Introduction
The Interbank rate is an essential tool used by the central authorities to control the money flow within the economy. Changes in the interbank rate can add or withdraw money from the system overall, which can stimulate growth or slow down the economy, respectively. The Interbank rate drives interest rates for bank loans, which are the significant sources of capital for businesses and the general public. The understanding of the Interbank rate is crucial for our analysis.
What is the Interbank Rate?
The interbank rate is the percentage rate at which the United States banks lend each other money. A country’s Central bank dictates the banking practices for the banks within the nation. For the United States, it is the Federal Reserve which decides the interest rates and the banking practices. The central banks, in general, demand 10% of their total deposits be held as reserves to maintain liquidity and meet withdrawal needs.
Based on the interbank rate, banks having excess cash can lend money to the banks, which are falling short of capital to meet their immediate requirements or to maintain their minimum reserves.
What is the Interbank Rate – Second Definition?
The interbank rate also refers to the rate at which banks exchange currencies in the global forex market. The forex market consists of an interbank market, which is a significant part of the forex market system overall. This interbank market consists of big players. Most of those are banks, large financial institutions, investment banks, and mutual funds corporations and do not include retail forex institutions or traders.
The interbank rate numbers are what you see when you search in Google the currency exchange rate for a particular pair, but this is not the rate at which you can trade a pair. This rate is only available for the interbank market participants who are usually big financial corporations trading in millions and billions. The price you see is a jacked-up price of the interbank rate in your platform. Your rate is the sum of interbank rate and the spread which your platform charges for trade as profit.
The minimum transaction in the interbank market is in millions; hence the retail traders will not be able to afford the interbank rate. The interbank market participants trade currencies to manage their exchange rate and control interest rate risk.
Although, you can neither control nor trade at the interbank rate, important for traders to be aware of the interbank rate to avoid getting scammed by Forex brokers who main charge way above the interbank rate. The decentralized system of Forex allows for self-regulation, and hence the interbank rates hand the actual exchange rates available to traders are competitive and self-correcting. However, novice traders who are not aware of this might lose money by paying an excessive spread to brokers.
Economic Reports
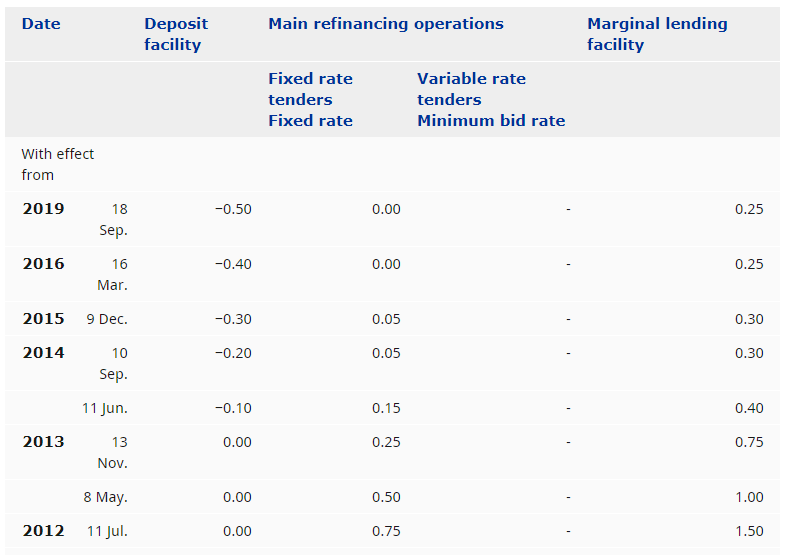
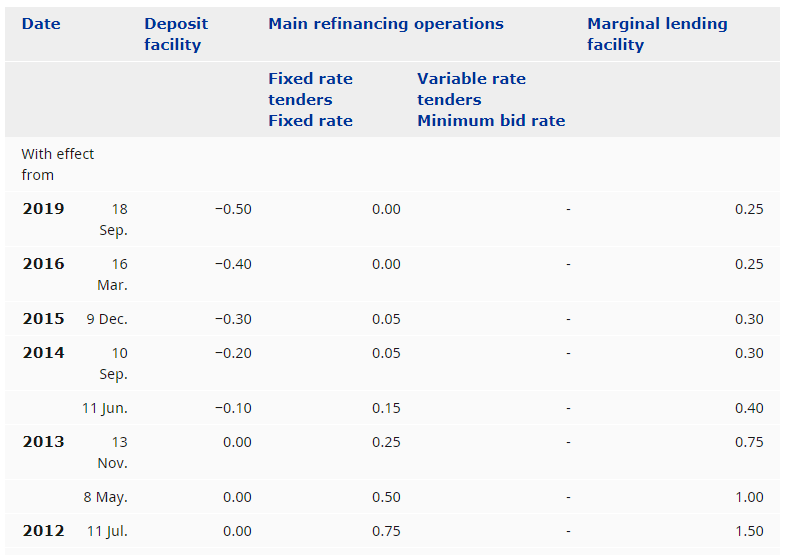
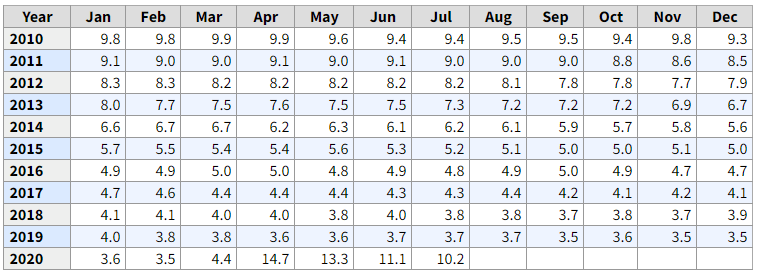
Federal Reserve determines the interbank rate, and the average of all the interbank rates in all the lending transactions between the banks in the United States is called the Fed Funds Rate.
The interbank credit system is applicable for a short period, usually ranging from overnight to a maximum of a week. Hence, the interbank rate is also called the Fed Funds Rate.
