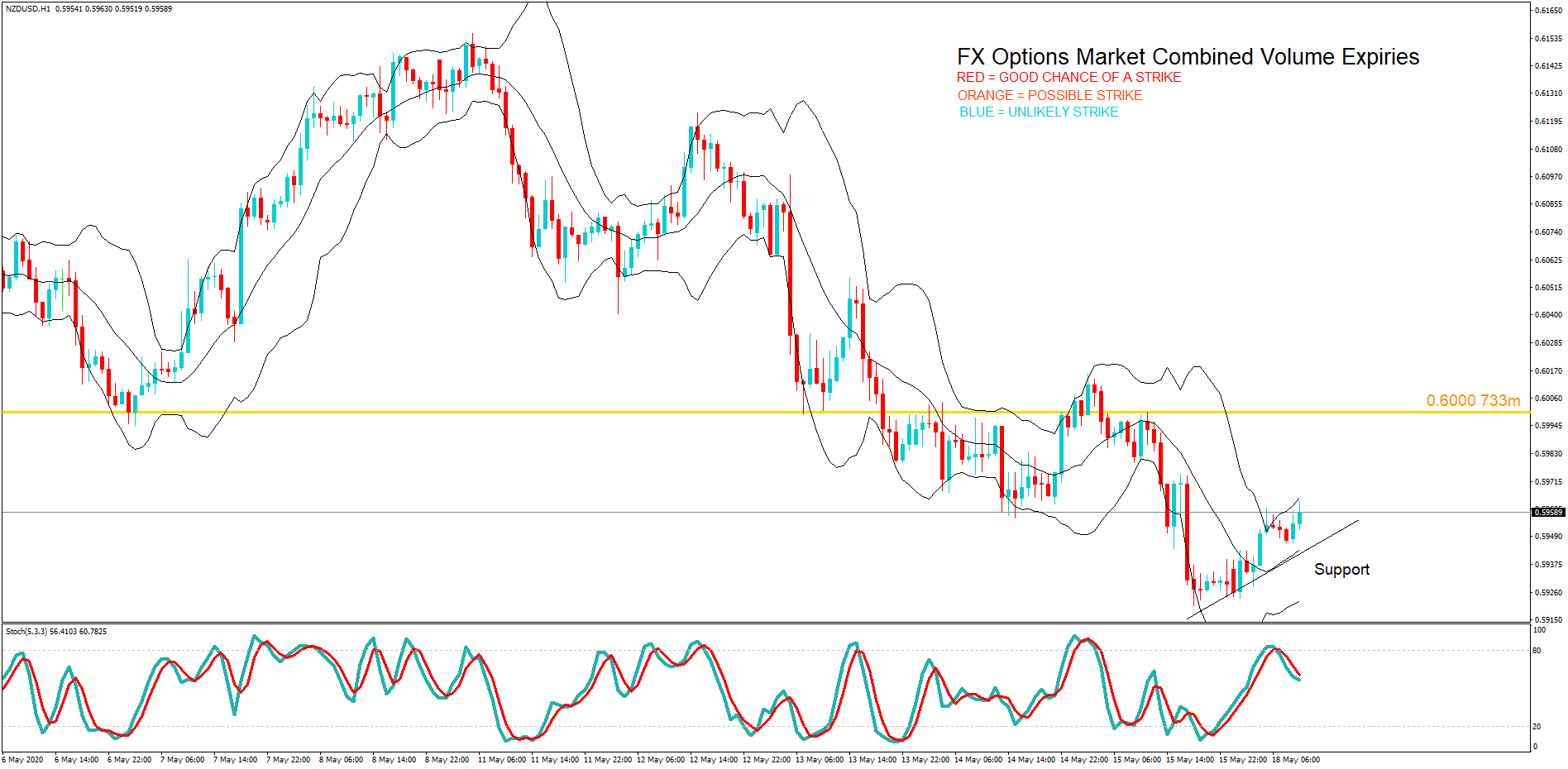
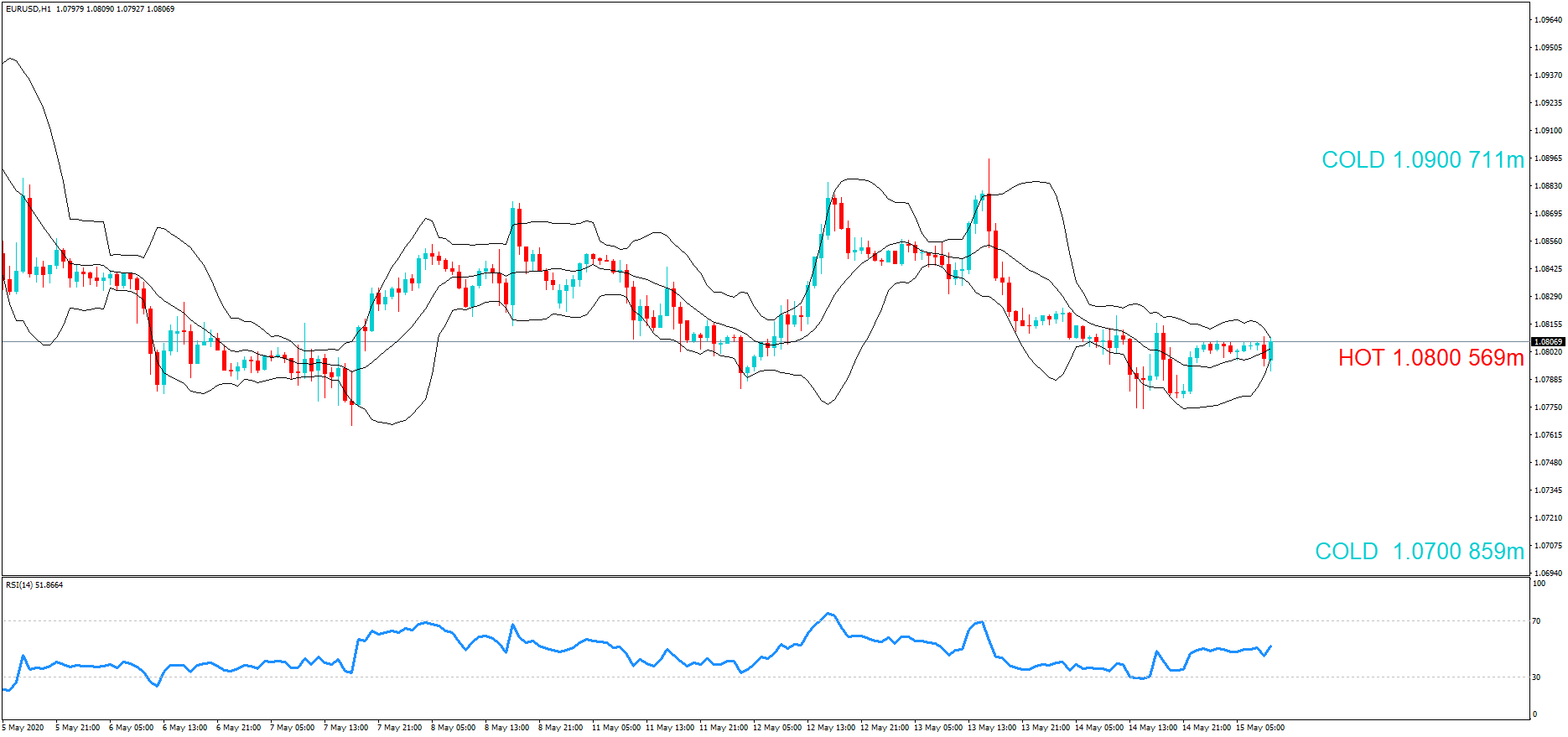
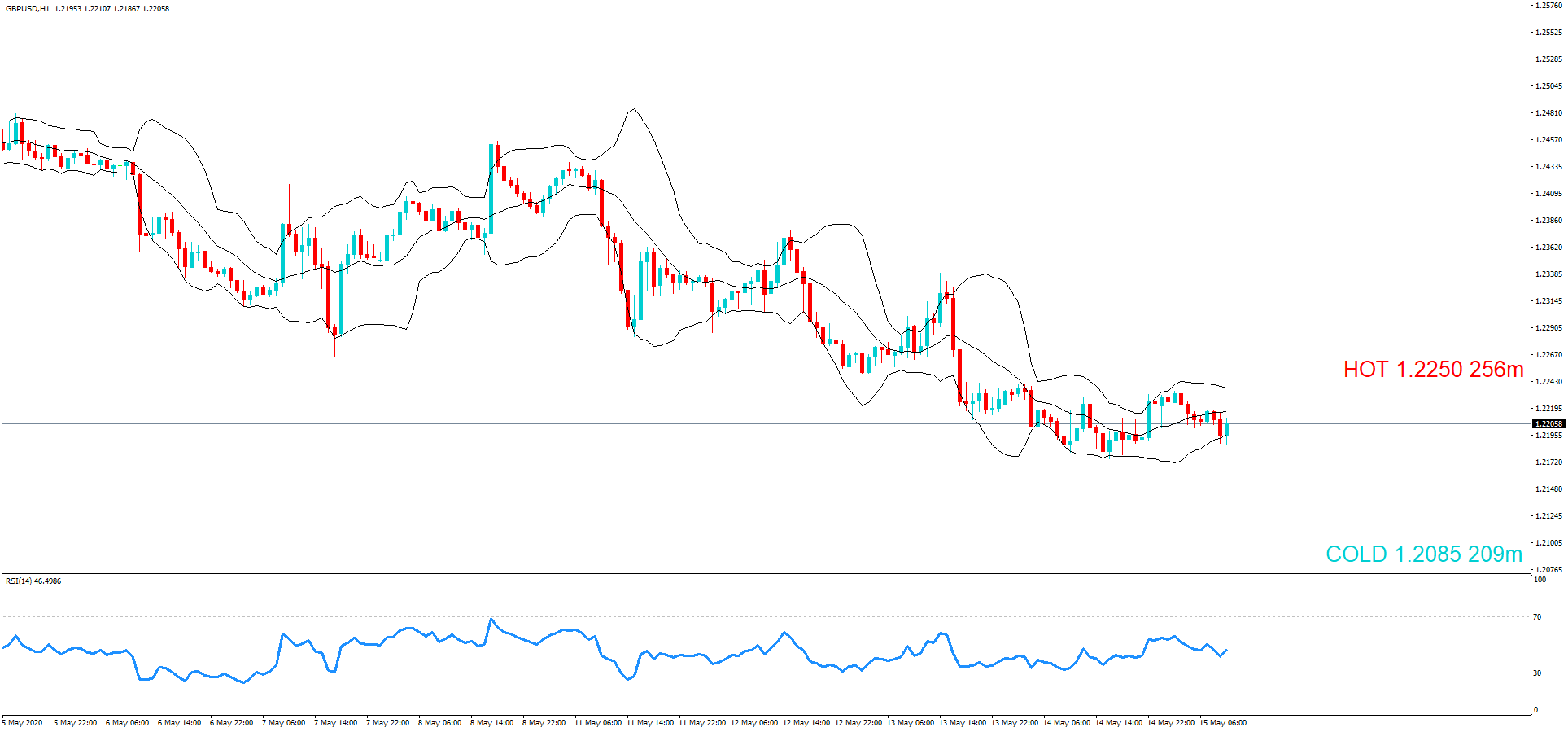
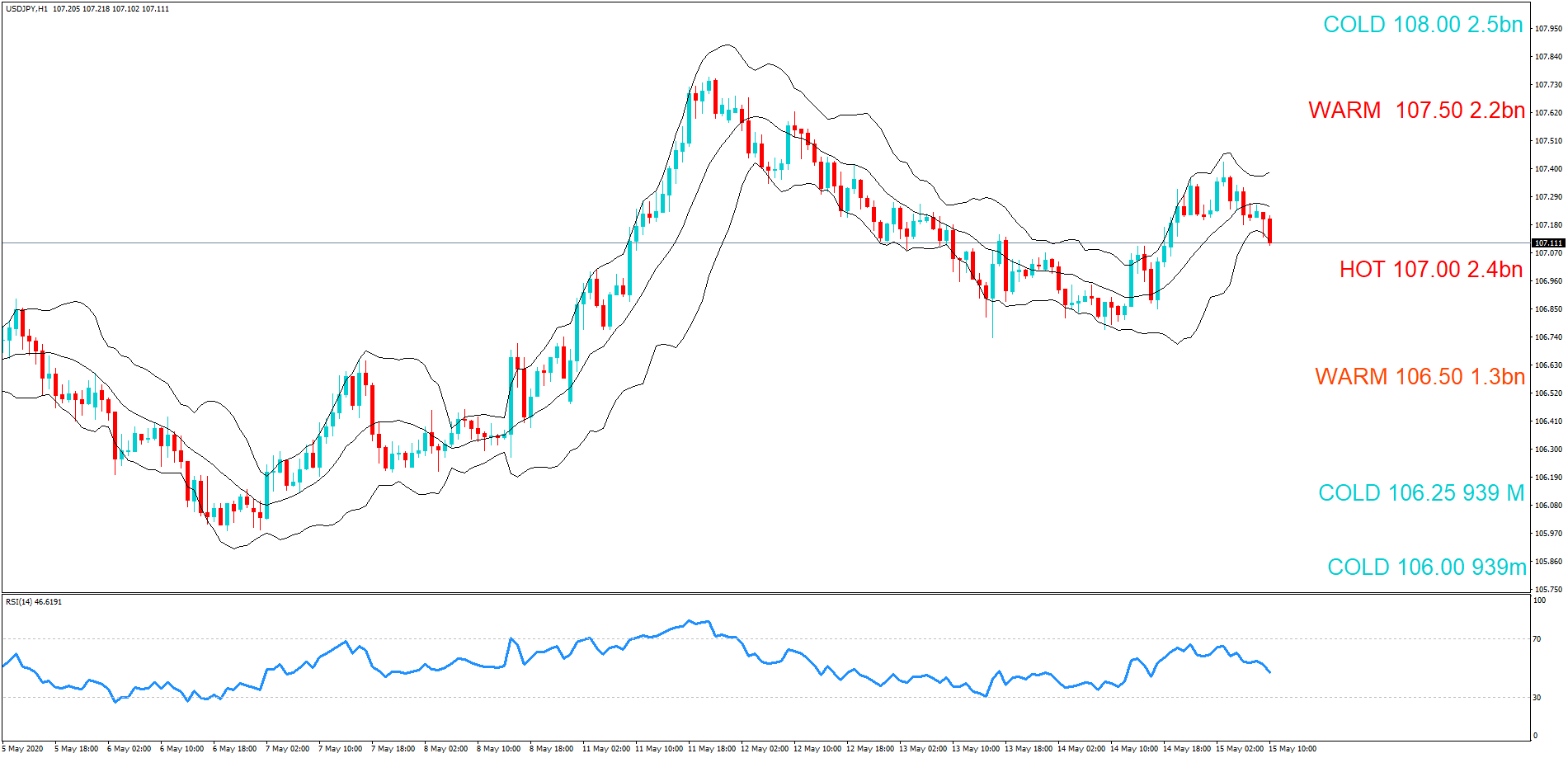
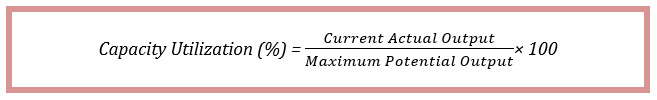Introduction
The credit rating of an institution, organization, the government is like a pseudo report card of its ability to pay back its debt. The credit rating process is thorough and detailed. The credit rating of a country or a government, in that case, can significantly impact the inflow of domestic and foreign Investments. It is one of the major indicators around which a lot of volatility occurs in the financial markets; therefore, understanding the credit rating system is important.
What is Credit Rating?
Credit Scoring
Among the general population, people who have a job are usually aware of a credit score that is attributed to them buy one or more agencies within that country. For example, in India, CIBIL, which stands for Credit Information Bureau (India) Limited, is the primary agency that assigns credit rating to individuals.
The credit rating of an individual largely determines the eligibility to apply for a loan from any financial institution. A high score would indicate that the individual is capable of repaying on time, and conversely, a low score would mean that there is a high risk of defaulting on repayment by the individual. The credit score of an individual takes into account the history of loans, repayment records and past defaulting records, and his current net income. Based on all these factors, the calculated score then tells their worthiness of credit.
For example, a CIBIL score greater than 750 in India is usually seen as a minimum requirement to be eligible for a loan by most banks. The individual usually seek out to maintain a high CIBIL score to be eligible to borrow a higher amount of loan and lower interest rates as a lower score would greatly diminish their loan eligibility, and even if they do get a loan, they will have to pay higher interest rate than people with a good CIBIL score.
Credit Rating
Credit scoring applies to individuals within a country, whereas credit rating applies to institutions, organizations, and governments. Similar to credit scoring credit rating tells whether that organization is credit working or not.
Credit rating becomes important as here the borrowers are big institutions, government, large financial organizations, and the lenders are also big investors or foreign bodies. The loan amount is high, often ranging in millions and billions, and the duration of the loan is also long. Hence, investors actively seek credit ratings before deciding to purchase a particular Bond and lending their money.
How are the Credit Ratings calculated?
There are many globally popular credit rating agencies. In the United States, three companies, namely, Fitch Ratings, Standard and Poor’s Global (S&P Global), and Moody’s Corporation, are the most famous and sought after agencies.
The credit rating process is very thorough and accounts for the entity’s entire debt and its repayment history. The process requires credit rating from the agency to meet with the organization and going over their financial records to assess their current financial status and assess their eligibility. They also take into account that past loan repayments and spending patterns, their current financial assets, and future economic prospects.
After this, a group of credit raters will work out the credit rating for that organization. The process may take up to 4 weeks in general. When the credit rating is ready, it is given out to the company and for a press release. The credit rating agencies usually follow an alphabet combination rating system.
For example, according to Standard and Poor’s Ratings, an organization having AAA rating is said to be outstanding, which is the highest rating possible. Next below is AA+, which means excellent this goes down a rating of D, which is the lowest score. The formats of writing may vary slightly from company to company, but in general, they have an understandable notation of alphabet combinations.
Are Credit Ratings important?
The credit ratings became particularly important after the 1936 rule, which restricted Financial Institutions to lend money to speculative bonds, i.e., having low credit ratings in other words.
Many companies now actively seek to get their credit rating assessed to gain the confidence of investors. The financial markets also have seen enough market crashes, the system collapses, and payment defaults even by the most reputed organizations and nations also. The European debt crisis and the Greece default one of the most popular instances wherein national level collapse of financial institutions and debt default occurred in the recent times of 2010-2011.
In one sense, there is a link between capital inflow and credit rating, hence government and financial corporations, when requiring money, the credit rating becomes a significant number.
The credit rating is not a performance report for a particular set year; instead, it is a continuously updated statistic that tells the credibility of the entity at the current time. For example, a country with the best credit rating last year may not have the same rating this year. The credit rating cuts through all the false alarms and directly gauges the financial numbers, which always tell the truth.
Hence, once the agencies publish credit ratings for a particular sovereign body, there tends to be a lot of volatility as investors either become gain or lose confidence in that body. Conversely, a decreased credit rating than the previous number, also stirs down the market in a negative direction.
Credit ratings, particularly sovereign credit ratings, are major indicators for investors, and hence the government bodies take utmost attention to loan repayment to avoid defaulting and thereby spoiling their credit rating, which will cost them future monetary indentures. Government bodies are aware that decreased credit rating will result in foreign investors stepping back, and consequently, losing their funding, which can, in extreme cases, lead to a total collapse of the institution or an economy at a large scale.
How can the Credit Ratings be Used for Analysis?
An institution with a low credit rating is considered a high-risk investment as the prospects of that company being able to repay is low.
A decrease in the sovereign credit rating signals an economic slowdown from which the country may take a significant time to recover. Conversely, a high credit rating for sovereign bodies and conglomerates indicates that the economy is stable and growing, and there are ample financial resources to pay back the debt on time.
Credit ratings are released quarterly, usually, after the financial numbers of the organization are released. They can be used as current macroeconomic indicators and also be used to predict future expansion plans of the borrowing party, as an institution borrows money to expand or invest in its growth.
Sources of Credit Rating Reports
For reference, Fitch credit ratings are published frequently on their official website.
Since Credit Rating is a major indicator, media coverage is huge and is easily available across the internet. For reference, this is a rating table given in Wikipedia.
