Introduction
Throughout the years, many professional traders and chartists spent thousands of hours in front of their screens and have invented hundreds of candlestick patterns that show in the market. Some of these patterns work very well, and some failed miserably. A lot of traders believe that pattern trading doesn’t work. But it is just a myth. Pattern trading does work if we use it in conjunction with other credible trading tools.
Most of the novice traders make the mistake of treating A candlestick pattern as a trading signal. They need to understand that the patterns alone do not hold enough power to reverse the trend of the market. Most of the candlestick patterns are defined by using the last three to four candlesticks alone. Also, most importantly, they ignore the price action context.
This is the reason why we always urge our readers to combines candlestick patterns with other trading tools like credible indicators or oscillators. In this article, we will be sharing one of the most profitable trading strategies that we have ever come across. It involves a candlestick pattern and a technical indicator.
Engulfing Pattern + Stochastic Indicator
After extensive research and backtesting, we found that the Engulfing Pattern is the most profitable Pattern when confirmed and traded with the Stochastic Indicator. Before going right into the strategy, let’s talk about the Stochastic Indicator and Engulfing Pattern in the interest of novice traders who have never heard of these things before.
Stochastic Indicator
George Lane developed the Stochastic Indicator in the Late 1950s. It is one of the most prominent indicators in the industry, and it has been identifying credible signals consistently in all the types of markets from the past 60+ years. The Stochastic is an oscillator, and it changes its direction even before the price action. It measures the relationship between the underlying asset’s closing price and its price range over a specific period of time. Just like other indicators, stochastic doesn’t follow the volume and price. Instead, it follows the momentum and speed of the price to identify the overbought and oversold areas.
Engulfing Pattern
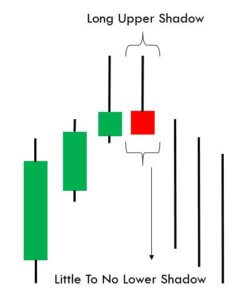
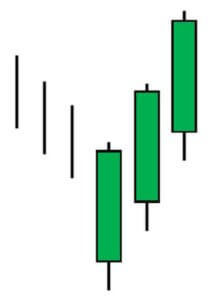