The Federal Reserve announces the Fed Funds Rate based on a variety of factors like inflation, GDP growth, recession, monetary policy, etc. On the 1st of every month, the Fed Funds Rate is released.
How can the Interbank Rate be Used for Analysis?
The Fed Funds Rate drives money in and out of the economy. The Fed Funds Rate drives the interest rate on bank loans that is available to the public and businesses.
A higher Fed Funds Rate would mean that loans are now expensive than before. To take a loan now would mean paying more interest rate. Hence the general public is discouraged from taking loans indirectly. On the other hand, now it would be more profitable to save as they receive a higher interest rate on their deposits. Both these factors can change the general public sentiment on money spending. A high-interest rate environment withdraws money from the economy, thereby slowing down economic activity as people are less willing to spend.
Conversely, a low interbank rate encourages banks to give loans at a cheaper rate, and hence more businesses and people will be able to afford loans; this will ultimately lead to the injection of money into the system overall. When more money is available to a company or an individual, the natural tendency is to increase spending, businesses may use for expansion plans. All of this will stimulate economic growth and result in printing higher levels of GDP.
Impact on Currency
Traders and investors can use the Fed Funds Rate as part of their analysis. Since Central authorities use the fed funds rate to manage the economy and money supply, a historical correlation of interest rates with GDP growth rates can help us to determine the direction of the economy and the value of its currency. It is a proportional indicator meaning higher interbank rates relate to currency appreciating phenomenon and vice versa.
Higher Interbank rates result in banks paying out higher interest rates for deposits, which can also attract foreign investors to purchase domestic currency to make a deposit and earn better returns on their investment. Therefore, an increase in capital flowing into the economy and decreased local currency circulation in the rest of the world, thereby increasing its demand and worth.
A low interbank rate results in increased money flow into the system, which can be inflationary, thereby depreciating the purchasing power of its currency. Conversely, a higher interbank rate results in decreased money circulation in the system, which will be deflationary for the economy, and the reduced demand for goods and services will increase the purchasing power of the currency as people would tend to save than spend.
Even though the interbank rate changes do not immediately get reflected in the macroeconomic numbers like GDP and currency value, it is a slow indicator in that sense that it takes a particular time (weeks to few months) to show its effect in actuality. It is also important to know that the authorities use the interbank rate as a response or corrective measure to the current economic situation.
It is more of a gate check for inflation or deflation. It is more of an effect to a cause and not a cause in itself. It is a passive indicator in comparison to other indicators. It reflects more the past and current economic activities than upcoming financial situations. The initial temporary volatility in the currency after the news release is typical, but the long term effect reflects after a certain number of weeks only.
