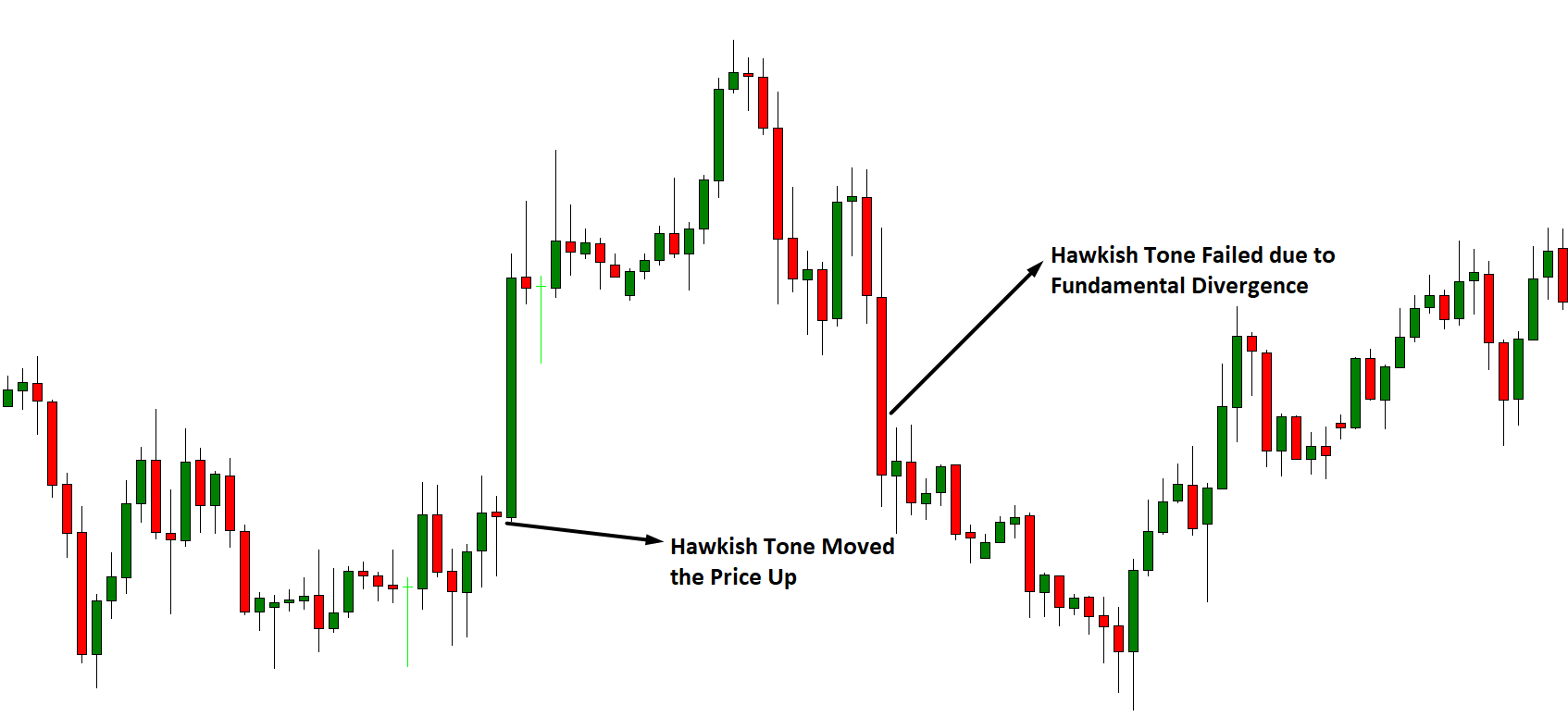
Introduction
Loan Growth is a suitable parameter for us to check whether the monetary strategies implemented by the Central Authorities are coming into play yet or not. Loan Growth also helps us to gauge the health of the economy in terms of liquidity. Loan Growth percentage serves as a litmus test, especially in a capitalist economy, where credit and inflation primarily drive the economy forward.
What is Loan Growth?
