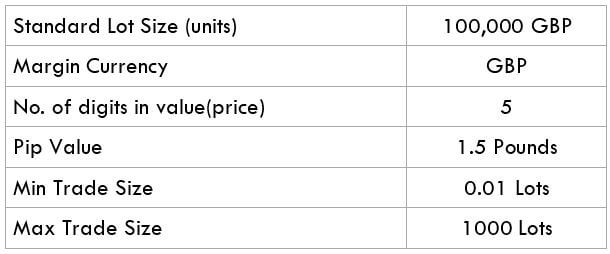
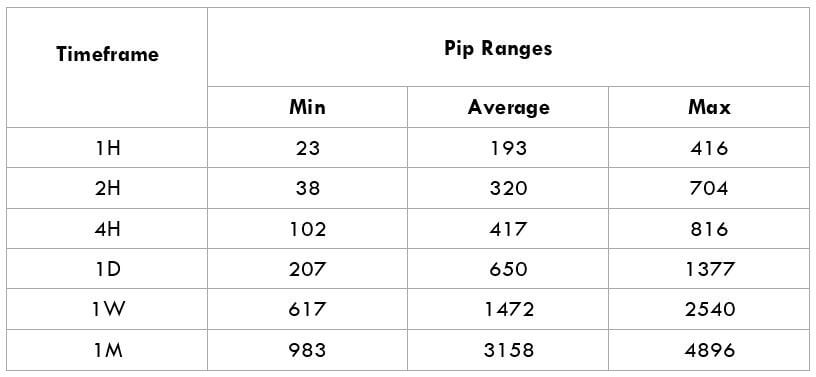
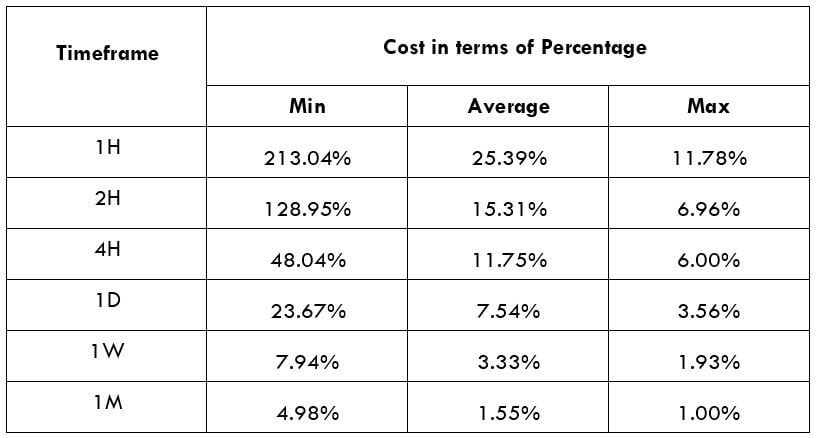
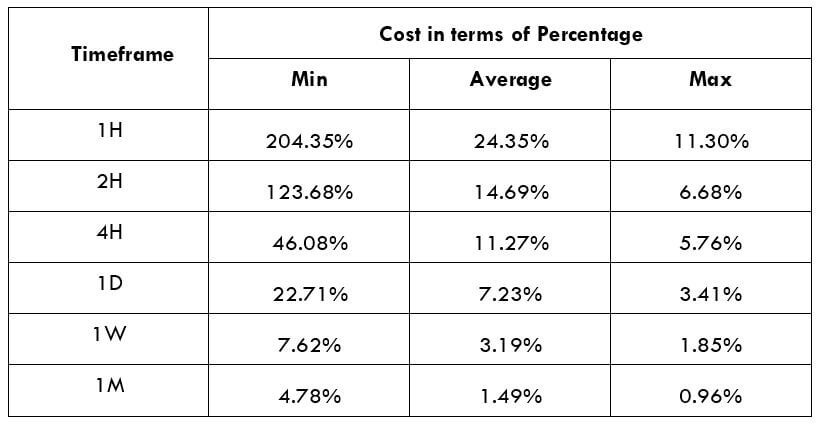
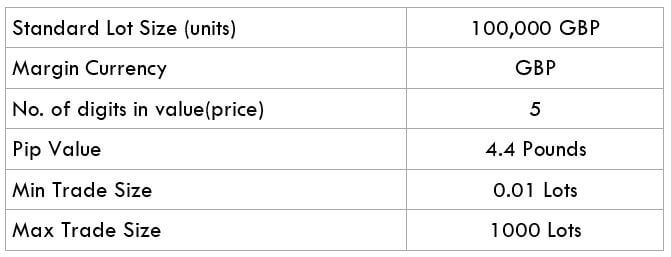
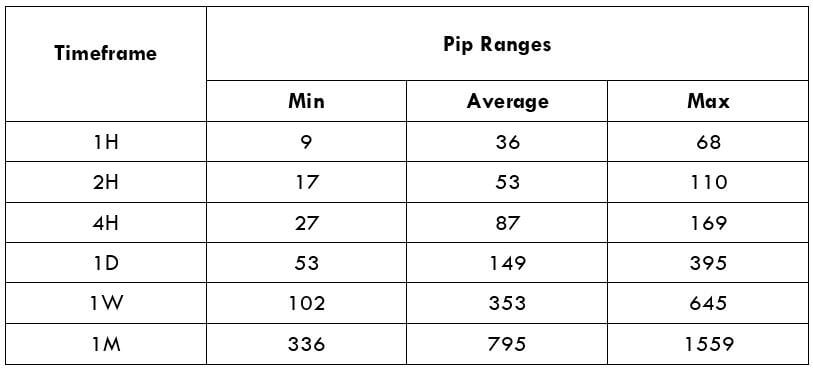
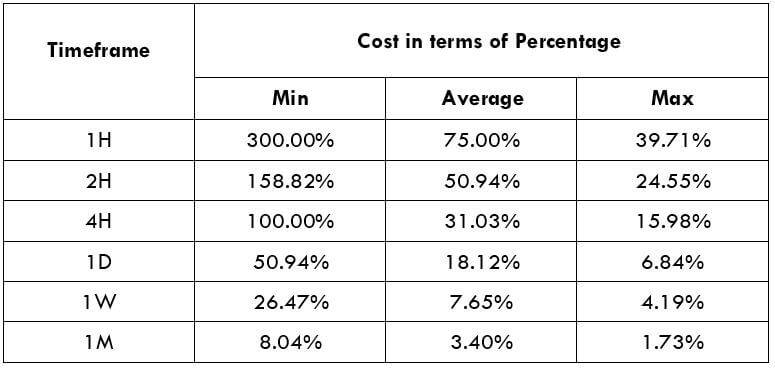
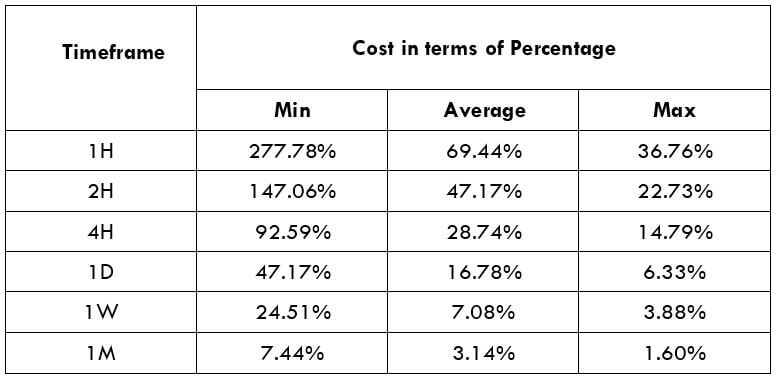
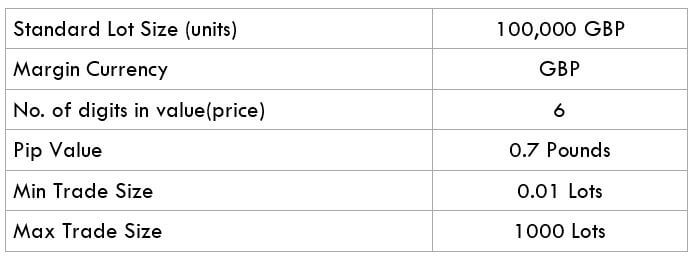
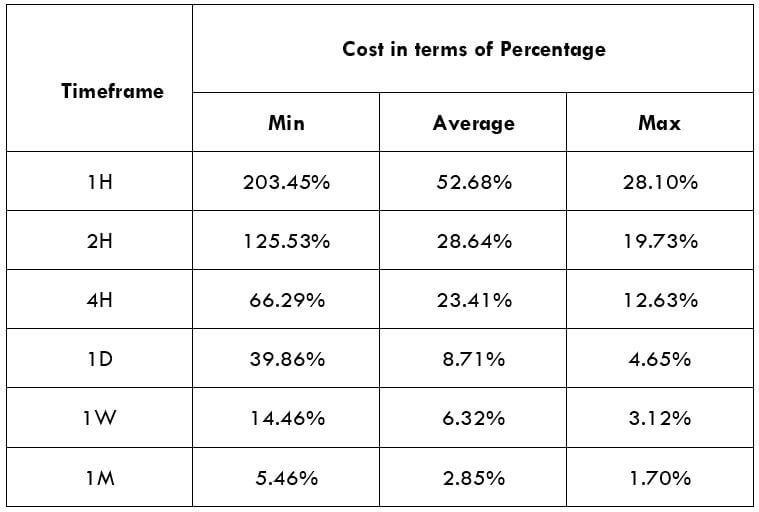
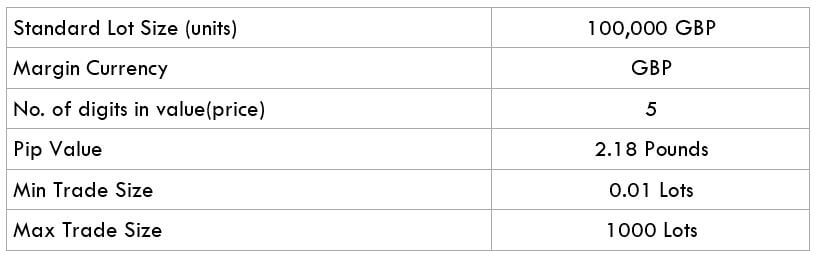
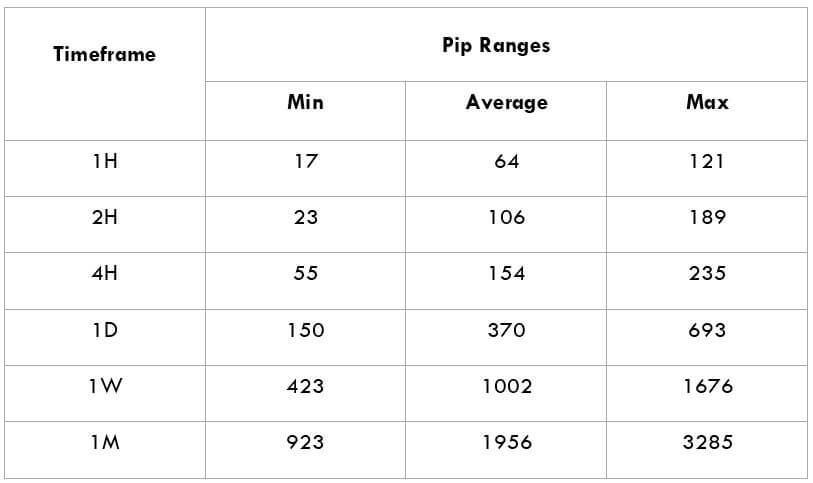
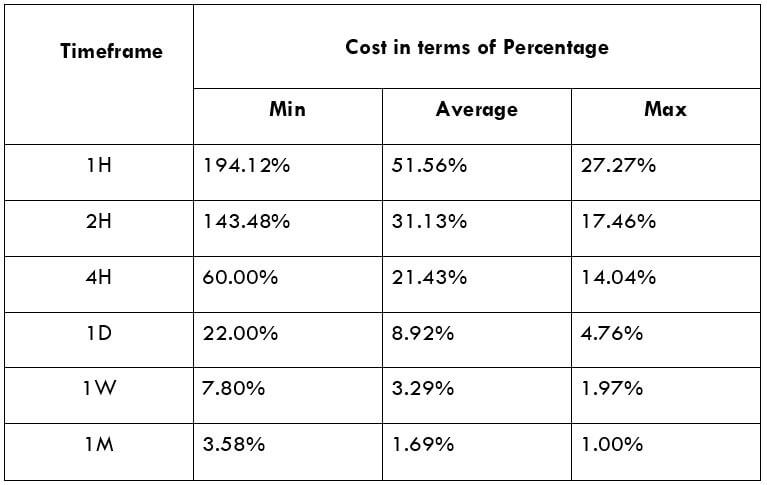
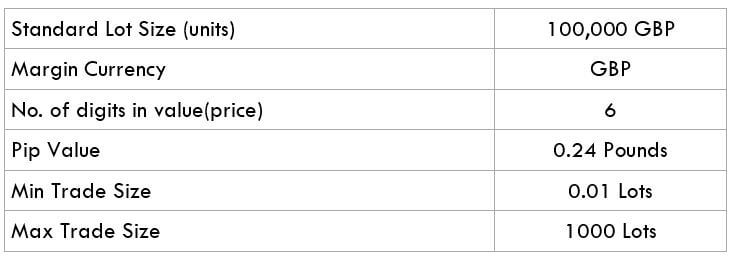
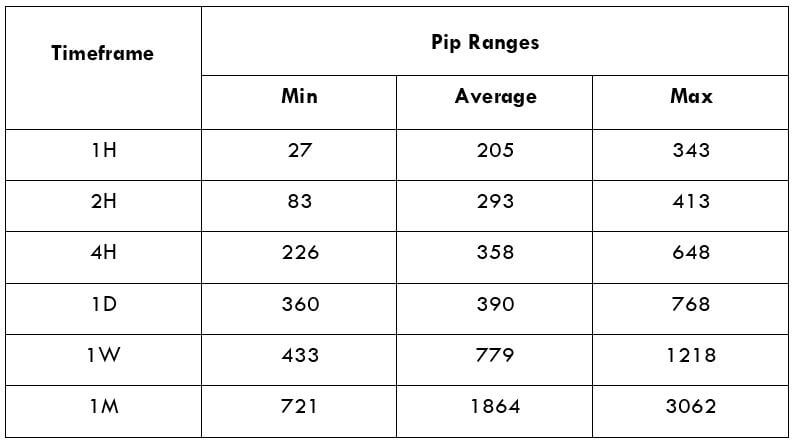
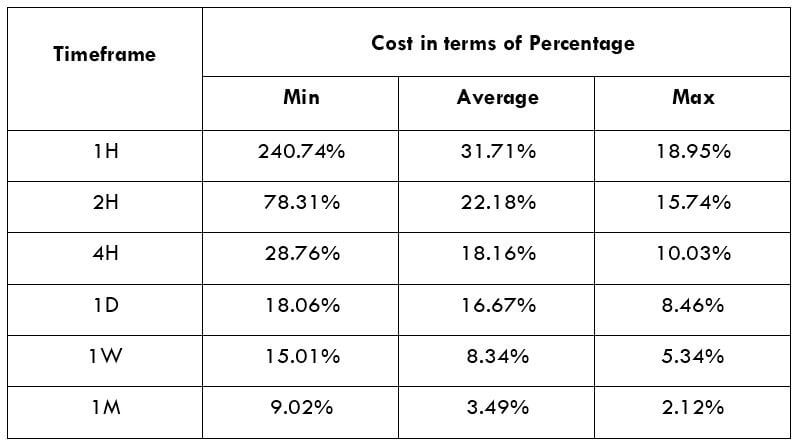
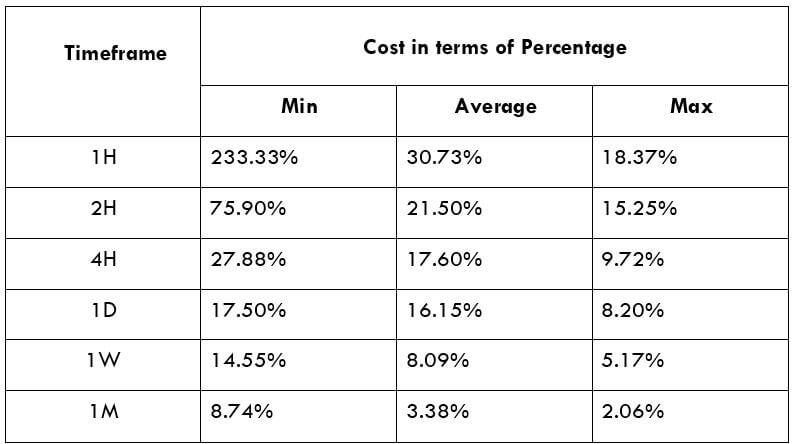
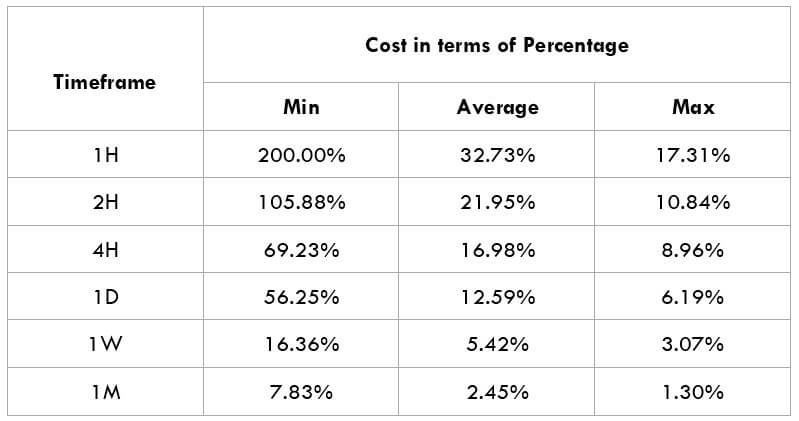
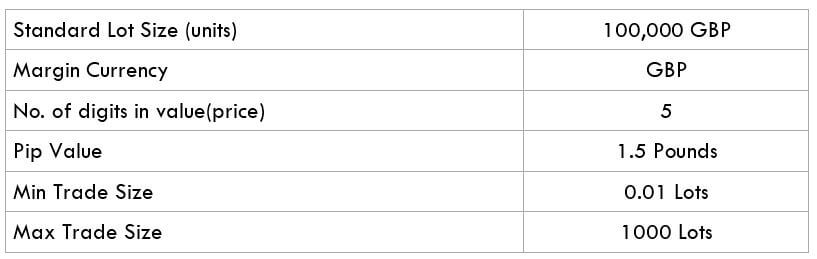
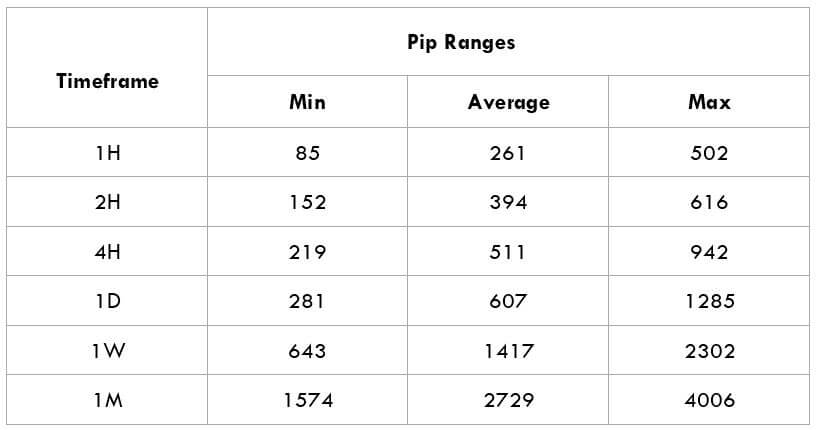
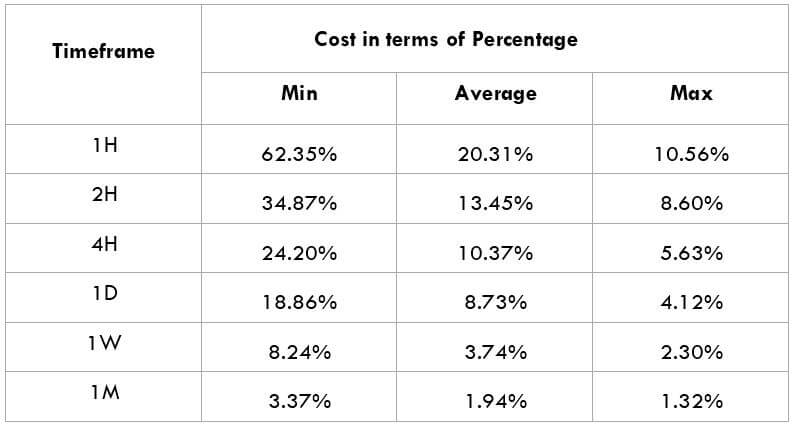
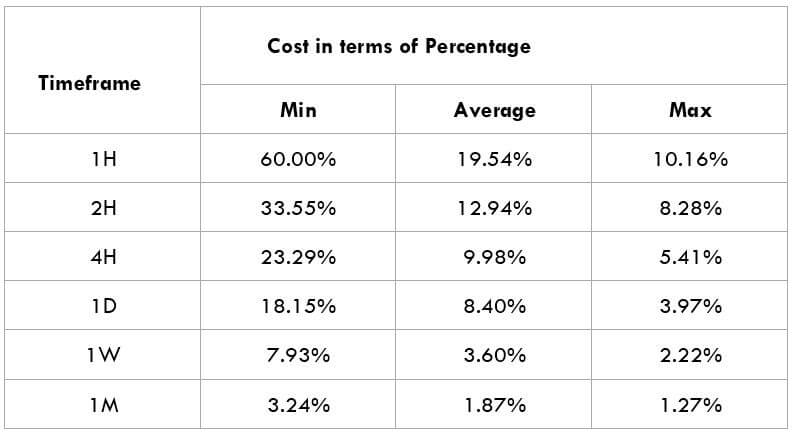
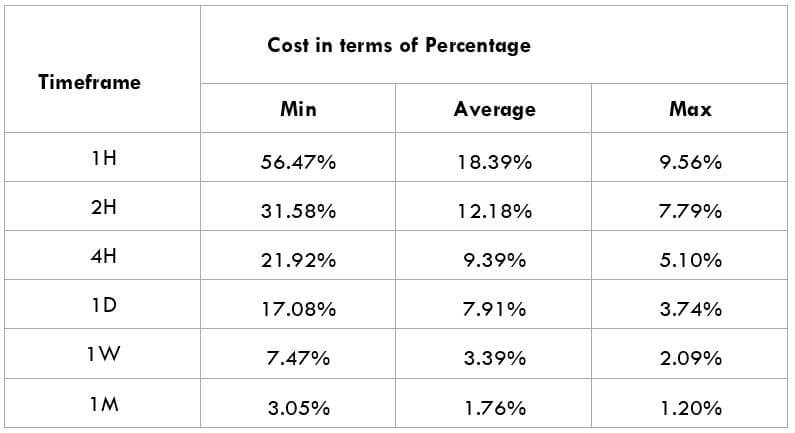
