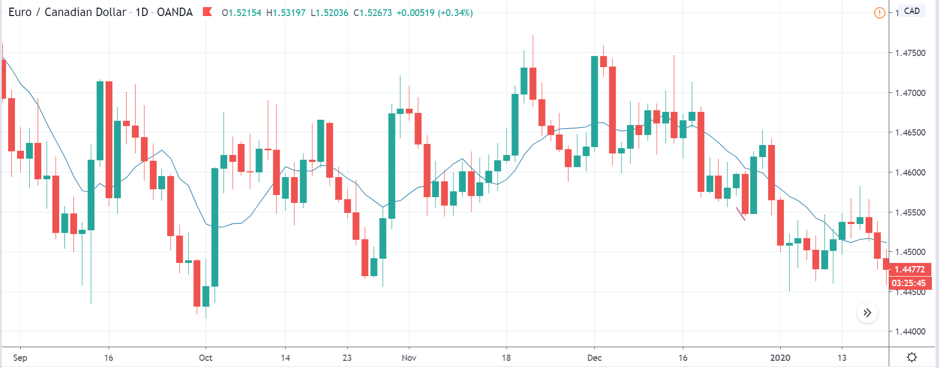
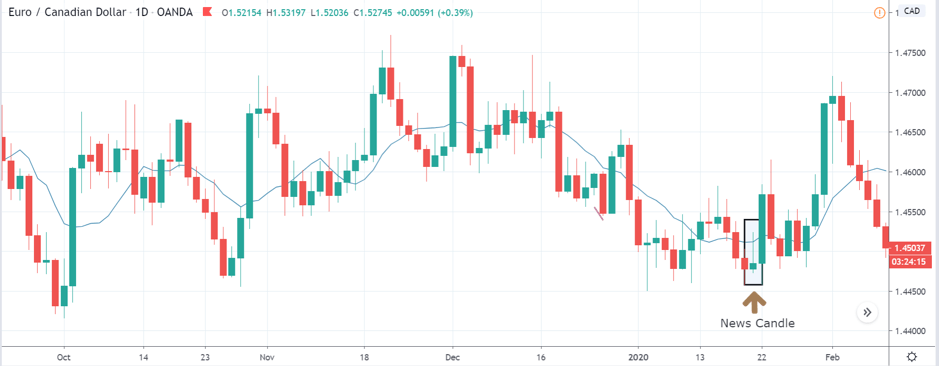
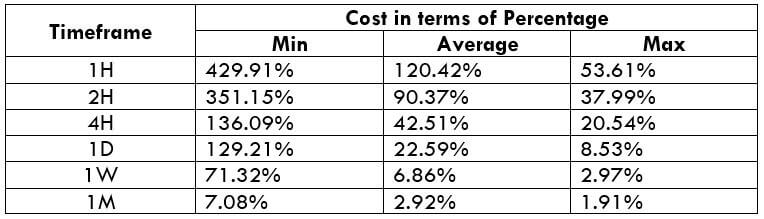
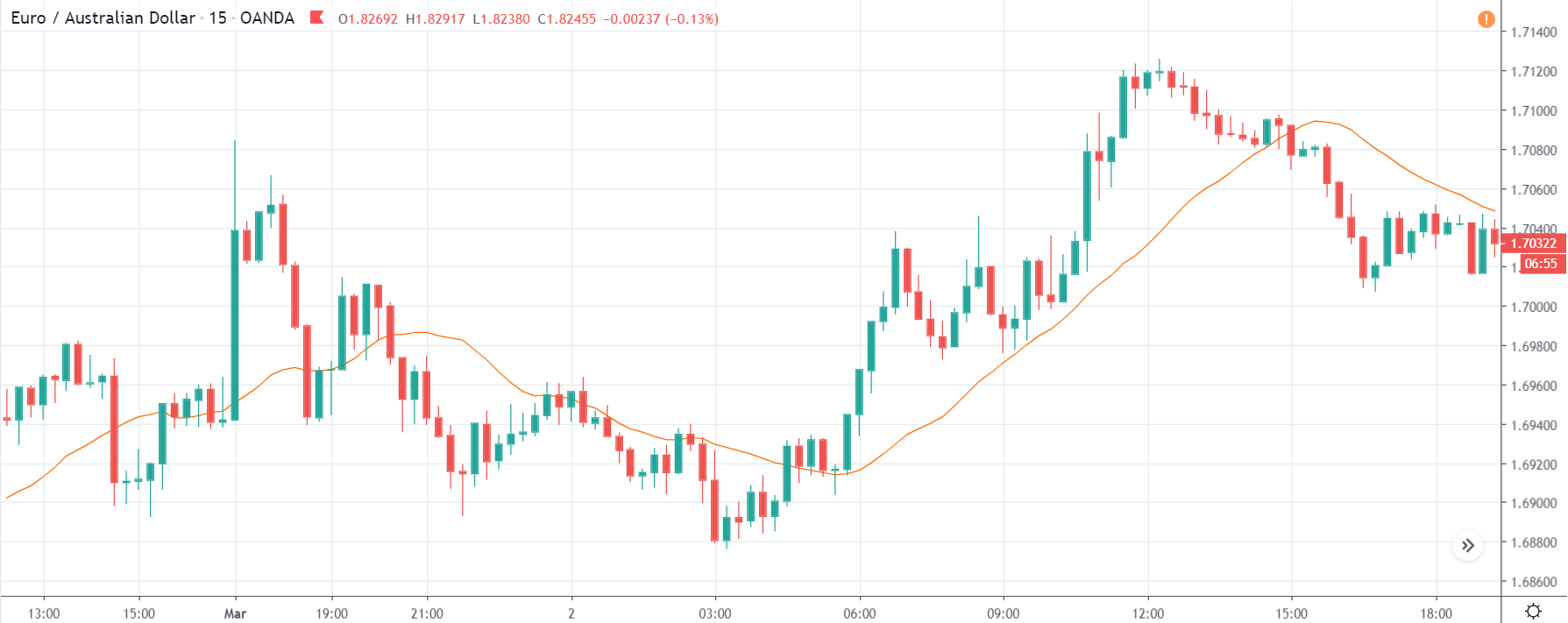
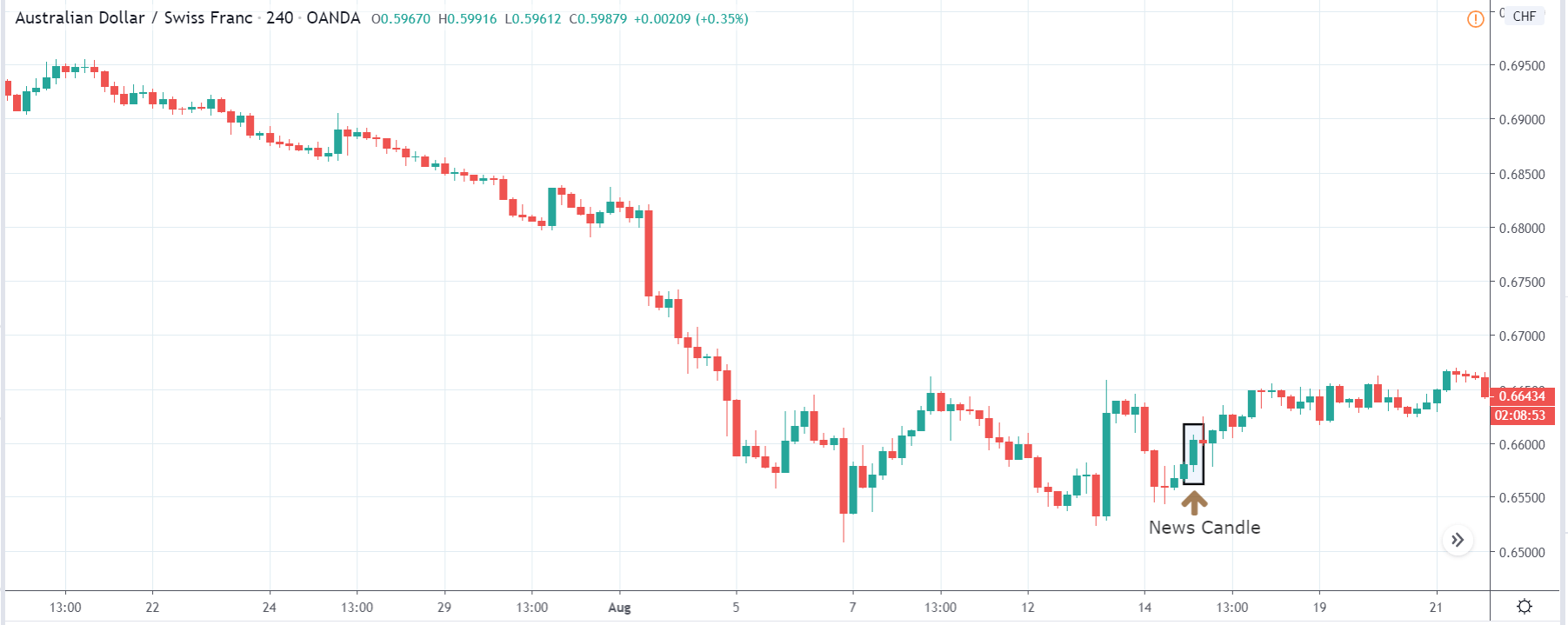
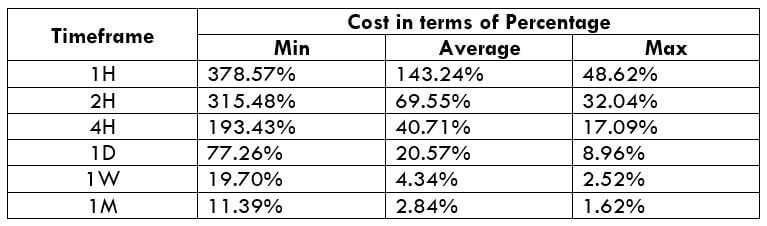
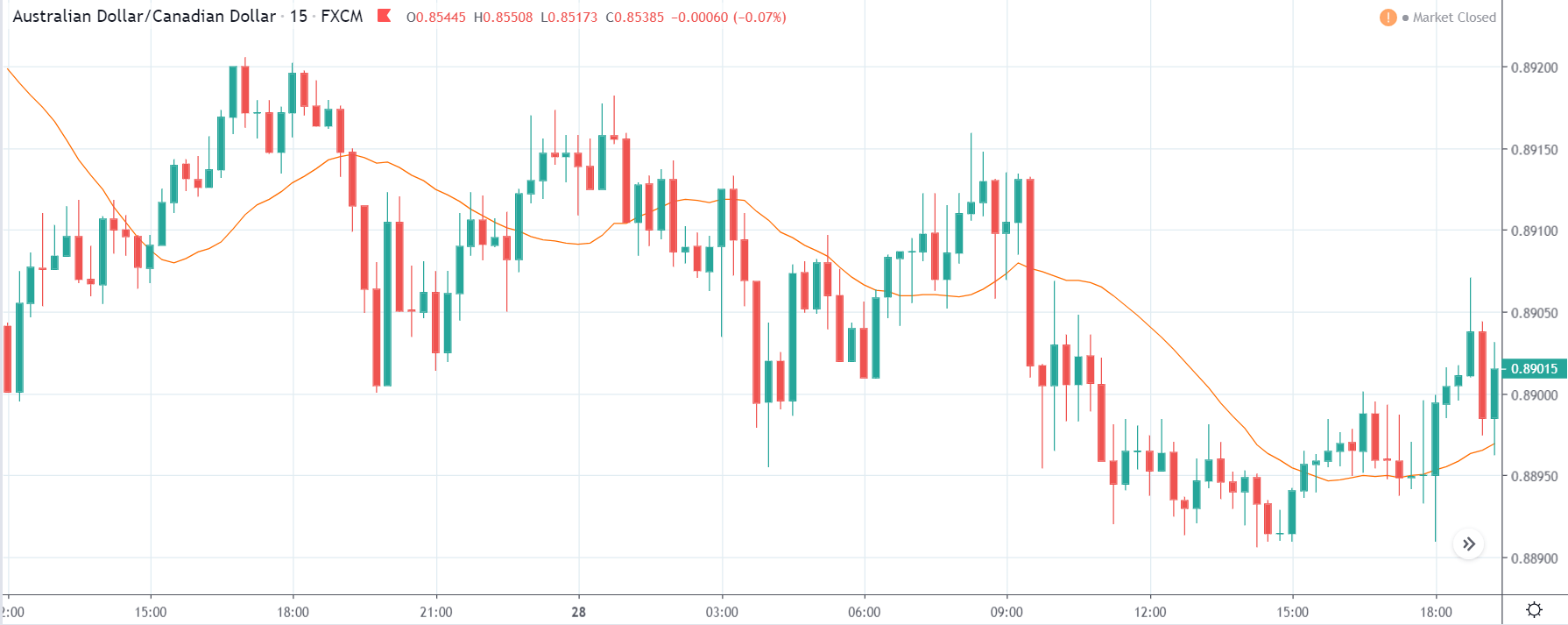
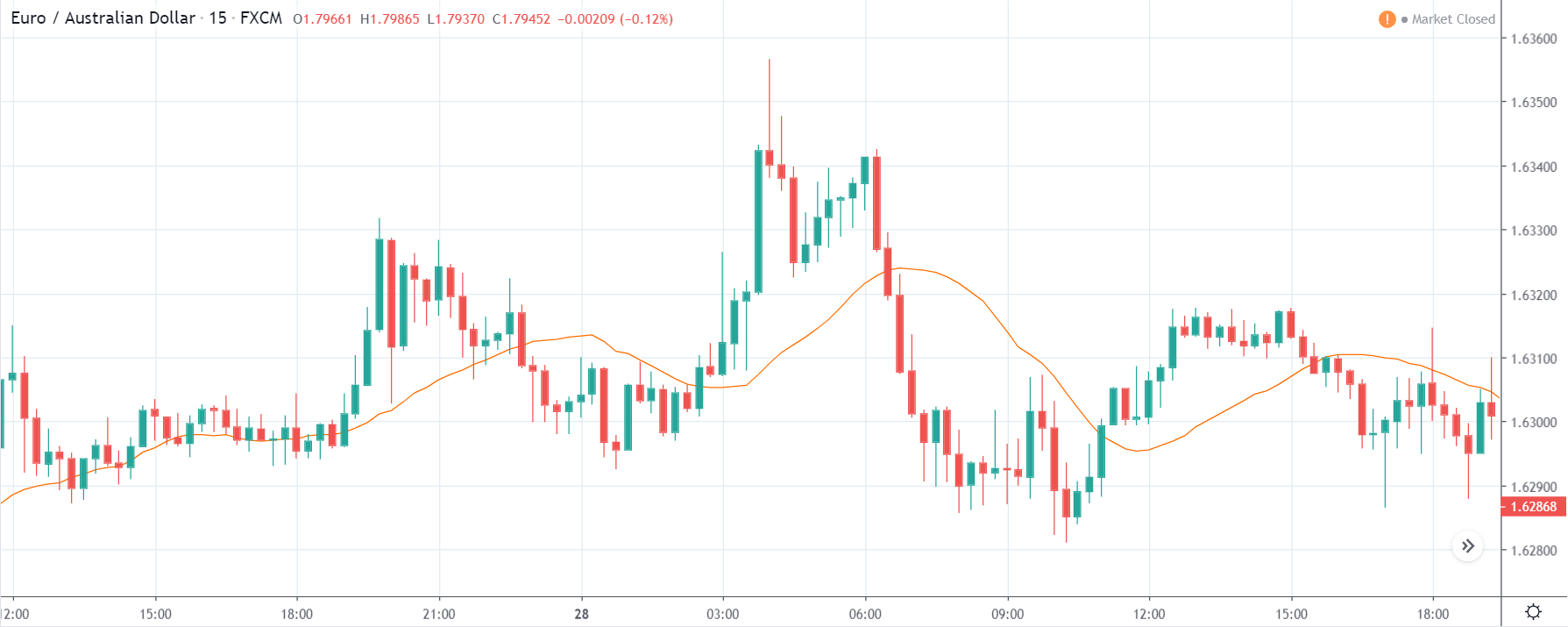
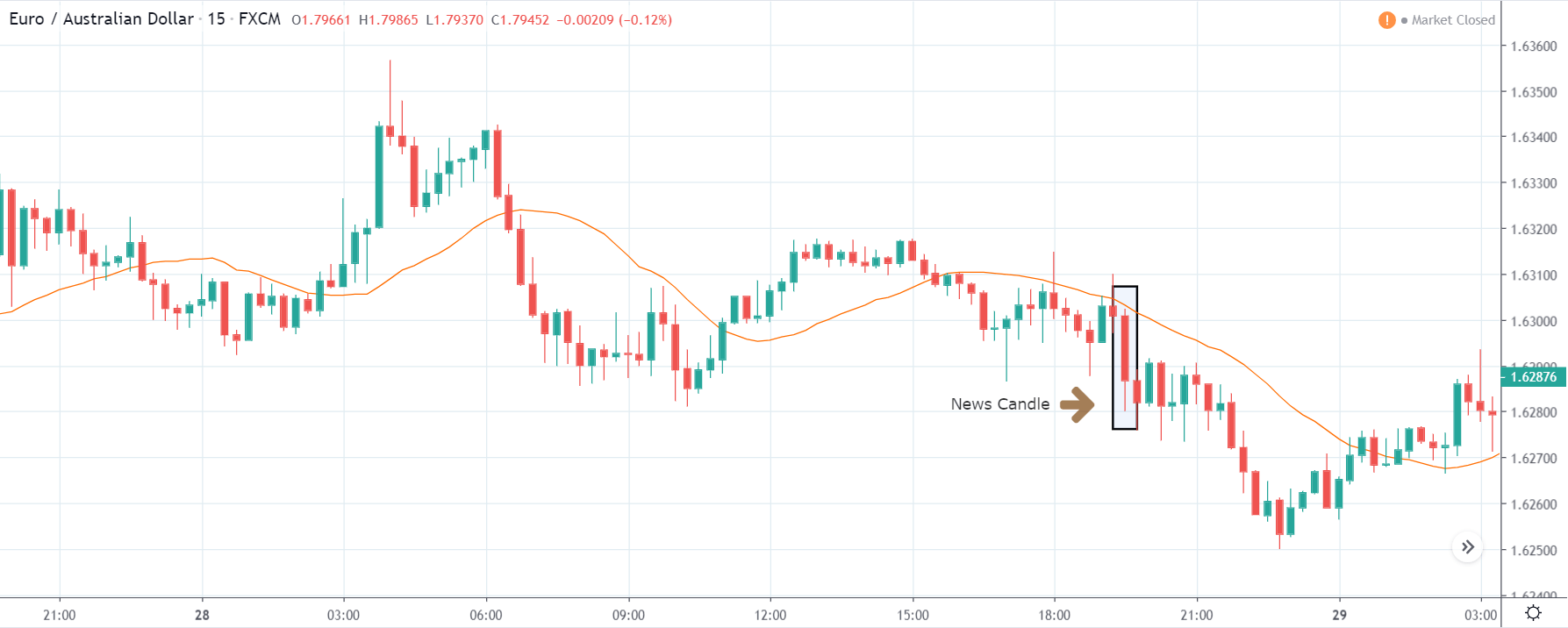
EUR/CAD | Before The Announcement
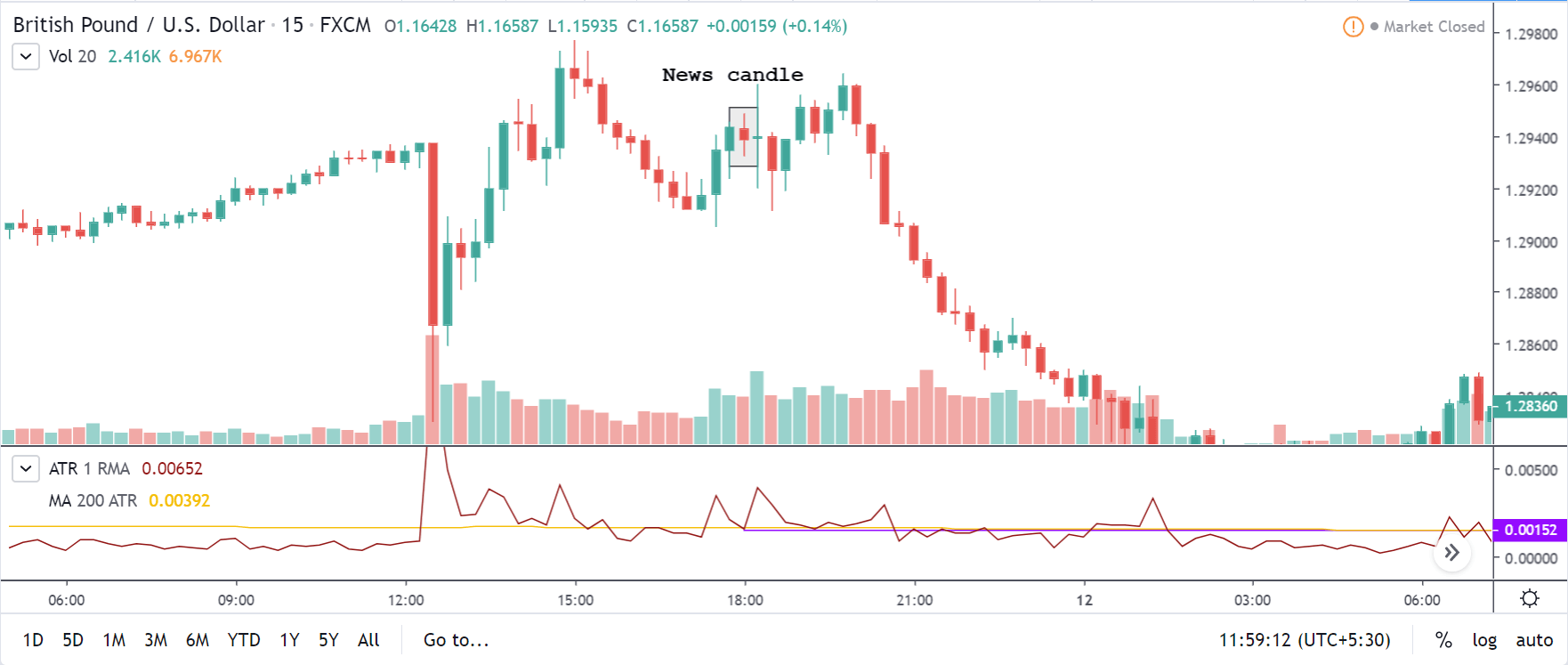
