Introduction
GBP Pound sterling, also known as the pound, is the official currency of the United Kingdom and many others. It is one of the oldest currencies and is further divided into pence. Where in HKD is known as Hong Kong Dollar, and it is the official currency of Hong Kong. One HKD is divided into 100 cents.
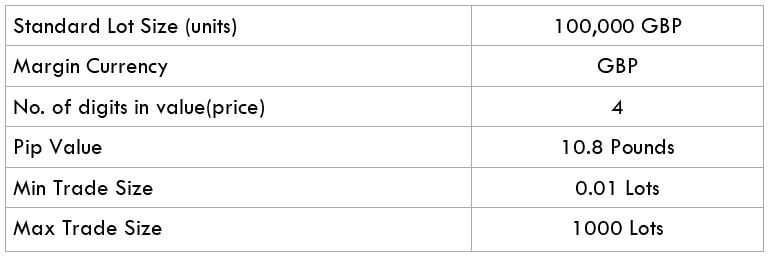
GBP/HKD is the abbreviation for the Pound sterling against the Hong Kong Dollar. Here, the first currency (GBP) is the base, and the second currency (HKD) is the quote currency. It is classified as an exotic-cross currency pair.
Understanding GBP/HKD
In Forex, to find out the relative value of one currency, we need another money to compare. The market value of GBP/HKD determines the strength of HKD against the GBP, i.e., It can simply be understood as 1GBP is equal to how much HKD, so if the exchange rate for the pair GBPHKD is 9.254. It means that we need 9.254 HKD to buy 1 GBP. If the value of the base currency goes down, the value of the quote currency goes up and vice versa.
Spread
Forex brokers have two different prices for currency pairs: the bid and ask price. The bid price is the selling price, and ask is the buy price. The difference between the ask and the bid price is called the spread. The spread is how brokers make their money. For this currency pair, the spread values for ECN & STP brokers are as follows.
ECN: 33 pips | STP: 36 pips
Fees
A Fee is simply the commission we pay to the broker on each position we open. There is no fee on STP account models, but a few pips on ECN accounts.
Slippage
Slippage refers to the difference between the trader’s expected price and the actual price at which the trade is executed. It can occur at any time, but it mostly happens when market orders are placed during high volatile conditions. It may also occur when large orders are placed at a time.
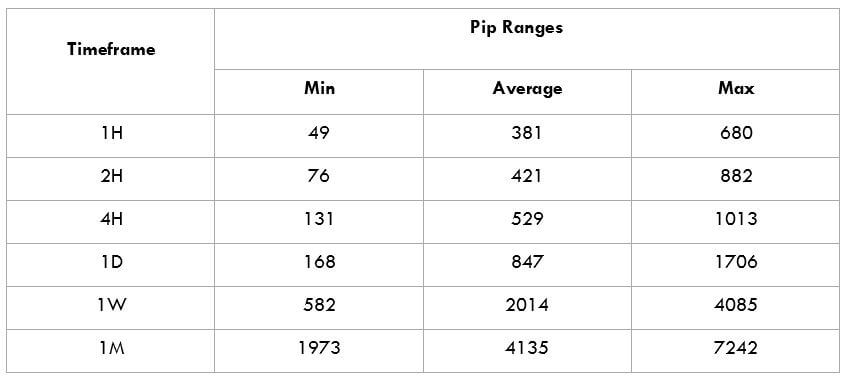
Trading Range in GBP/HKD
The amount of money we win or lose in a given amount of time can be assessed using the trading range table. The following table is a representation of the minimum, average, and maximum pip movement in a currency pair. This can be assessed very easily by using the Average True Range (ATR) indicator combined with 200-period SMA.
Procedure to assess Pip Ranges
- Add the ATR indicator to your chart
- Set the period to 1
- Add a 200-period SMA to this indicator
- Shrink the chart so you can assess a large time period
- Select your desired timeframe
- Measure the floor level and set this value as the min
- Measure the level of the 200-period SMA and set this as the average
- Measure the peak levels and set this as Max.
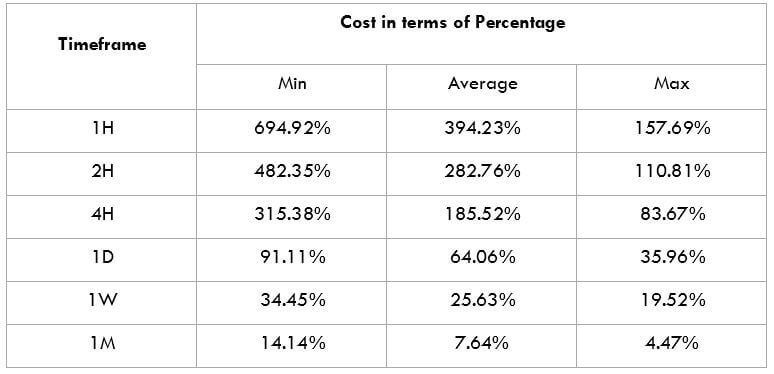
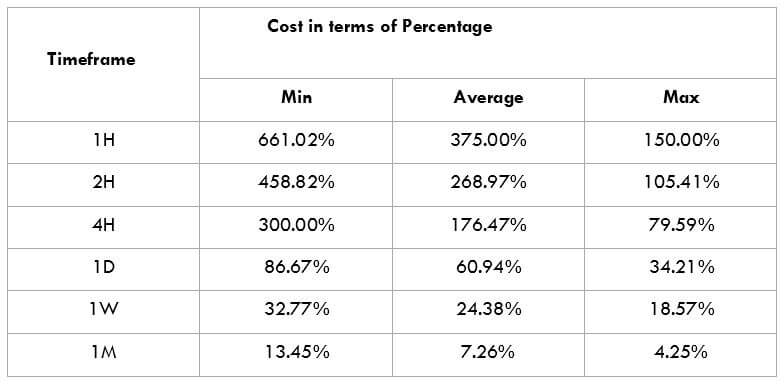
GBP/SGD Cost as a Percent of the Trading Range
The cost of trade varies based on the volatility of the market. This is because the total cost involves slippage and spreads apart from the trading fee. Below is the representation of the cost variation in terms of percentages. The comprehension of it is discussed in the coming sections.
ECN Model Account
Spread = 33 | Slippage = 3 |Trading fee = 5
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 3 + 15 + 5 = 41
STP Model Account
Spread = 36 | Slippage = 3 | Trading fee = 0
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 3 + 19 + 0 = 39
Trading the GBP/HKD Currency Pair
The GBPHKD is an exotic-cross currency pair and is a normal ranging market. For instance, the average pip movement on the 1H timeframe is only 49 pips. Note that the higher the volatility, the lower is the cost of the trade. However, this is not an advantage as it is risky to trade highly volatile markets.
Also, the larger/smaller the percentages, the higher/lower are the costs on the trade. So, we can infer that the costs are higher for low volatile markets and high for highly volatile markets. To reduce our risk, it is recommended to trade when the volatility is around the minimum values. The volatility here is low, and the costs are a little high compared to the average and the maximum values. But, if your priority is towards reducing costs, you may trade when the volatility of the market is around the maximum values.
Advantage from Limit orders
When orders are executed as market orders, there is slippage on the trade. But, with limit orders, there is no slippage as such. Only trading fees and the spread will be taken into consideration to calculate the total costs. This method will bring down the cost significantly.