Security issuance in the traditional world is faced with so many challenges. And many of these challenges stem from the centralized nature of the system – from costly intermediaries to inaccurate records to fraud-prone processes.
Blockchain technology provides an opportunity for the industry to rectify these shortcomings. It facilitates the decentralized and peer-to-peer exchange of assets as it does trustless and fraud-free transactions.
The Standard Tokenization Protocol is a blockchain effort that wants to make this possible. And it has the bonus of making sure these assets are legally compliant, eliminating any potential friction with authorities.
How does it achieve that? This article is an attempt to answering that question.
Breaking Down STP
The Standard Tokenization Protocol is a blockchain effort aimed at cross-chain assets tokenization. It wants to differentiate itself from similar protocols by supporting assets in a way that makes them compliant with various jurisdictions. The end goal for STP is to popularize the knowledge and usage of digital assets around the world.
The STP whitepaper describes itself as “a decentralized platform for digital asset issuance powered by the STP token, a new smart contract protocol framework for compliance offerings.” It also states that it aims to “enable the movement of digital assets in a globally compliant manner.”
STP wants to address the issues of traditional security-issuing platforms.
The Problems with Traditional Options
- Security issuance in the traditional system involves intermediaries who add to the bloat and expenses of the process
- Often, there’s a limit on the scale of participants that can be involved in security issuance and trading at any time, in an attempt to minimize the manual process
- The restrictions lead to the securities being less liquid in the market
Benefits of Digital Assets
#1. Digital assets are programmable
Blockchain enables programmability for digital assets. Blockchain-enabled smart contracts can automatically move value in a peer-to-peer manner from one party to another when certain thresholds are met. This massively reduces costs.
#2. Fractional ownership
Fractional ownership enables investors to purchase part of traditionally valuable assets such as rare art and antique cars, and even assets that were previously a preserve of the wealthy such as real estate. This enables such assets to be liquid as opposed to if the process involved looking for one single buyer.
#3. Increased liquidity
Liquidity is how fast a product is sold once it’s listed on the market. It’s the opposite of illiquidity, which is when a product takes too long to find an exit position once it’s listed. Fractionalization of assets increases liquidity since it increases the number of buyers interested in purchasing a product.
#4. Peer-to-peer transactions
At its core, decentralization stands for the transfer of assets between parties without the involvement of overseeing authorities or intermediaries. The STP protocol ensures the peer-to-peer transfer of assets executed via smart contracts.
#5. Automated compliance
Traditional compliance procedures involve lengthy Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) procedures to ensure trust. On the other hand, blockchain-powered transactions are inherently transparent, making them trustless and legally compliant.
The STP Standard
The STP Standard is a protocol that oversees the generation, issuance, and transfer of tokenized assets. The protocol has a Compliance Validator that checks whether token issuance meets all the requirements -whether it’s accreditation, AML, and so on. There’s a validator committee whose work is to ensure this compliance is met. The STP network enables assets to move across geographical borders in a compliant manner.
Use Cases of the STP Protocol
The STP standard can be applied to several use cases across different industries. Let’s take a look at three of them:
#.1. Compliant asset tokenization
Asset owners from anywhere can use the STP protocol to tokenize their assets on the blockchain, increasing their liquidity.
#2. Mobile platform
Various users, such as retail investors, can access the STP platform conveniently via their mobile app. Not only will they be able to access wealth management tools, but they can also find projects to invest in, and if they’re the owners of a project, they can find the right audience in the platform.
#3. Blockchain-based crowdfunding
With the native cryptocurrency, STP, investors will be able to access new financial tools such as blockchain-based crowdfunding via smart contracts. Such onchain crowdfunding is safer, more secure, and more transparent than traditional crowdfunding.
STP Protocol’s Community Growth Strategies
The STP team plans to implement several strategies in the near future in a bid to build a bigger community. These strategies are as follows:
- Team up with various industry players so as to expand its ecosystem
- Hold airdrops and similar marketing campaigns to build community engagement
- Engage with the community on various social media platforms
- Keep the community updated on quarterly initiatives
- Launch Ambassador Programs to promote the idea of decentralization everywhere
The STP Token
The native cryptocurrency of the STP network is known as STPT. The token will serve several crucial roles in the network, including the following:
- Enable users to fractionalize assets or features of those assets
- As ‘gas’ for powering verification processes and transactions
- As staking so as to take part in the proof of stake consensus mechanism
- As a governance mechanism through which to contribute to major decisions of the network
- As a reward for good behavior
STP’s token distribution was as follows:
- Bittrex IEO token sale – 3.75%
- First private sale – 25%
- Second private sale – 5%
- Team tokens – 18.75%
- Token treasury tokens – 7.5%
- Token reserve tokens – 40%
Key Metrics of STP Token
If you’re interested in buying the STP token, then you need to know its current standing in the market. As of Sep 22, the token is trading at $0.019297 while ranking at #396. It has a market cap of $15,793,071, with a 24-hour volume of $2,738,104, a circulating supply of 818,409,893, and a total supply of 1,942,420,283. The token’s all-time high was $0.094944 (June 27, 2019), while its all-time low was $0.005800 (Sep 30, 2019).
Where to Buy STP Tokens
You can purchase STP tokens at any of several crypto exchanges, including Coinone Upbit, Coinone, VCC Exchange, Bithumb Global, BitMax, Huobi Global, Bittrex Poloniex, Bitsonic, Gate.io, and CoinDCX.
Closing Thoughts
STP is leading from the front to set a new standard for assets issuance. Issuers no longer have to deal with the burden of complying with regulations. All in all, users can expect a more accessible, inclusive, and efficient token issuance platform.

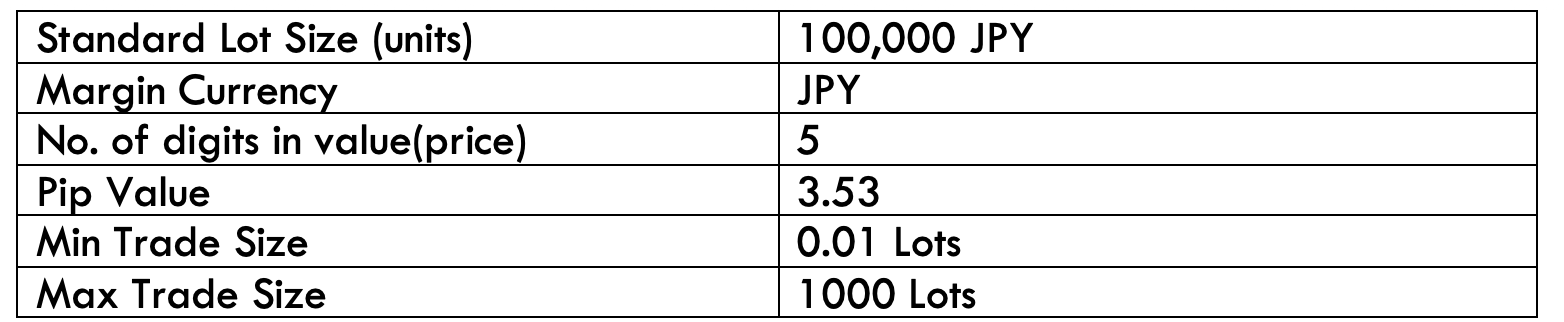
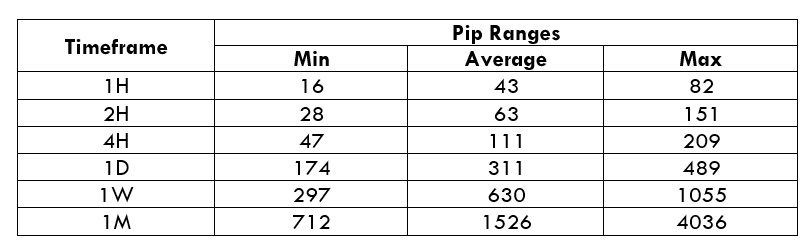
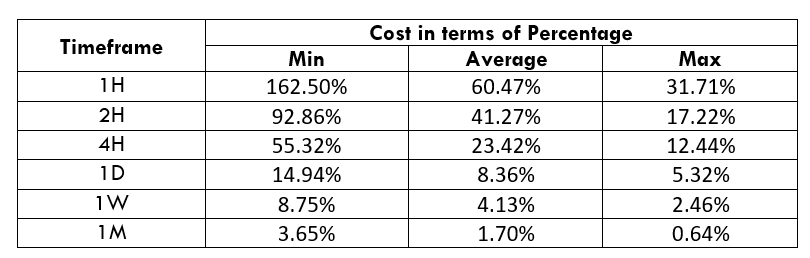
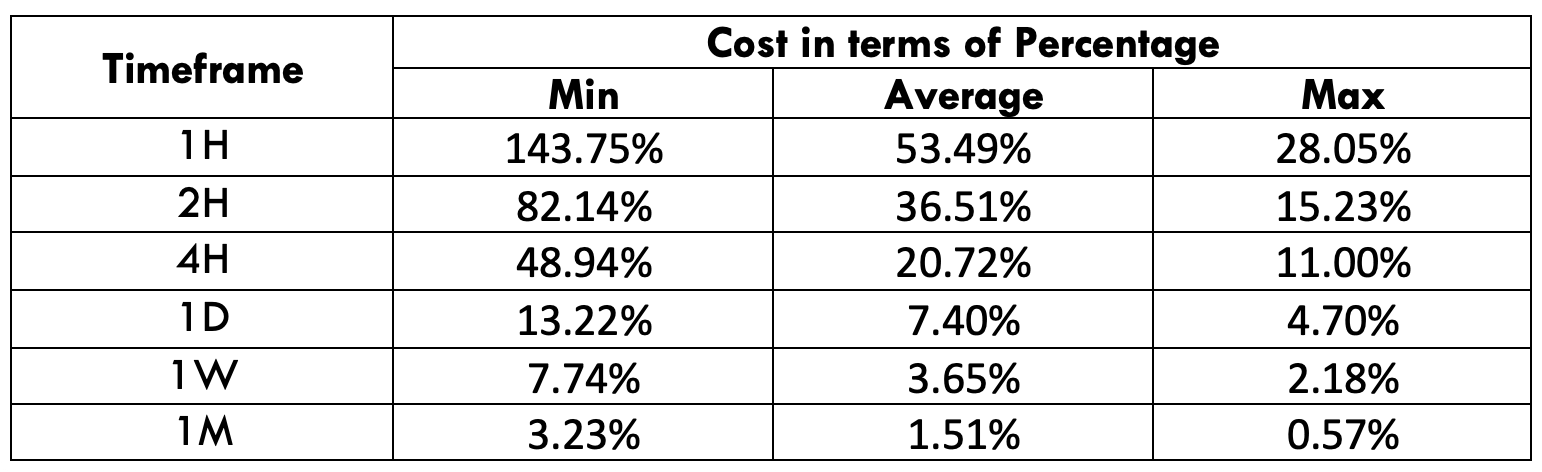
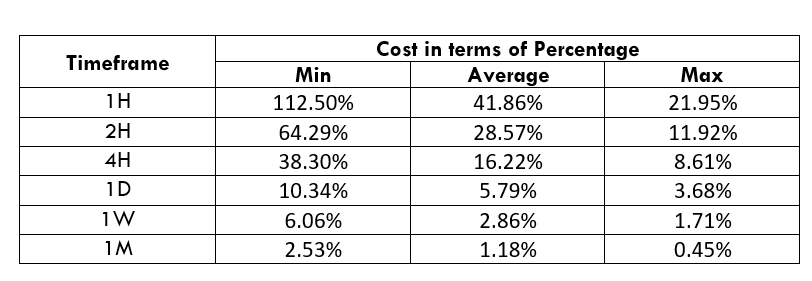


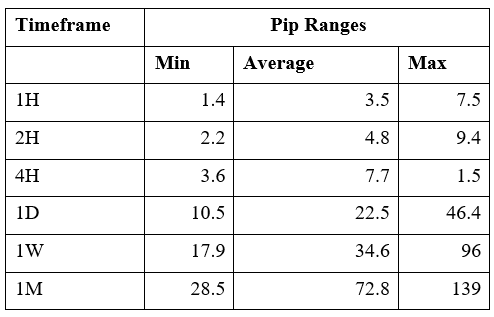
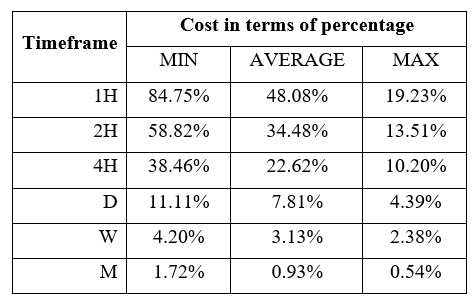

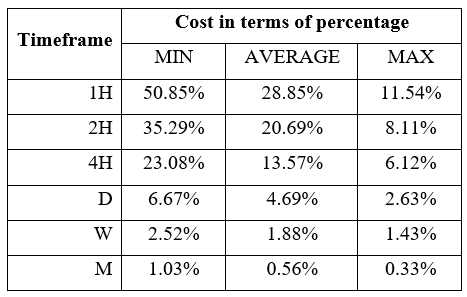
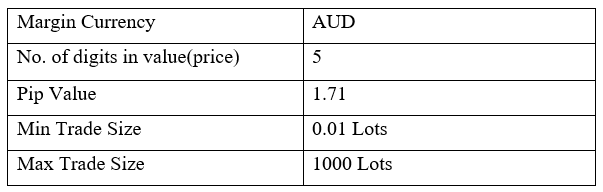
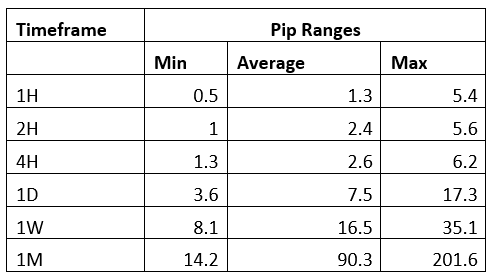
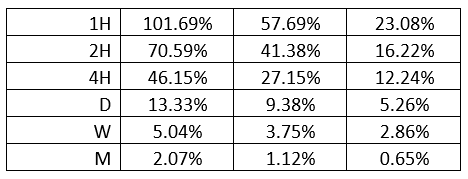
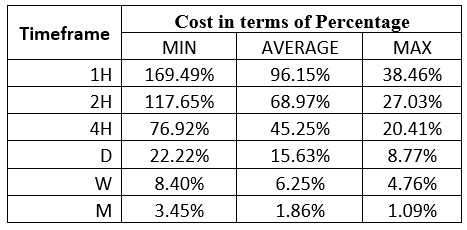
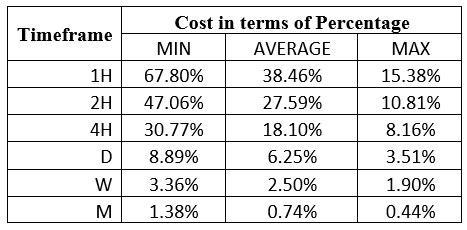

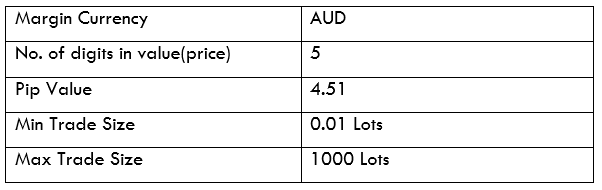
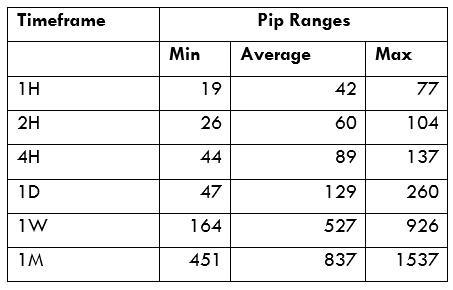
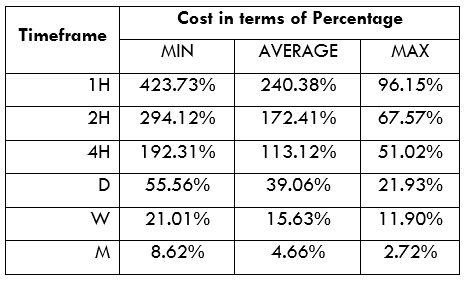
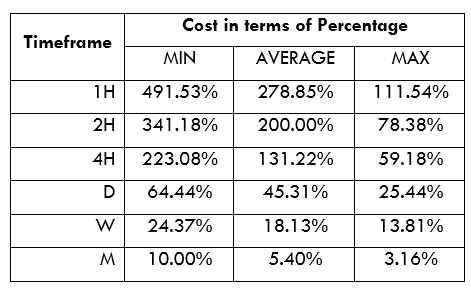
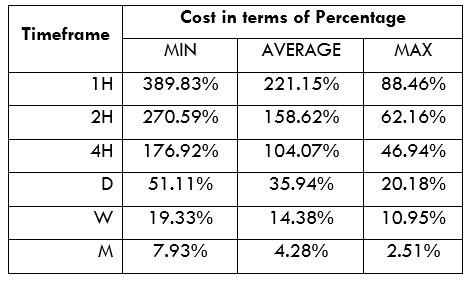

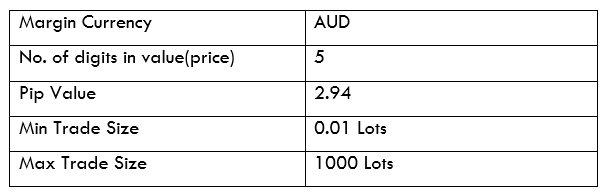
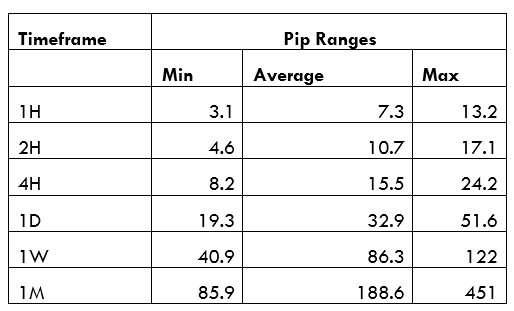
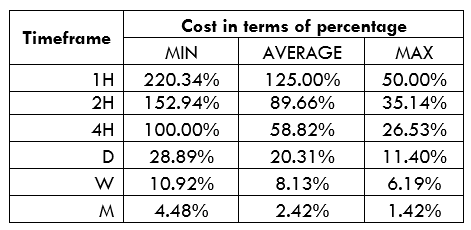