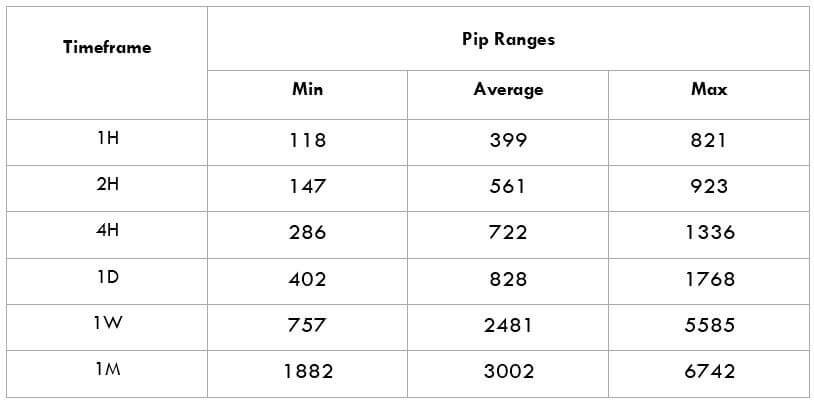
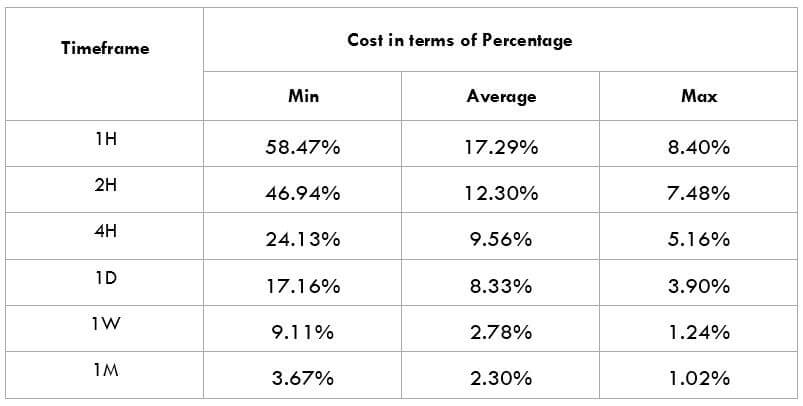
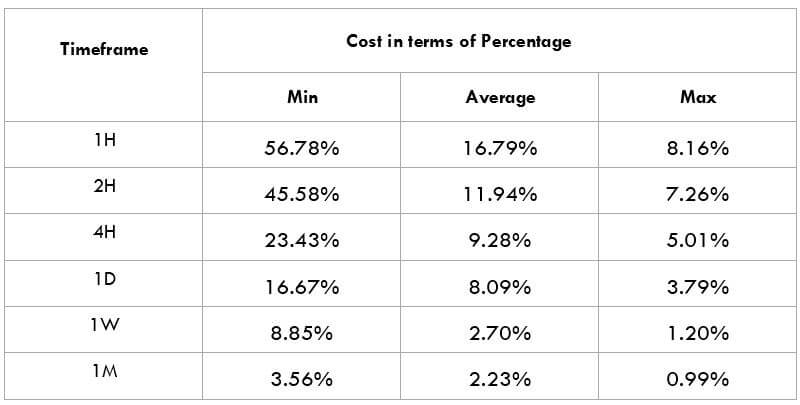
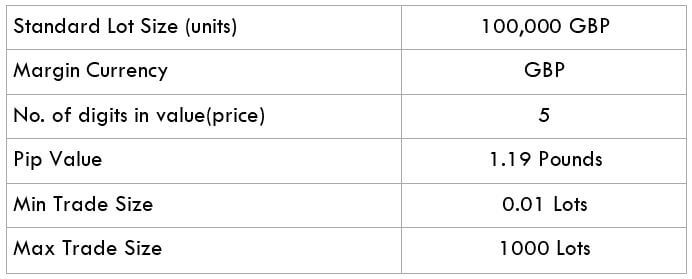
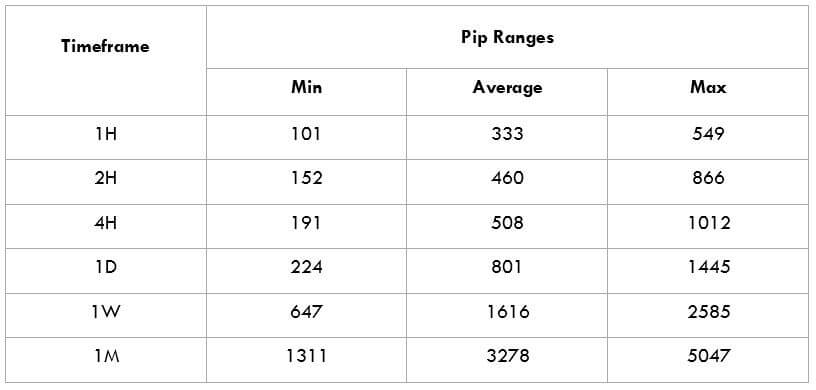
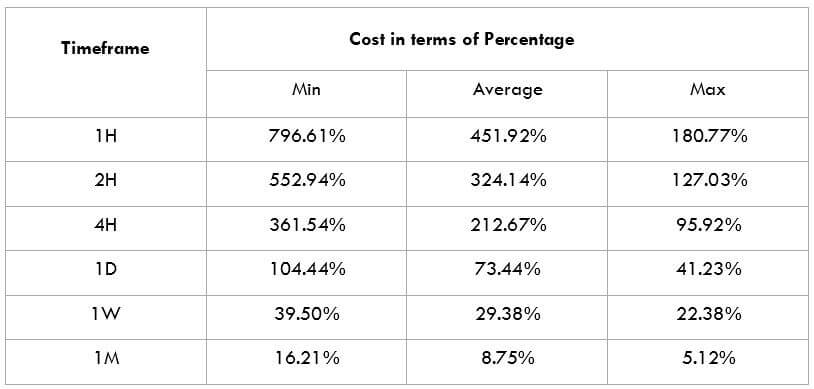
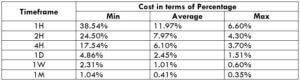
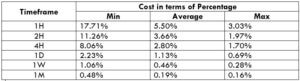
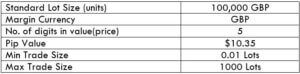
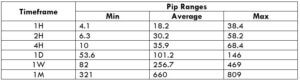
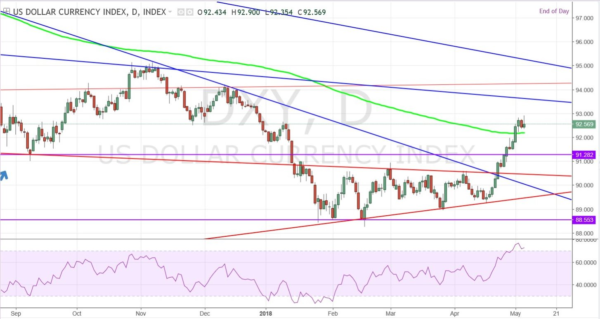
The British pound, whose use spans across more than 5000 years, is the oldest currency in the world. Originating from continental Europe under the Roman era, the official currency of the today’s United Kingdom was once also a unit of currency in Anglo-Saxon England, equivalent to 1 pound weight of silver, dating back to as early as 775 AD. Derived from the Latin word poundus which translates as weight, the name of the currency we use today is still in use.