Sources of Interbank Rates
We can find out the Fed Funds Rate from the official website of the Federal Reserve System of the United States: Federal Reserve System | Selected Interest Rates. We can also find a historical graphical representation of the effective fed fund rate changes in the St. Louis FRED website. For reference – Fed Fund Rate
Impact of Interbank Rate News Announcement
The ultimate goal of any fundamental analysis is usually to determine if there will be a hike or a cut in the interest rates. As mentioned earlier, the interbank rate can also be referred to as the Federal funds rate. In the US, the Federal Reserve releases the interbank rate is determined by the FOMC which meets eight times in a year to set this rate
Below is a screengrab of the Federal Funds Rate from Forex Factory. On the right, we can see a legend that indicates the level of impact the Fundamental Indicator has on the corresponding currency.
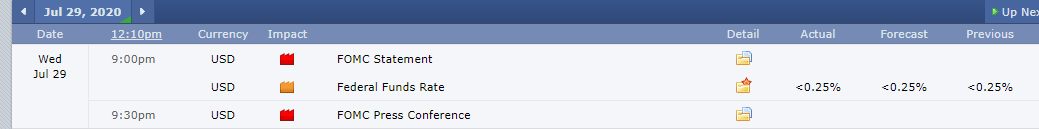
The snapshot below shows the latest release of the Federal Funds Rate on July 29, 2020, at 1.00 PM ET. In the latest release, the FOMC recommended that the rate remains within the target of 0% and 0.25%. This range was within the analysts’ expectations.
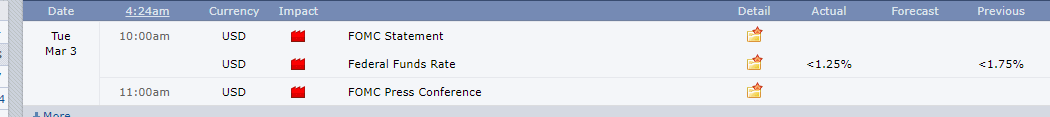
It is worth noting that this year, the Federal Reserve has conducted two emergency rate cuts to combat the Coronavirus inflicted economic shocks. The first emergency rate cut was on March 3, 2020, at 10.00 AM ET, as shown by the screenshot below. The Federal funds rate was reduced to a target range of 1.00% to 1.25% from the previous range of 1.50% to 1.75%.
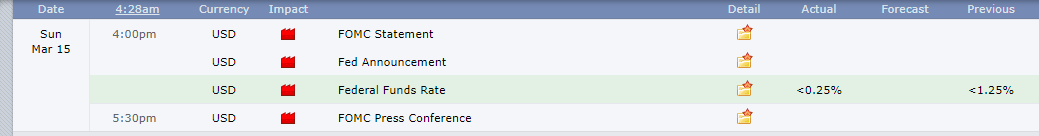
At another unscheduled emergency meeting on March 15, 2020, at 4.00 PM ET, the FOMC cut the federal funds rate by 1.00% to a target range of 0.00% to 0.25%.
Now, let’s see how this news release made an impact on the Forex price charts.