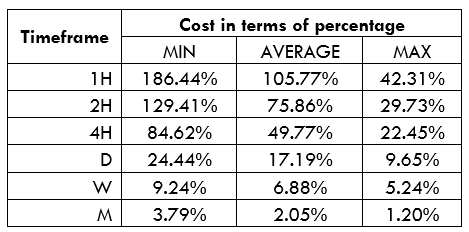

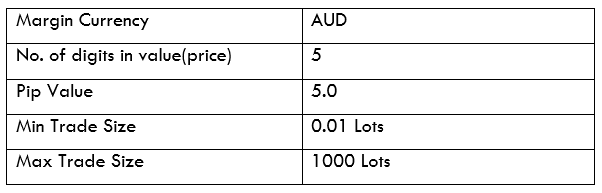
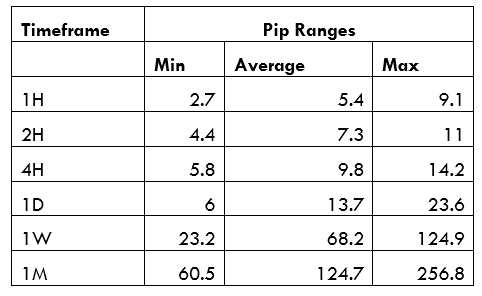
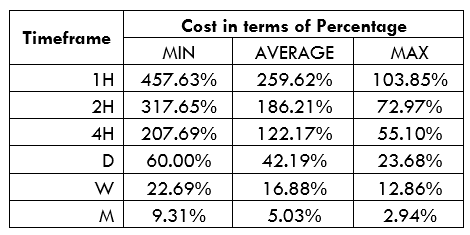
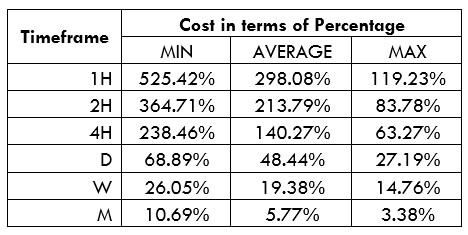




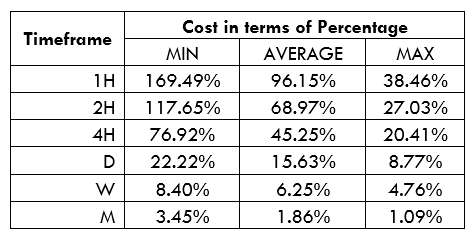
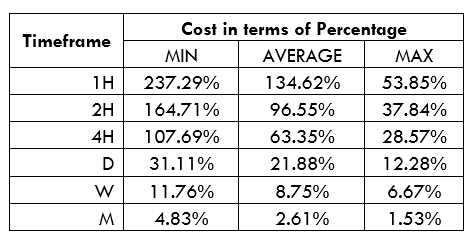
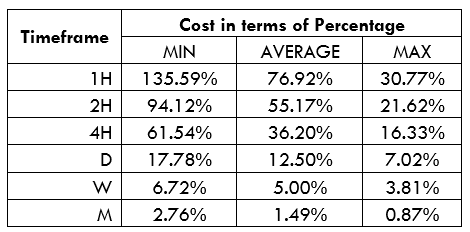


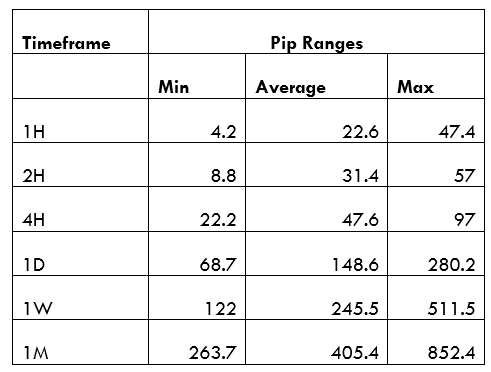
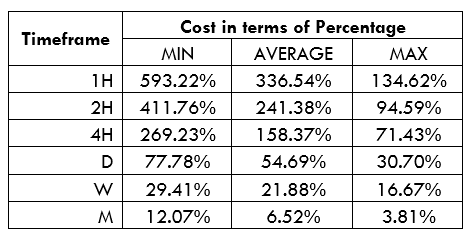
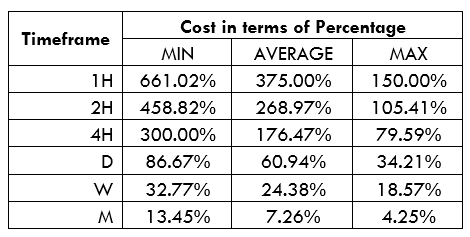
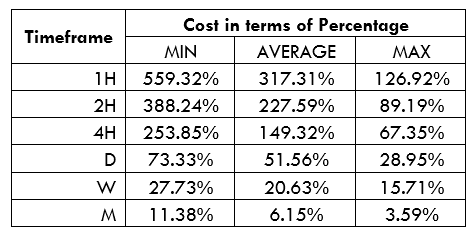

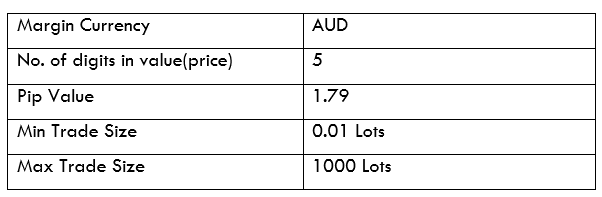
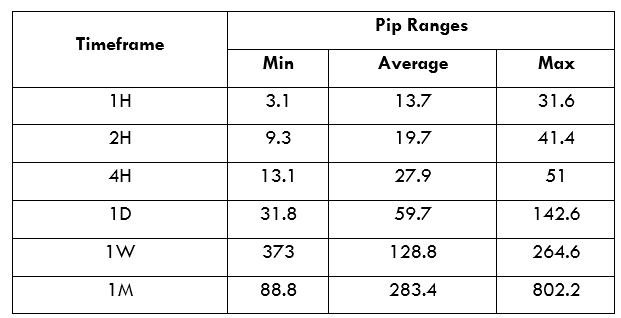
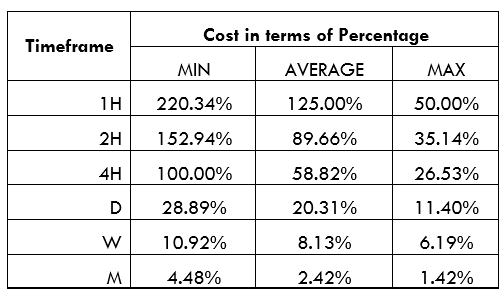
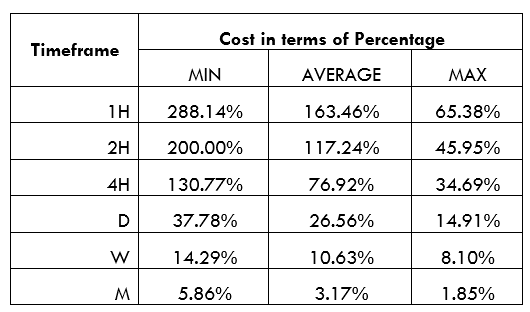
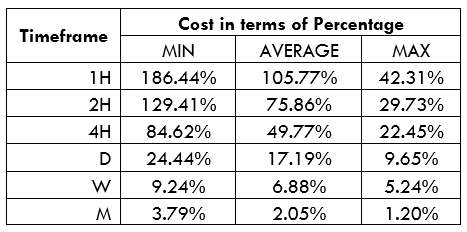

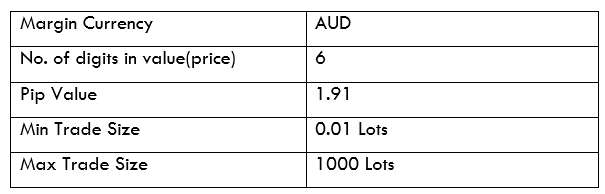
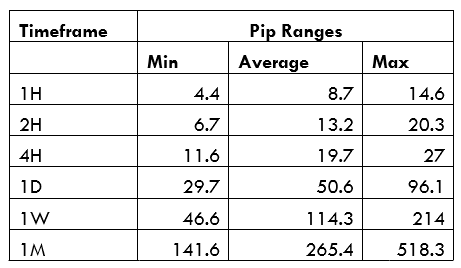

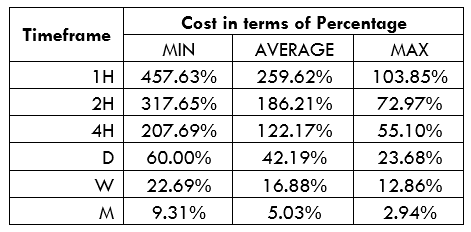


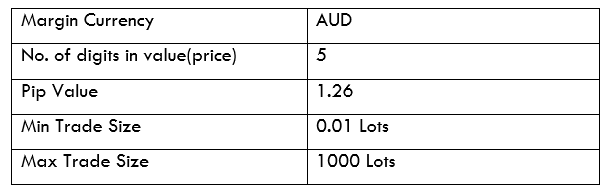
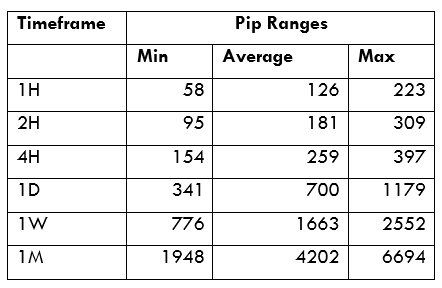

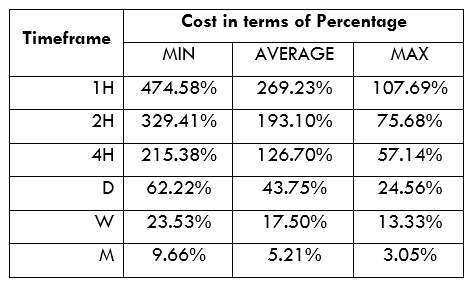
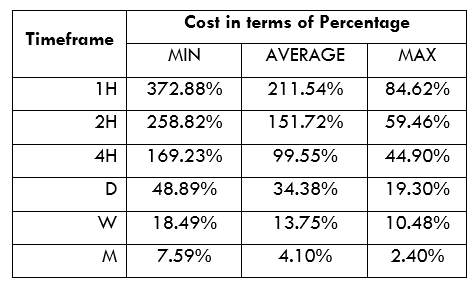

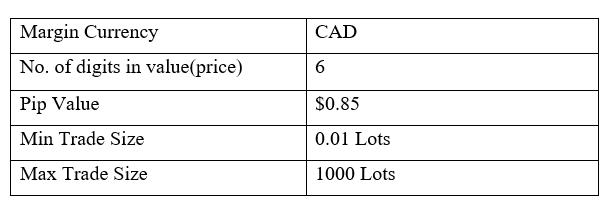

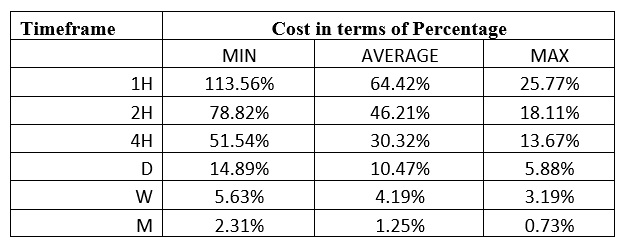
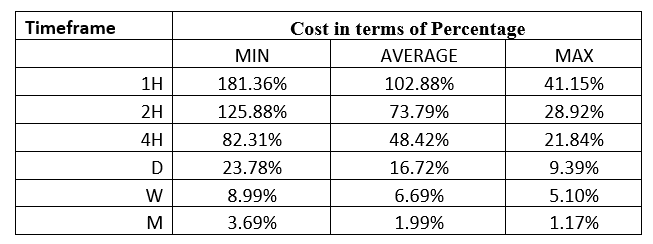
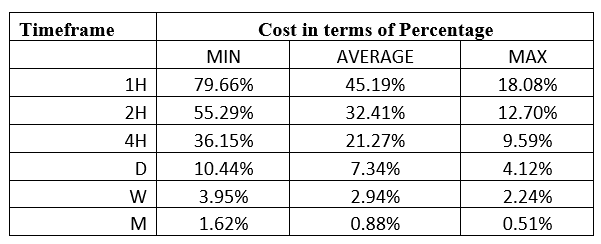

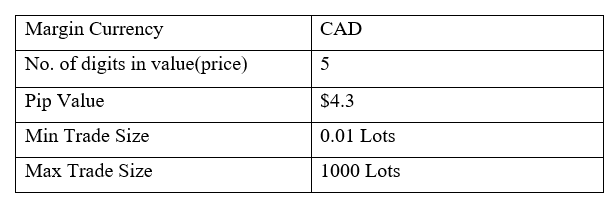
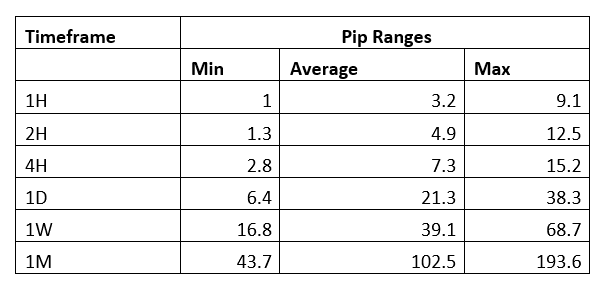
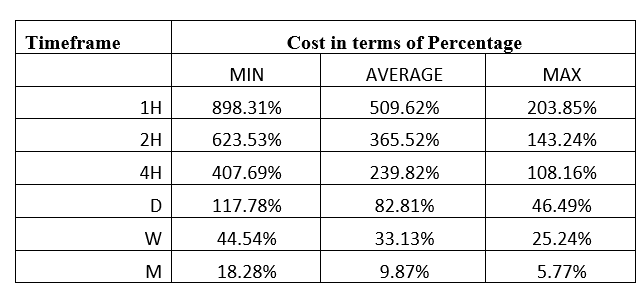
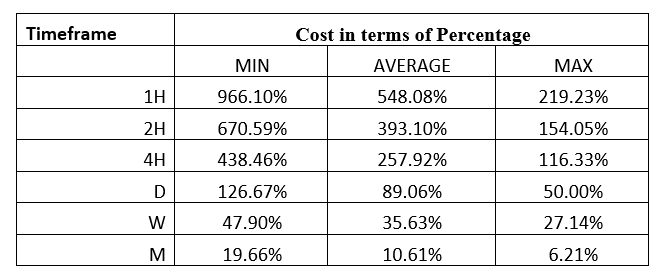
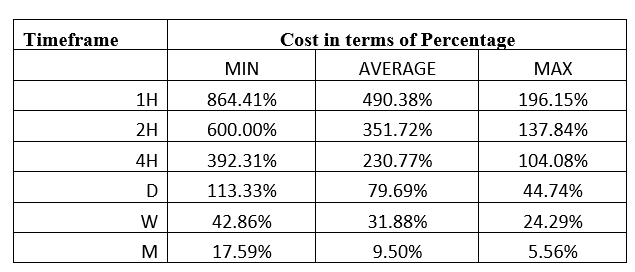

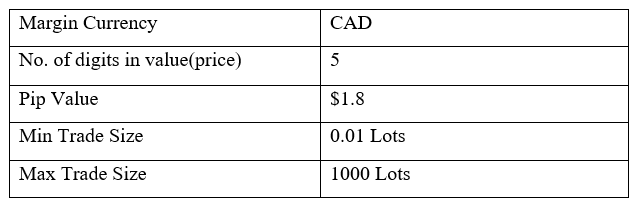
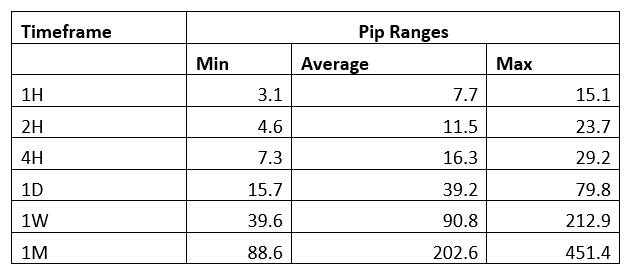
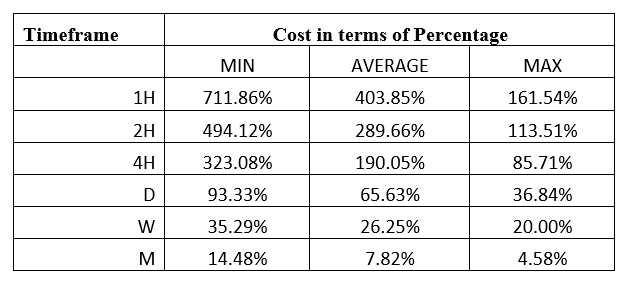
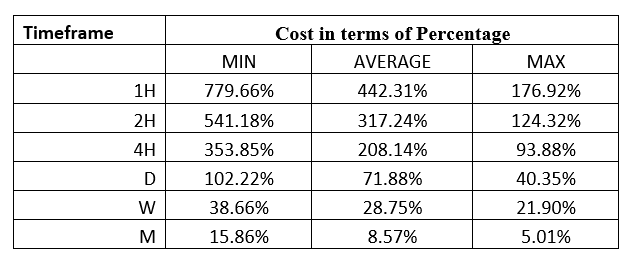


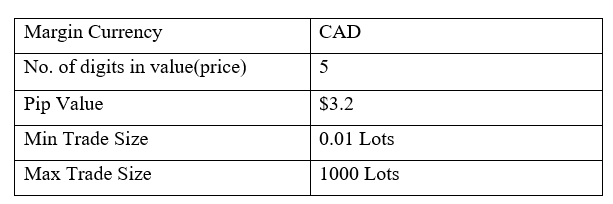

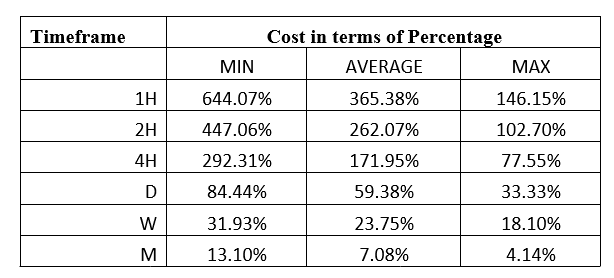
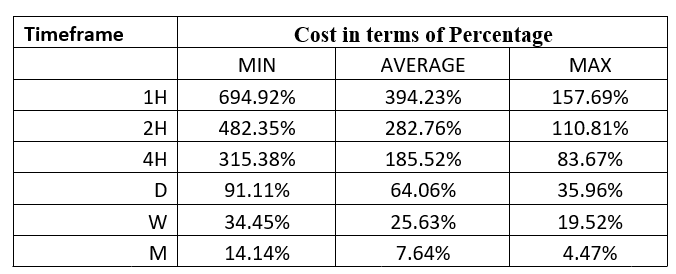
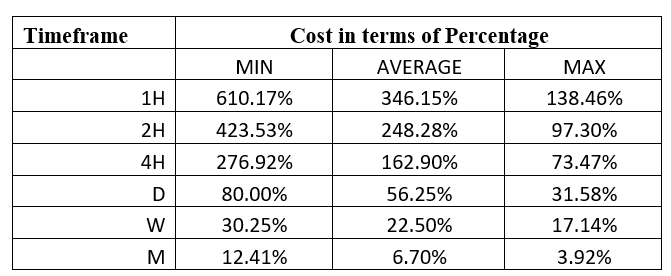