Engulfing is one of the most prominent candlestick patterns in the market. This Pattern frequently appears in the Forex market than the stock or futures market. There are two types of Engulfing Patterns in the market – Bullish Engulfing Pattern & Bearish Engulfing Pattern. Engulfing is either a bullish or bearish reversal pattern, and it prints at the end of any prevailing trend.
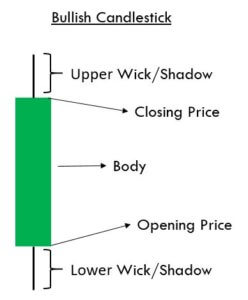
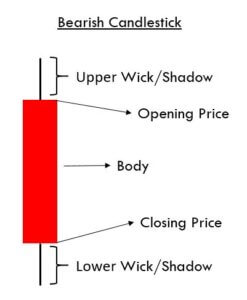
Bullish and Bearish Engulfing Patterns
The Bullish Engulfing Pattern always appears in a downtrend. It is a three candle pattern. The first candle is Red; the color of the second candle doesn’t matter. Most of the time, the second candle is a Doji candle. The third candle is super important as it must be Green in color for the pattern confirmation. Also, it must close above the first Red candle.
Conversely, the Bearish Engulfing Pattern appears in an uptrend, and it indicates the bearish reversal. The first candle is Green in color, and that suggests the uptrend is still ongoing. The second candle is Doji, and the color doesn’t matter much. The third one is the decision making candle, which must be Red in color. This indicates the buyers not having enough power to lead the market.
Trading Strategy
Buy Example
This strategy works very well in all the timeframes. So irrespective of you being an intraday trader, swing trader, or an investor, you can still use this strategy. If you are a 60-minute trader, only trade with the current timeframe trend. Adding additional timeframes to this strategy often creates confusion, and as a result, it leads to wrong decision making. The strategy is as follows:
- The very first step is to find a downtrend in any underlying security.
- With a bullish view, look for a Bullish Engulfing Pattern.
- Then apply the Stochastic Indicator on to the charts
- To take a trade, the Stochastic must be in the oversold area. If the Stochastic is at the overbought area and you see a Bullish Engulfing Pattern, do not take the trade.
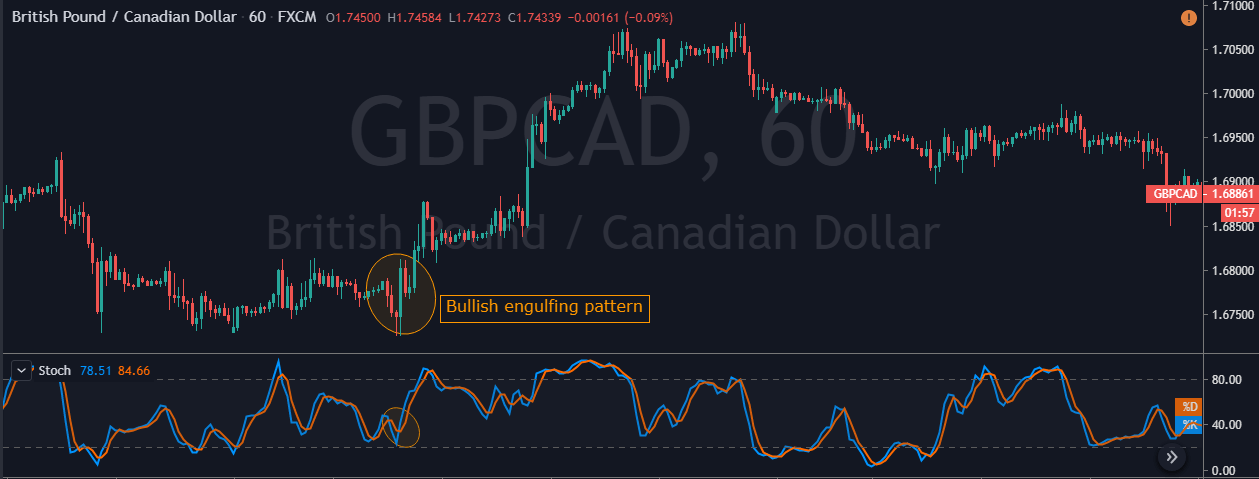
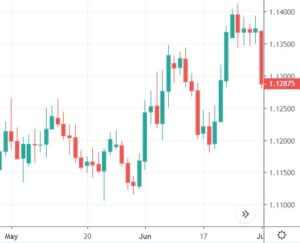
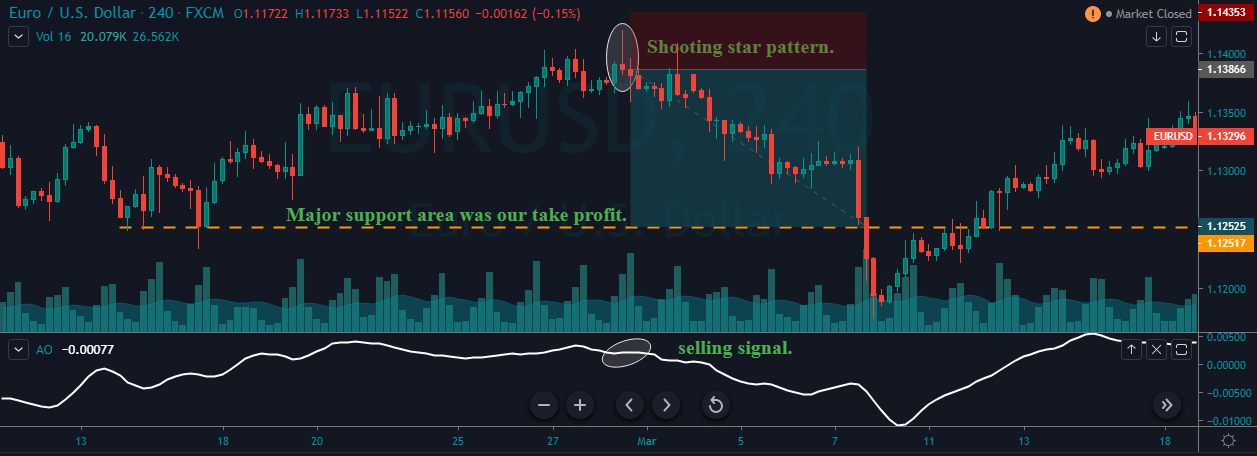
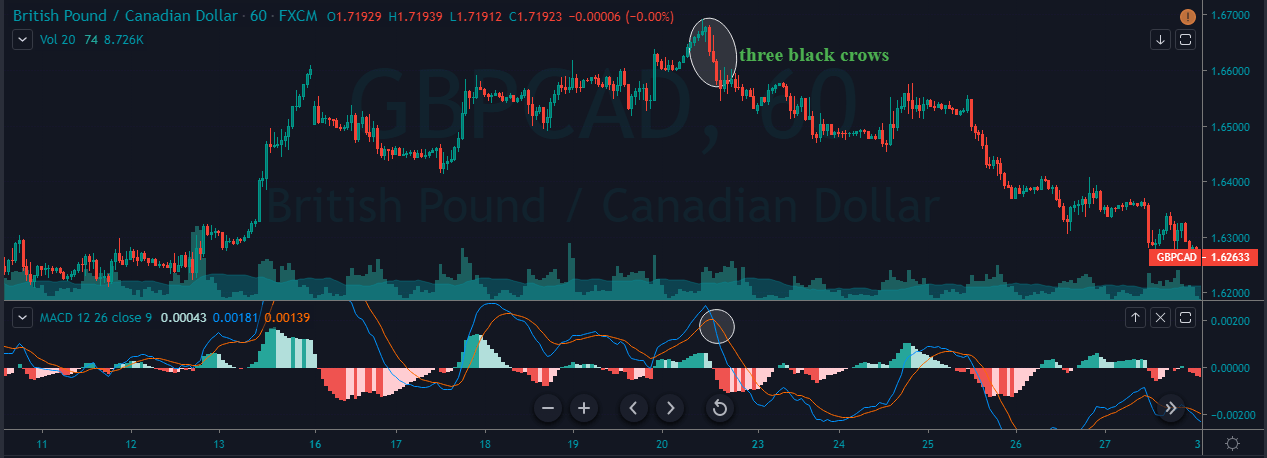
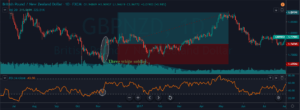
In the below GBP/CAD Forex chart the bottom panel shows the Stochastic Indicator. We can see the market was in an overall downtrend. At the end of the downtrend, we can notice the market printing the Bullish Engulfing Pattern. We can also see the crossover of the stochastic indicator at the same time.
