Introduction
Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP) is the go-to indicator for monitoring inflation statistics in the European Union (EU). Inflation reports are vital for the currency markets, as inflation directly erodes currency value. Hence, domestically and internationally, inflation statistics play equally critical roles in currency valuations. Understanding HICP is mandatory for building fundamental analysis related to the European Union countries.
What are Harmonized Consumer Prices?
Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP)
It is a list of the final price paid by European end-consumer for a basket of commonly used goods and services. Like the United States has the Consumer Price Index (CPI) as a means of regularly measuring inflation levels month over month, the European Union (EU) has HICP. The average change in the price of the selected goods and services gives us a clear idea about the inflation rates in the EU.
The HICP differs from United States CPI because it takes inflation data from each member nation of the European Central Bank (ECB). It is also a weighted index, meaning that goods are given a specific weightage based on demand, or how essential and frequently used by the consumers. The consumer goods basket is derived from data of both rural and urban areas of each member nation.
How can the Harmonized CP numbers be used for analysis?
The Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP) is measured and given by each of the European Union (EU) member states. European Union is a political and economic union of 27 states located primarily in Europe. It is given out to measure inflation and help the European Central Bank (ECB) to form monetary policies accordingly if required. Every member country’s HICP measures the shifts over time in the prices of the basket of selected goods and services purchased, used, or paid for by households of that nation.
The “commonly used goods and services” include coffee, meat, tobacco, fruits, household appliances, electricity, clothing, pharmaceuticals, cars, and other commonly used products. It is also worth mentioning that the index excludes owner-occupied housing costs.
The HICP is also used for the Monetary Union Index of Consumer Prices (MUICP), an aggregate measure of consumer inflation for all countries of the eurozone. The eurozone represents all countries of the European Union that have incorporated the Eurodollar as their national currency. The primary aim of HICP is to maintain price stability. It defines the stable inflation rate in the euro area as below two percent annually.
Amongst HICP and MUICP, the HICP is a broader measure of inflation, but for trading, traders would prefer MUICP as it tells about the inflation concerning the European Dollar (EUR). The MUICP is calculated by selecting HICP from the eurozone countries only. All the member nations use the same methodology to calculate their respective HICP, enabling them to compare with each other and easily calculate the MUICP directly.
The selected goods and services are updated annually to account for the changes in consumer spending patterns. Each country’s weightage represents its consumption expenditure share in the entire euro area.
Inflation is the fuel that drives the economy. It is a double-edged sword, too much inflation erodes currency value, and citizens become poorer, and too low causes deflation, which slows the economy making money “costly.” A low and steady inflation rate is the only solution to keep the economy growing for capitalist economies.
When inflation rates fall below the long-term averages, the central authorities may use fiscal (government actions, ex: tax cuts) or monetary levers (central bank actions, ex: lower interest rates) to counter deflation and induce inflation. When the inflation rate is above the long-term rate, it is called hyperinflation, and central authorities may intervene and tighten the belt to deflate the economy. They can raise interest rates, increase taxes to deflate the economy to normal levels.
Inflation statistics like the HICP are coincident indicators as they tell us about the current price inflation. They are affected by leading indicators and policymaker’s responses. The HICP is closely watched by economists, central authorities, consumers, and even traders. In the currency markets, relative inflation can help us predict which currency’s value is eroding relatively faster. Inflation also affects the GDP of the country, which is a primary macroeconomic indicator for currency trading.
Impact on Currency
Currency markets emphasize on leading indicators over coincident indicators to always stay a step ahead of market trends. Coincident indicators confirm the trends rather than predict. Due to this, the impact of the HICP indicator in the market is low. For currency traders, MUICP and currency-specific aggregates are more useful than aggregate metrics like HICP to check inflation. Hence, overall, HICP is a low impact coincident indicator that can be overlooked for more country-specific inflation statistics.
Economic Reports
HICP data is published by Eurostat every month. It is the statistical office of the European Union. A brief estimate for the euro is published at the end of the month, followed by the detailed version containing indices of all member states approximately two weeks later. On the Eurostat page, we can find monthly, annual data, a detailed listing of country weights, item weights, prices, etc.