The symbol £ comes from an ornate L in Libra, whereas the ISO code under which it is recognized globally is GPB. Unlike other currencies, the GBP has endured such a vast portion of history and now tells a tale of how a currency once set the grounds for the future. In 928, the first King of England, Athelstan, adopted sterling as the first national currency, and one unit of the currency could actually buy off 15 heads of cattle. The name sterling, however, came to use only after the Norman Conquest, initially referring only to pennies and not pounds. This anterior name is of vague origin due to its connections to esterlin, a Norman word for little star, and lesterling, an Arab word meaning money.
In the late 1600s, upon suffering naval defeat in the Battle of Beachy Head, King William III established the Bank of England to fund the war with France. As the first central bank ever created, the Bank of England and the British helped create laws and principles which are today considered essential for regulating currencies. In 1717, for the first time in history, the country defined the currency’s value in terms of gold rather than silver, and the gold price of £4.25 per fine ounce set by Sir Isaac Newton lasted throughout most of the following two hundred years.
The country first adopted the gold standard in the 1800s, supporting the idea that the nation should back up its currency with an equivalent quantity of gold reserves. The United Kingdom briefly left the gold standard in 1914 to support itself during the war, yet the heavy borrowing led to high inflation that considerably devalued the pound. In 1925, Winston Churchill returned to the gold standard only to come off of it a few years later, in 1931, when the sterling once again underwent a significant drop. The 20th century gave birth to another nickname of the GDP, the cable, due to the creation of the first trans-Atlantic telecommunications cable used for stock exchanges between New York City and London. The term became part of today’s vernacular to the extent that the phrase what’s the quote on the cable is understood easily as the interest in knowing how many dollars are needed to buy pounds.
Overall, the British pound holds so much history and truly embodies the qualities of an enduring currency. The British were the first to put together a stable government and currency, which remained a safe haven for hundreds of years. Nowadays, the GBP has lost its previous value and power as it stands approximately third in reserves, right behind the USD and the EUR. The 2016 Brexit led to one of the worst falls of the GBP in history and the attempts to foretell the future of this once great currency seem more challenging than ever before.
The Bank of England
Under the rule of King William and Queen Mary, upon the issuance of the 1694 Royal Charter, the Bank of England was founded in the hope of promoting stability and providing benefits to the people, which are still held as dominant values of the institution. As one of the longest central banks in its entire existence, created right after the Swedish Riksbank, the Bank of England (BoE) served as a model for other central banks around the world. Today the bank’s responsibilities include the issuance of banknotes, control of the country’s gold reserves, and setting the official interest rates. The BoE has a dual mandate consisting of two main objectives – monetary stability and economic stability. The former involves influencing interest rates so as to deliver the objectives of the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), whereas the latter entails ensuring liquidity, together aimed at promoting growth and employment in the British economy.
While the Bank of England bears the responsibility for printing money, it only includes the territory of the United Kingdom, while Ireland, which uses the EUR, is exempt from its authority. What is more, the BoE issues notes in both England and Wales, but Scotland and Northern Ireland can also do the same through several other banks. Coins are, however, manufactured by the Royal Mint, an export mint located in Llantrisant, South Wales. Since its opening by the Queen in 1968, the Royal Mint has been in charge of making and distributing the United Kingdom coins and supplying blanks and official medals. This government-owned institution now makes coins and medals for approximately 60 countries a year.
