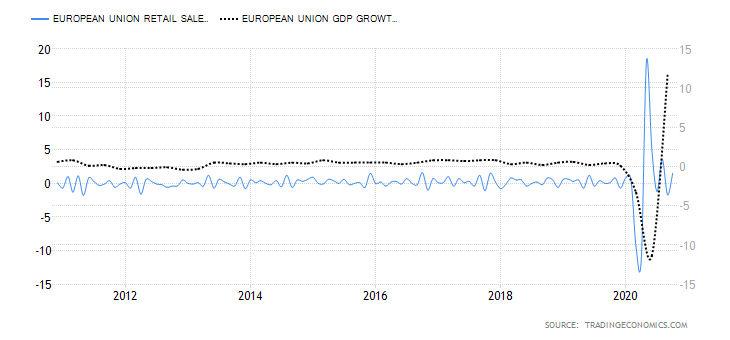
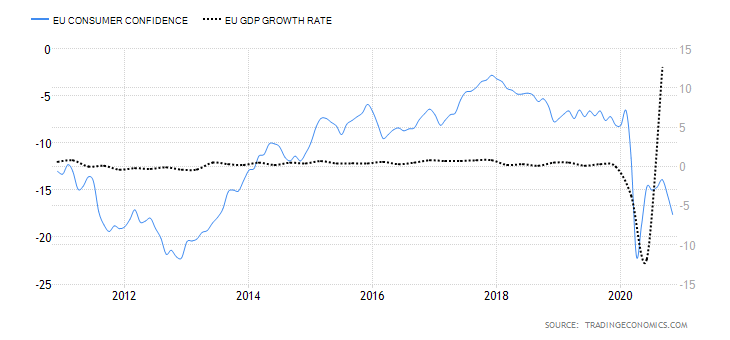
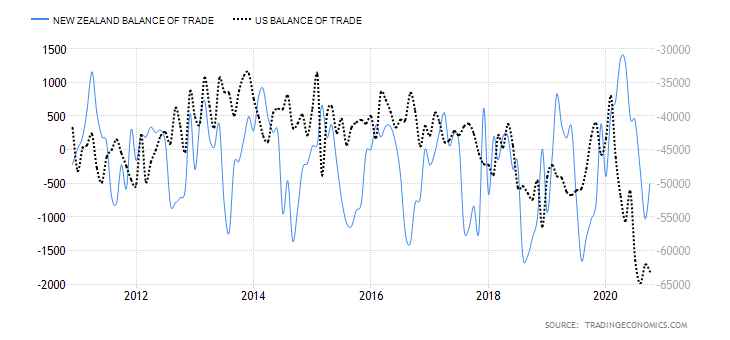
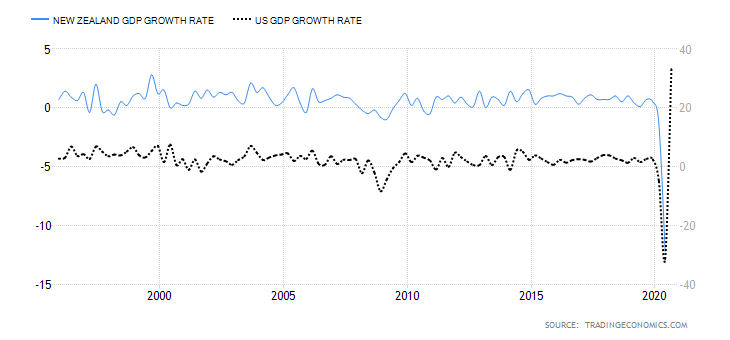
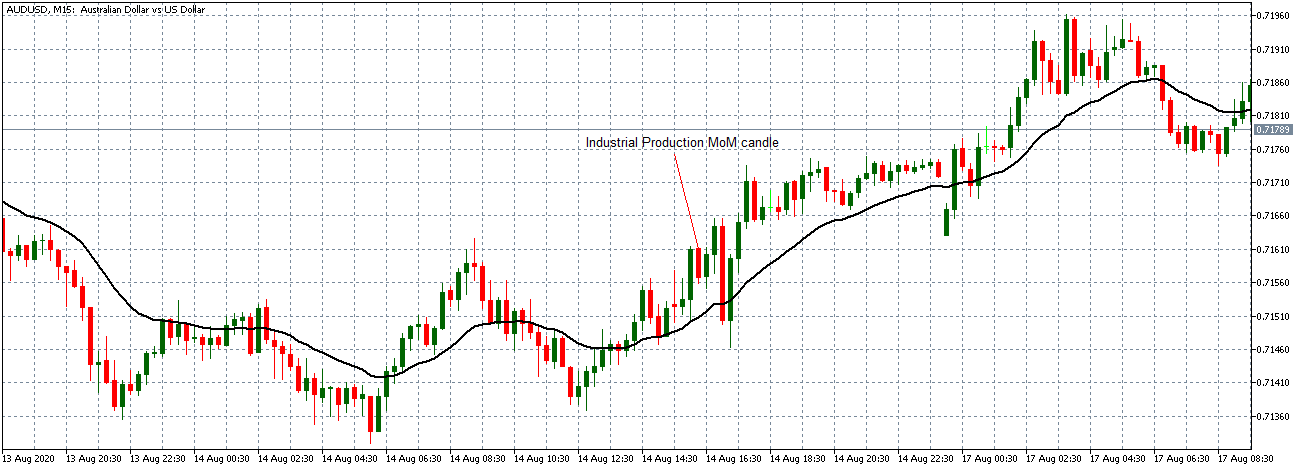
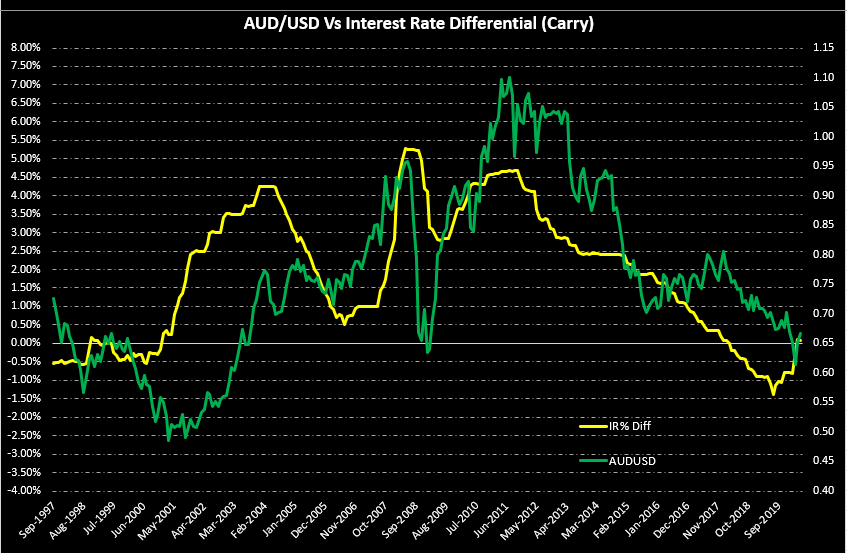
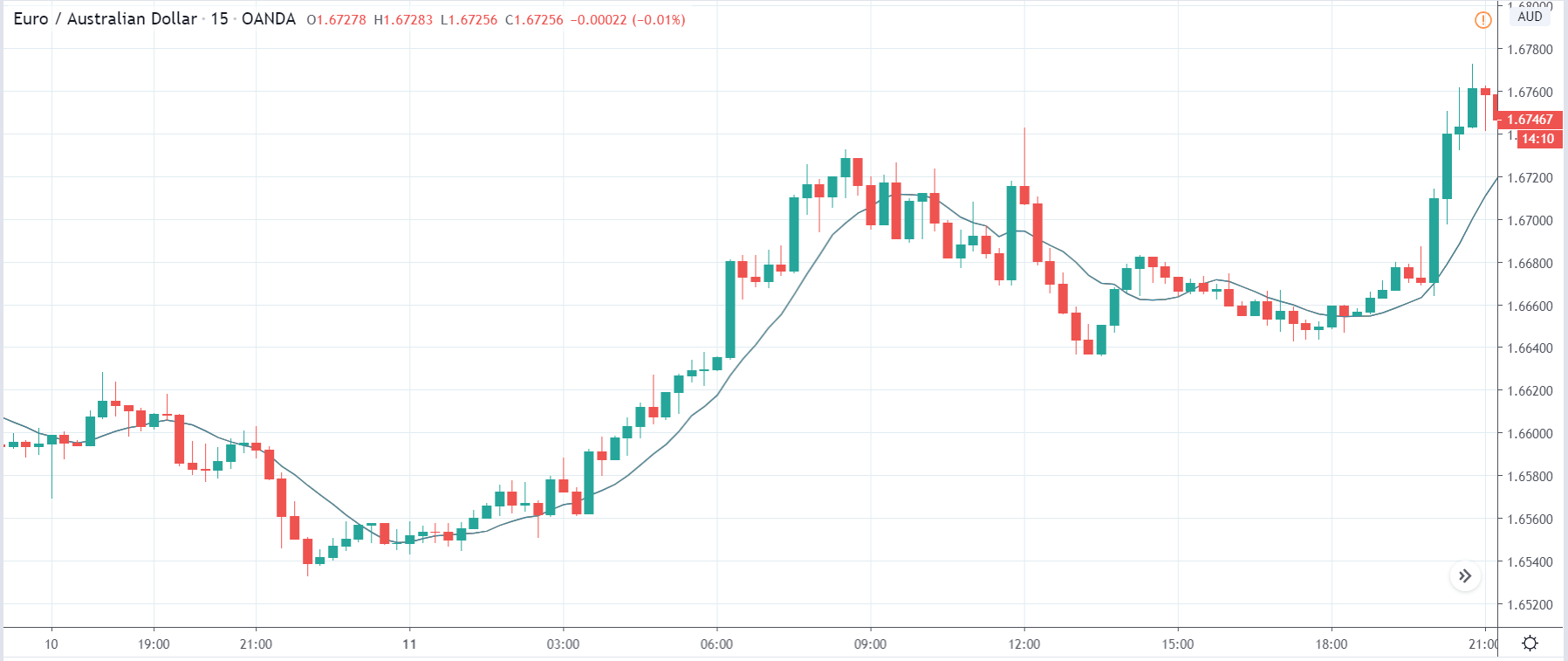
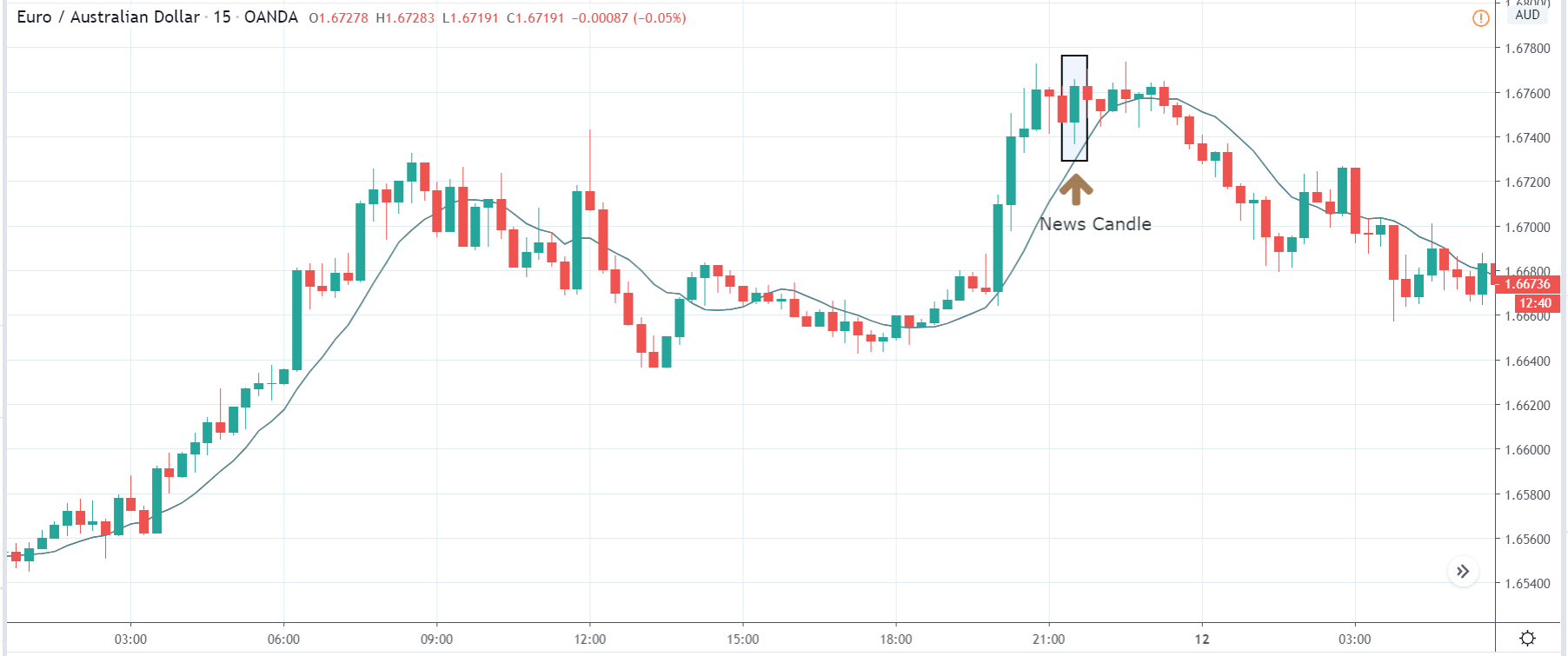