Sources of Harmonized Consumer Prices
We can know more about HICP in detail from the European Central Bank’s official website and the official data on the Eurostat page. We can find the consolidated monthly reports of HICP on Trading Economics.
Harmonized Consumer Prices – Effect on Price Charts
The Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP) is a coincident indicator. In essence, this indicator does not predict the future price action of currency but is coincident with it. Typically, metrics such as MUICP and other price reports induce volatility in the market. But HICP alone does not increase the volatility of the market.
Impact
The data is exclusive to the European Union and is released by the Federal Statistical Office. The impact of HICP on the currency market is negligible.
Harmonized Consumer Prices Report June
Below is the report of HICP for the month of June released in July. As per the data, the HICP increased from 108.47 to 108.58.
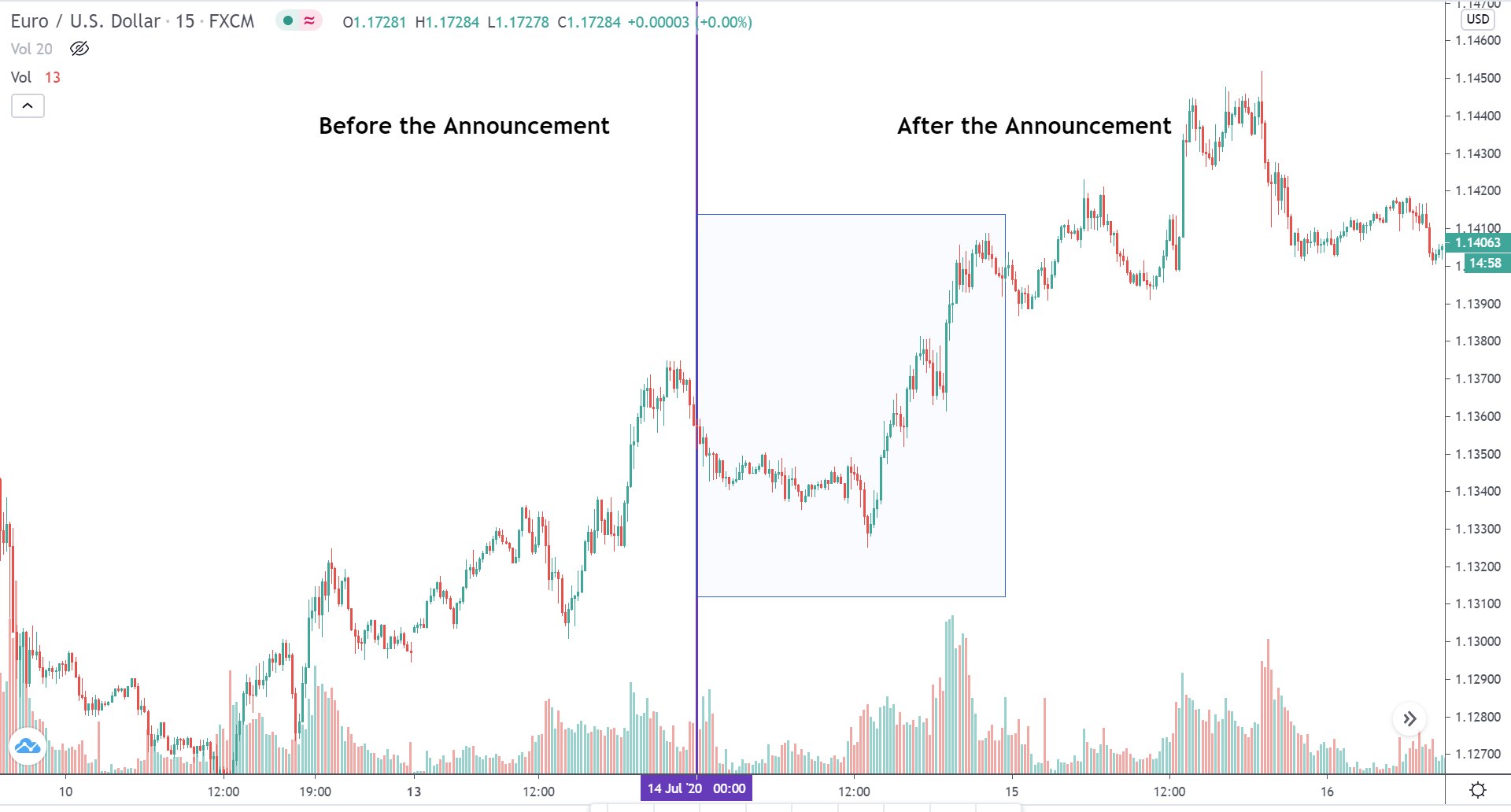
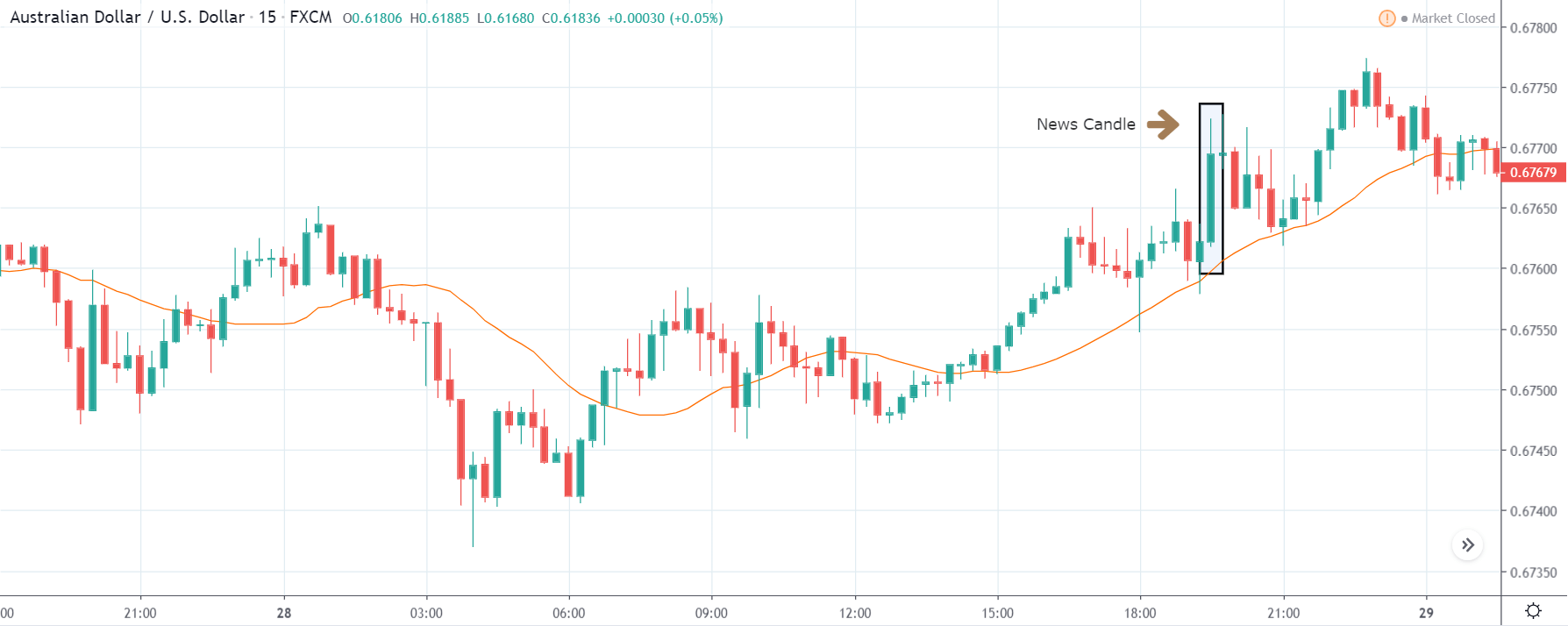
EURUSD – Before the Announcement
Before the announcement of the report, the market was in an uptrend making higher highs and higher lows.