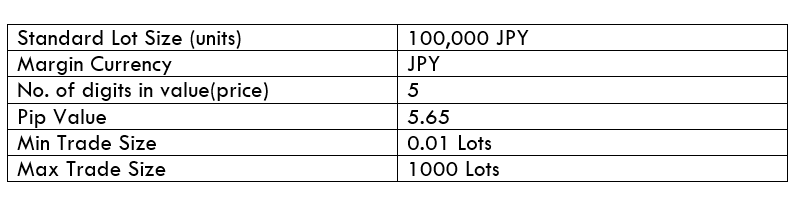

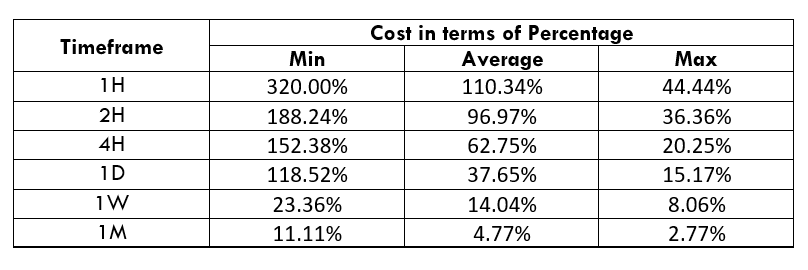
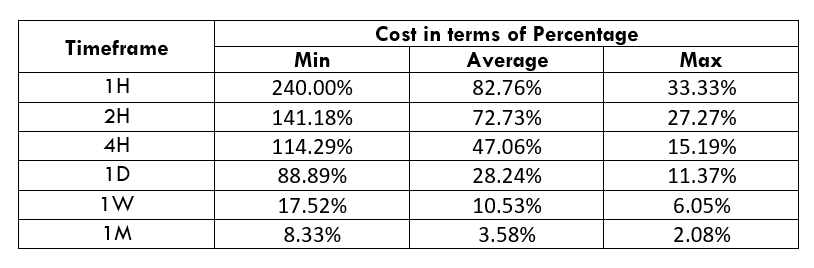
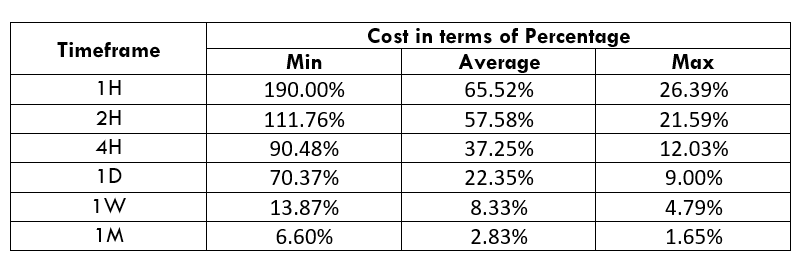

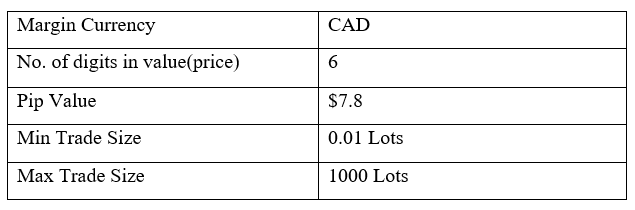
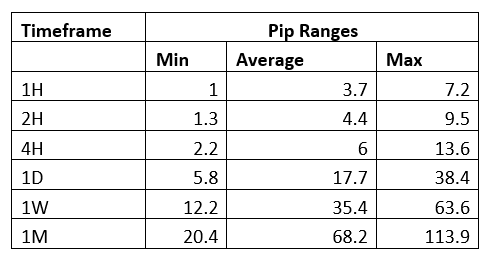

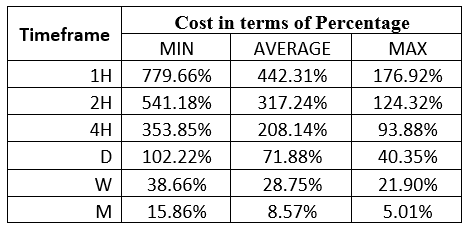
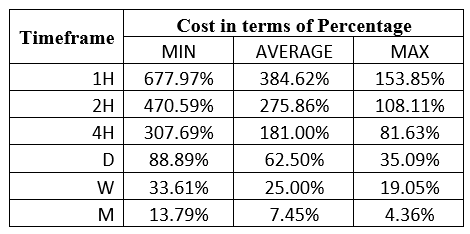

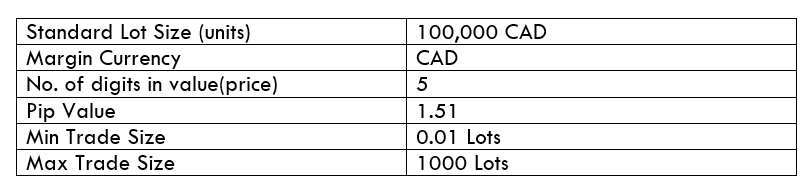
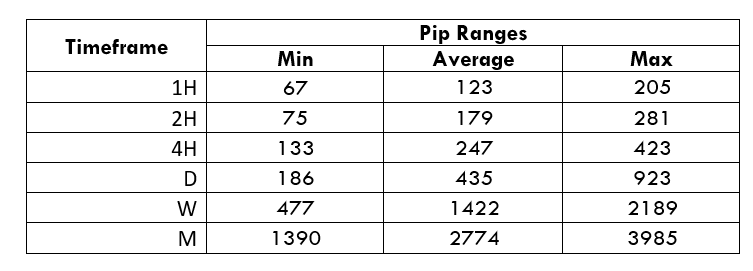
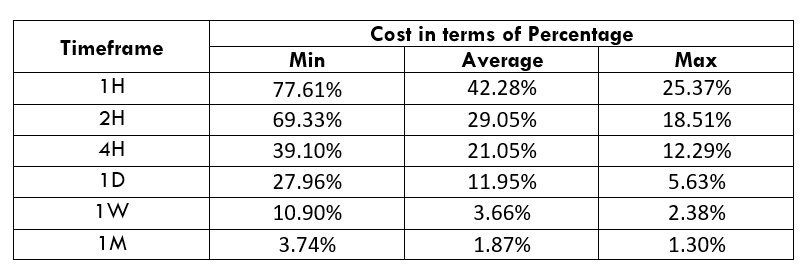
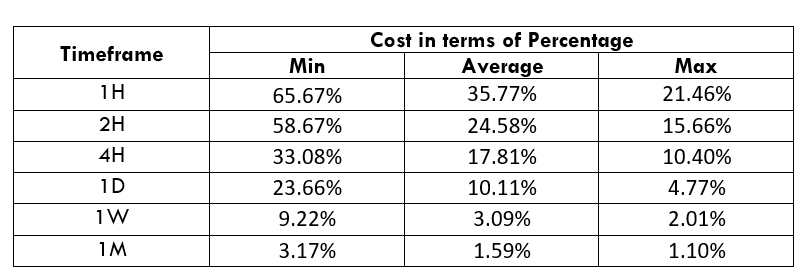


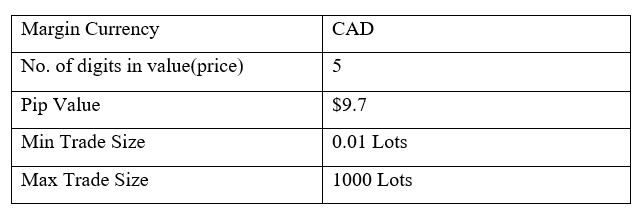
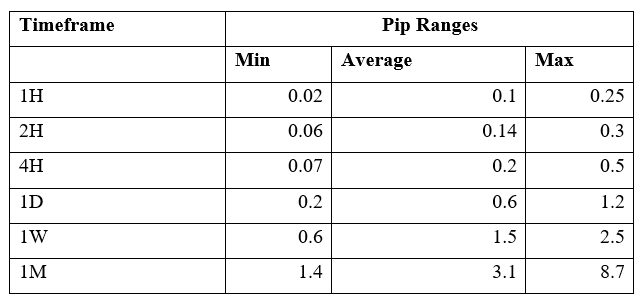
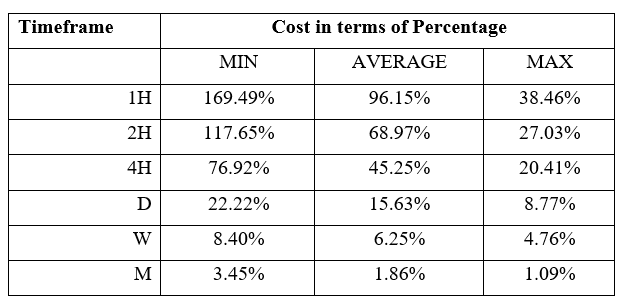
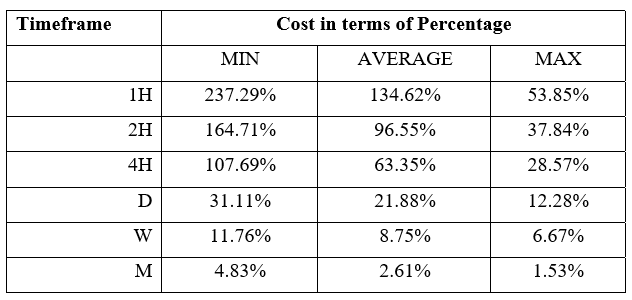
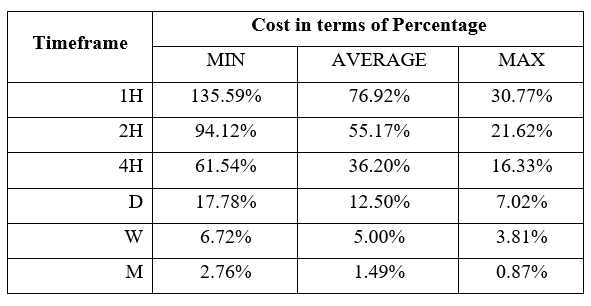
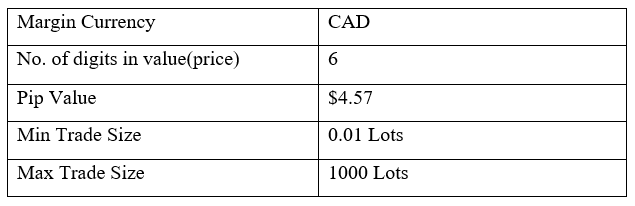

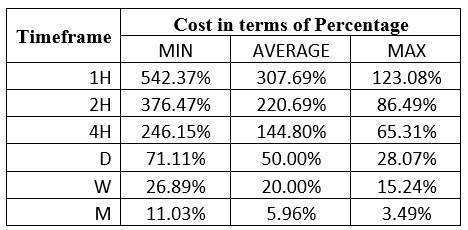

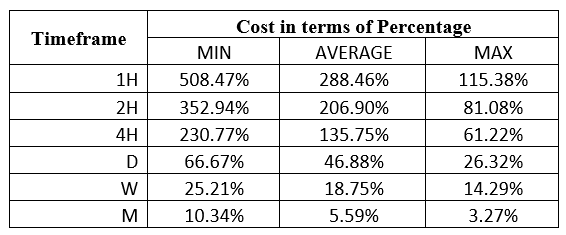
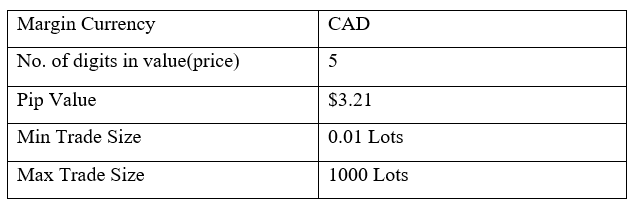
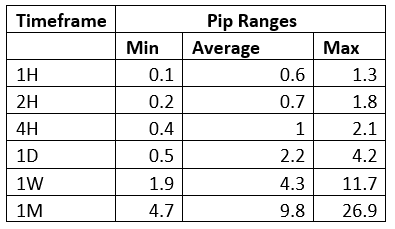


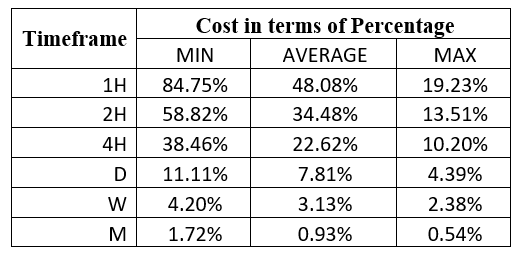

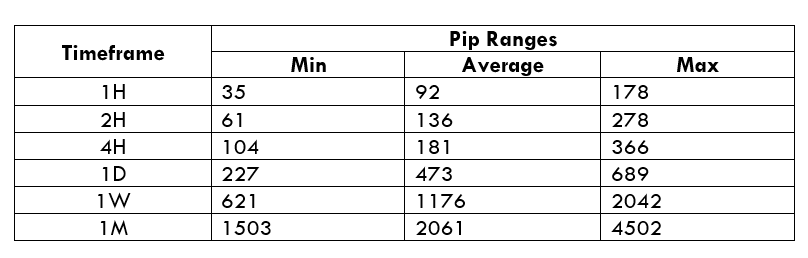


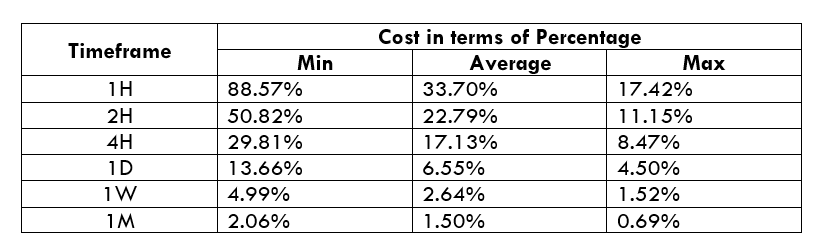

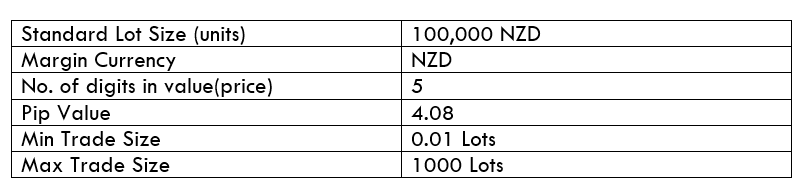
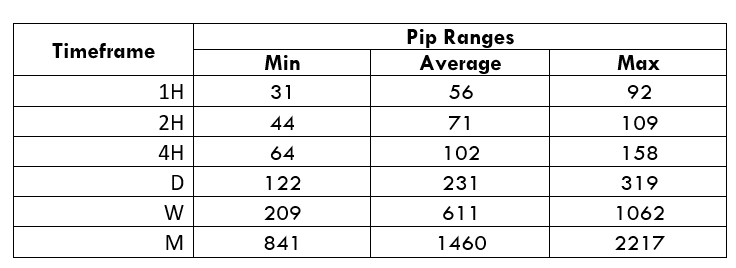

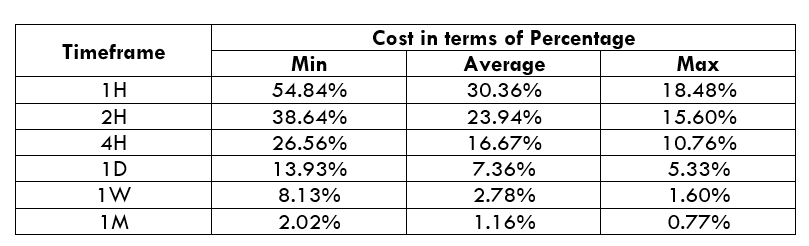
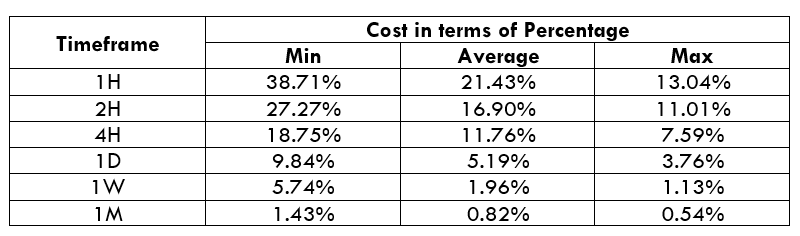
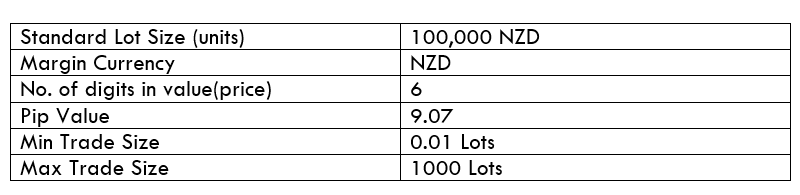
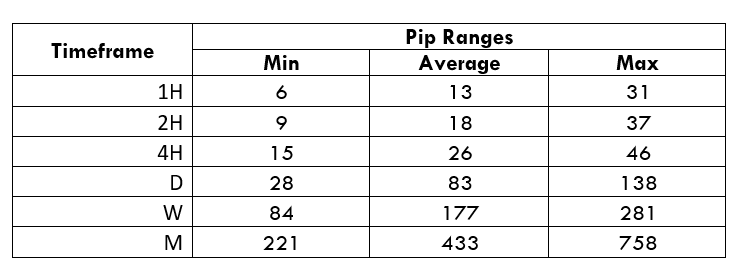
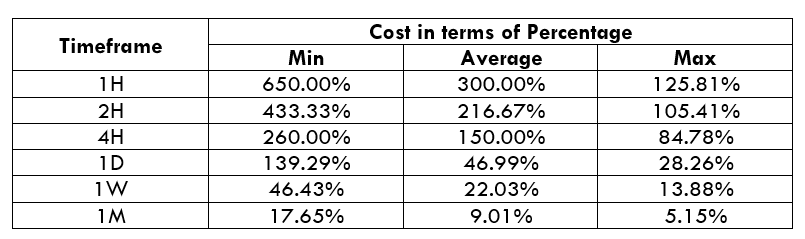