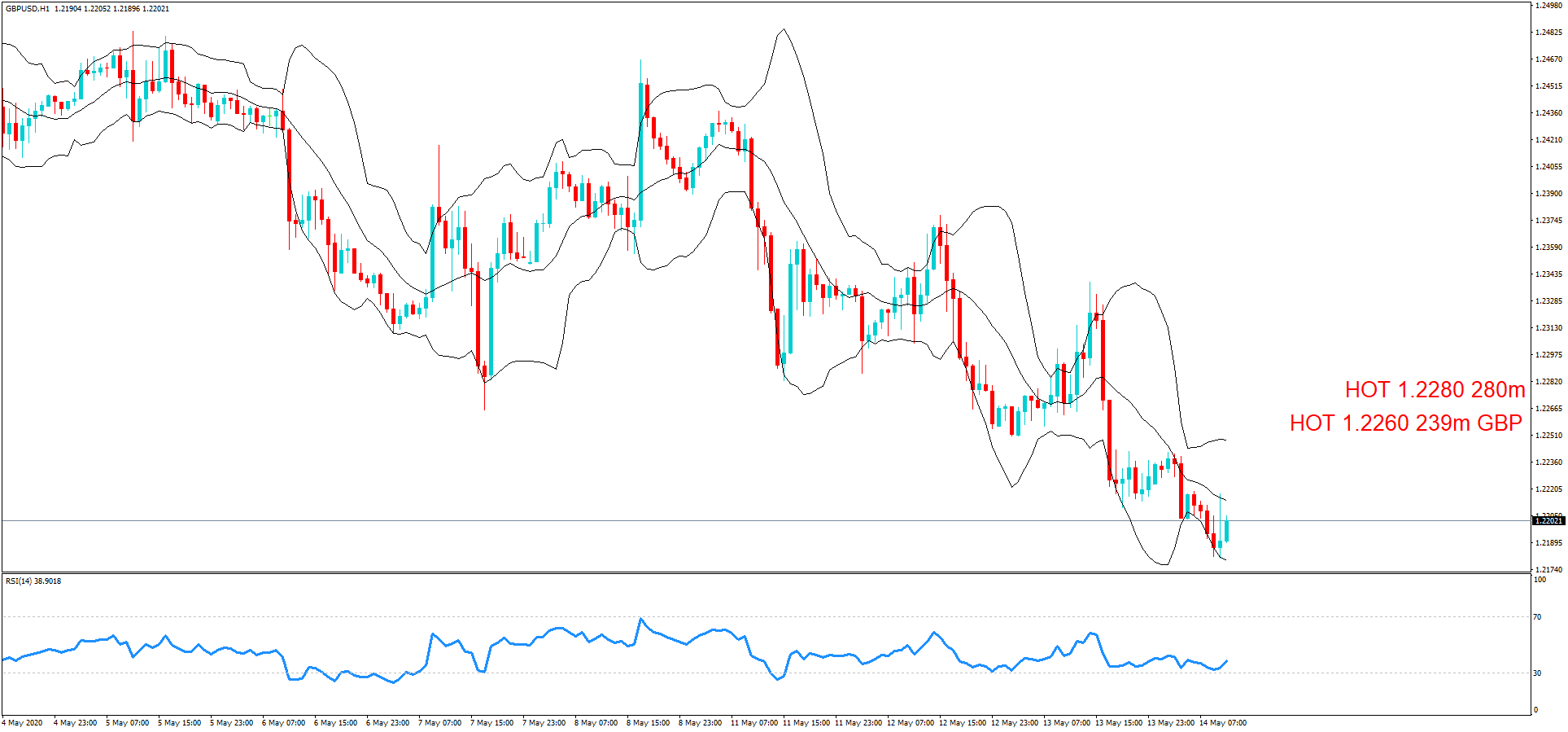
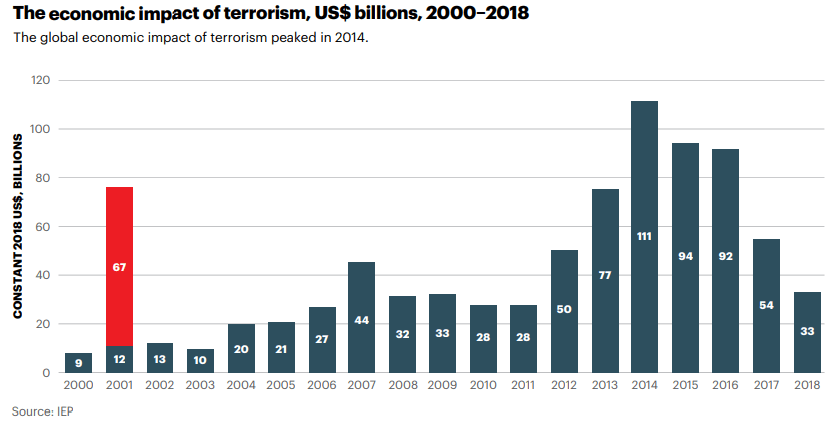
Impact of the ‘Credit Rating’ news release on the price charts
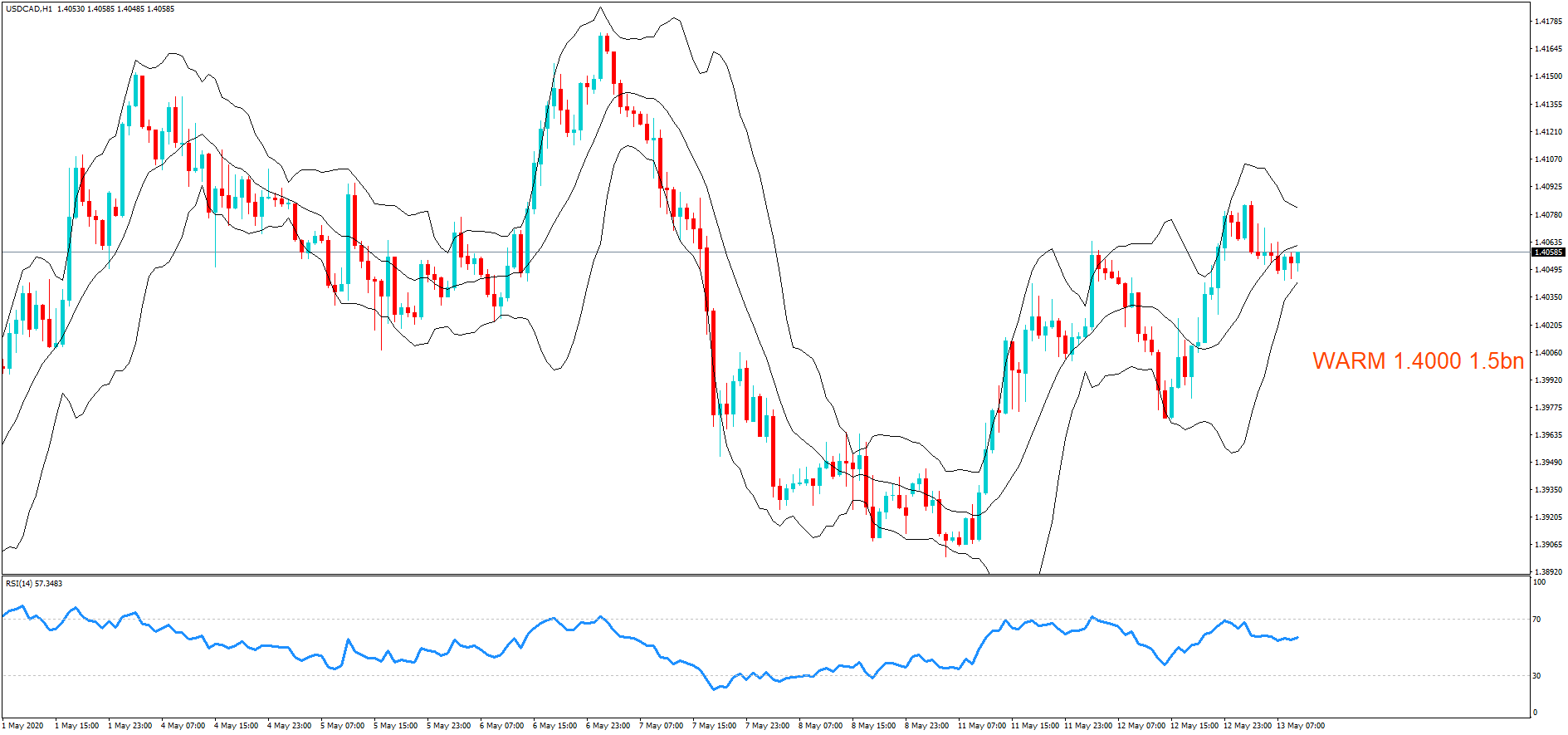
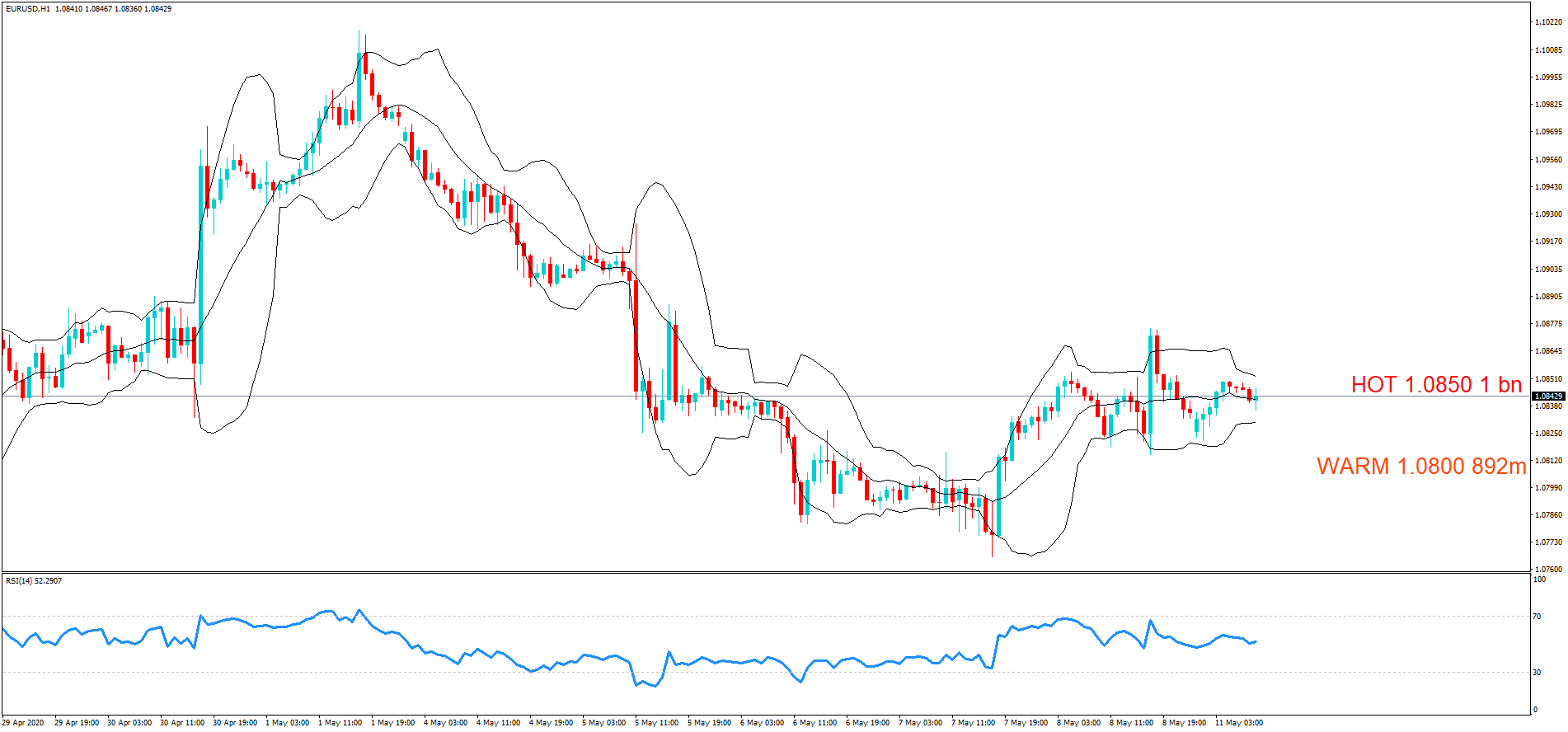
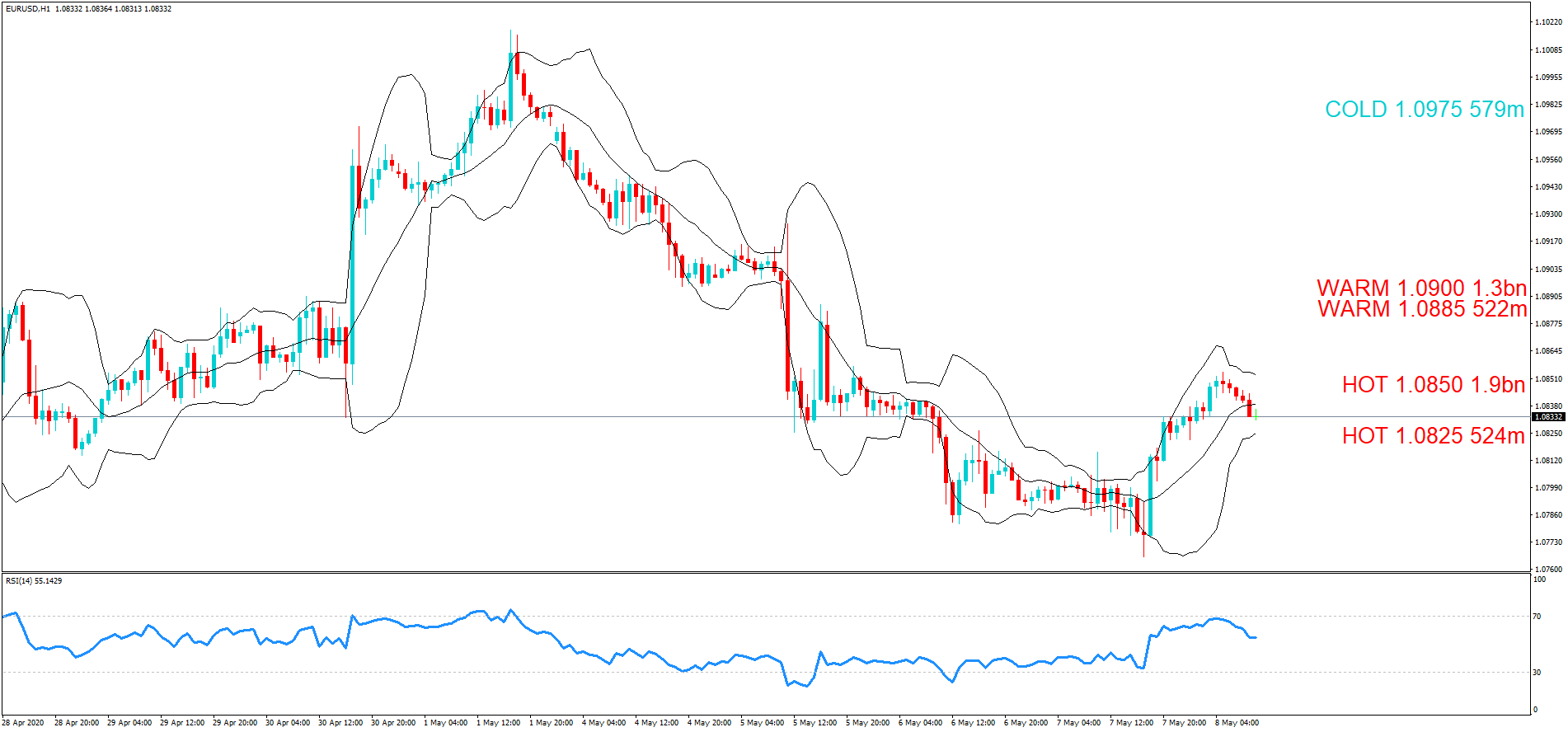
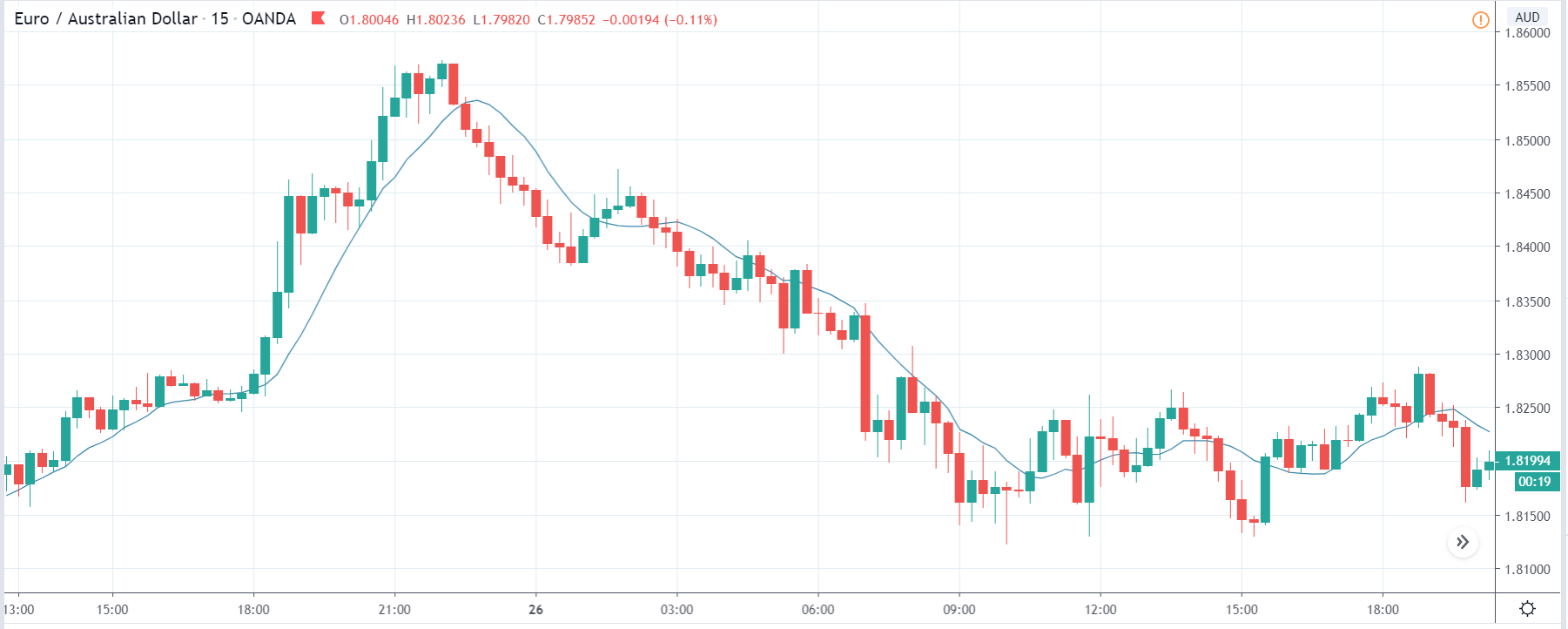
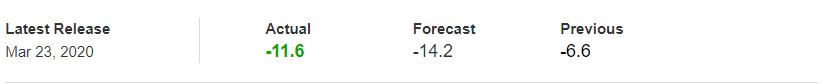
After understanding the meaning and significance of Credit Rating in a country, we shall now see the impact it makes on the currency after the Ratings are declared. There are many agencies that give Ratings to different countries, but the two most reliable and followed are the Ratings given Fitch and Standard and Poor’s (S&P). In today’s article, we will be analyzing the Credit Rating of the United Kingdom announced in the month of December. Credit Rating is said to be a major event in both the forex and stock market, which has a long-lasting effect on the value of a currency. Therefore, the rating could largely determine the degree of volatility in the currency pair.
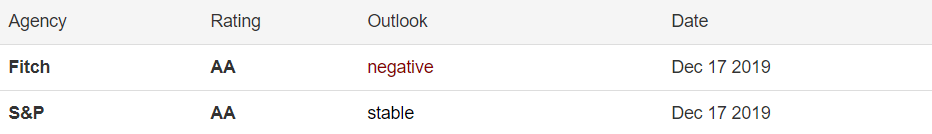
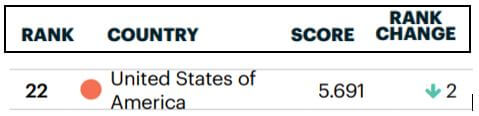
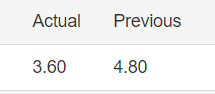
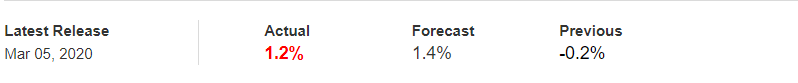
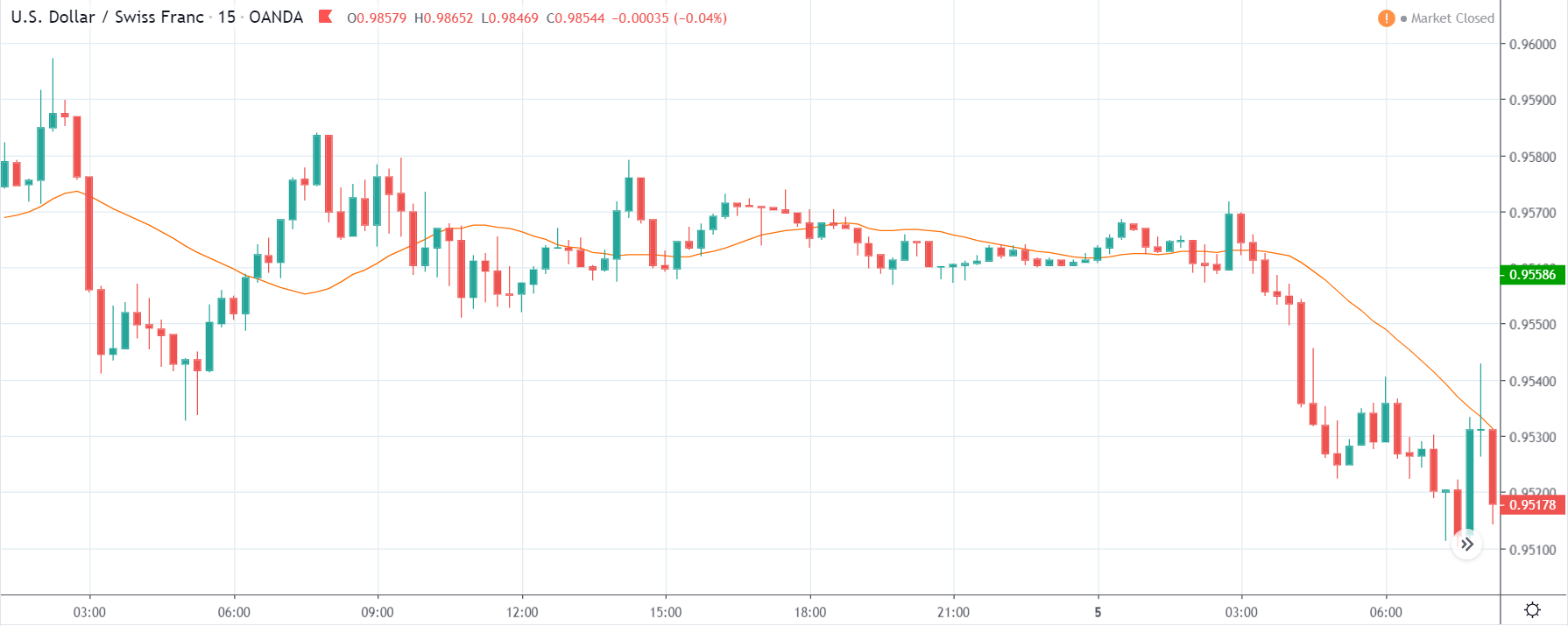
In forex trading, Credit Rating is used by sovereign wealth funds, pension funds, and other investors to gauge the creditworthiness of a county, thus having a big impact on the country’s borrowing costs. As we can see in the above image that Fitch’s Credit Rating for the United Kingdom was last reported at AA with a negative outlook. Since the rating was unhealthy for the economy, let us see how the market reacted to this.