This shows that the sellers are exhausted and buyers gaining control in this pair. If at all you are trade the Engulfing patterns alone, make sure to wait for two to three confirmation candles after the Pattern to enter the trade. Here, in our case, there is no need to wait for the next two-three candles as Stochastic confirms the Bullish Engulfing Pattern’s signal. Also, if we would have placed the Take Profit accurately, the winning pips in this trade would be huge. Hence we call this the most profitable candlestick pattern.
Sell Example
- Firstly, check if the market is in an uptrend.
- With a bearish view, look for the Bearish Engulfing Pattern.
- The third step is that the Stochastic must be in the overbought area.
- If the Stochastic is at the oversold area and market prints a Bearish Engulfing pattern do not take the trade.
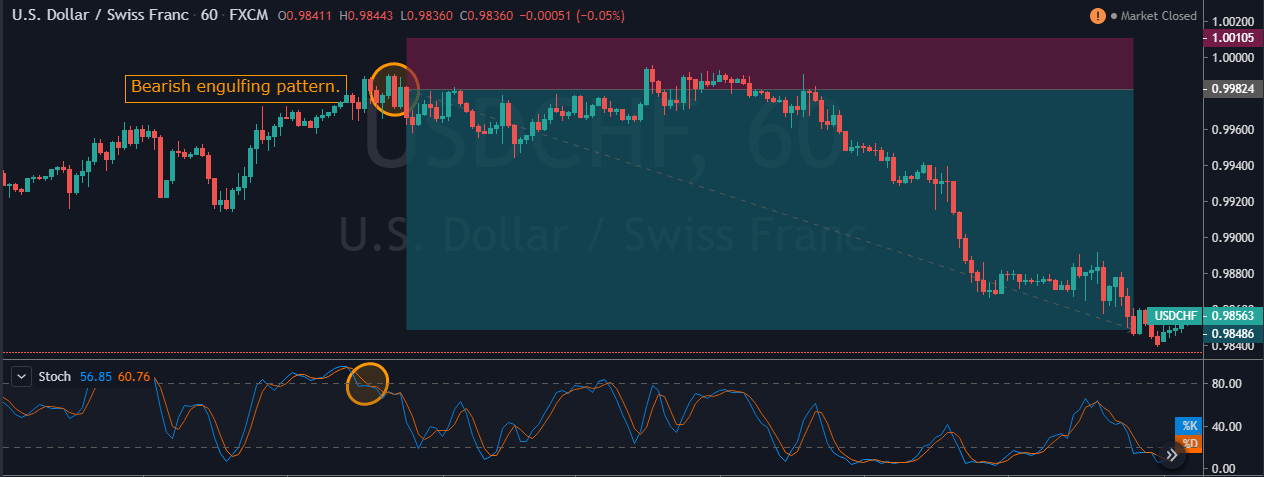
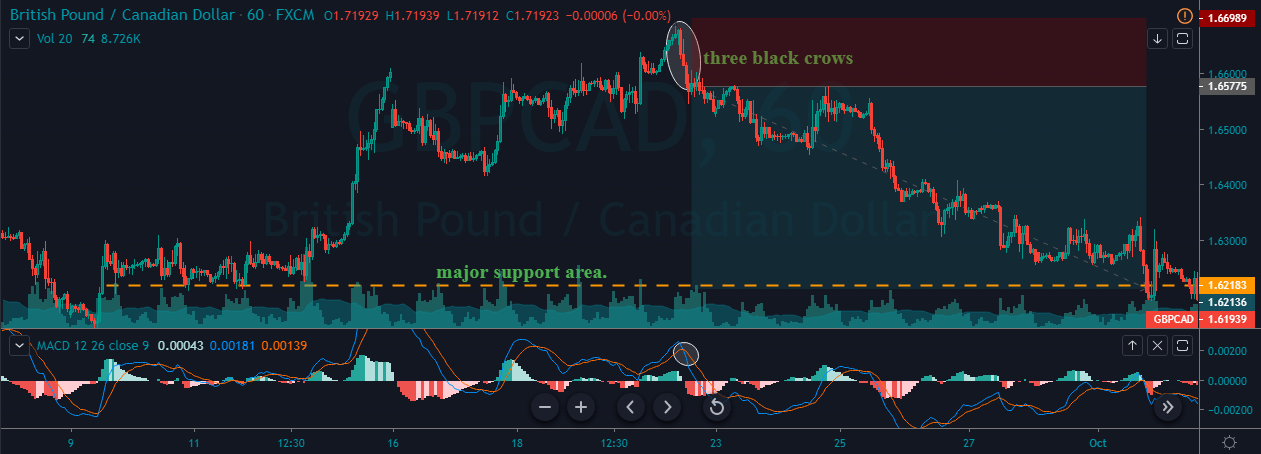
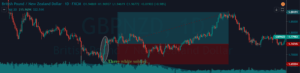
In the below USD/CHF Forex pair, the overall market was in an uptrend. When the market turned sideways, it has printed the Bearish Engulfing Pattern. We can also see the Stochastic Indicator in the overbought area. Hence this is a clear indication of Sell trade in this pair. After the signal, price action turned sideways for a longer period. Here, a lot of amateur traders exit their positions if the price takes too long to respond.
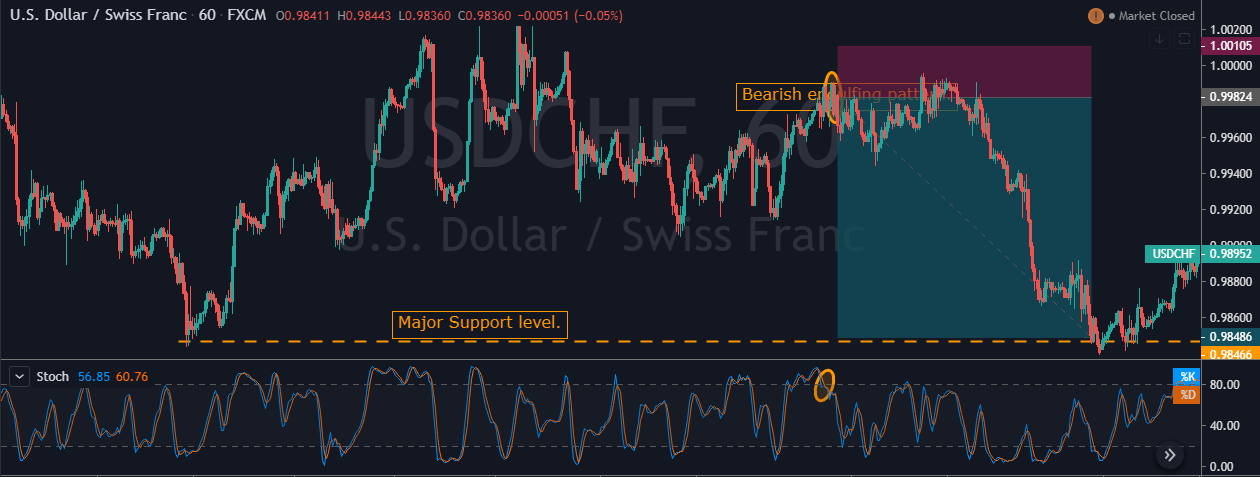
But we suggest you have faith and only exit your trades when it hits the stop loss. In our case, we can see the price action holding for sometimes, and when it rolls over, it gave stronger moves. In the below image, we can see that after holding sideways, price action dropped very hard, and we booked full positions at the major support area.
Bottom line
Engulfing Pattern is quite popular, and one of the most profitable patterns that exist in the industry. It often provides good risk-reward ratio trades. When we master the combination of Engulfing Patterns and the Stochastic Indicator, we can easily take our trading to a whole next level. Combining these two technical tools is a sound approach, as they quickly help us in filtering low probability trades. This strategy works well in both ranging market conditions and trending/dying market conditions.
We hope you find this information useful. Test this strategy in a demo account before applying it to the live markets. Cheers!





