Introduction
The unemployment rate is a fundamental indicator of macroeconomics. Before getting into defining the unemployment rate, let’s first understand what even unemployment is. Later, we shall get deep into understanding the unemployment rate and its effects on the economy and the currency (using price charts).
What Is Unemployment?
To put it in simple terms, Unemployment is a scenario where a person is constantly looking for work but is unable to find it. So, works are considered to be unemployed if they do not work but are capable and are willing to do so. This is a great factor in determining the health of the economy. And the measure of unemployment is what is termed as the unemployment rate.
Understanding Unemployment Rate
The unemployment rate can be defined as the percentage of unemployed workers in the total labor force, where the total labor force comprises of all the employed and unemployed citizens within an economy. Mathematically, it is the number of labor force divided by the number of unemployed people. And as mentioned, to be considered unemployed, the person must have an active history of them looking for jobs. So, if you’ve given up looking for a job or work, you will not be considered unemployed.
More about Unemployment
Unemployment is a vital economic indicator as it indicates the inability of the workforce to obtain work to contribute to the productive output of the economy. The simple implication of unemployment would be less total production than that could have been possible. Also, an economy with high unemployment would have lower growth output with disproportional fall in the requirement for basic consumption.
On the flip side of things, a low unemployment rate implies that the economy is producing goods almost at its full capacity, having a commendable output, and rising standard living standards. Talking it further, an extremely low unemployment rate would mean an overheating economy and signs for inflationary pressures. It could be a hard time for businesses that would be in need of additional workers.
Types of Unemployment
Now that the definition of unemployment is clear, let us go ahead and understand how economists have classified unemployment. Unemployment is broadly classified into two types, namely, voluntary and involuntary. Voluntary unemployment is the case when the person has quit the job voluntarily in search of another job. But, in the case of Involuntary unemployment, the person has been fired by the organization. Now, the person must look for other employment. Voluntary and involuntary unemployment can be further divided into four types.
- Frictional Unemployment
- Cyclic Unemployment
- Structural Unemployment
- Institutional Unemployment
Frictional Unemployment
Frictional Unemployment is the most obvious type of unemployment. This occurs when a person is in between jobs. When a person quits a company, it takes some time to search for a new job. However, this unemployment is typically short-lived. Moreover, this type of unemployment does not really cause problems for the economy. Frictional unemployment is something natural, as ideally, it is not possible to find a job right after a person leaves a job.
Cyclic Unemployment
Unemployment varies based on the cycles of the economy is termed as cyclic unemployment. During the course of economic growth and declines, there is variation in the number of unemployed workers. For example, during economic recessions, unemployment rises, and during economic growth, unemployment decreases.
Structural Unemployment
This type of unemployment causes due to the advancements in the technology, or the structure through which the labor markets operate. The technological advancements could be the automation of manufacturing or the use of automobiles in place of horse-drawn transport. Such things lead to unemployment because there is no requirement of labor for it.
Institutional Unemployment
The consequence of permanent or long-term institutional factors and incentives in the economy could be unemployment. Such unemployment is called institutional unemployment. Some of the factors leading to institutional unemployment include
Government policies
- High minimum wage floods
- Generous social benefit programs
- Restrictive occupational licensing laws
Labor market phenomena
- Efficiency labor
- Discriminatory hiring
Labor market institutions
- A high rate of unionizations
How the Unemployment Rate Affects the Economy
We know that the unemployment rate is a vital indicator, as it gauges the joblessness in an economy. This, in turn, gauges the economic growth rate as well.
The unemployment rate economic indicator is a lagging indicator. This indicator does not predict that the market is going to rise or go under recession, but it measures the effect of the economic events. Based on the event, this indicator makes a move. For example, the unemployment rate does not rise until the recession has officially begun. But, a point to note is that the unemployment rate continues to rise even after the recession starts to fade away.
There are two reasons for it. One of them is that the companies are reluctant to lay off their people when the economy takes a downside. For large companies, it might take a few months to come up with a layoff plan. Secondly, the companies are more reluctant to hire new workers until they have a confirmation that the economy has stepped into the expansion phase of the business cycle.