EUR/USD: Before Interbank Rate release on July 29, 2020, Just Before 1.00 PM ET

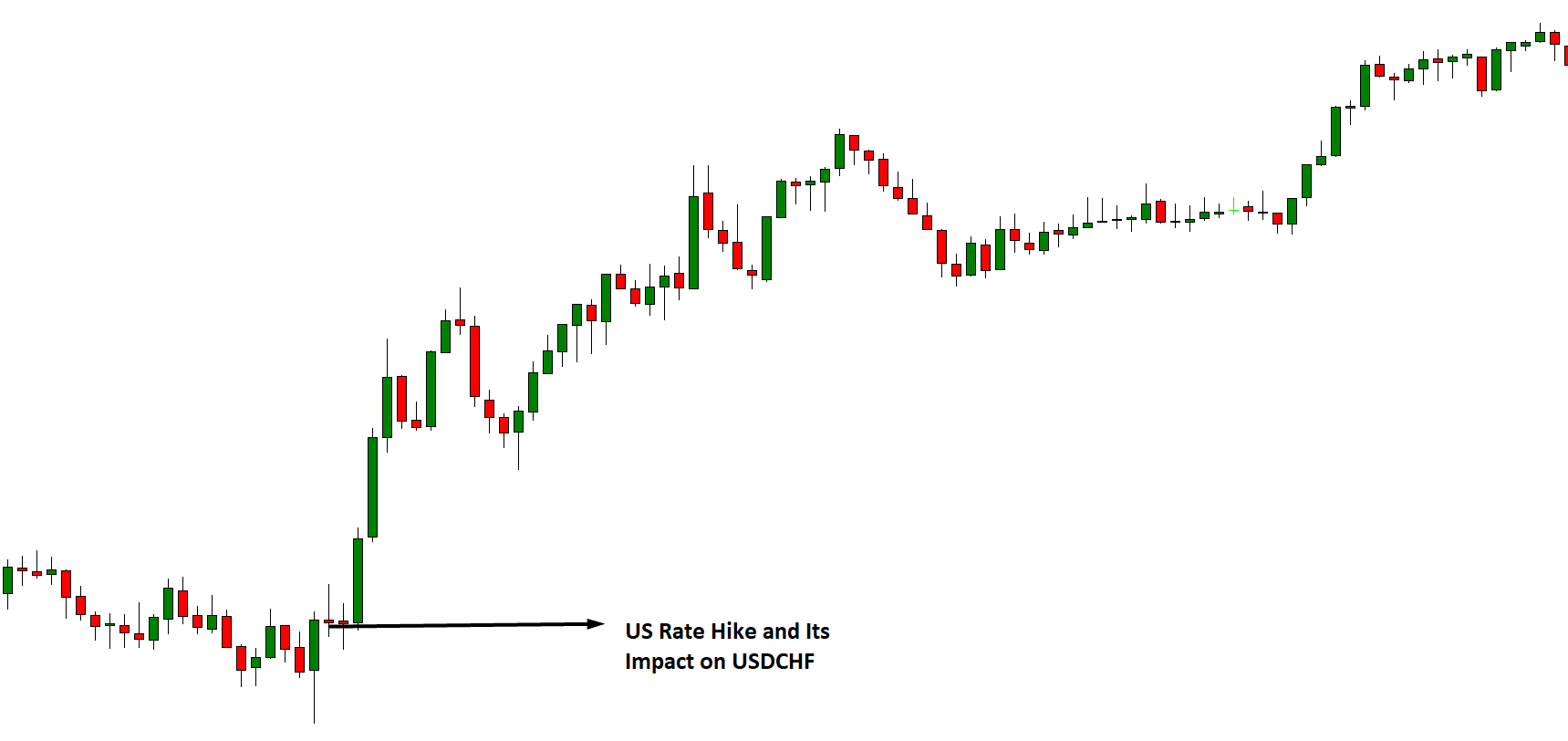
As shown on the above 15-minute chart of the EUR/USD, the pair was on a progressing uptrend between 7.45 AM and 12.45 PM ET. This uptrend as evidenced by the subsequent bullish candles forming above the 20-period Moving Average.
EUR/USD: After Interbank Rate release on July 29, 2020, 1.00 PM ET
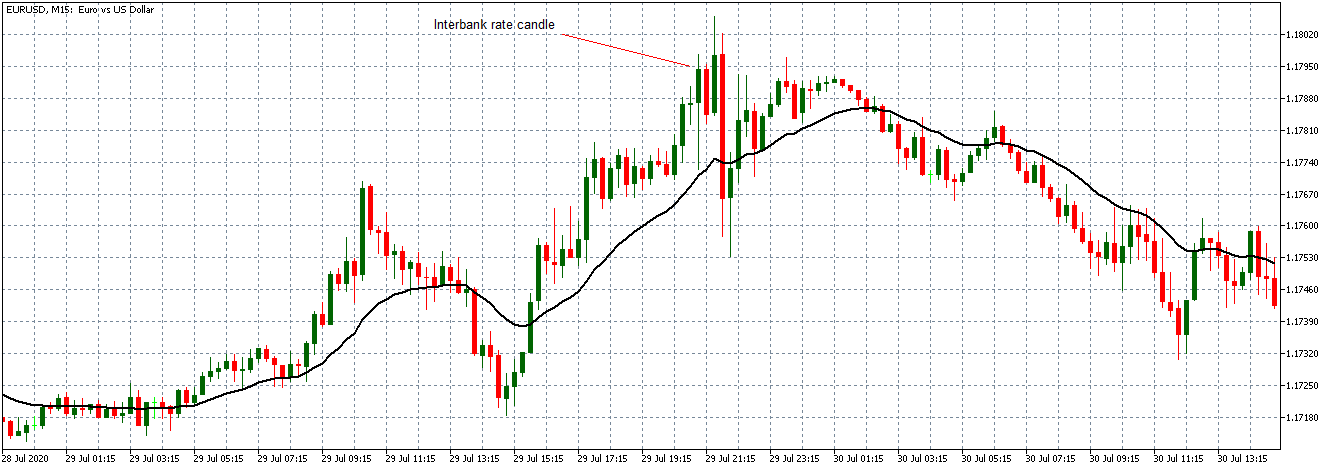
After the FOMC release of the Federal funds rate, there is a renewed volatility in the market. The initial market reaction was negative for USD since the FOMC kept the rate unchanged. The rate release did not result in a shift in the trend since most traders anticipate it and price in their expectations in the market.
