Introduction
NZD/CZK is the abbreviation for the Euro Area’s Euro against the Czech Koruna. This pair is considered an exotic-cross currency pair. Here, the NZD is the base (first) currency, and the CZK is the quote (second) currency. NDZ is the official currency used in New Zealand, while CZK is the native currency of the Czech Republic.
Understanding NZD/CZK
The price of this pair in the foreign exchange market defines the value of CZK equivalent to one NZD. It is quoted as 1 NZD per X CZK. So, if the value of this pair is 14.8124, these many Korunas are required to purchase one NZD.
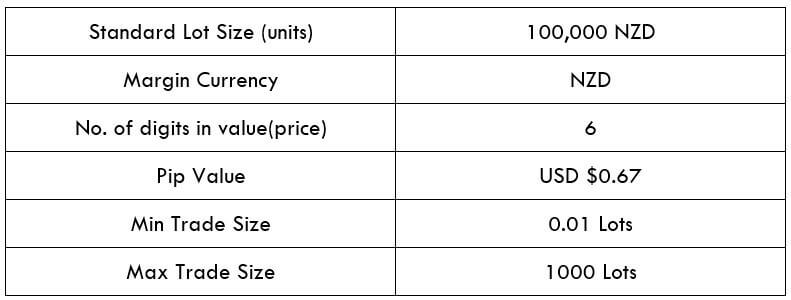
Spread
Spread is the mathematical difference between the bid and the asking price offered by the broker. This value is distinct in the ECN account model and STP account model. An approximate value for NZD/CZK pair is given below.
ECN: 43 pips | STP: 48 pips
Fees
The fee is the price/compensation that one pays for the trade. There are no charges on STP accounts, but a few additional pips are levied on ECN accounts.
Slippage
Slippage is a variation between the value proposed by the trader, and the trader indeed received from the broker.
Trading Range in NZD/CZK
The tabular interpretation of the pip movement of a currency pair in separate timeframes is called as the trading range is the. These values are helpful in influencing the profit that can be produced from a trade before-hand. To uncover the value, you must multiply the below volatility price with the pip value of this pair.
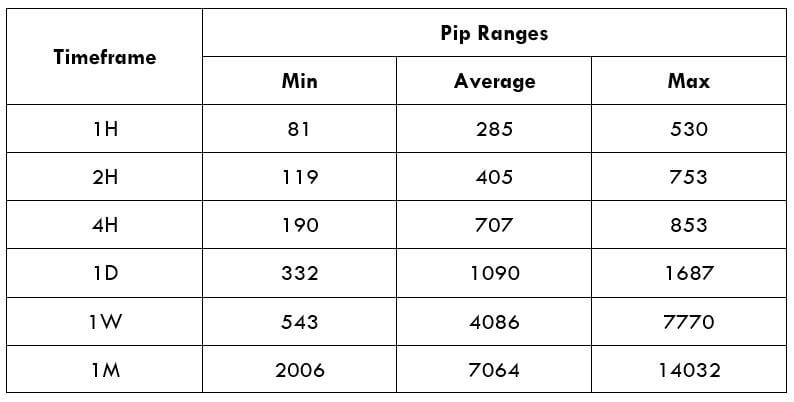
Procedure to assess Pip Ranges
- Add the ATR indicator to your chart
- Set the period to 1
- Add a 200-period SMA to this indicator
- Shrink the chart so you can assess a large time period
- Select your desired timeframe
- Measure the floor level and set this value as the min
- Measure the level of the 200-period SMA and set this as the average
- Measure the peak levels and set this as Max.
NZD/CZK Cost as a Percent of the Trading Range
Trading Range is the interpretation of the total price variation of trades for distinct timeframes and volatilities. The values are achieved by discovering the ratio amongst the total price and the volatility value; it is expressed as a percentage.
ECN Model Account
Spread = 43 | Slippage = 5 |Trading fee = 8
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 3 + 43 + 8 = 56
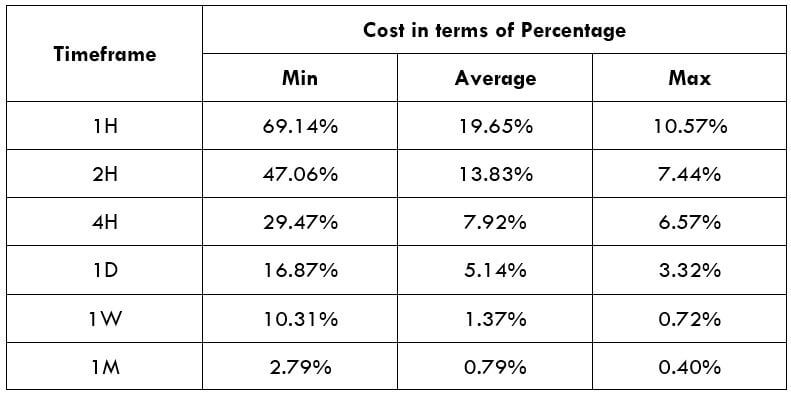
STP Model Account
Spread = 48 | Slippage = 5 | Trading fee = 0
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 5 + 48 + 0 = 53
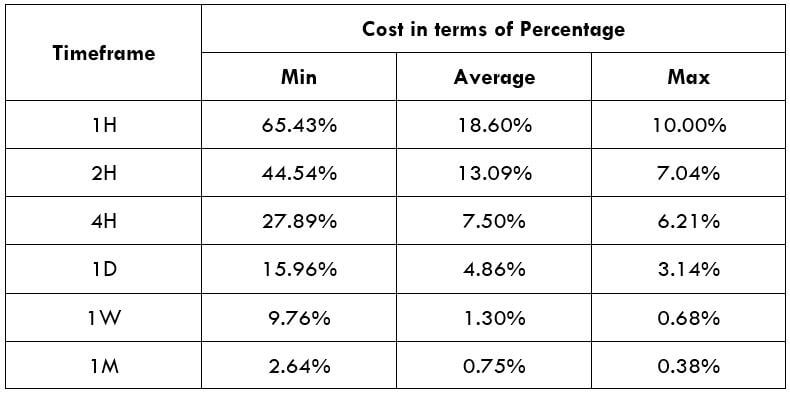
Trading the NZD/CZK
The bigger the percentage values, the higher is the price on the trade. From the preceding tables, we can see that the values are sizeable in the min column and relatively less significant in the maximum column. This means that the prices are high when the volatility of the market is low.
It is neither suitable to trade when the market’s volatility is elevated nor when the costs are high. To balance out between both these aspects, it is perfect to trade when the volatility of the pair is in the array of the average values.
Additionally, to decrease your costs even beyond, you may place trades using limit orders as a substitute for market orders. In executing so, the slippage will not be involved in the computation of the total costs. And this will put down the cost of the trades by a sizeable number. An example of the same is given below.
STP Model Account (Using Limit Orders)
Spread = 48 | Slippage = 0 |Trading fee = 0
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 0 + 48 + 0 = 48
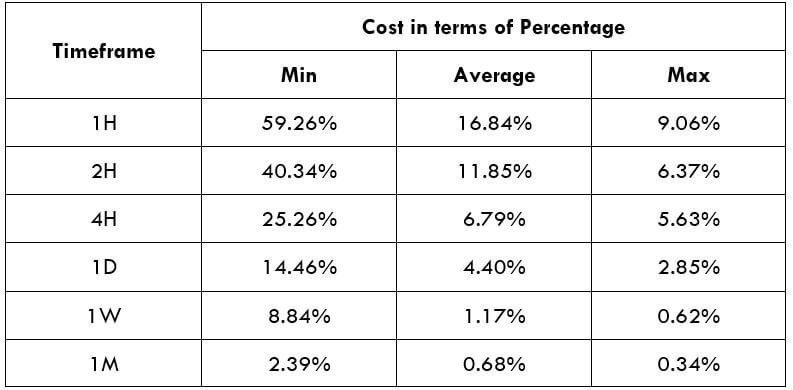