For example, during the well-known financial crises that happened in 2008, the recession actually began during the first quarter of the year. The US GDP had 1.8 percent. Until May 2008, the unemployment rate was 5.5 percent. But, when the recession came down, and the economy started to do well, the unemployment rate hit 10.2 percent in October 2009.
So, with this, we can entitle the unemployment rate as a powerful confirmation indicator rather than a lagging indicator. For example, if the other leading indicators are already showing an expansion in the economy, and the unemployment rate has started to decline, then you are confident that the companies are yet again going to hire people.
Unemployment Rate and its Impact on the Currency
As already discussed, unemployment signals the economic growth of a country. If the economy is doing is bad, then then the unemployment rate rises. And if the economy is growing fairly, the unemployment rate declines. When it comes to currency, it is proportional to the economic growth of a country. This, in turn, implies that unemployment is inversely proportional to the value of the currency.
Frequency of the release of the Unemployment rate
The unemployment rates are released by the Bureau of Labor Statistics on Friday of every month. Typically, the present values are compared with the previous month’s values. Sometimes, a year-to-year comparison is made as well.
Dependable Sources of Information
With the list of sources mentioned below for different countries, one can obtain valuable statistical information on the unemployment rates. Specifically speaking, one can get a visual representation of the historical values over a period of as high as 25 years. Apart from that, users get access to information regarding the actual, previous, highest, lowest unemployment rates as well.
USD | CAD | CHF | AUD | JPY | EUR | GBP
How the ‘Unemployment Rate’ News Release Affects the Price Charts?
Now that we have a good amount of theoretical information on the Unemployment rate, let’s get a little technical. In this section, we shall analyze how the prices of the currencies are affected after the release of the reports.
