Introduction
CAD/SEK is a Forex exotic currency pair, where CAD is the primary currency of Canada, and SEK (Swedish Krona) is the currency of Sweden. In this exotic currency pair, CAD is considered the base currency, and SEK as the quote currency. This pair’s price determines the value of SEK, which is equivalent to one CAD. We can quote it as 1 CAD per X numbers of SEK. For example, if the CADSEK pair’s value is at 6.5877, we would need almost 6.5877 SEK to buy one CAD.
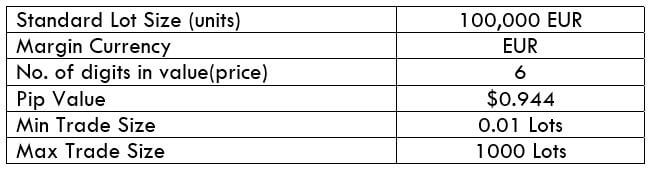
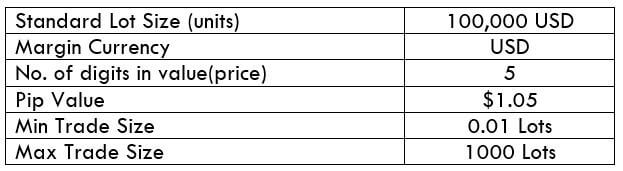
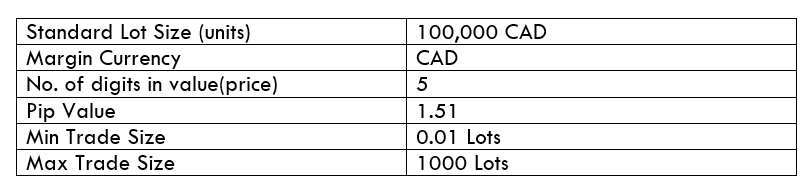
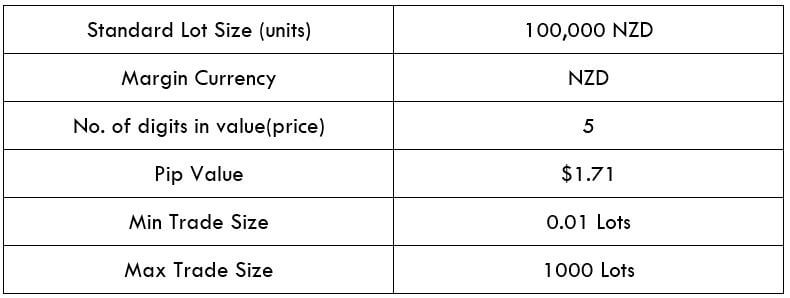
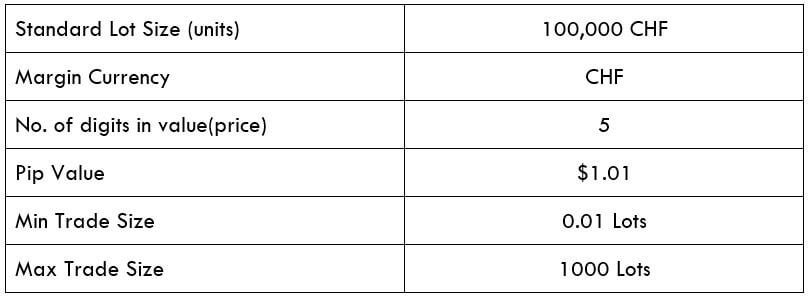
CAD/SEK Specification
Spread
In all the financial markets, the spread represents the difference between the Bid and Ask prices. It is typically a charge that is deducted by the Forex broker. These spread values vary on the type of execution model used for trade execution.
The spread of the CAD/SEK pair on ECN is 39 pips, and on the STP model account is 44 pips.
Fees
The trading fees that forex brokers are similar to the stock market. It is deducted from the traders’ accounts as soon as they open a new position. There is no fee charged on STP accounts, but a few pips are charged on ECN accounts.
Slippage
Slippage occurs when a trader opens a trade at a price, but it opens at another price by expanding the spread. The main reason for the slippage to occur is the market volatility and the broker’s execution speed.
