Introduction
AUD/TRY is an exotic currency pair in the forex market. The AUD is the short form of the Australian Dollar and the TRY for Turkish Lira. Forex traders interested in such exotic pairs should be aware that trading them comes with high volatility compared to trading major forex pairs. In this exotic currency pair, the AUD is the base currency, while the TRY is the quote currency. Thus, the AUD/TRY price represents the amount of TRY that 1 AUD can buy. For instance, if the AUD/TRY pair’s price is 5.8362, it means that 1 AUD can buy 5.8362 TRY.
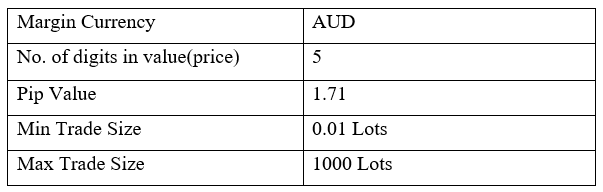
AUD/TRY Specification
Spread
In the forex market, your broker sells a currency pair to you at a higher price and buys it from you at a lower price. The value difference between these two prices is the spread. It is the primary way in which forex brokers earn their revenue.
The spread for the AUD/TRY pair is – ECN: 3 pips | STP: 8 pips
Fees
Forex traders with ECN account normally pay a trading fee to their broker whenever they open a position. This commission depends on the size of the trade, and not all forex brokers levy it. STP accounts do not have commissions.
Slippage
In forex trading, slippage refers to the price you expect your market order to be filled at and the price at which it is executed. The difference is a result of delays by your forex broker or high volatility.
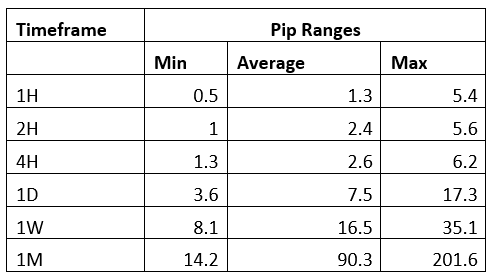
Trading Range in the AUD/TRY Pair
The trading range refers to the analysis of the price fluctuation of a currency pair across various timeframes. The trading range shows the volatility in pips for a currency pair throughout the trading period ranging from minimum to maximum.
The Procedure to assess Pip Ranges
- Add the ATR indicator to your chart
- Set the period to 1
- Add a 200-period SMA to this indicator
- Shrink the chart so you can determine a larger period
- Select your desired timeframe
- Measure the floor level and set this value as the min
- Measure the level of the 200-period SMA and set this as the average
- Measure the peak levels and set this as Max.
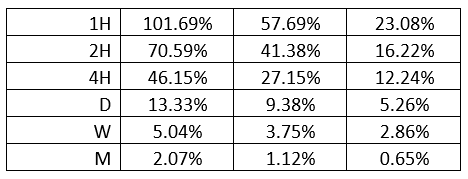
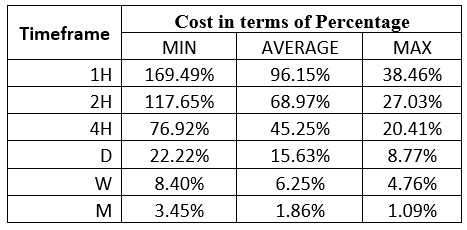
AUD/TRY Cost as a Percentage of the Trading Range
After determining the trading range, we can then determine the trading costs associated with these trading ranges. The total trading cost is expressed as a percentage of the pip volatility. Here are the trading costs for the AUD/TRY pair on both ECN and STP accounts.
ECN Model Account costs
Spread = 3 | Slippage = 2 | Trading fee = 1
Total cost = 6
STP Model Account
Spread = 8 | Slippage = 2 | Trading fee = 0
Total cost = 10
The Ideal Timeframe to Trade AUD/TRY Pair
From these analyses, we have established that longer timeframes have lower trading costs while the shorter timeframes attract higher trading costs. Note that the highest trading costs coincide with periods of lower volatility.
Therefore, the ideal timeframe to trade the AUD/TRY pair would be on longer timeframes when volatility is the highest. For shorter-term traders, opening positions when volatility is above the average can potentially lower the trading costs. Furthermore, traders across all timeframes can lower their trading costs by using the forex limit order types. With these types of orders, the cost of slippage is removed.
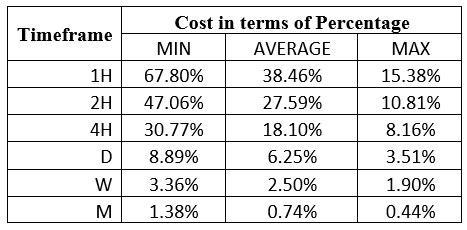
Below is an example using the ECN account.
ECN Account Using Limit Model Account
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading fee
= 0 + 3 + 1 = 4
Using the forex limit order types has lowered the trading costs across all timeframes. You can notice that the highest cost has reduced from 101.69% to 67.8%.