Loan: It is a debt incurred by an individual or entity. The lender is generally a bank, financial institution, or the Government. The lender credits the borrower a sum of money. The borrower agrees to specific terms and conditions that can include finance charges, interest payments, due dates, and other conditions.
Loans can be secured or unsecured. In secured loans, the loan is given out against collateral with a financial value like a property, mortgages, or securities, etc.
Loan Growth: Loan Growth refers to the percentage increase in the number of loans issued overall by banks in a particular region over a particular time frame. The time frame can be monthly, semi-annual, or annual.
Most modern economies today we see are capitalist economies, i.e., they grow through capitalism. A capitalist economy requires money to expand and grow. Hence, credit is an inevitable fuel required for economic growth.
How can the Loan Growth numbers be used for analysis?
A healthy increase in the percentage of Loans is suitable for a stable and healthy economy. But as with any case, there is no perfect economy, and there are two sides of analysis to Loan Growth.
First Scenario
A healthy economy means it is growing at a stable rate year over year with mild inflation each year. Credit fuels economic growth in this type of economy. In this type of economy, an increase in the number of loans taken can be considered a positive sign for the economy.
Businesses can grow beyond just cash in hand. Householders can purchase homes without saving the entire cost before purchase. Governments can meet their spending needs without relying solely on tax revenues. Be it a business, householder, or a Government can smoothen out their economic activities in terms of money. They will take credit when in deficit and payback when in surplus.
An increase in Loan Growth can imply that more people are creditworthy, and more businesses are taking credit to expand and grow. Both of these scenarios are good for the GDP and is a good sign for the economy.
Second Scenario
The first scenario takes into the assumption that the economy is strong and stable. In reality, currently, most of the developed nations are struggling to maintain their economic growth. For example, the United States debt to GDP ratio is above 100%, which indicates that even if the entire GDP were given out to repay the debt, it would still be in some debt. Most of the developed nations have taken substantial credits to keep the economy from ticking over.
Keeping economic growth and global competency in mind, most countries have invested heavily in overgrowing in the short-term. By taking on more and more debts, countries may have achieved the necessary growth and needs now but have pushed their problems to the future.
Economists argue that eventually, there would be a time when countries cannot afford any more debt and would be backed into a corner. The only way out then would be at a considerable cost of losing out more than what they had made. Studies also show that rapid loan growth than the long term average also has seen an increase in underperforming or bad loans.
It is also essential to know that increase in Loan Growth should be accompanied by the fact that no bad loans are given out. Giving loans to people and businesses who do not have the eligibility but just because money is lying around is also a problem.
In the United States itself, the Government has been injecting money into the economy since the financial crisis in the form of Money Supply and Quantitative Easing programs to inflate their way out of depression or recession. Until now, the Government has not been able to reduce debt and is only taking on more debt to sustain the current growth.
An increase in loans is good or bad for the economy remains debatable for many. Without credit, sector growth is almost unimaginable in present times. For our analysis, we can use the Loan Growth rate as a litmus test to see whether the injected money from the Central Authorities has started reaching the public and businesses.
When the Central Authorities want to inflate the economy, they reduce interest rates by injecting money into the interbank market. The injected money takes time to get into the economy, and loans are one form in which this money gets circulated.
Overall, for our analysis, once Loan Growth shows increasing numbers, we can assume that the injected money is reaching the intended sectors, and consequent effects could be predicted on businesses and consumers. Loan Growth is indicative of a growing economy in general and is more prominent in developing countries.
Impact on Currency
Loan Growth is a by-product of a reduction in interest rates from the Central Banks of the country and an increase in employment and business growth. An increase in Loans indicates that money is “cheaper” to borrow. It is inflationary for the economy and is given out to induce growth (which may or may not happen).
An increase in Loan Growth depreciates currency as more money is competing against the same set of goods and services. A decrease in Loan growth appreciates the currency as the reduced liquidity forces goods and services to come at reduced prices.
Overall, Loan Growth is a low-impact indicator, as the Central Bank’s interest rates are the leading indicators, and the desired effect from increased loans can be traced from other leading indicators like Consumer and Business surveys.