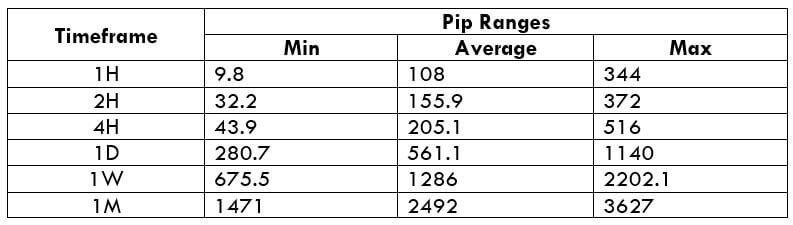
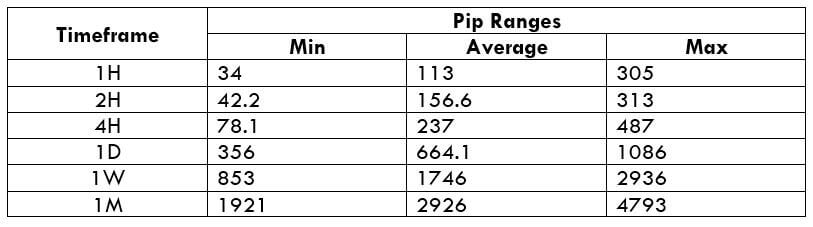
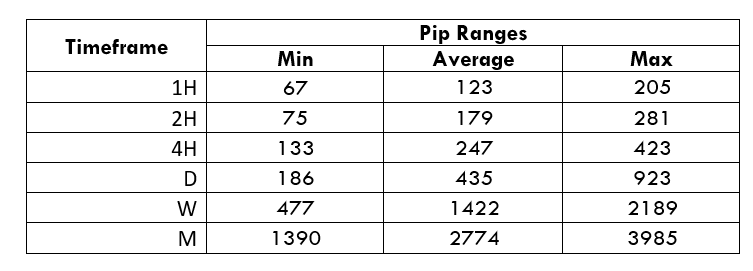
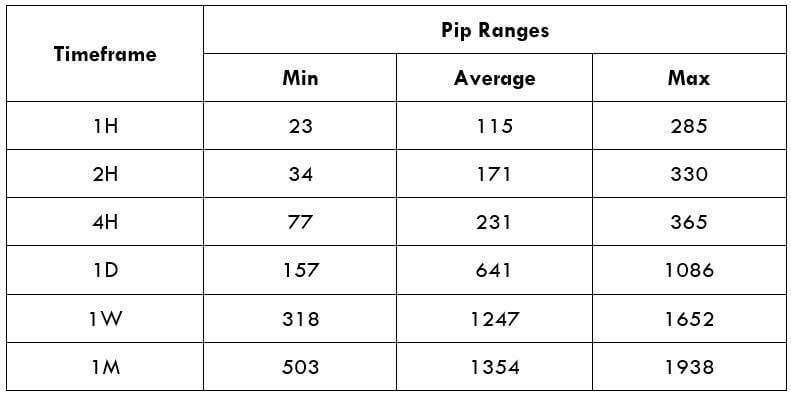
Trading Range in CAD/SEK
Procedure to assess Pip Ranges
- Add the ATR indicator to your chart
- Set the period to 1
- Add a 200-period SMA to this indicator
- Shrink the chart so you can assess a large time period
- Select your desired timeframe
- Measure the floor level and set this value as the min
- Measure the level of the 200-period SMA and set this as the average
- Measure the peak levels and set this as Max.
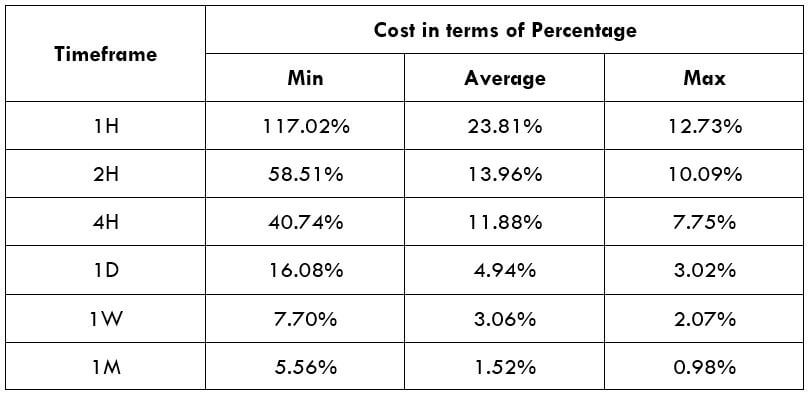