Another important segment of the bank involves the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) that consists of nine members – the Governor, the three Deputy Governors for Monetary Policy, Financial Stability and Markets and Banking, the Chief Economist, and four external members appointed directly by the Chancellor. These members are selected based on their expert knowledge of economics and monetary policy in order to decide on the best monetary policy action for the Bank of England to keep inflation low and stable. As of March 16, 2020, Andrew Bailey is the Governor, replacing Mark Carney. The new Governor was said to be the favorite choice in a number of media due to his extensive experience in the field of banking and, in particular, previous responsibilities and successes at the Bank of England.
Some say that the BoE has been the main pillar of support of the United Kingdom during the past crises. The country’s economy is believed to fall into crisis approximately every 70 years and some past events, such as the Great Fire of London or the aftermath of the tea hegemony collapse, can support this viewpoint. It appears that every time the economy collapses the Bank of England steps in to provide support and safeguard the country and the currency against complete destruction. The Bank of England now has another task of helping the UK’s economy withstand the outcomes of Brexit-related decisions, which will be discussed later in the text, as one of the strongest factors impacting the country in the past few years.
UK Economic Reports
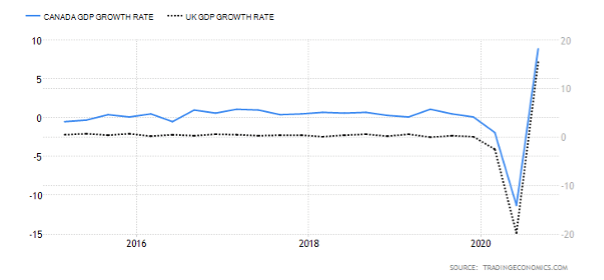
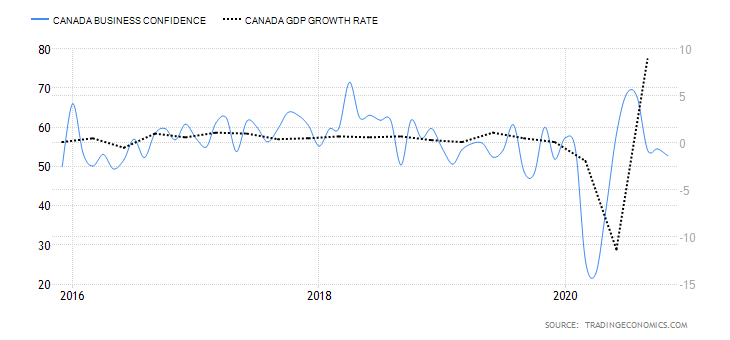
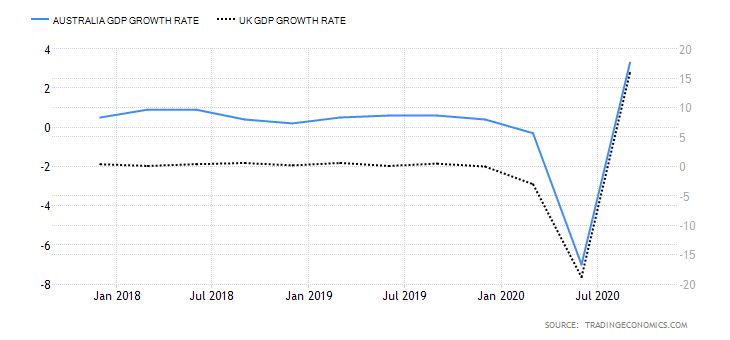
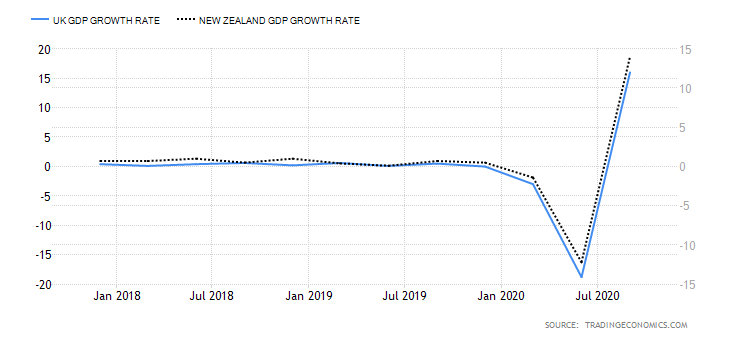
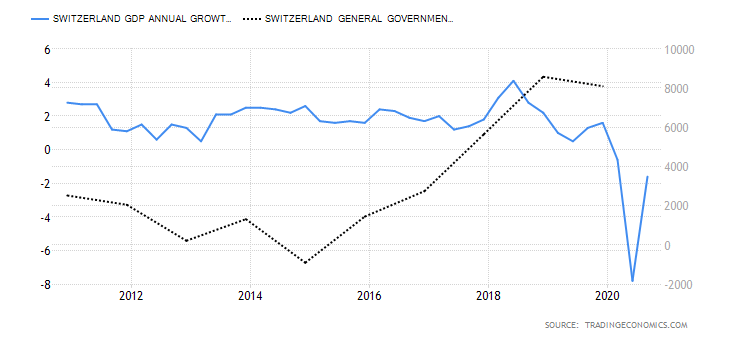
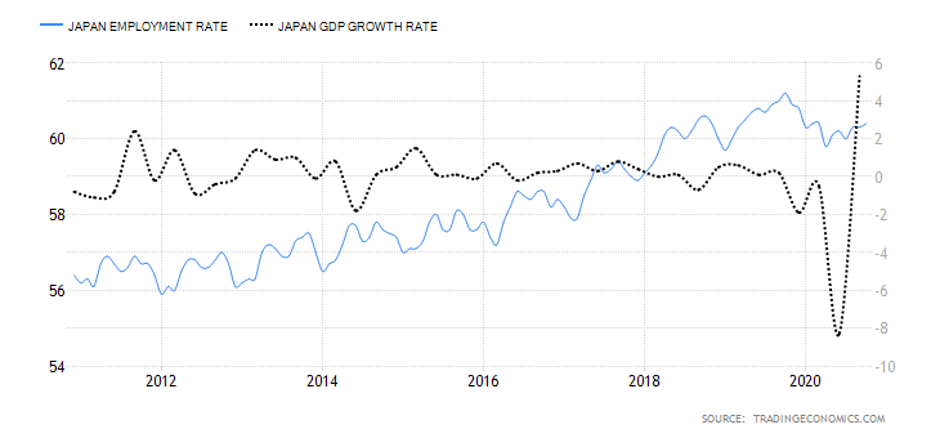
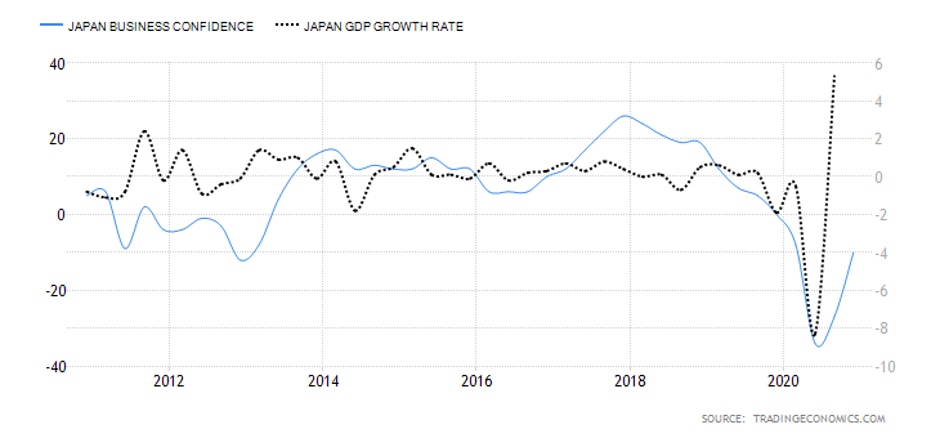
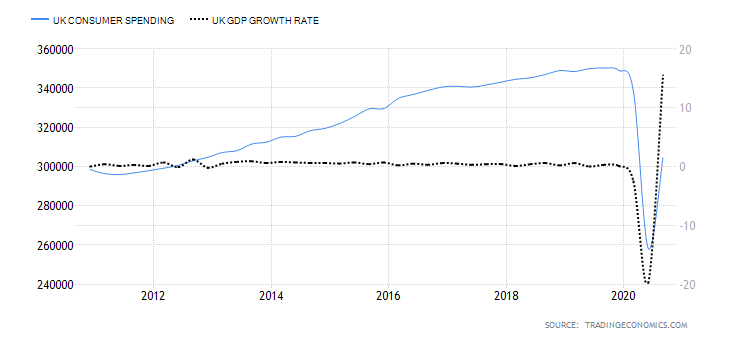
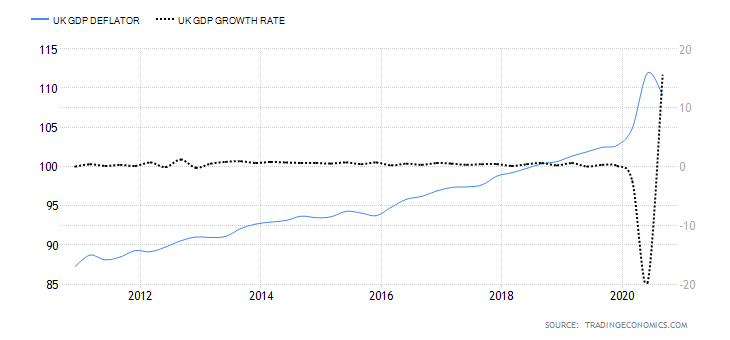
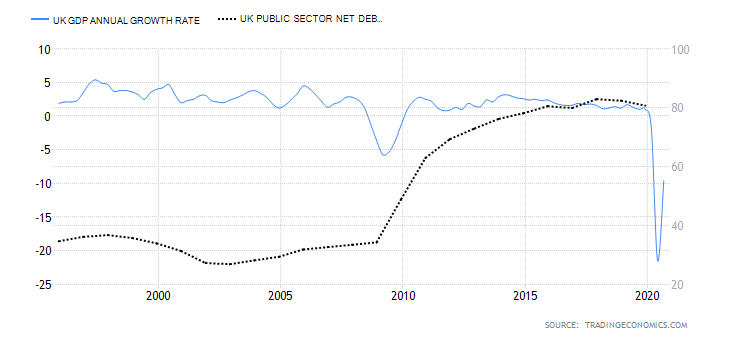
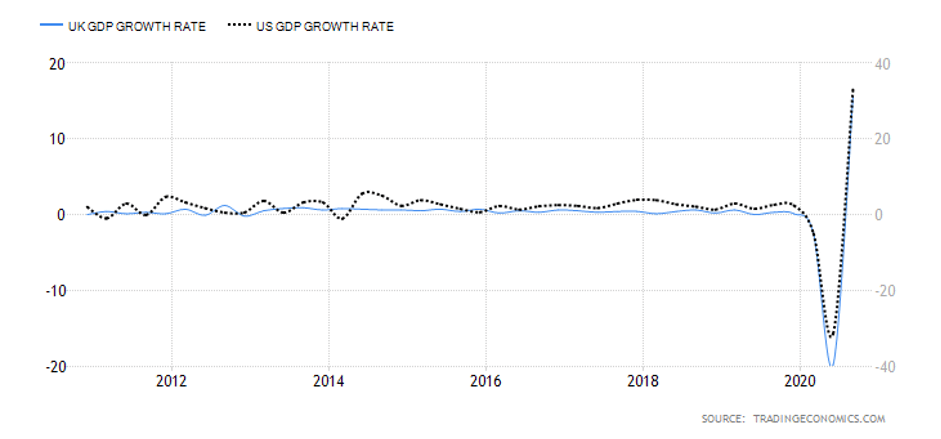
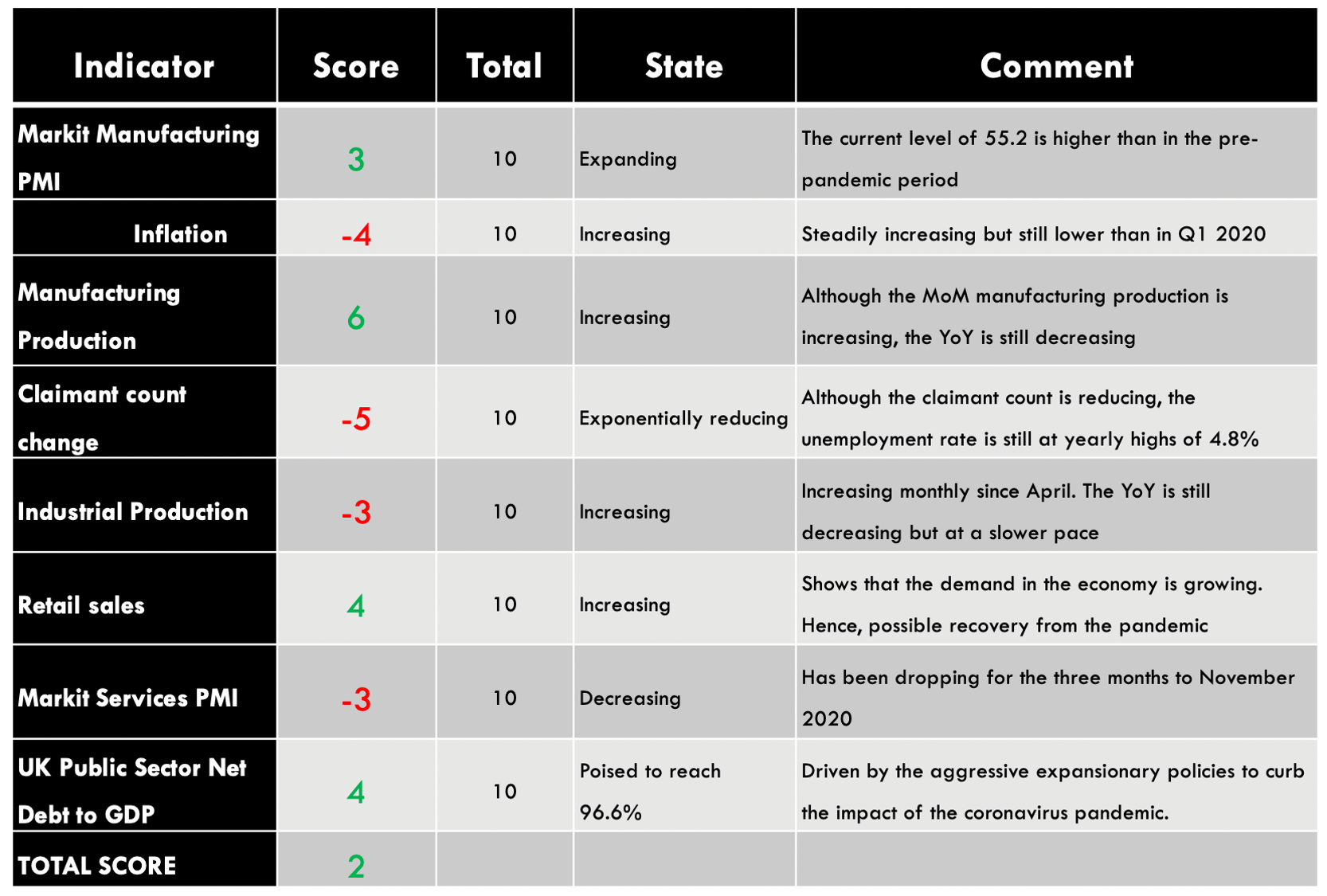
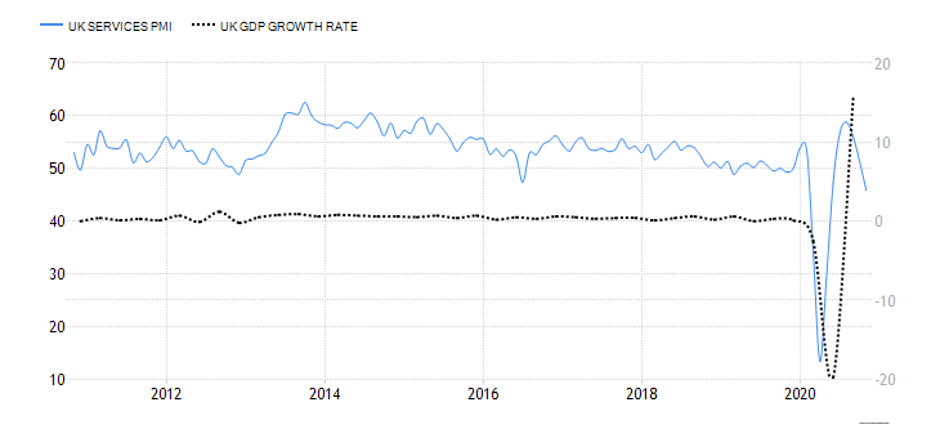
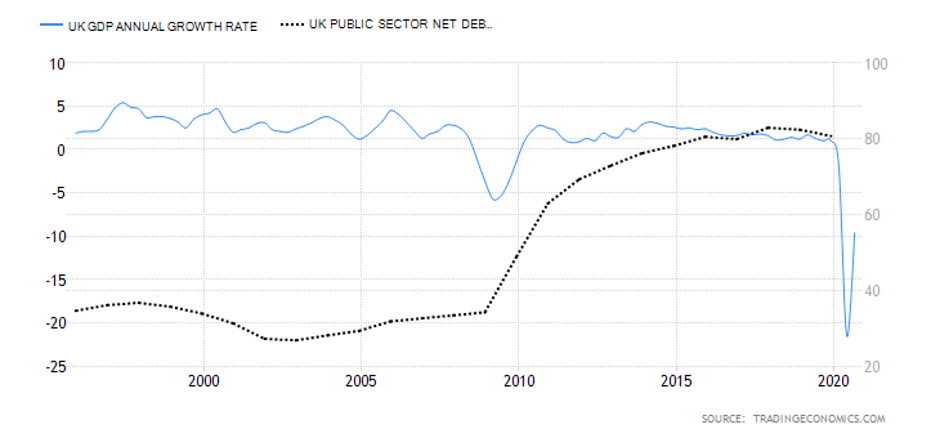
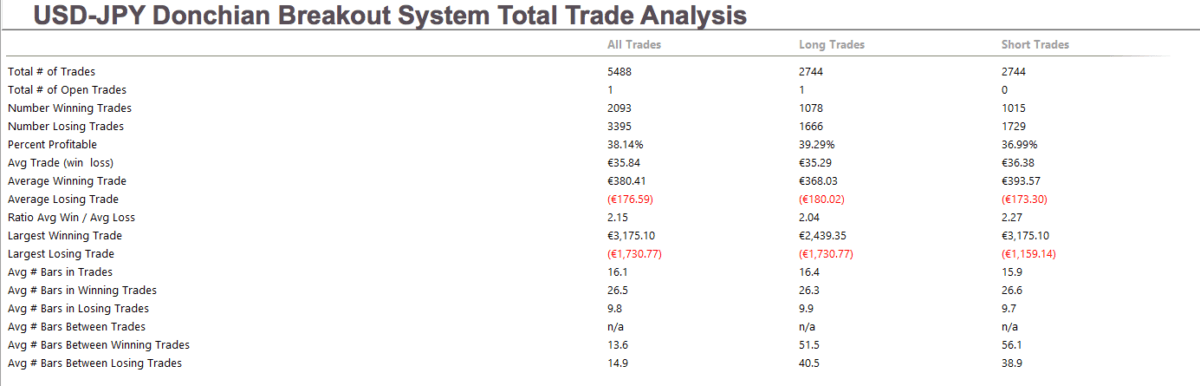
The GDP reports come out in three stages: the initial, the actual, and the final. Similar to the US GDP reports, the preliminary estimate is the most relevant piece of information as it first produces insight into the country’s economy. At the same time, this initial GDP report is also the least accurate, which is why the data is then revised in the following two reports. The current data shows how GDP is estimated to have fallen by a record of 20.4% in Quarter 2 (April to June), which was the second quarterly decline in a row after falling by 2.2% in the first quarter (January to March) this year. Despite the poor performance in the second quarter, the UK’s economy did see some improvement in June upon the easing of governmental decisions on lockdown (see the chart below). Currently seen as the worst in all G-7 states, the country’s GDP is estimated to fall by 8.3% in 2020, with a 6% annual growth rate anticipated in 2021. The UK’s economy is believed to rely heavily on social outdoor activities and the implications of the pandemic and related decisions can already be felt, as seen from the latest GDP report.
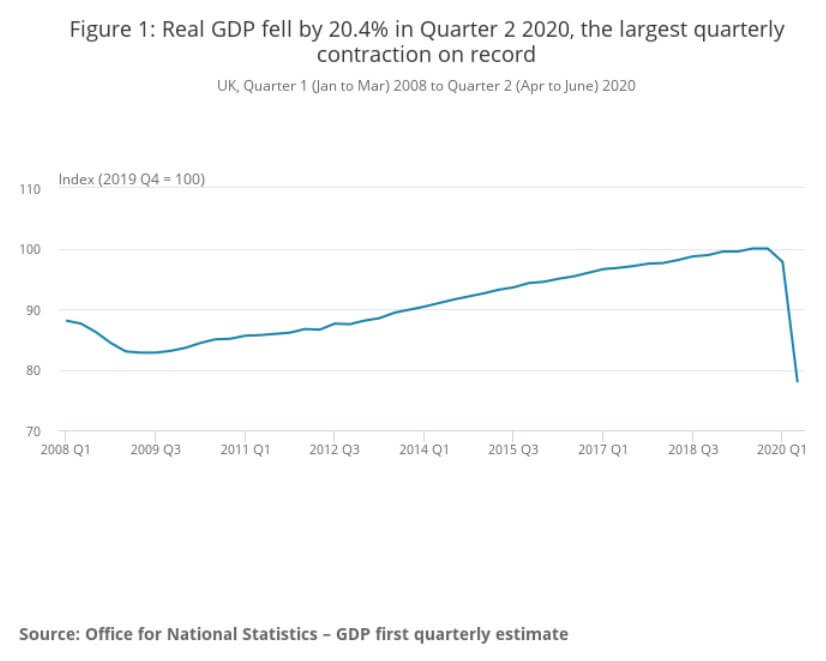
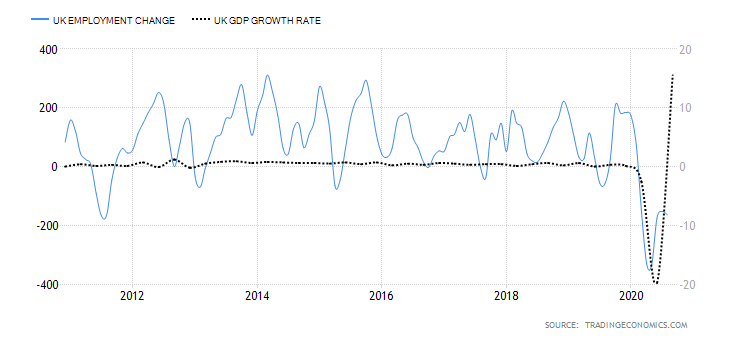
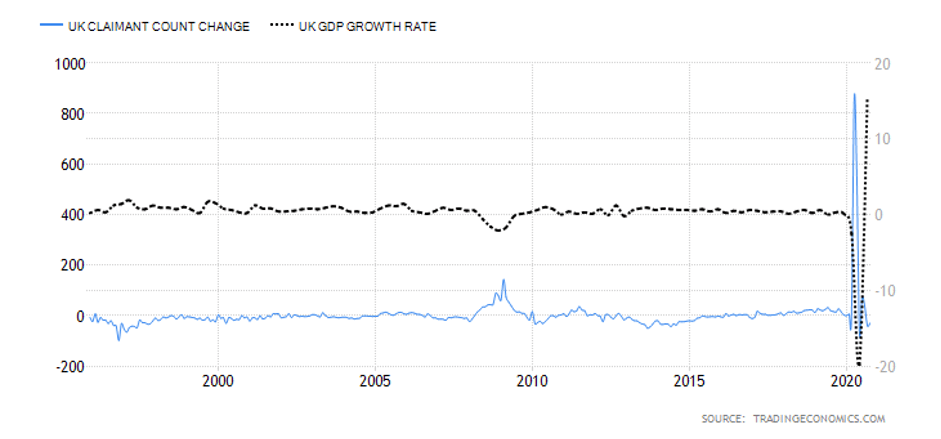
Claimant Count Change is a monthly report that provides information on the employment changes upon measuring the number of unemployed people in the UK during the reported month. It is interesting to note how the Claimant Count Change averaged 3.70 thousand between 1971 and 2020, reaching an all-time high of 858.10 thousand in April of this year. The last report issued on August 11, 2020, signaled weakness in the labor market, with the number of people claiming unemployment benefits having gone up by 94.4 thousand to 2.7 million in the previous month.
- Inflation/Monetary Policy Reports
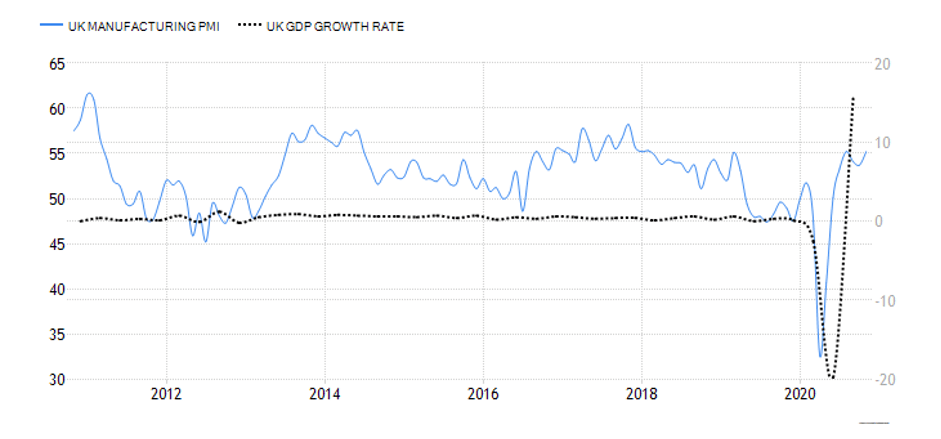
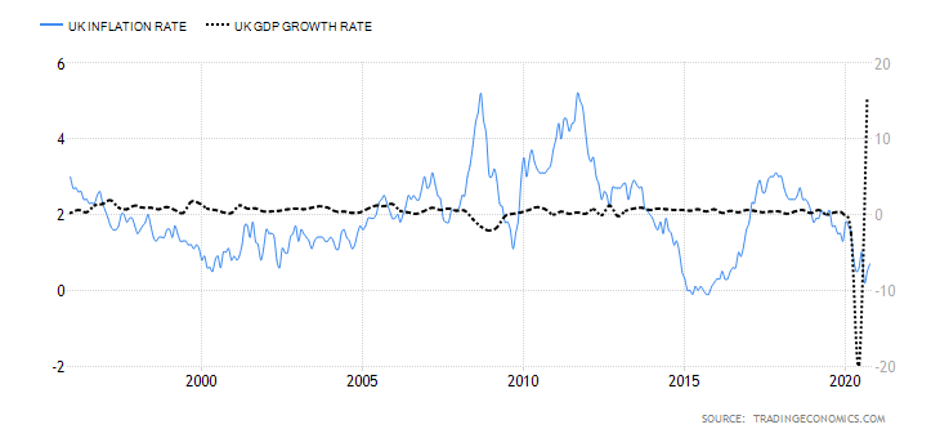
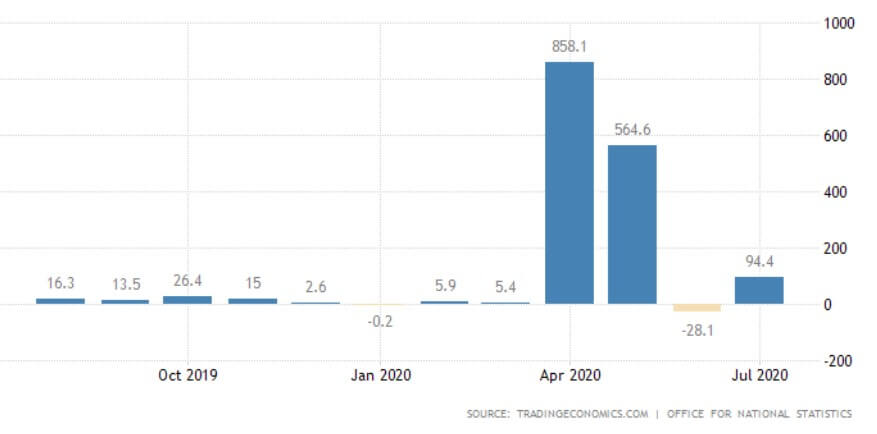
The quarterly Inflation Reports comprise the Monetary Policy Committee’s economic analyses and inflation forecasts that are further utilized in making interest rate decisions. As of November 2019, the Inflation Report is called the Monetary Policy Report, yet its purpose has remained the same. The last Monetary Policy Report that came out on August 6, 2020, reported the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on reducing jobs and incomes in the country. The report includes information on the assistance provided by the Bank of England to UK citizens. Moreover, the Monetary Policy Report states where the economy is in comparison to the overall monetary policy of the BoE. The Bank of England has already put effort into returning inflation to the 2% target which aligns with its 1989—2020 average of 2.53%. Inflation is considered as one of the key indicators used in trading in the spot forex market. Traders are generally advised to keep informed in order to understand the situation in the country at the time for trading.