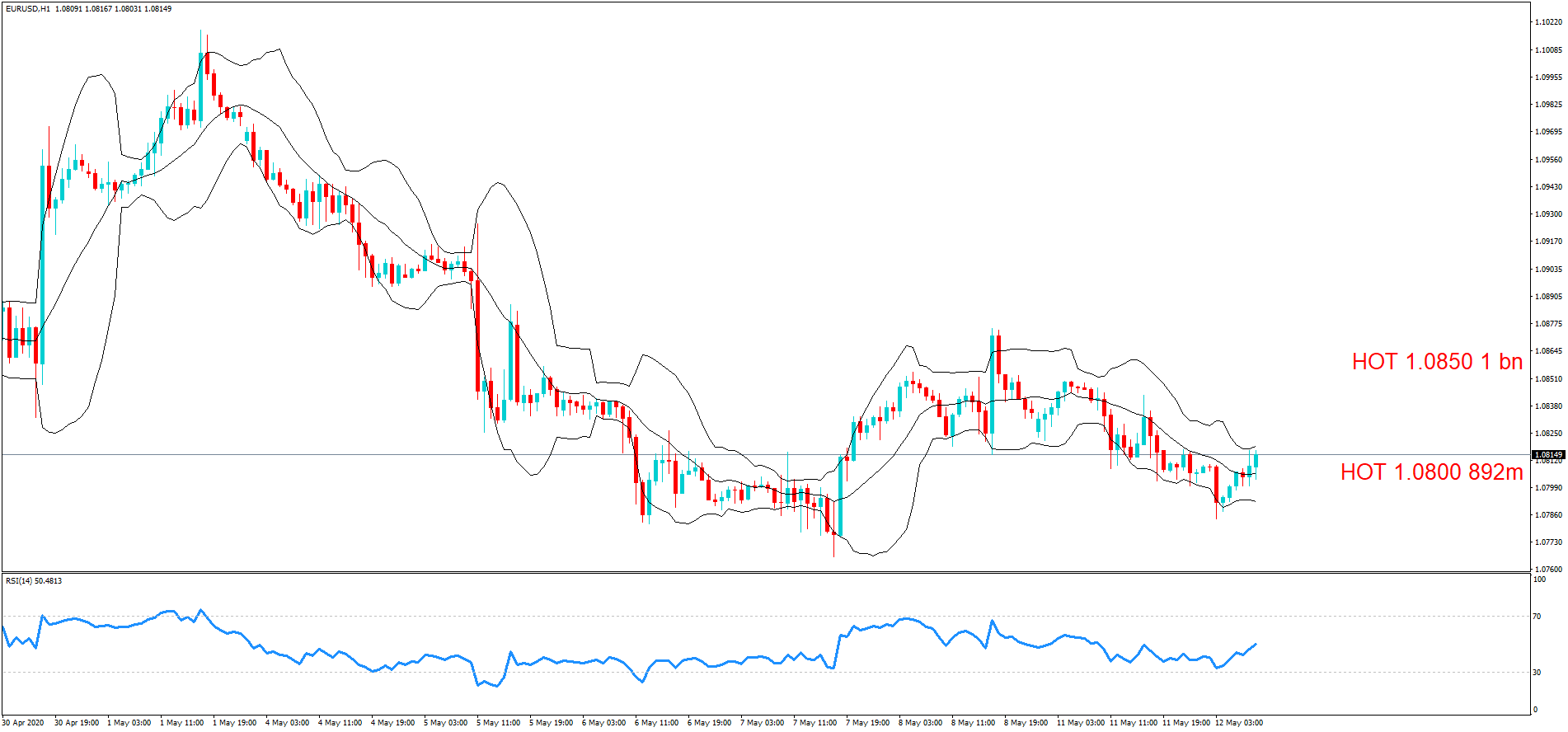
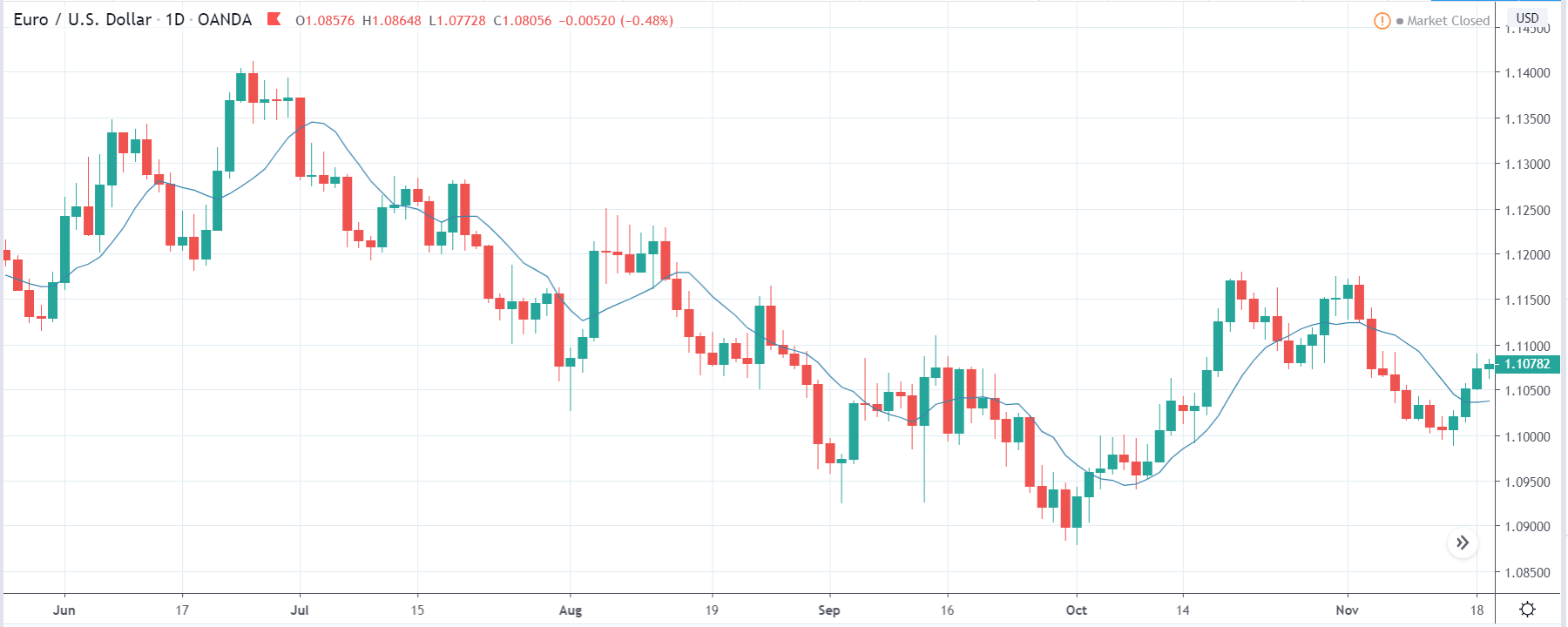
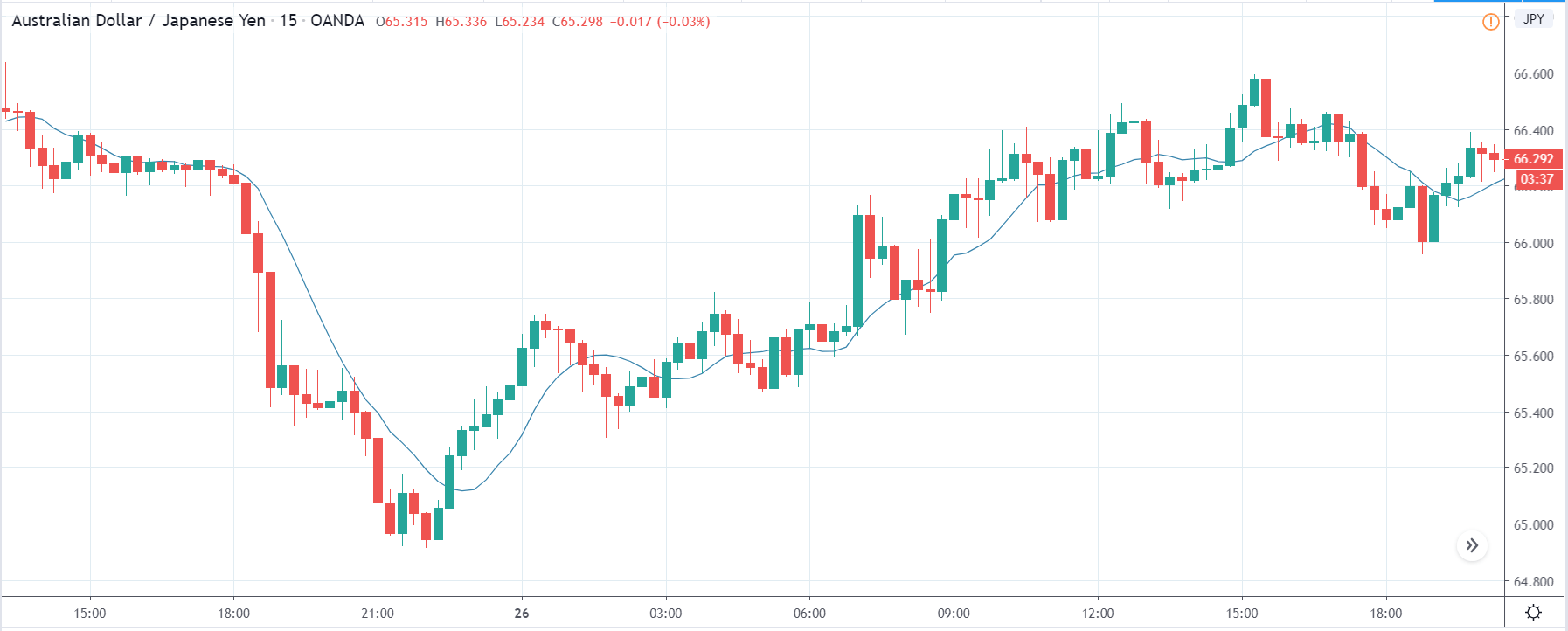
GBP/CAD | Before The Announcement
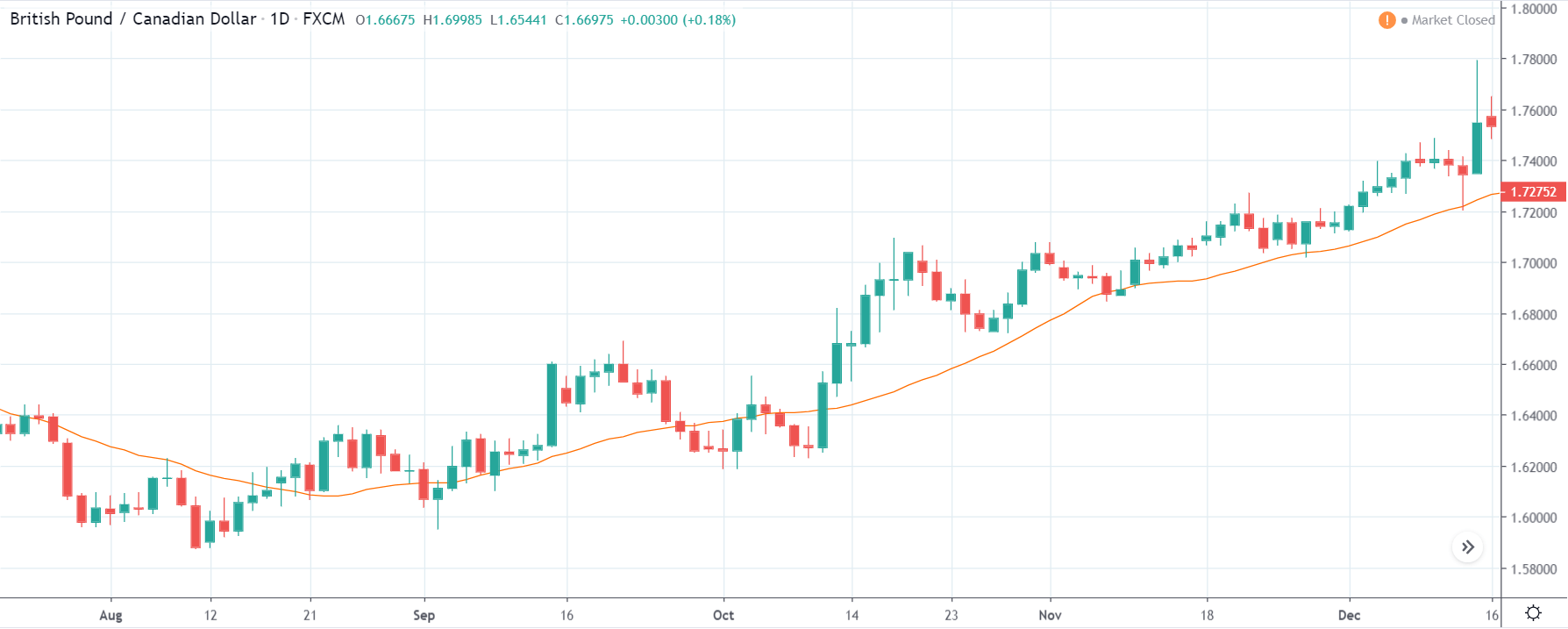
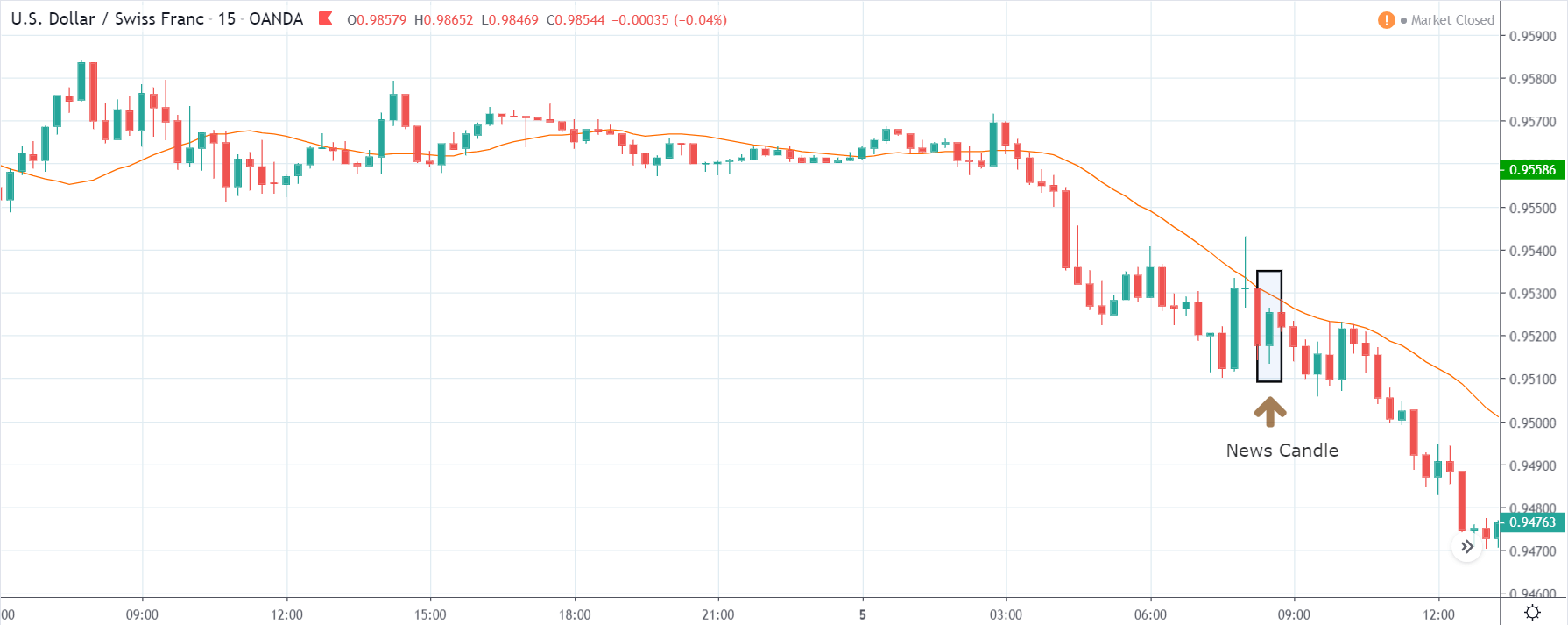
As the Credit Rating announcement is one of the biggest data releases of a country, volatility caused by the news release can be witnessed more clearly on a daily time-frame chart. Likewise, we have considered the ‘daily’ chart of GBP/CAD that shows an uptrend market. As we do not have any forecasted data available for the same, we cannot take any position in the market based on predicted ratings. The only way we position ourselves in the market before the news announcement is through the ‘options’ segment, where we can essentially take advantage of the increase in volatility on either side.
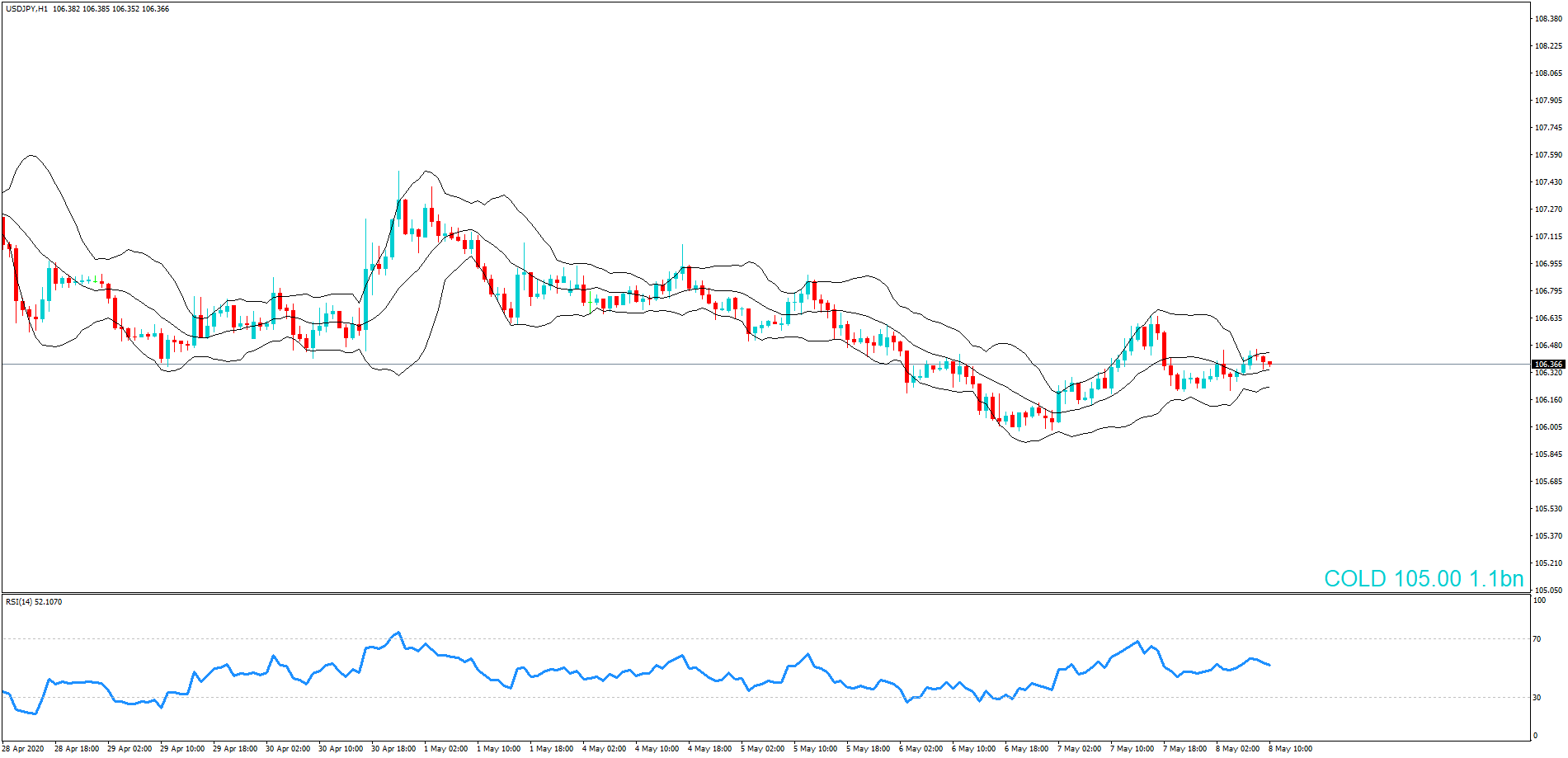
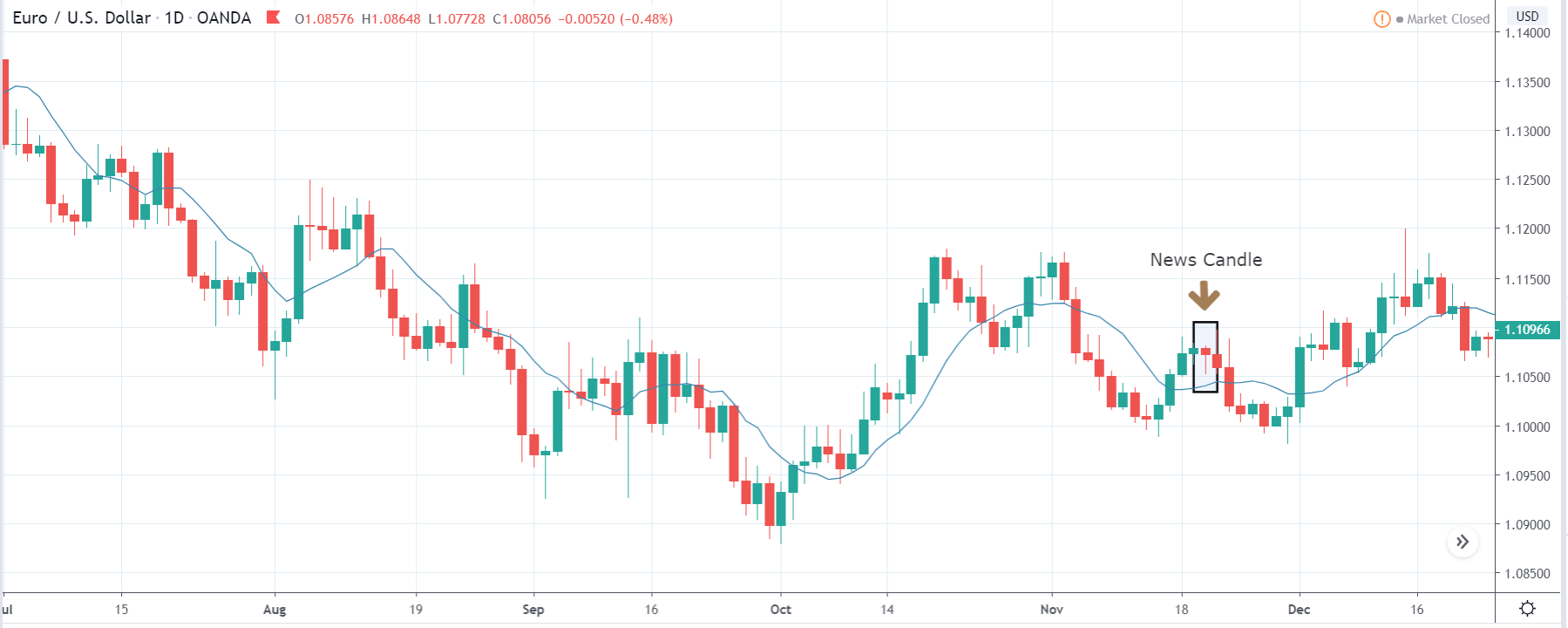
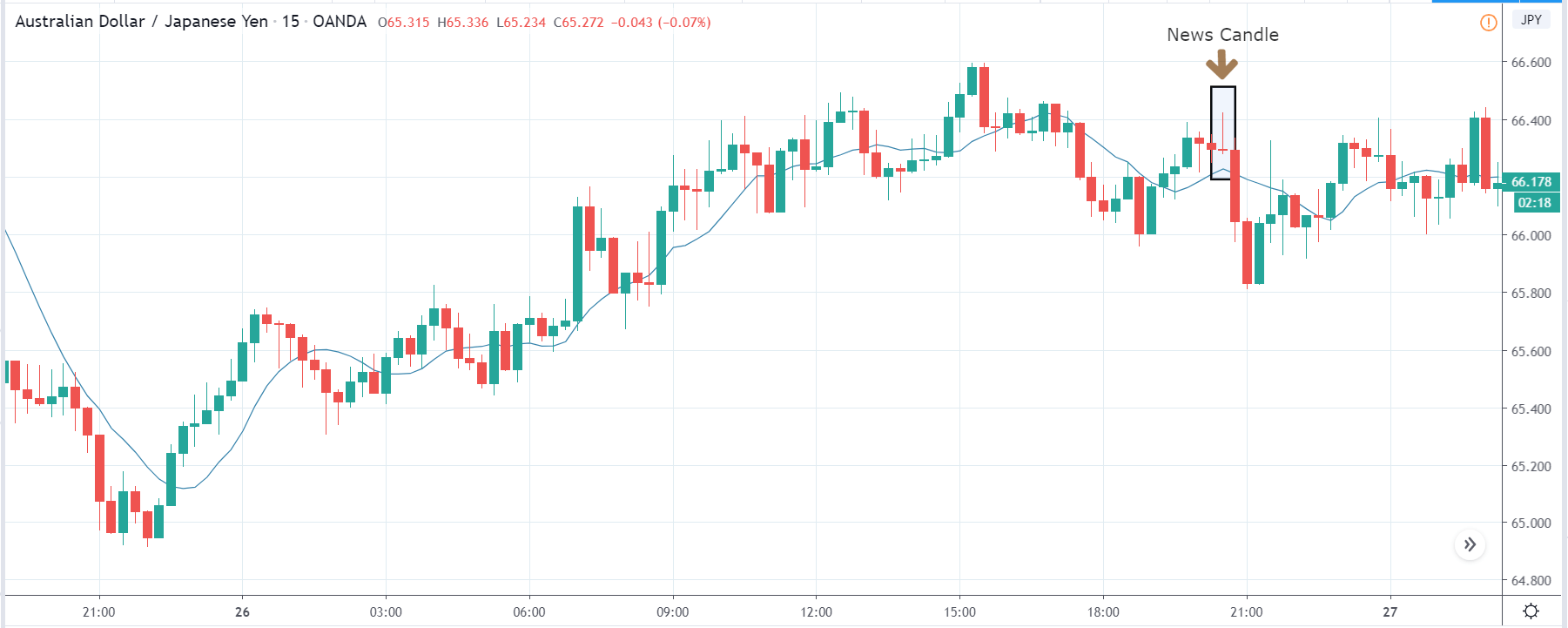
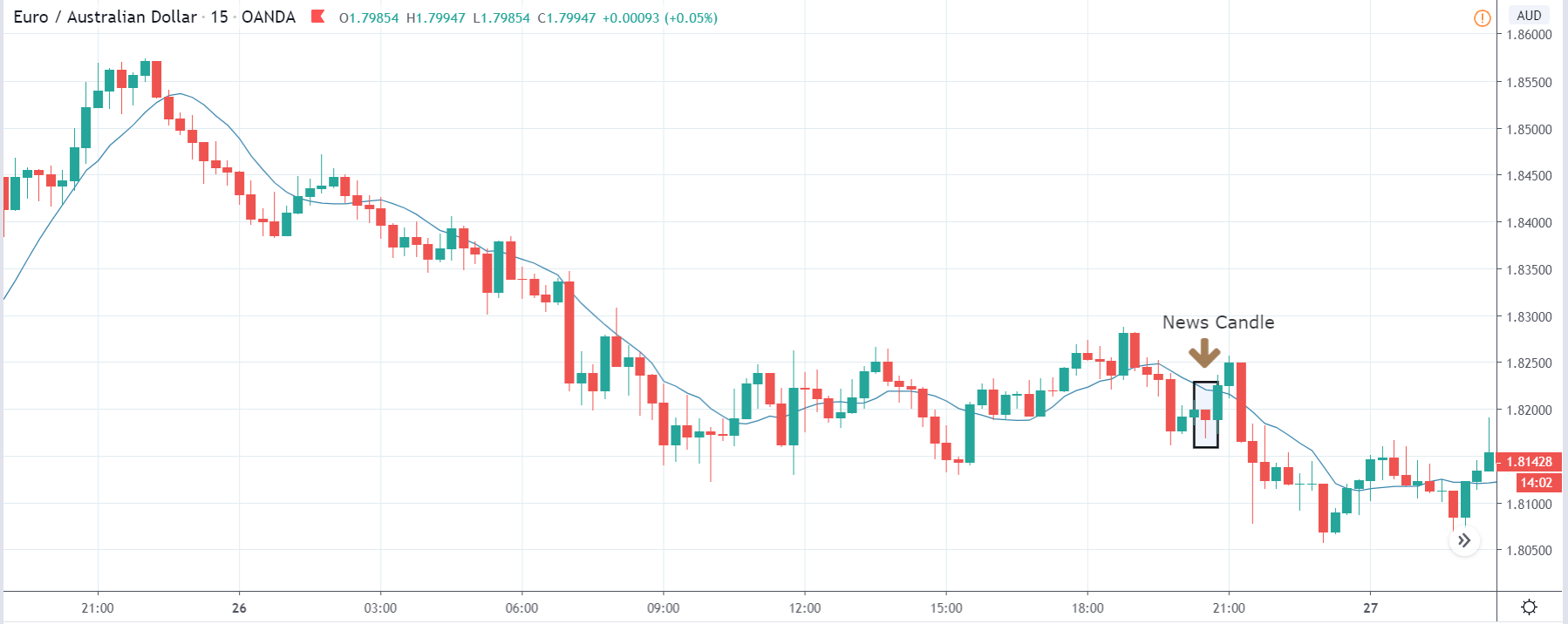
GBP/CAD | After The Announcement
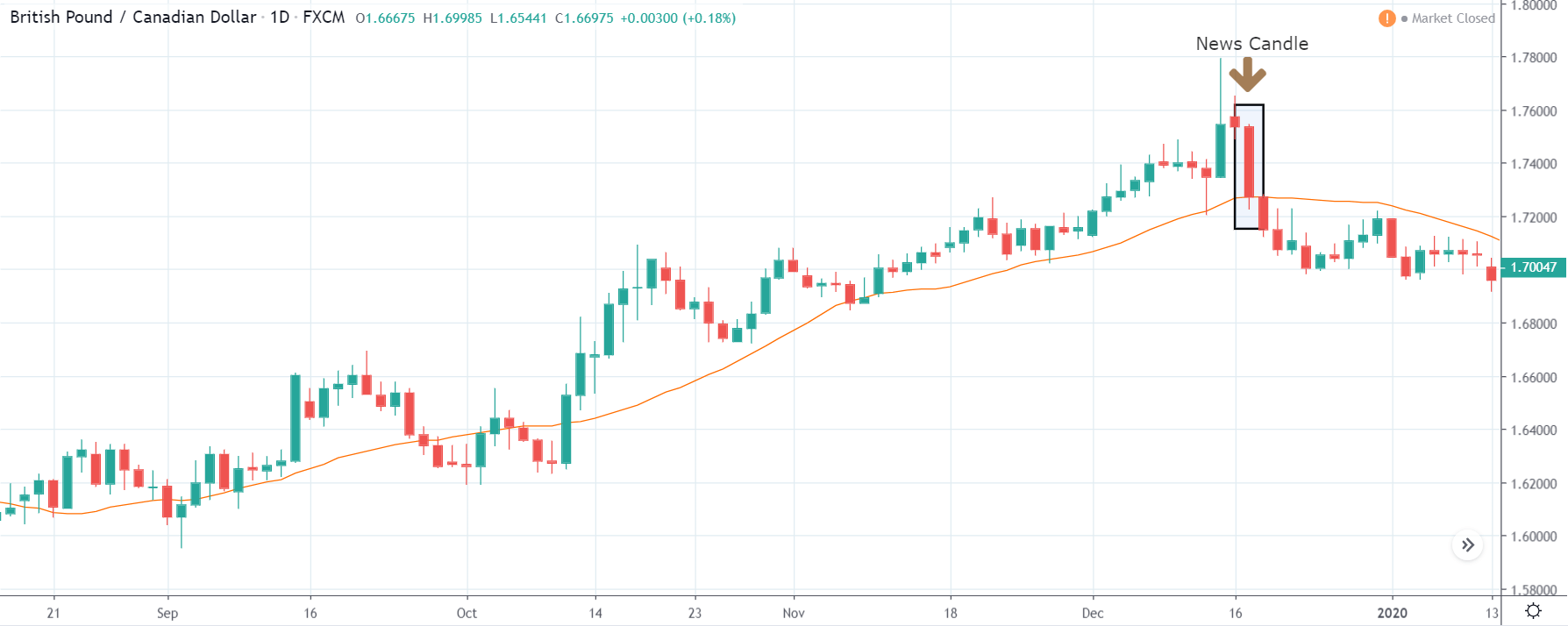
On the day of the Credit Rating announcement, we see that the market falls by more than 500 pips resulting in a complete reversal of the trend. This shows the extent of the impact of Credit Rating on a currency pair. The reason behind the collapse of the British Pound is negative Credit Rating given by the two most renowned agencies.