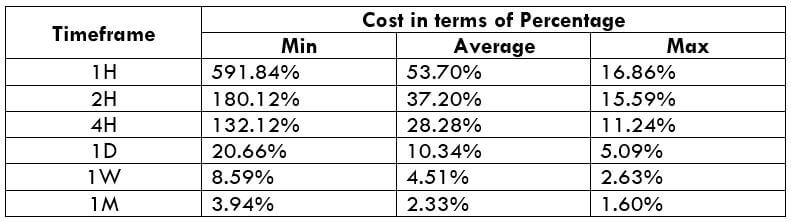
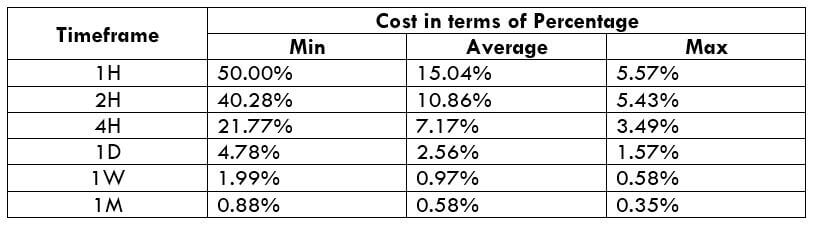
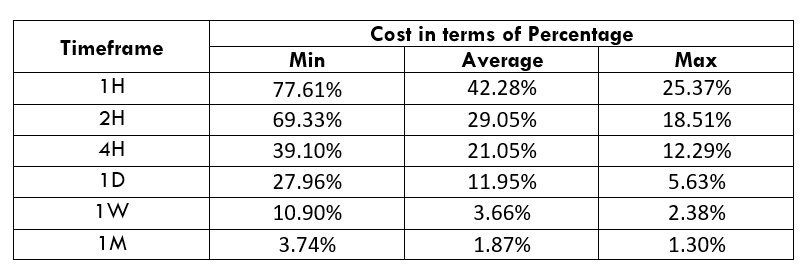
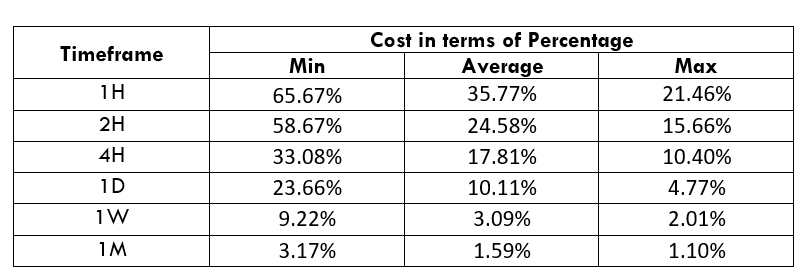
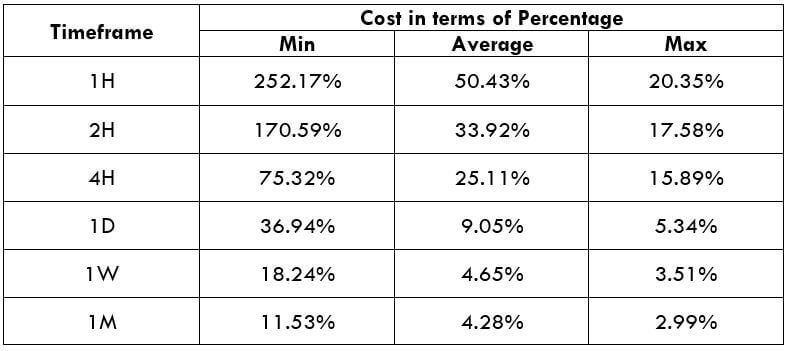
CAD/SEK Cost as a Percent of the Trading Range
The below tables represent the percentage values of trading costs involved while trading this particular Forex asset in various time frames. Please note that these values must be used for directional purposes only. So, for instance, if the percentage of costs involved is high in the one-hour time frame, it implies that this pair is expensive to trade in that particular time frame.