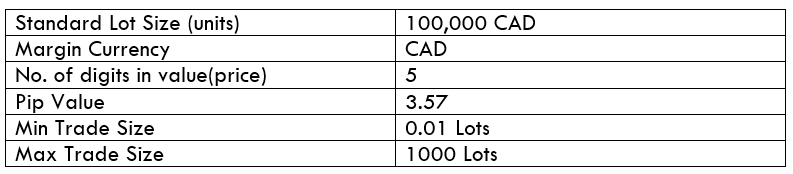

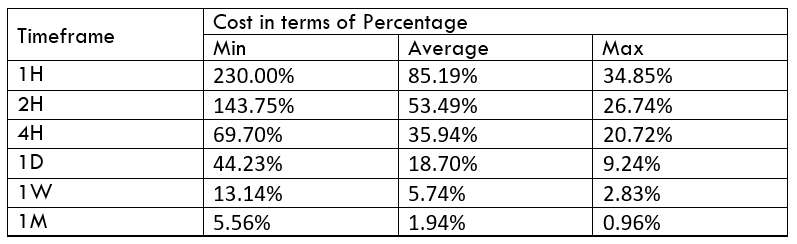
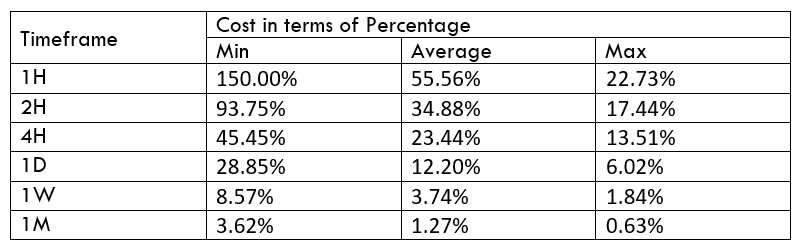
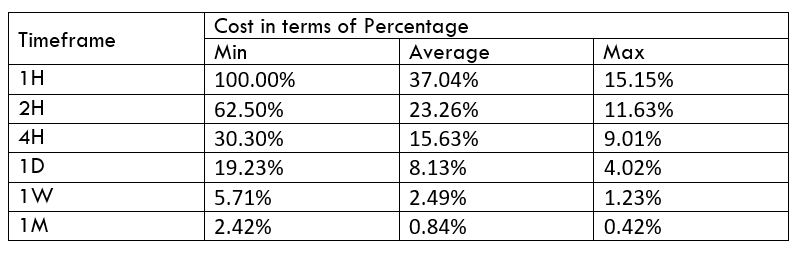

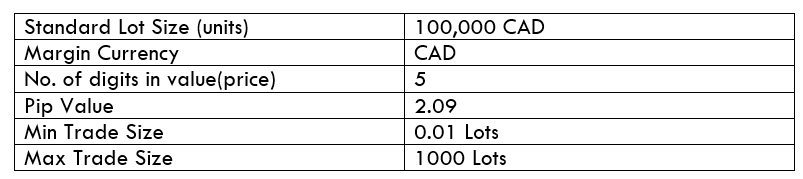
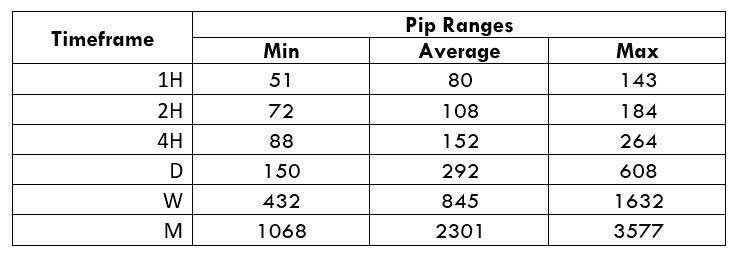
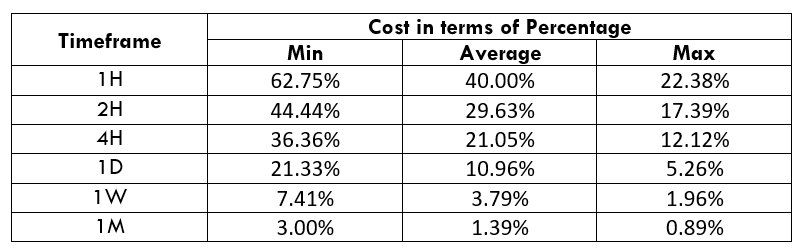
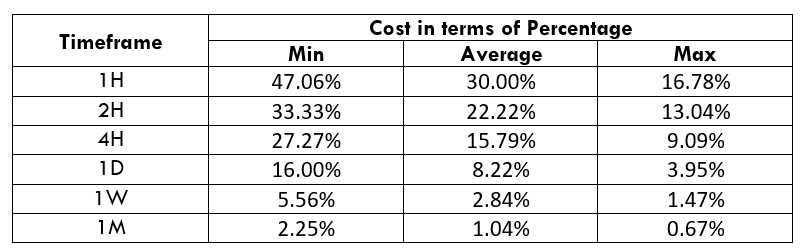
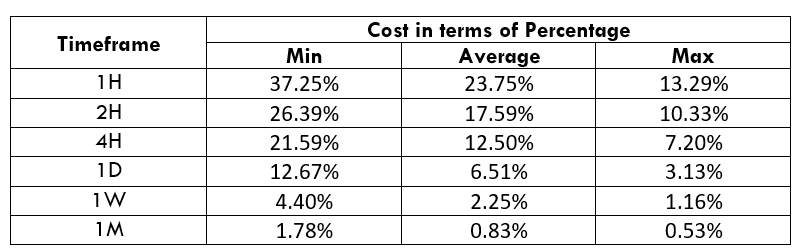


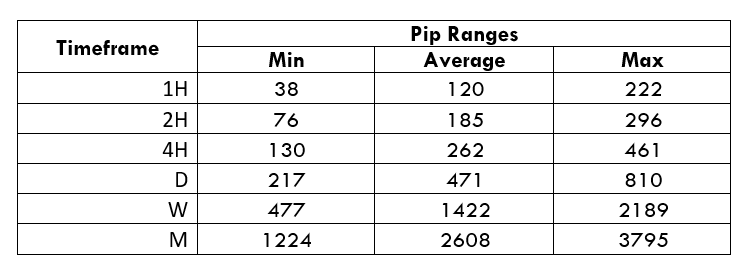
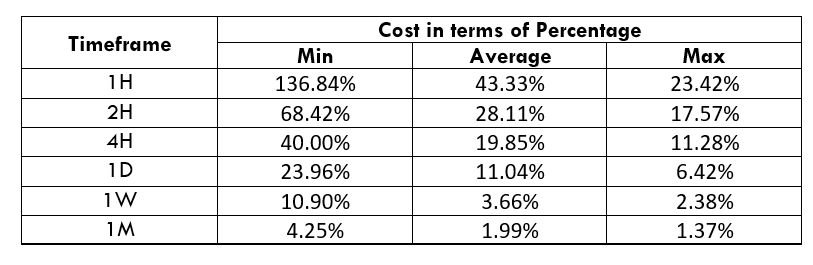
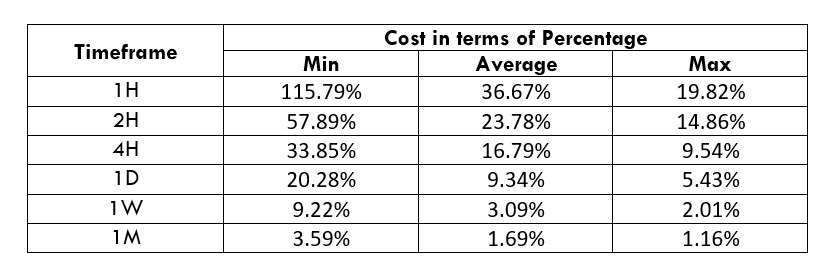



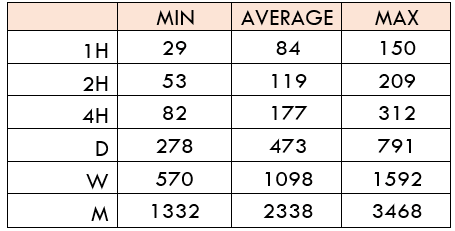
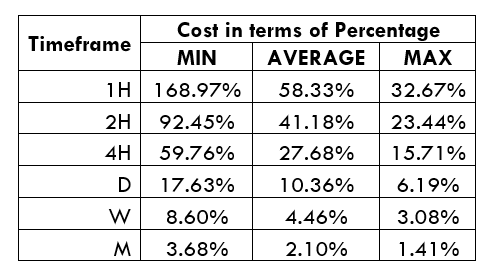
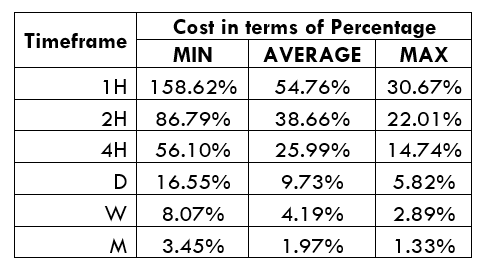
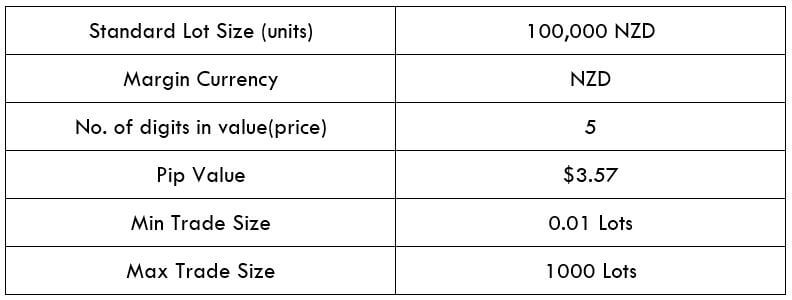
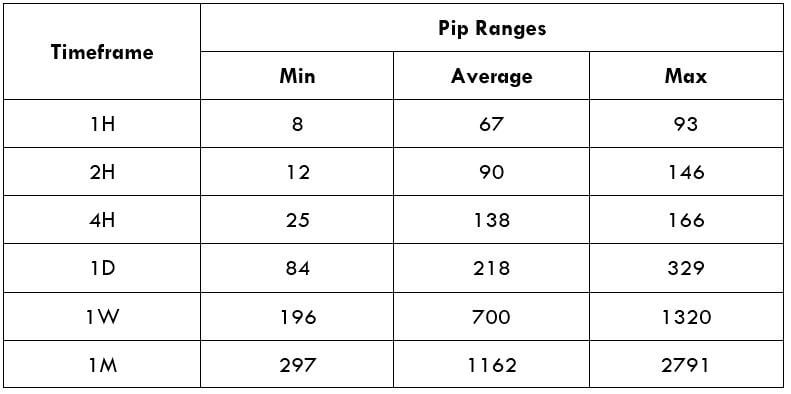
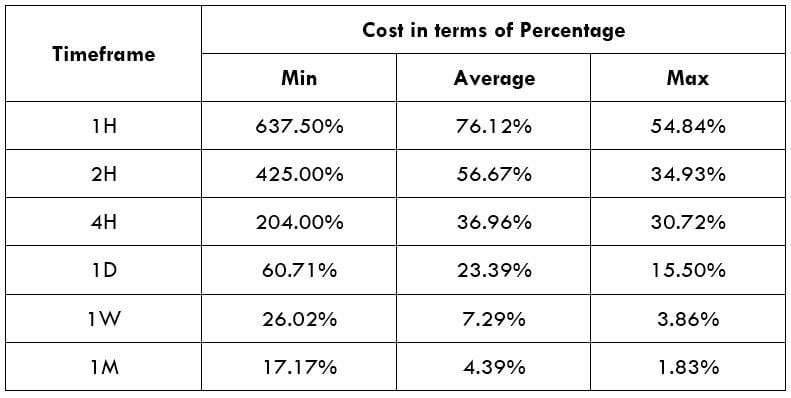
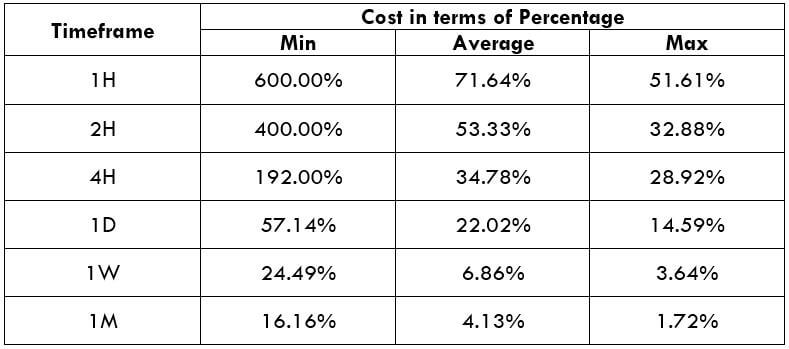
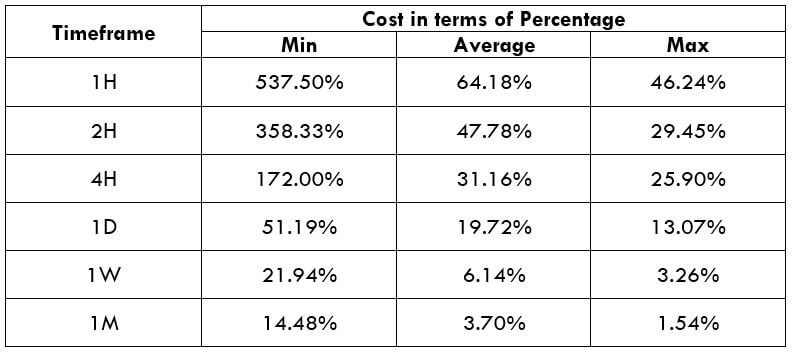
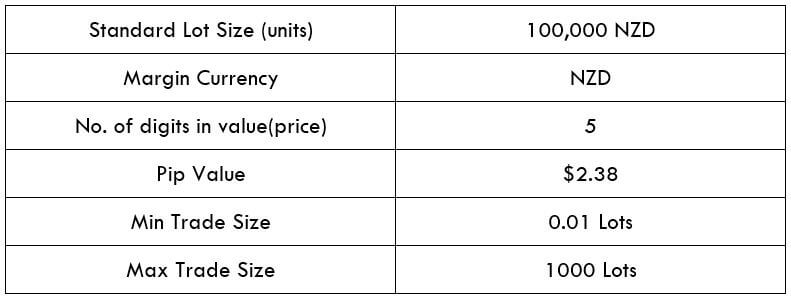
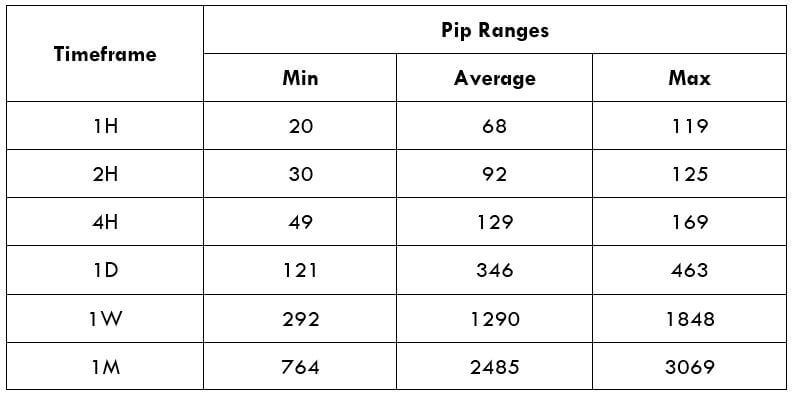
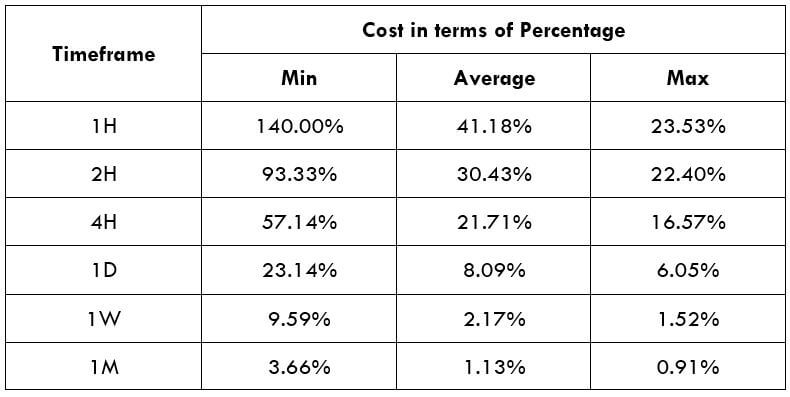
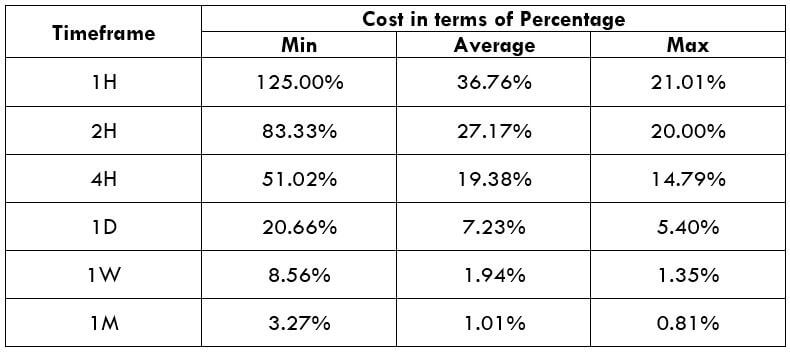