Economic Reports
Since Loan Growth is not a significant economic indicator, official publications for significant countries are not explicitly published but can be obtained through reports analysis. For our reference, the Trading Economics website consolidates the Credit Growth in different sectors for data available countries on its official website. Since it is a consolidation, frequency and time of publication vary from country to country.
Sources of Loan Growth
Loan Growth consolidated available data for different countries are available here.
“The impact of bank lending on Palestine economic growth: an econometric analysis of time series data” has been referenced for this article.
How Loan Growth Affects The Price Charts
Loan growth is not a statistic. Most forex traders keep an eye when making their trades. The lack of interest is because it is considered a their-tier leading indicator. It is, however, essential to know how the release of this fundamental economic indicator affects the forex price charts.
In the EU, loan growth data is released monthly by the European Central Bank about 28 days after the month ends. It represents the change in the total value of new loans issued to consumers and businesses in the private sector. The most recent release was on July 27, 2020, 8.00 AM GMT can be accessed here. A more in-depth review of the economic news release can be accessed at the ECB website.
Below is a screengrab of the Forex Factory website. On the right, we can see a legend that indicates the level of impact the Fundamental Indicator has on the EUR.
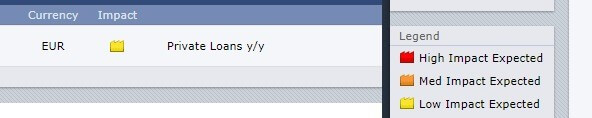
As can be seen, low impact is expected on the EUR.
The screengrab below is of the most recent change in the loan growth in the EU. In June 2020, private loans grew by 3% as compared to the same period in 2019. This change represented a flat growth from the previous release. Based on our fundamental analysis, this should be positive for the EUR.
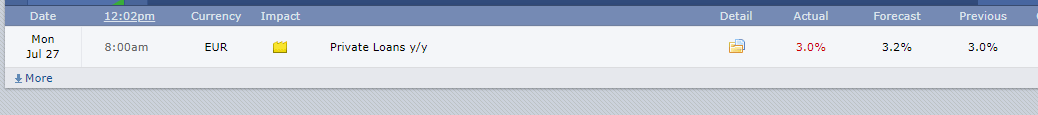
Now, let’s see how this positive news release made an impact on the Forex price charts.
EUR/USD: Before Loan Growth release on July 27, 2020,
Just Before 8.00 AM GMT
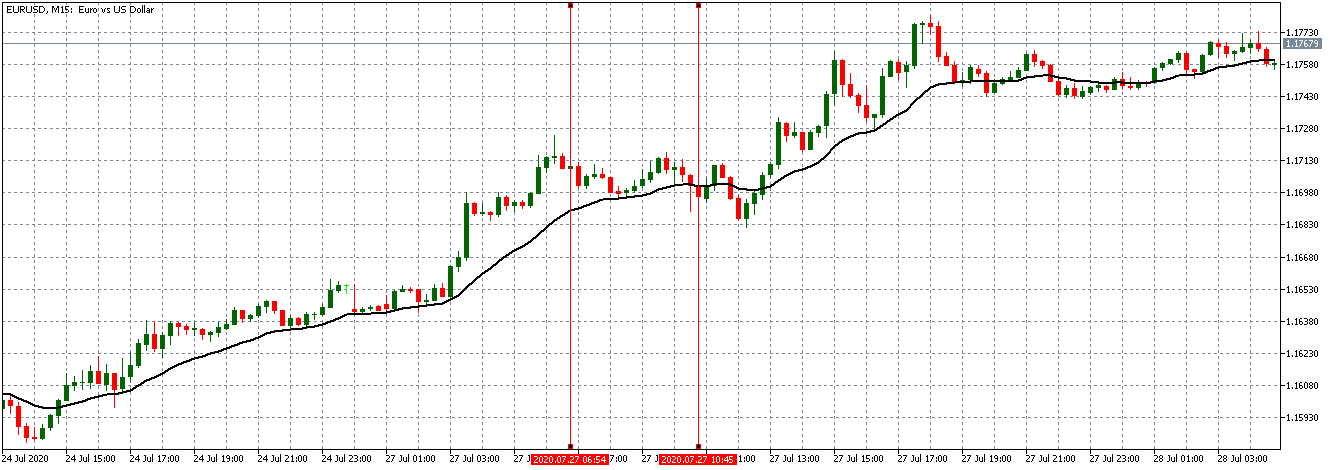
From the above chart, the EUR/USD pair is trading on a neutral trend before the data release. The candles are forming around the flattening 20-period Moving Average. This trend is an indication of relative market inactivity.