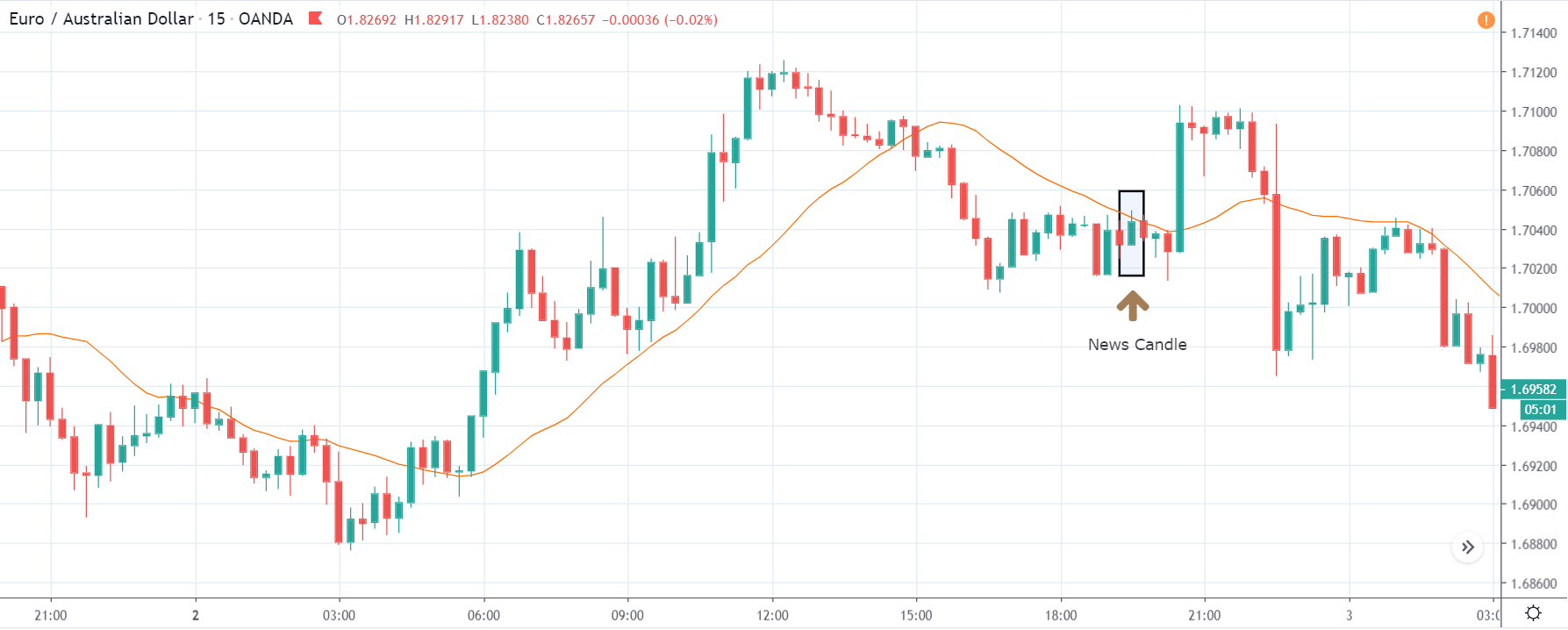
EUR/CAD | After The Announcement
The above images represent the EUR/CAD currency pair. In the first image, we see that the price is moving within a range, and just before the announcement of Income-tax rates, the price is at the bottom of the range. Since the price is at an optimal place for going ‘long’ in the market, aggressive traders can buy the currency pair with a strict stop loss of a few pips below the ‘support’ area.