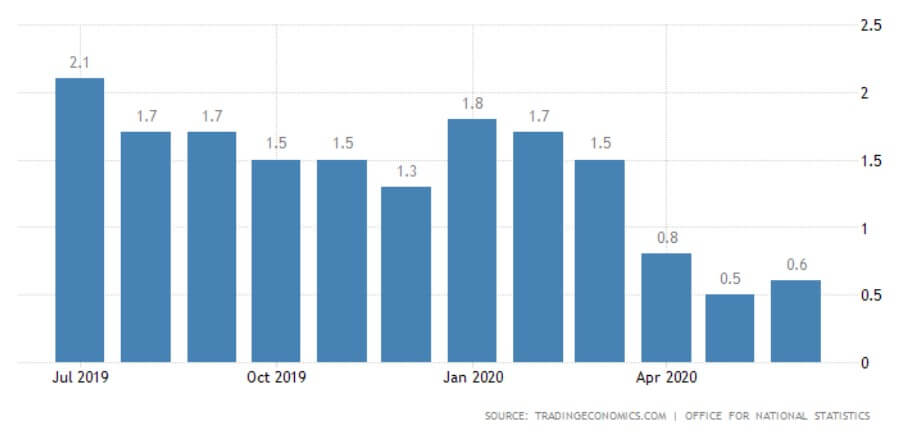
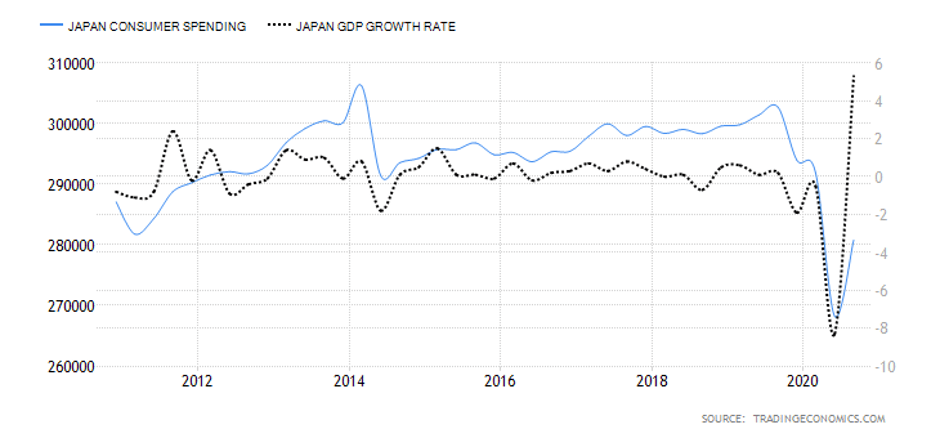
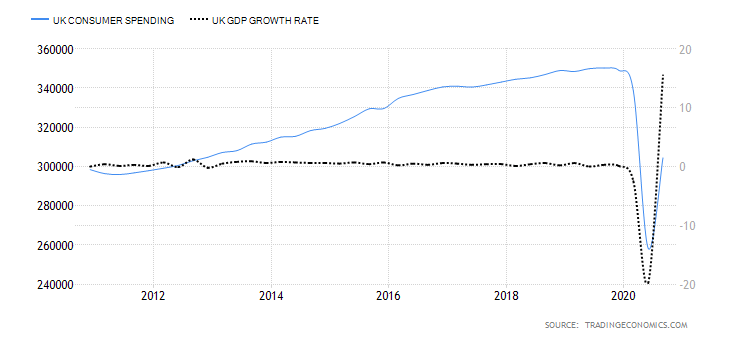
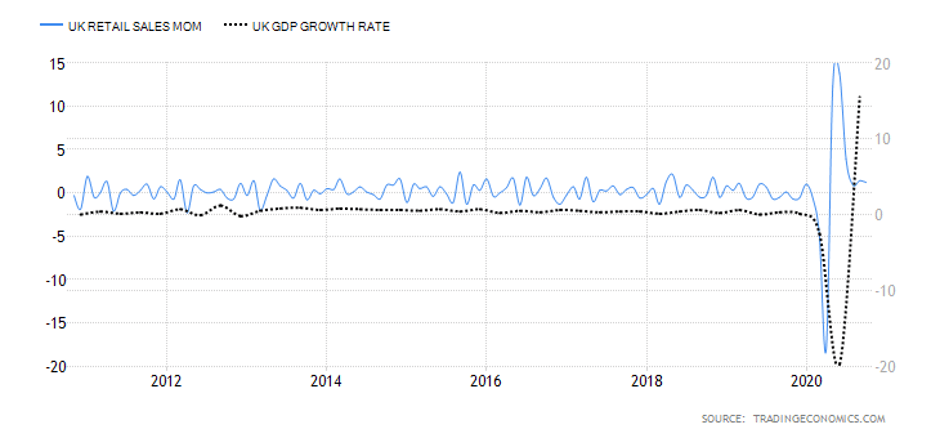
The Retail Sales report is an in-depth analysis of the latest macroeconomic and consumer trends affecting the UK retail industry. The last report issued in June 2020 indicated a 13.9% retail sales increase, which marks the second monthly increase in a row, resulting from the early economy recovery stages from the effects of the pandemic. Quite interestingly, while the United Kingdom’s retail sales averaged 0.23% between 1996 and 2020, they reached their all-time high of 13.90% in June 2020 and a record low of -18% in April of the same year. The next release of the report will be issued on August 21, which should give more information on whether the previous two-month increases will continue, further maintaining total sales to the pre-pandemic levels.
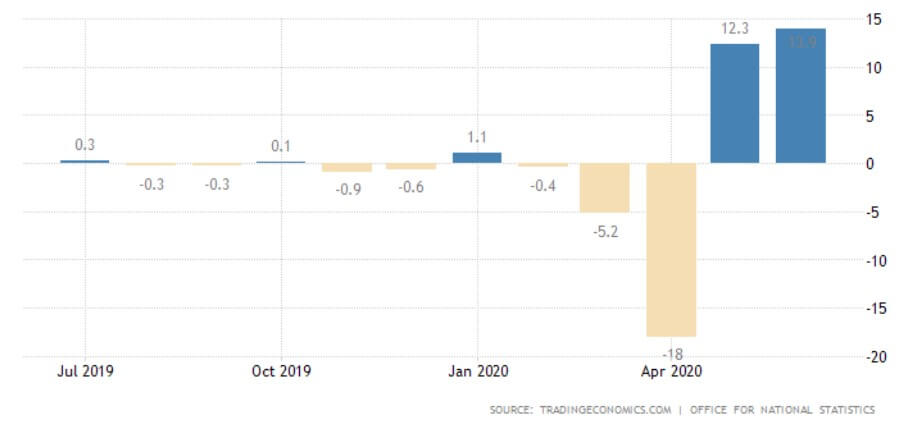
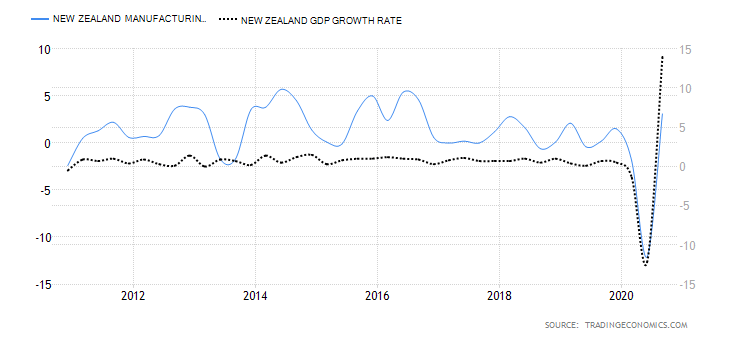
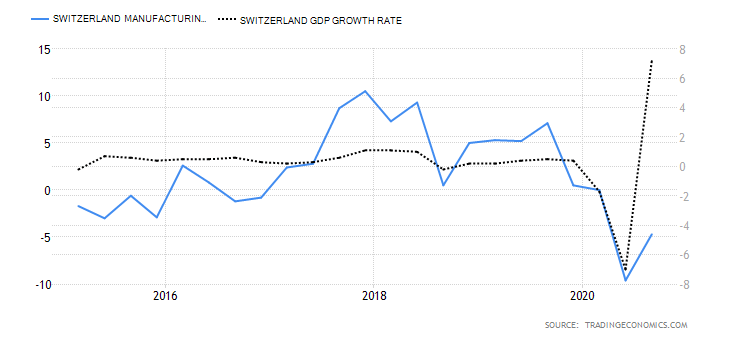
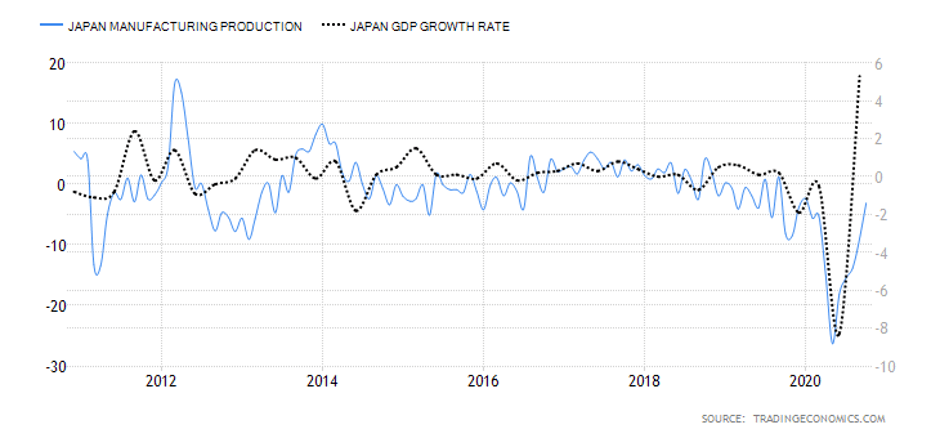
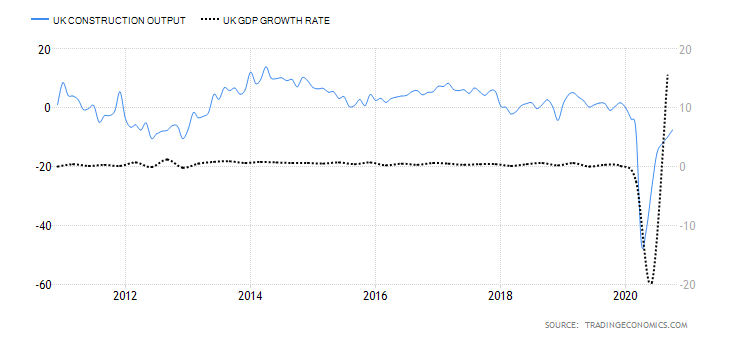
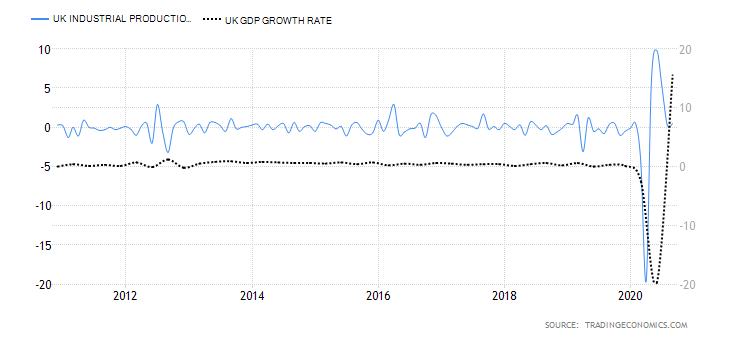
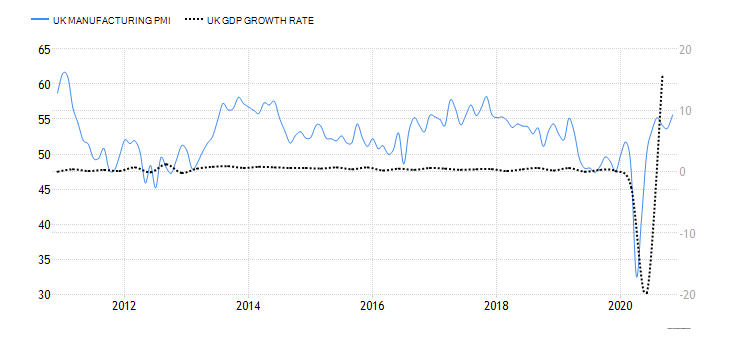
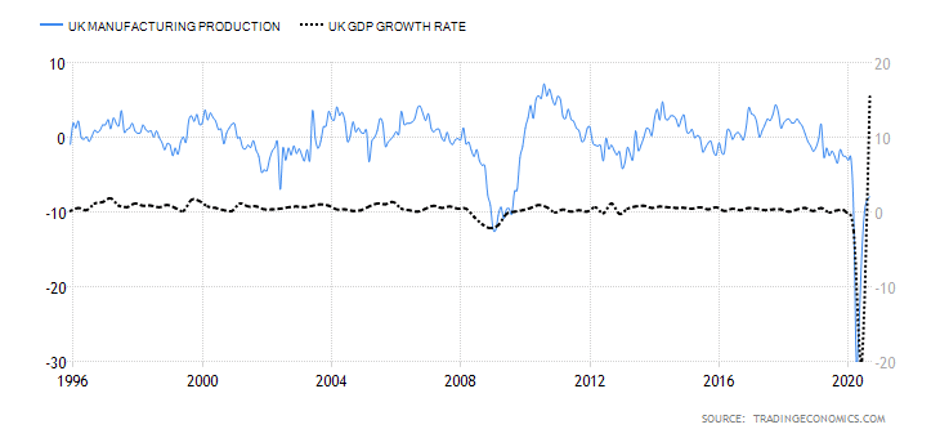
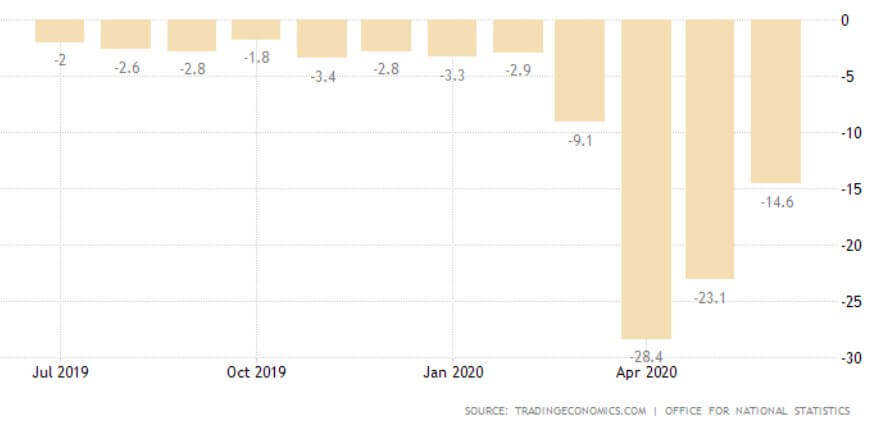
Deemed the most vital indicator for the UK manufacturing industry, the Manufacturing Report reveals the manufacturers’ contribution to the country’s regions with regards to past 12-month output, jobs, investment, and business confidence and export. Over the last year, the UK has been largely affected by the attempts to leave the European Union and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, which have caused prolonged industry volatility. UK manufacturing production’s 1969—2020 average of 0.42% was exceeded by far in April of this year with an all-time low of -28.40%. The last statistics in June indicate a fall of 14.6% in comparison to the previous year, but the forecasts seem to be more positive for the following 12-month period.