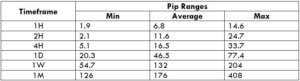
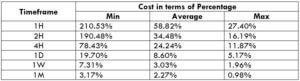
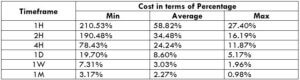



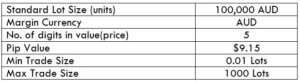
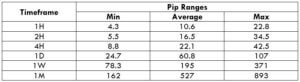
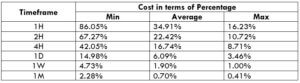
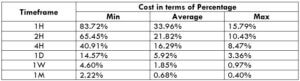
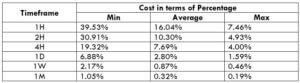

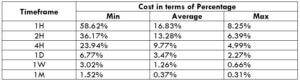


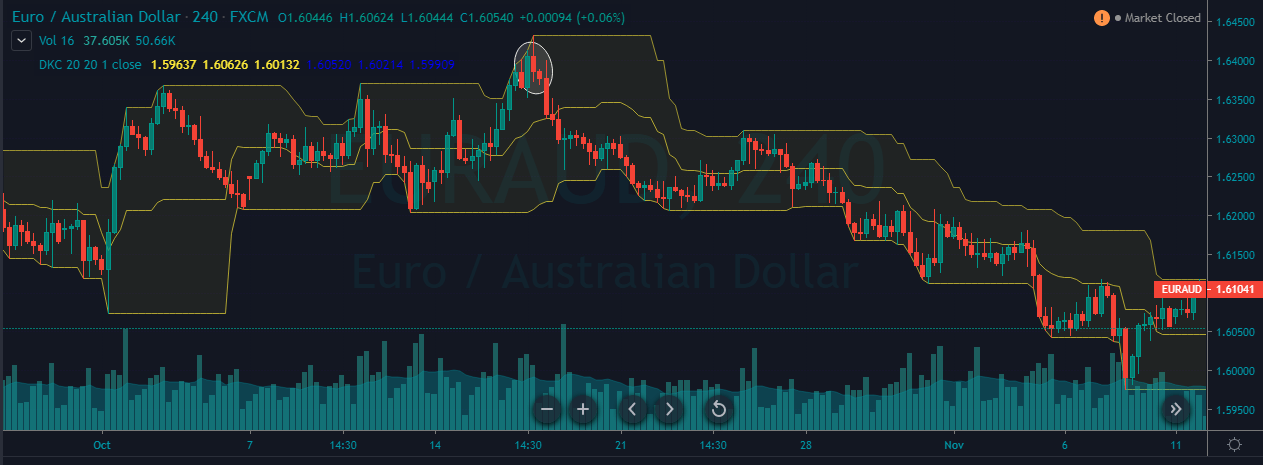
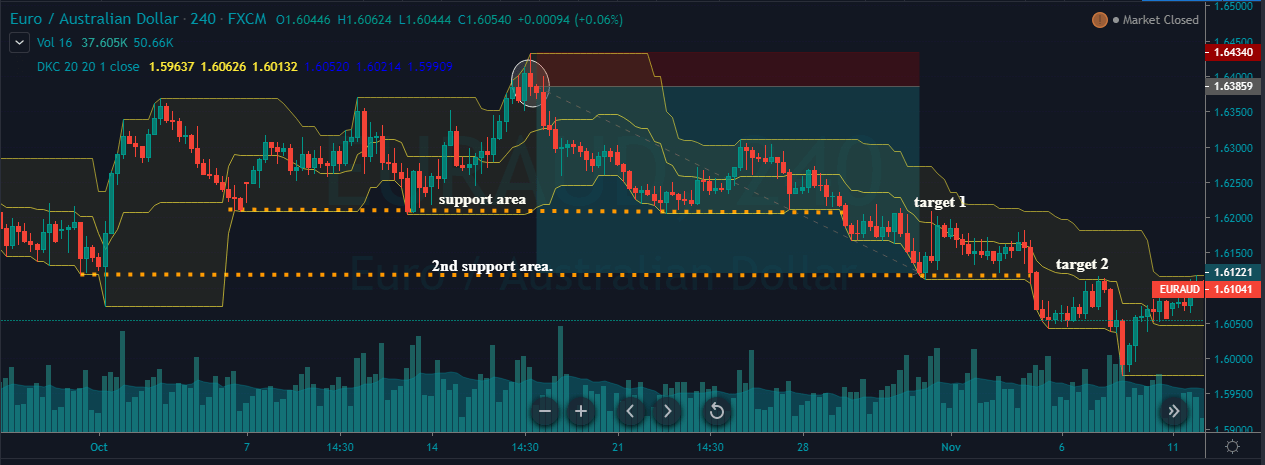
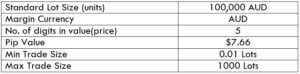
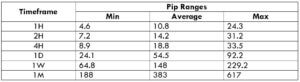
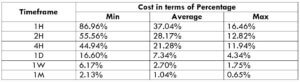
 The Ideal way to trade the AUD/CAD
The Ideal way to trade the AUD/CAD
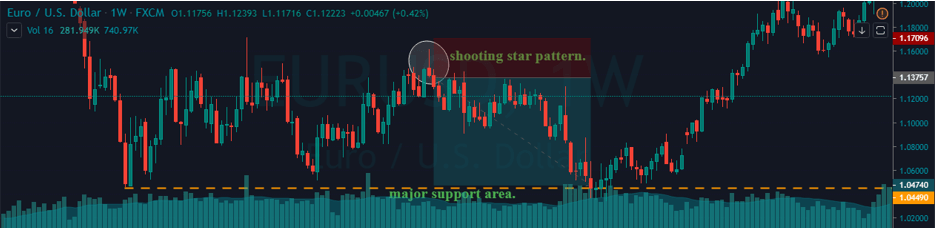
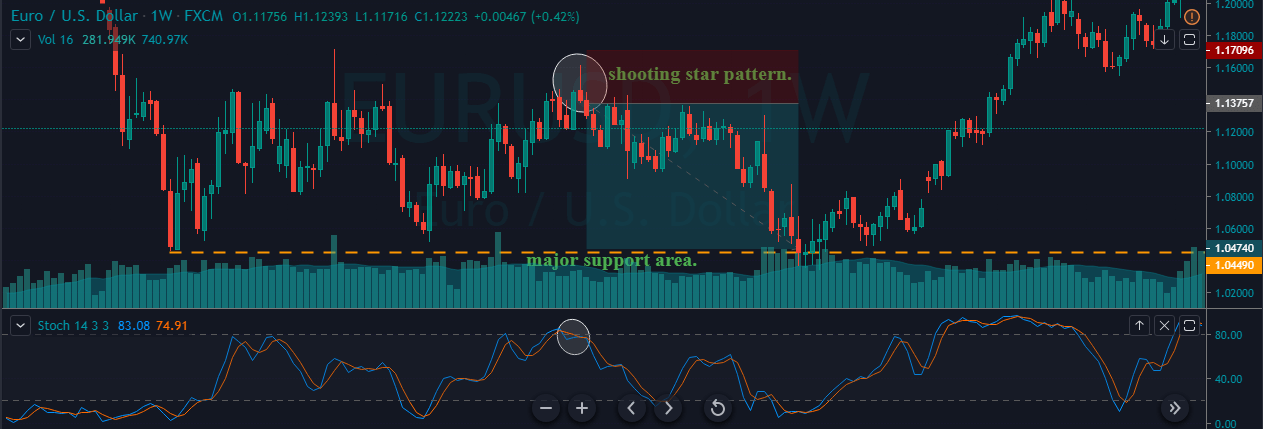