EURUSD – After the Announcement
On the day of the announcement of the report, the prices retraced in the first half of the day and shot north aggressively and made a new higher high during the New York session. On the volumes side, there was feeble volatility in the Asian and European sessions, while it increased with the open of the US markets. That said, the increase in the volatility was not abnormal, which is typically seen during the release of major economic reports.
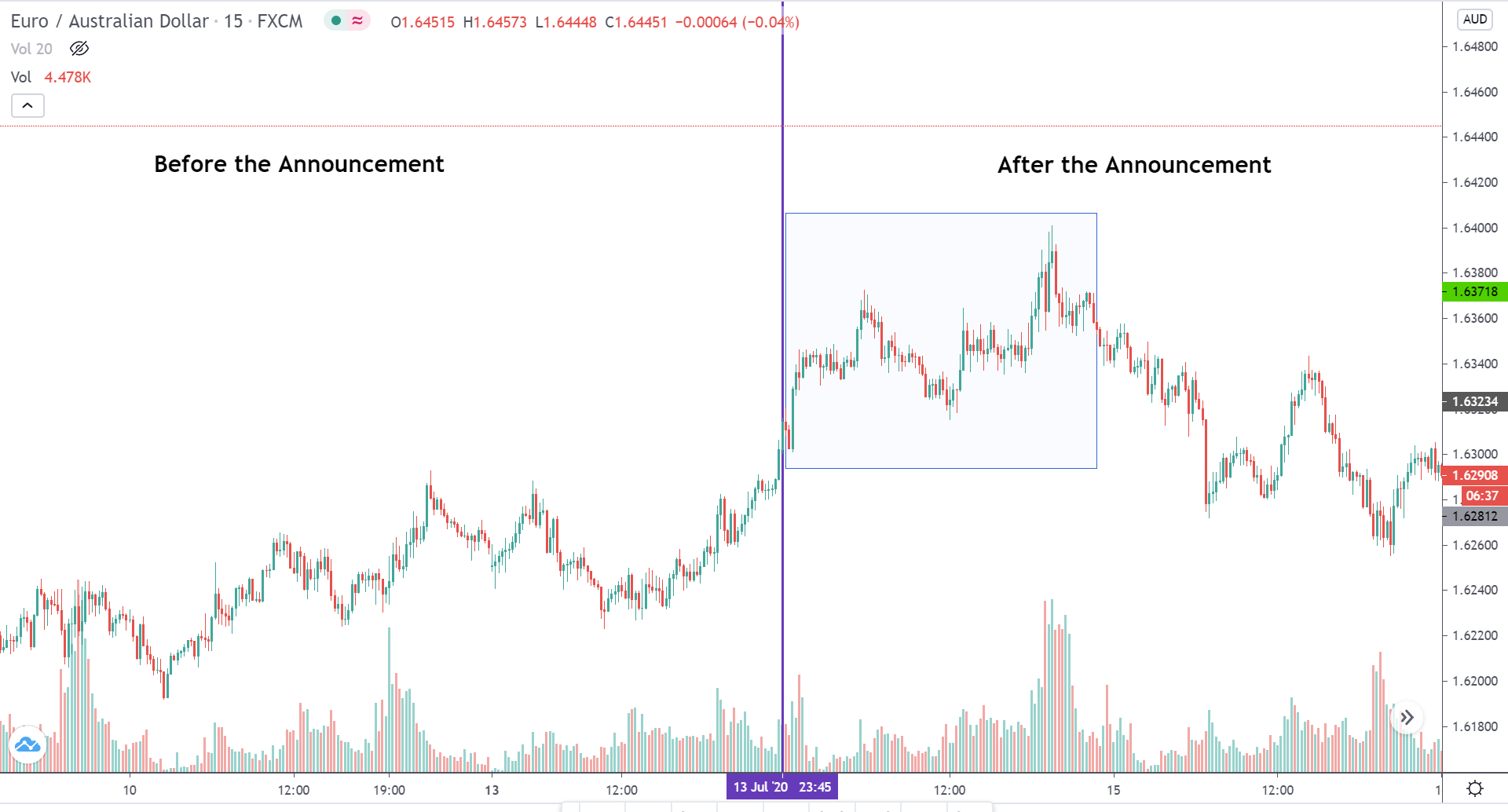
EURAUD – Before the Announcement
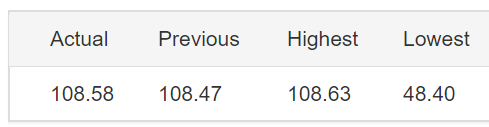
Before the report was released, the market was moving in an inclined channel showing EUR strength.