EUR/USD: After Loan Growth release on July 27,
2020, 8.00 AM GMT
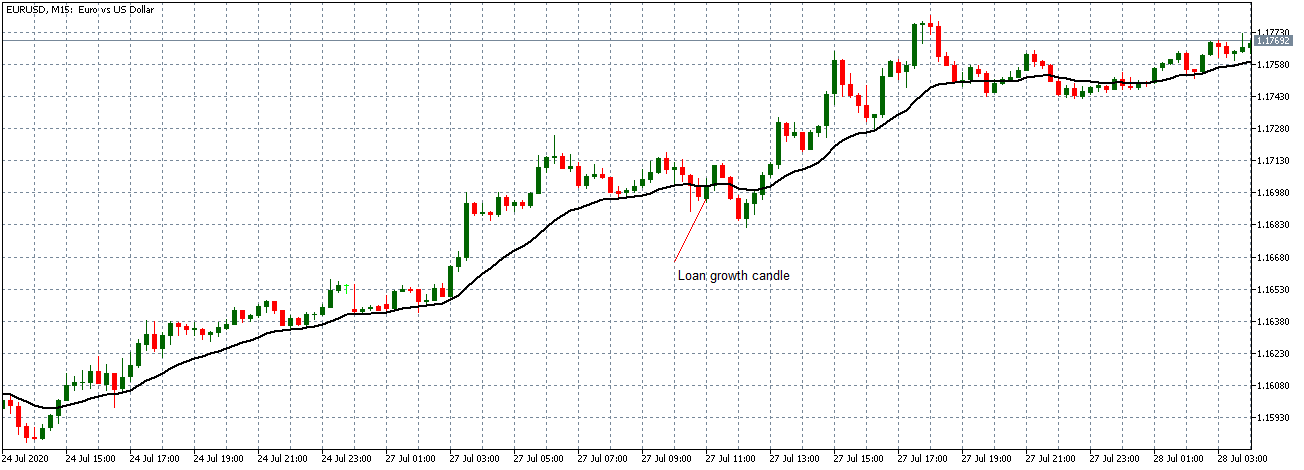
After the news release, the pair forms a 15-minute bullish candle as EUR becomes stronger as expected. However, the news release was not strong enough to cause a shift in the pair’s trend since the pair continued to trade in the previously observed neutral trend.
Now let’s see how this news release impacted other major currency pairs.