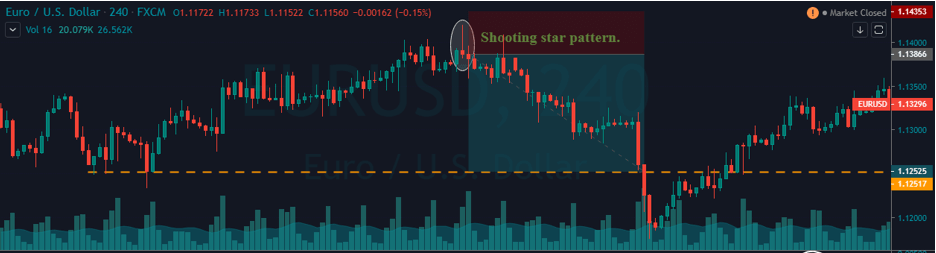
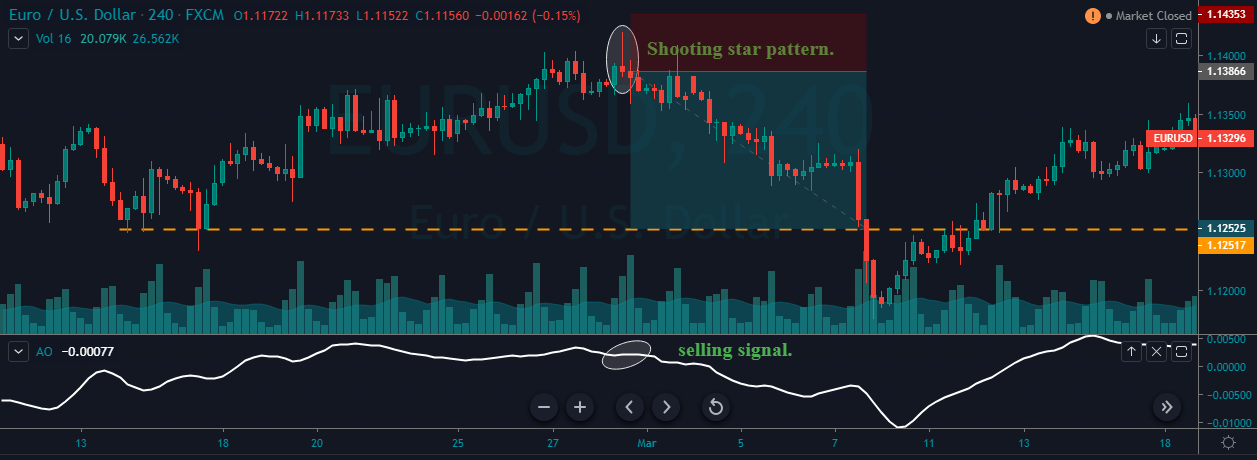




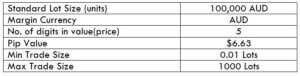
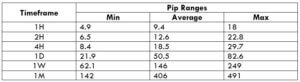
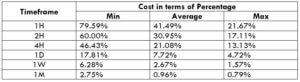
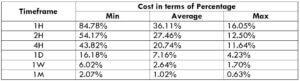
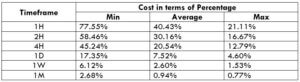 The Ideal way to trade the AUD/NZD
The Ideal way to trade the AUD/NZD



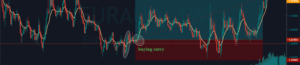
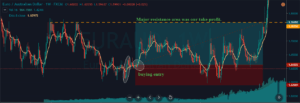
 Step 3 – Step Loss & Take Profit
Step 3 – Step Loss & Take Profit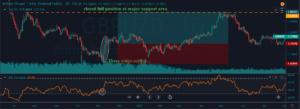

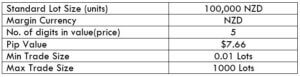
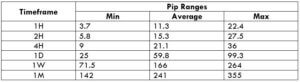
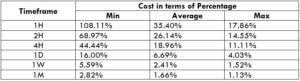
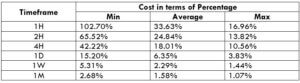



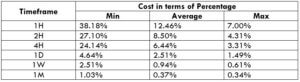
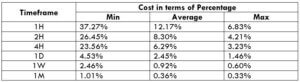 The Ideal way to trade the GBP/NZD
The Ideal way to trade the GBP/NZD
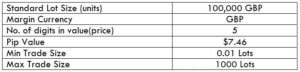
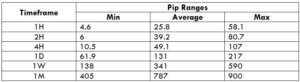
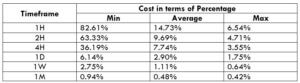
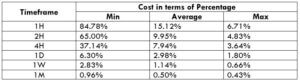
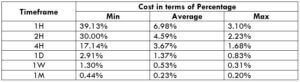

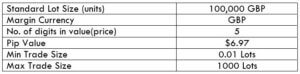
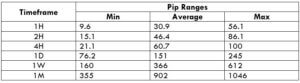
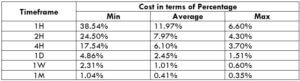
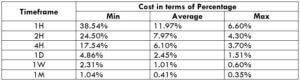
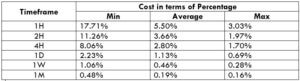


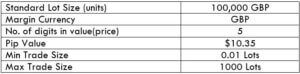
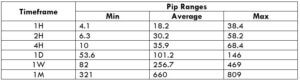
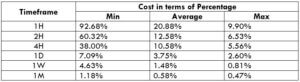
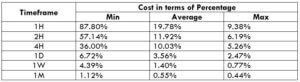
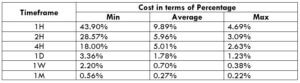



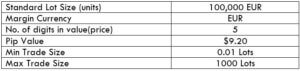
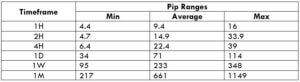
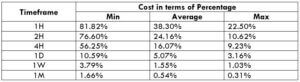
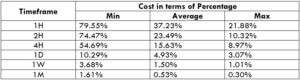
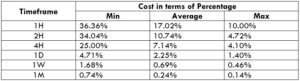