We are essentially advantage of the increased volatility and movement in the pair. After the Income Tax rates are published, the market moves higher similar to the GBP/CAD pair, but later, the market gets sold into, and the candle closes with a large wick on the top. We can say that the news data was neutral to negative for the economy. Thus, there some confusion among traders can be seen. As the ‘news candle’ is not a bullish candle, it is wise to wait for the price to cross above the moving average and then a ‘buy’ trade.
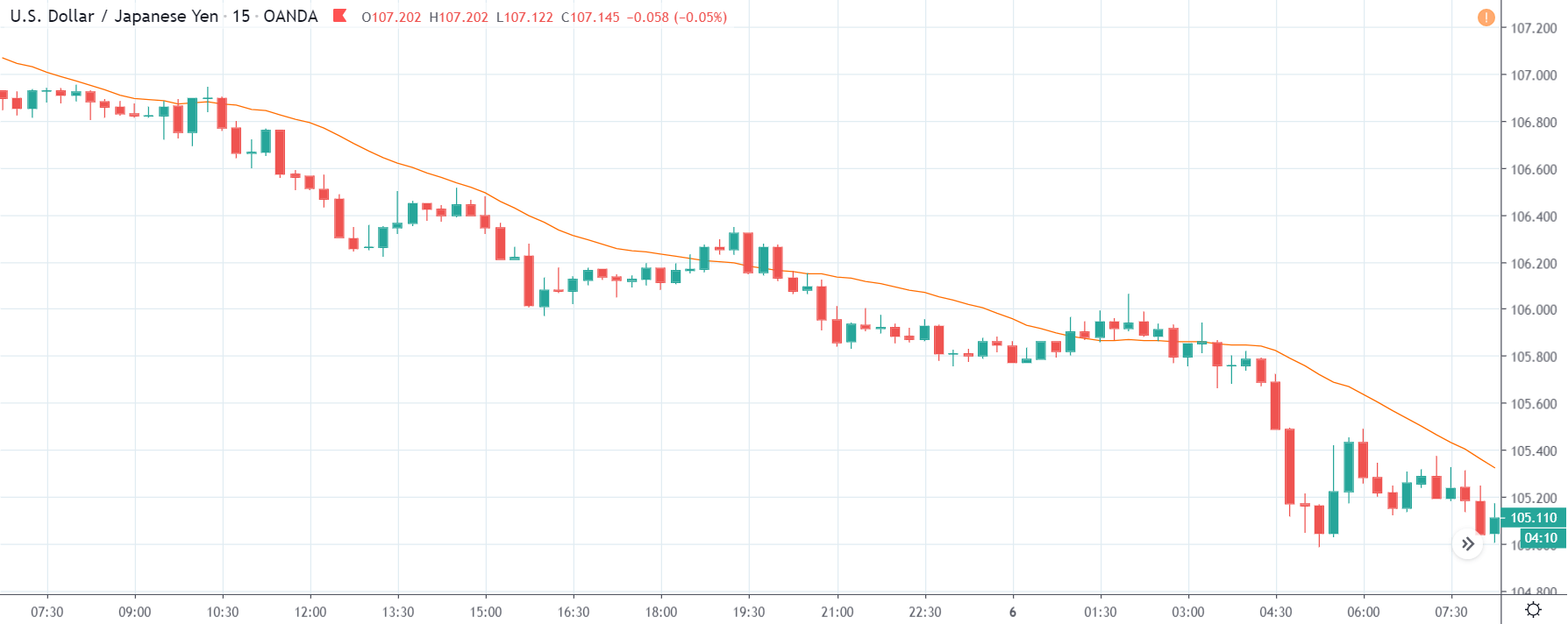
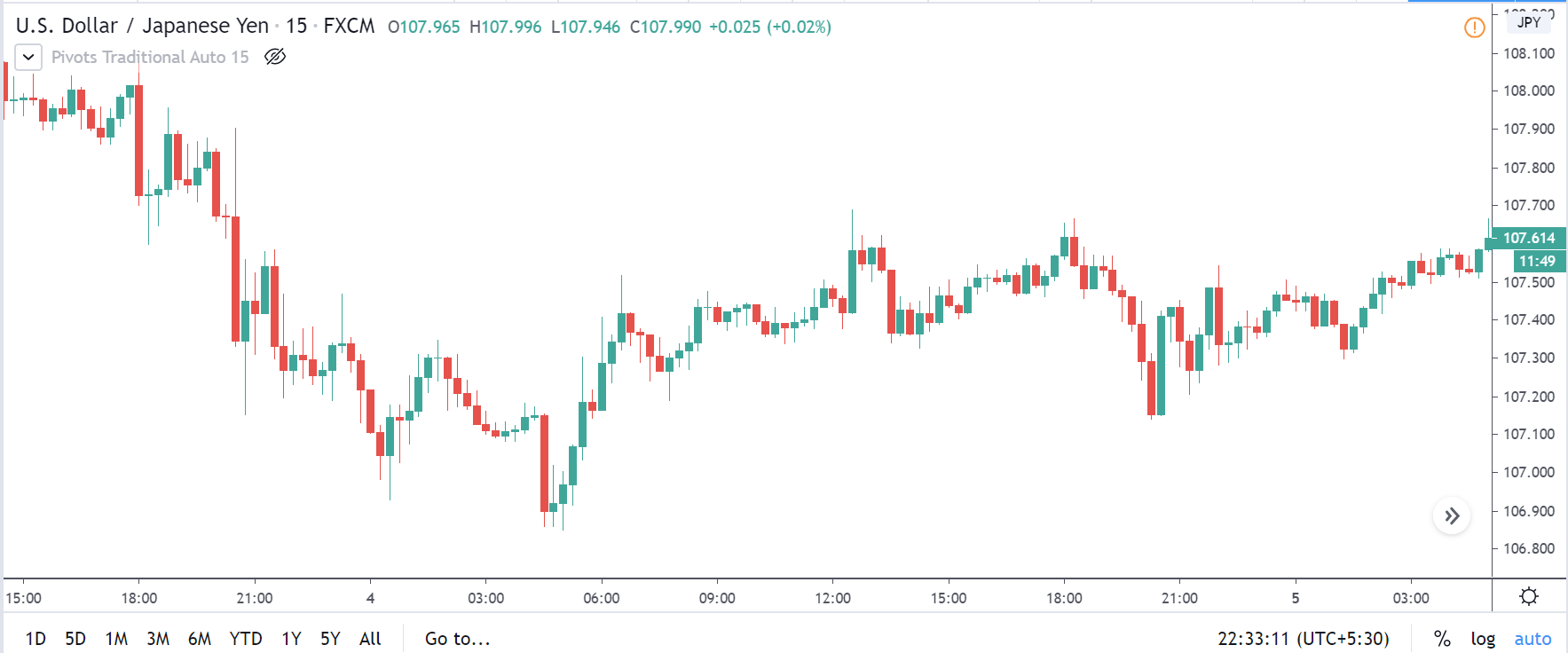
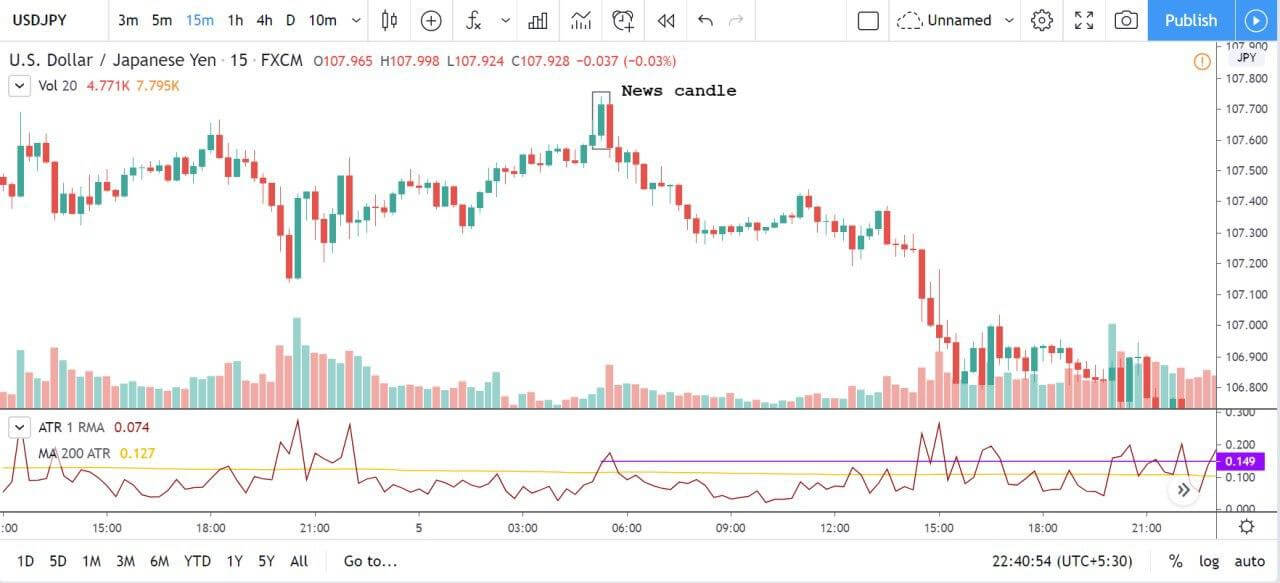
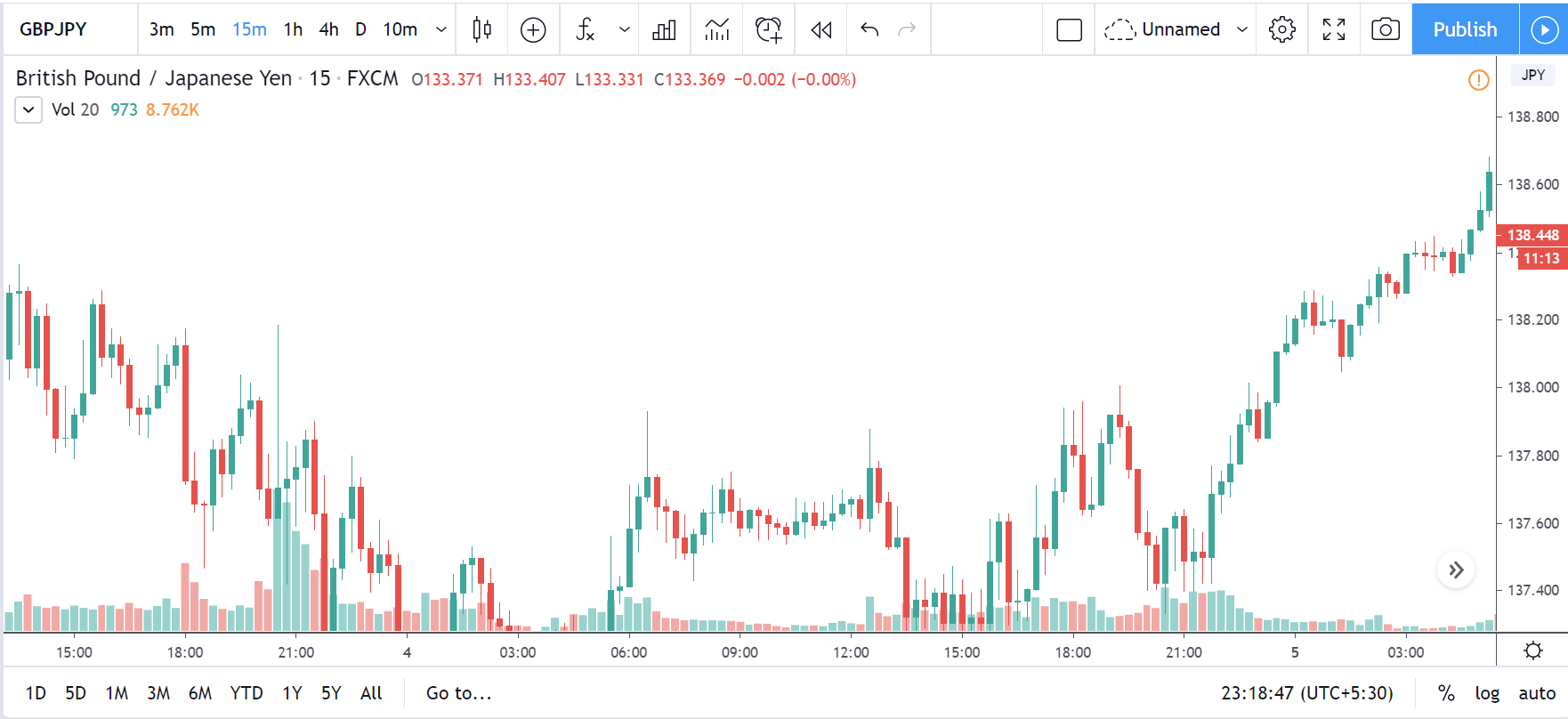
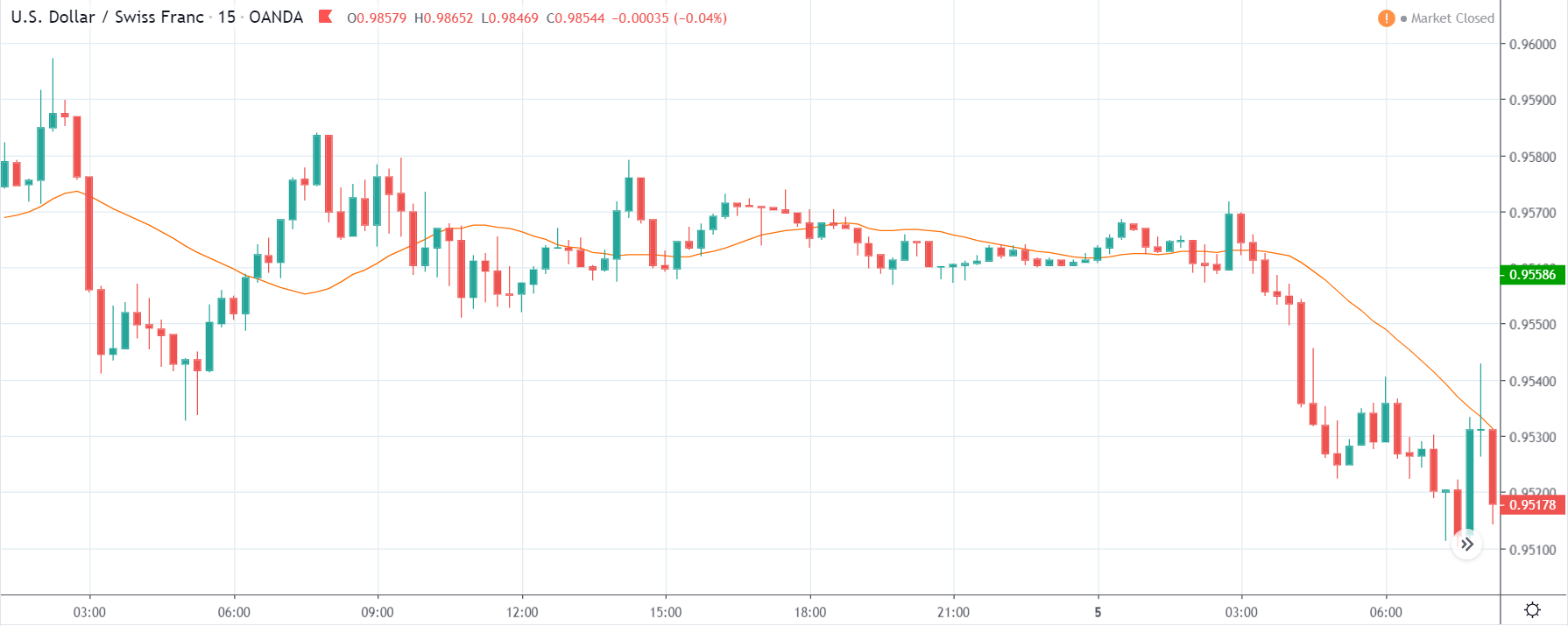
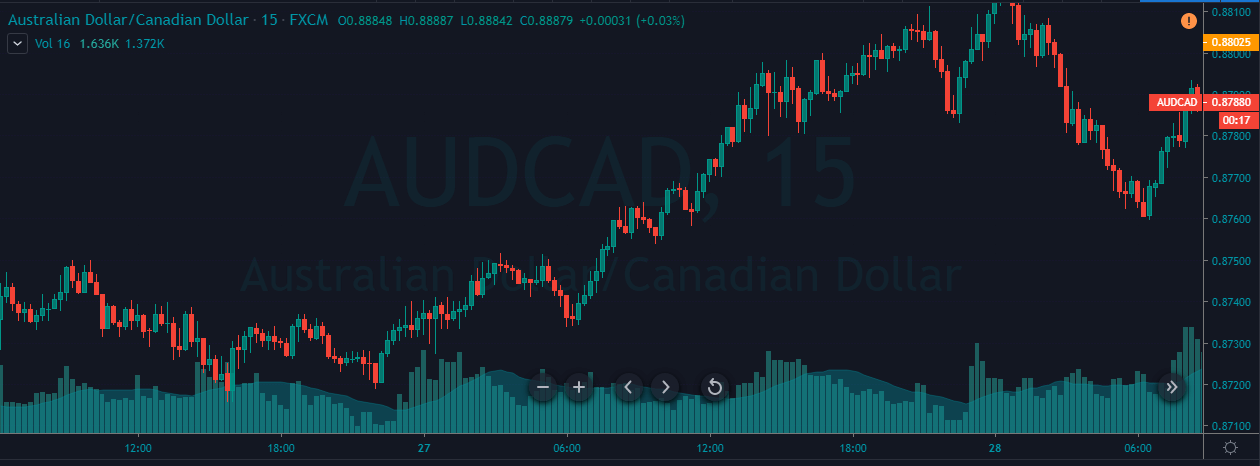
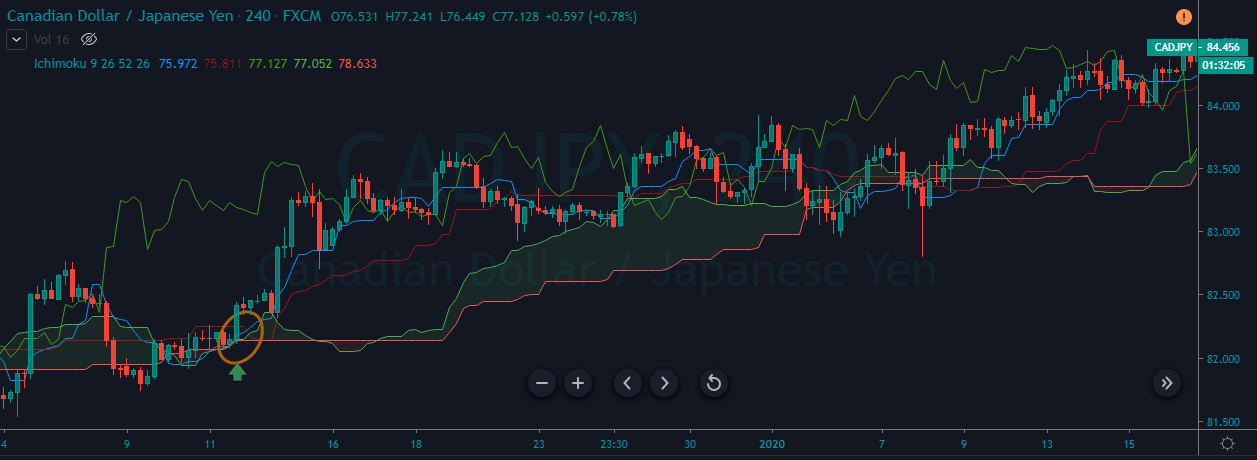
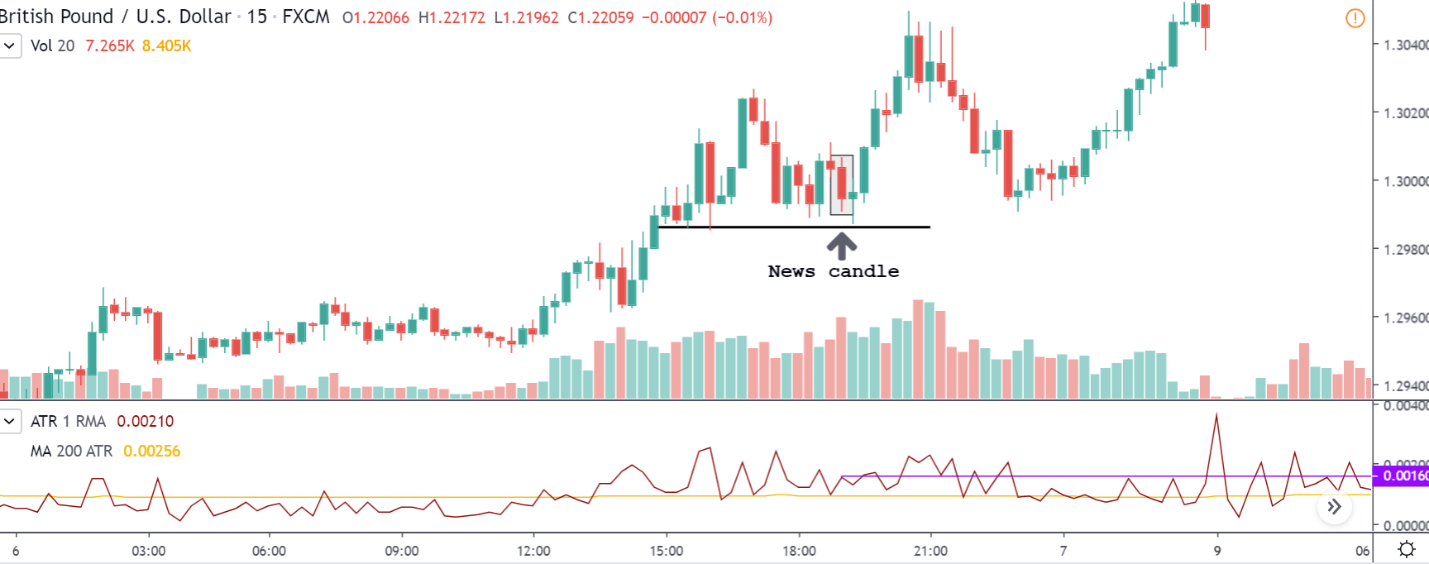
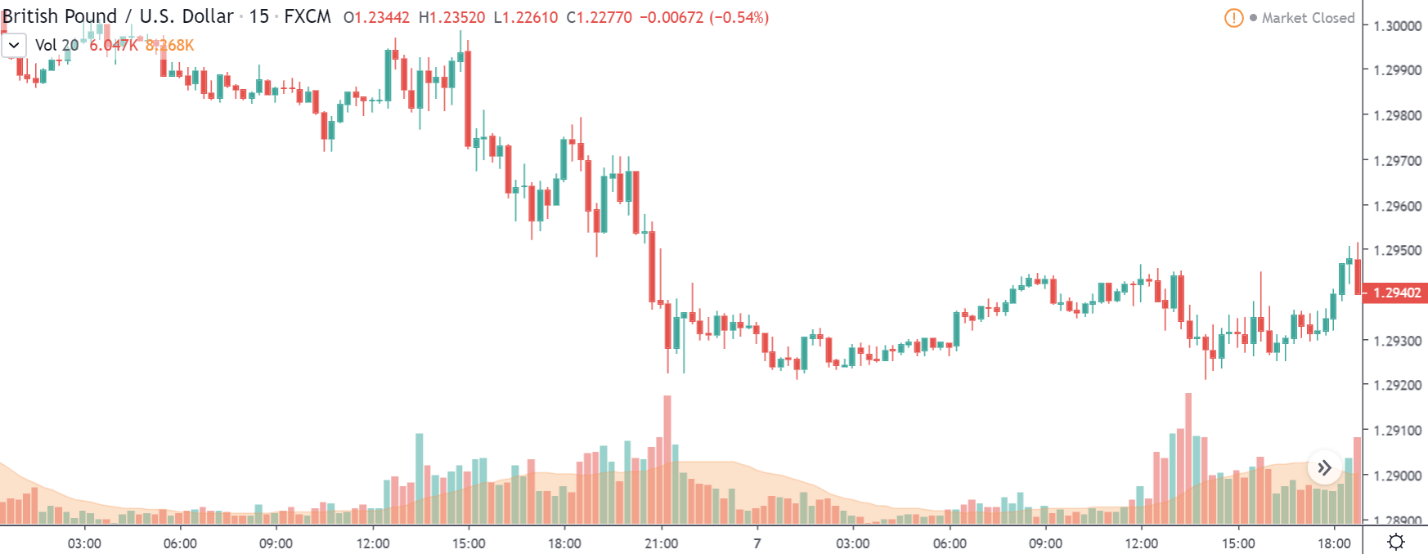
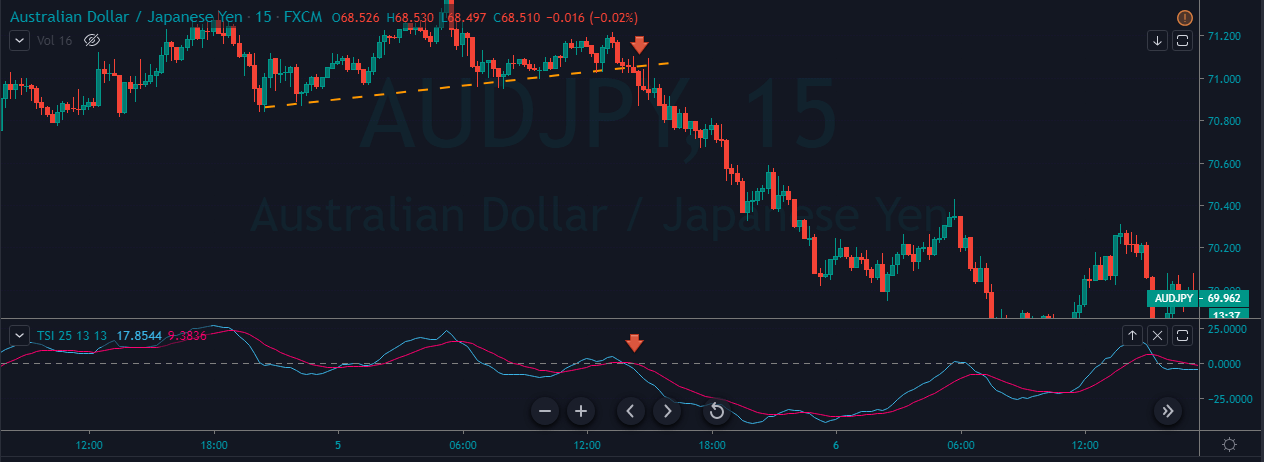
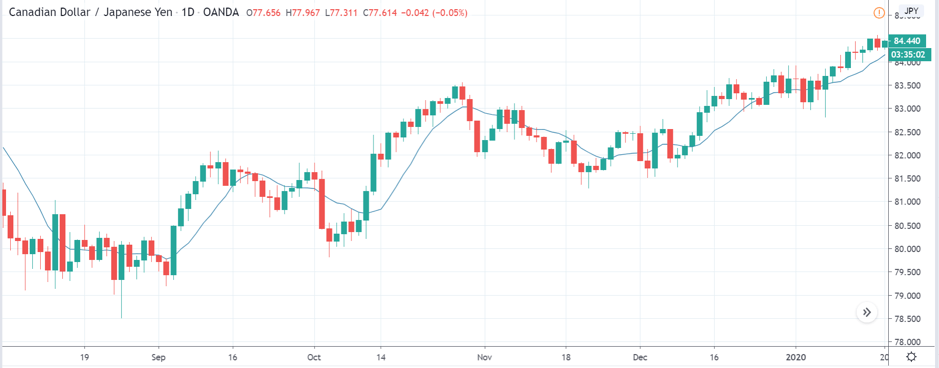
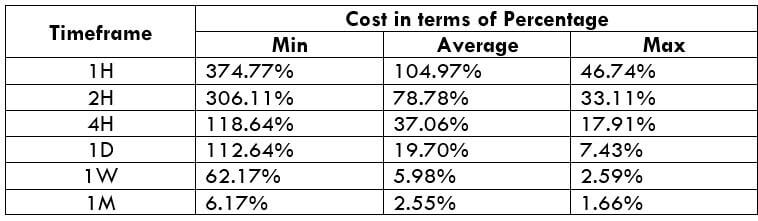
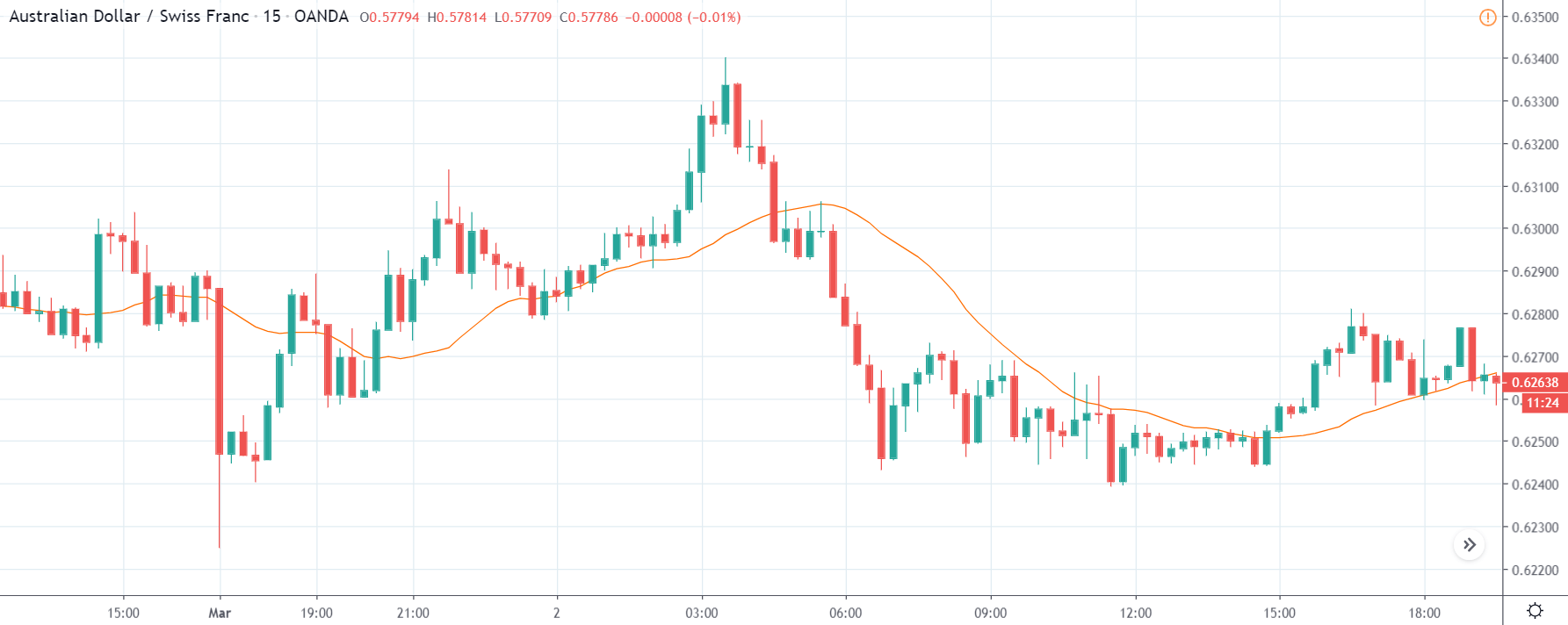
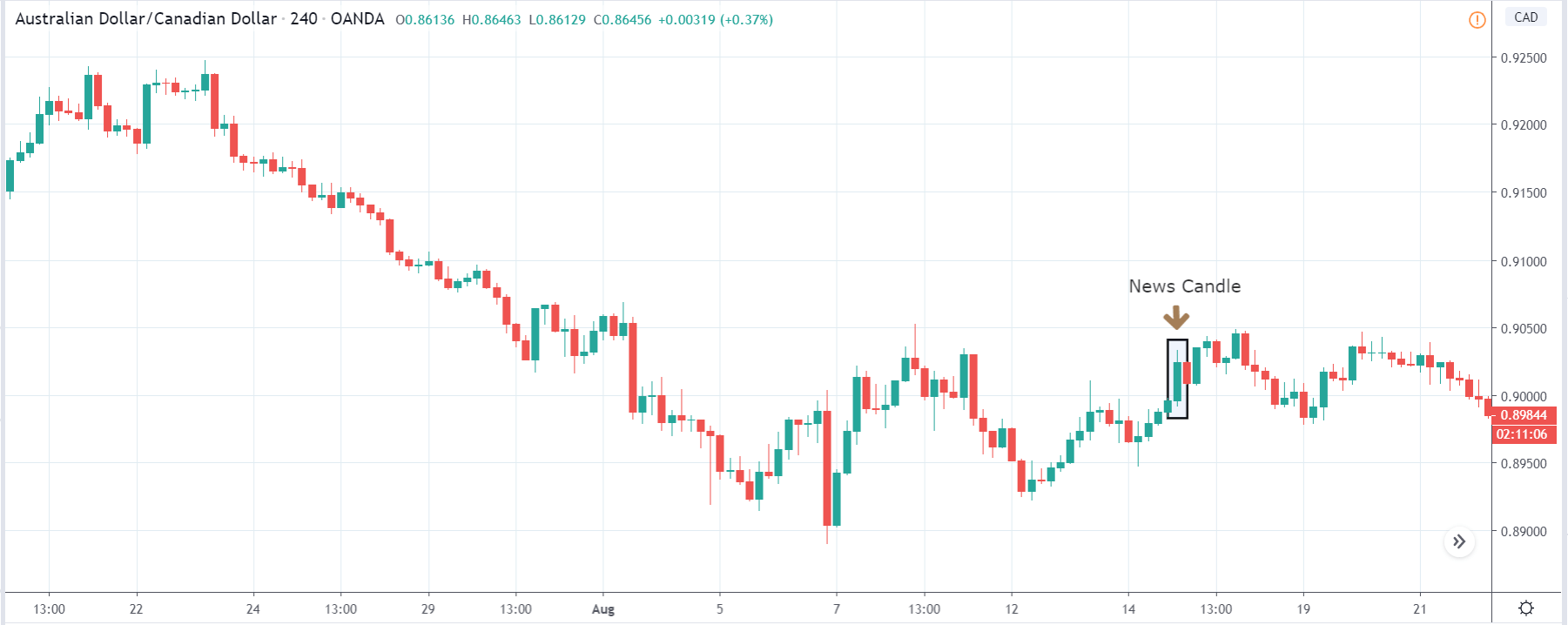
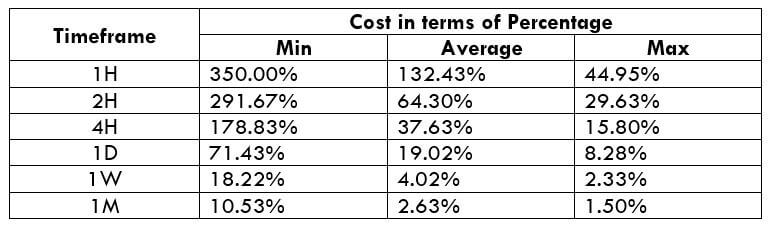
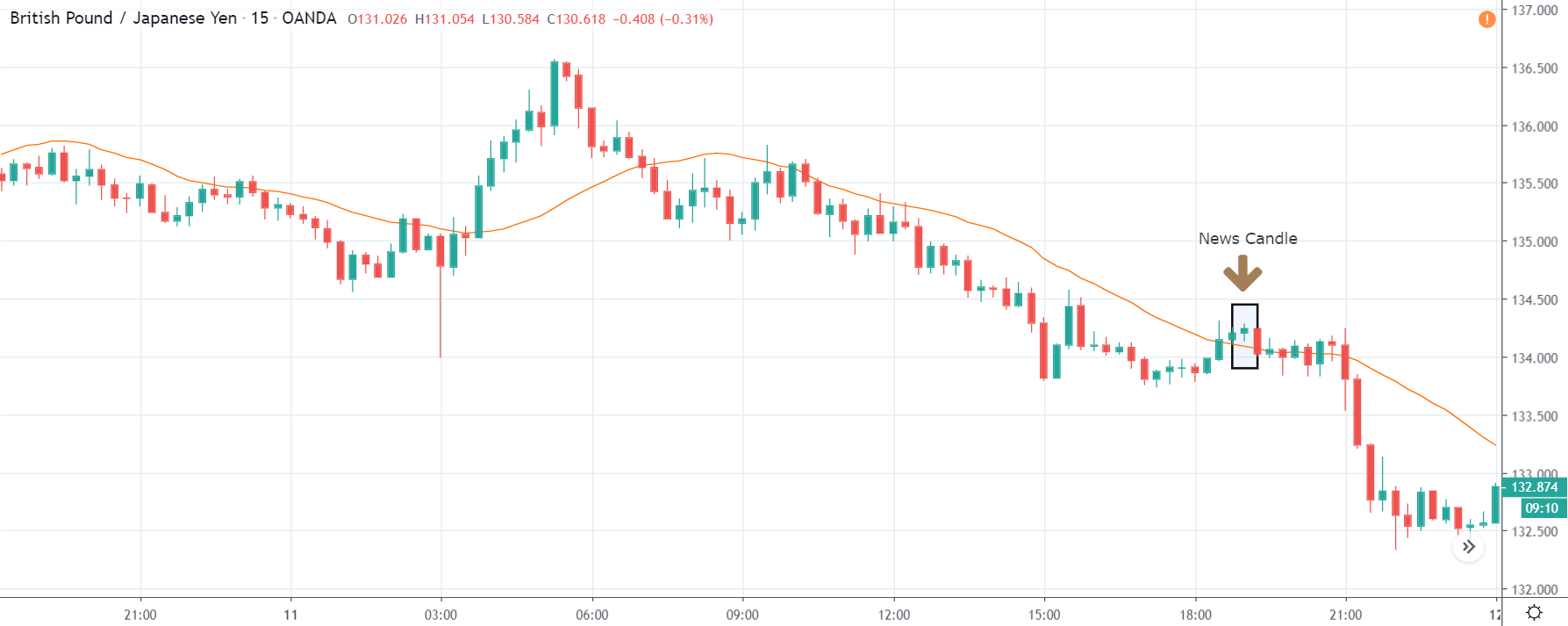
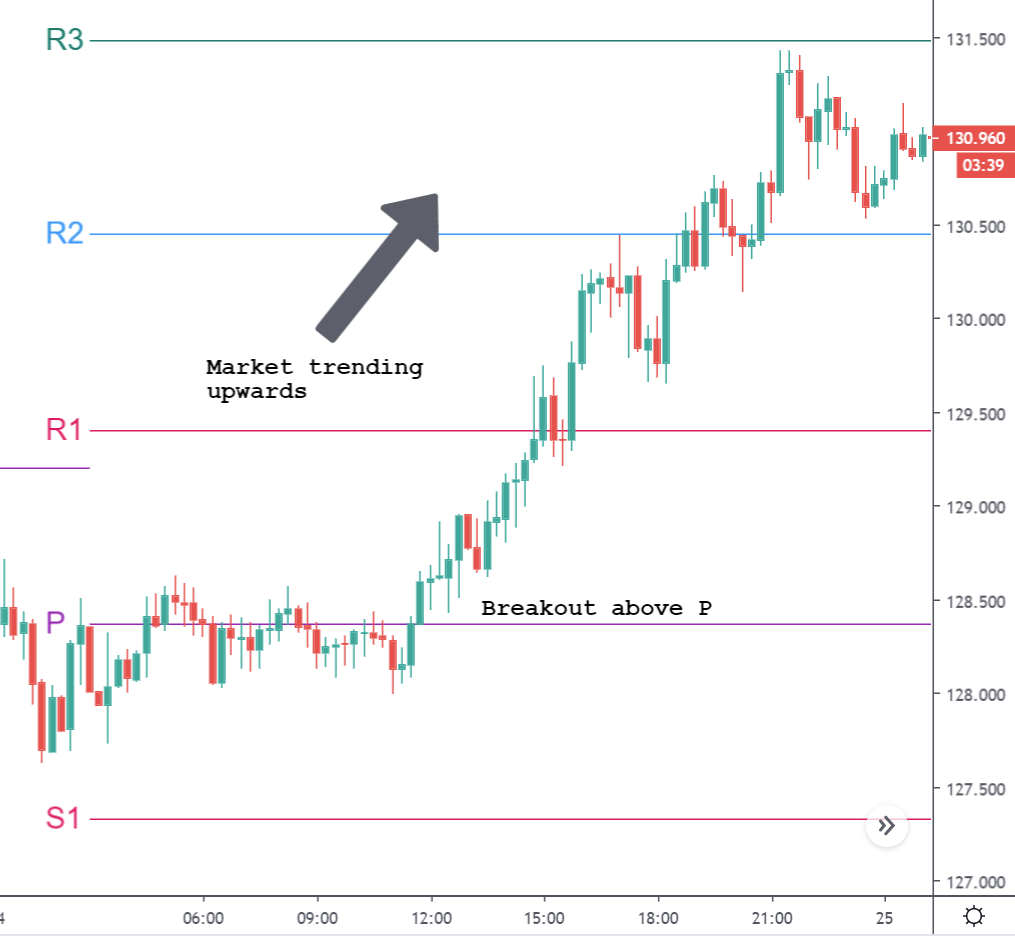
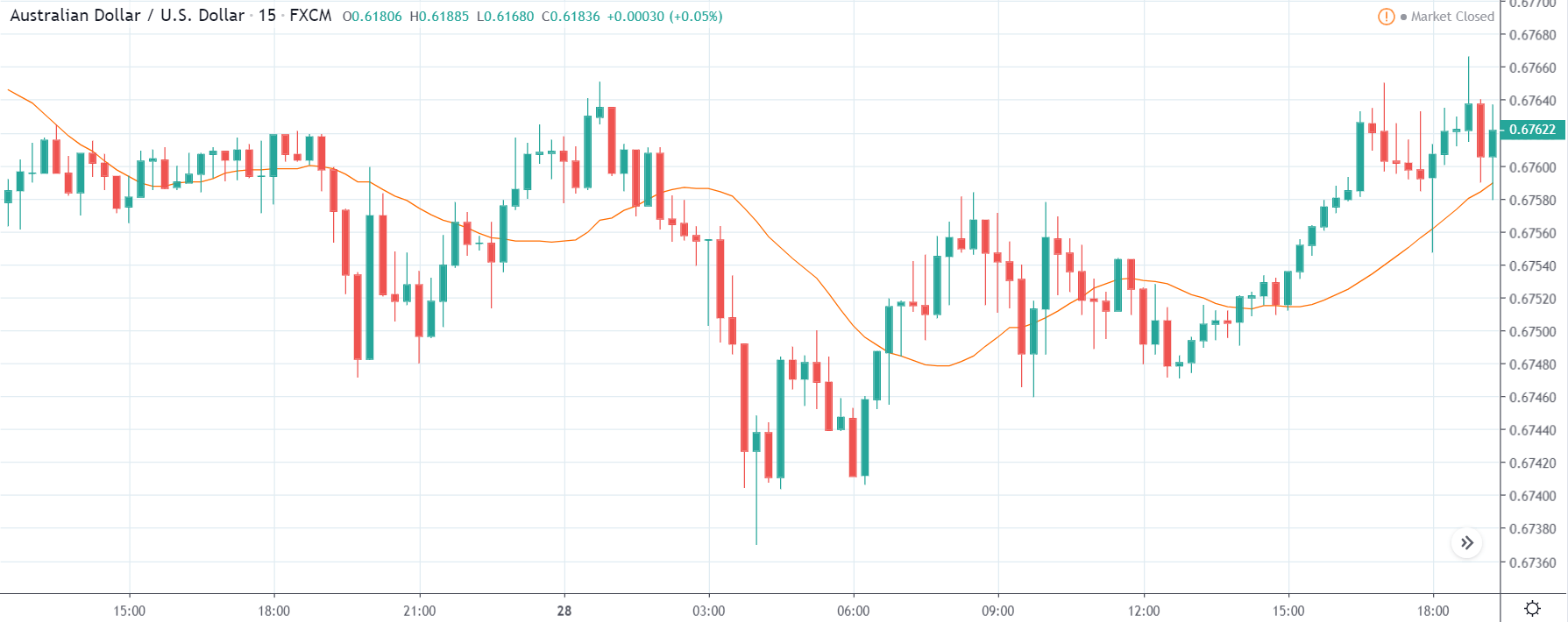
CAD/JPY | Before The Announcement
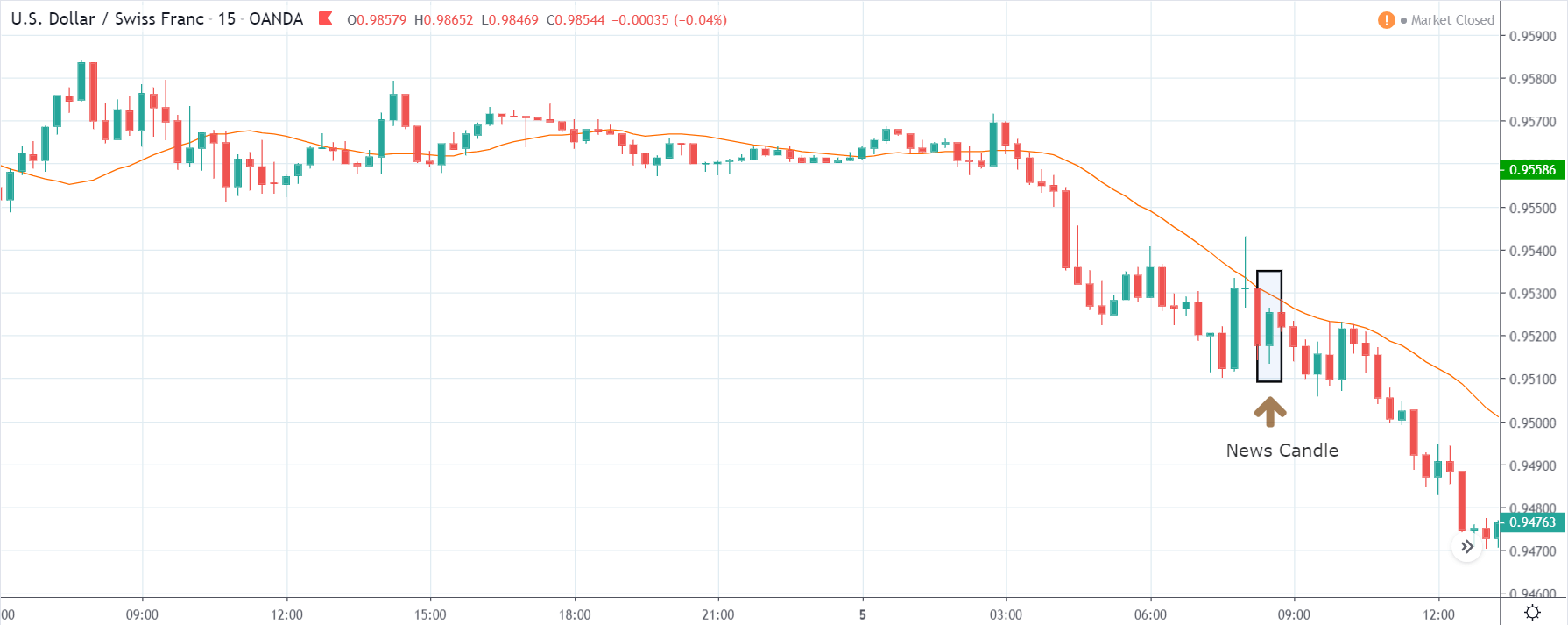
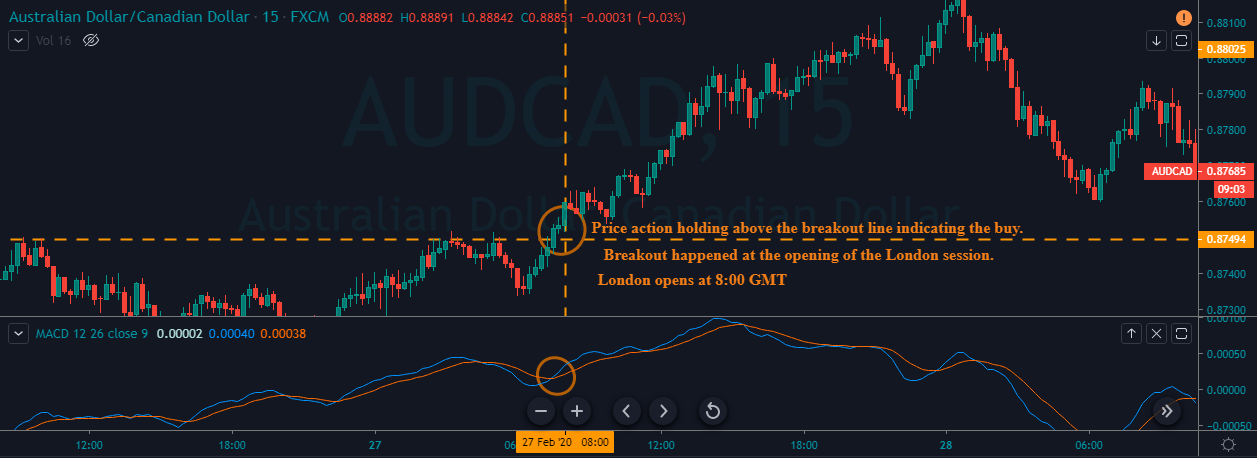
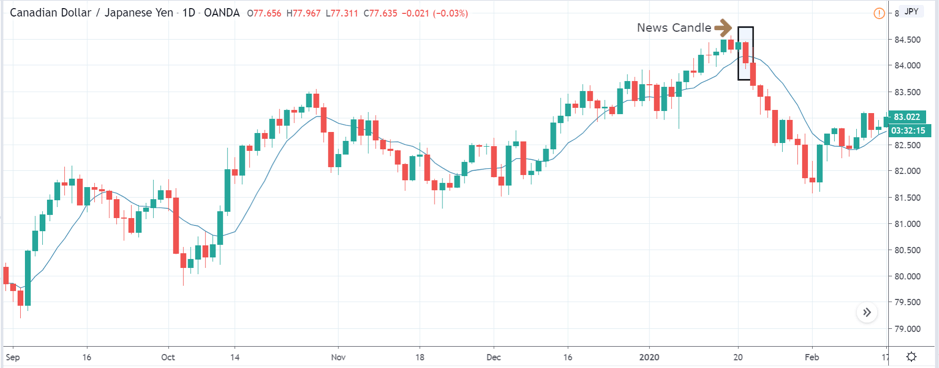
CAD/JPY | After The Announcement
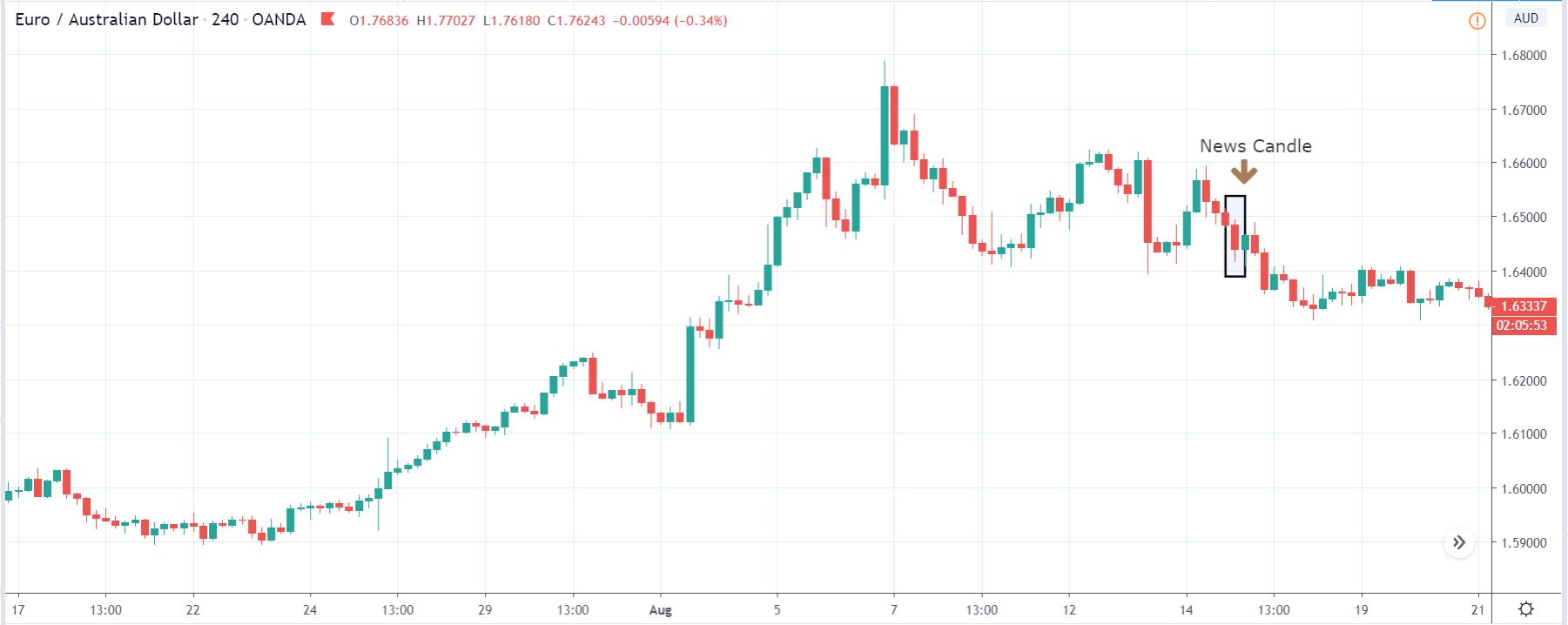
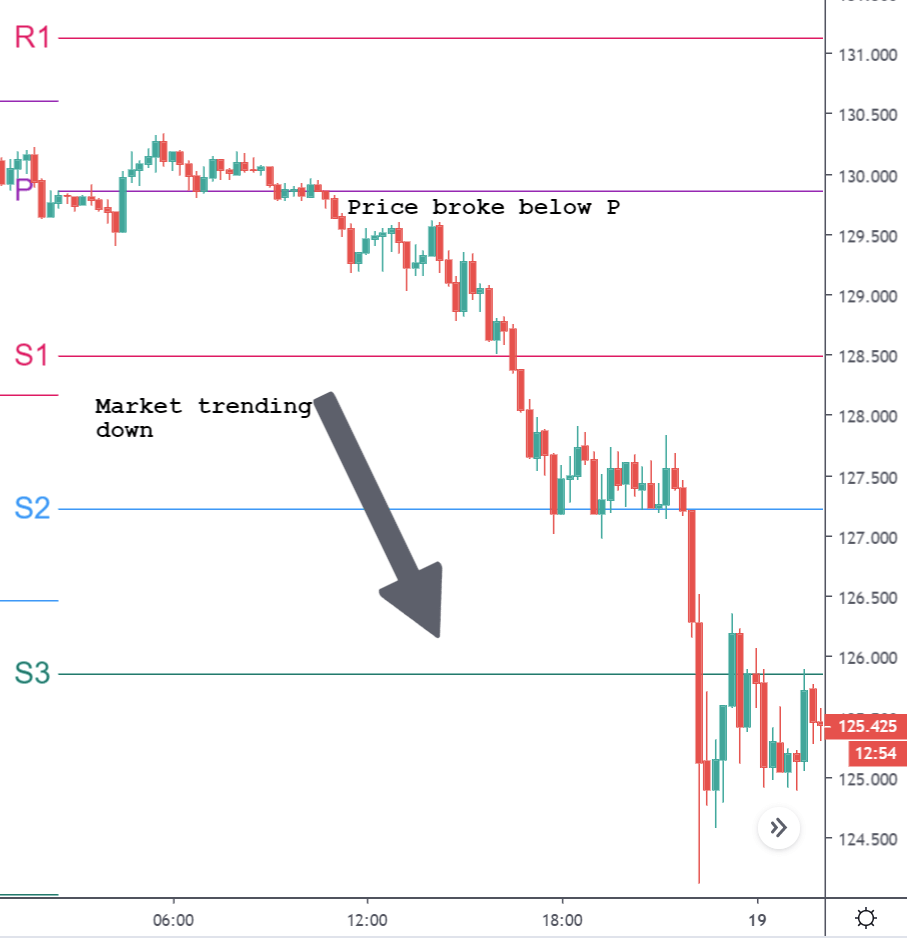
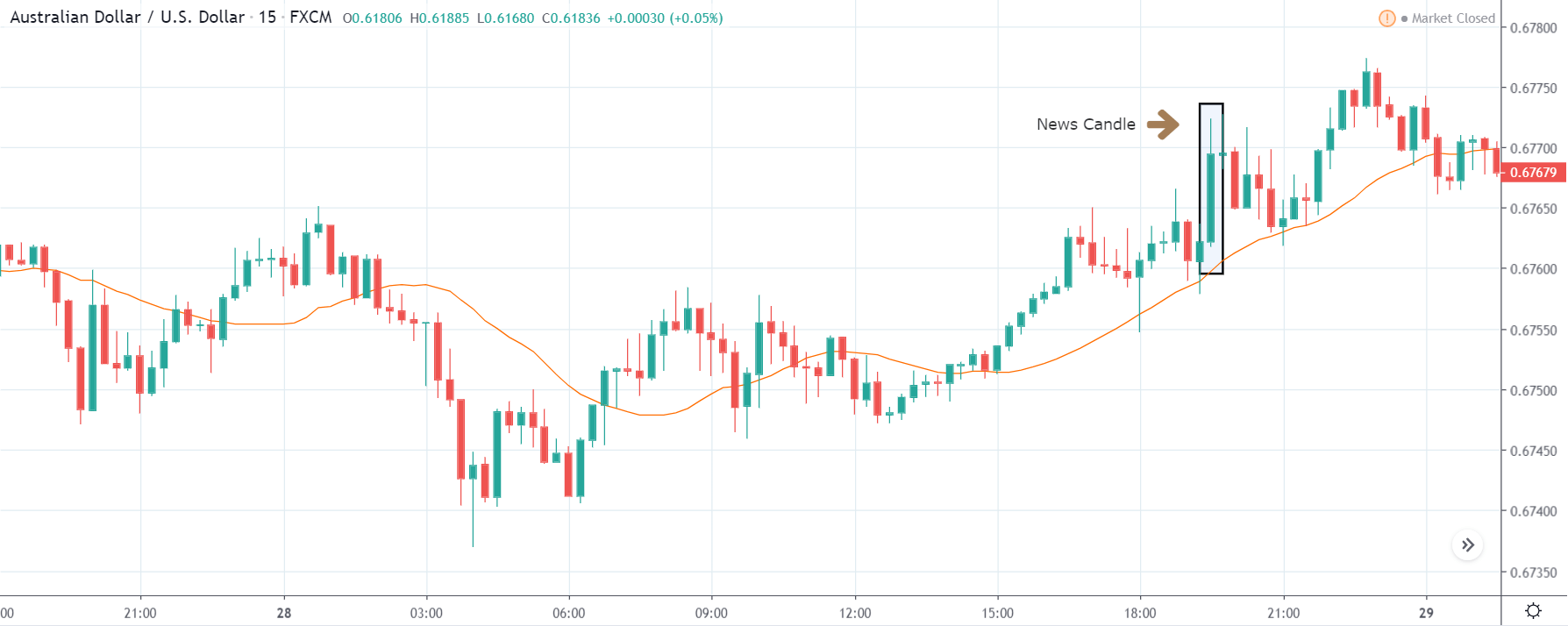
Lastly, we discuss the CAD/JPY currency pair, where the characteristics of the chart appear to be different from the above two pairs. Since the Canadian dollar is on the left-hand side, an uptrend in the first image signifies a great amount of strength in the currency. As the market is continuously moving higher before the announcement, we need a lot of confirmation from the market in order to go ‘short’ in the market. I