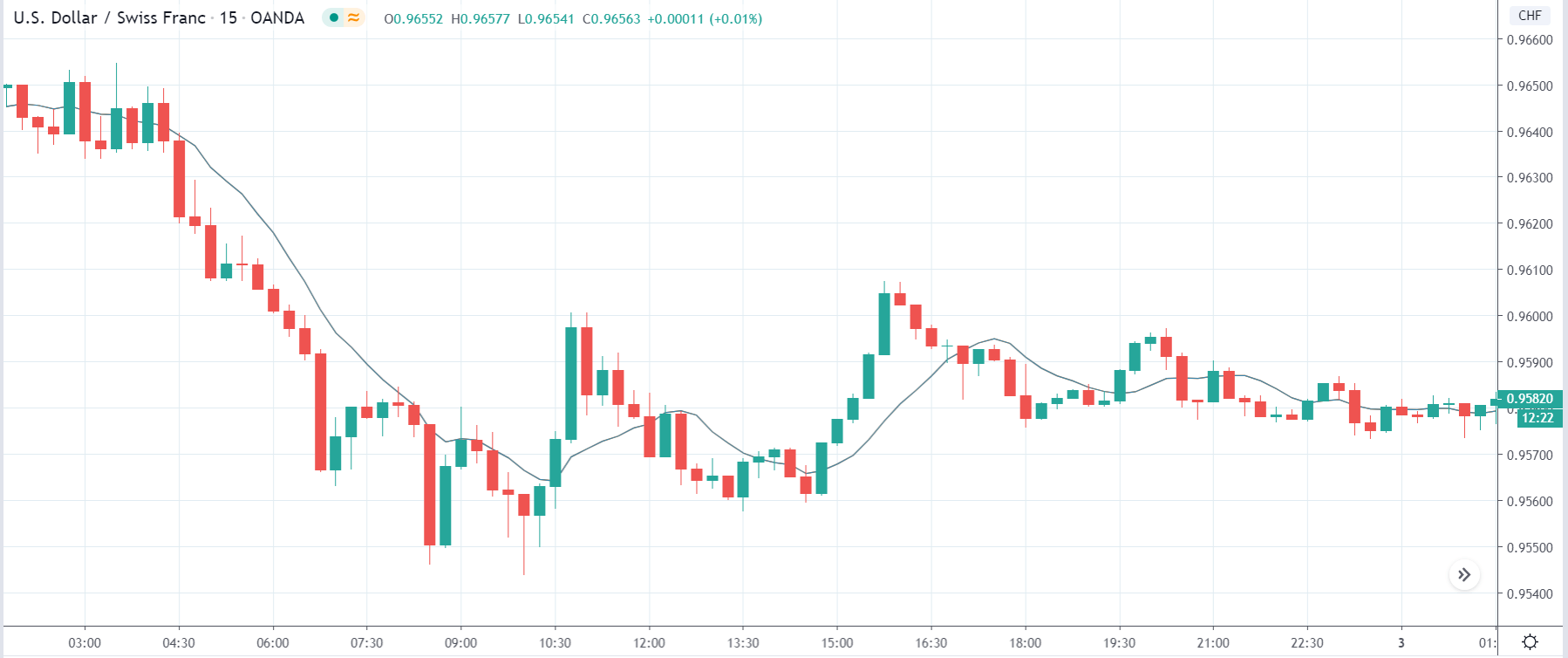
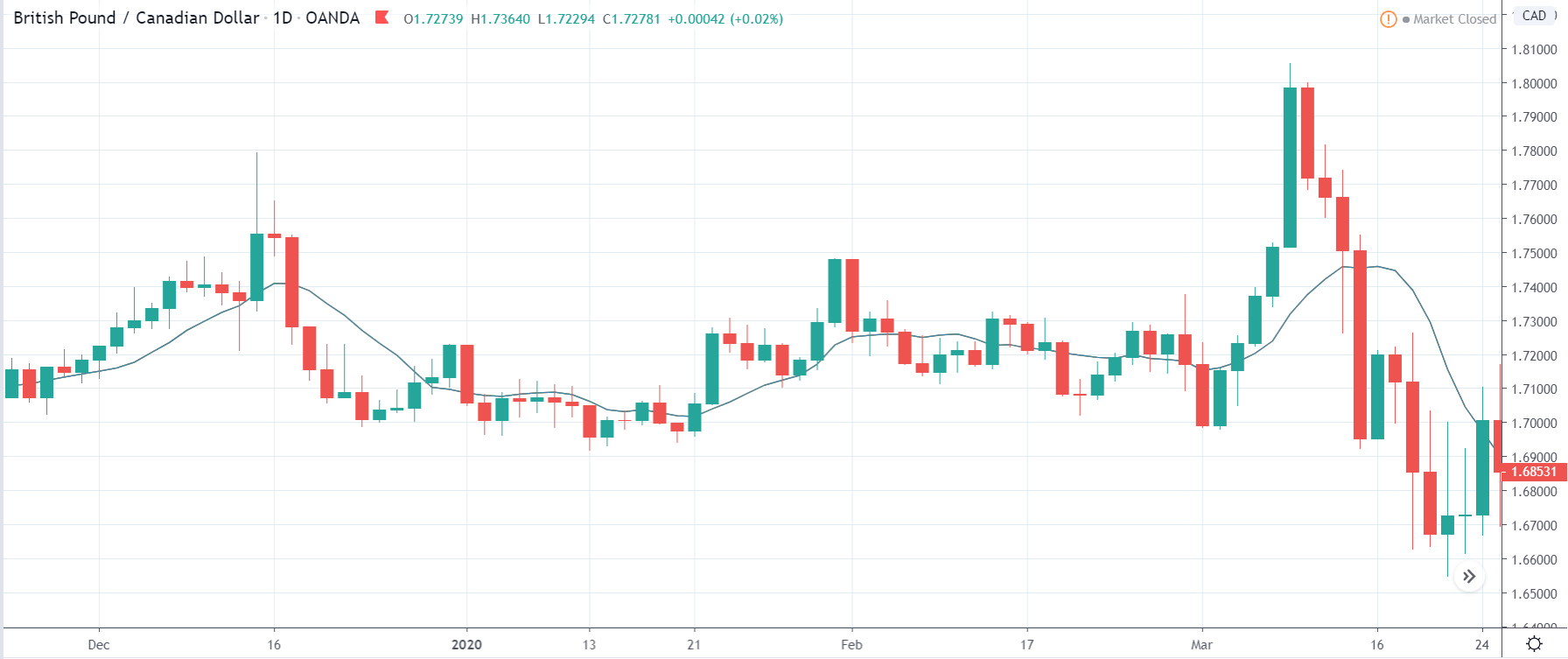
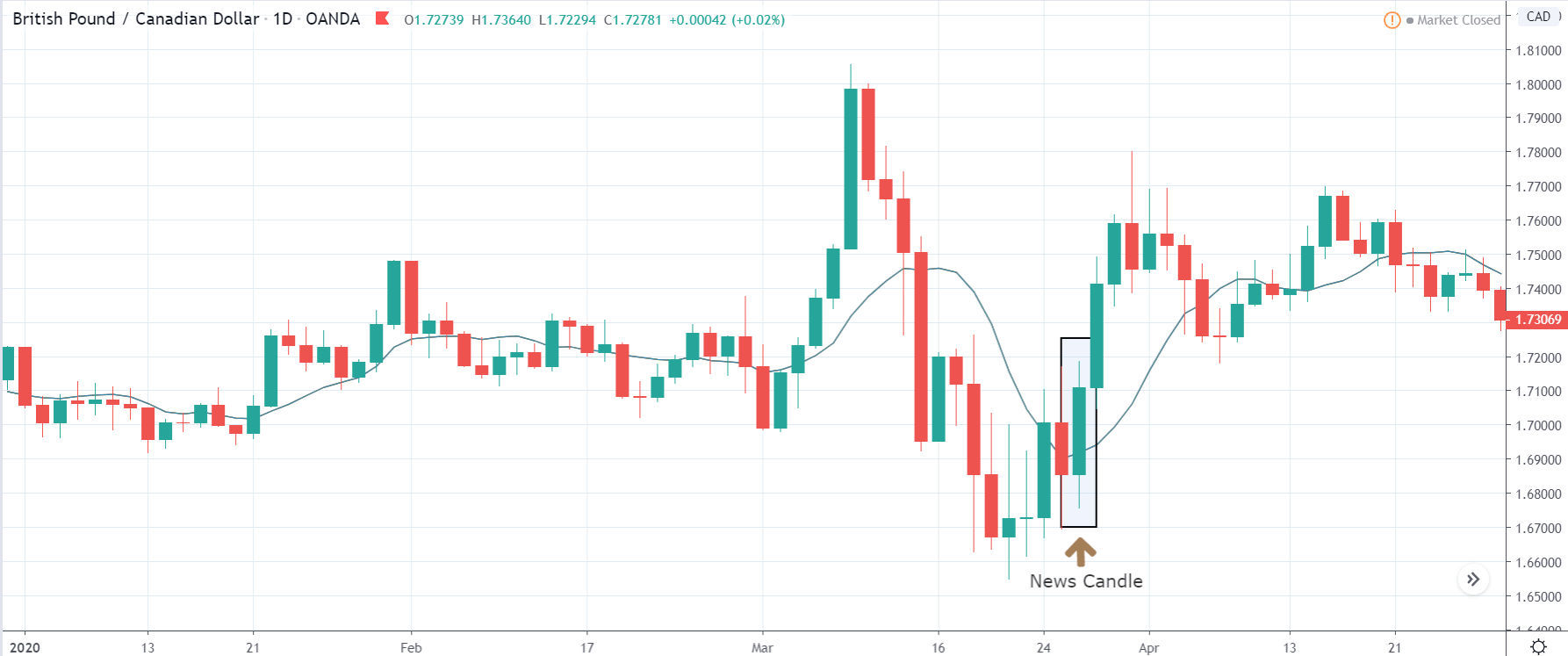
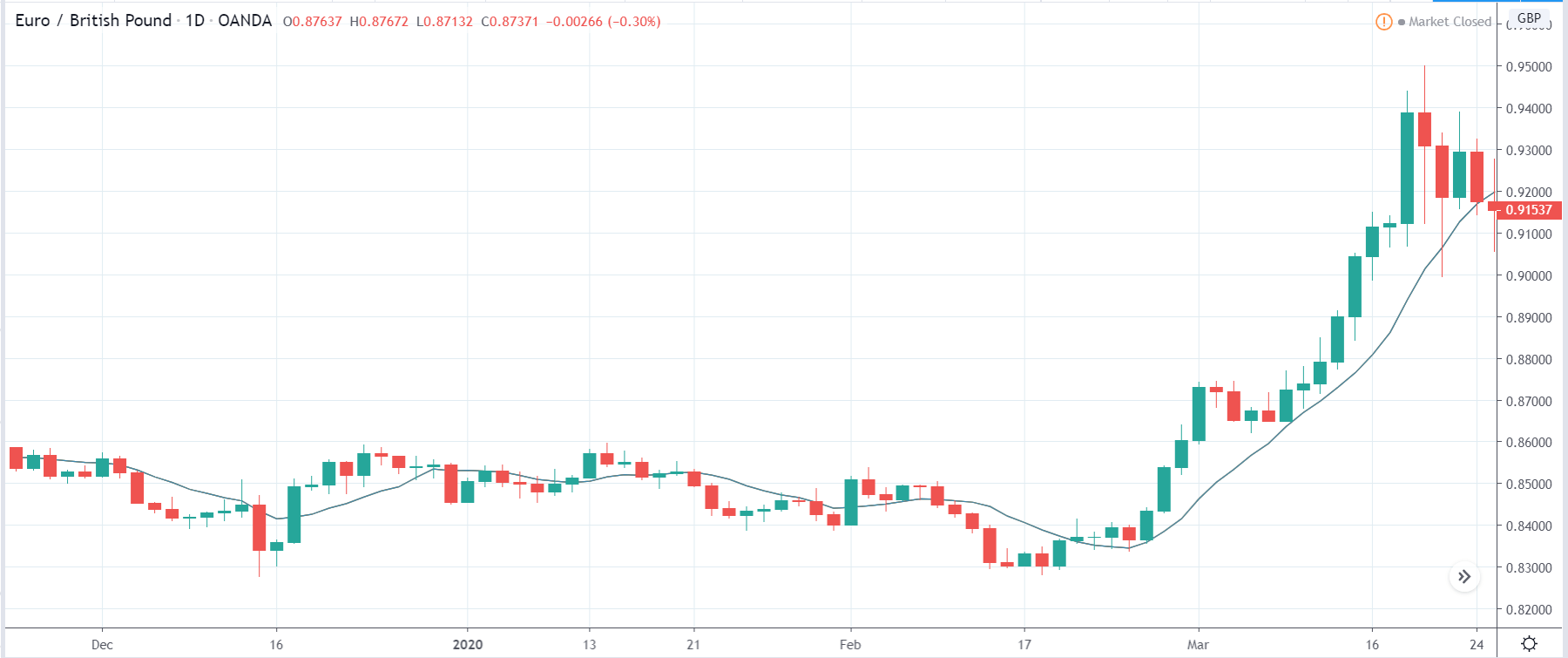
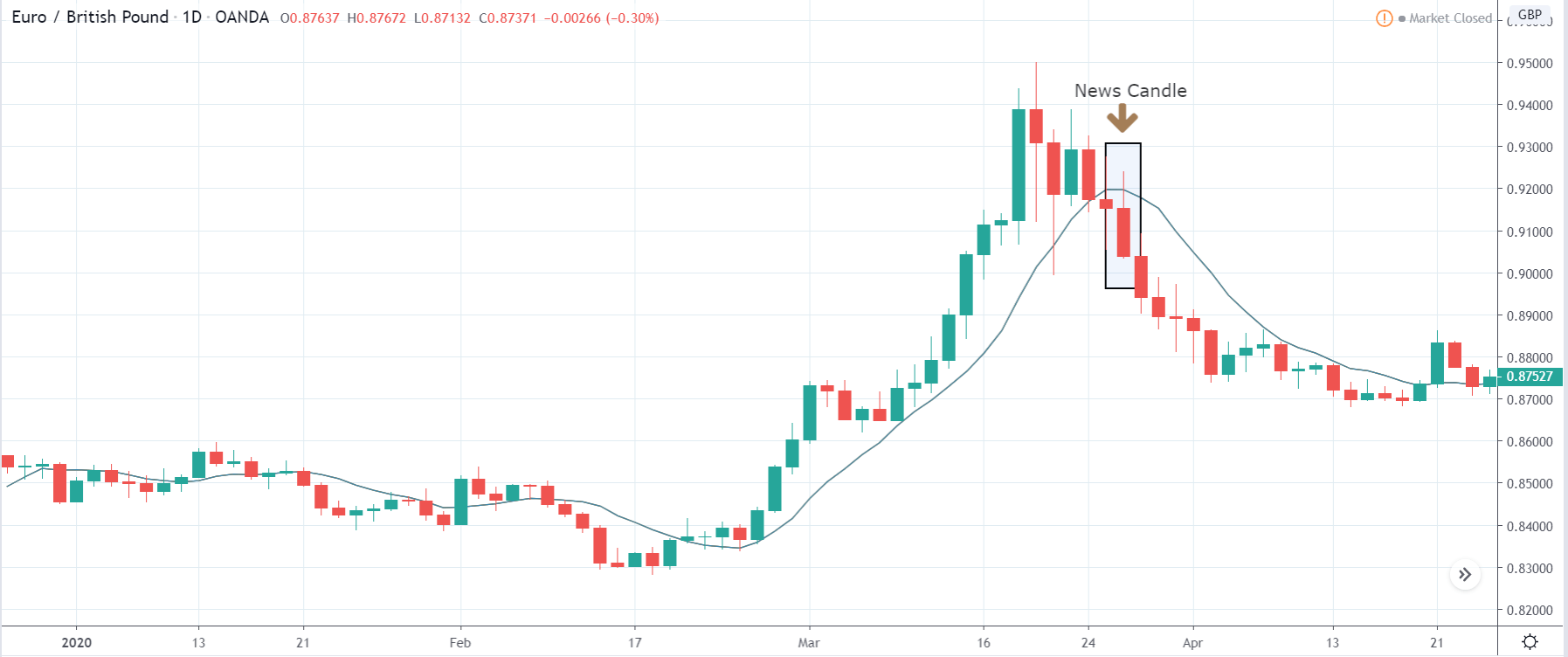
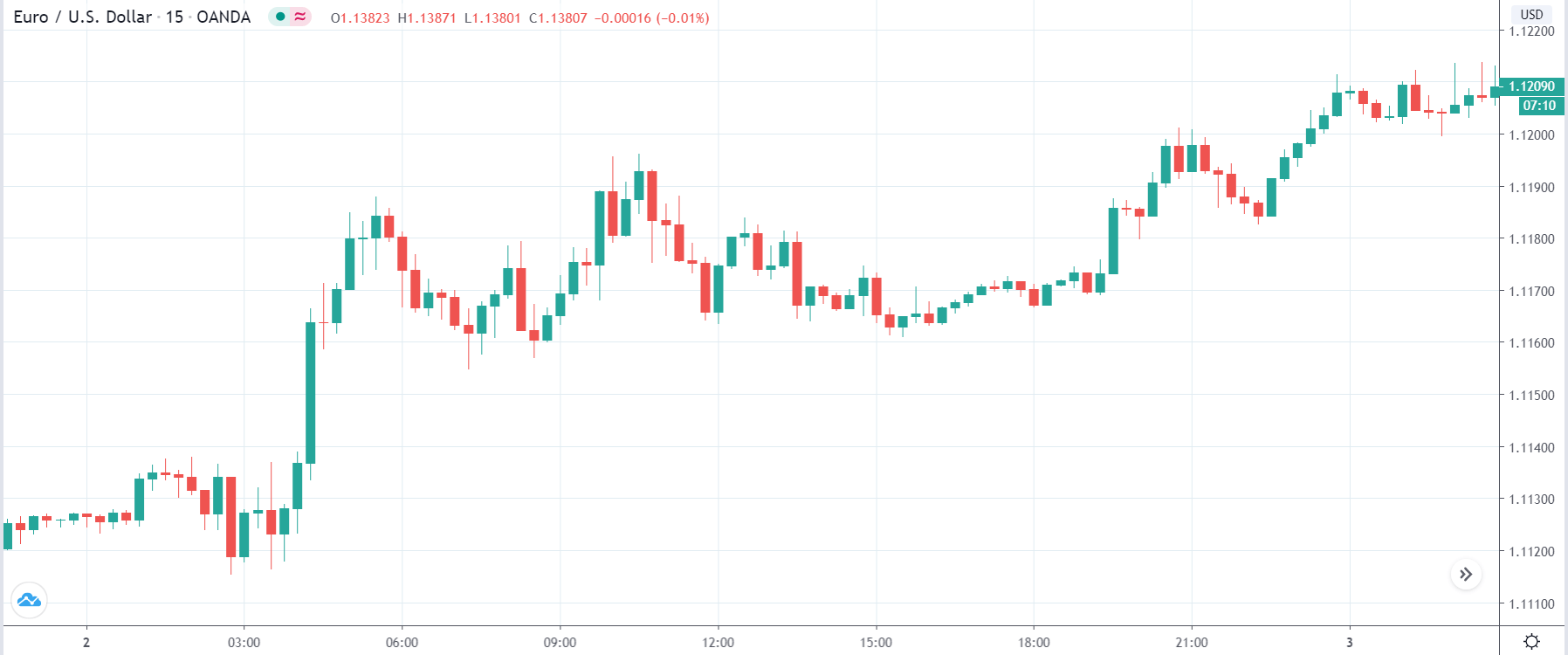
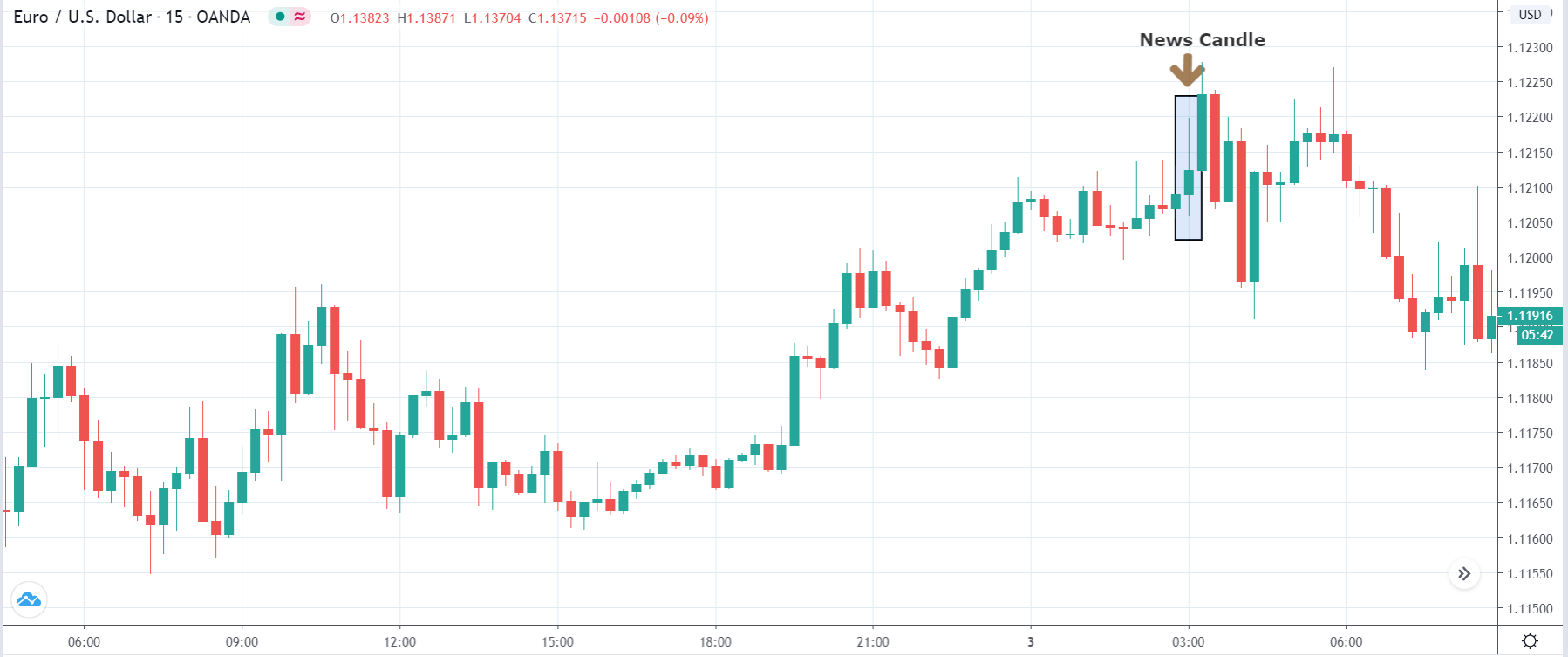
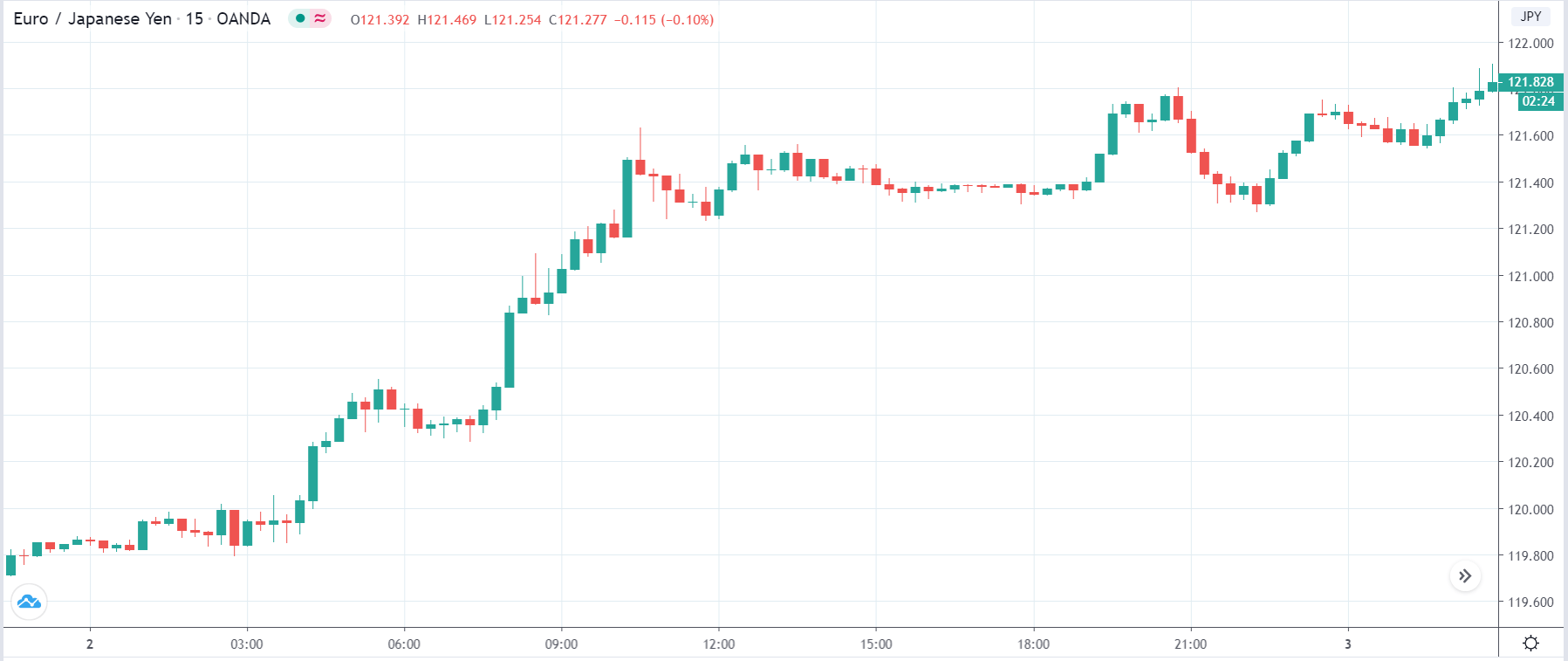