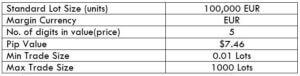
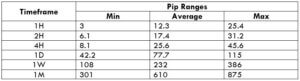
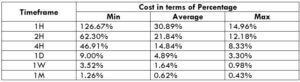
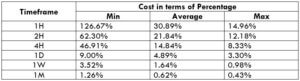


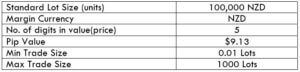
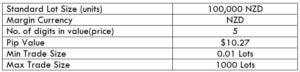
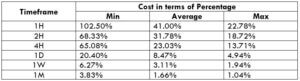
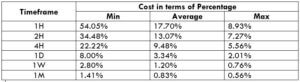
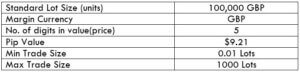
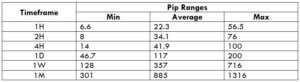
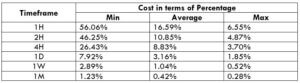
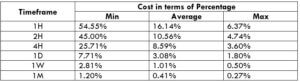
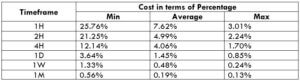
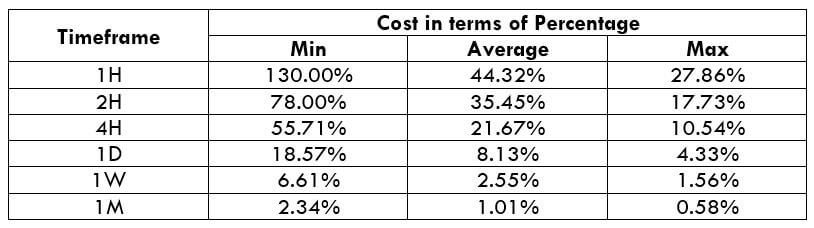
 Spread
Spread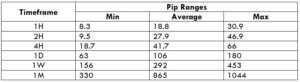
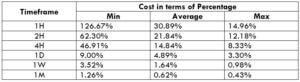
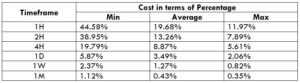
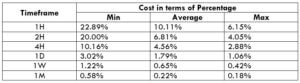

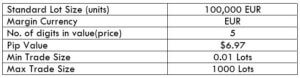
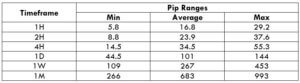
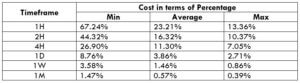
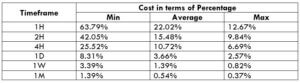
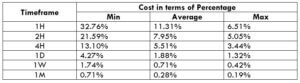
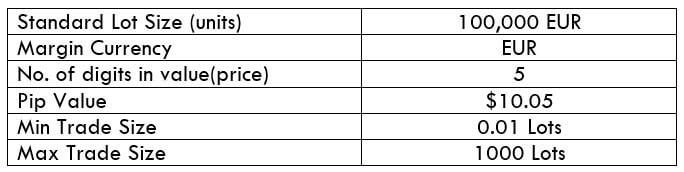
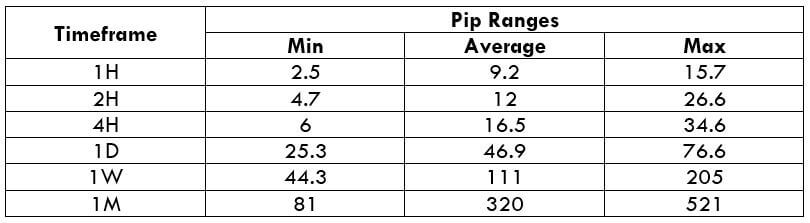
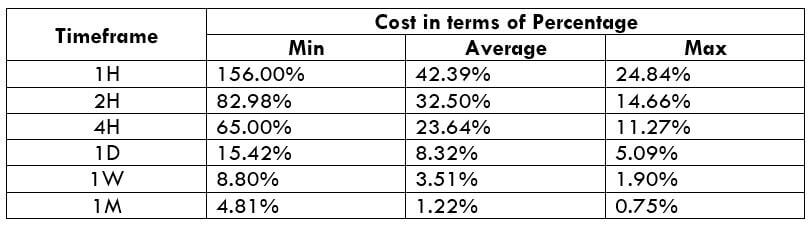
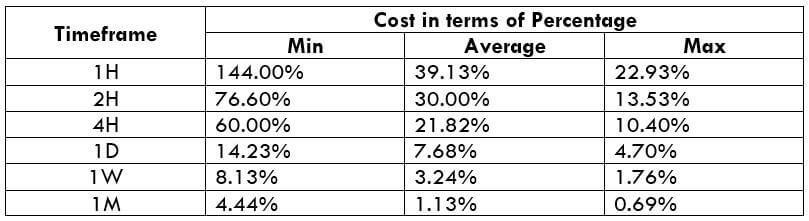
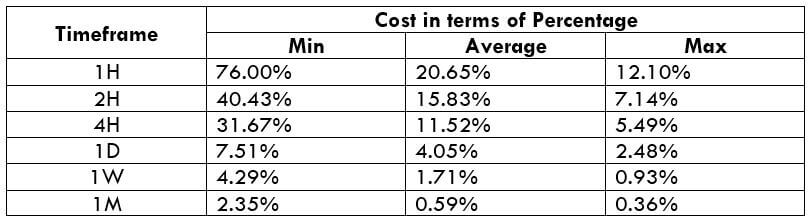