f the news data is positive for the economy, the move gets accelerated to on the upside and, in that case, once can join the trend after a retracement. After the news announcement, the market crashes, and volatility increases to the downside, thereby indicating a possible reversal. The bearish ‘news candle’ shows that the Income Tax rates were not very positive for the economy, and thus traders sold Canadian dollars. One should take ‘short’ trade only after the price goes below the moving average.
That’s about Income Tax and the impact of its new release on the Forex Market. Let us know if you have any questions in the comments below. Cheers.



























 IoT stands for the Internet of things. It is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital devices. These devices are provided with unique identifiers that can transfer data in the network without human-to-human or human-to-machine interaction. This is possible as the devices are extended with internet connectivity and sensors so that the transfer of data is possible.
IoT stands for the Internet of things. It is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital devices. These devices are provided with unique identifiers that can transfer data in the network without human-to-human or human-to-machine interaction. This is possible as the devices are extended with internet connectivity and sensors so that the transfer of data is possible. The concept of IoT enables smart homes. Most of the devices we use at home can be embedded with sensors, and with the help of IoT, we can control them remotely using our smartphones. When at home, they can easily be controlled using Alexa, Google Home, with the help of voice recognition. To enable all these functionalities, sensitive data such as voice and facial recognition should be stored. This data can be stored securely in the blockchain, which allows strict access restrictions. It can be accessed by anyone else if required only through individual permissions using smart contracts.
