Introduction
GBPNZD is the abbreviation for the Great Britain pound against the New Zealand dollar. Here, the pound is the base currency, while the New Zealand dollar is the quote currency. Though it is not a major currency, it has considerable volatility and liquidity.
Understanding GBP/NZD
The value of GBPNZD represents the value of NZD equivalent to one pound. It is quoted as 1 GBP per X NZD. For example, if the value of GBPNZD is at 1.9677, then to buy one pound, the trader has to pay 1.9677 NZ dollars for it.
GBP/NZD Specification
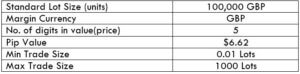
Spread
Spread is the medium through which brokers generate revenue. They set two different prices for buying and selling a currency pair. The difference between the prices is their profit. This difference is referred to as the spread. The prices usually vary from type of account model.
ECN: 1.2 | STP: 2.1
Fees
The fee is basically the commission on each trade a trader must pay. Typically, there is no fee on STP accounts, but a small fee on ECN accounts. The fee is usually between 6 and 10 pips.
Slippage
Slippage takes place when positions are opened/closed using market orders. The trader wishes to pay a specific price, but in reality, he receives a different price. And the difference between these two prices is called slippage.
Trading Range in GBP/NZD
The trading range is the depiction of the pip movement of a currency pair on different timeframes. With it, one can analyze how many dollars they can win/lose in a given timeframe. For example, if the average pip movement on the 1H timeframe is 30 pips, then you will either be in a profit of $198.6 or a loss of $198.6 in an hour. Knowing this, a trader can plan their lot sizes accordingly.
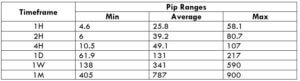
Procedure to assess Pip Ranges
- Add the ATR indicator to your chart
- Set the period to 1
- Add a 200-period SMA to this indicator
- Shrink the chart so you can assess a large time period
- Select your desired timeframe
- Measure the floor level and set this value as the min
- Measure the level of the 200-period SMA and set this as the average
- Measure the peak levels and set this as Max.
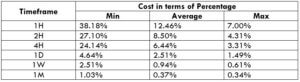
GBP/NZD Cost as a Percent of the Trading Range
Having knowledge of the cost of the trade is necessary. Note that the cost varies based on the volatility and the timeframe traded. So, it becomes vital to know when the right moments to enter the market are. Below are two tables illustrating the total costs as a percentage for varying timeframes and volatility.
ECN Model Account
Spread = 1.2 | Slippage = 2 |Trading fee = 1
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 2 + 1.2 + 1 = 4.2
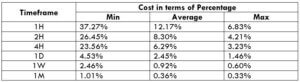
STP Model Account
Spread = 2.1 | Slippage = 2 | Trading fee = 0
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 2 + 2.1 + 0 = 4.1
 The Ideal way to trade the GBP/NZD
The Ideal way to trade the GBP/NZD
The above tables show that the costs are high in the min column and low in the max column. The higher the value of the percentage, the high is the cost. So, this means that the costs are high for low volatility markets and vice versa. It is neither ideal to trade during low volatility nor during high volatility. To have an equilibrium between the costs and the volatility, it is best to enter the market when the volatility is around the average mark.
Slippage is a parameter for calculating the total cost. It has a great weight in the total cost. However, there is a way to minimize and nullify it. This can be simply be done by trading using limit orders instead of market orders.