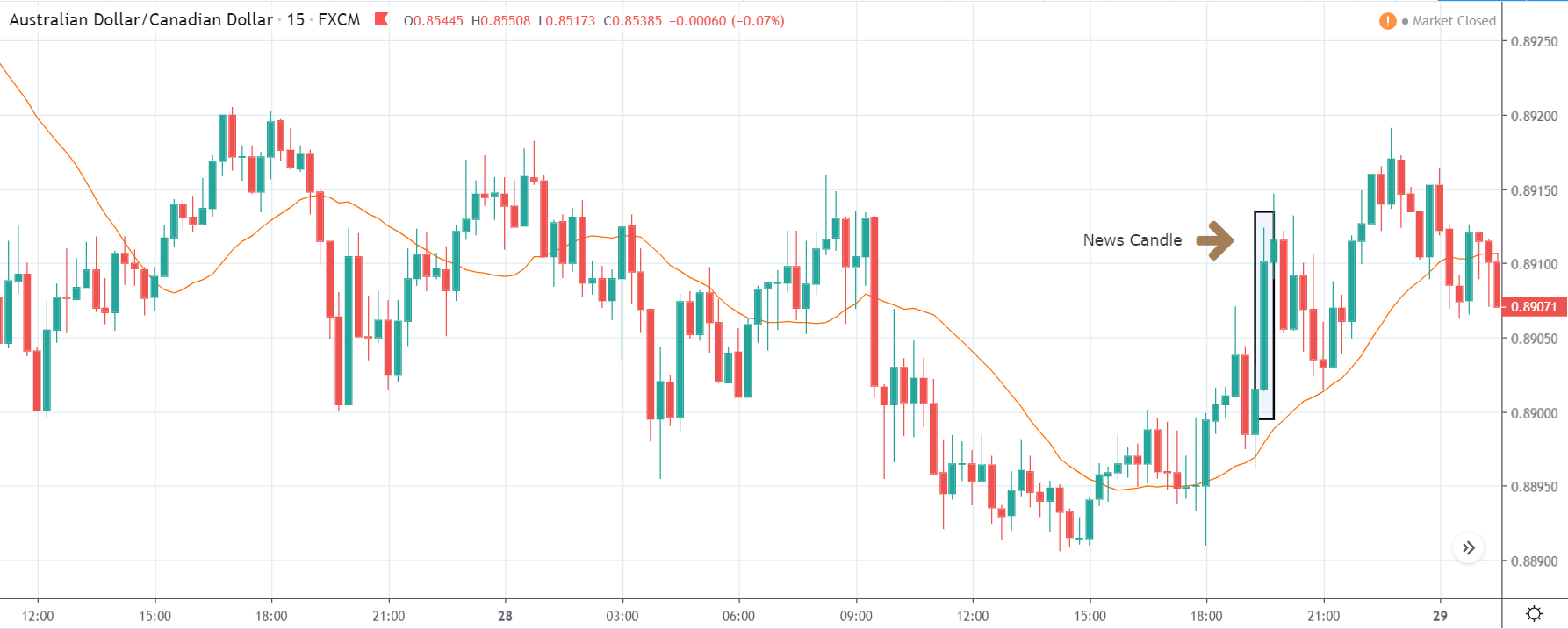
EURAUD – After the Announcement
After the report came out, the price break through the channeling market and began to trend. By the end of the day, the EURAUD price was up 0.65% from the previous day. This bullishness could perhaps be from the incident HICP report. However, the subsequent day, the market lost all its gains.