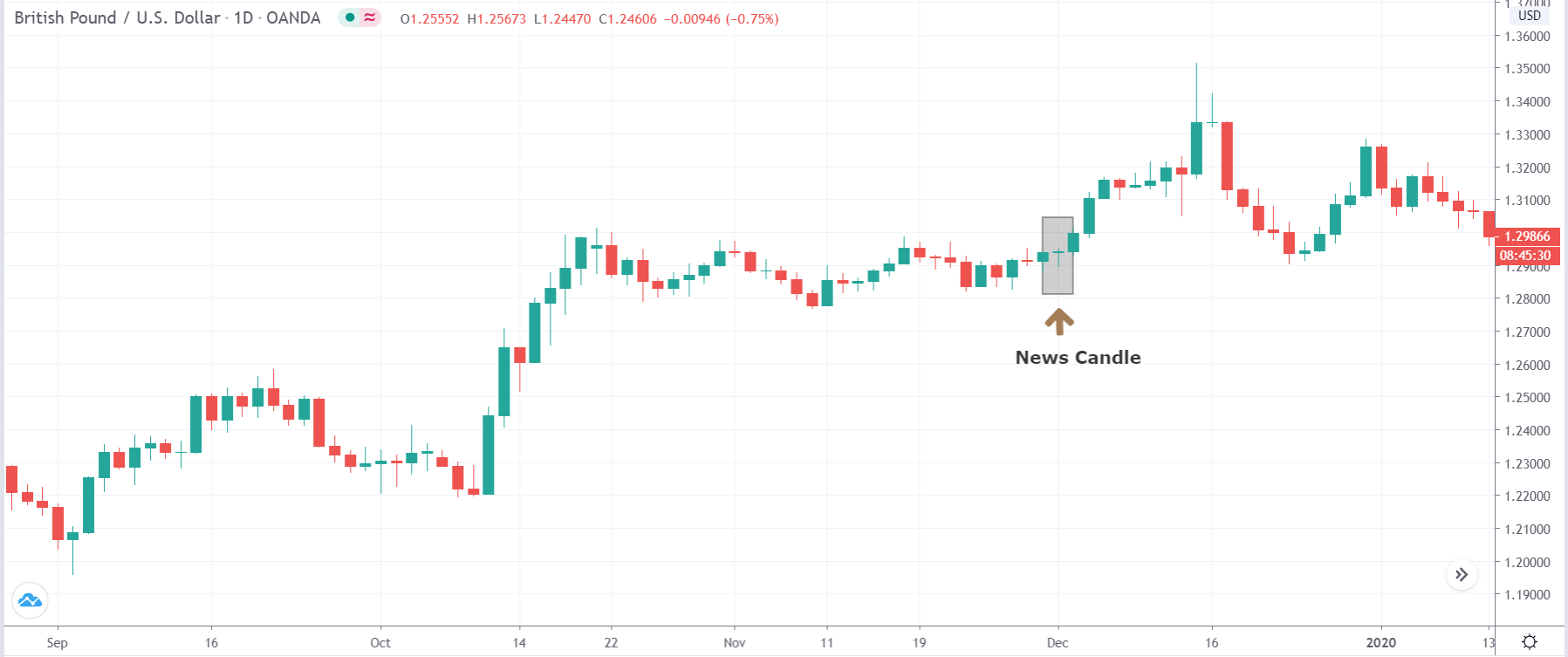
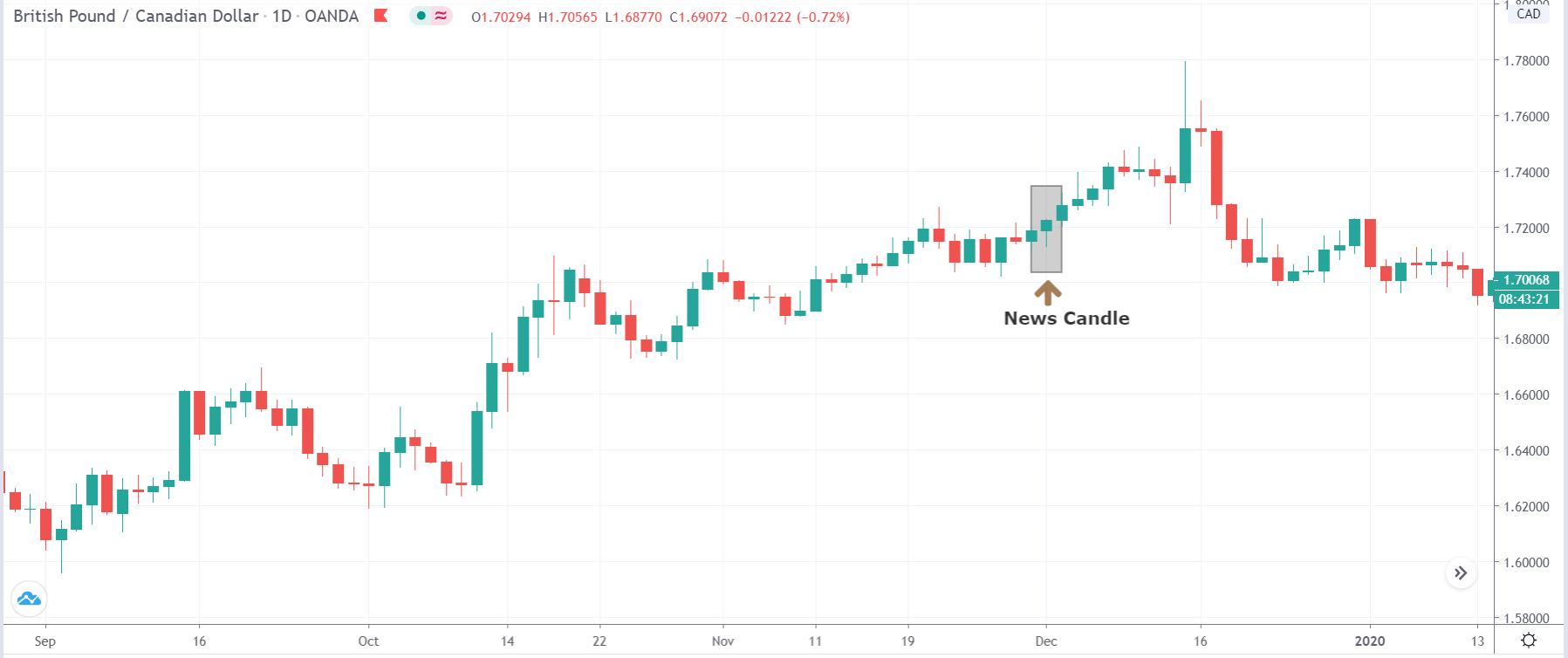
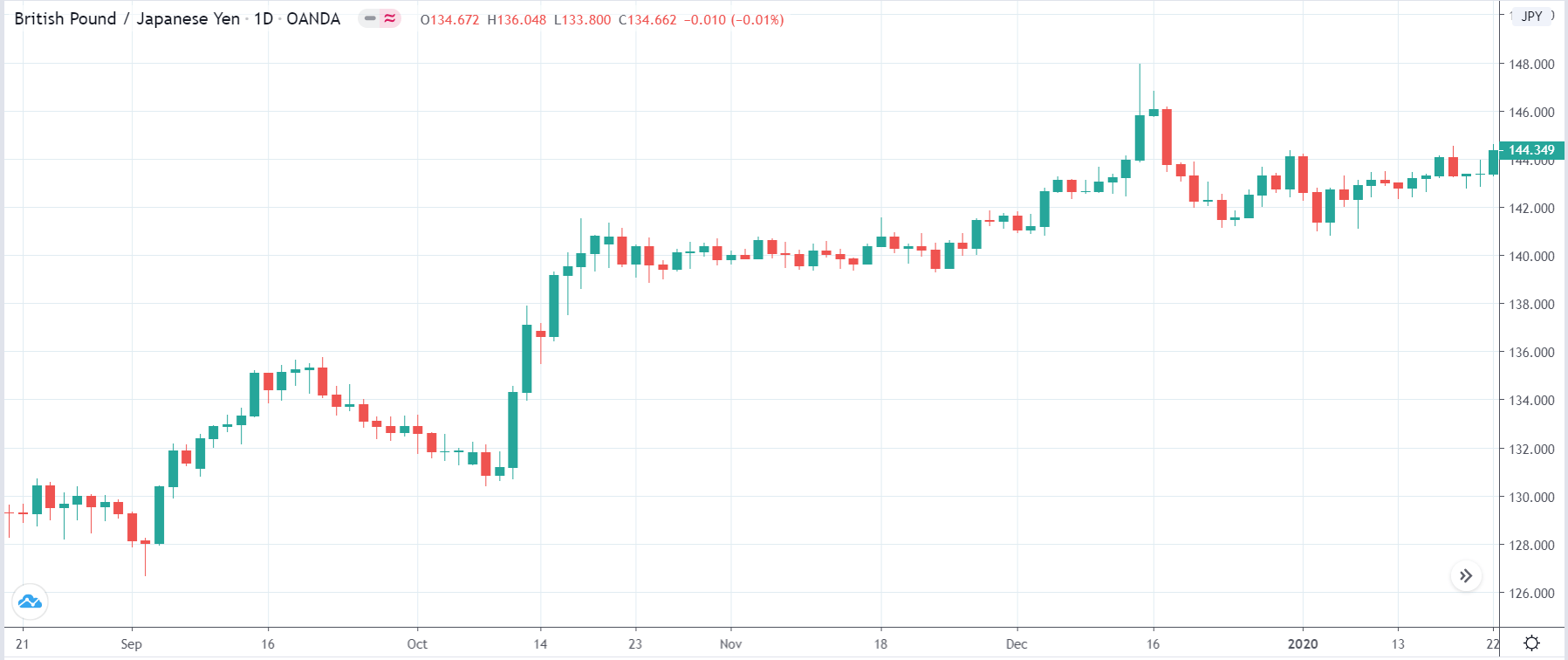
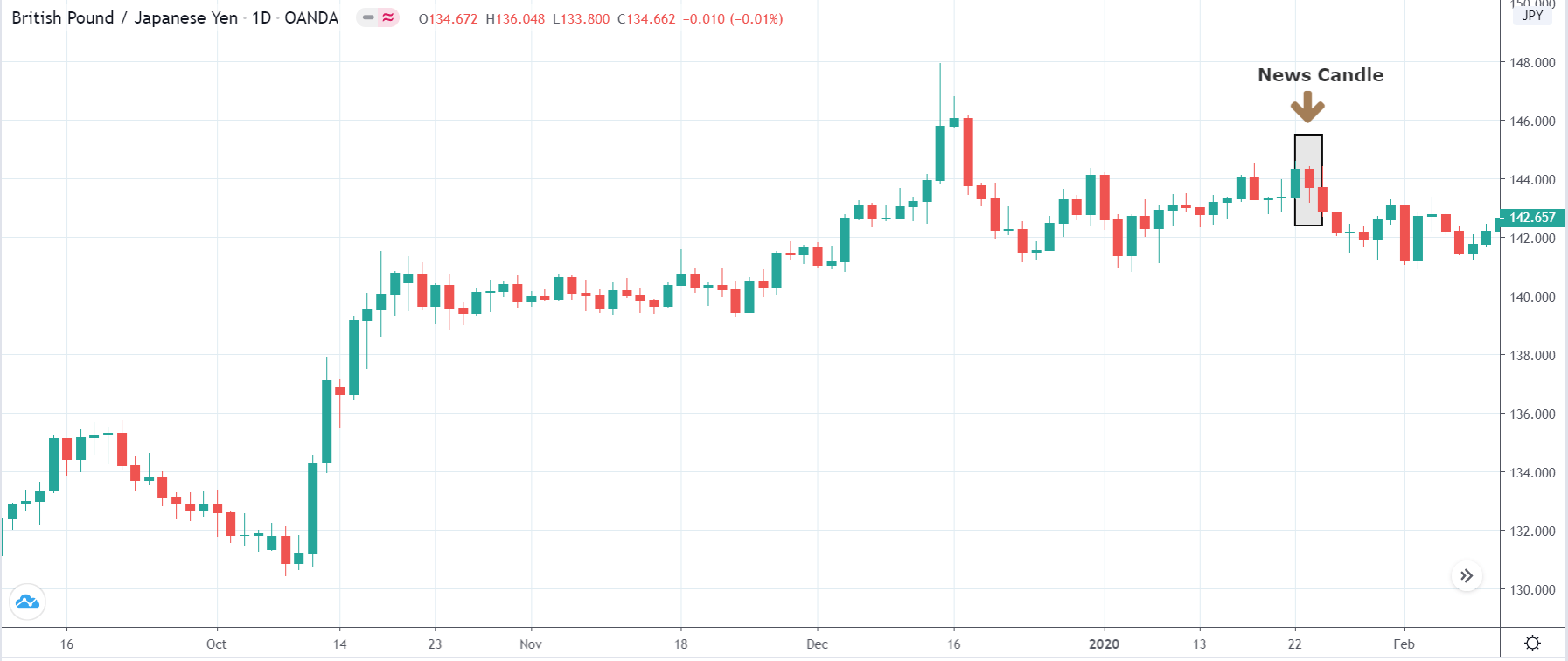
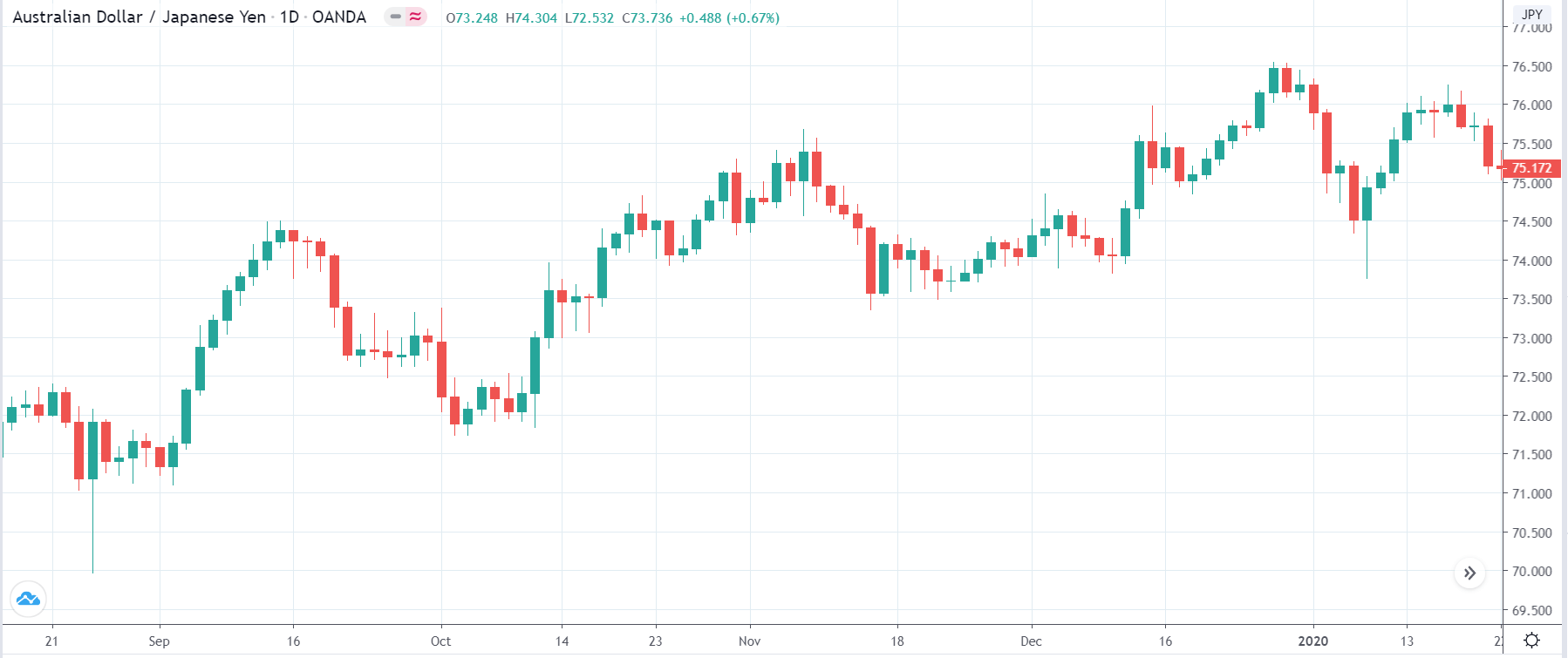
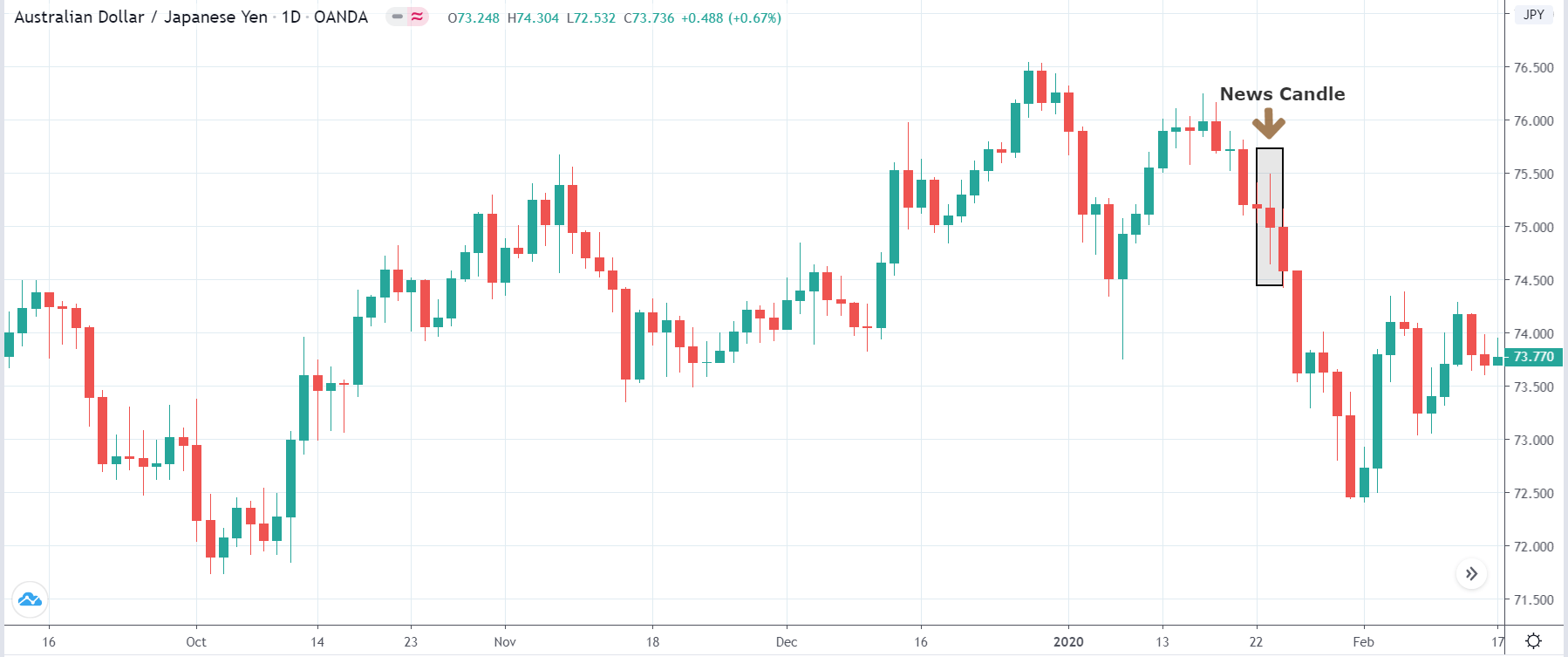
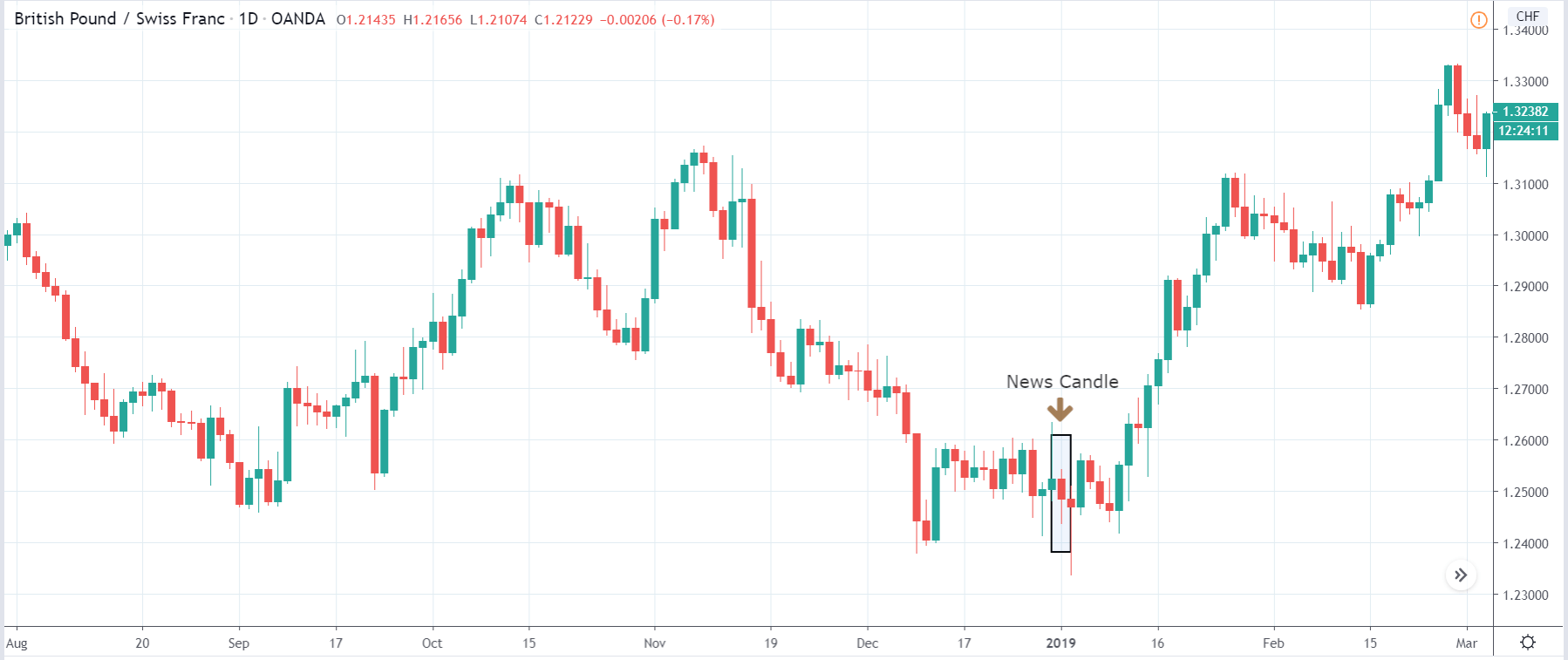
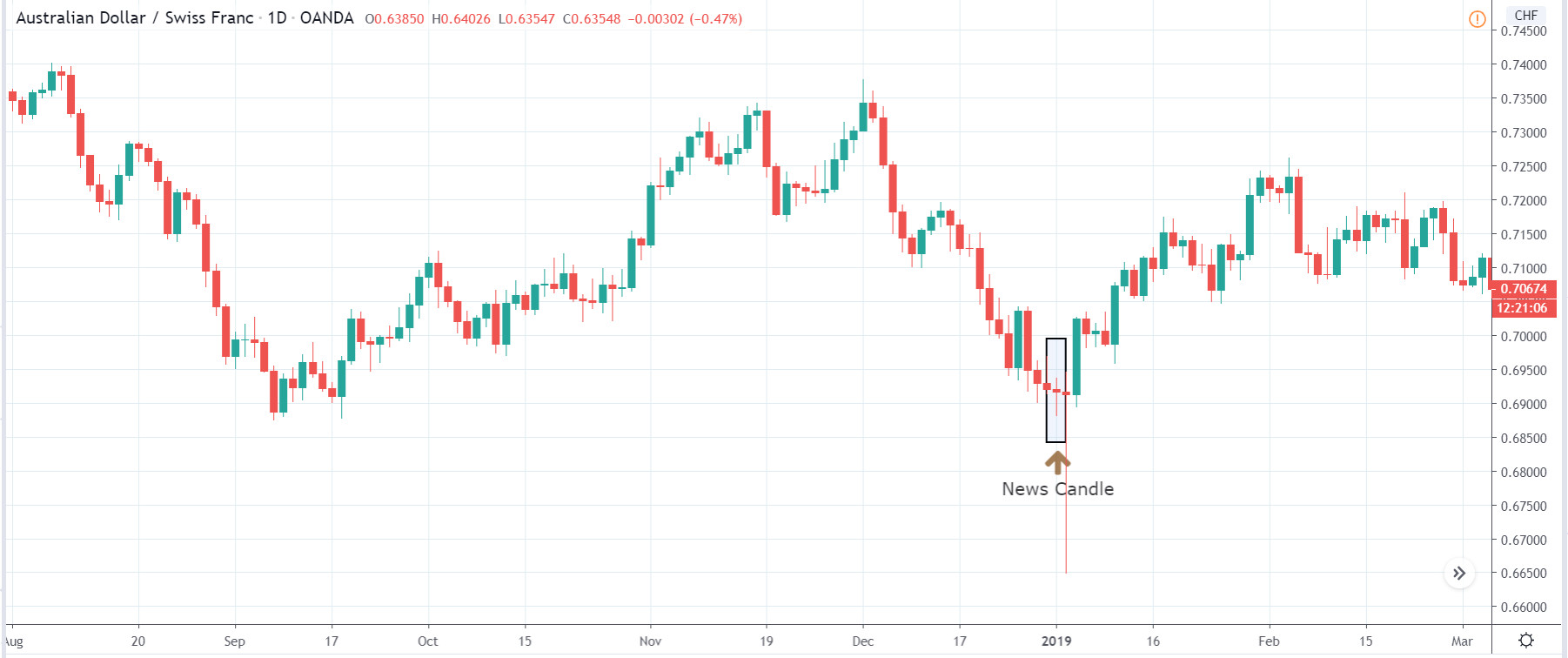