As mentioned, the reports on the unemployment rate are released by the Bureau of Labor Statistics on a monthly basis, typically on Fridays. As a usual effect, it is said that the actual data less than the forecasted data is good for the currency.
Also, note that, as per sources (Forex factory), this news is expected to have a high impact on the currency. For our illustration, we have taken into account of the Unemployment rate of the US released on 7th February.
In the below image, we can see that the Actual percentage is 3.6%, which is 0.1% higher than the forecasted percentage (3.5%). Also, it is higher than the previous month’s value. So, we can conclude that the unemployment rate in the US has increased in February compared to January.

When it comes to the effect on the forex exchange market, we can expect the US dollar to drop as the unemployment rate has increased (which is not good for the economy).
Now, let’s see its effect on few USD charts by pairing it with other major currencies.
USD/CAD | Before Announcement – 7th February
Below is the candlestick chart of USD/CAD on the 15min timeframe. If we were to look at the recent trend, we could see that the market is in an uptrend. Now, we need to see if the trend continues after the release of the news or reverses its direction.

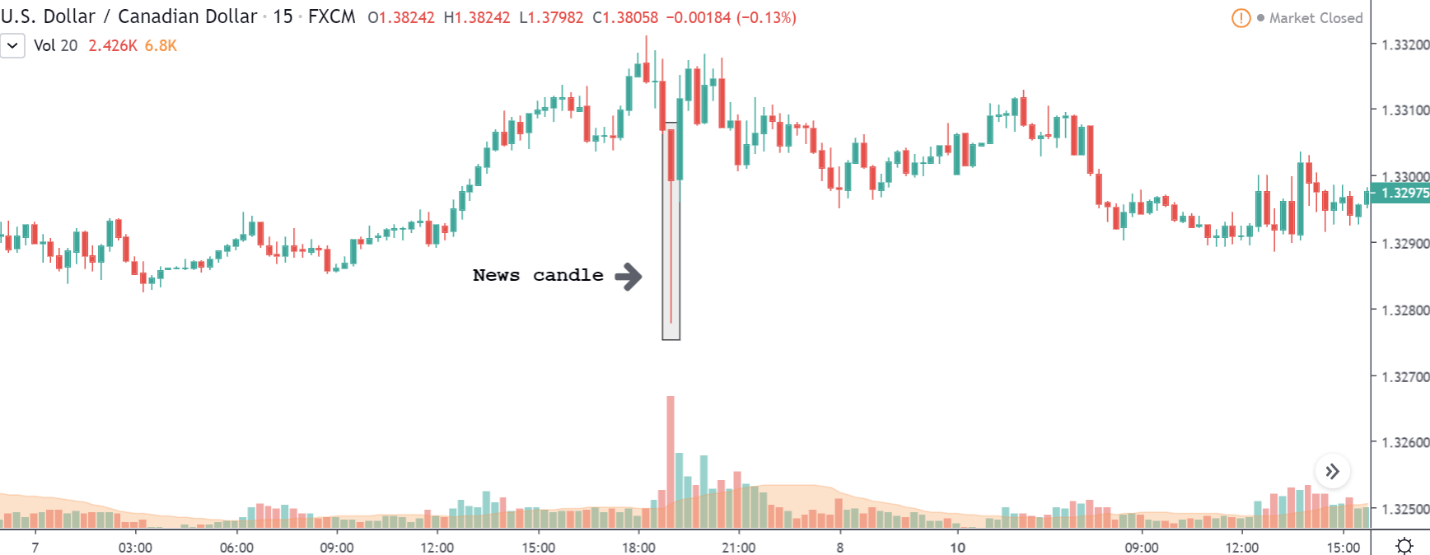
USD/CAD | After Announcement – 7th February
Below is the candlestick chart of USD/CAD on the 15min timeframe after the release of the news. The news candle is indicated as shown. We can see that when the news was released, the market just plunged down. Here, we can infer that the market moved as the way we expected it to move. Also, the volatility surged up when the news came out. If you look at the volume indicator as well, we can see that the volume shot up high.
However, in hindsight, the market recovered from the drop and left a wick on the bottom. With this, we can conclude that the drop in price was consumed by the strong buyers. The buyers did not let sellers reverse the market.