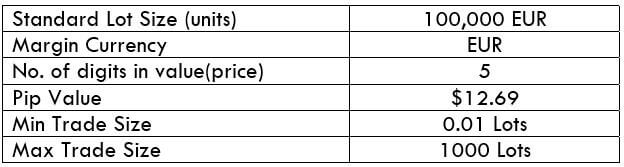
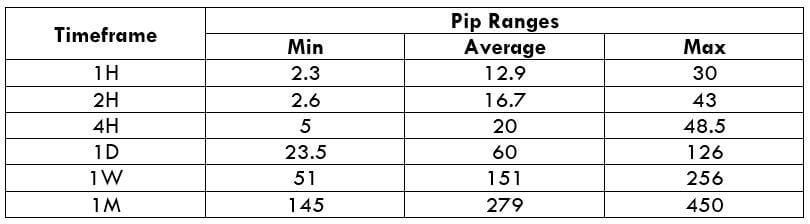
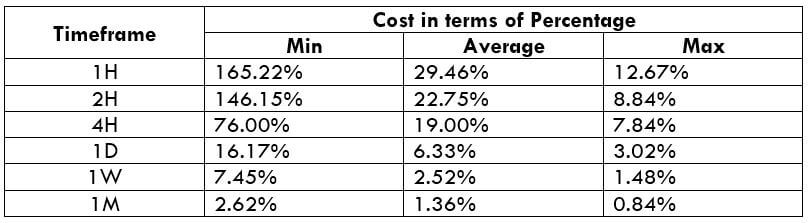
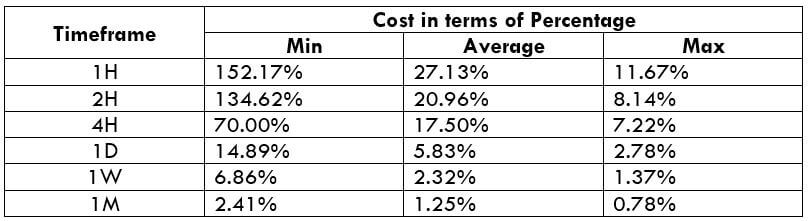
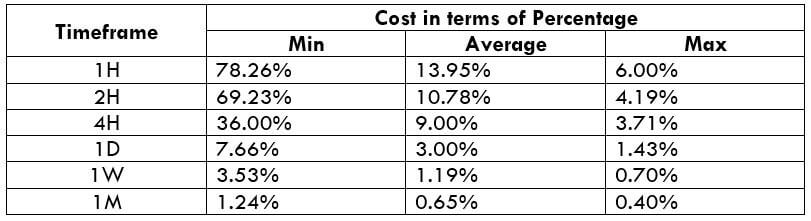

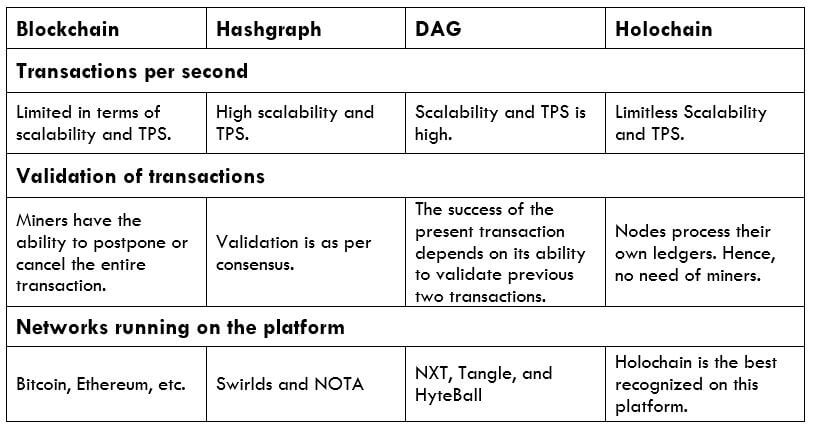


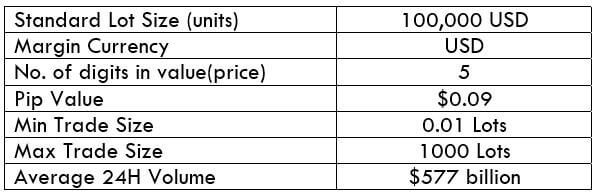
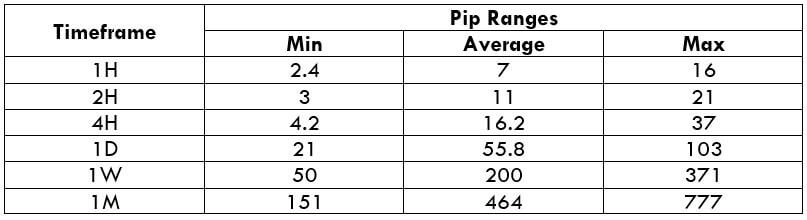
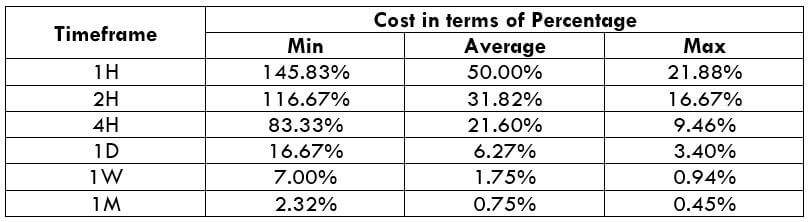
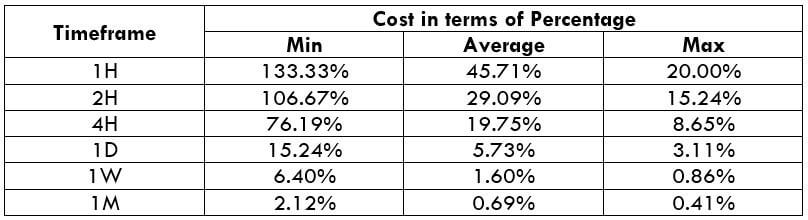



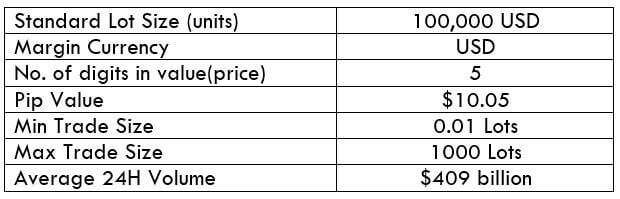
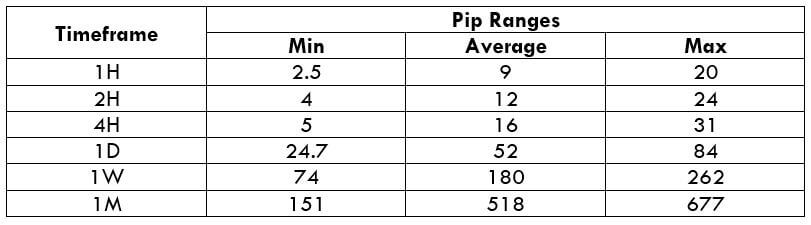
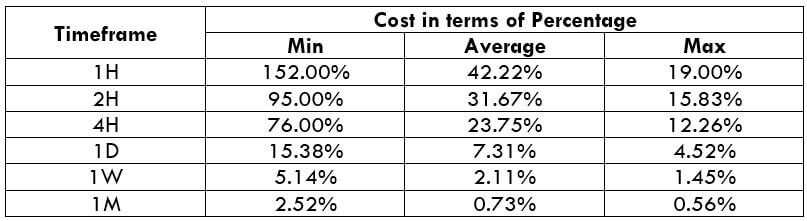
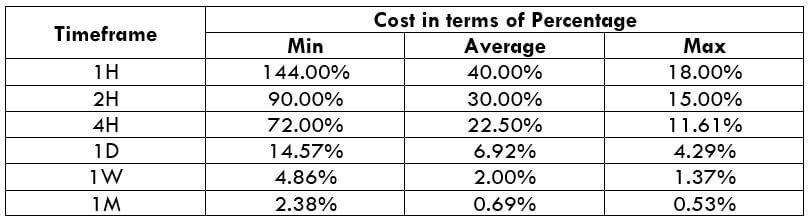
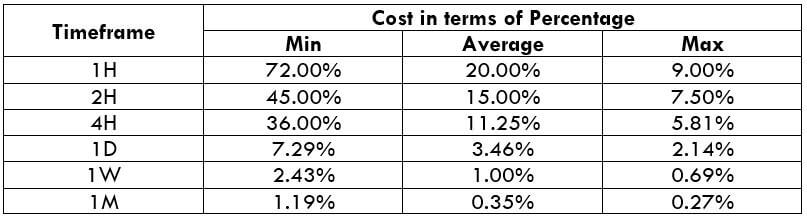