The Most Traded Pairs
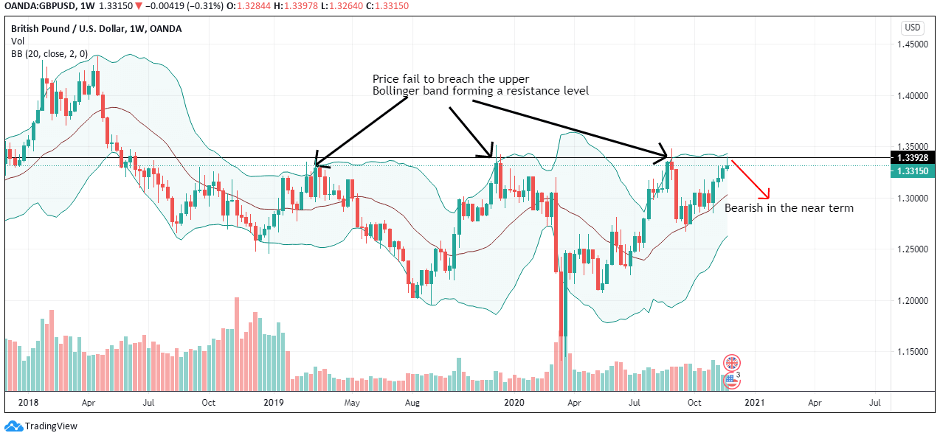
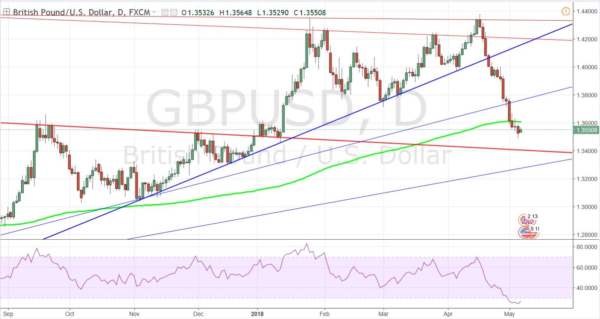
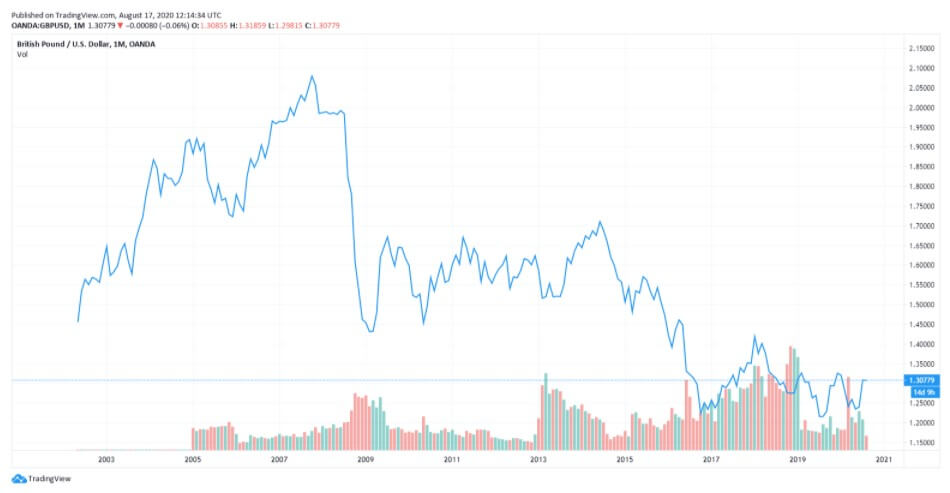
GDP/USD or the cable is probably the most frequent currency pair traded that, like EUR/GBP, has a lot of volume with an estimated 15% of the total daily volume of forex transactions. As it comprises two of the most traded currencies in the world, the focus of attention is often pointed towards this particular cross. This week’s economic calendar is rather quiet and the chart below reveals a continuation of a bullish pattern. Nonetheless, with the Brexit talks ever-present, the pair could overall entail slightly more volatility than usual.
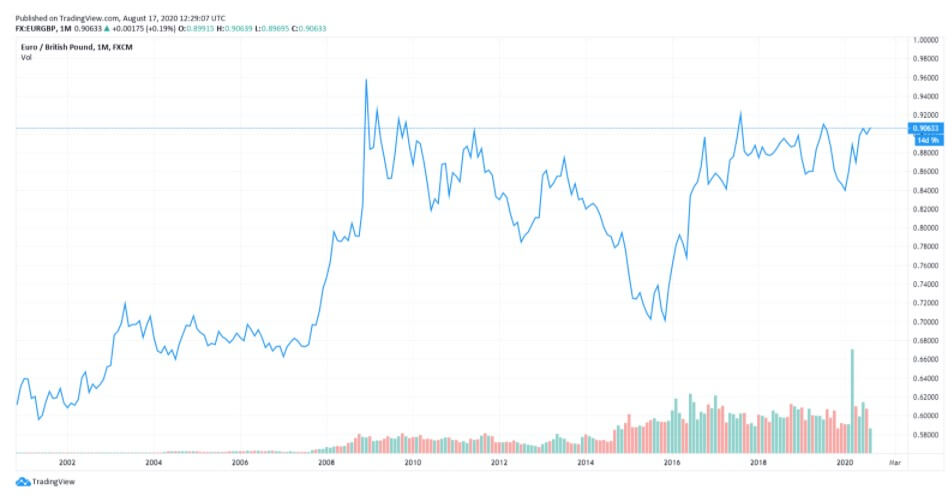
These two major currencies rank as one of the top eight most frequently traded currencies in the world. From the perspective of daily forex volume, the EUR is second only to the USD, with a market share of 39.1%, whereas the GBP ranks fourth with a 12.9% market share. This currency pair is said to be significantly less volatile than other EUR- or GBP-based crosses due to the economic closeness and interdependence between them. Nonetheless, the (ongoing) changes in monetary policy between the central banks of the UK and Europe can make this pair highly sensitive.
The GBP/JPY currency pair is said to be quite a volatile pair. As a low yielding currency, the JPY is commonly used as a funding currency of trade. Therefore, since the GBP belongs to one of the biggest economies in EUT, this particular pair can reveal the state of the global economy. It also reveals risk-off moves in the market resulting in the development of strong trends exceeding thousands of pips.
The lower volatility of the pair is said to originate from the economic and geographic proximity of the two nations with both the GBP and CHF used as reserve currencies around the globe. This pair along with the ones mentioned above fall under the more liquid group of pairs, whereas outside this particular set, one can find some more exotic crosses.