Let’s quickly see how this new release has impacted some of the other major Forex currency pairs.
GBP/USD: Before Interbank Rate release on July 29, 2020, Just Before 1.00 PM ET
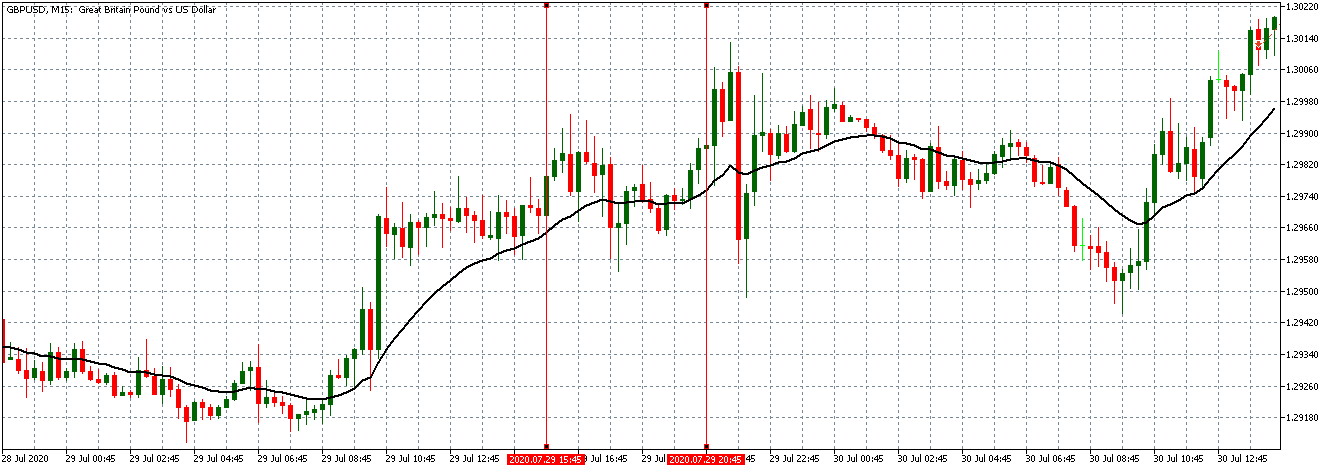
GBP/USD: After Interbank Rate release on July 29, 2020, 1.00 PM ET

The GBP/USD pair shows similar trends, as observed with the EUR/USD. There is a steady uptrend hours before the interbank rate release. Market volatility is present after the news release but not significant enough to alter the prevailing trend.