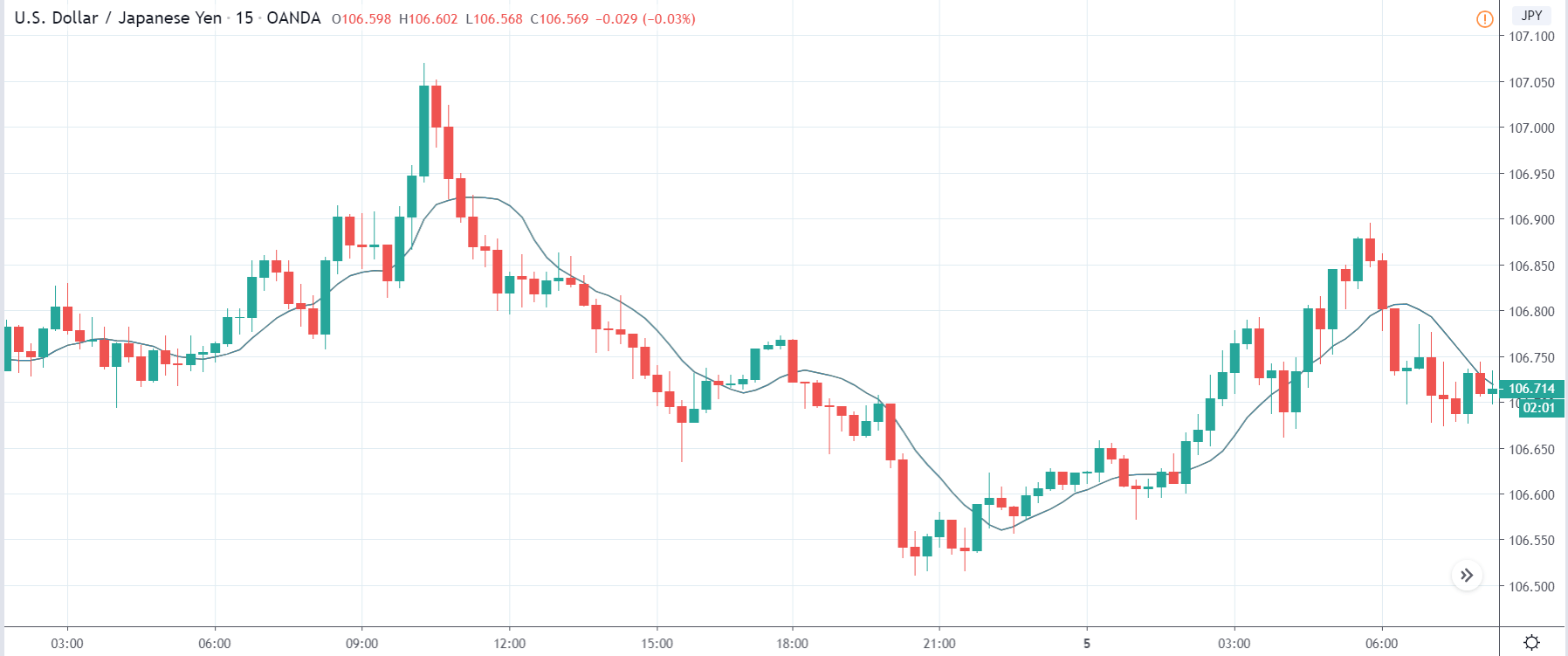
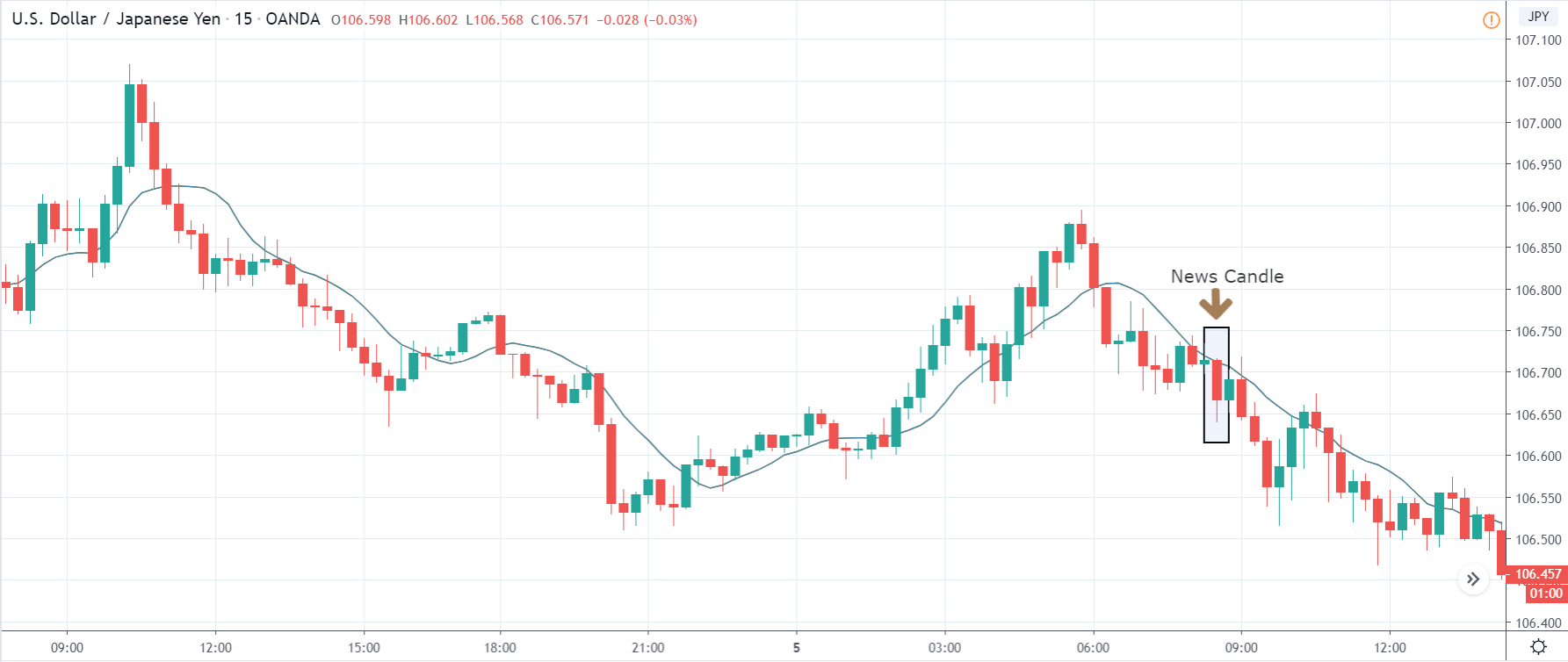
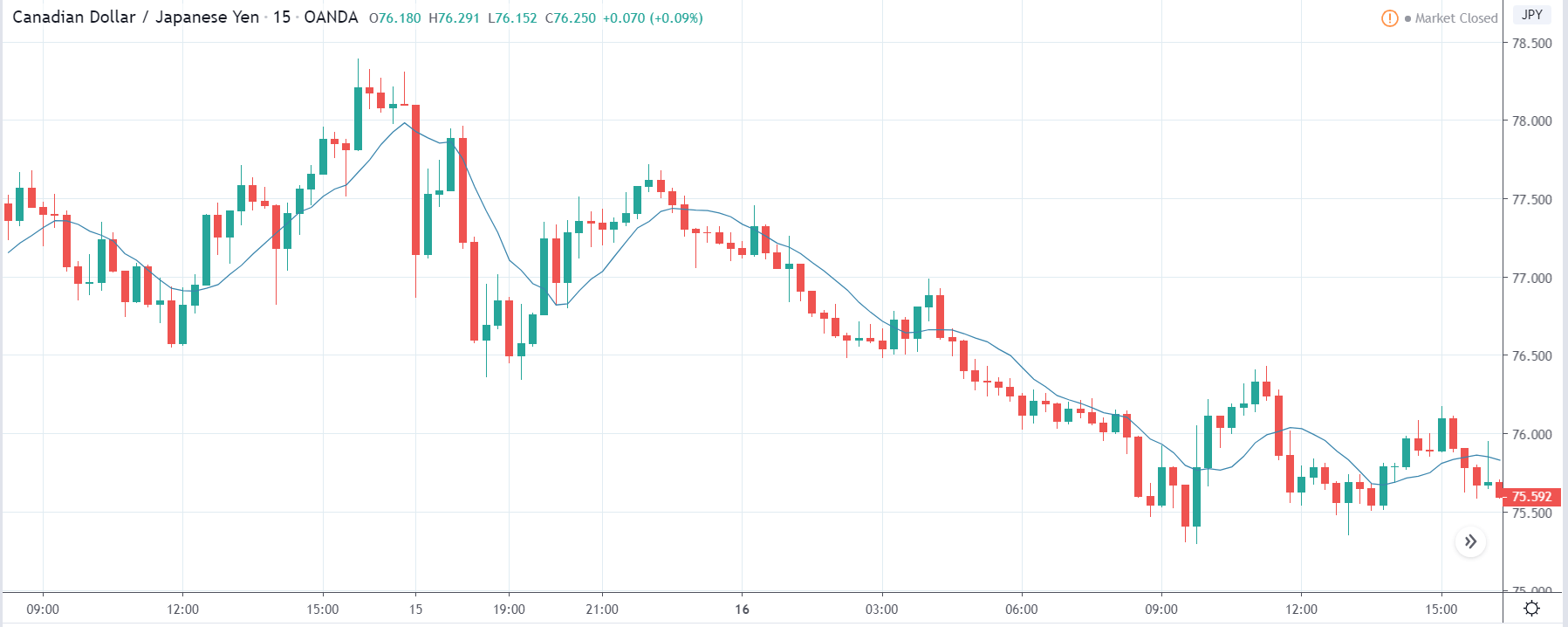
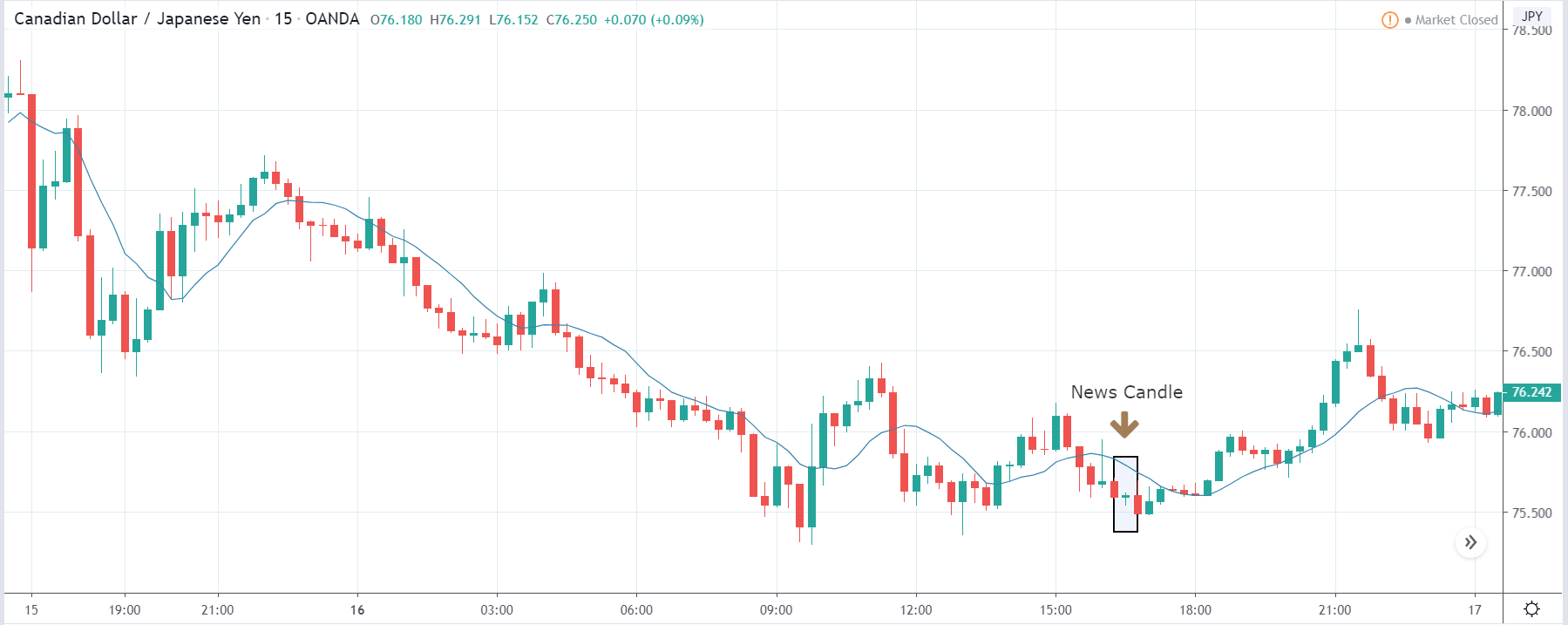
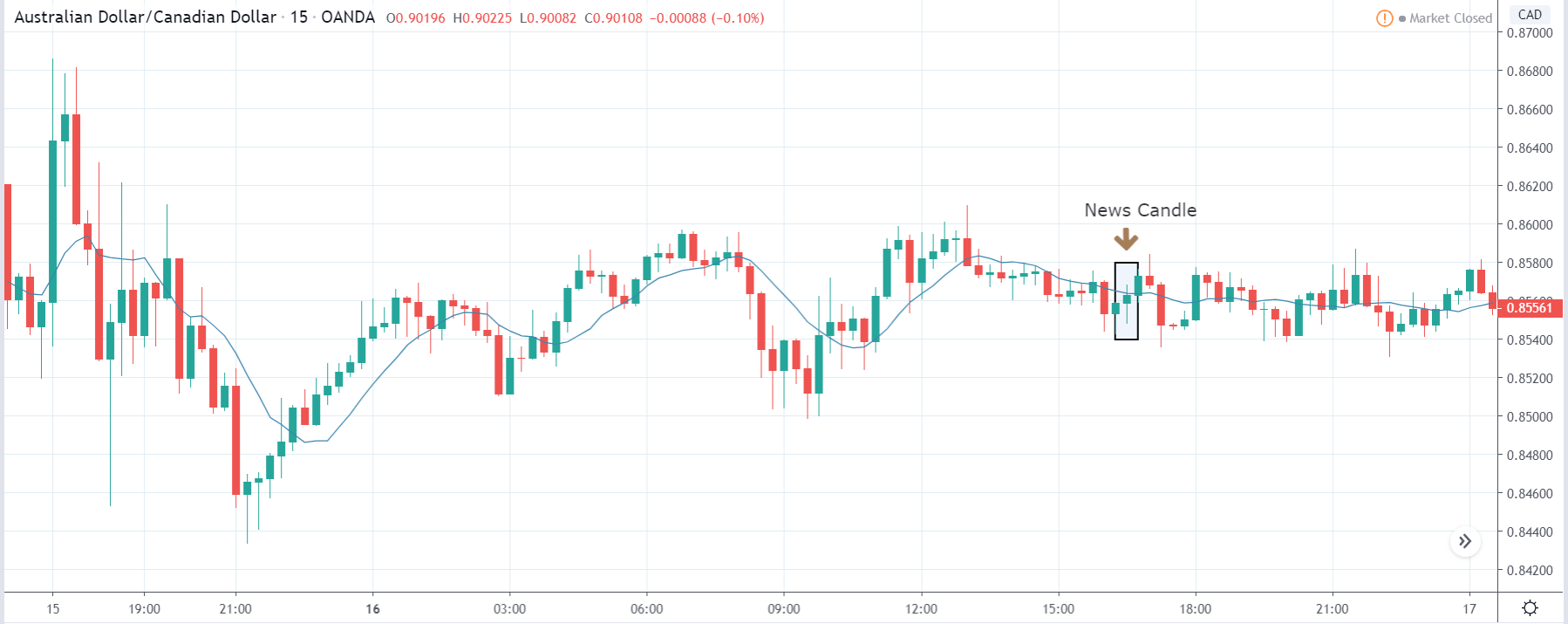
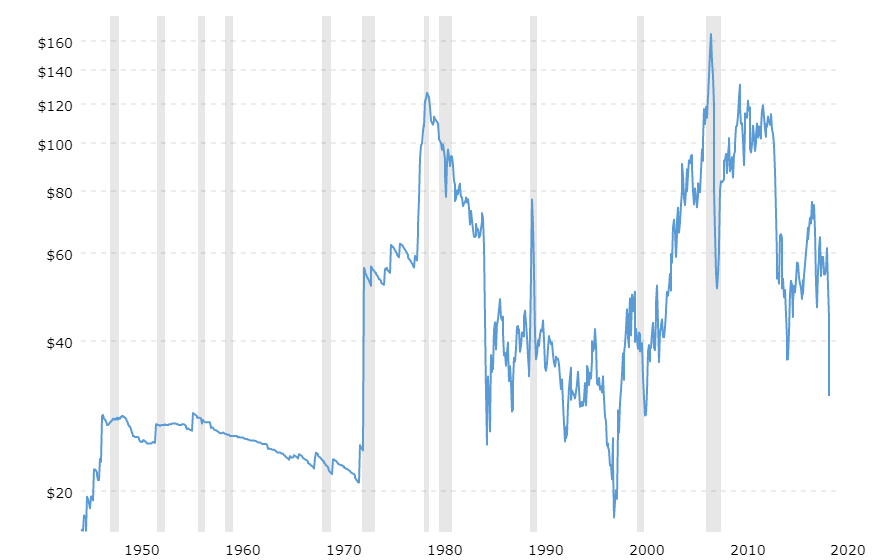
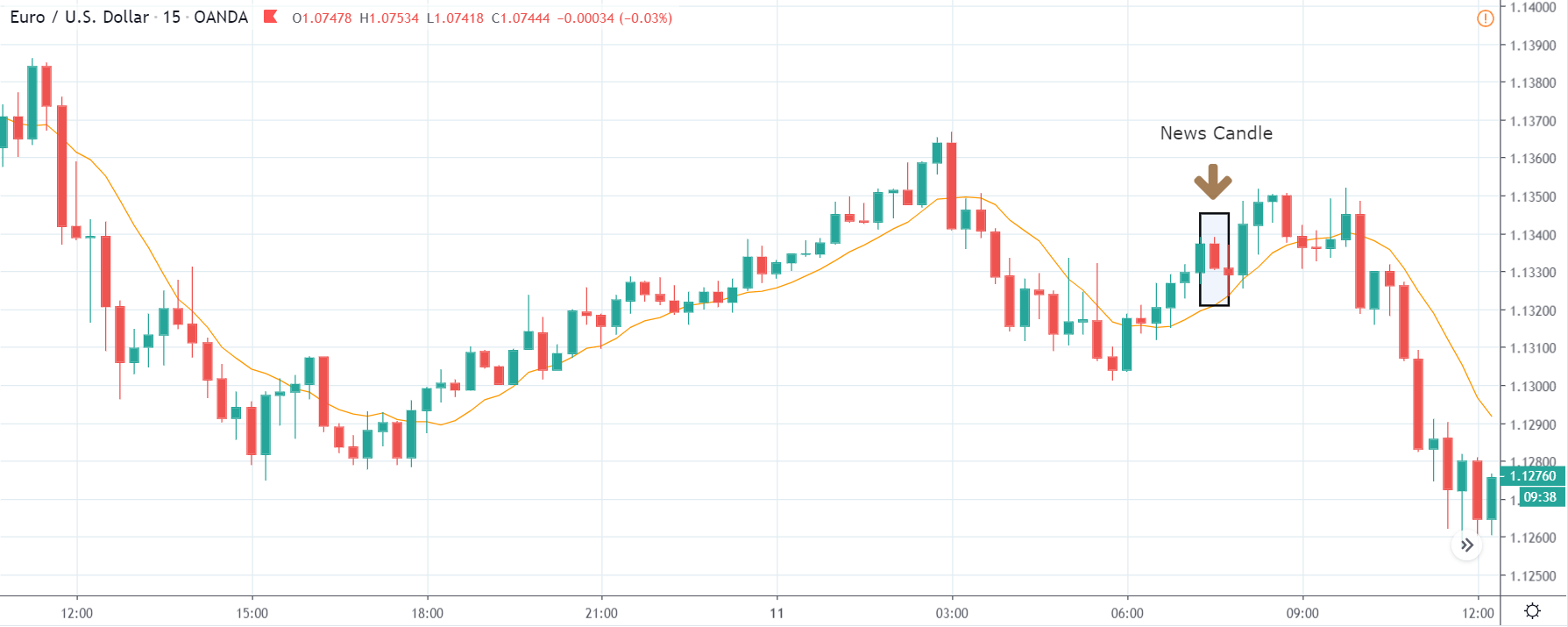
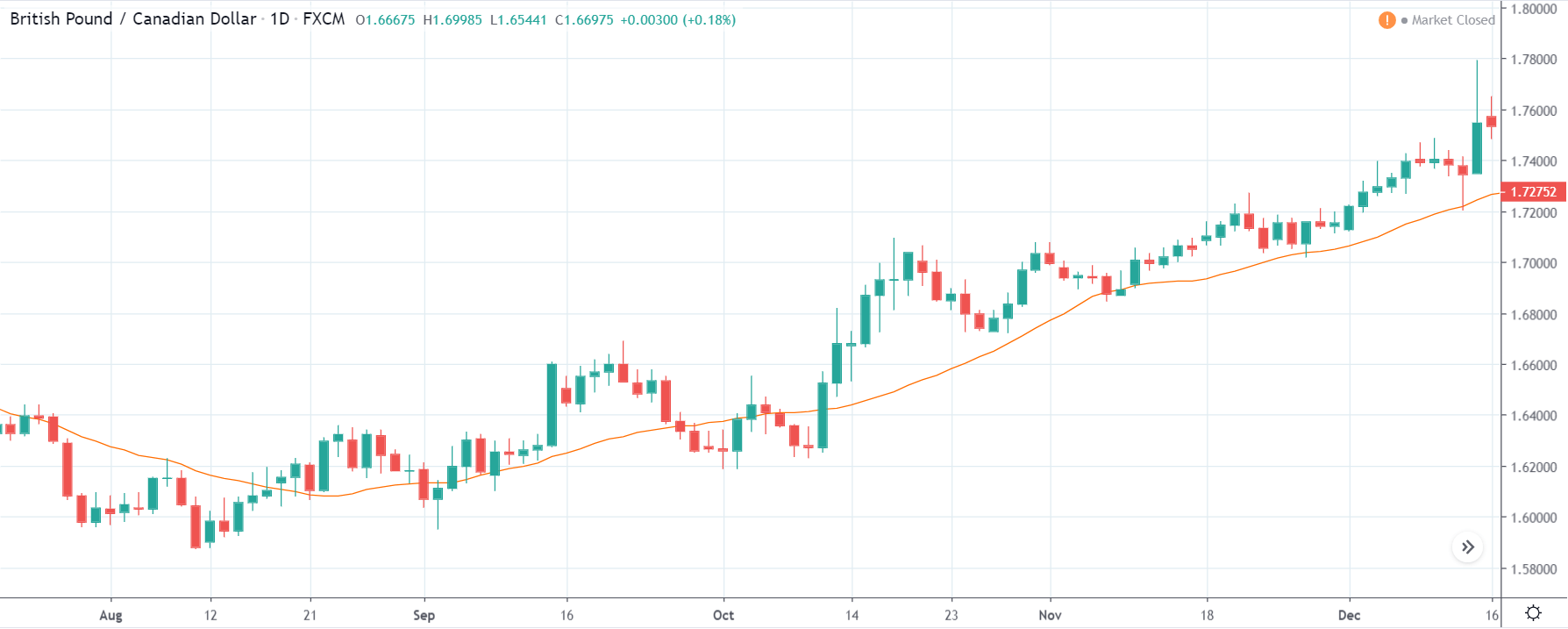