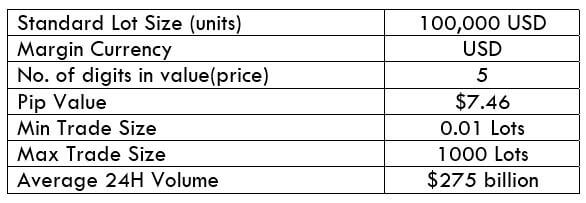
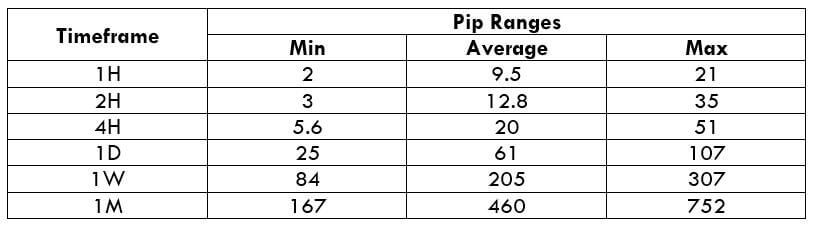
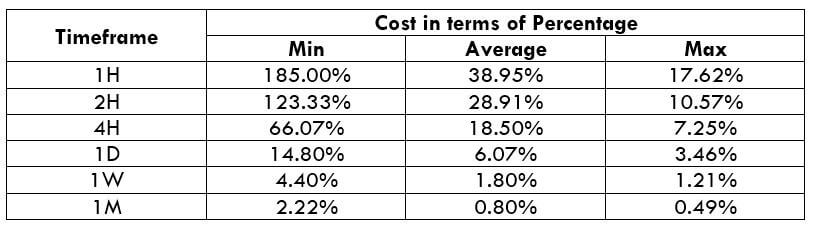
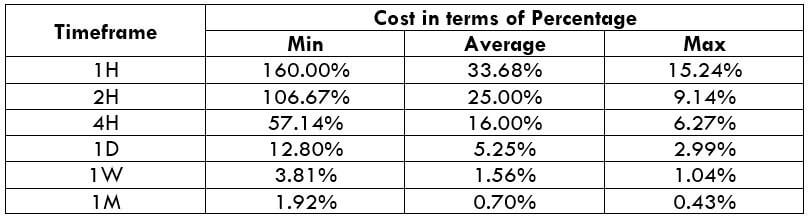
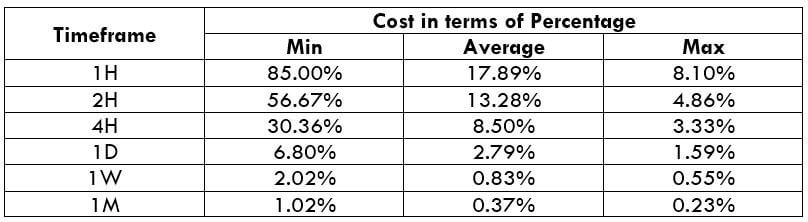




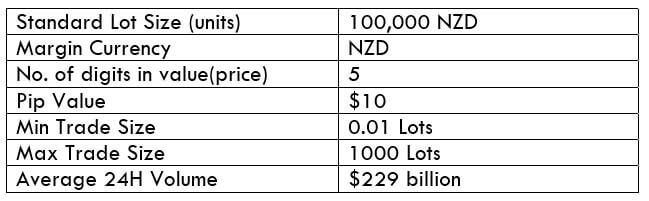
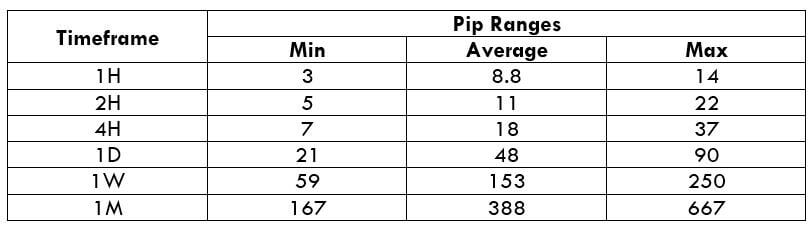
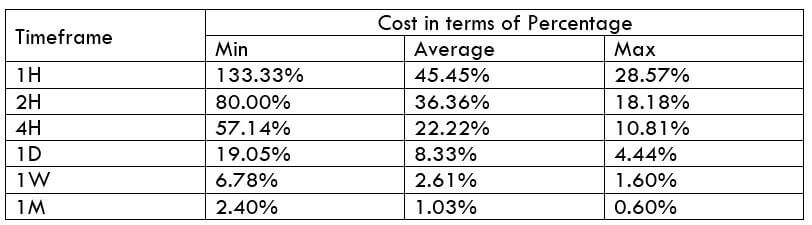
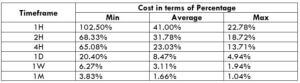
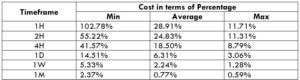
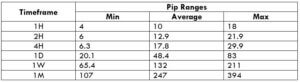
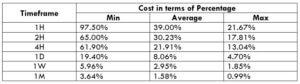
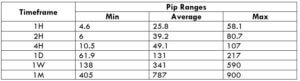
 The Ideal Timeframe to Trade NZD/USD
The Ideal Timeframe to Trade NZD/USD