The concept of IoT enables smart homes. Most of the devices we use at home can be embedded with sensors, and with the help of IoT, we can control them remotely using our smartphones. When at home, they can easily be controlled using Alexa, Google Home, with the help of voice recognition. To enable all these functionalities, sensitive data such as voice and facial recognition should be stored. This data can be stored securely in the blockchain, which allows strict access restrictions. It can be accessed by anyone else if required only through individual permissions using smart contracts. IoT plays a very crucial role in health care these days. Remote health care can be achieved using IoT. Elderly care is essential to most of the countries these days as the elderly population is increasing in countries like China, Japan, and the US. Since there are fewer people to take care of the elderly, IoT can come to our rescue.
IoT plays a very crucial role in health care these days. Remote health care can be achieved using IoT. Elderly care is essential to most of the countries these days as the elderly population is increasing in countries like China, Japan, and the US. Since there are fewer people to take care of the elderly, IoT can come to our rescue. Agriculture can be widely improved by deploying IIOT (Industrial IOT) sensors and satellite imagery to monitor the millions of acres of land. With IoT used in the supply chain, provenance tracking can be enabled. Crops can be sold by using smart contracts even before harvesting them as all this data ensures the buyer of the quality of the product from the fields to their floor. This makes a profitable trade for all the parties involved.