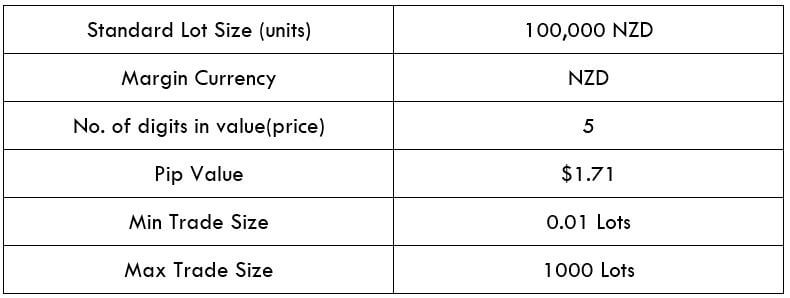
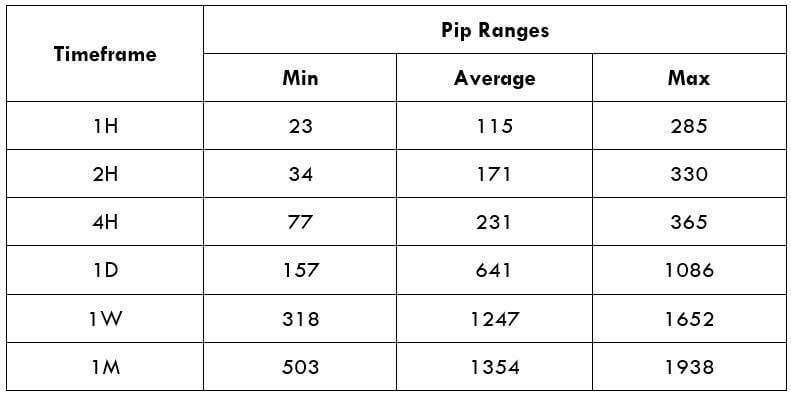
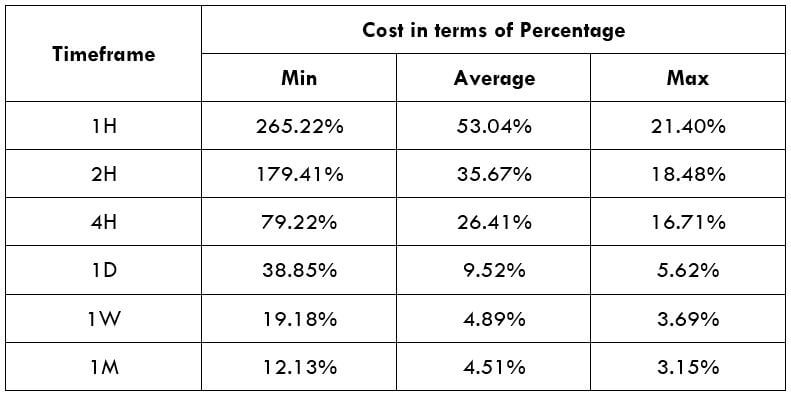
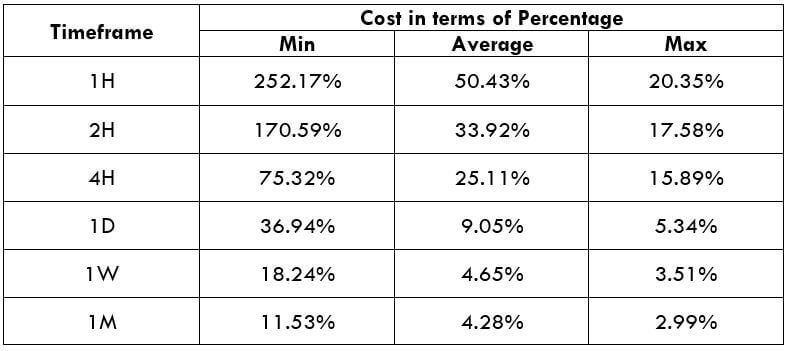
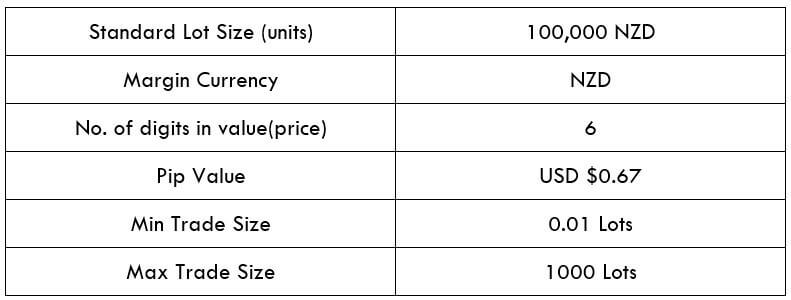
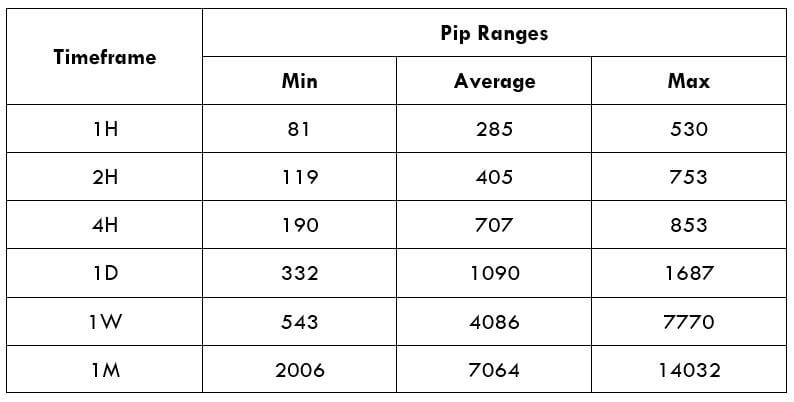
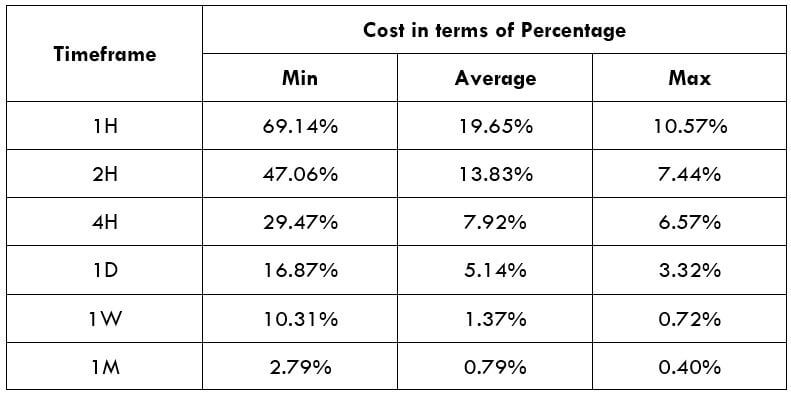
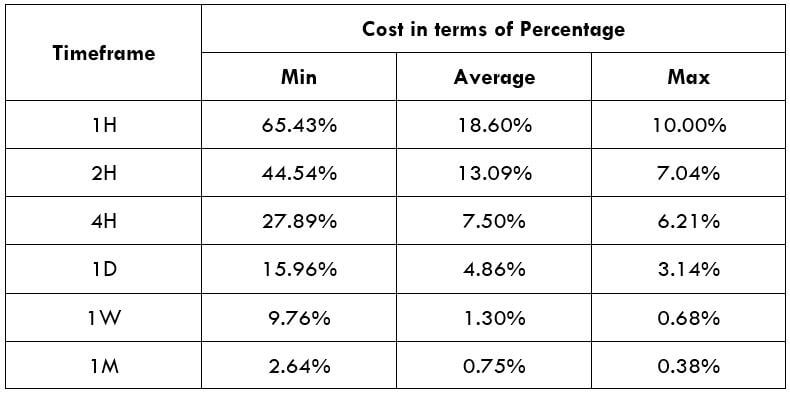
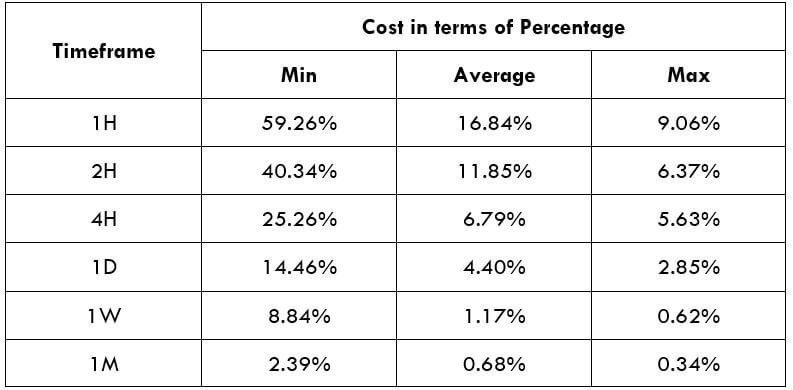
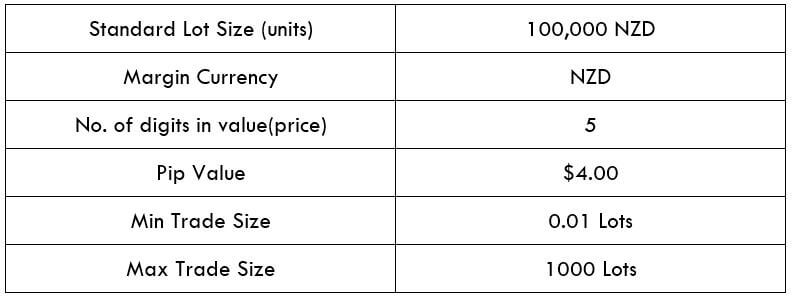
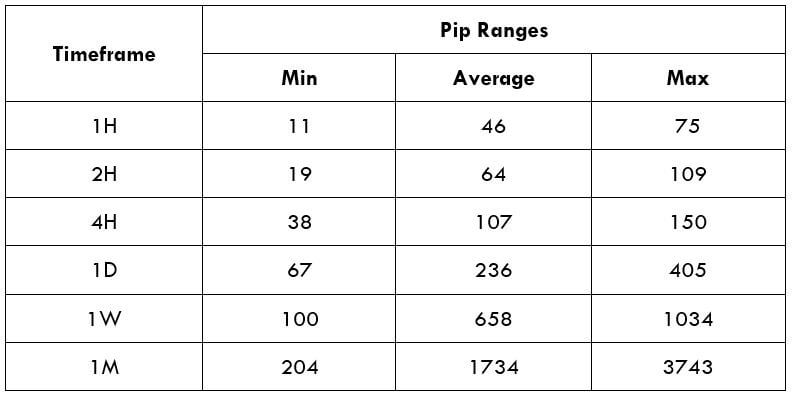
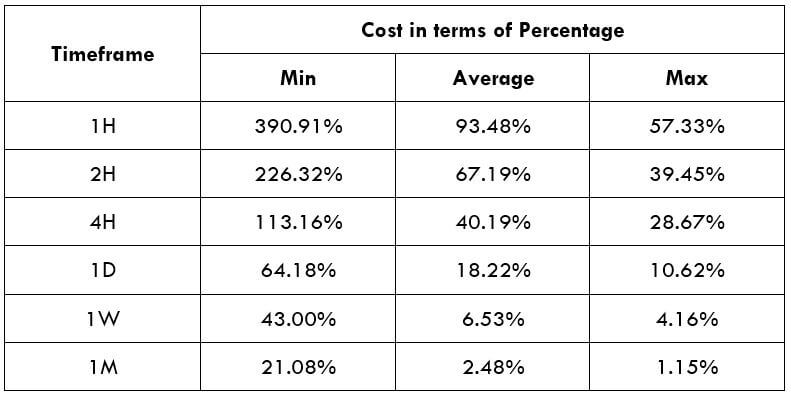
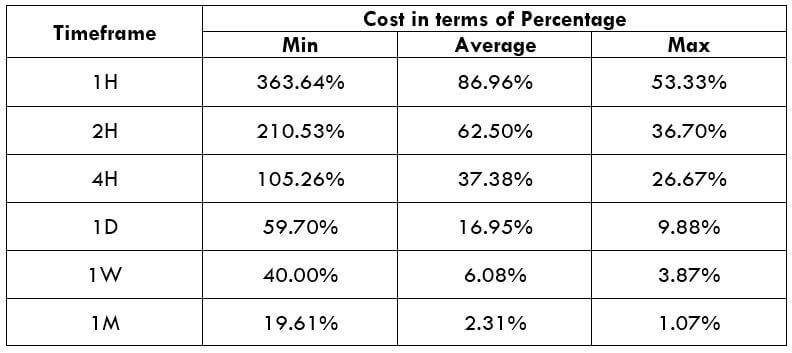
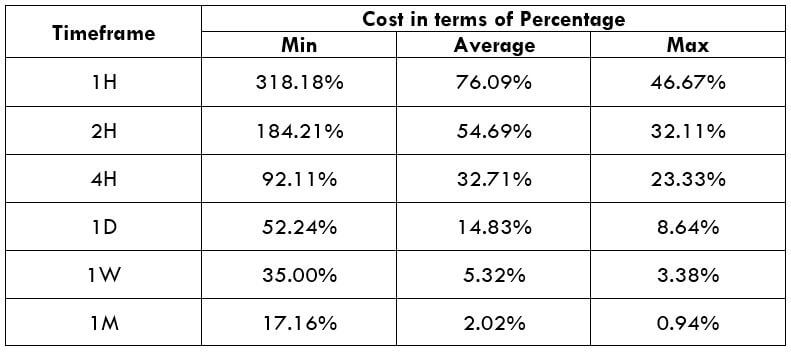