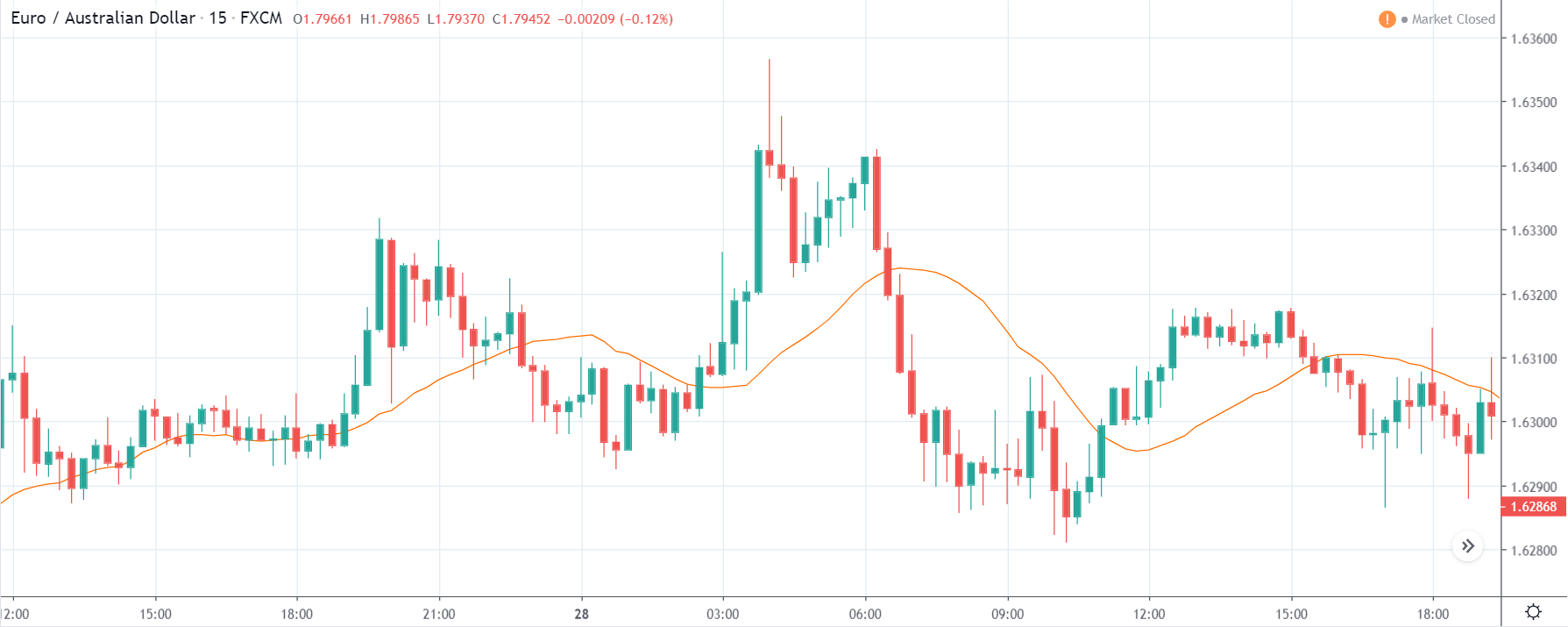
EURNZD – Before the Announcement
Prior to the announcement of the report, the market which was consolidating had begun to show mild bullishness.
EURNZD – After the Announcement
On the day the news was announced, the price continued to rise higher and higher for the entire day. In fact, EURNZD outperformed both EURUSD and EURAUD. There would be several factors that could’ve inflated the price, but a moderate effect could be through the positive HICP news. On the volatility side, there was no aggressive rise in volatility. However, the volume significantly increased during the North American session.
Thus, traders can analyze the technical factors of the market and open positions without any hesitation from the HICP report. That said, conservative traders may wait for the reports to be released, and then enter if the report is in favor of their speculated direction.