EUR/JPY: Before Loan Growth release on July 27, 2020,
Just Before 8.00 AM GMT
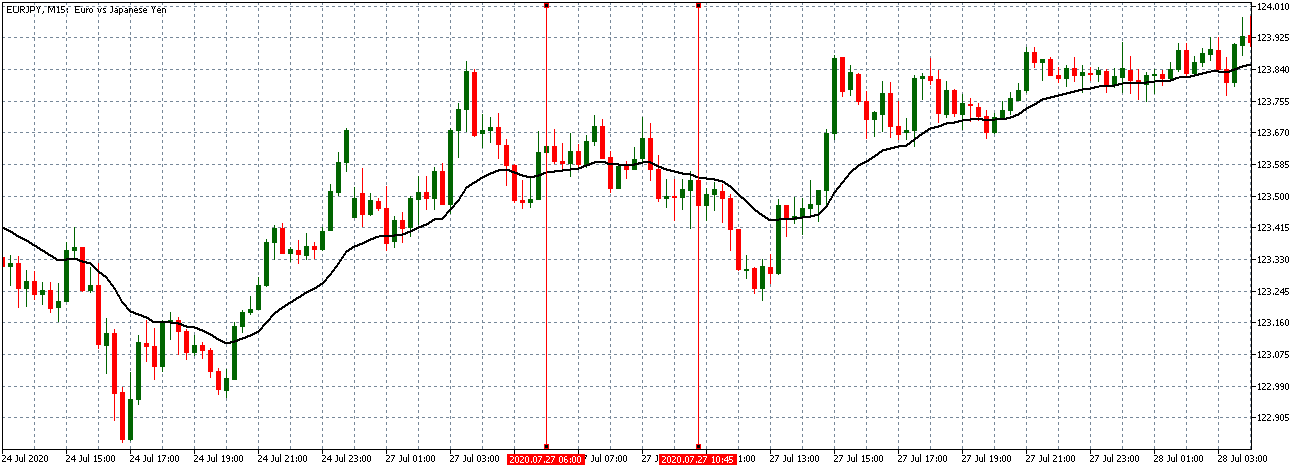
Before the news release, EUR/JPY traded in a similar neutral trend as observed with the EUR/USD with the candles forming around a flattening 20-period Moving Average.
EUR/JPY: After Loan Growth release on July 27,
2020, 8.00 AM GMT
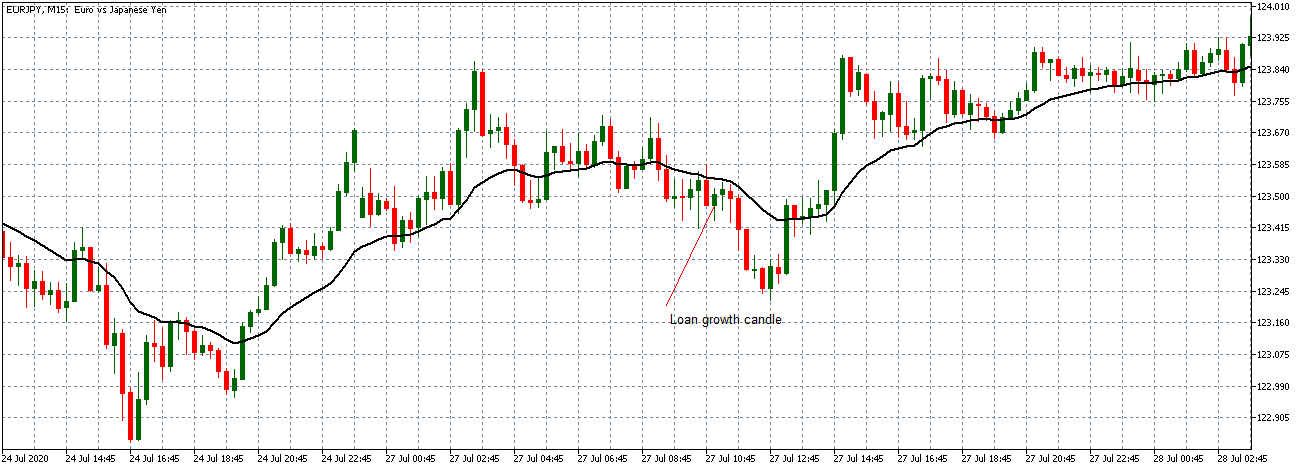
As observed with the EUR/USD pair, EUR/JPY formed a 15-minute bullish candle after the news release as expected. The subsequent trend does now significantly shift.