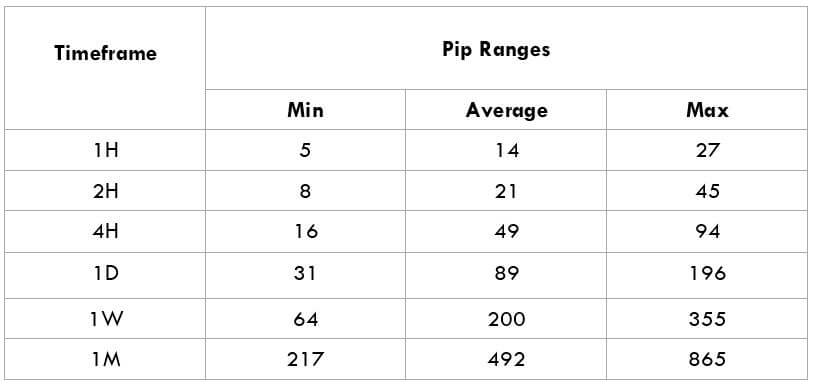
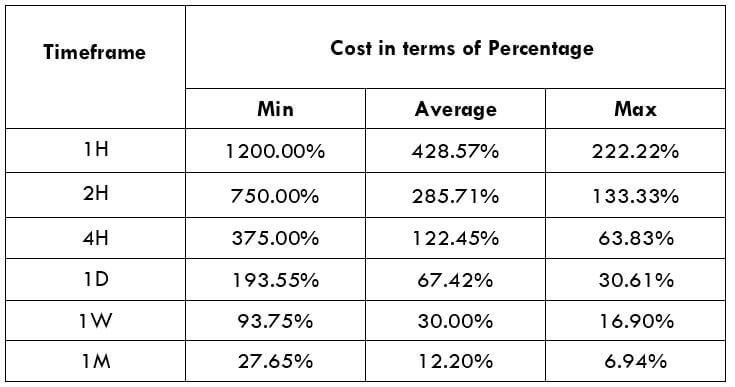
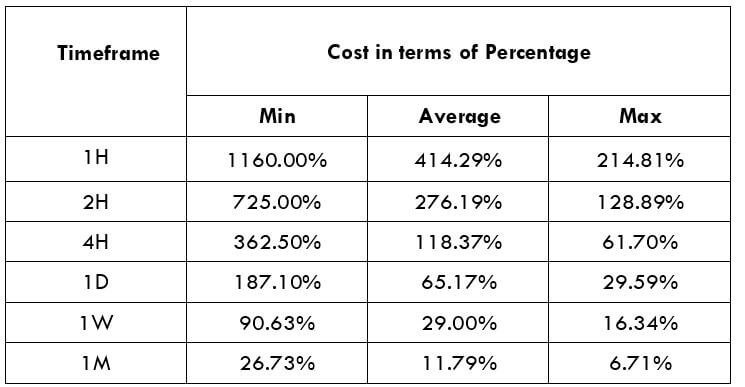
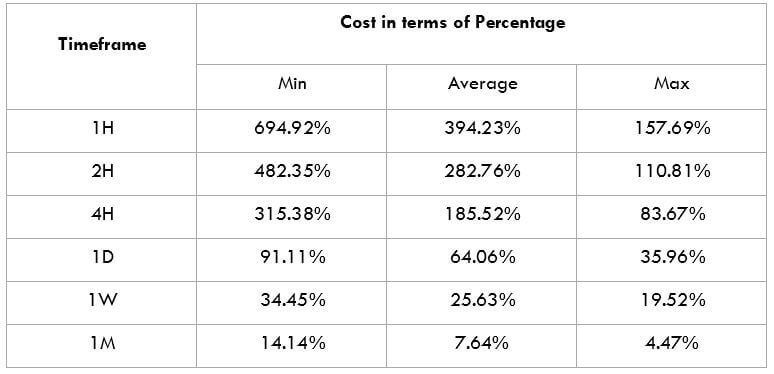
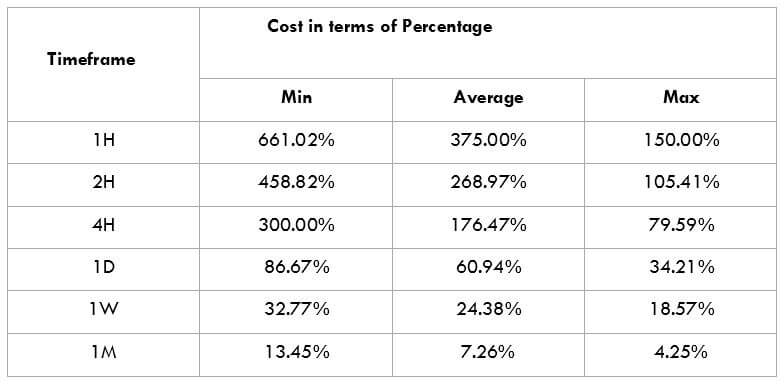
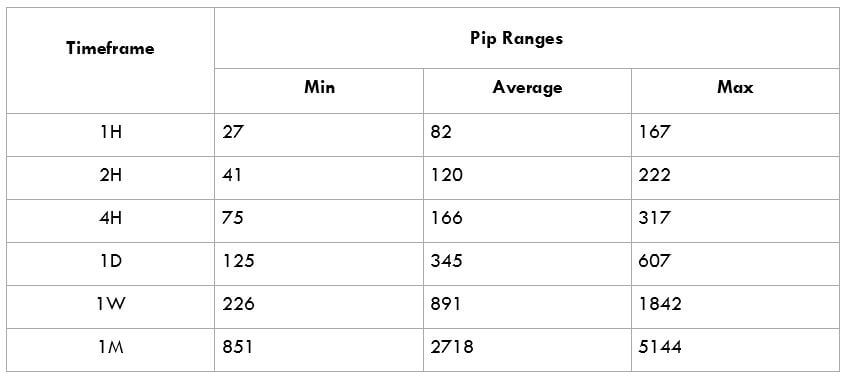
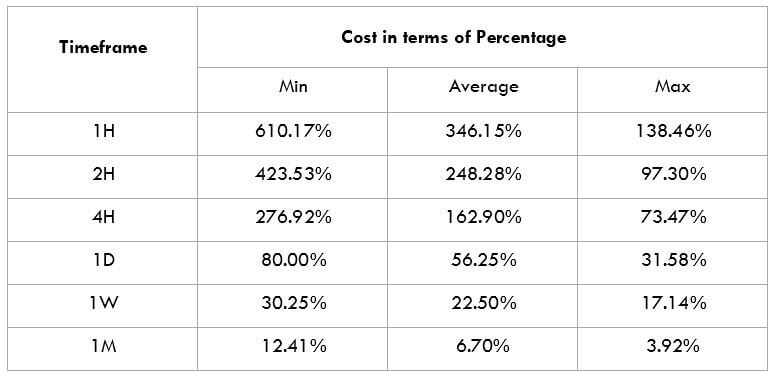
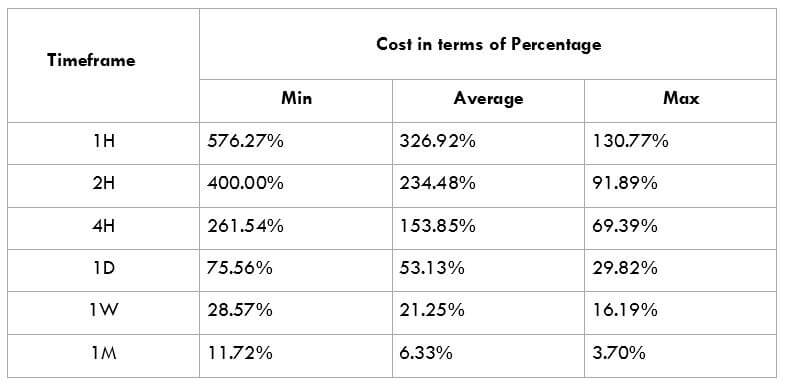
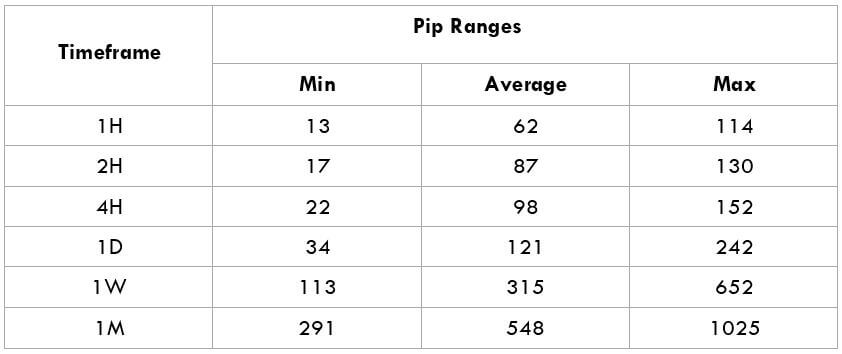
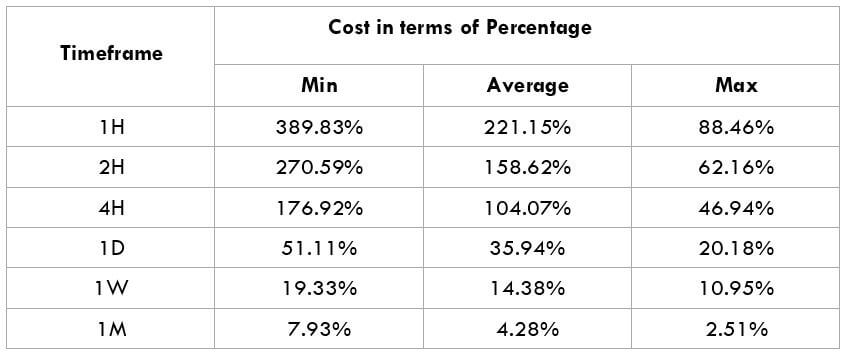
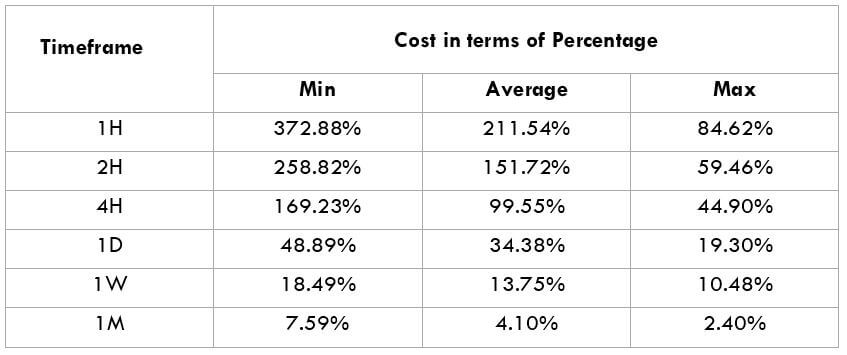
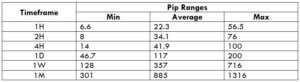
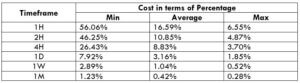
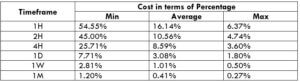
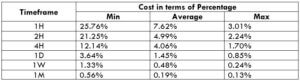
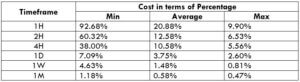
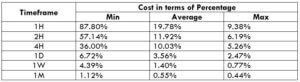
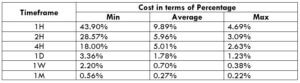
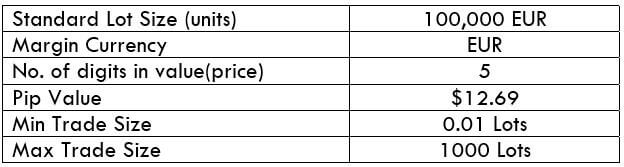
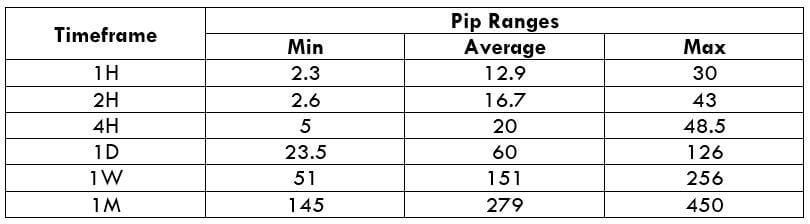
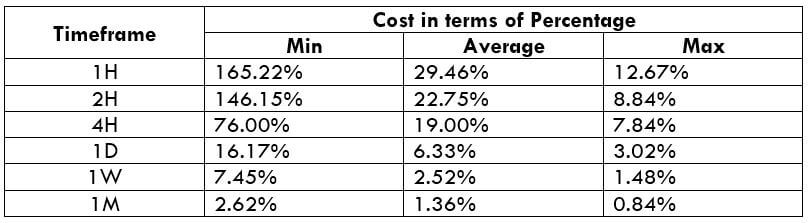
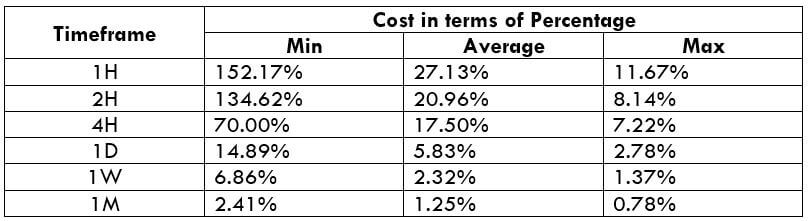
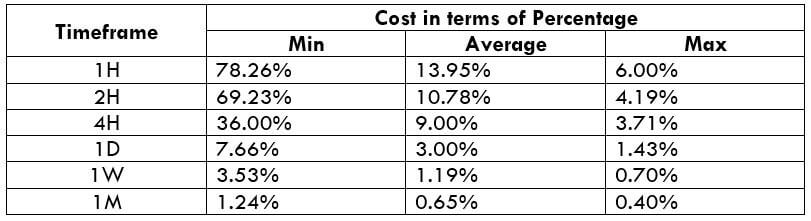
This currency pair reveals a lot of big moves that signal a much lower value of 100 pips than in pairs such as NZD.JPY for example, where 100 pips would equal a 1.3% move. In this currency pair, however, the same number of pips would turn out to be only a 0.5% move up or down. The percentage return will demonstrate the amount that a trader can expect to get. A number of GBP crosses typically entail many pip moves and, whenever the GBP is traded, smaller position sizes are to be expected owing to the fact that the base currency is as high.
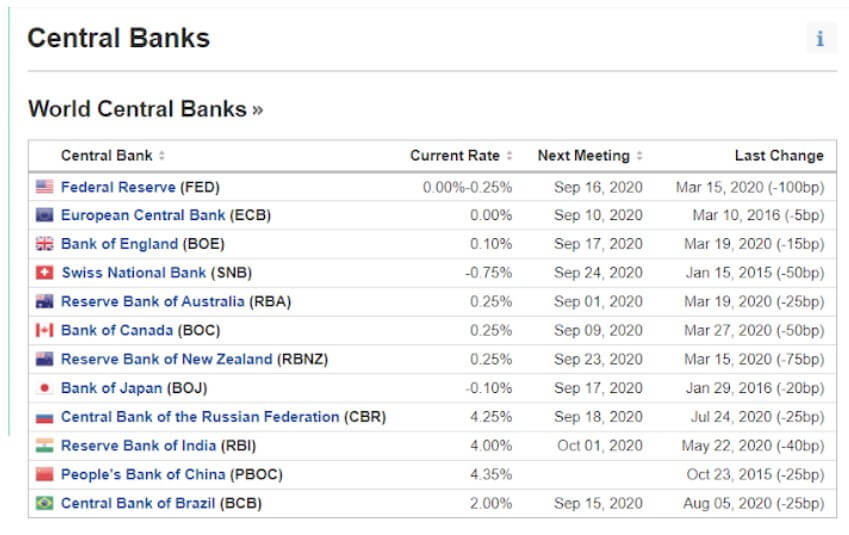
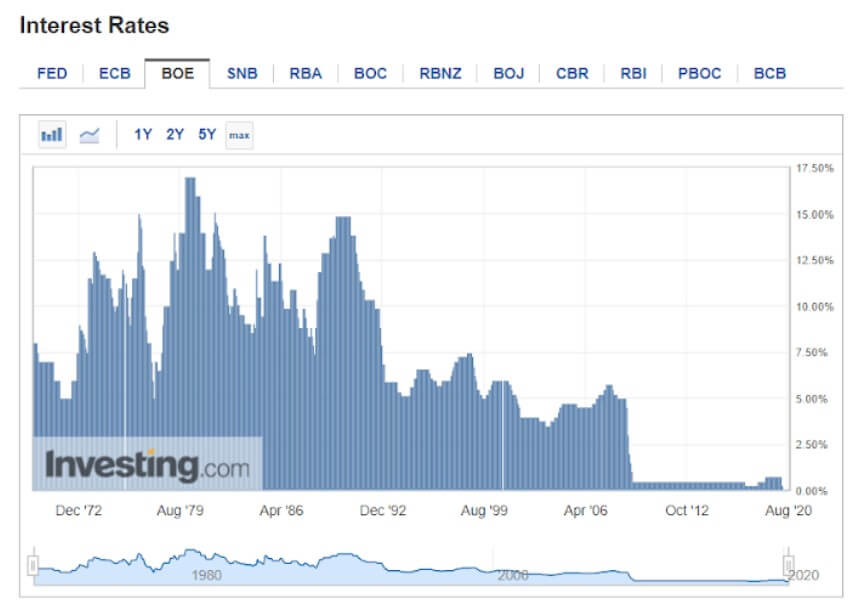
Interest Rates
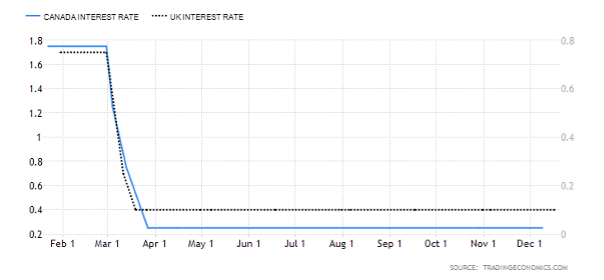
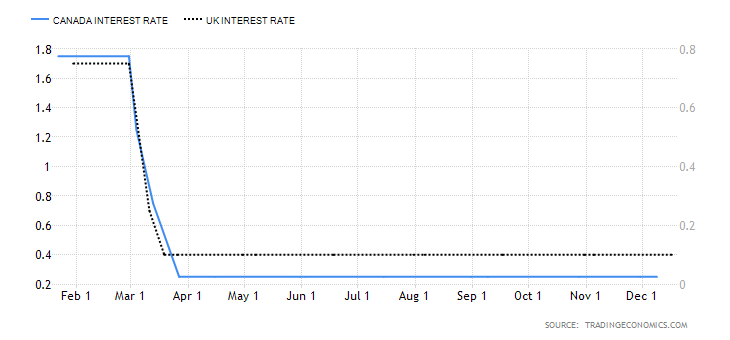
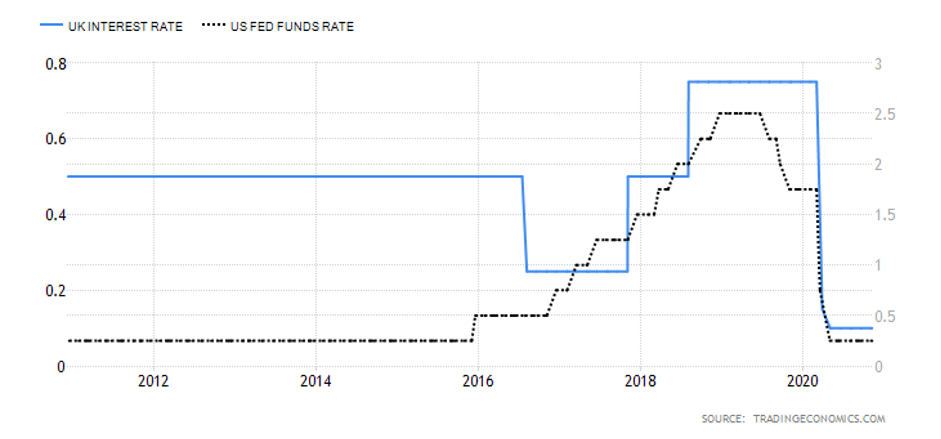
The GBP is generally believed to be doing better than the USD or JPY similar to other risk-on European currencies. Compared to other central banks, the Bank of England’s current 0.10% does reveal it to be one of the lower interest rates on the spectrum. At the same time, the current interest rate of the United Kingdom poses as a record low in the 1971—2020 average of 7.36%.