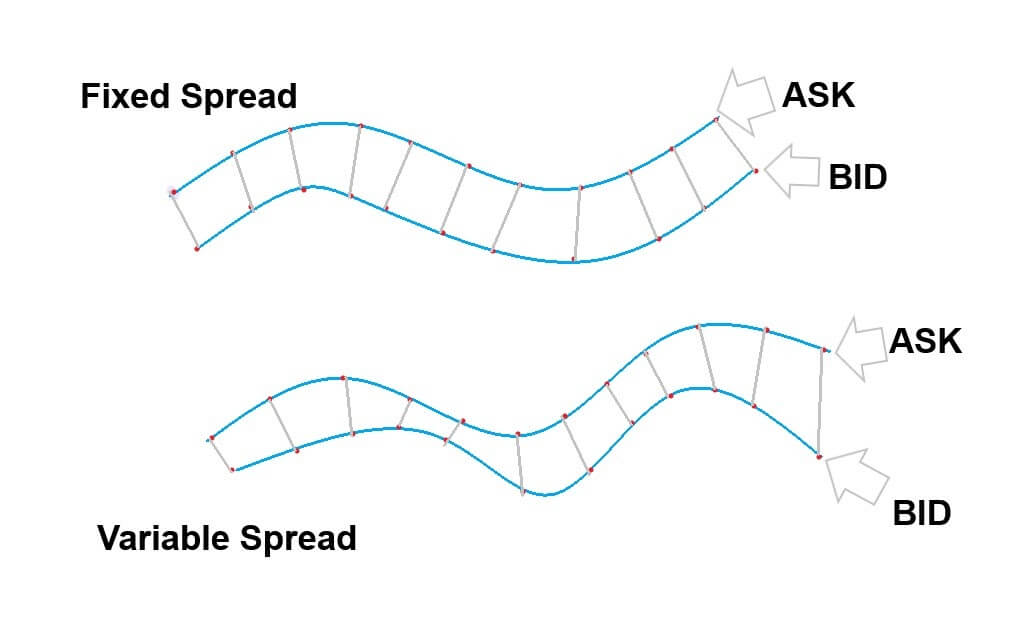

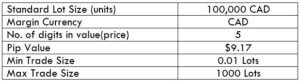
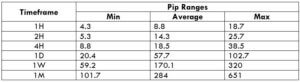
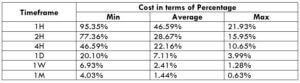
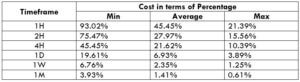
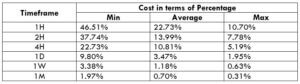


 Table 1 – ETFs Based on Gold
Table 1 – ETFs Based on Gold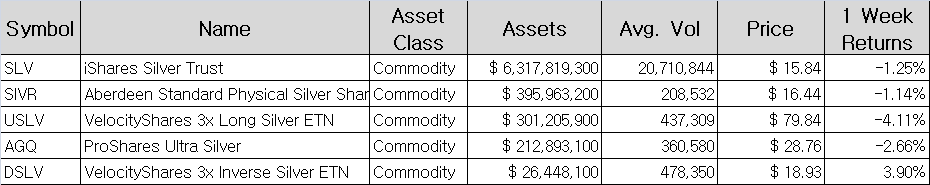 Table 2 – ETFs Based on Silver
Table 2 – ETFs Based on Silver