Agriculture can be widely improved by deploying IIOT (Industrial IOT) sensors and satellite imagery to monitor the millions of acres of land. With IoT used in the supply chain, provenance tracking can be enabled. Crops can be sold by using smart contracts even before harvesting them as all this data ensures the buyer of the quality of the product from the fields to their floor. This makes a profitable trade for all the parties involved.



 One primary application of smart contracts lies in the healthcare industry. Transferring and sharing patients’ electronic medical records (EMR) should be done in the most secure way. We are not saying that the current technology is not secure at all. We are just saying that using this technology will enhance the existing security.
One primary application of smart contracts lies in the healthcare industry. Transferring and sharing patients’ electronic medical records (EMR) should be done in the most secure way. We are not saying that the current technology is not secure at all. We are just saying that using this technology will enhance the existing security. Banking systems have undergone a lot of changes proportional to technology adoption by the people. Smart contracts can play a crucial role in the mortgages provided by banks or any non-banking financial institutions. Banks spend a lot of money to check if the property that is being mortgaged currently is already mortgaged or not. To check if the property does indeed belong to the person applying for the mortgage or not. If the documents of the property are placed in blockchain with the help of smart contracts, this can be verified in a click. This saves a lot of money to both consumers and banking, reportedly in billions.
Banking systems have undergone a lot of changes proportional to technology adoption by the people. Smart contracts can play a crucial role in the mortgages provided by banks or any non-banking financial institutions. Banks spend a lot of money to check if the property that is being mortgaged currently is already mortgaged or not. To check if the property does indeed belong to the person applying for the mortgage or not. If the documents of the property are placed in blockchain with the help of smart contracts, this can be verified in a click. This saves a lot of money to both consumers and banking, reportedly in billions. These days we have to provide our KYC documents at various places like to open a bank account, to take a sim card, driving license, registering property to name some. If the KYC documents are stored in a blockchain, with the help of smart contracts, the right people can be given proper authority to access them. Also, if any changes required from our side, we need to make a change at one single repository instead of making changes at every entity where we have given the documents.
These days we have to provide our KYC documents at various places like to open a bank account, to take a sim card, driving license, registering property to name some. If the KYC documents are stored in a blockchain, with the help of smart contracts, the right people can be given proper authority to access them. Also, if any changes required from our side, we need to make a change at one single repository instead of making changes at every entity where we have given the documents. Supply Chain is one major area that can benefit hugely using blockchain adaptability and thereby using smart contracts. There are various documents throughout the supply chain cycle which can be misplaced and tough to authenticate at and every area required. If smart contracts are used to share and verify these documents, a lot of time and money can be saved to clear the goods at national highways, significant seaports, etc. Provenance tracking can also be done, thus increasing the bar of trust among consumers.