EUR/USD | Before Announcement – 7th February
In the below chart of EUR/USD, we can see that the market is in a downtrend, where the purple line represents the support and resistance line. Currently, before the release of the news, the market is in the S&R area. We need to see how the market will react after the news.

EUR/USD | After Announcement – 7th February
When the news was announced, we can see that the market went up, came down, and closed below the open price. There was strength from both sides, and the volatility was pretty high. If you look at the volume bar corresponding to the news candle, we can see that the volume too was high at that point in time.
In this currency pair, EUR is the base currency, and USD is the quote currency. According to the impact of the news, the market was supposed to shoot up. The market did try to go higher but got rejected by the sellers. So, basically, the seller’s market was more dominated than the news in this case.

GBP/USD | Before Announcement – 7th February
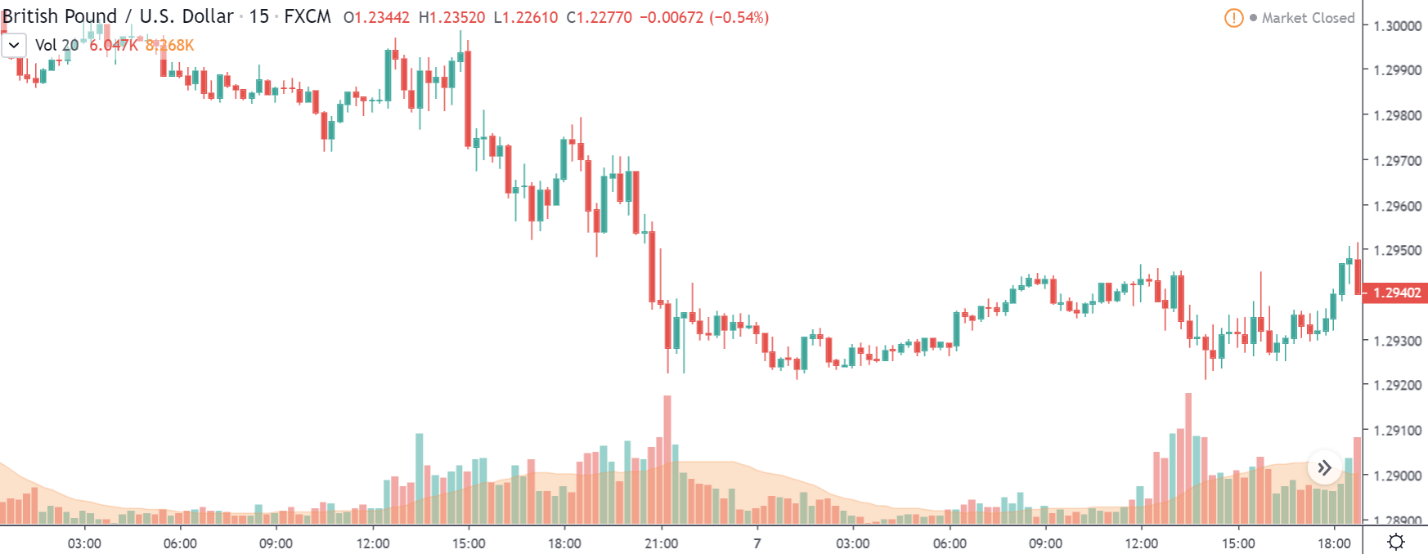
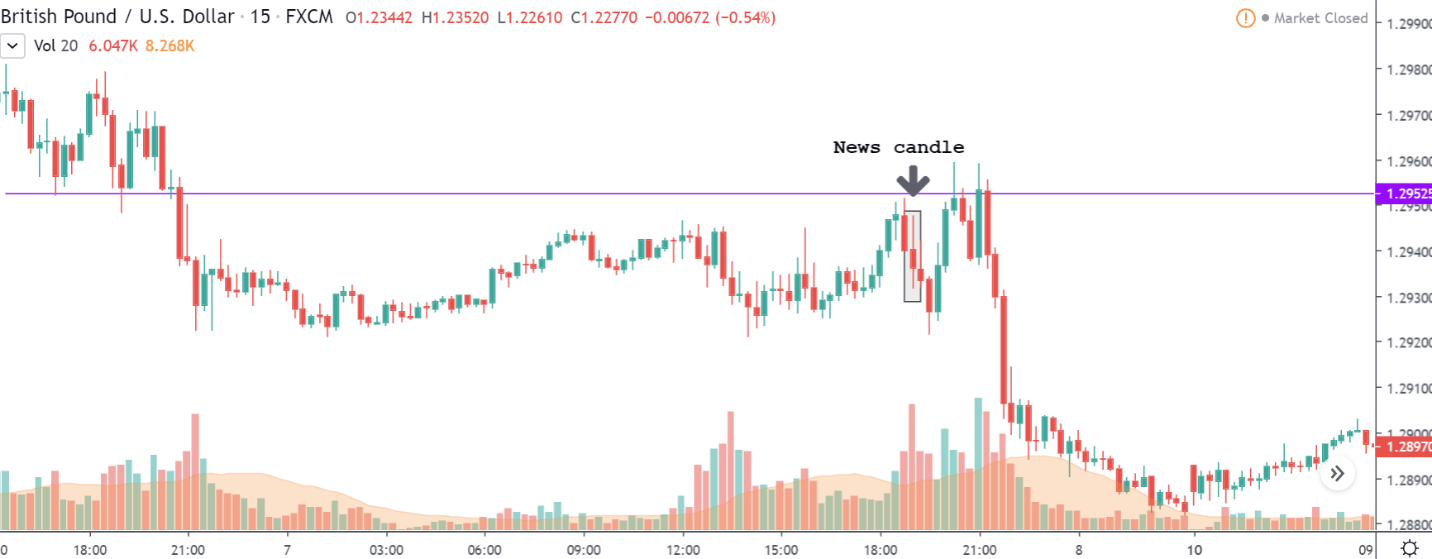
GBP/USD | After Announcement – 7th February
Below is the chart of GBP/USD on the 15min timeframes after the release of the news. We can see that this chart is very similar to the EUR/USD chart. The news candle initially shot up, but came down and closed red. The volatility during this time was quite high, which can be inferred from the corresponding volume bar below. And according to the news, the market was supposed to go north, but the market continued its downtrend.
Bottom line
The unemployment rate, though a lagging indicator, should not be taken for granted. It is as vital as the other economic indicators such as GDP, inflation rate, interest rate, etc. Employment is one of the primary reasons for the economies do well. Economies with high unemployment rates are being hit hard. Coming to the investors’ and traders’ point of view, one must keep an eye on the rate of this indicator and treat it as a powerful confirmation tool rather than just a lagging indicator.