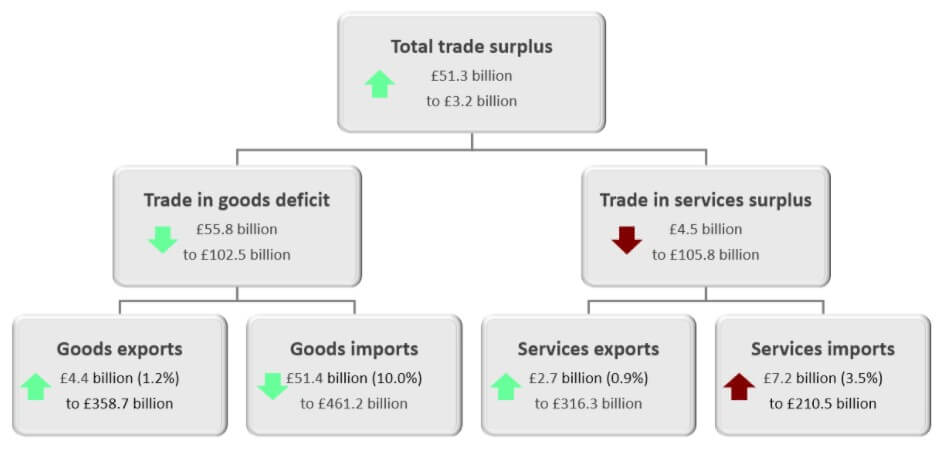
Trade Deficit
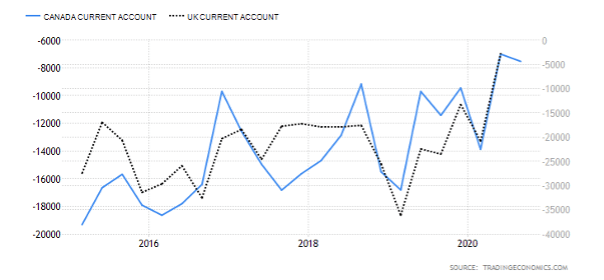
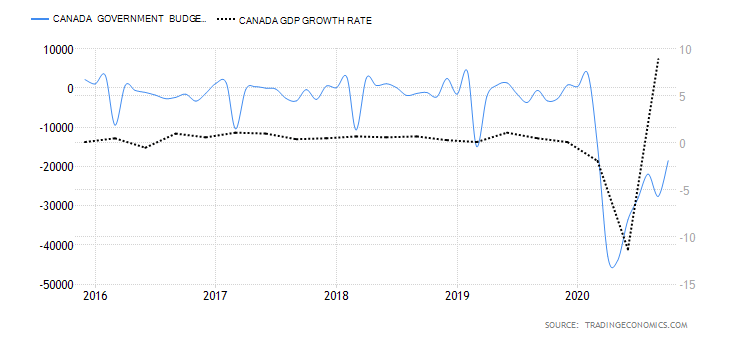
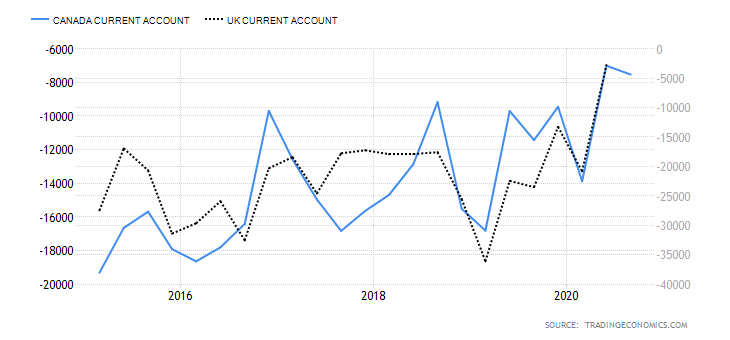
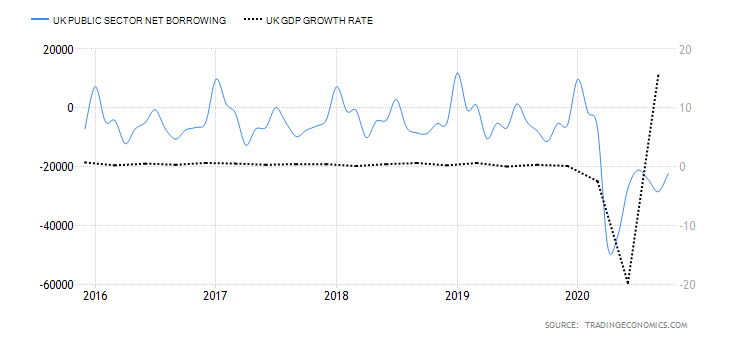
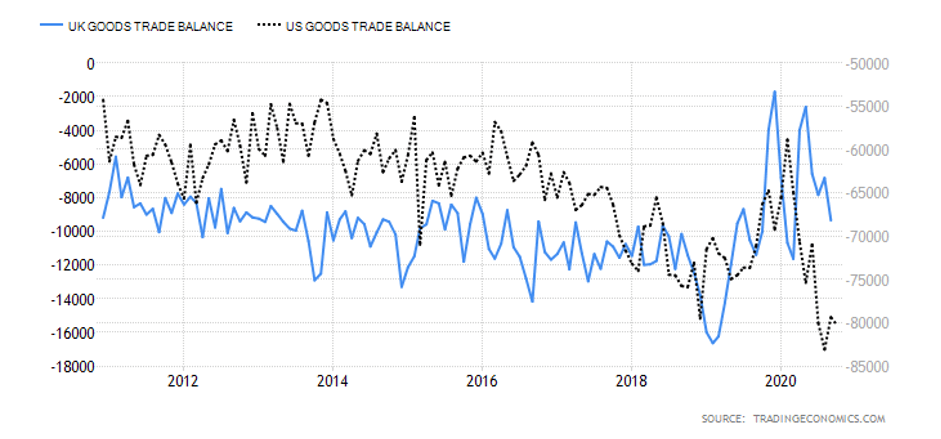
Like the US, the UK imports more than it exports which leads to large trade deficits with foreign countries. In April of 2020, the total trade deficit of goods and services, without non-monetary gold and other precious metals, dropped down to 7.4 billion GBP in the past 12 months, with imports falling by 34.6 billion GBP and exports falling by 7.8 billion GBP. The total trade deficit for March 2020 was revised up by £2.7 billion to £4.0 billion, driven by a £2.2 billion downwards revision to services imports. These revisions also include the impact of the adjustments of GDP balancing applied to component series (including trade) to improve the alignment of the quarterly GDP position. The overall changes in the trade of the United Kingdom are presented in the image below and were certainly impacted by the strained relations with the EU and the overall state of the global trade under COVID-19.
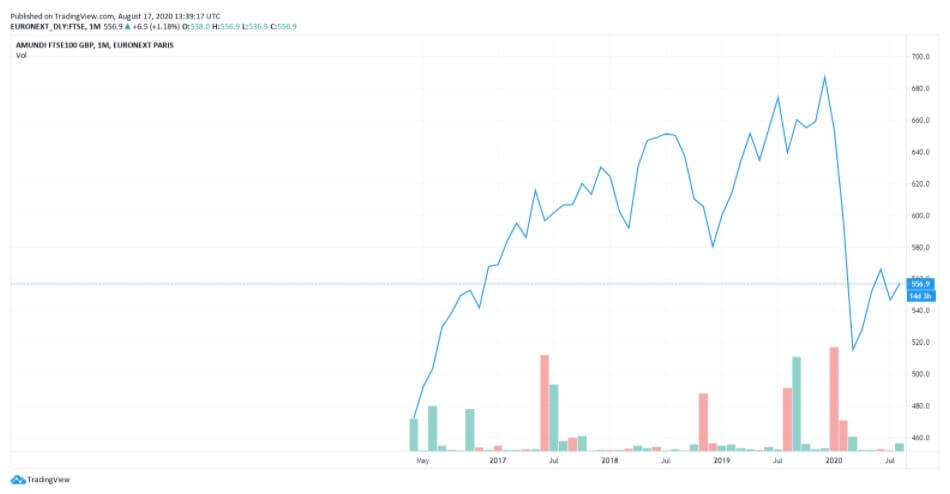
Economic Activity
In order to understand the general state of the economy of the United Kingdom, one should look into the previously discussed GDP reports as well as FTSE (Financial Times Stock Exchange). FTSE 100 is the index of the 100 companies listed on the London Stock Exchange that will generate insight into the UK’s stock market. The chart below is an example of how the set of indices can provide market participants with information on the performance of the UK equity market. The current situation seems to have improved since the major drop in March of this year, but the likelihood of the return to the pre-pandemic state is still questionable.
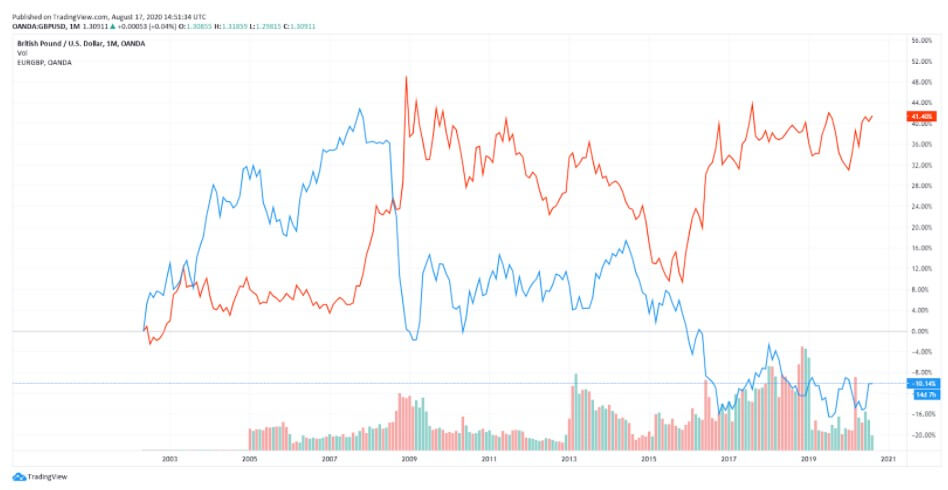
Brexit
When Britain voted to leave the European Union in 2016, its currency plunged on world markets and 2020 still offers no actual resolution. The UK has officially rejected the notion of extending the transition period until December 31, 2020. After the video conference between UK PM Boris Johnson, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen, and European Council President Charles Michel, both the UK and the EU came to terms with having more negotiations in the summer months so as to come to an agreement ahead of the EU summit on October of the same year. With both sides showing a willingness to mitigate the tension, the EUR/GBP currency pair seems to be caught in between the risk sentiment and Brexit. GBP improves along with the improvement of risk sentiment, yet the lack of Brexit progress drags the currency in the other direction.
The various currency pair charts above reveal the progression of the GDP across the years. It appears that the UK’s official currency has suffered quite a lot in the past few years. Upon the 2016 referendum, the GBP fell 8% against the USD and 6% against the EUR. The initial hopes of a weaker currency to increase exports and raise demand for the UK goods/services did come through to a certain degree, but the trade deficit is still very much present. The exports have been increased by the weaker GBP and the unexpected increase in import prices has led to a reduction in pay and, therefore, a drop in consumer demand. Some predictions of the future of the British pound are quite gloomy as some economists believe that the GBP could drop to the 1.10—1.19 USD range should the UK leave the EU without a deal.
Furthermore, without the trade agreement, the economy could shrink by 8%, which would lead to an employment crisis. The overall implications of the unresolved relationship challenges between the UK and the EU are already vivid; for example, after the Brexit referendum, the Dow Jones decreased 600 points, removing $2 trillion from the global markets. A sharp increase in the USD versus a weakened GBP and EUR could obstruct US exports, causing difficulty in the US manufacturing sector, already encumbered by the trade war with China. Apart from the US, the JPY was also feared to experience a major surge in value due to investors’ tendency to flock to domestic currency.
The past December election in the UK was believed to be able to bring some relief, yet 2020 witnessed more negotiations and equally unresolved questions. The possibility of coming to a mutually beneficial deal (termed soft-Brexit in the media) may help the GBP surge in the following months. The currency market is expected to remain unpredictable until the resolution of current matters and the economy was publicly described as high risk by Governor Andrew Bailey himself. The long-term consequences of the UK leaving the EU are largely unknown, very much like the realization of the Brexit supporters’ hopes of economic growth and the pound’s appreciation.
The UK appears to be putting extra efforts in maintaining and preserving the economy, especially with the support of 300 billion GBP of quantitative easing. Combined with the COVID-19 pandemic, the UK’s Brexit struggles seem to be magnified despite the country’s attempts to keep the economy under control.
2007 Financial Crisis
The British economy was said to have been booming with UK tourists visiting the US and the financial sector enjoying the golden days before the financial crisis of 2007. The GBP soared from 2002’s 1.40 up to 2.10 USD in October of 2007, when it decreased by 35% to 1.40 USD at the beginning of 2009. The United Kingdom is believed to have been affected by the crisis more than other countries due to several factors: without a big manufacturing base, the economy depended on financial services, real estate, and retail sales for development. The growth was not based on strong grounds and it heavily relied on credit borrowing/lending.
The bubble burst in 2007 and once the housing prices dropped and credit sources dried up, the economy of the United Kingdom was left in dire straits. The impact of the 2007 crisis would remain long-felt with numerous consequences. The moment the big banks understood what was happening, bank-to-bank lending was reduced immediately.
The number of financial institutions that would still borrow discovered that the interbank lending interest rate doubled and the credit ensuring costs increased as well. Once the lending ceased, the effects were already felt across all sectors and especially in the housing industry. The FTSE 100 dropped by 5.5% in January 2008, which was perceived as the greatest loss since the crash of 2001. Soon people found it difficult to pay mortgages, resulting in fewer retail sales. Cutbacks in housing and retail sales were followed by a number of redundancies and unemployment was staggeringly high.
All of the events further aggravated the already weekend UK economy. With such a vast number of people unemployed, there was a decrease in tax revenue and the downturn continued with the fourth consecutive quarterly drop of GDP at the end of 2008.
In the hope of jump-starting the economy, the UK government reduced the VAT rate, but the effects of the crises were already too severe. The 31.3% FTSE decrease in 2009 was the biggest annual drop since 1984 and the economy just kept shrinking. The financial crisis caused a global recession with many assuming that it resulted from the recklessness of bankers.
The UK’s GDP fell more during the 1930s’ Great Depression and the GBP overall experienced elevated volatility during the entire period of the crisis. The GBP/USD hit a 26-year high in 2007 and the pound kept revealing difficulties in equities and the banking industry. Soon after, in January of 2009, the GBP market hit a 24-year low against the USD, repeating a similar scenario to the one with the EUR in 2008.
Conclusion
With the virus spreading across China in December and January, most UK businesses seemed to be preoccupied with Brexit. The ramifications of these external factors are yet to be seen, but one may see the current GBP struggles as part of its long-lived pattern. The Bank of England has once again stepped in to help the troubled economy and the benefits of those steps are already noticeable. The pound has indeed lost its safety position, placed somewhat in the middle. The currency tends to appreciate more during an economic expansion, so we have yet to see some major moves as the UK’s economy further stabilizes.
The negative impact of Brexit on the GBP has been extensively documented over the past years, but considering the current selloff, one cannot but recall a previous episode of intense Sterling selling: the financial crisis. Investors seem to be fearful of the GBP difficulties and history seems to be repeating. The UK’s deficit is masked by a secure flow of investor capital, which in turn maintains the value of GBP above where it would be if it only reflected imports/exports. The pound largely struggled towards the beginning of the month of August, with the number of virus-inflicted patients rising across the country.
The global economy also went through a difficult period, but the GBP experienced some bigger moves against the USD, returning to 1.30. Looking throughout August, the final resolution of Brexit is still far ahead and the expectations of a new trade deal between the UK and the EU keep the tension up. Aside from the Brexit-related challenges, the virus pandemic also affected the currency market, making it even more unpredictable. August is witnessing the release of several important reports (GBP already came out a few days ago) and traders should pay attention to market volatility and adjust position sizing accordingly. At 1.31 USD, the GBP stands firm ahead of new Brexit negotiations.
Policymakers are said to be meeting soon to discuss the relationship between London’s financial sector and the EU market. The past weekend economy was predicted to be soon seeing a rapid recovery from the impact of the virus on consumer spending. Last, the British pound is estimated to be trading at 1.30 by the end of this quarter and at 1.28 in the upcoming 12 months.