This rating is used by institutional investors and fund managers to decide if they want to park their cash in the economy. Therefore, when the rating is downgraded, investors withdraw their money from the market and sell British Pound. From a trading point of view, one can take a ‘short’ position in the market with a high much higher ‘take profit’ since the market has the potential to go much lower.
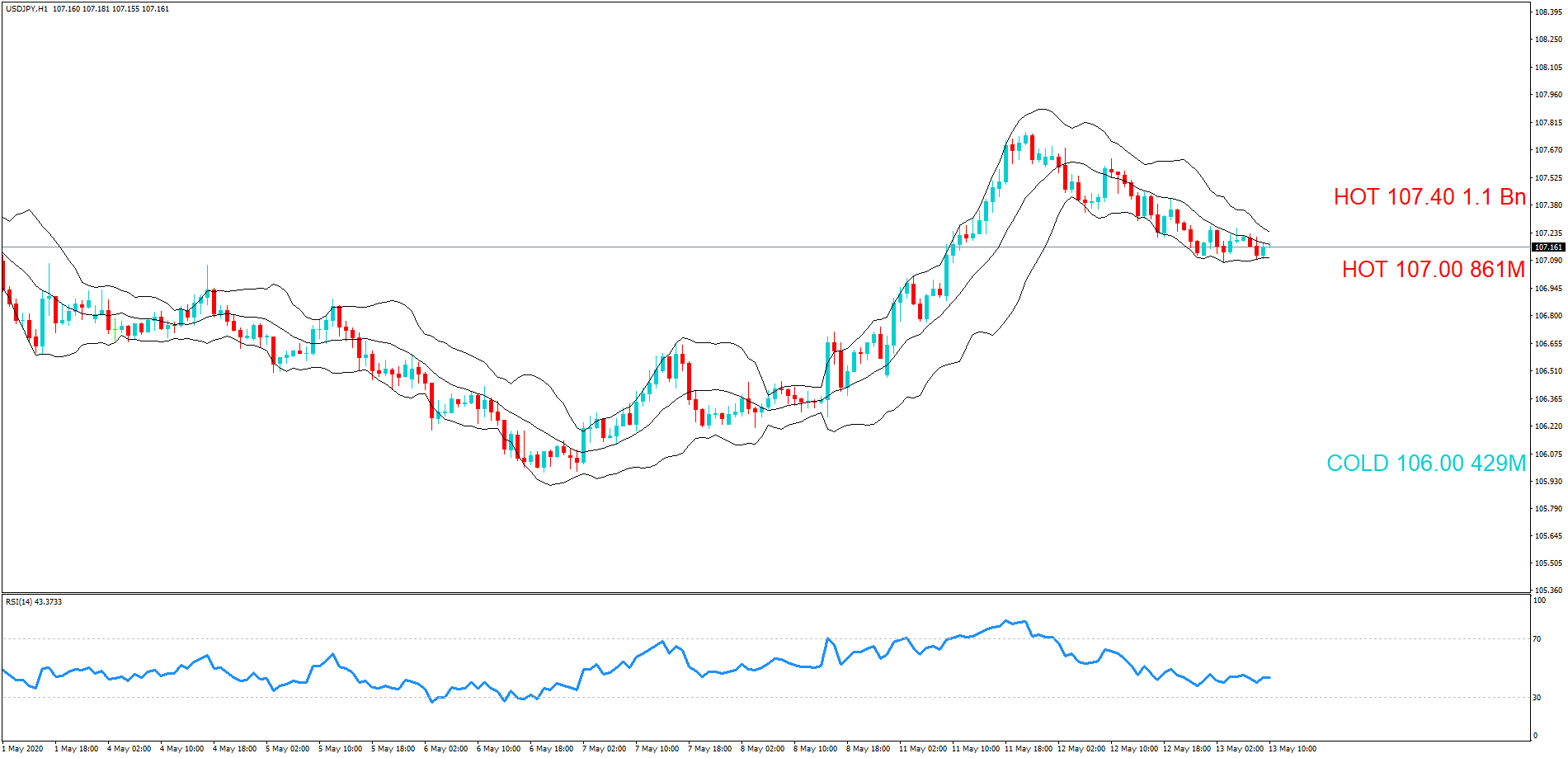
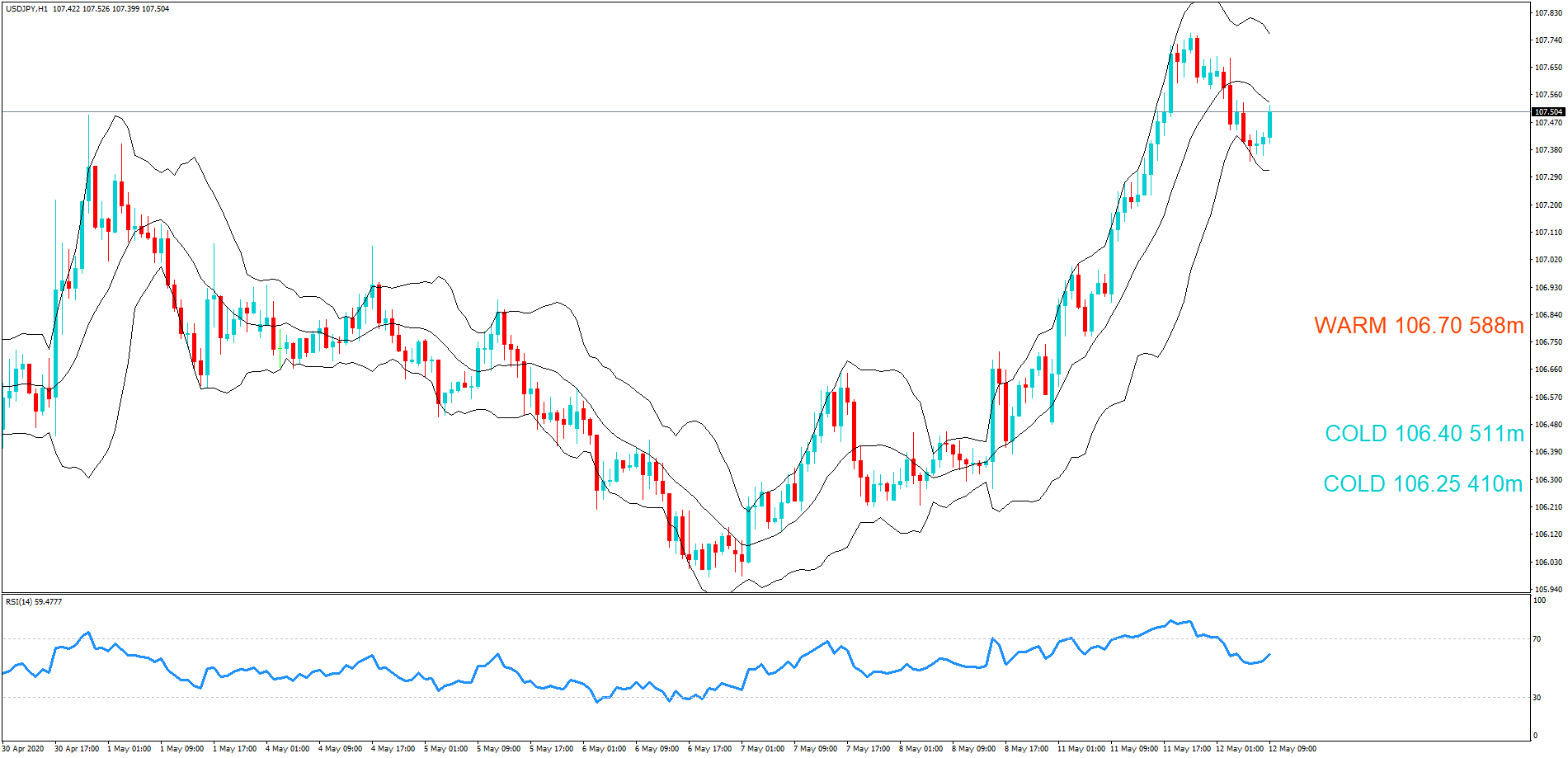
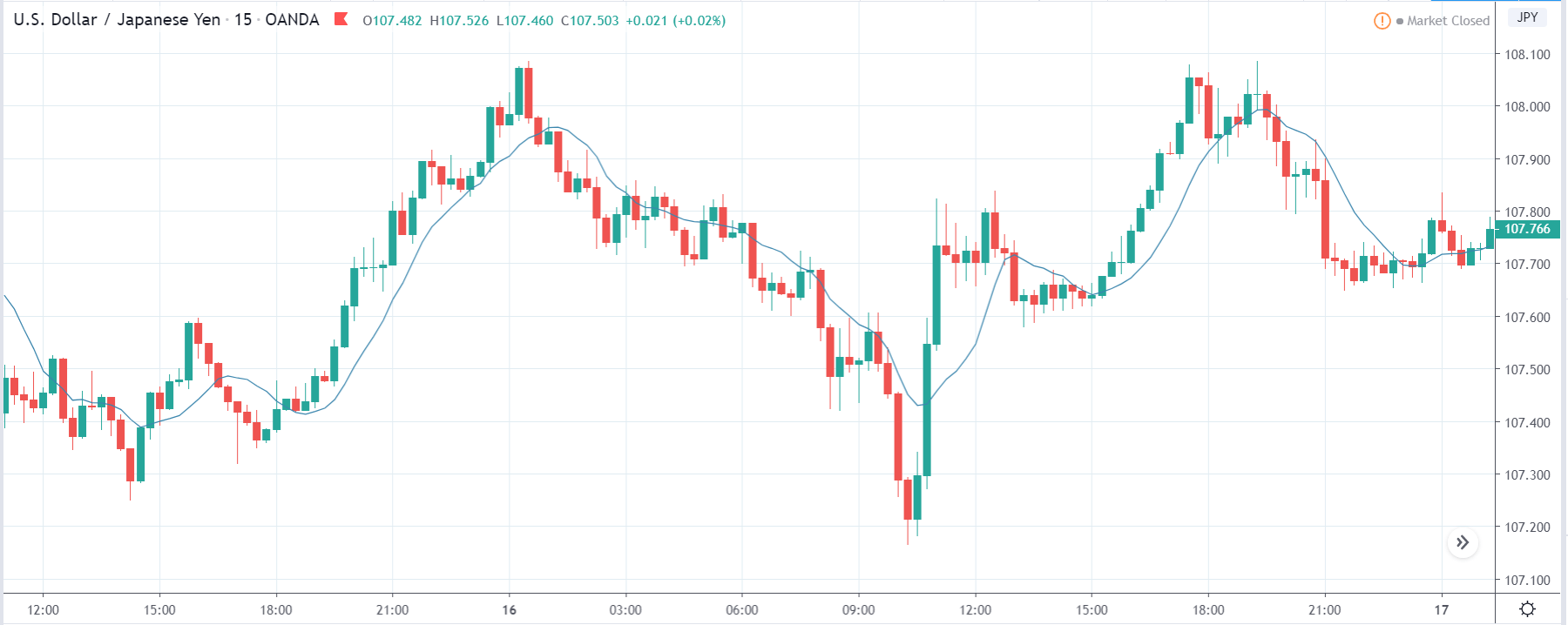
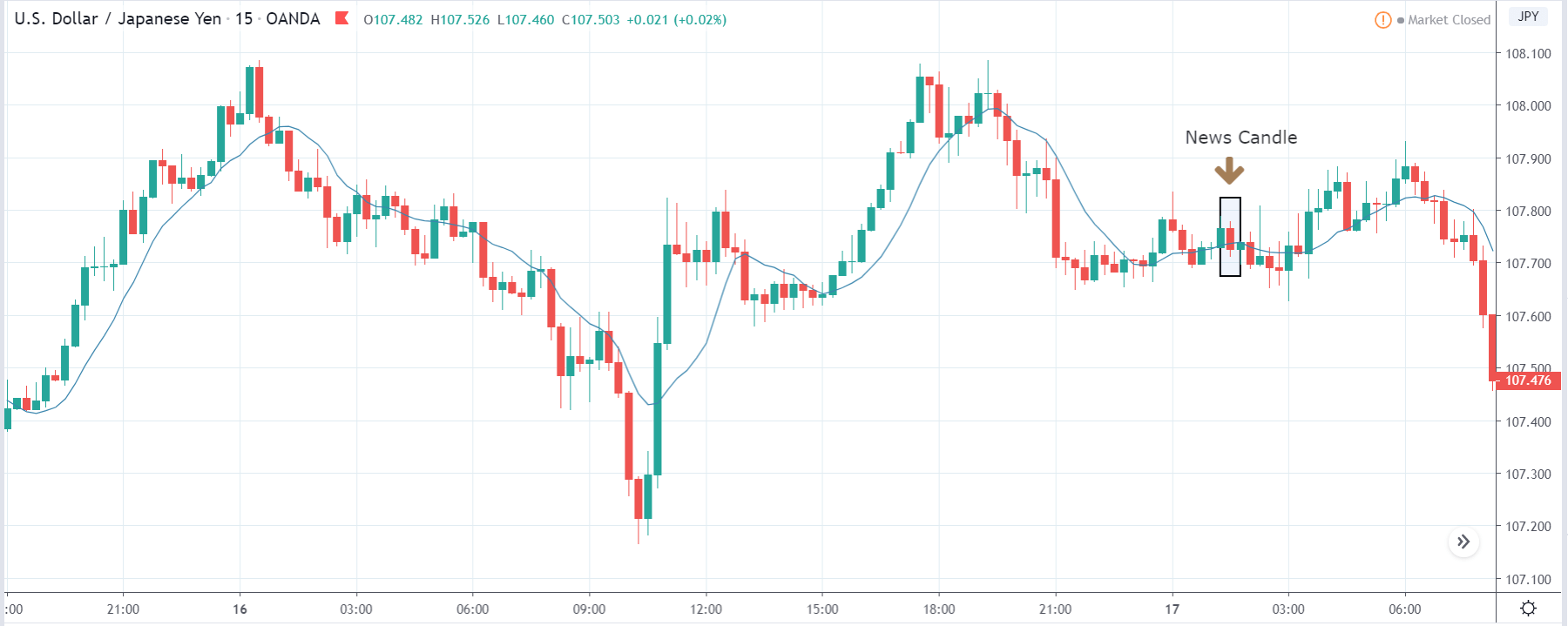
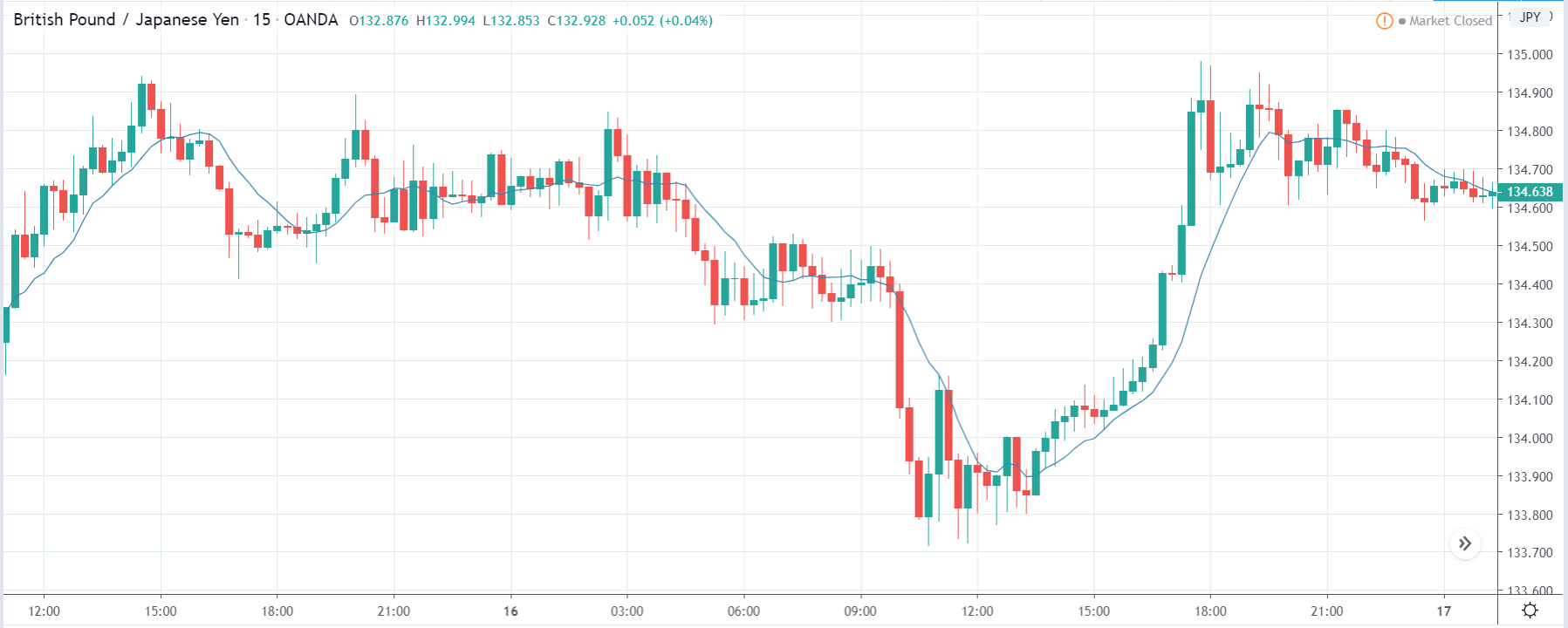