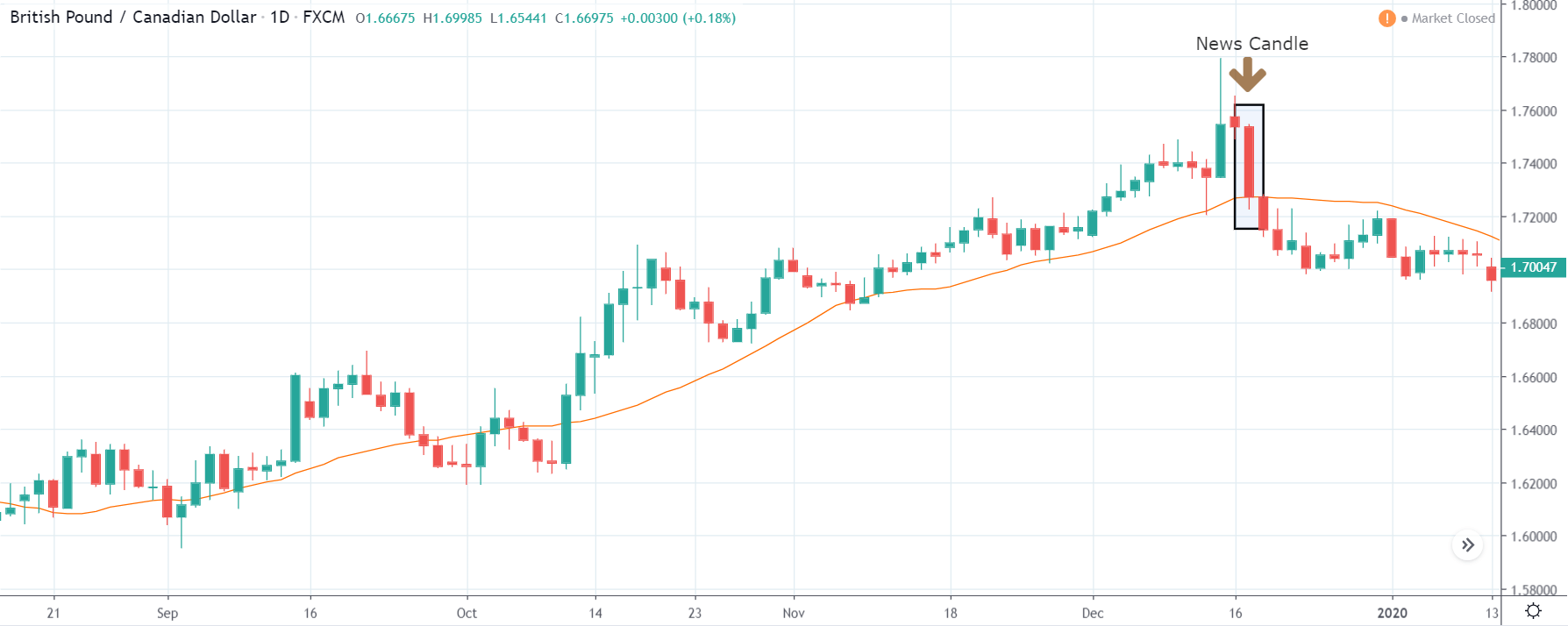
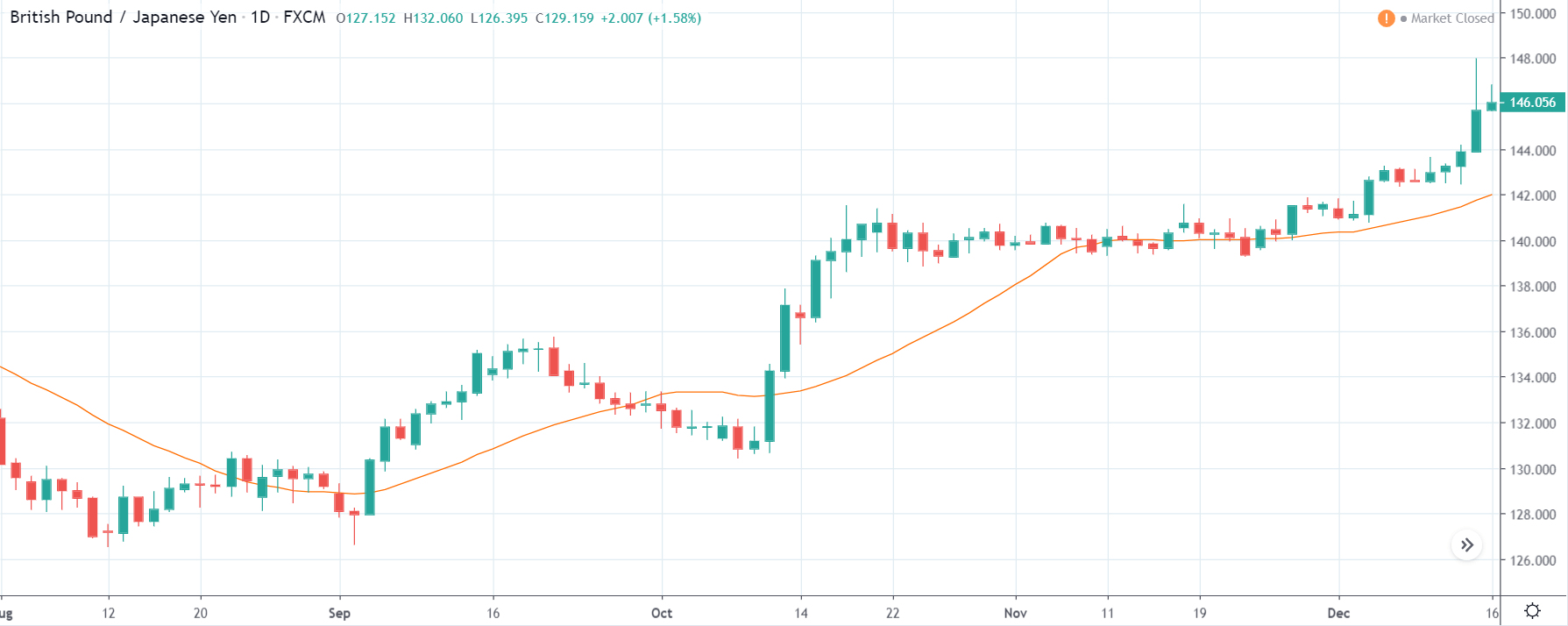
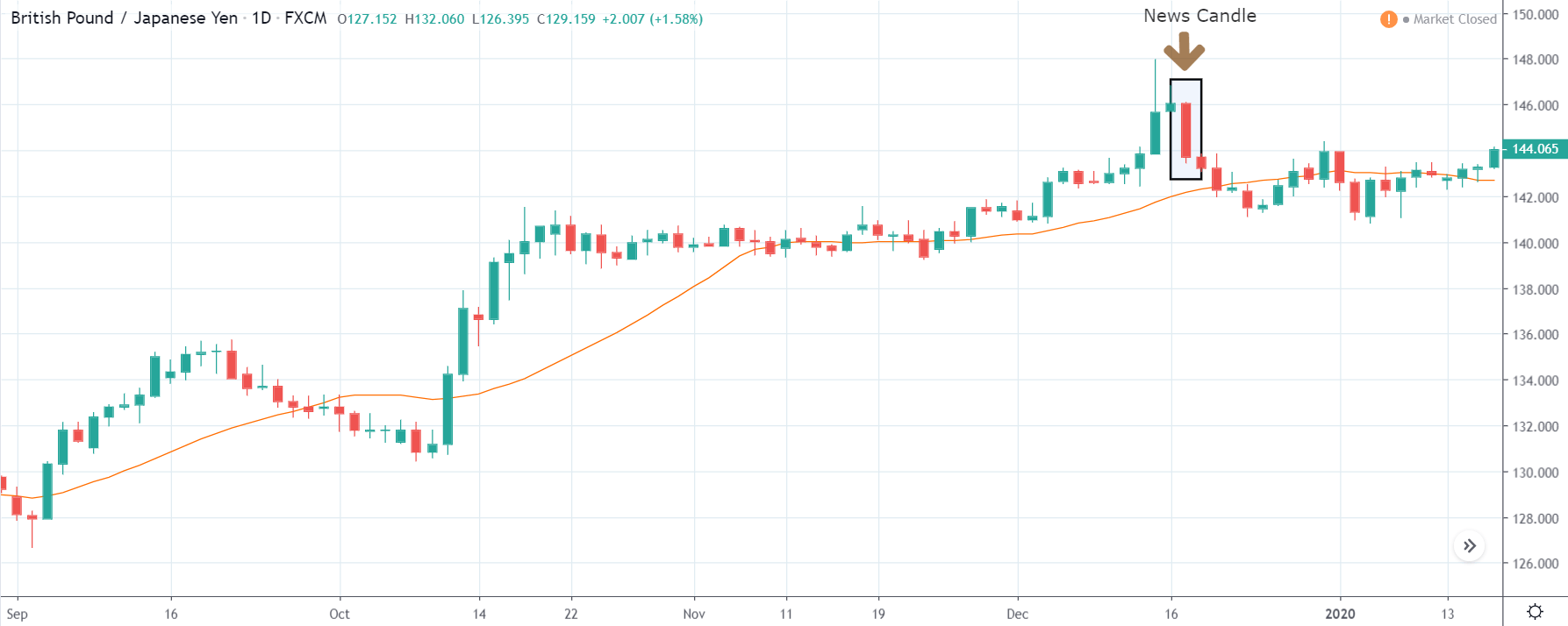
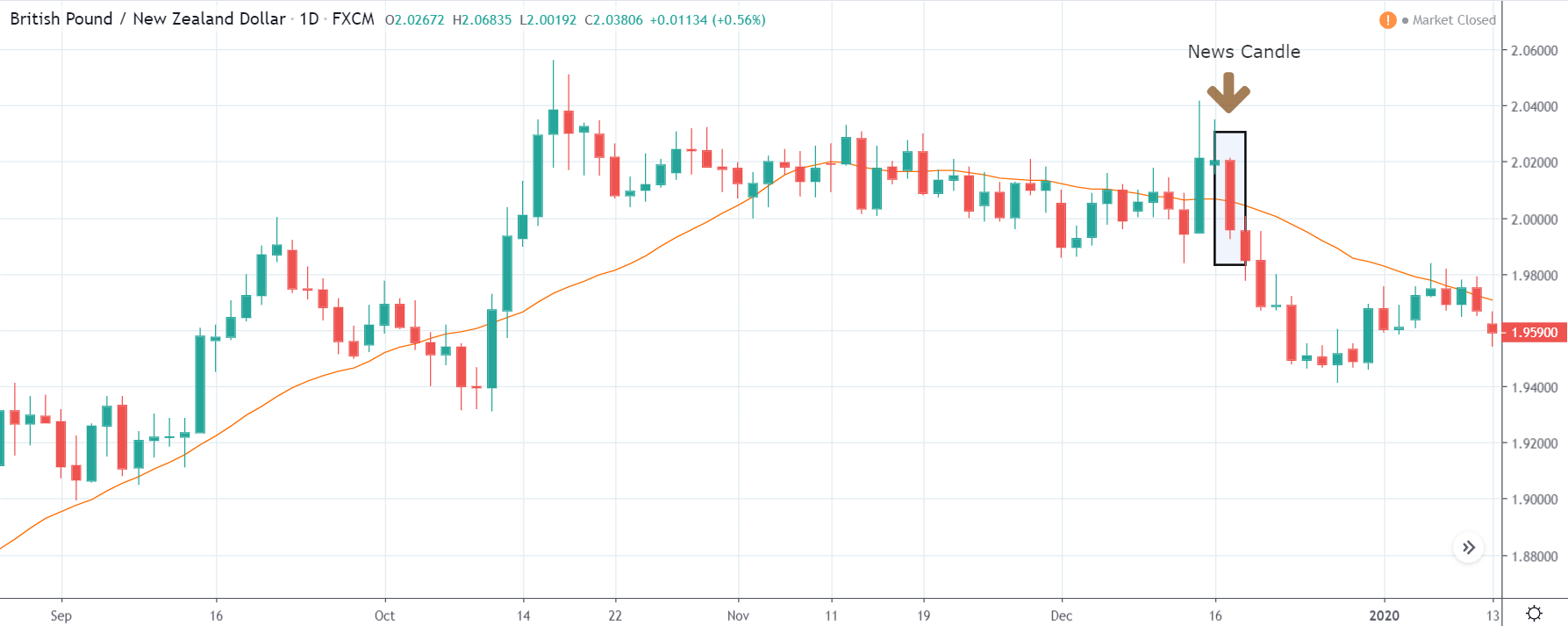
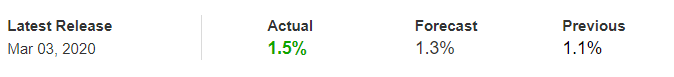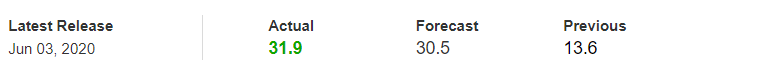It is possible that you have come this far because you are thinking about trading when news is published and taking advantage of the big moves that occur at that time. You may also simply wonder if this is possible or how it can be done. The best thing is to go point by point to see how and what news affects when we do trading, everything you should contemplate, and some things that don’t usually tell you.
