Introduction
AUDJPY is the abbreviation for the Australian dollar and the Japanese yen. It commonly referred to as “Aussie yen.” It is one of the cross-currency pairs in the forex market. AUD, being on the left, is termed as the base currency and JPY as the quote currency.
Understanding AUD/JPY
The market price of AUDJPY corresponds to the value of JPY that needs to be paid to buy one AUD. It is quoted as 1 AUD per X JPY. For example, if the value of AUDJPY is 74.571, then these many units of the yen are to be produced to purchase one Australian dollar.
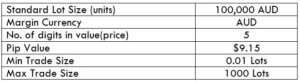
AUD/JPY Specification
Spread
Spread is the medium through which brokers generate their revenue. They set different prices for buying a currency and selling a currency. The difference amount becomes their profit margin. The spread usually changes from time to time and varies on the type of execution model.
ECN: 0.7 | STP: 1.6
Fees
Apart from spreads, one needs to pay a charge for every execution a trader makes. It is essentially the commission levied by the broker on each trade. As a matter of fact, there is no fee on STP accounts. But, on ECN accounts, there is a fee of few pips.
Slippage
Going by the definition, slippage is the difference between the price executed by the trader and the price he actually received. It could be in favor of the trader or against him. It all depends on the broker’s execution speed and the change in the volatility of the market.
Trading Range in AUD/JPY
A trading range is a tabular representation of the minimum, average, and the maximum pip movement in a currency pair on different timeframes. These values help in determining the profit that can be made or loss one must bear in a given time frame. And this can be found out by simply finding the product between the pip movement and the value per pip ($9.15).
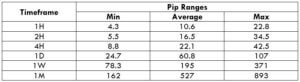
Procedure to assess Pip Ranges
- Add the ATR indicator to your chart
- Set the period to 1
- Add a 200-period SMA to this indicator
- Shrink the chart so you can determine a large time period
- Select your desired timeframe
- Measure the floor level and set this value as the min
- Measure the level of the 200-period SMA and set this as the average
- Measure the peak levels and set this as Max.
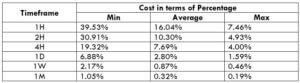
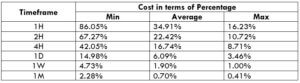
AUD/JPY Cost as a Percent of the Trading Range
Cost as a percent of the trading range is an illustration of the cost variation by considering the total cost and the volatility of the market in different timeframes. These values are expressed in a ratio that is converted to percentages. And the magnitude of these percentages helps in determining the cost variation in each trade.
ECN Model Account
Spread = 0.7 | Slippage = 2 |Trading fee = 1
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 2 + 0.7 + 1 = 3.7
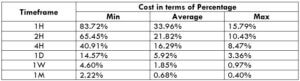
STP Model Account
Spread = 1.6 | Slippage = 2 | Trading fee = 0
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 2 + 1.6 + 0 = 3.6
The Ideal way to trade the AUD/JPY
Though Forex is a 24/7 market, it is not ideal to enter any time in the market. There are certain times when you must enter the market, which can help reduce costs significantly. Let us determine that using the above tables.
Note that the higher the magnitude of the percentage, the higher is the cost of the trade. From the table, it can be ascertained that the values are high in the minimum column, implying that the costs are high when the volatility of the market is low. Similarly, the costs are low when the volatility is high. However, it is not ideal to trade during these times. To ensure optimum volatility and affordable cost, one must trade during those times when the volatility is around the average range.
Furthermore, there is another way through which you can reduce your costs. Trading using limit orders instead of the market orders brings down the total cost significantly, as the slippage becomes zero. The decline in the costs on the trade when slippage is made zero is shown below.