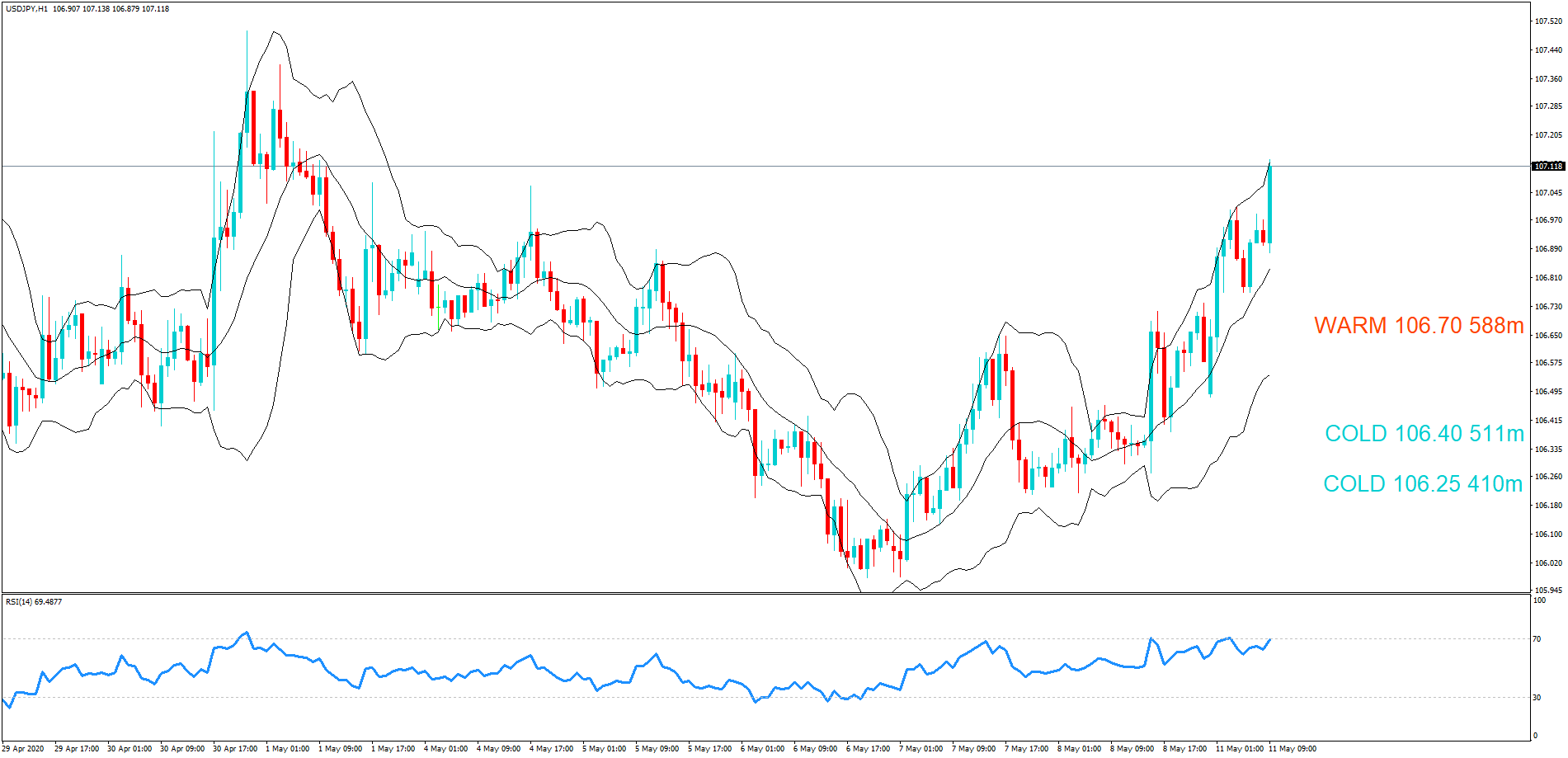
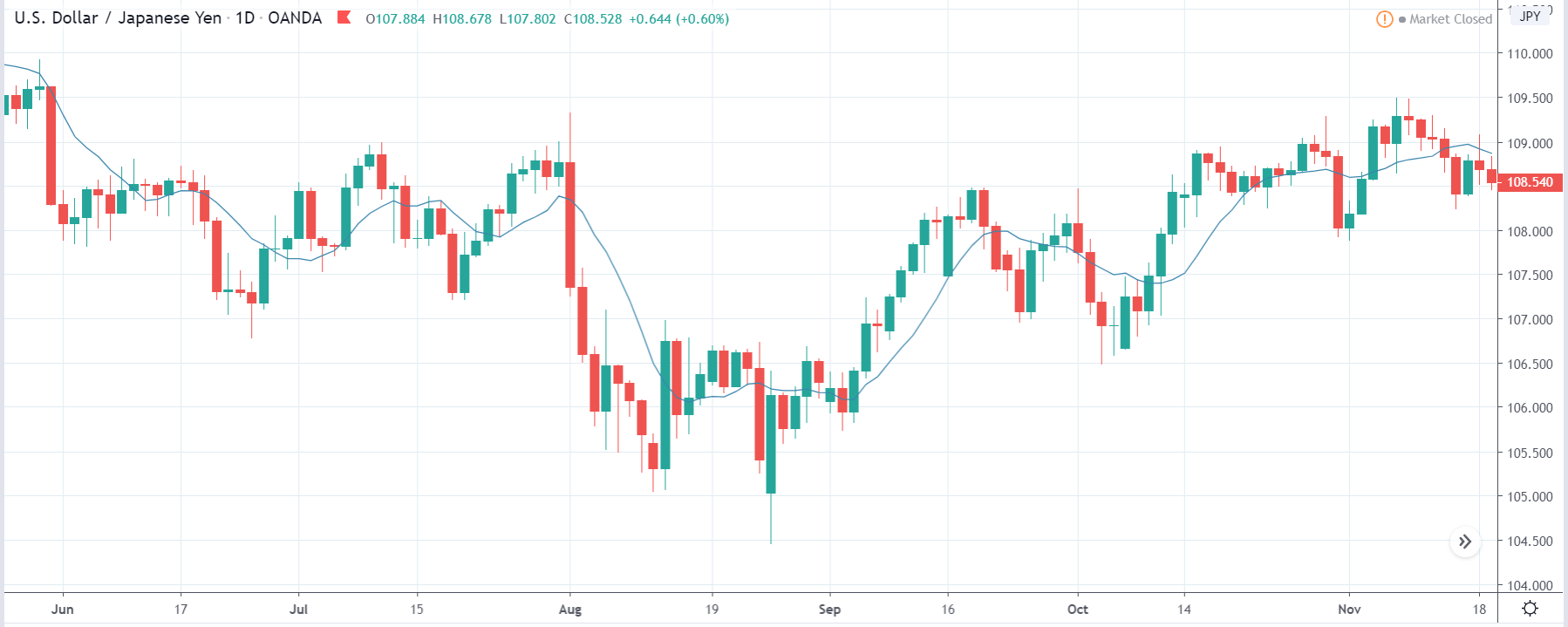
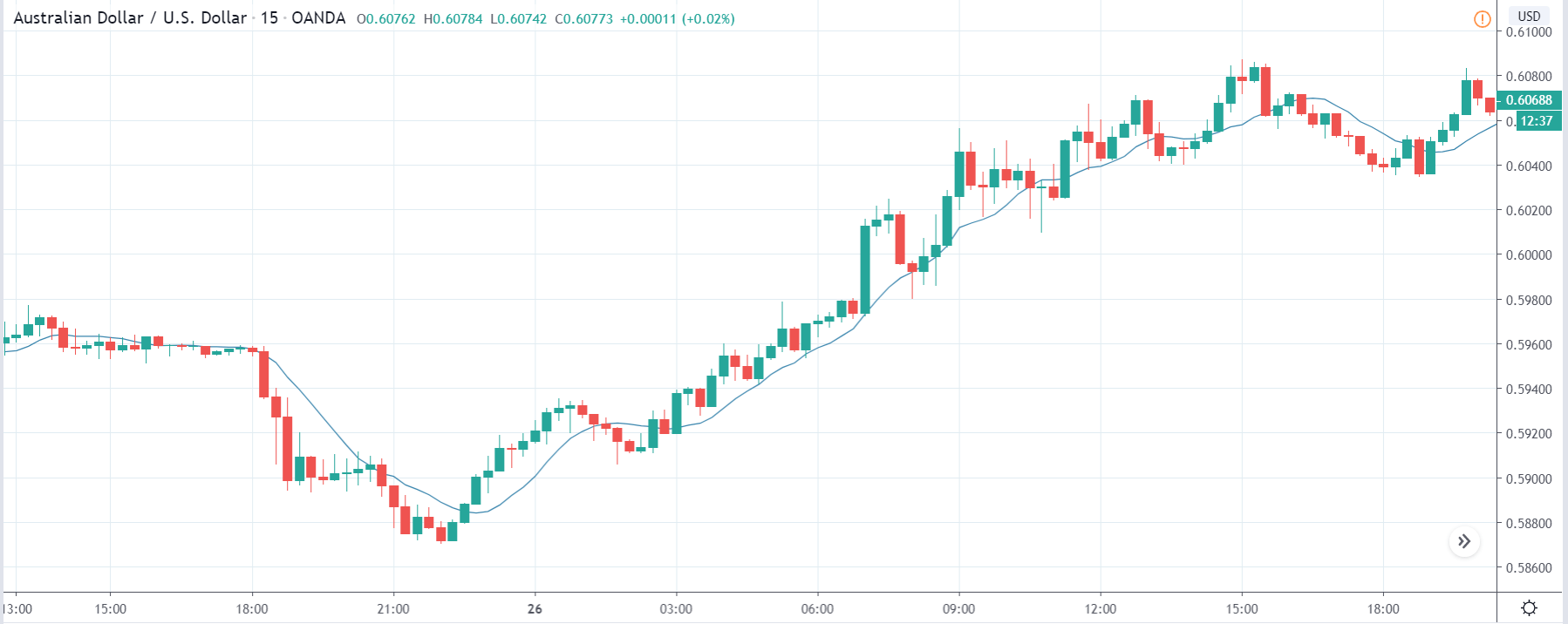
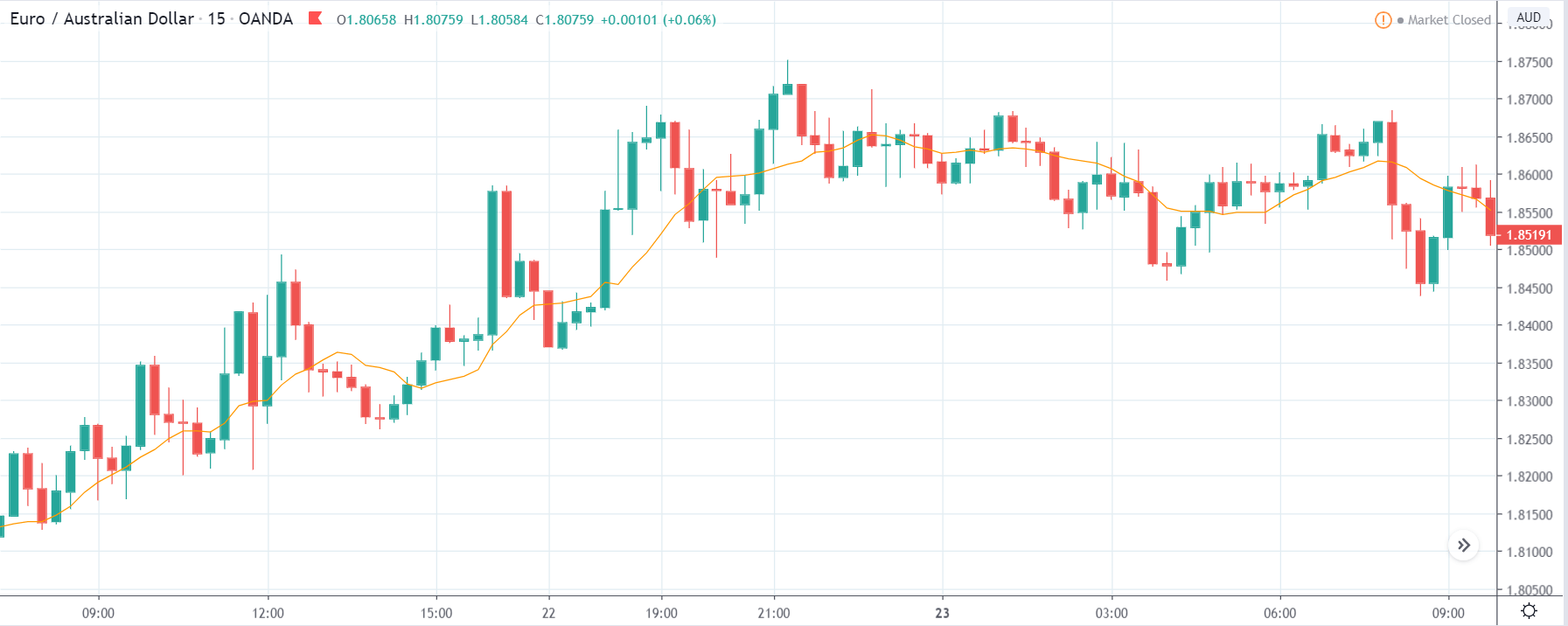
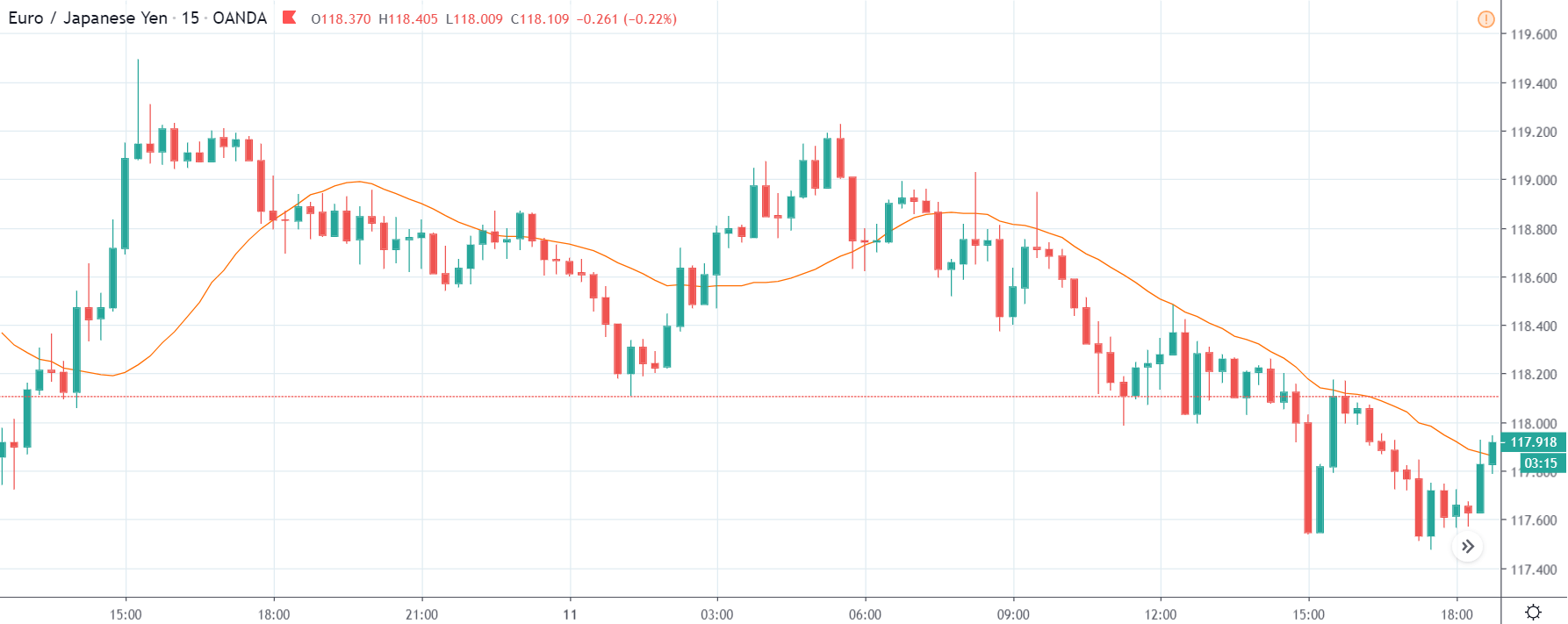
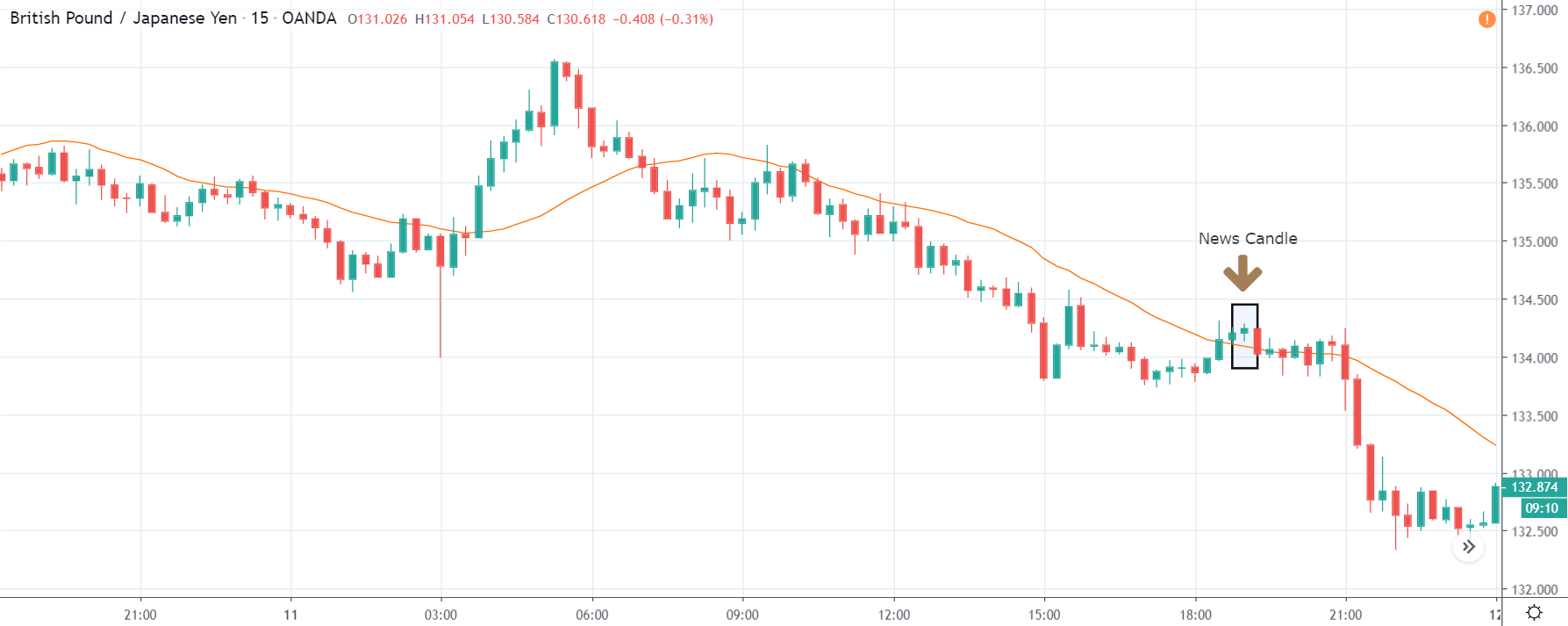
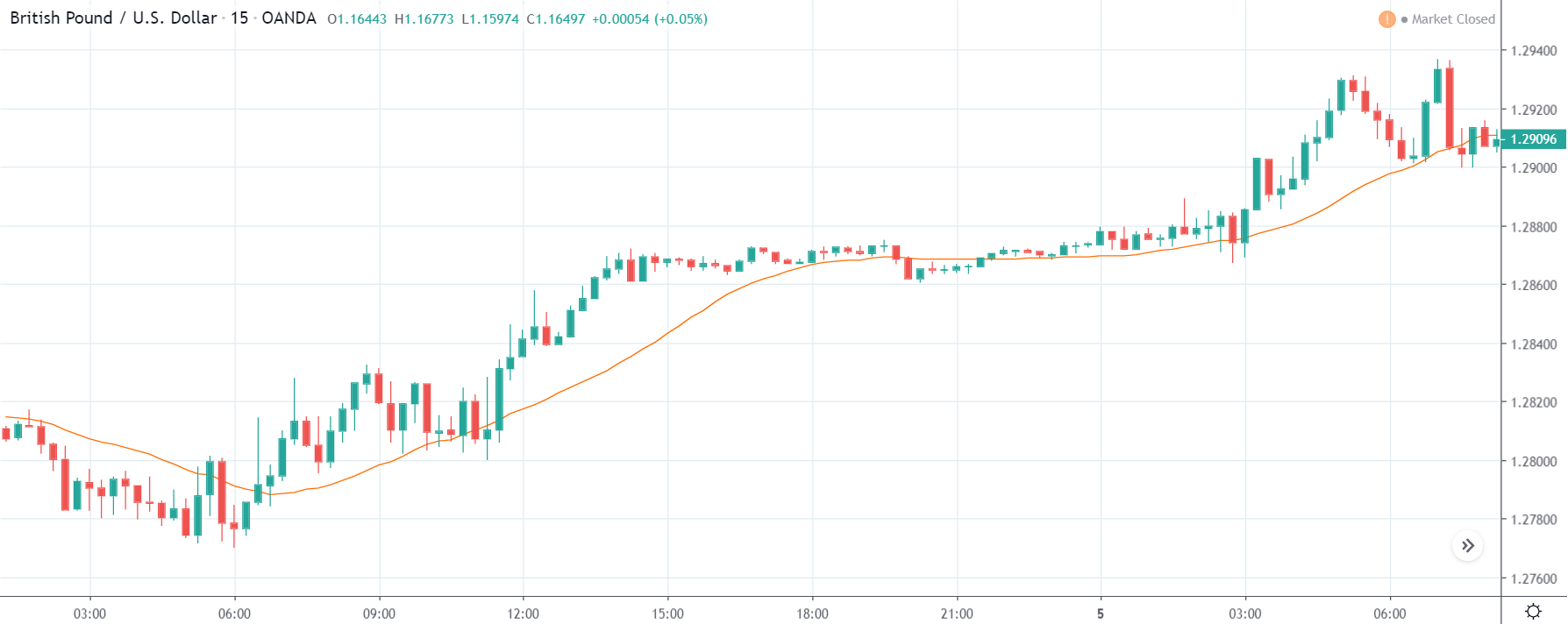
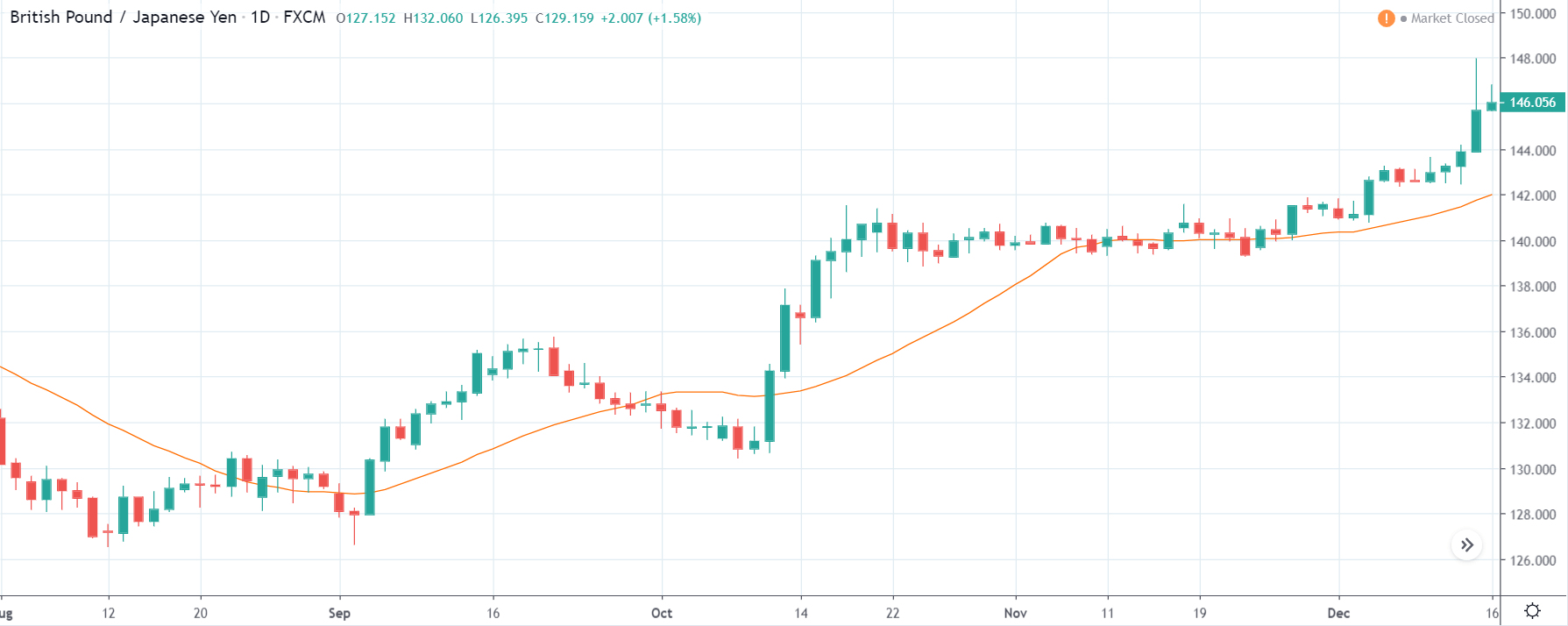
GBP/JPY | Before The Announcement
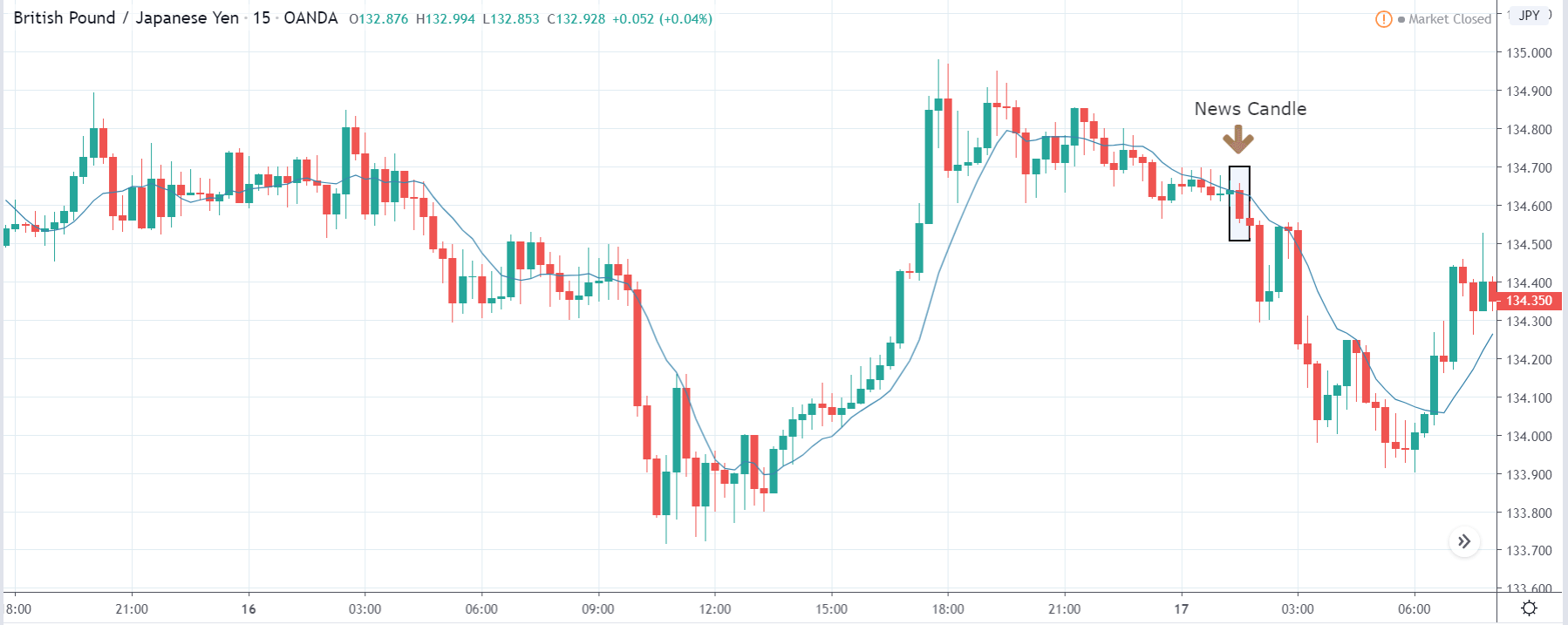
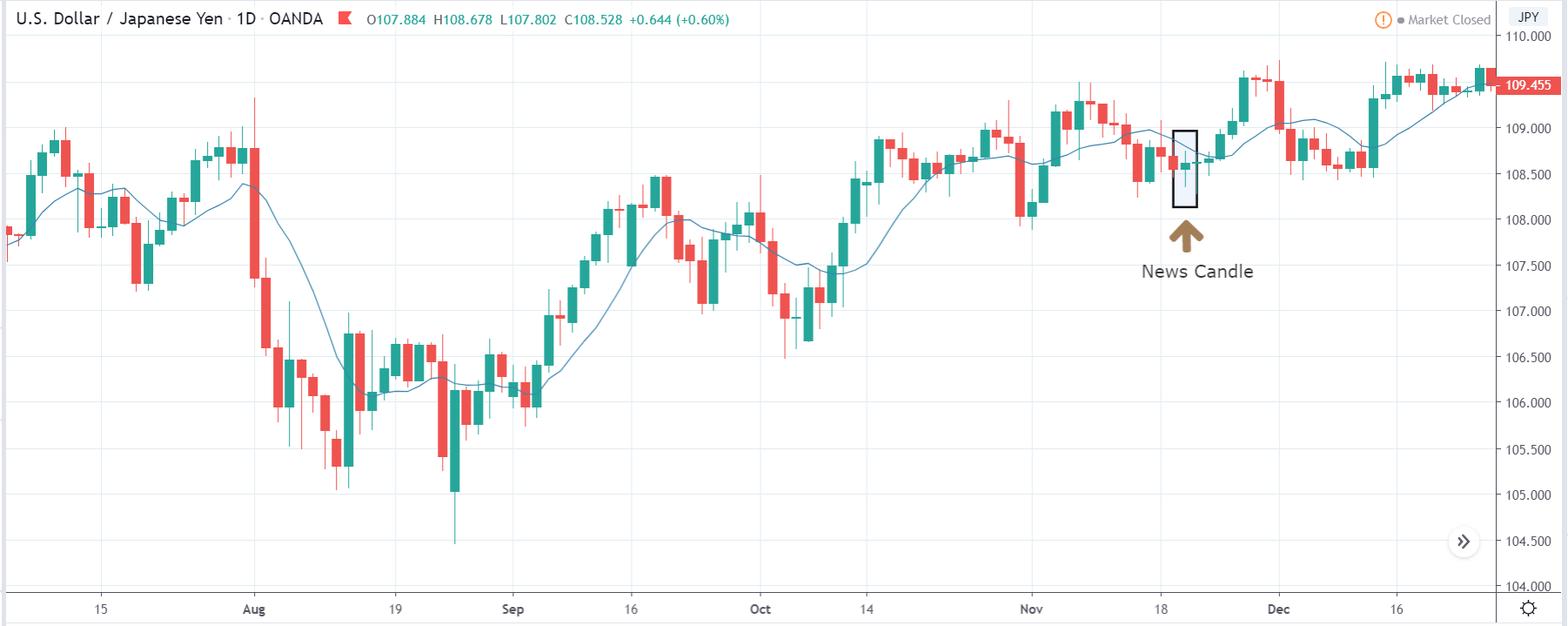
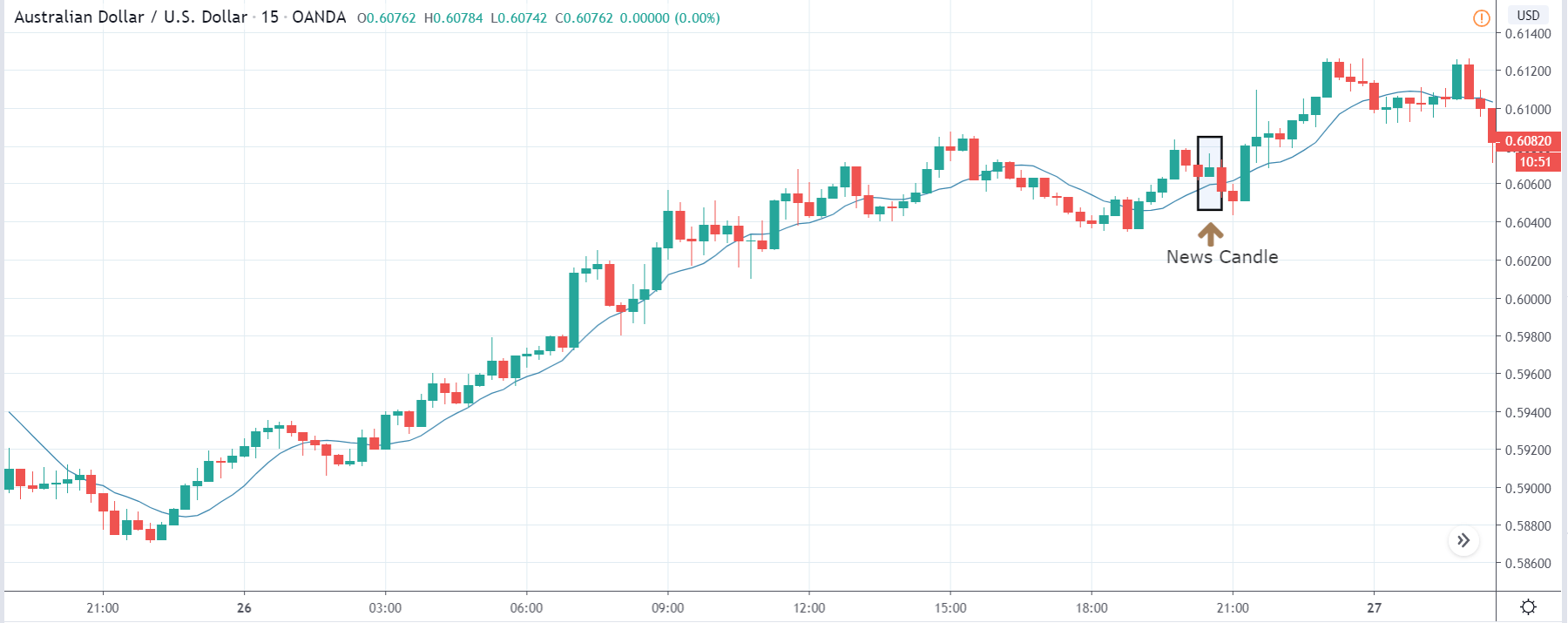
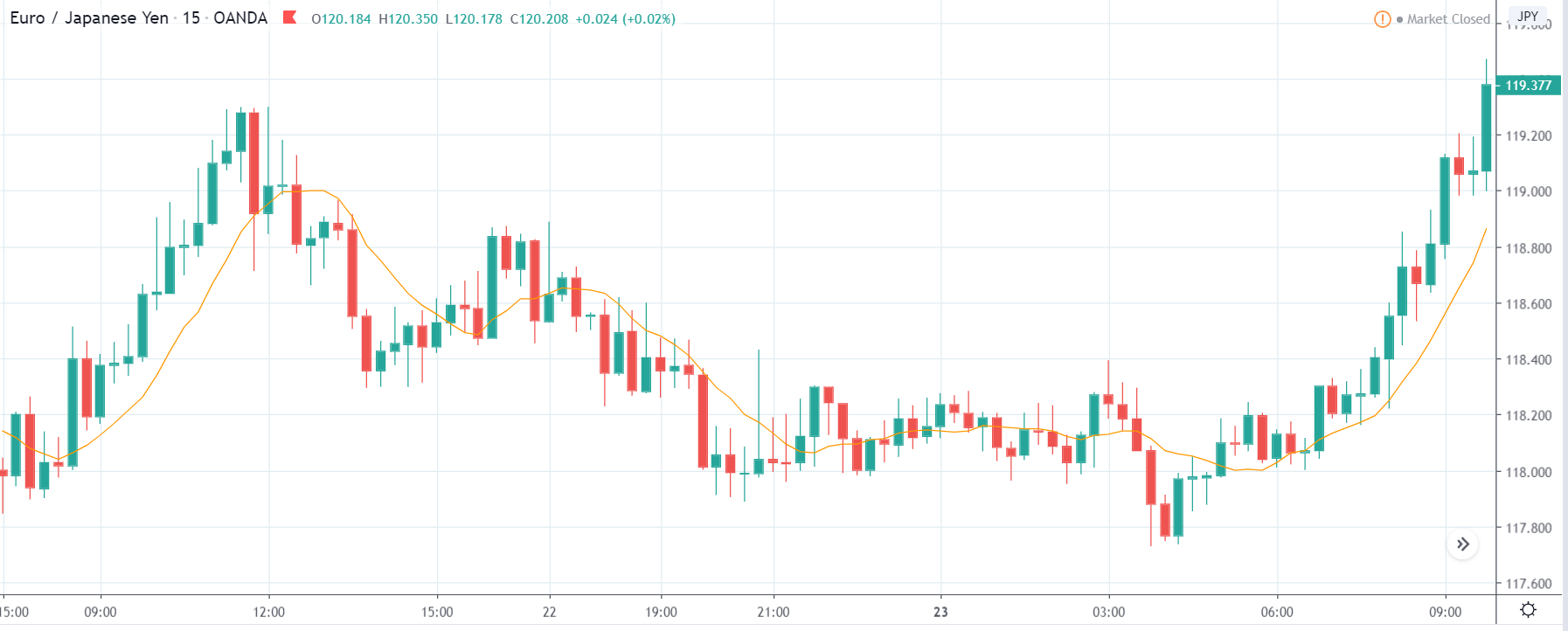
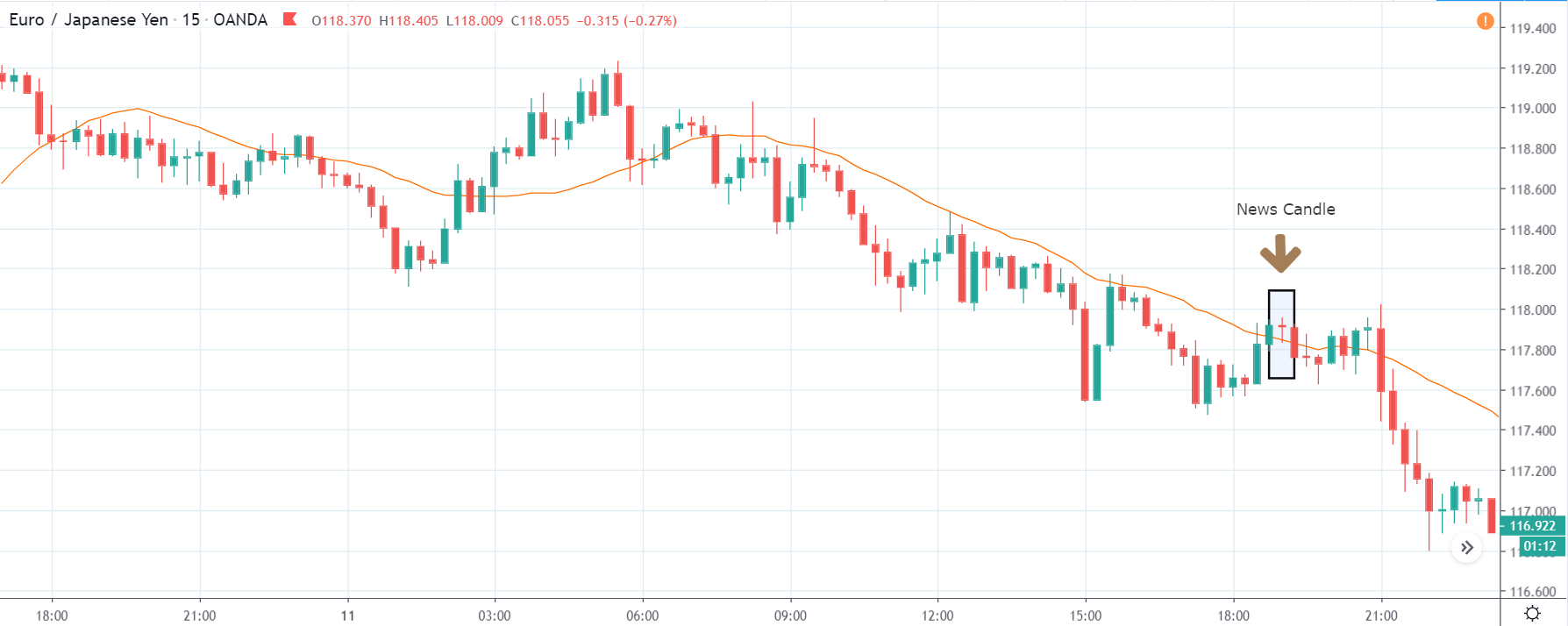