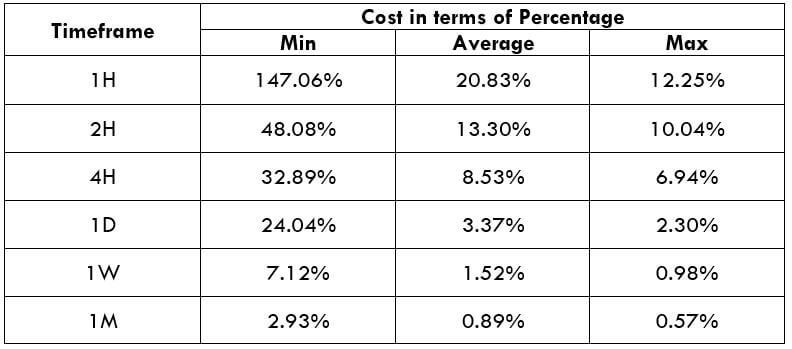

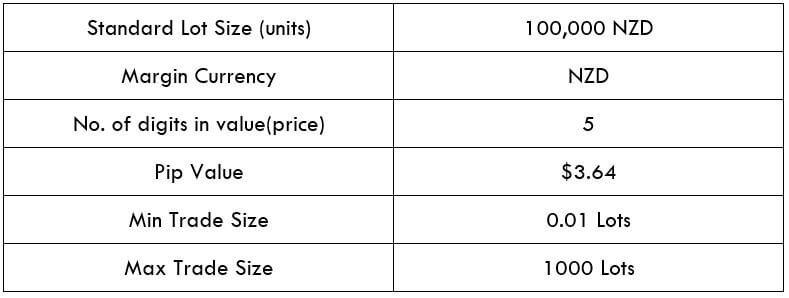
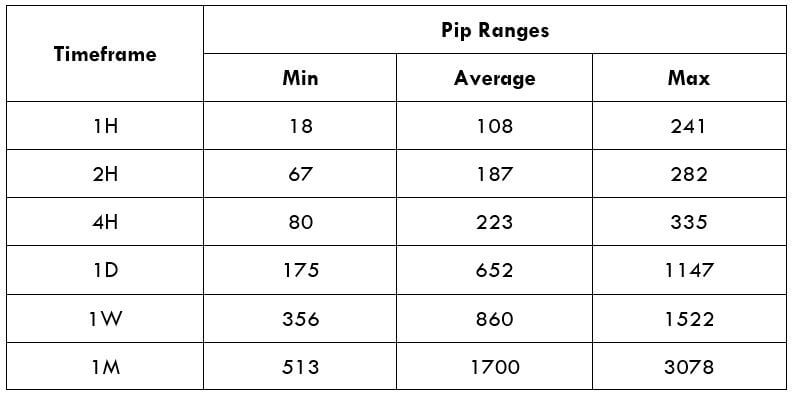
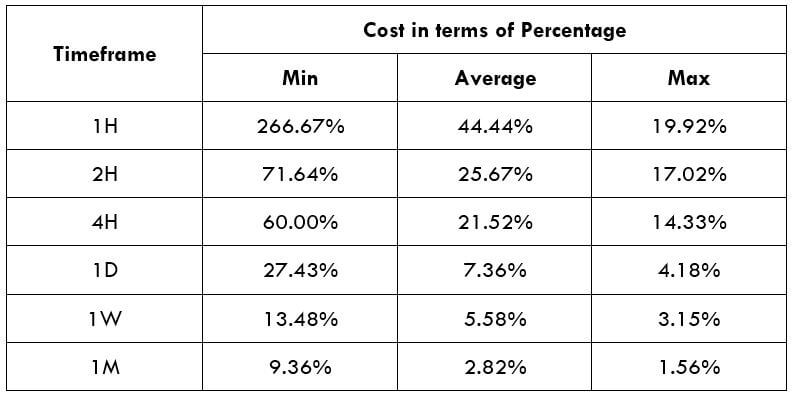
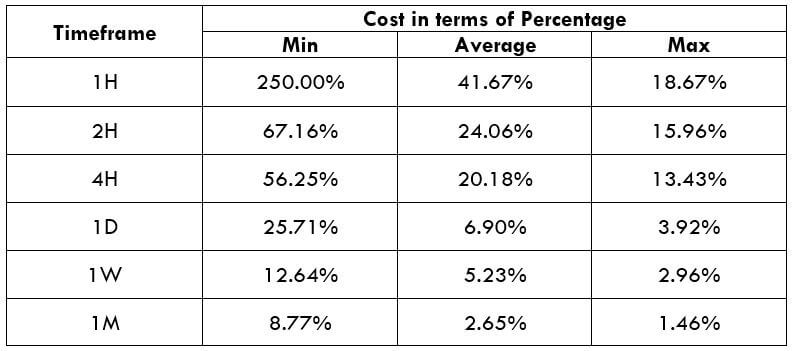
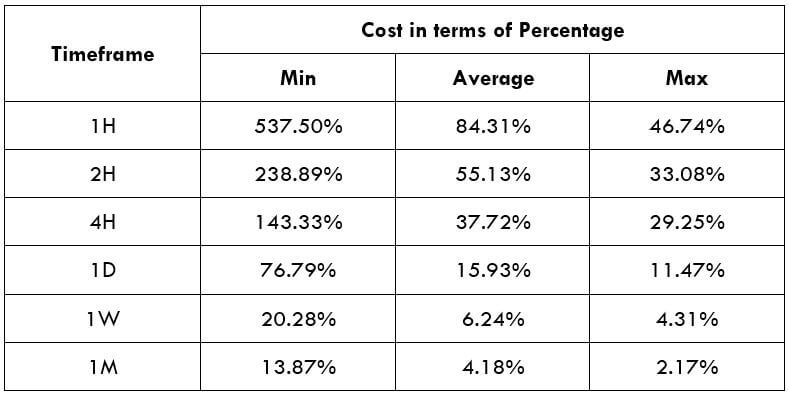
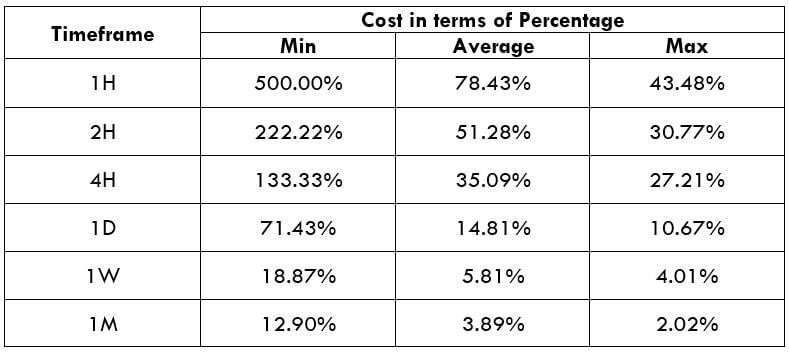
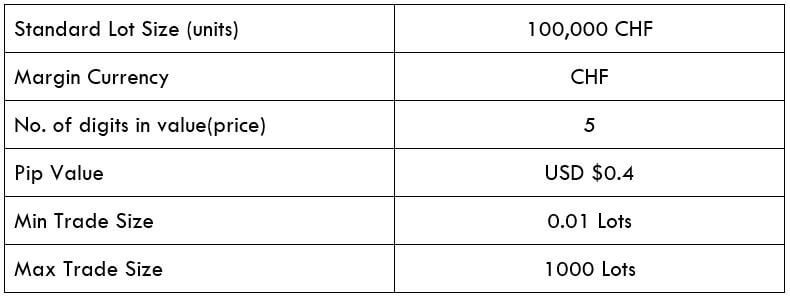
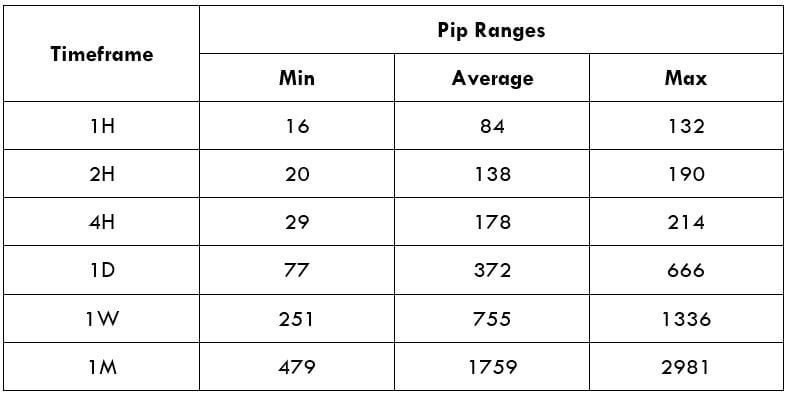
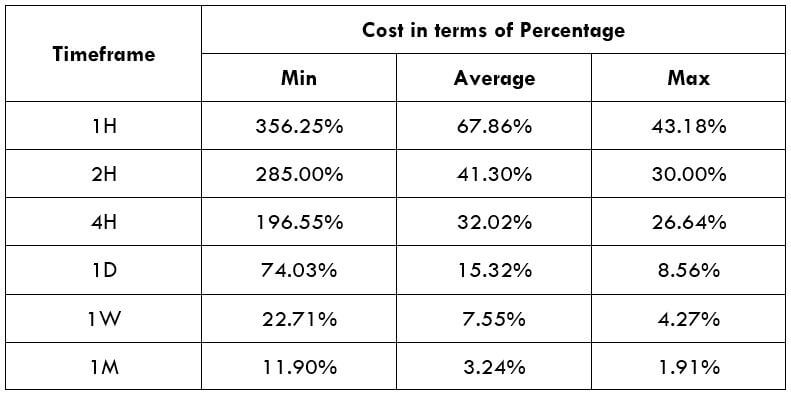
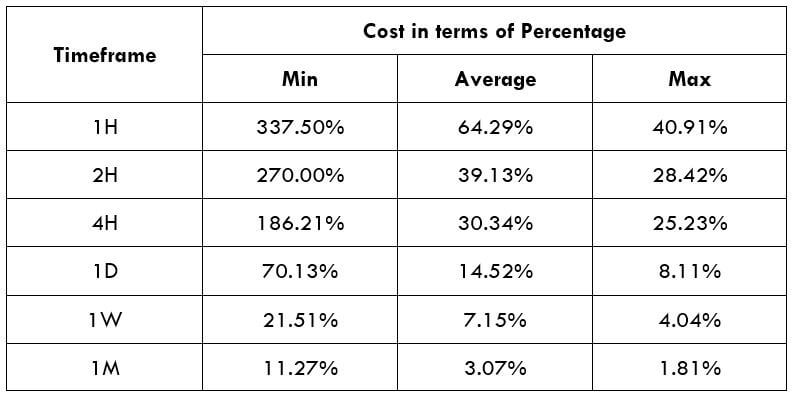

