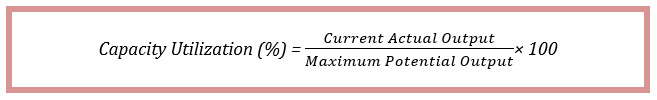Introduction
One of the primary ways any government funds its budget is through debt – borrowing. When borrowing, a government can do this from the international markets or locally, from its citizens and businesses. When taking debt locally, a government uses treasury bills and bonds. As is with any form of debt, borrowing using treasury bills, the government is obligated to pay interest upon the maturity date.
The interest rate that the government offers for its treasury bills gives an invaluable insight into the confidence investors have in the economy. Therefore, to understand the borrowing patterns of the government, the interest rates it is obligated to pay, we need to understand treasury bill auctions.
Understanding Treasury Bill Auction
To better understand how the treasury bid auction works, we first need to understand a few terms.
Treasury bill is a short-term debt instrument used by governments to borrow money over a short period – usually less than one year. Because the central banks back the treasury bill, they are considered to be of lower risk and secure form of investment.
Treasury bill auction is a weekly public offering of treasury bills by the central government with maturities ranging from one month to one year. The auction is the official avenue through which central banks issue their treasury bills.
Maturity is the maximum time that a treasury bill holder can hold it before they are eligible for redemption. Treasury bills have maturities ranging from days up to one year. Note that the longer the maturity period of a treasury bill, the higher the interest rate will be.
Discount is the difference between the price at which the treasury bills are issued and the face value of the treasury bills. It is customary for the treasury bills to be issued at a discount and be redeemed at face value upon maturity.
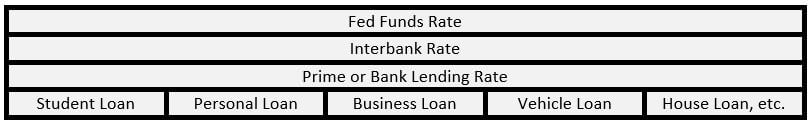
During the auctions, participants are generally divided into two categories – competitive and non-competitive bidders. Before the auctioning process begins, the central banks make public the following information about the treasury bills: the date of the auction; the day of the treasury bill issue; eligibility of auction participants; the amount of the bills being auctioned; and the time when the bidding ends.
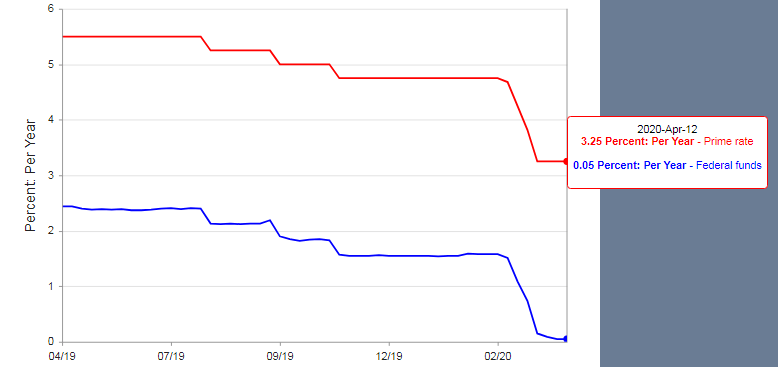
When the auction begins, the competitive bids are accepted first to determine the discount rate for the treasury bills. These competitive bills are submitted on a pro-rata share of every Treasury bill auction. It is worth noting that the winning bid determines the interest rate that will be paid out on each issue of a treasury bill. Furthermore, the demand for treasury bills is determined by the prevailing market and economic conditions and sentiment. It is this demand and the interest rate that will be of importance in our subsequent analyses.
Since the pricing of the treasury bills is done through a bidding process, the winning bid is usually one that has the lowest discount rate. Such bids are preferred to ensure that the interest rate the government pays investors is kept as low as possible.