USD/CAD: Before Interbank Rate release on July 29, 2020, Just Before 1.00 PM ET
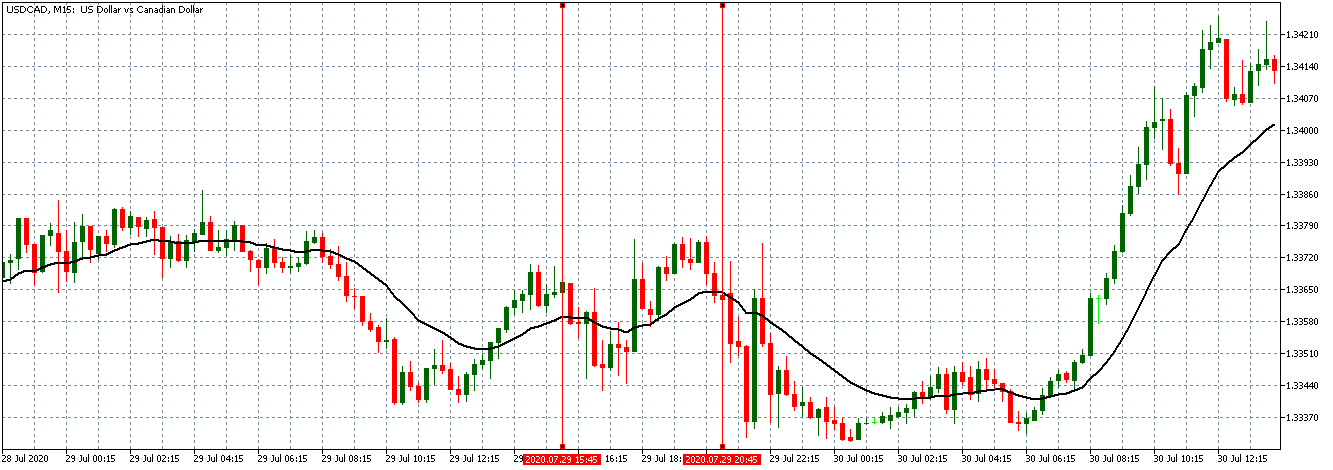
USD/CAD: After Interbank Rate release on July 29, 2020, 1.00 PM ET
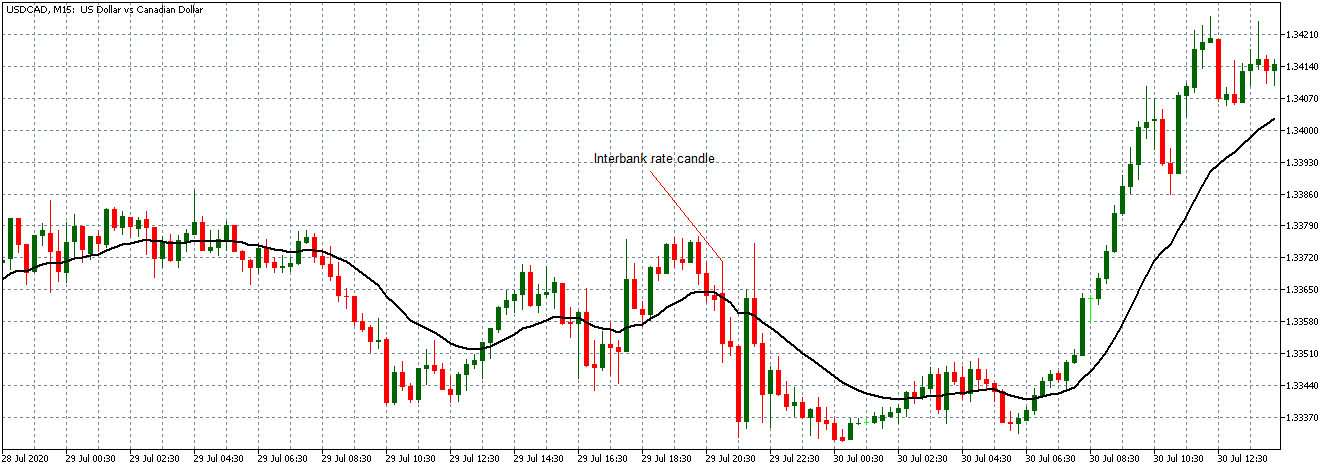
For the USD/CAD pair, a weak uptrend is observed, with candles forming just around the 20-period Moving Average. After the interbank rate release, the pair shows the same weakness for the USD as observed with the EUR/USD and the GBP/USD.
Bottom Line
The interbank rate is a high-impact fundamental indicator in the forex market. The FOMC Statement, however, dampens its impact since it is focused on the future. It is therefore advisable for traders to avoid opening significant positions before this news release. Furthermore, reading the FOMC statement will help to gauge whether the Fed is hawkish or dovish about the future.