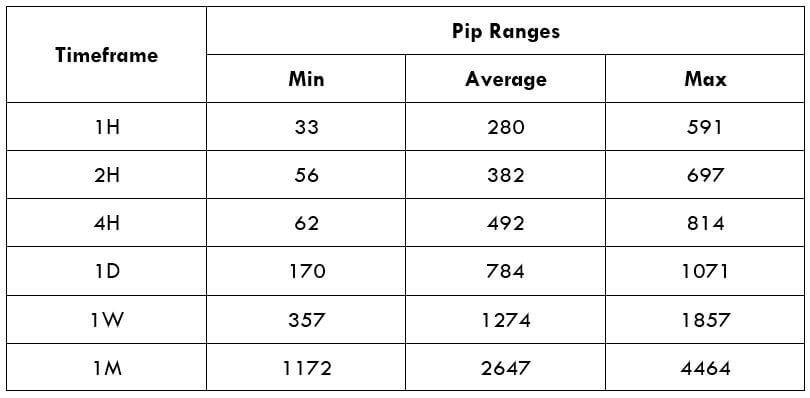
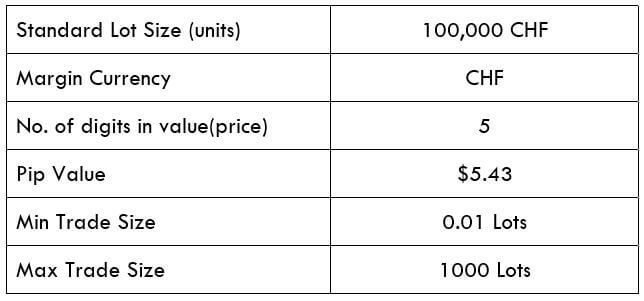
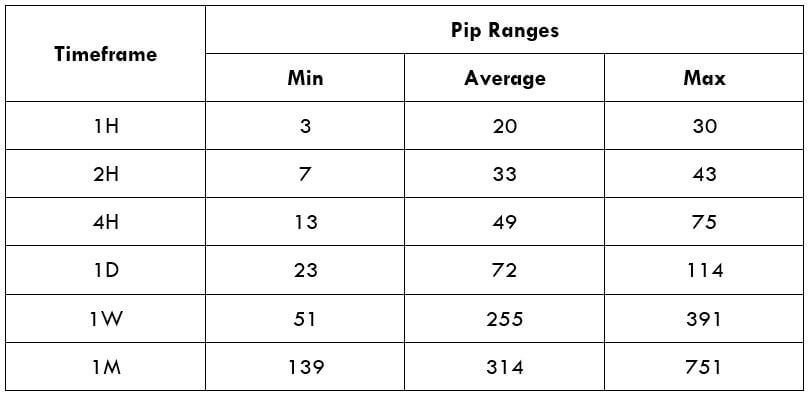
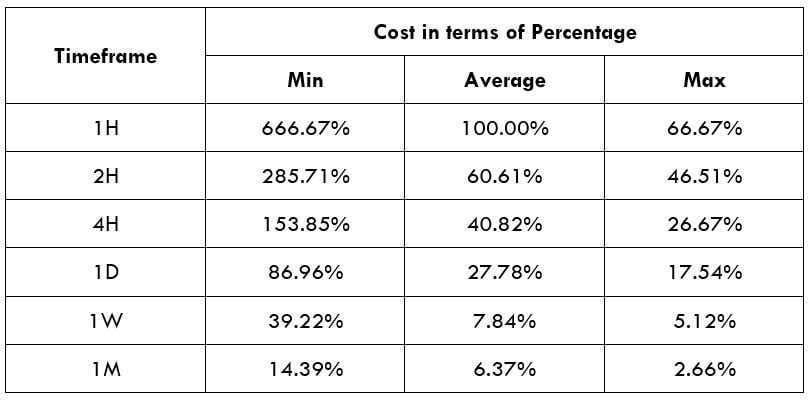
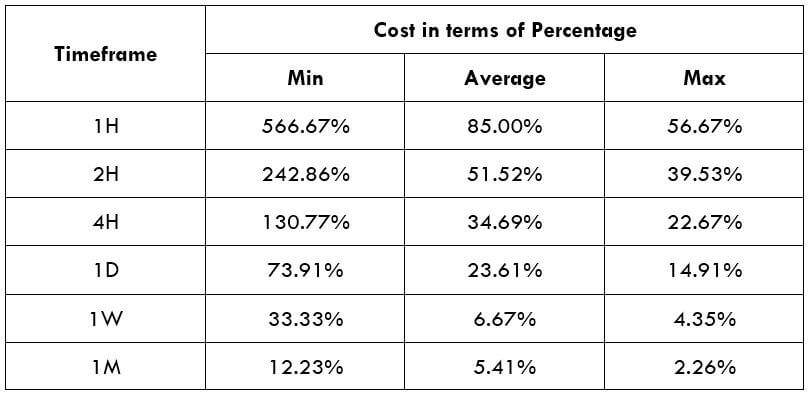
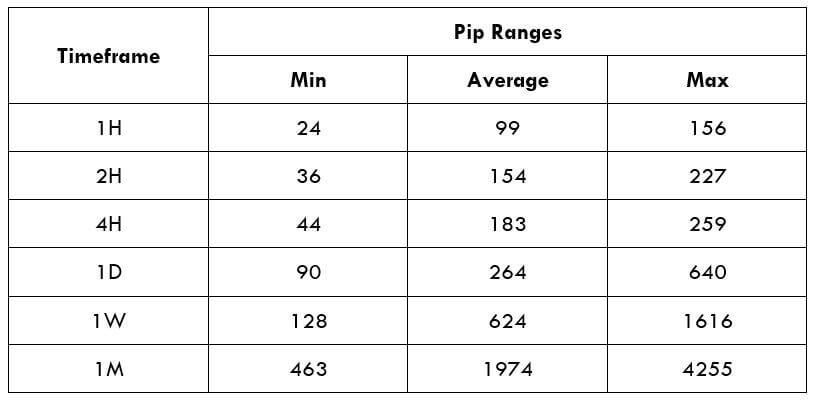
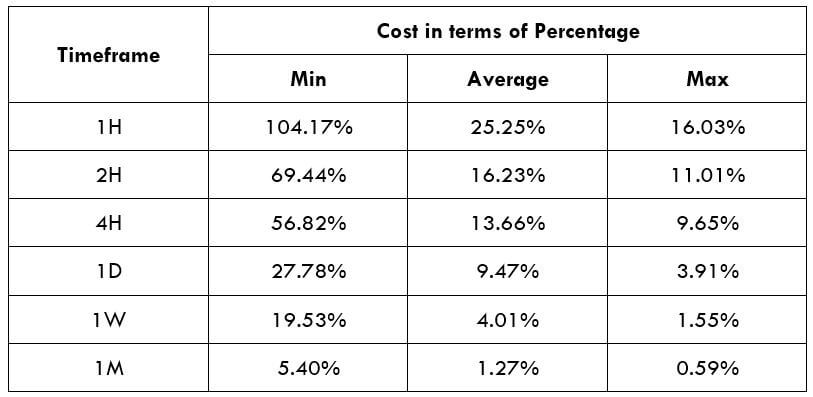
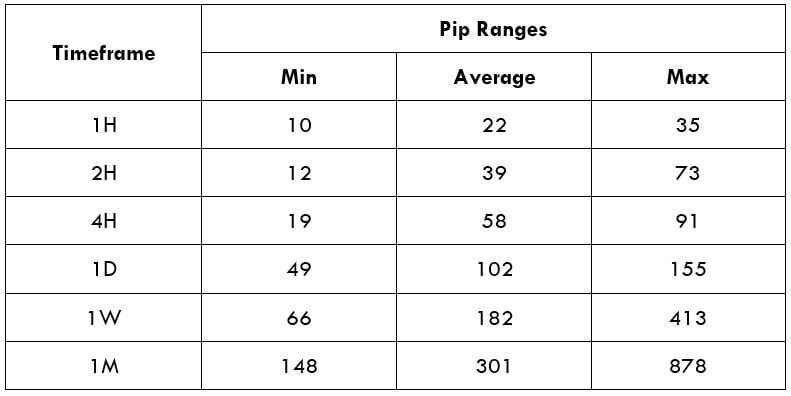
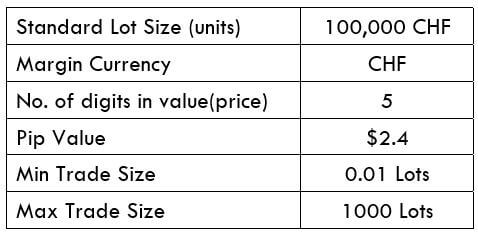
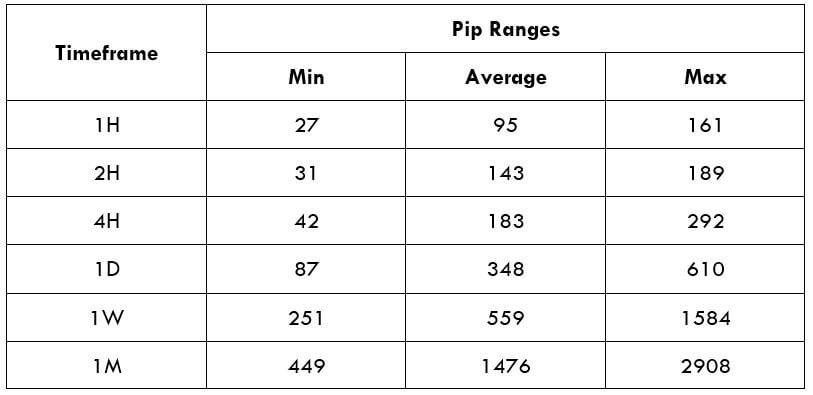
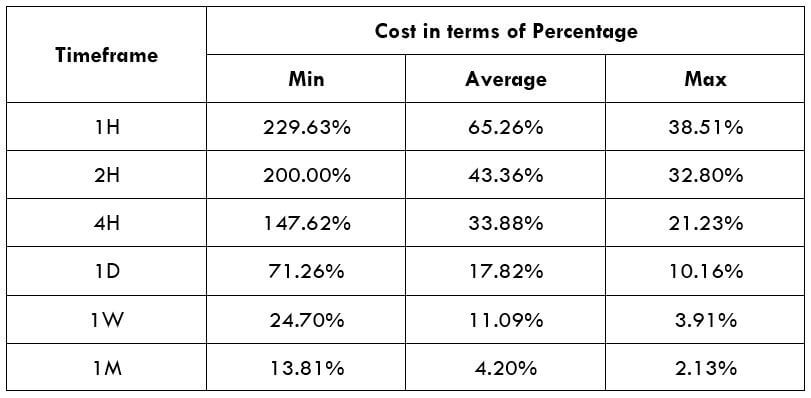
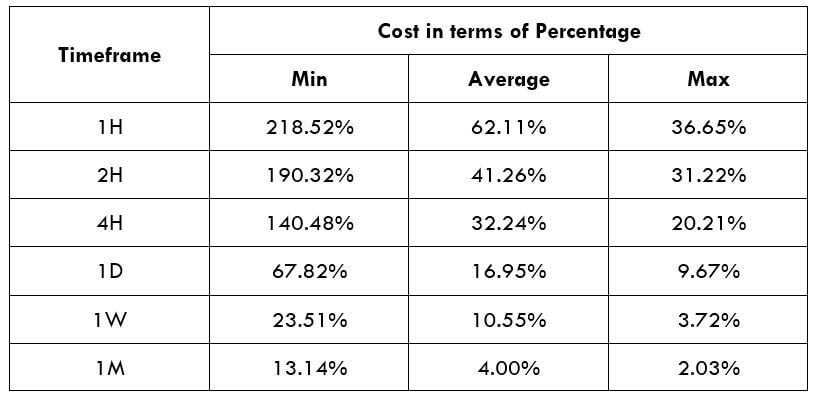
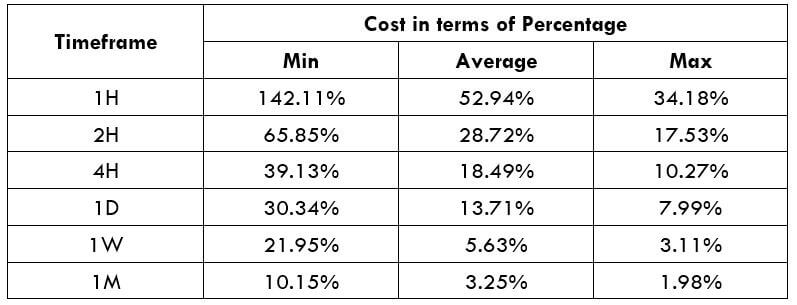
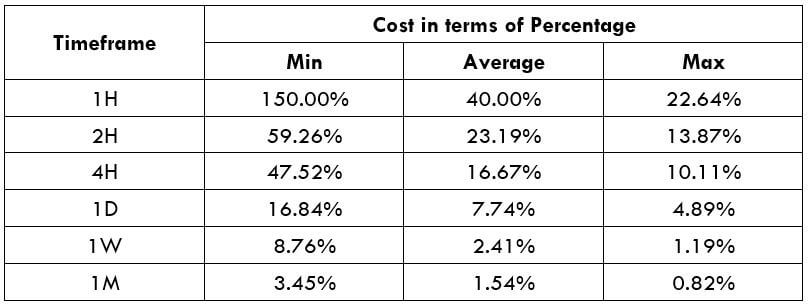
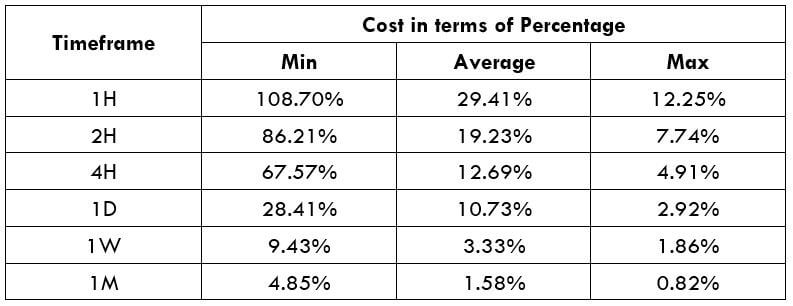
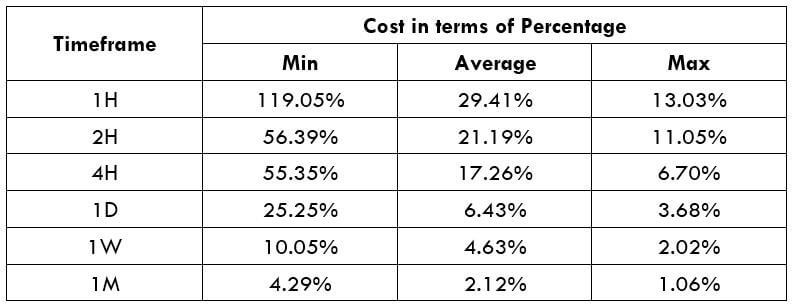
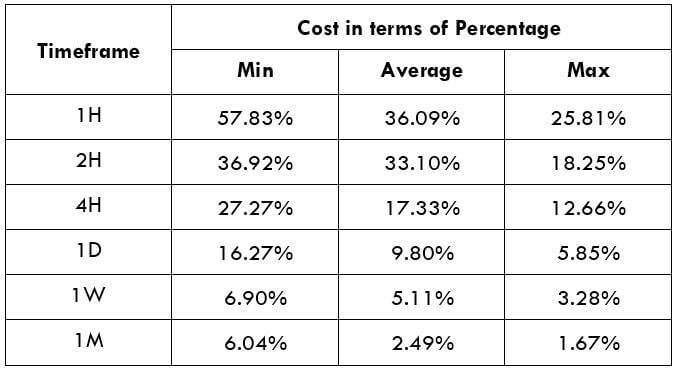
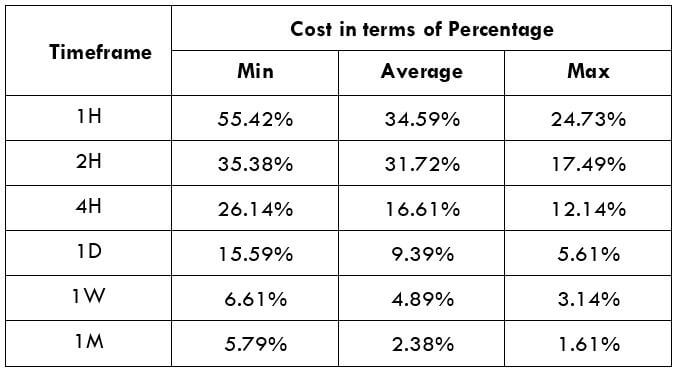
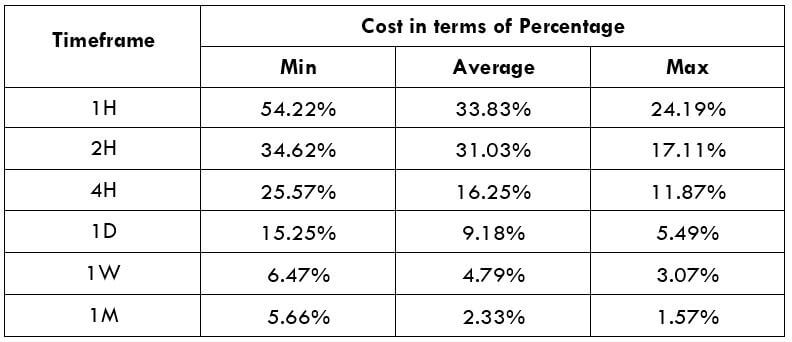
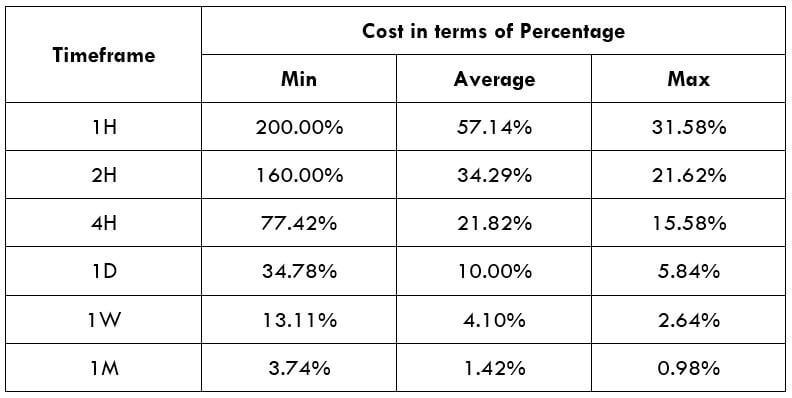
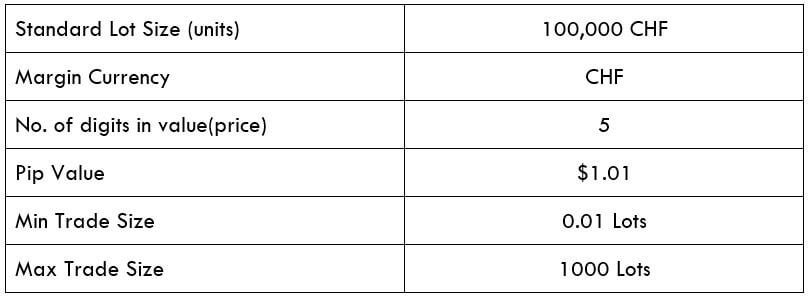 Spread
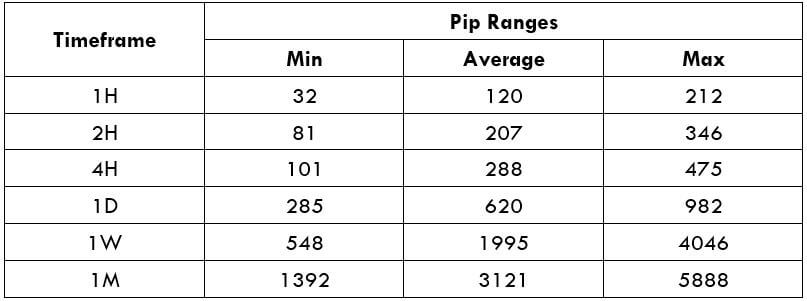
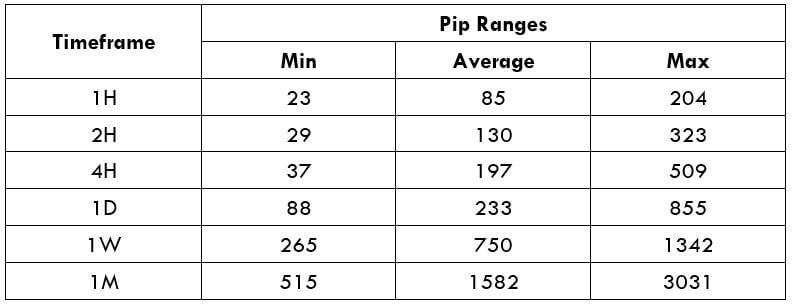
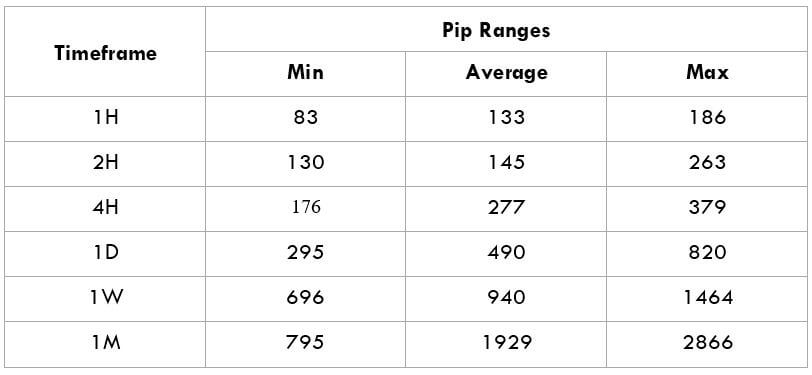
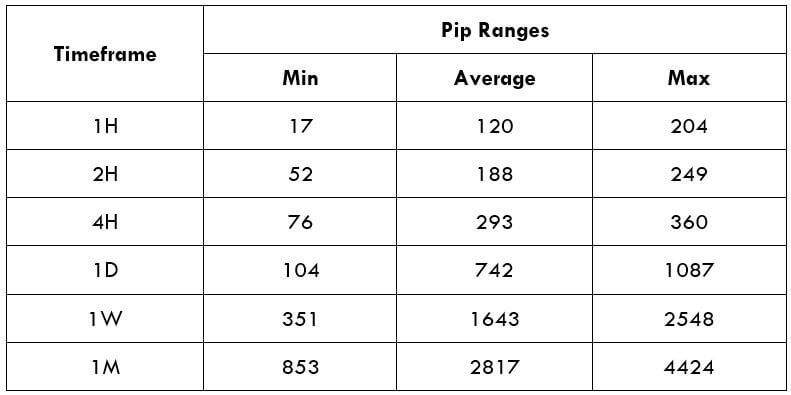
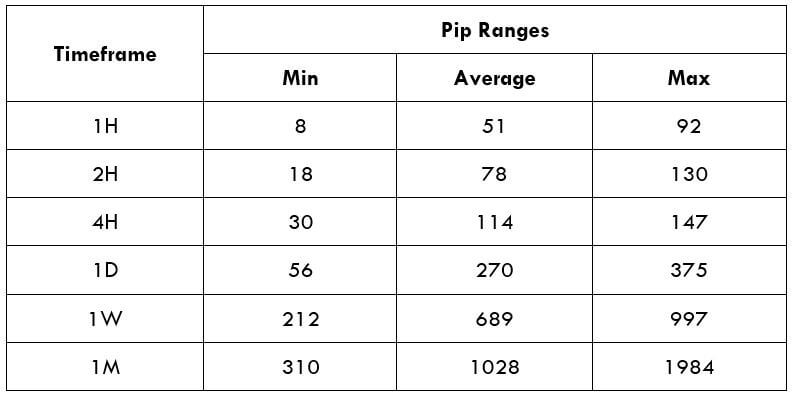
Spread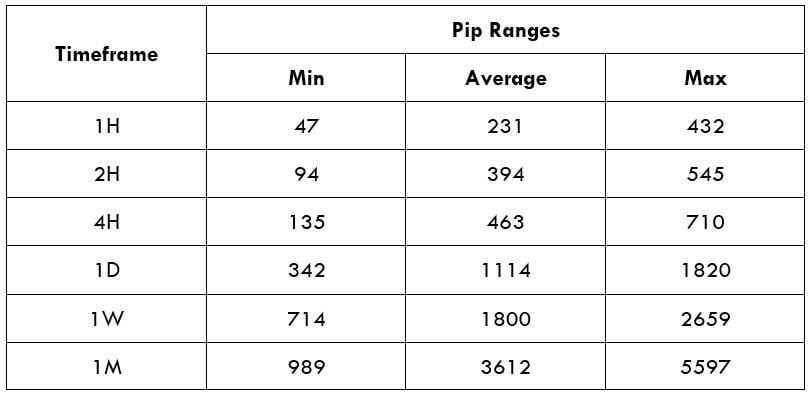 Procedure to assess Pip Ranges
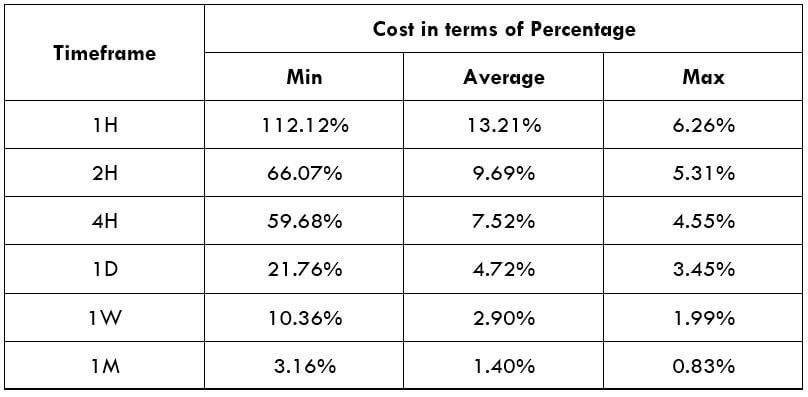
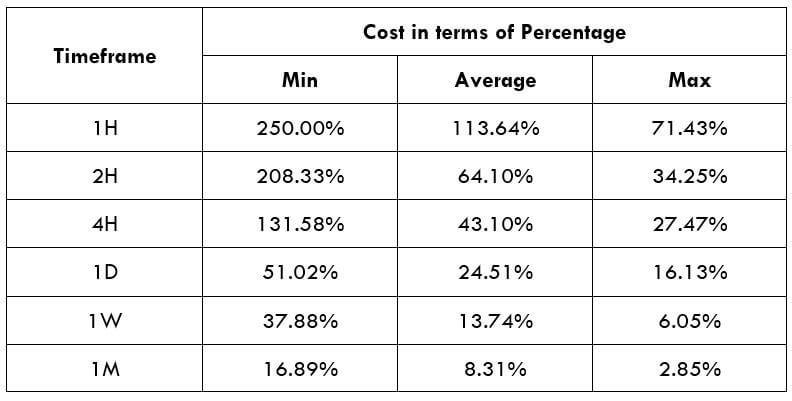
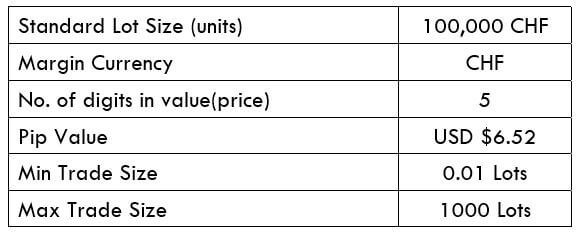
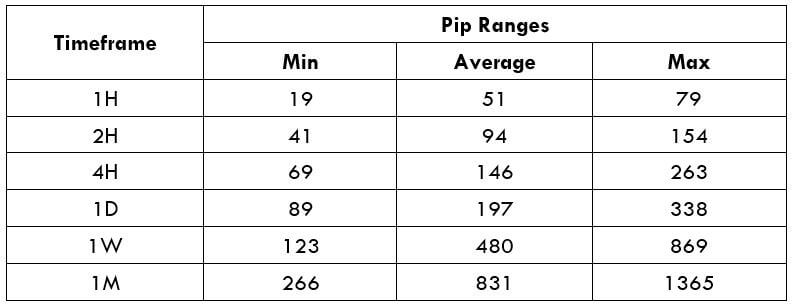
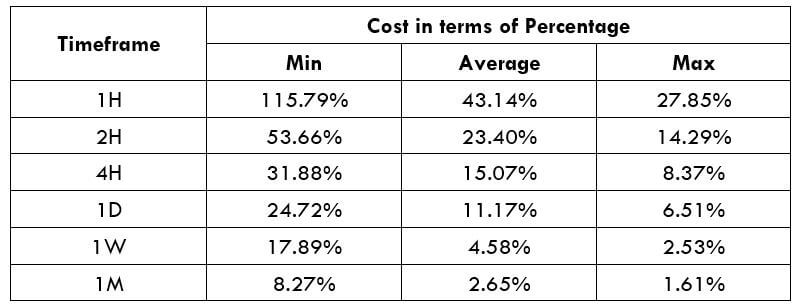
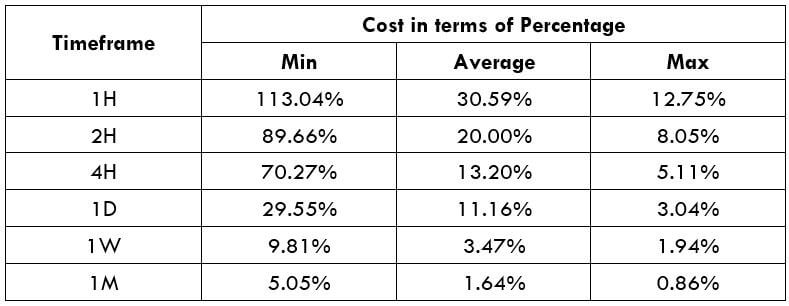
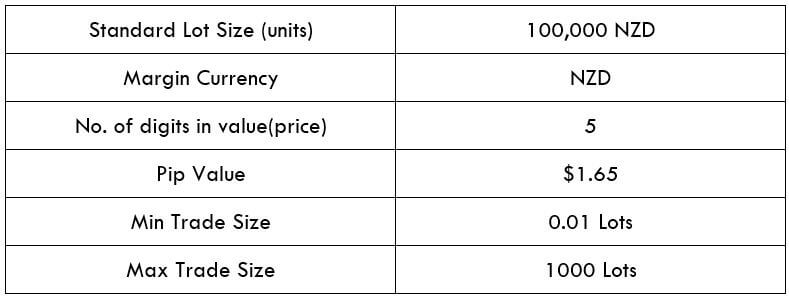
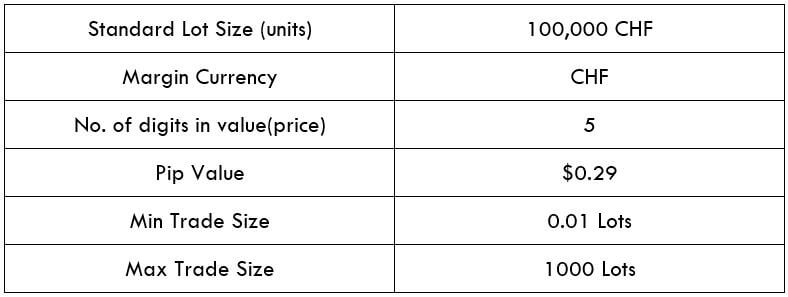
Procedure to assess Pip Ranges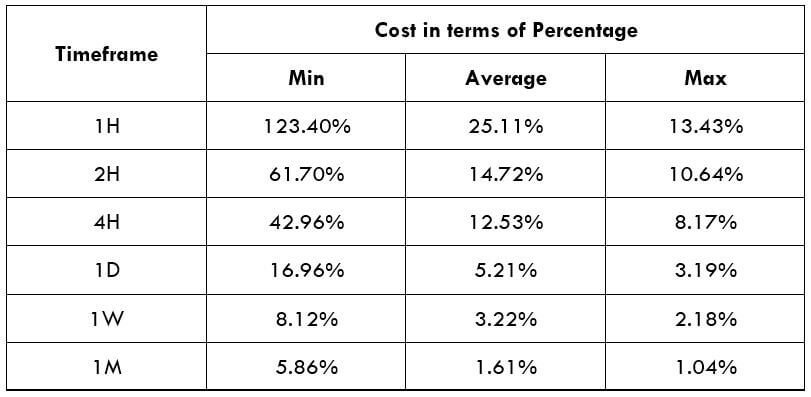 STP Model Account
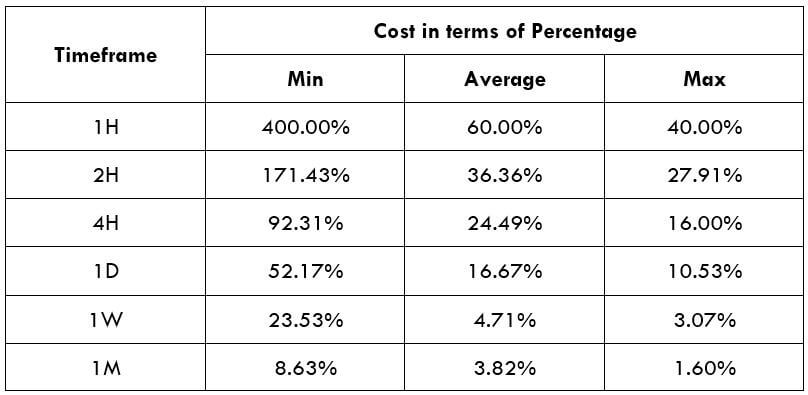
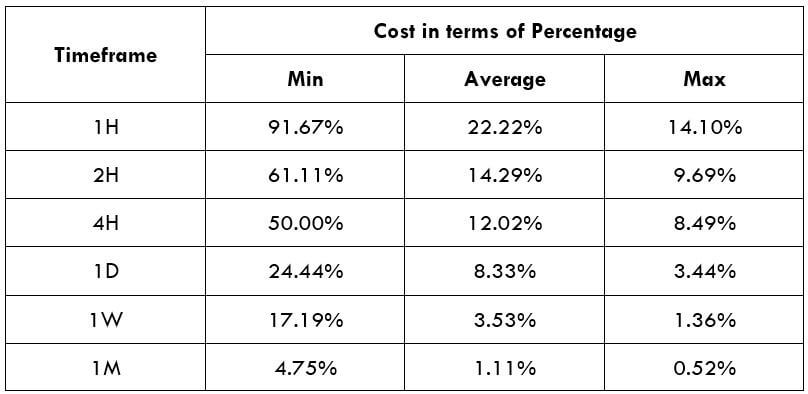
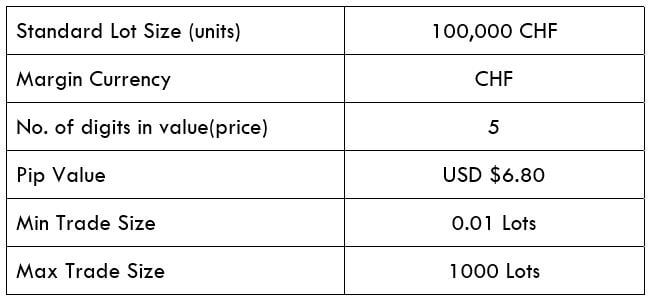
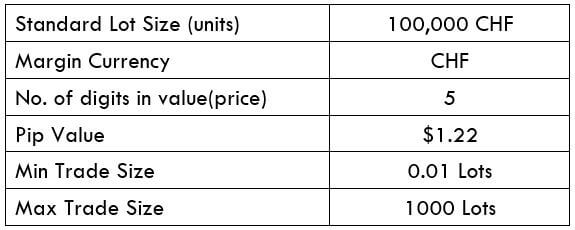
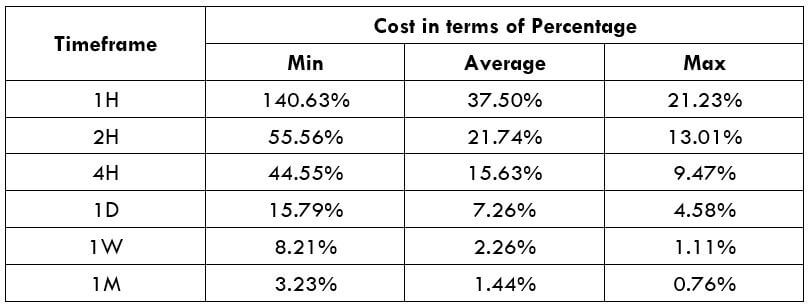
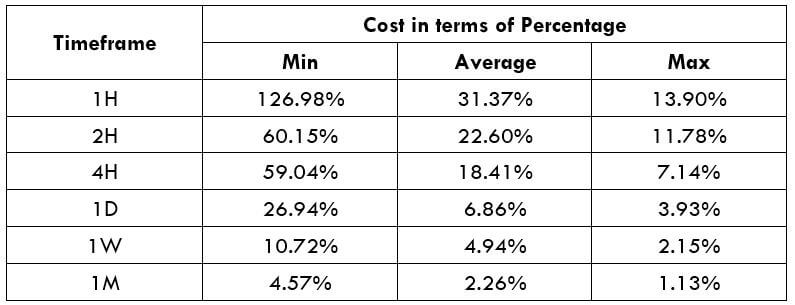
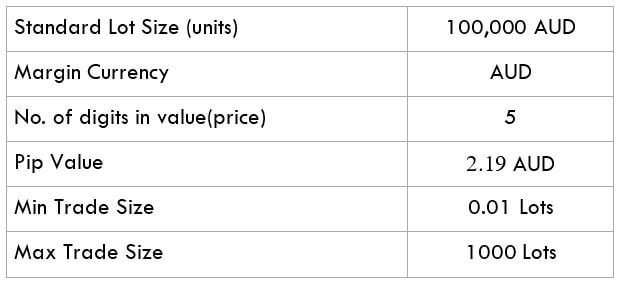
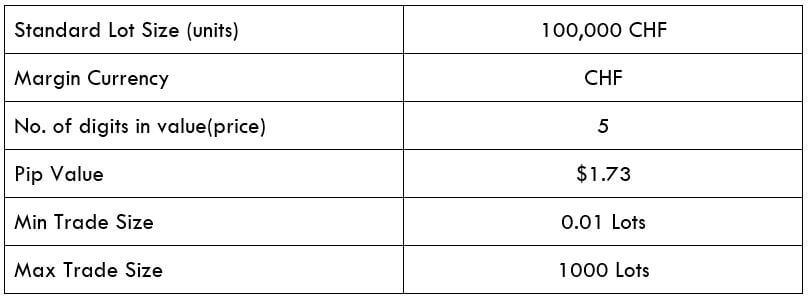
STP Model Account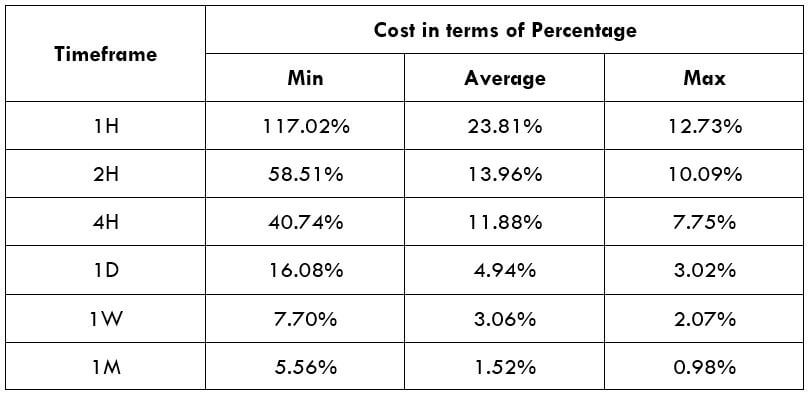
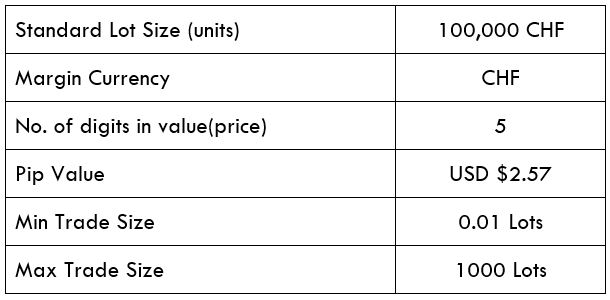
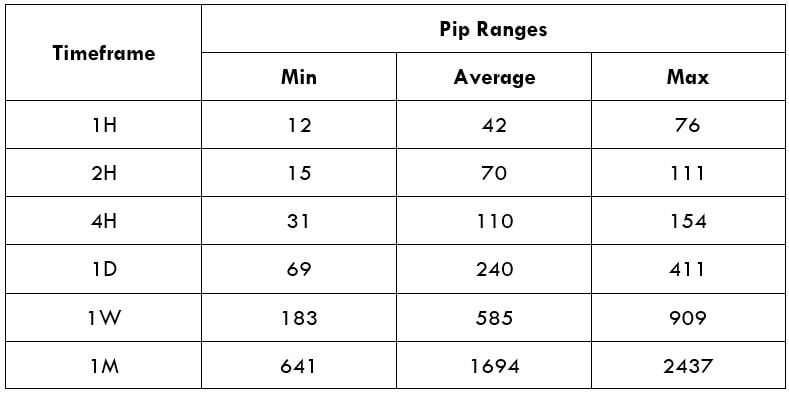
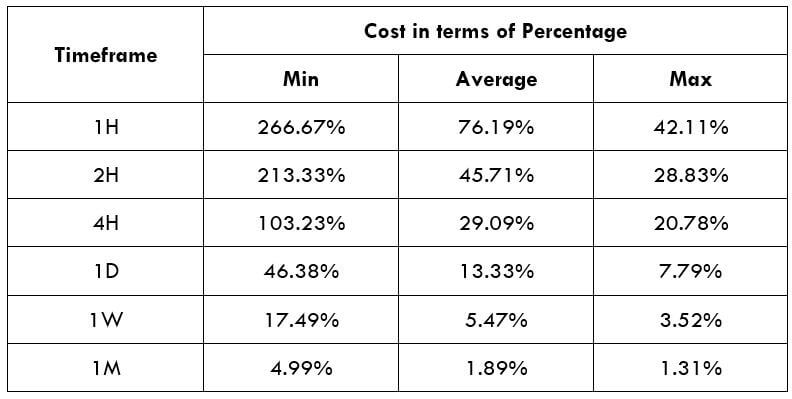
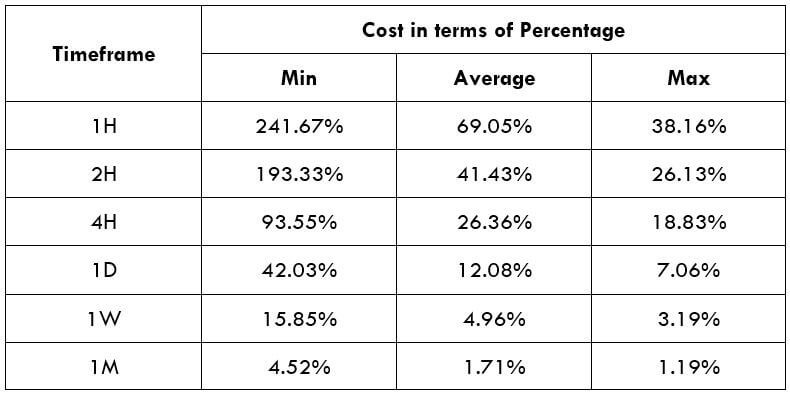