ECN Model Account
Spread = 39 | Slippage = 5 | Trading fee = 8
Total cost = Spread + Slippage + Trading Fee
= 39 + 5 + 8 = 52
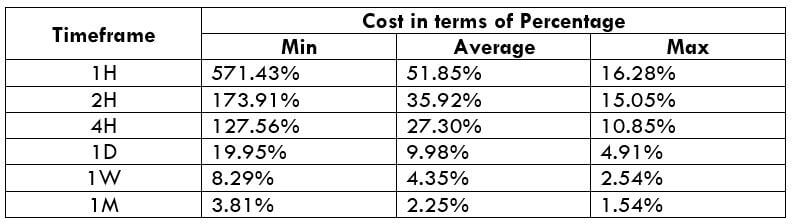
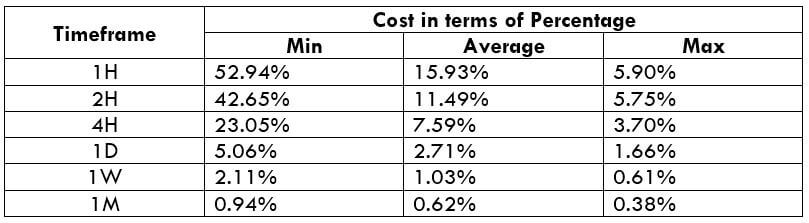
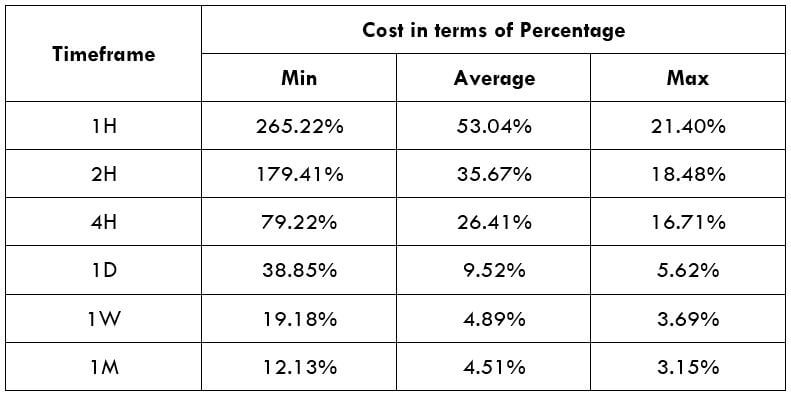
STP Model Account
Spread = 44 | Slippage = 5 | Trading fee = 0
Total cost = Spread + Slippage + Trading Fee
= 39 + 5 + 0 = 49
The Ideal way to trade the CADSEK
The CAD/SEK is an exotic cross currency pair with sufficient liquidity. As a result, traders may find it easy to trade in this pair. If we look at the table, we would see that the percentage values did not move above 65%, representing a lower trading fee even in the lower timeframe. Therefore, trading in this currency pair is suitable for intraday, swing, and even scalping. However, the best decision is to trade when the cost of trading is at the average value.
There is another way to reduce the cost while trading this pair, and it is to place a pending order. We can either place a limit or stop order instead of the market order. In that case, the slippage won’t be considered while calculating the total costs. Therefore, in our example, the overall cost will be reduced by five pips, as shown below.
STP Model Account (Using Limit Orders)
Spread = 44 | Slippage = 0 | Trading fee = 0
Total cost = Spread + Slippage + Trading Fee
= 44 + 0 + 0 = 44





 Spread
Spread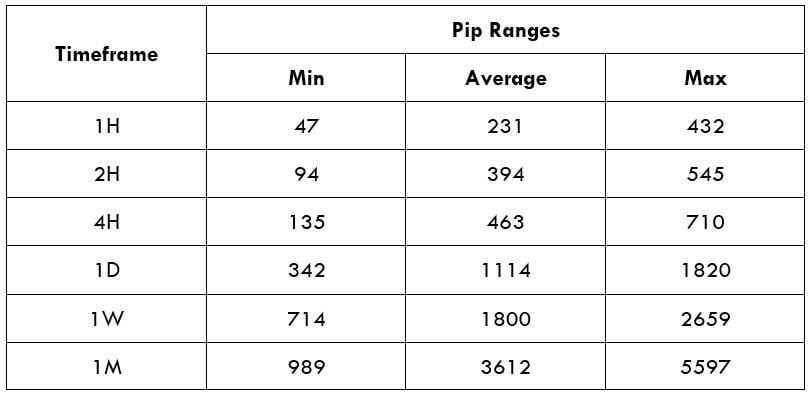 Procedure to assess Pip Ranges
Procedure to assess Pip Ranges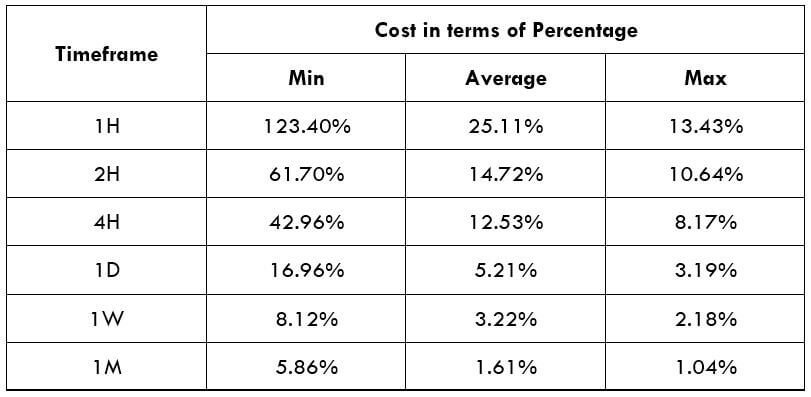 STP Model Account
STP Model Account