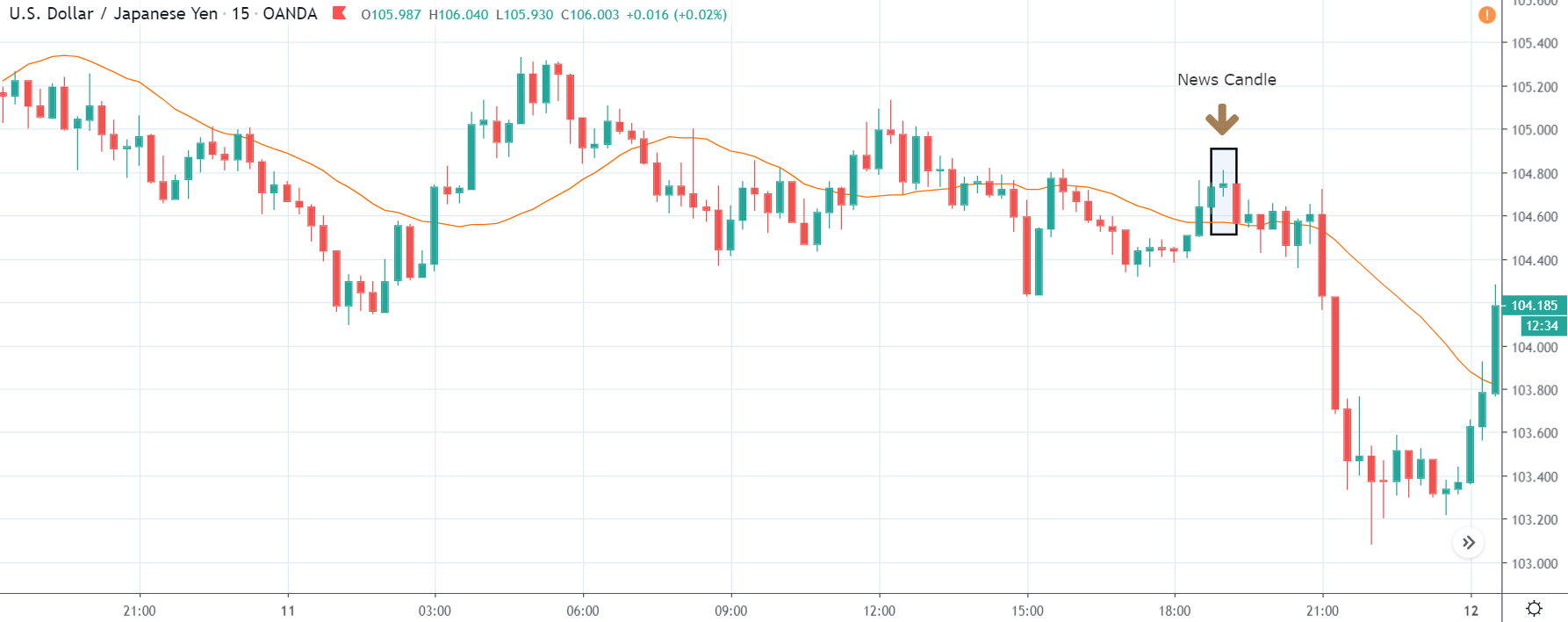
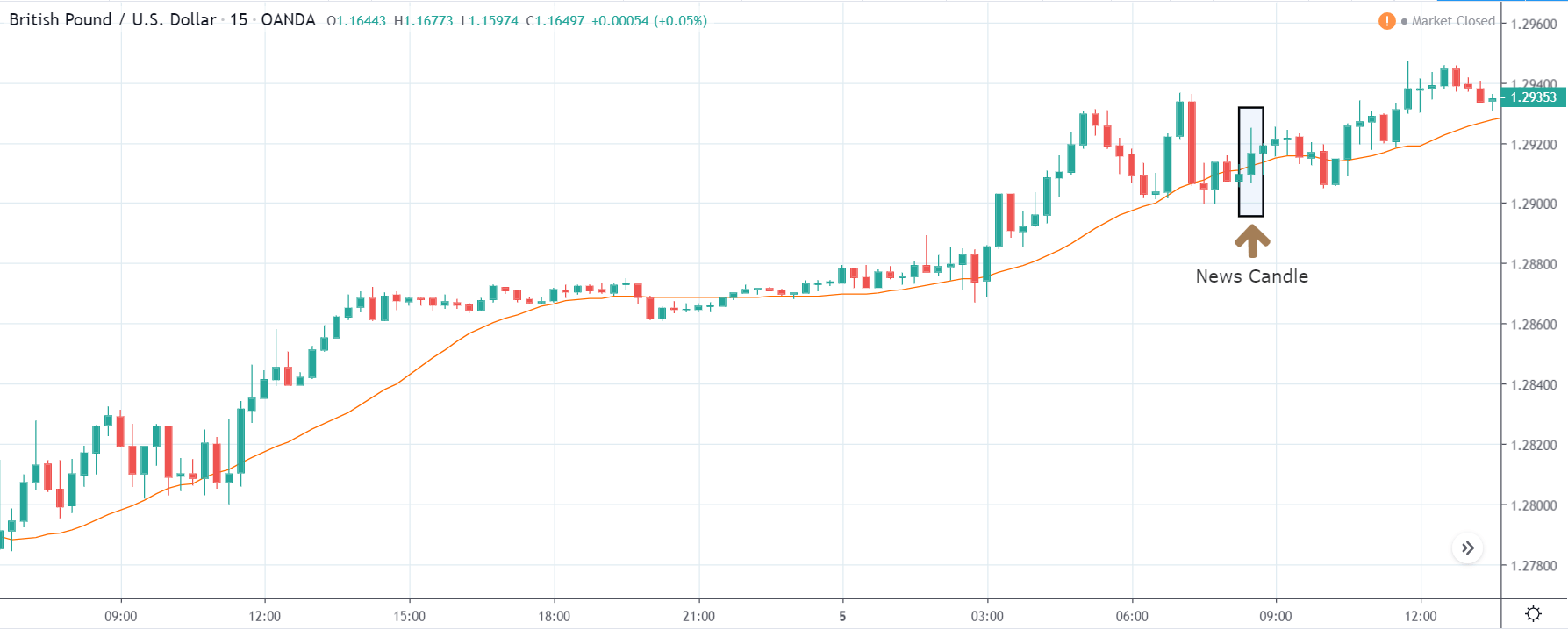
GBP/JPY | After The Announcement
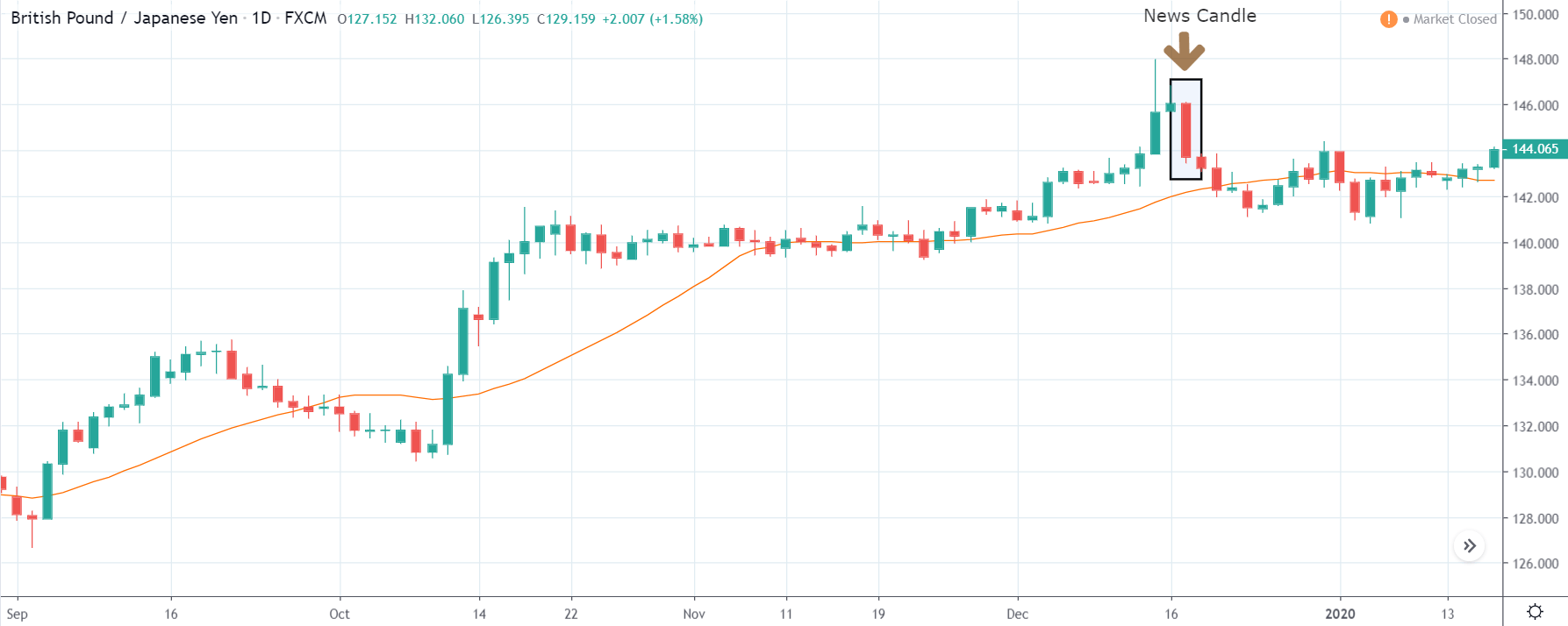
The above images represent the GBP/JPY currency pair where the chart characteristics are almost the same as that of the GBP/CAD, but with a difference that, the uptrend is more extended in this pair. When the market is trending strongly in one direction, we need to cautious while making trades in the opposite direction of the market. Here too, since we are not sure of the Credit Rating data, we cannot position ourselves on any side of the market.