What Economic News Impacts Trading?
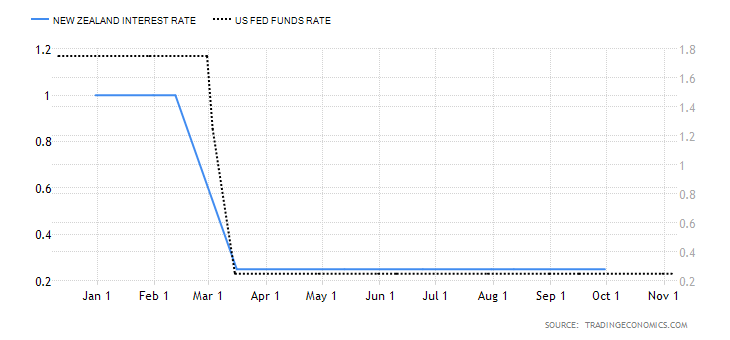
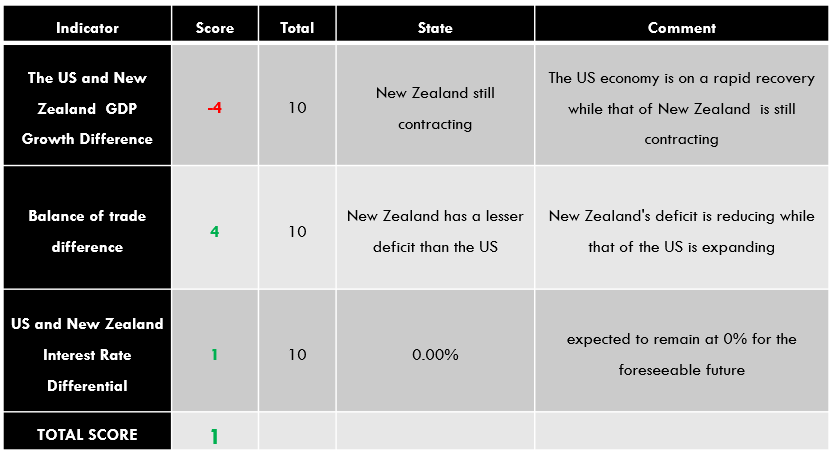
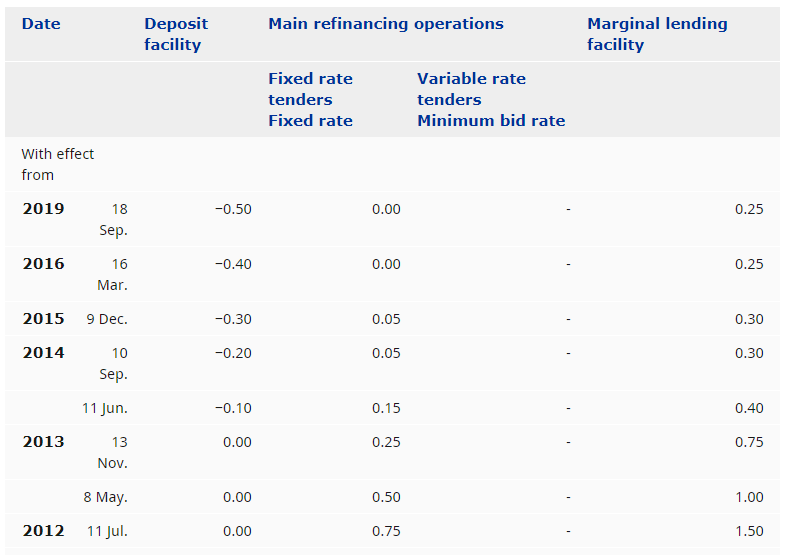
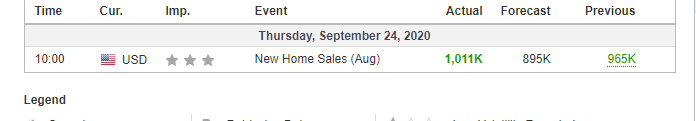
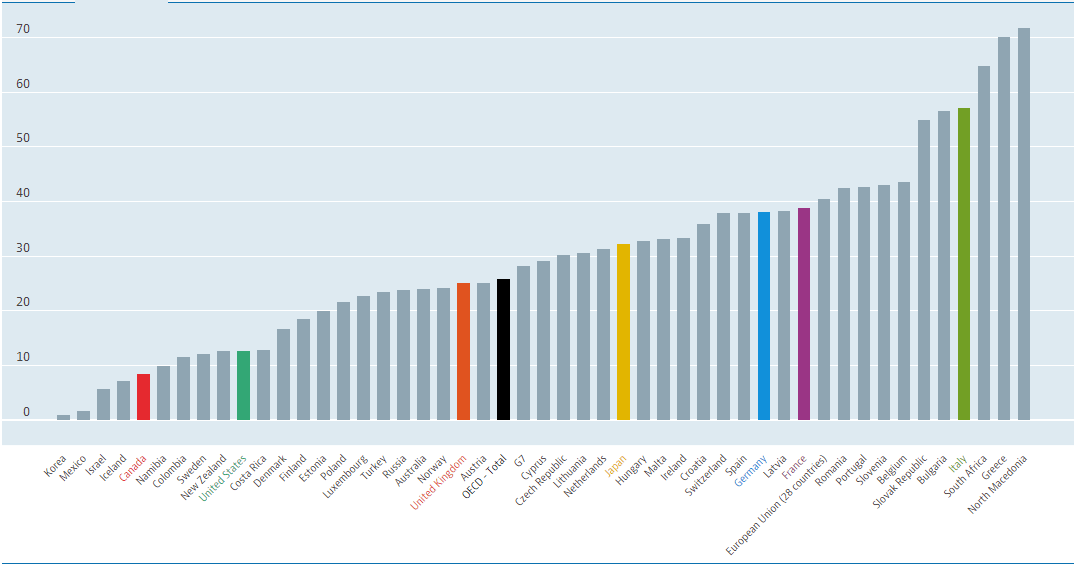
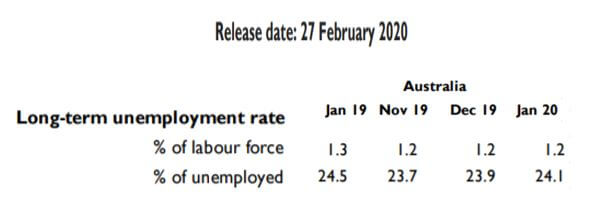
As you may know, there are different news items that affect trading, especially in forex, such as macroeconomic events (for example, interest rate decisions), government policy decisions, employment news publications. Basically, we can distinguish between:
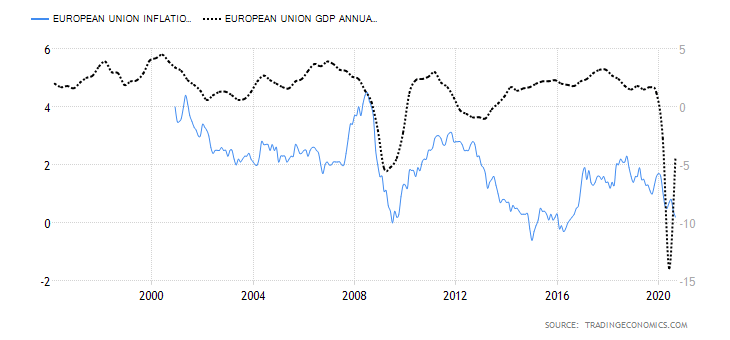
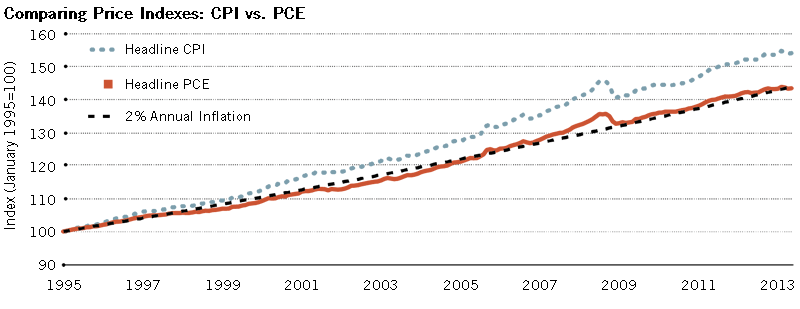
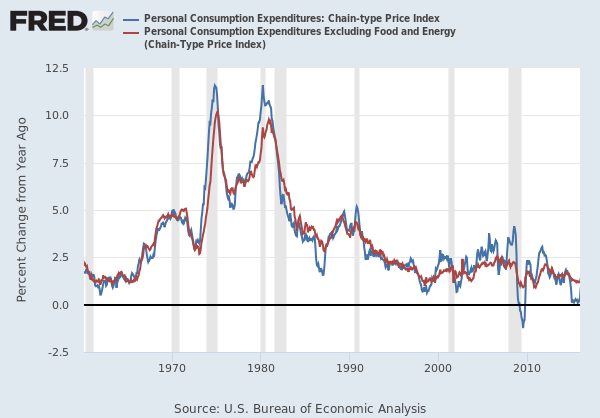
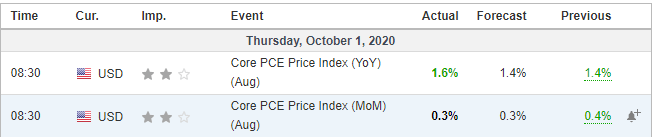
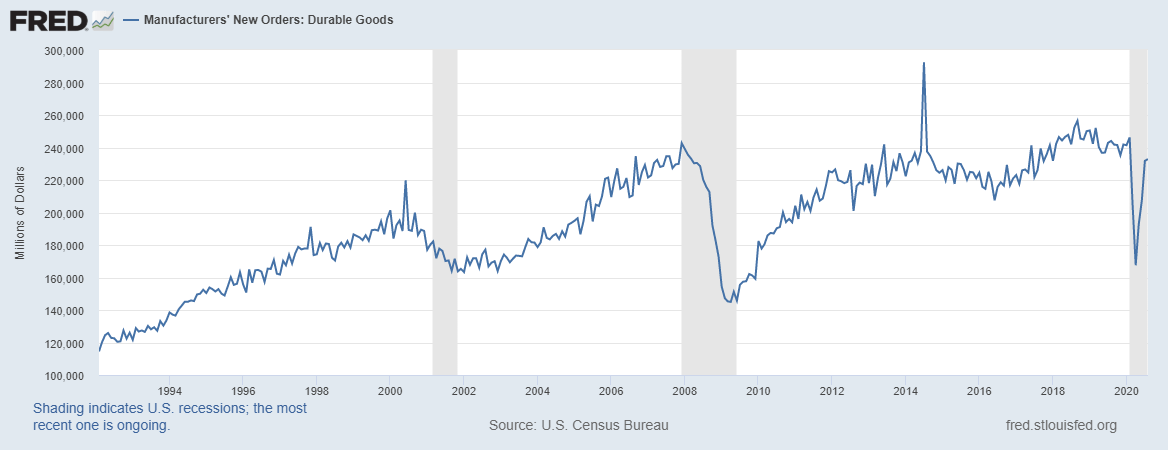
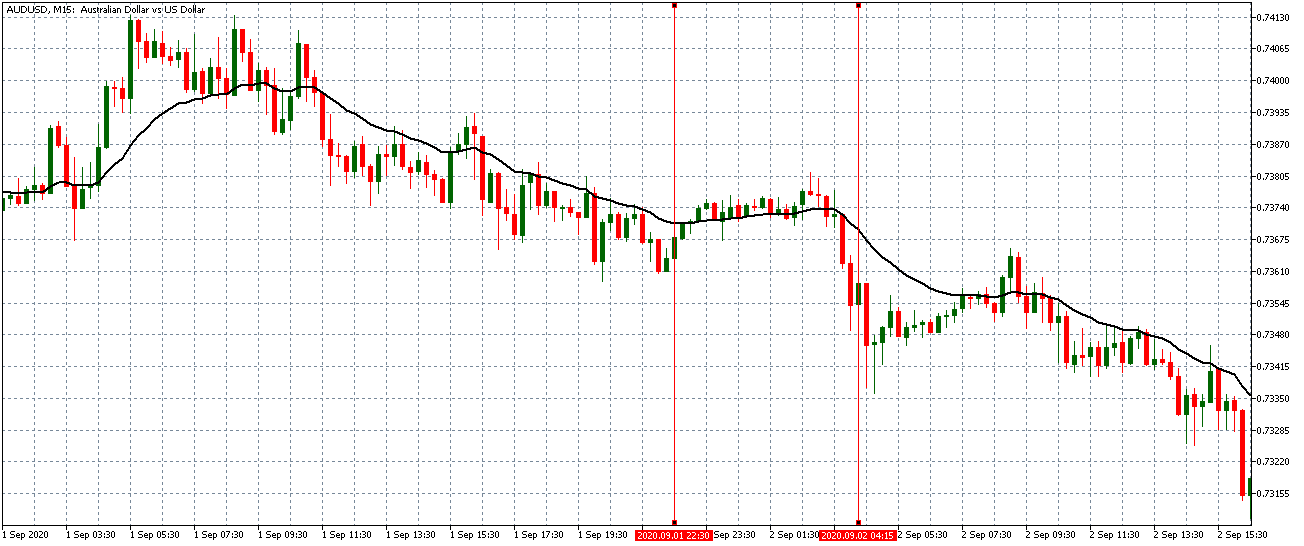
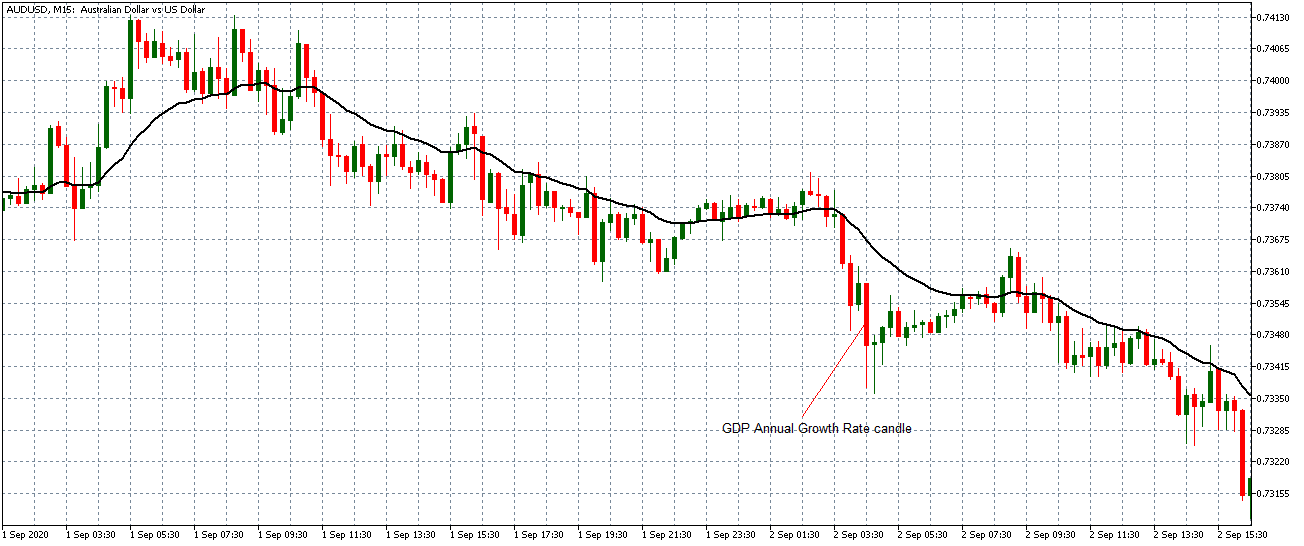
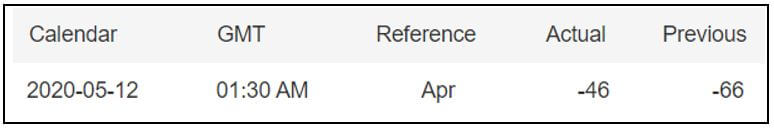
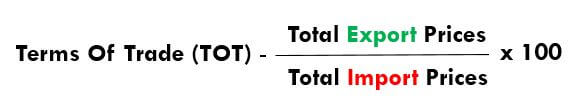
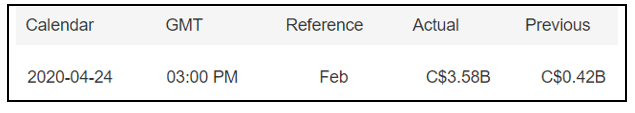
Economic News: GDP, inflation, unemployment or oil reserves, any related economic aspects that can affect a country and its currency.