After investors have purchased the treasury bills, they are then free to sell, trade them, or hold until maturity.
How can treasury bills auction be used for analysis?
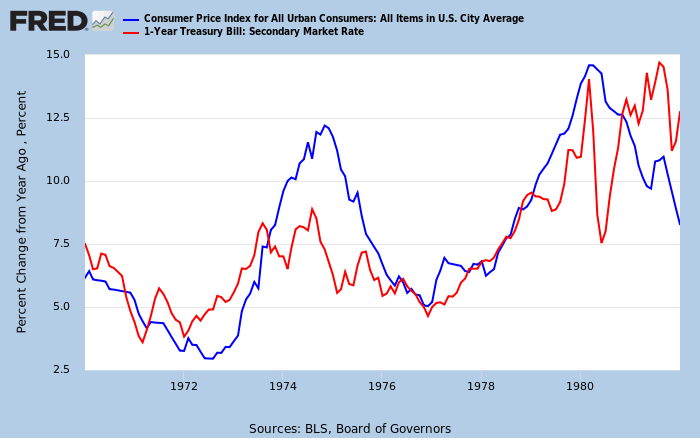
Using the auction of the treasury bills in the analysis is relatively straightforward. The biggest draw of the treasury bills is because of the presumed zero risks of default since the government backs them. As we mentioned earlier, the primary determinant of the discount rate at the treasury bill auction is the demand. This demand is driven by factors such as macroeconomics, market risks, and monetary policies.
When other markets such as equity markets appear to be less risky or offer better returns, investors in the treasury bills will demand higher discounts. The higher discount translates to a higher interest rate attached to the treasury bills. Furthermore, when the rate of inflation is rising, investors will demand a higher discount rate for the treasury bills to offset the effects of inflation.
Source: St. Louis FRED
When there is rapid economic growth, investors have several options that could earn them higher returns. Therefore, they will demand a higher discount from the government, which results in a higher rate. Similarly, when the economy is heading towards a recession, investors deem treasury bills as safe-haven investments. The resulting excess demand for the treasury bills leads to lower discounts received by the investors.
Thus, the change in the yield attached to the treasury bills gives us significant insight into the state of the economy.
Impact on currency
We have seen that the rate of the treasury bills being auctioned is a reflection of the prevailing market conditions or anticipated economic performance.
When the rate received at auction is higher, it signals that the economy is performing well. Furthermore, higher rates for the treasury bills imply that there will be increased interest in investment opportunities in the country, which results in increased demand for the local currency. Higher rates could also translate to the increasing rate of inflation, which forestalls contractionary monetary and fiscal policies. For the forex market, this translates to a well-performing economy hence the appreciation of the currency relative to other currencies.
Conversely, when the rate of treasury bills at auction are falling, it implies that the economic fundamentals are performing poorly. There will be a net outflow of capital and investment. Furthermore, the forex market would anticipate expansionary monetary policies, which result in the depreciation of the currency relative to others.
Sources of Data
In the U.S., the treasury bills are auctioned by the U.S. Department of Treasury. You can access the latest data on the auction of treasury bills here. The data on the upcoming auction of the U.S. treasury bills can be accessed from TreasuryDirect, which allows you to buy and redeem securities directly from the U.S. Department of the Treasury in paperless electronic form. You can access the in-depth review of the current and historical data on the U.S. treasury bills from St. Louis FRED. You can access the global data on Treasury bills from Trading Economics.
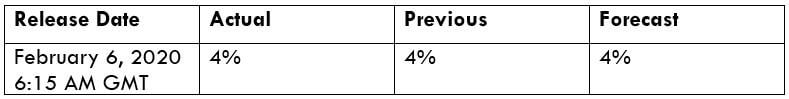
That’s about Treasury Bill Auction and the respective details related to this fundamental indicator. We did not see any reaction at all on the Forex price charts related to this indicator, but as explained above, we know the relative impact. We hope you have found this article informative. Cheers!