After the news announcement, the British Pound falls but as much as in the above case. There is an increase in volatility on the downside but not sufficient enough to take a ‘short’ trade. Another reason behind a lesser fall in price could be the weakness of the Japanese Yen. Also, the price, even after bad news, is still above the moving average.
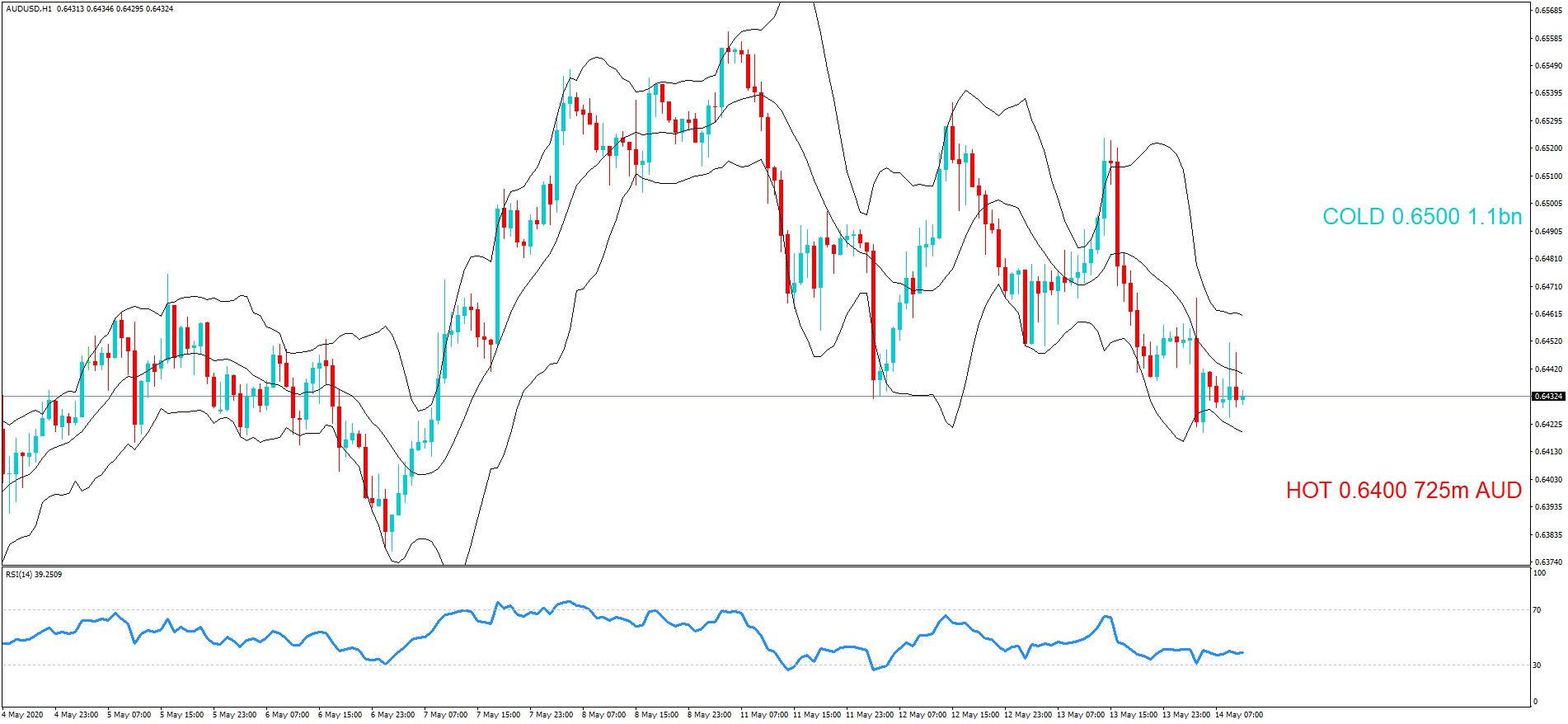
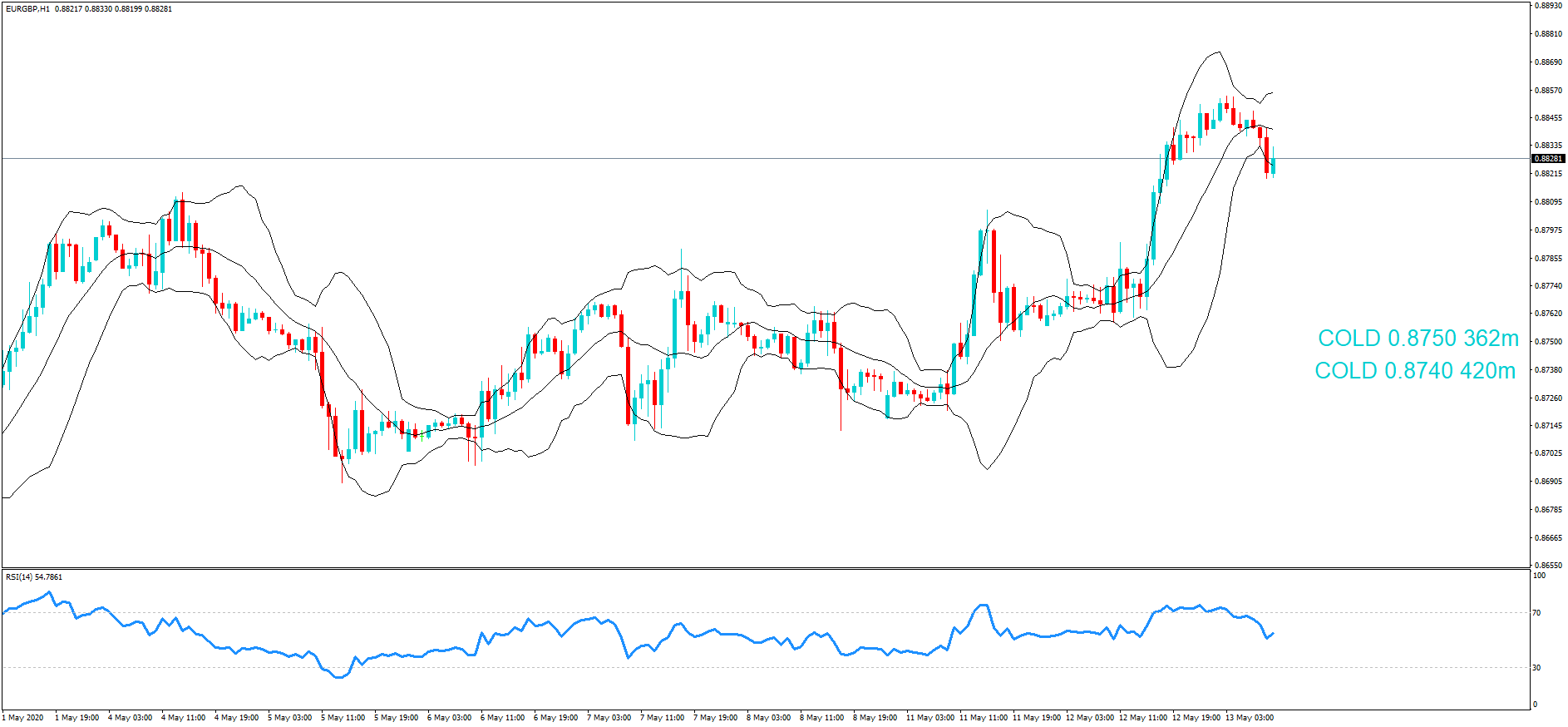
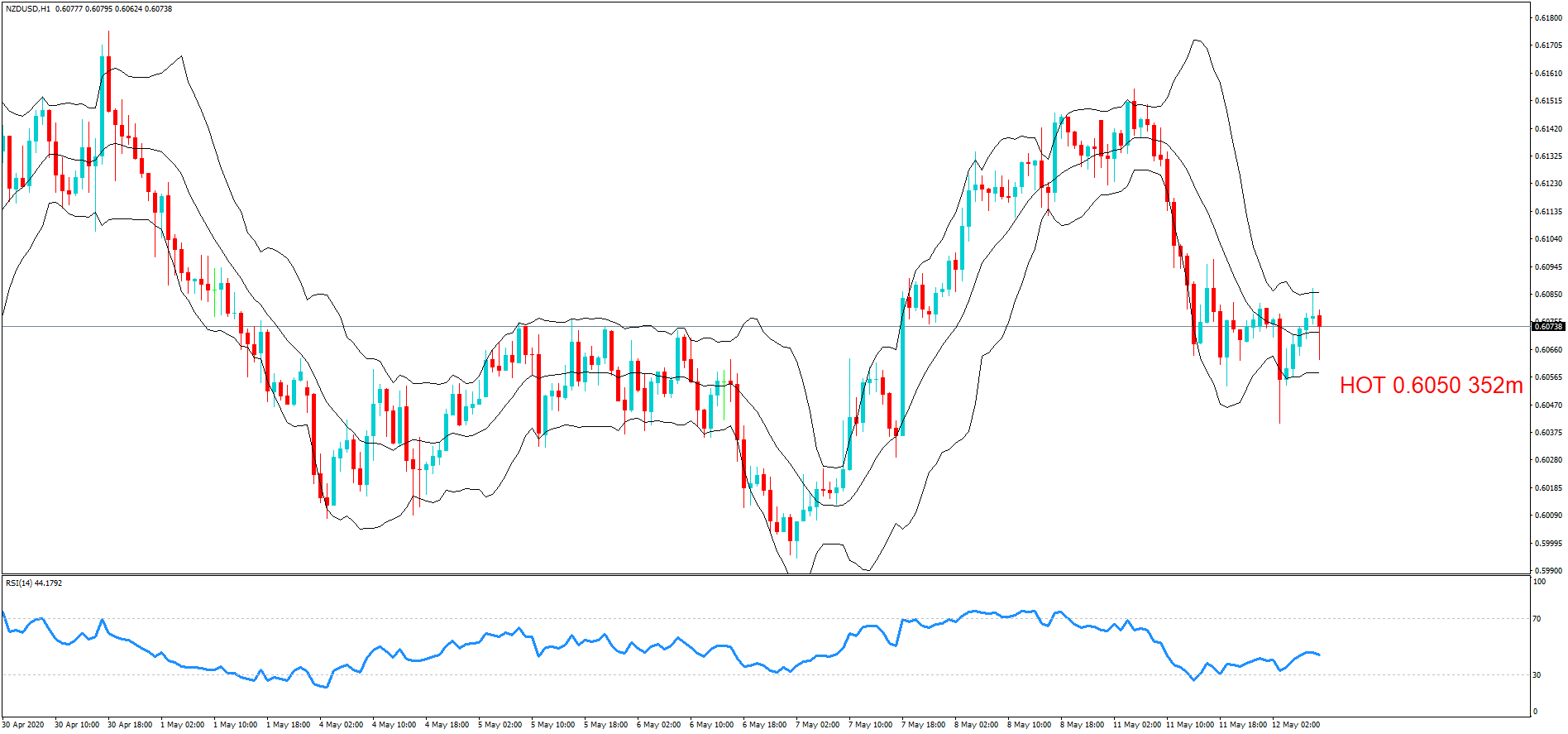
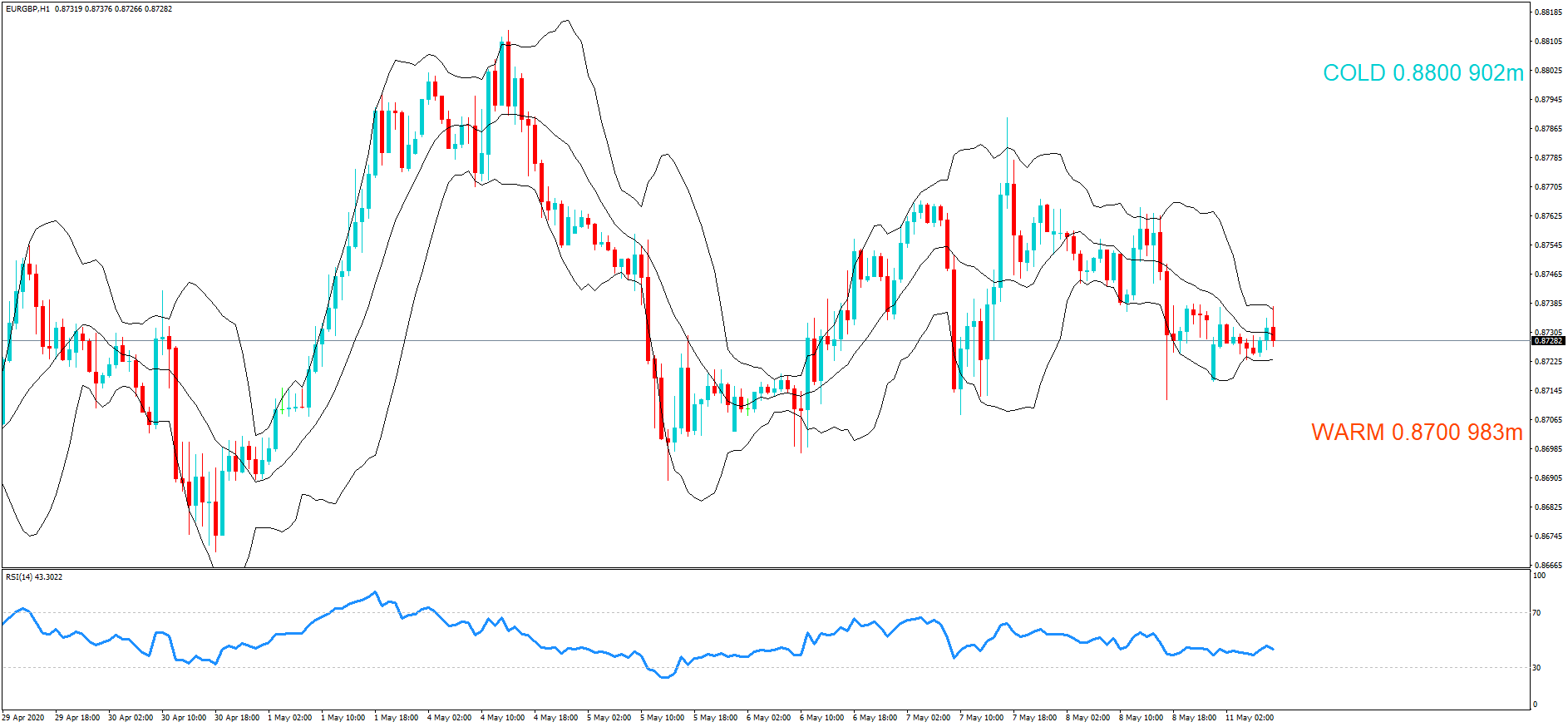
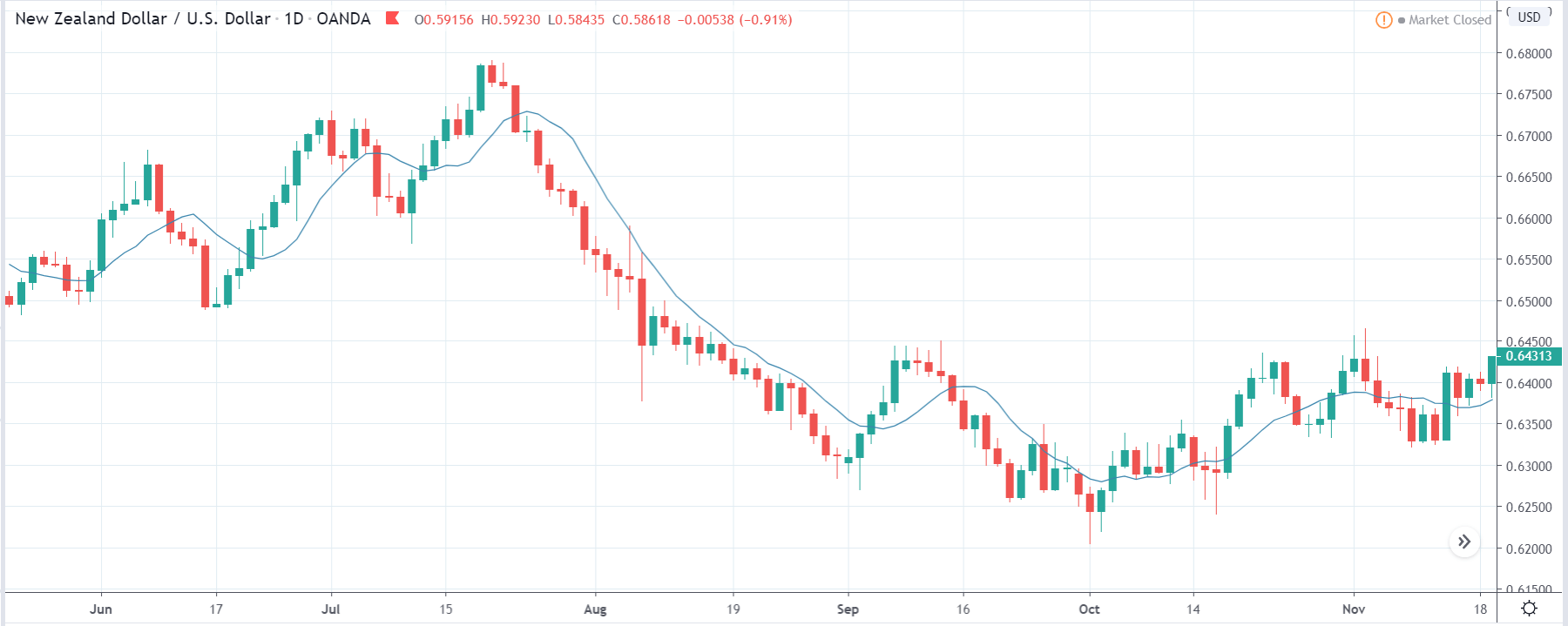
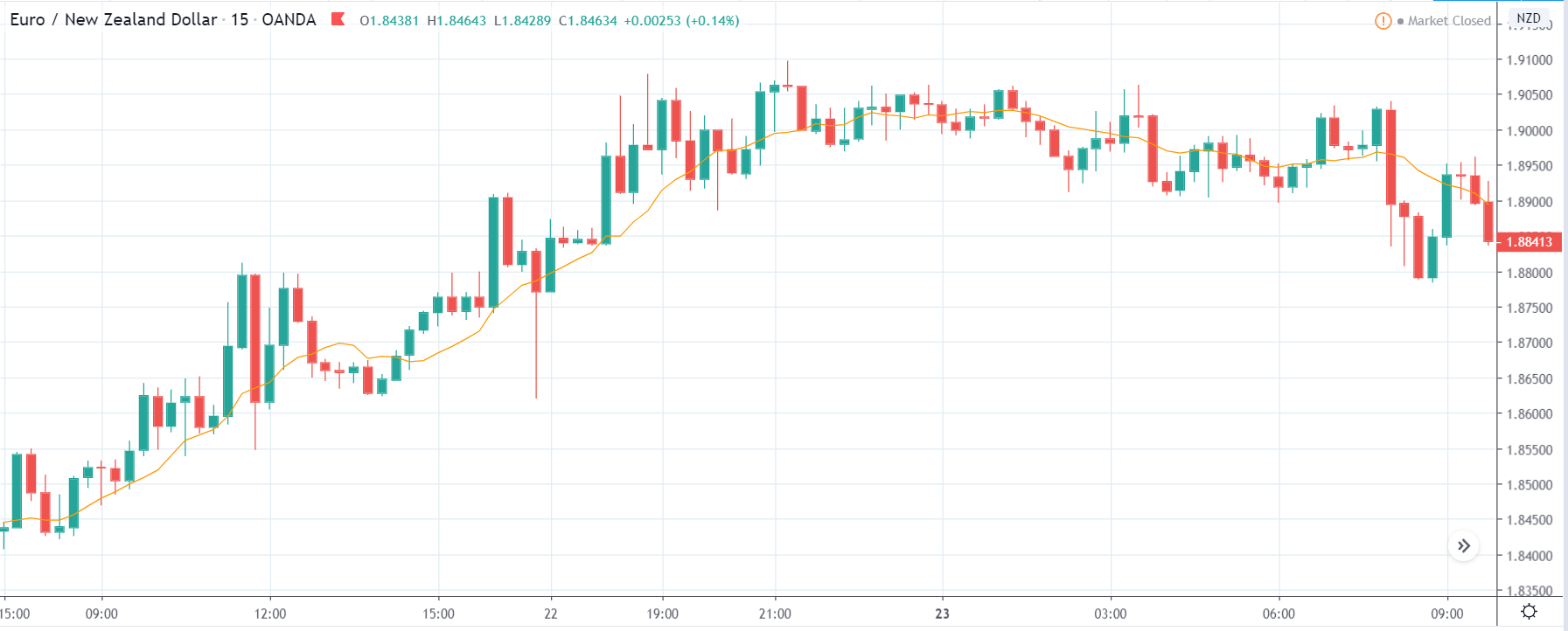
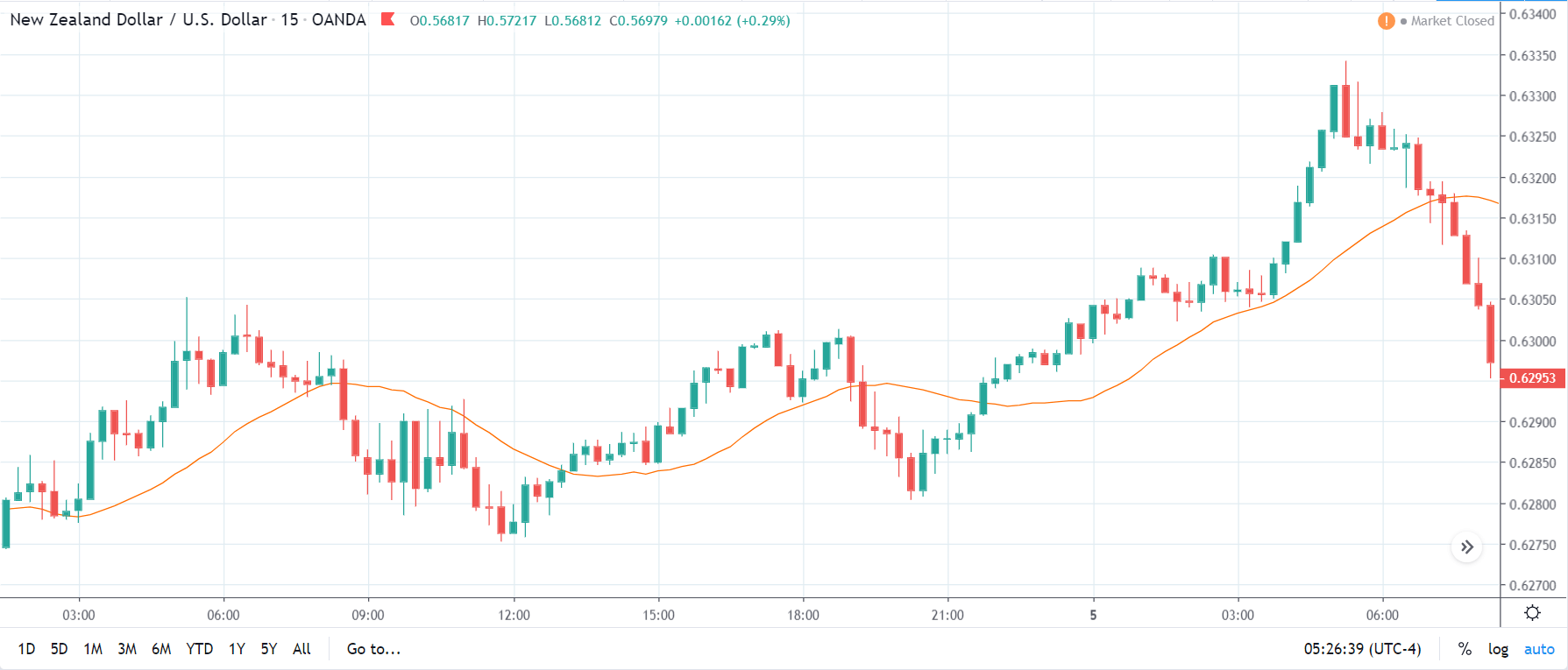
GBP/NZD | Before The Announcement
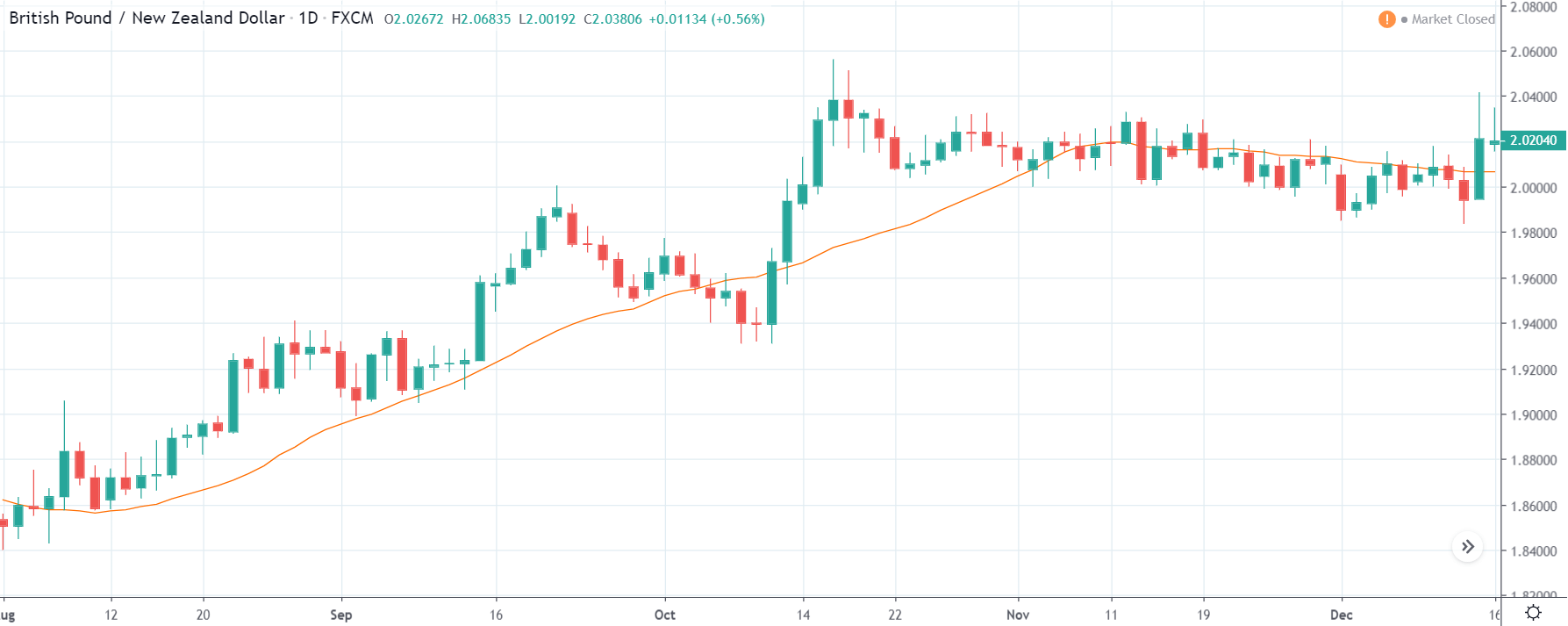
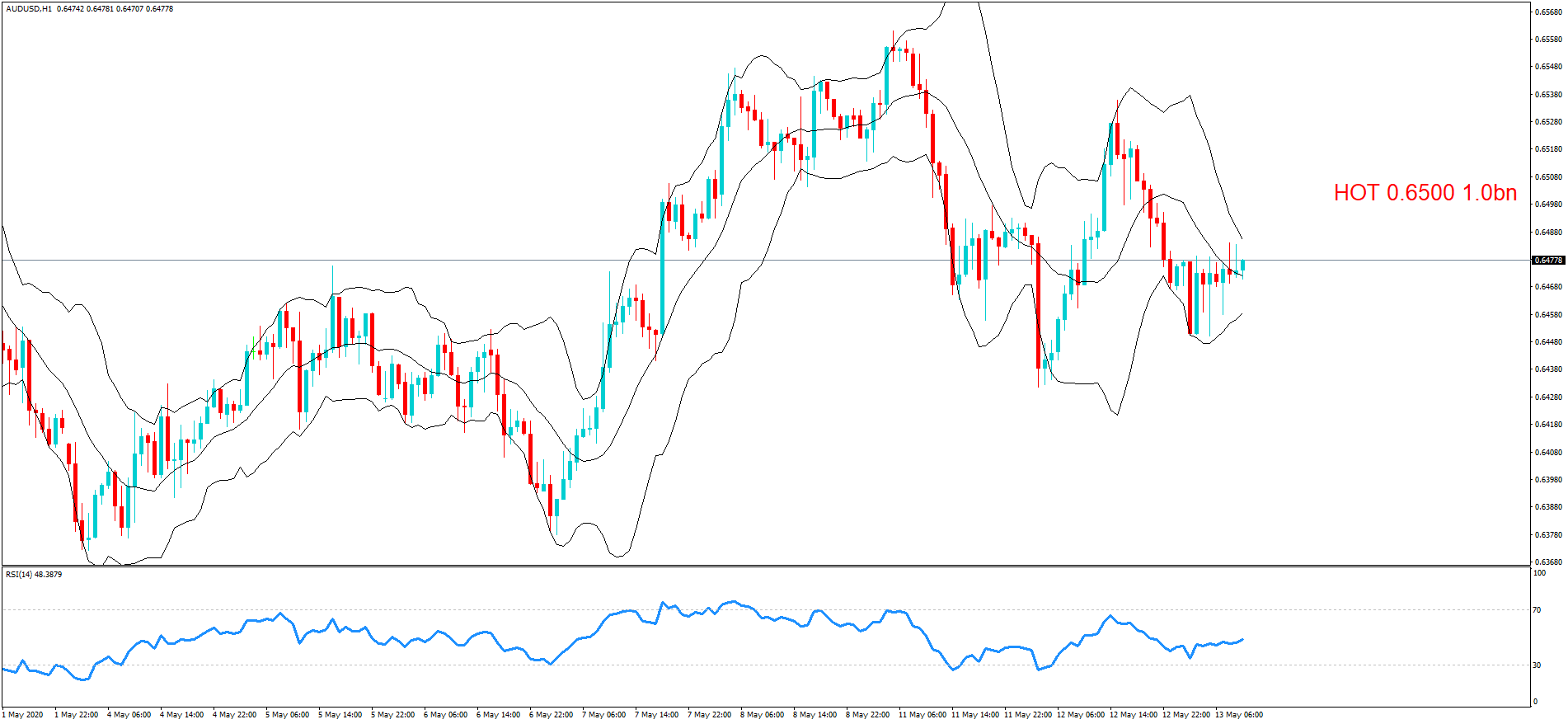
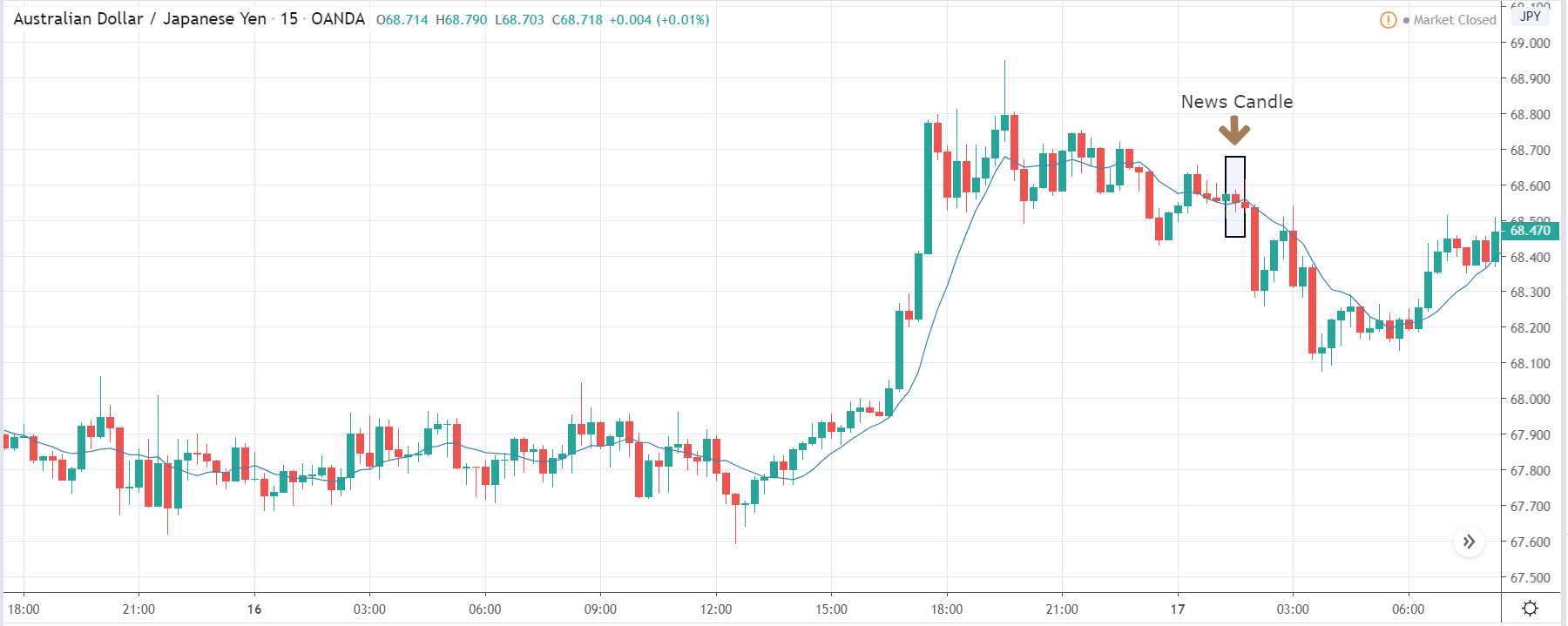
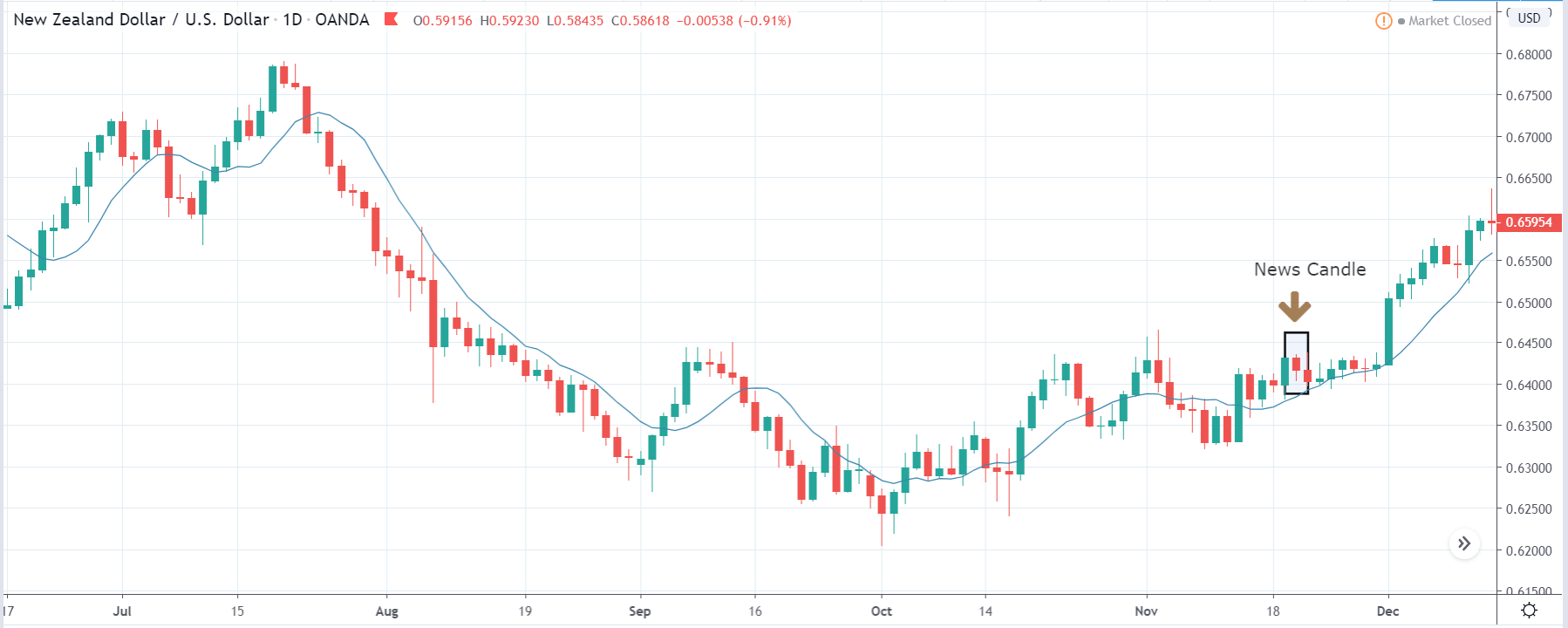
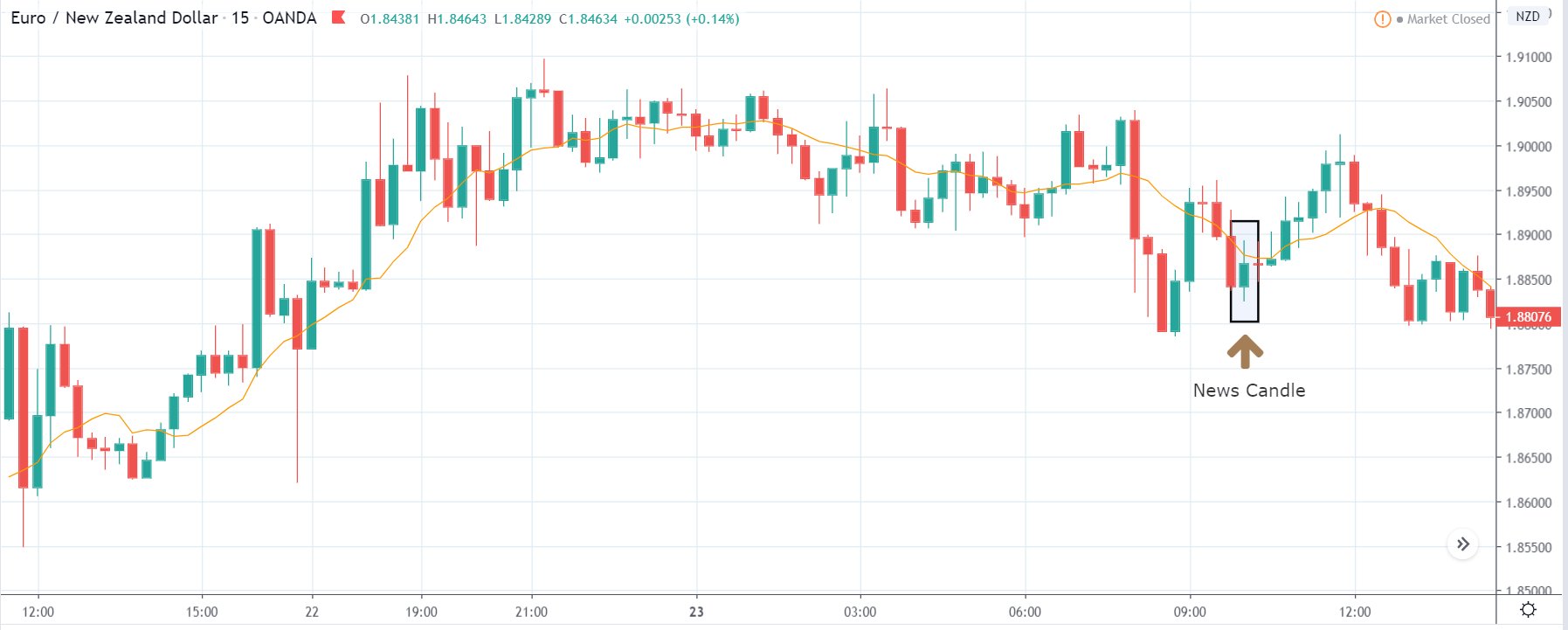
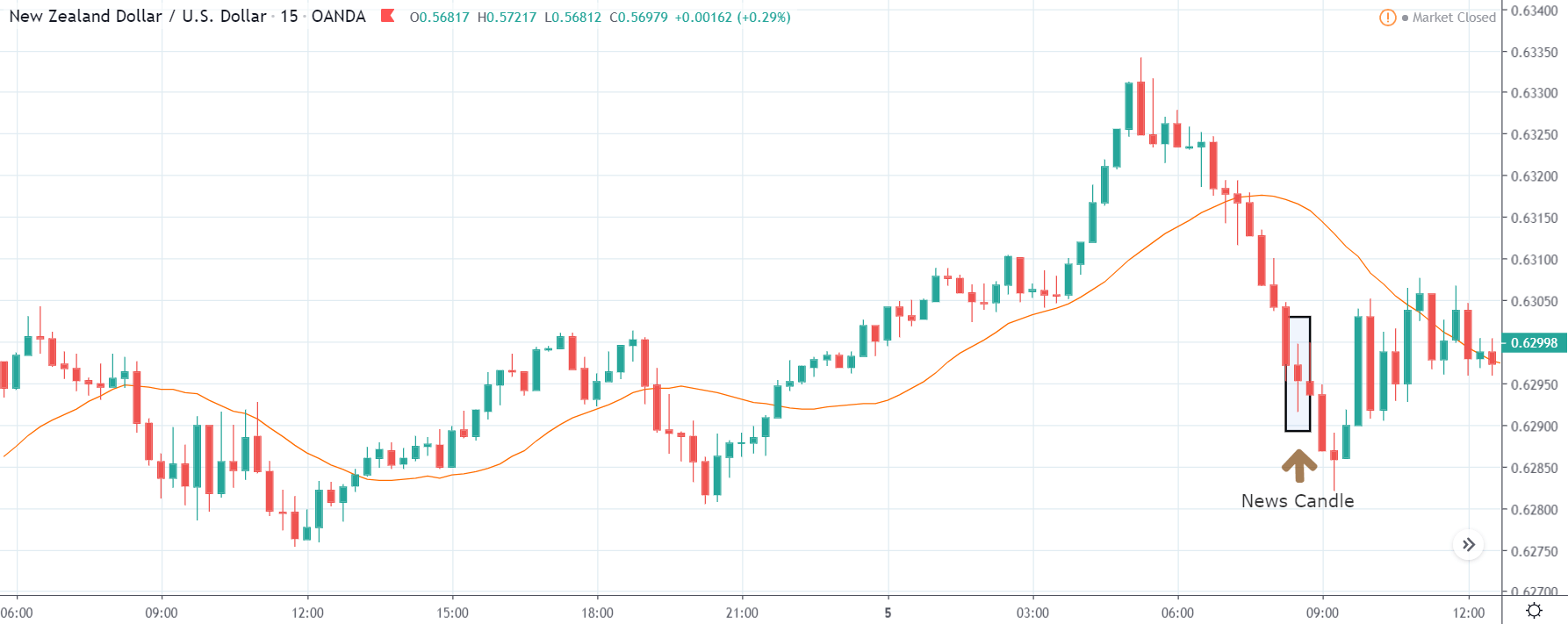
GBP/NZD | After The Announcement