Supply Chain is one major area that can benefit hugely using blockchain adaptability and thereby using smart contracts. There are various documents throughout the supply chain cycle which can be misplaced and tough to authenticate at and every area required. If smart contracts are used to share and verify these documents, a lot of time and money can be saved to clear the goods at national highways, significant seaports, etc. Provenance tracking can also be done, thus increasing the bar of trust among consumers. Voting can be achieved relatively and transparently using blockchain and smart contracts. With blockchain involved, no one can tamper with the election process, and with the smart contracts, it is possible to ensure the correct person is voting instead of the duplicity of votes.
Voting can be achieved relatively and transparently using blockchain and smart contracts. With blockchain involved, no one can tamper with the election process, and with the smart contracts, it is possible to ensure the correct person is voting instead of the duplicity of votes. We all know it takes time for the insurance industries to clear the claims as it takes time to check the claims for its authenticity. With the adoption of smart contracts, the respective authorities can easily fact check the claims. For example, for travel insurance, we can easily verify whether the flight is a delay or canceled, thus passing the request.
We all know it takes time for the insurance industries to clear the claims as it takes time to check the claims for its authenticity. With the adoption of smart contracts, the respective authorities can easily fact check the claims. For example, for travel insurance, we can easily verify whether the flight is a delay or canceled, thus passing the request.