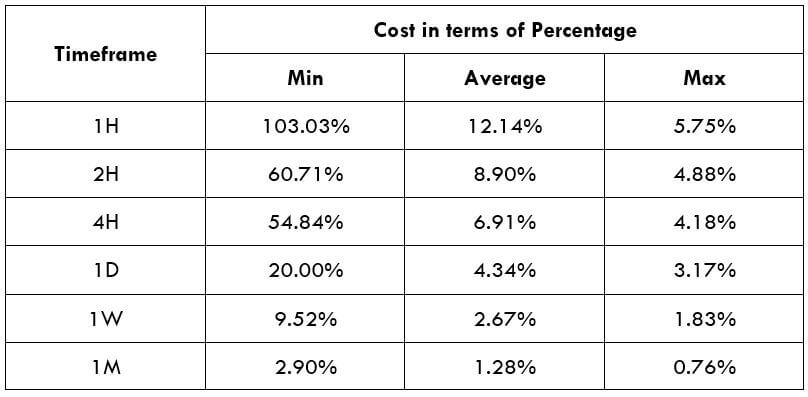
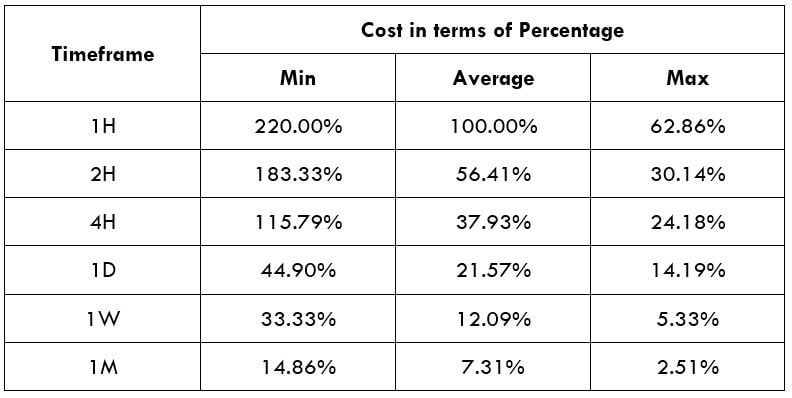
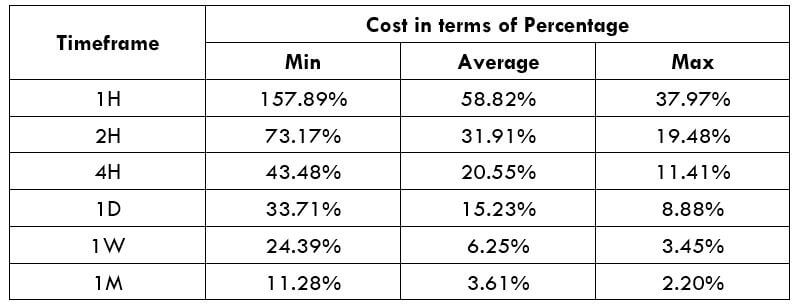
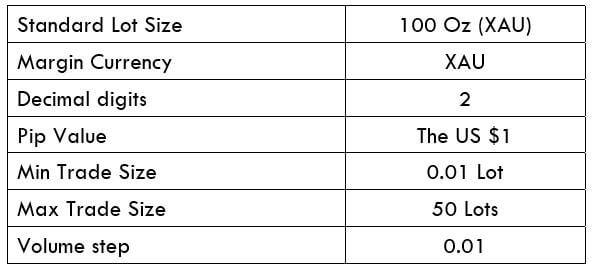
 Spread
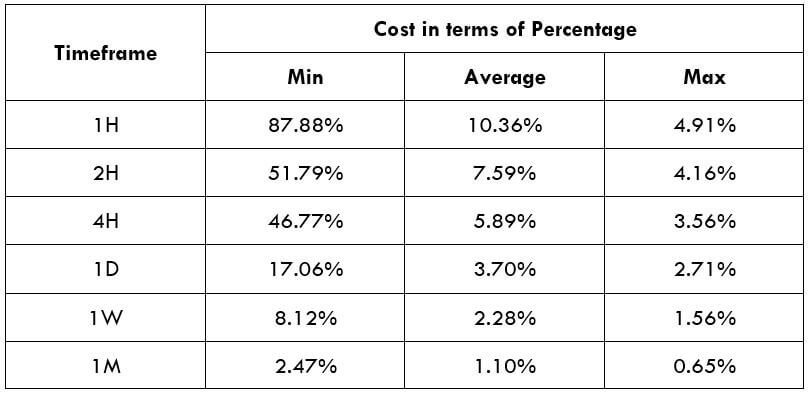
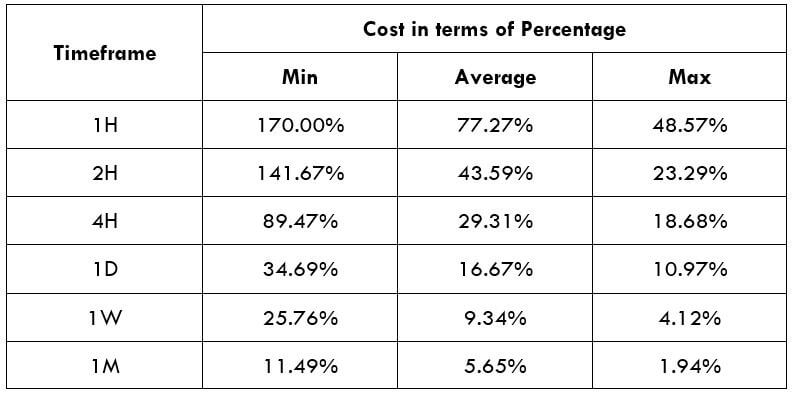
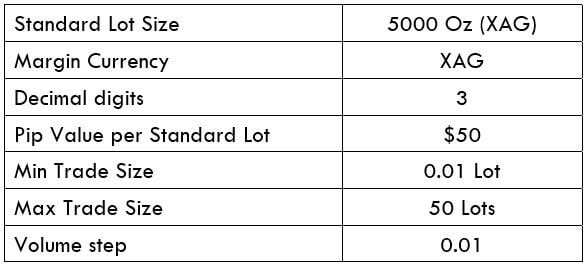
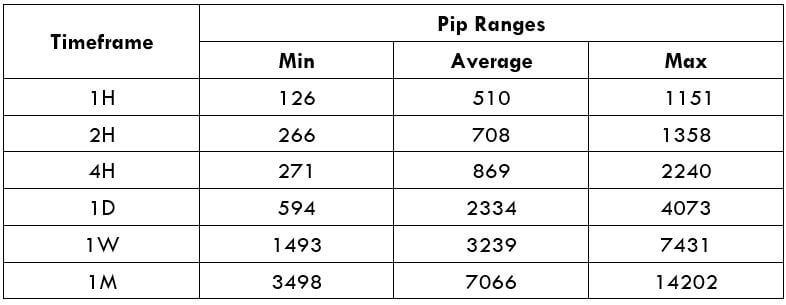
Spread