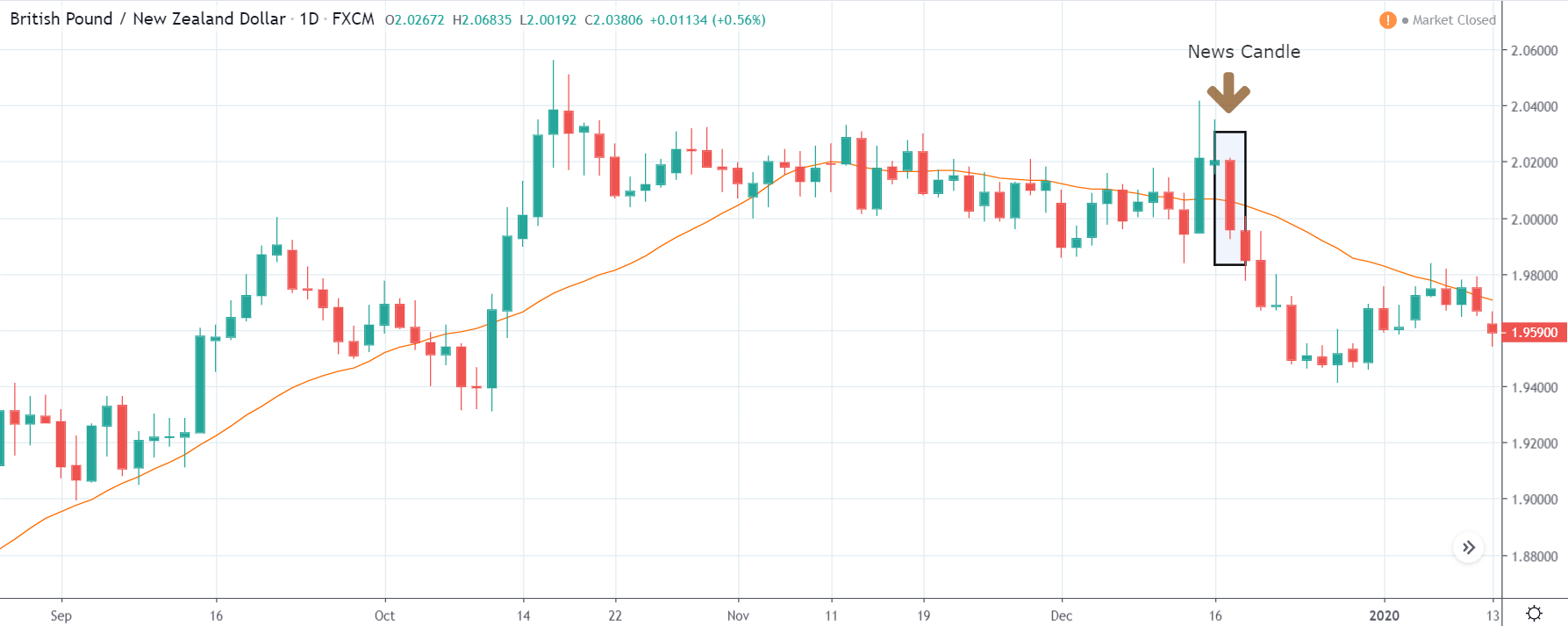
In GBP/NZD currency pair, before the Credit Ratings are declared, we can see that the market is showing signs of weakness. Since the overall trend is up, we need to wait for the news release and get a confirmation from the market. We can still trade in the ‘options’ segment of the market and profit from the increased volatility on either side after the news announcement.
After the Credit Rating data is announced by different agencies, the market falls, and volatility increases on the downside. This is a result of the negative Credit Rating given to the United Kingdom, which disappointed the market participants. Since the market was already showing weakness, this could prove to be the best pair to go ‘short’ with a much higher risk-to-reward ratio.
That’s about ‘Credit Rating’ and its relative impact on the Forex market after its news release. If you have any queries, let us know in the comments below. Cheers!