EUR/CAD: Before Loan Growth release on July 27, 2020,
Just Before 8.00 AM GMT
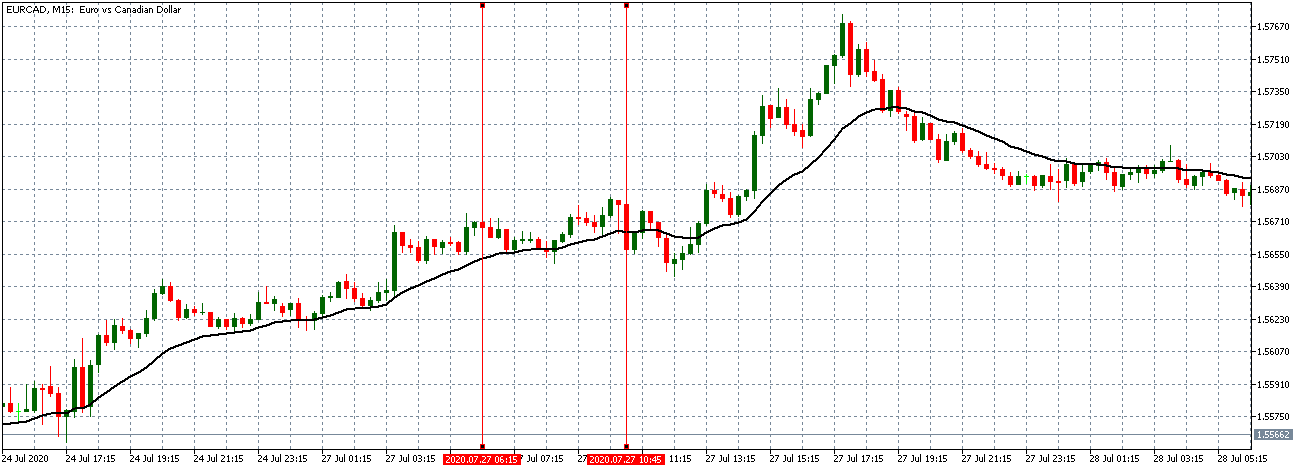
EUR/CAD: After Loan Growth release on July 27, 2020,
8.00 AM GMT
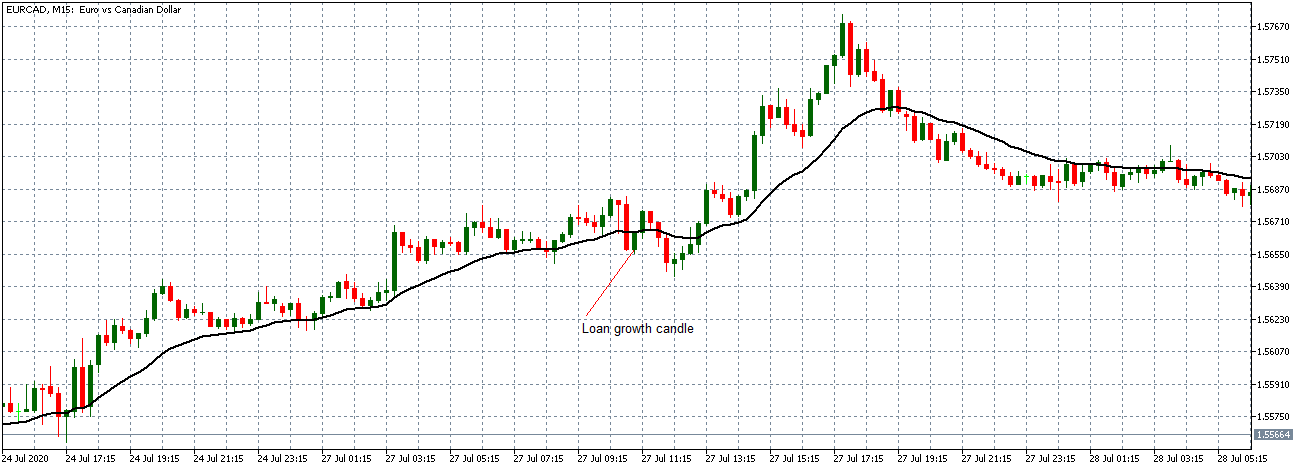
The EUR/CAD pair shows a similar neutral trading pattern as the EUR/USD and EUR/JPY pair before the news release. After the news release, the pair forms a 15-minute bullish candle but later continued trading in the earlier observed neutral trend as the 20-period Moving Average flattens.
The release of the loan growth data has an instant short-term effect on the EUR. The data is, however, not significant enough to cause any relevant shift in the prevailing market trend.