Political News: decisions and governmental actions that are carried out in the country in question and have direct involvement in currency.
All of them are important (though some to a lesser or greater extent than others) and you can often see how when they are published it makes the currency pair in question move significantly. But how do we know when and what data will be published and the impact it will generate?
How to NOT Predict Trading News
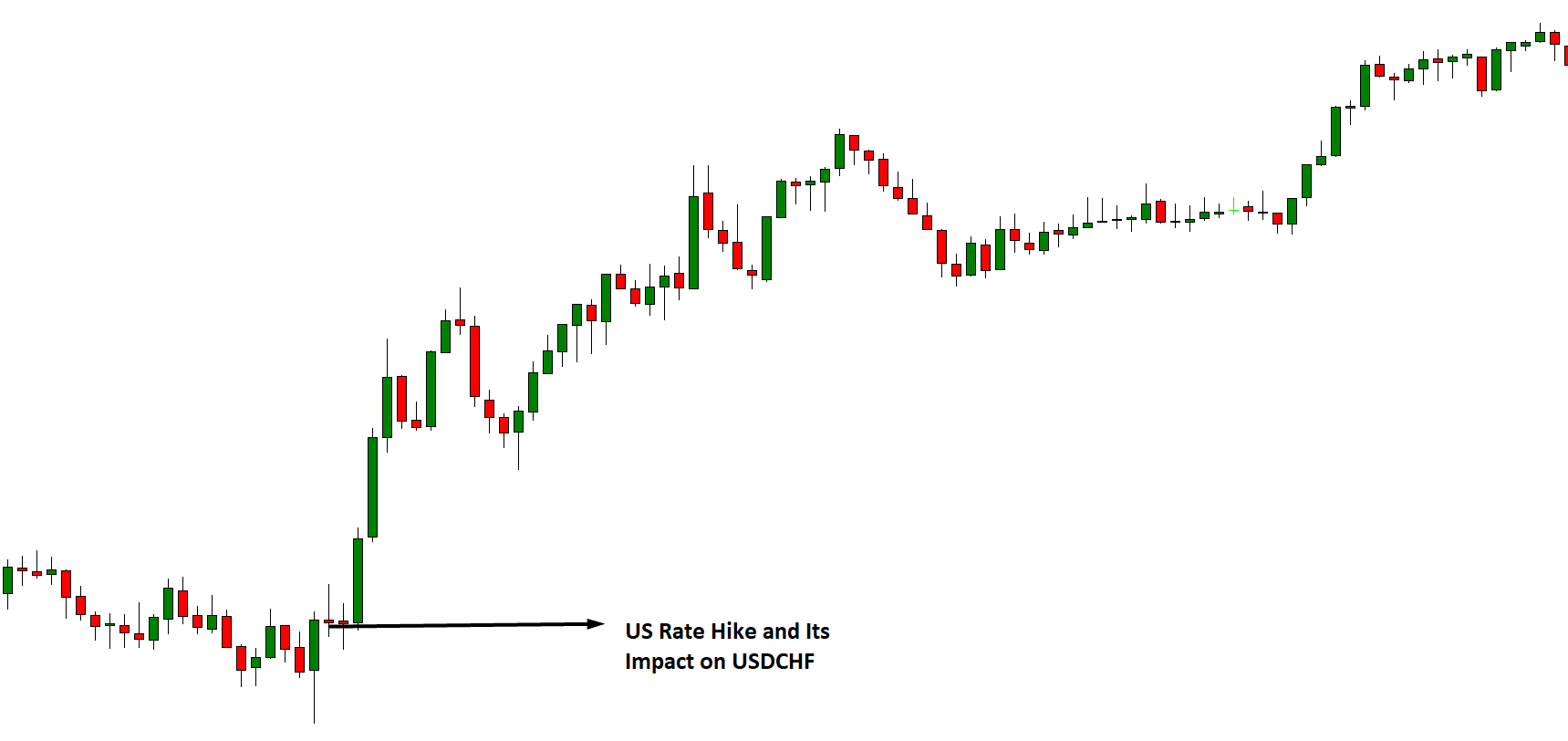
It’s obvious, isn’t it? We already know when they’re going to be published, we’re going to put a lot of money in and let the flute play. NO. This might not work for you. And even if you get it right, you’ll end up losing everything. Events such as the one that occurred in the Swiss Franc (black swan) or the Brexit have left the graveyard full of traders. Even some brokers have had to close. Why?

News Trading Errors
Behind an excuse of losing money by trading when a story is published there is usually one or several of these causes:
Strong Leverage: Enter the market strong with a small account to earn a lot of money in a short time. In the end, your account does not resist and a minimal movement to the contra makes you lose count. Serious error.
Bet Mode: not having a trading system and think that this goes up or down because it comes out in the media, my brother-in-law has told me or because yes. If you don’t have a system, start working for it.
Stop-loss Strategies: Strategies with very small stops often do not have good results when the price moves aggressively. The institutional (the big ones) sweep them away. It’s not that these kinds of strategies are wrong or anything, but consider reviewing how they behave when these data are posted and limiting your trading if it doesn’t affect them in a positive way. This can be done not by being in front of the screen if you operate manually or by disconnecting your systems if you do so automatically.
News-Based Trading Systems
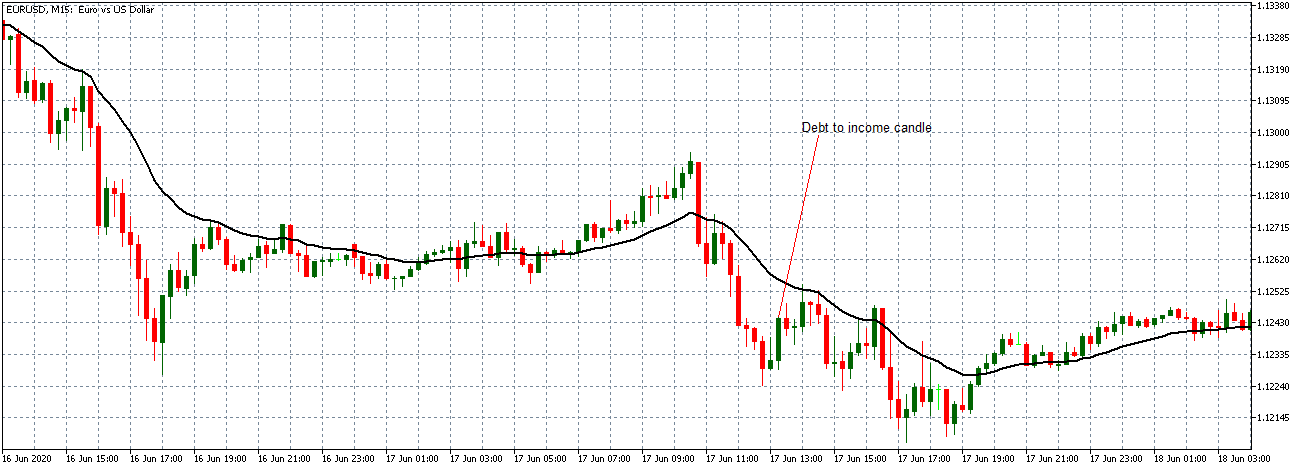
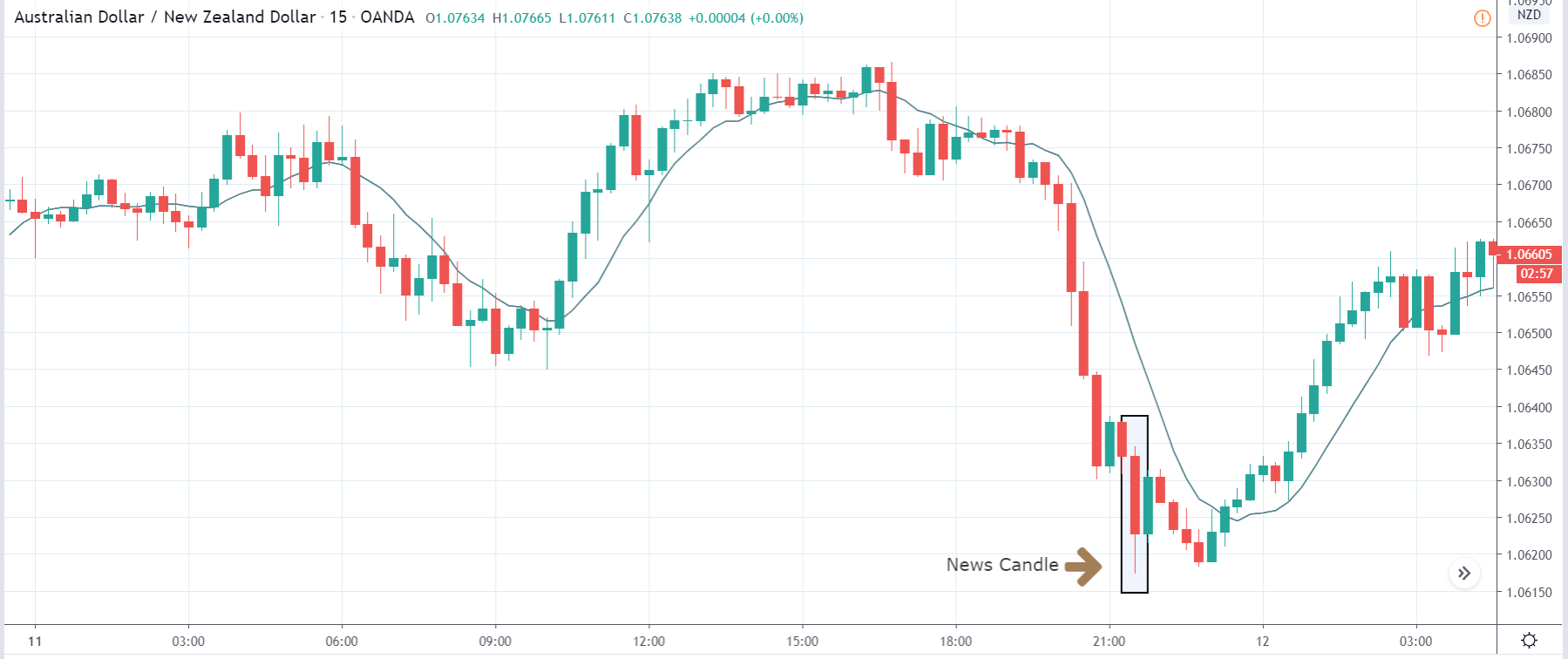
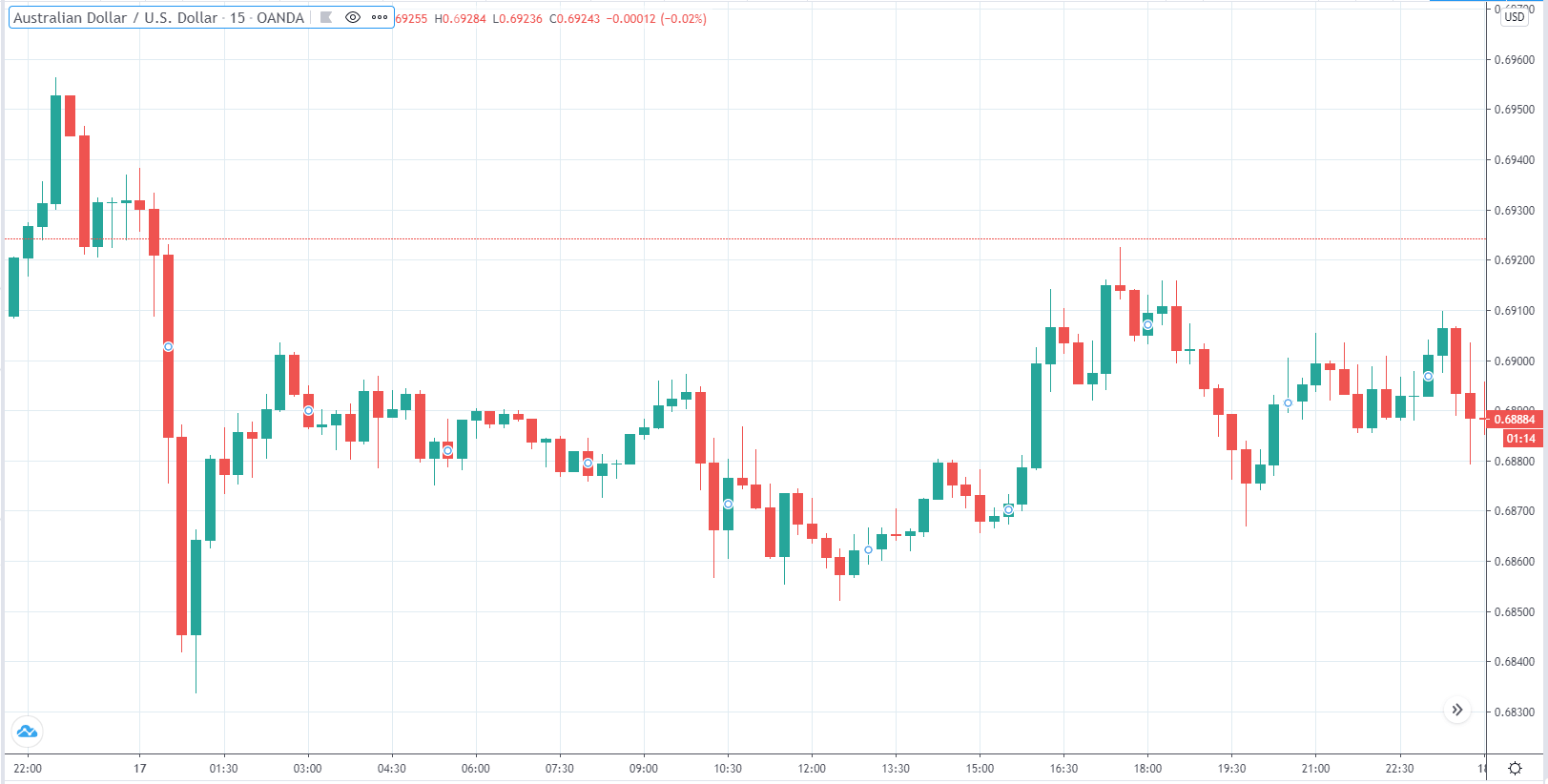
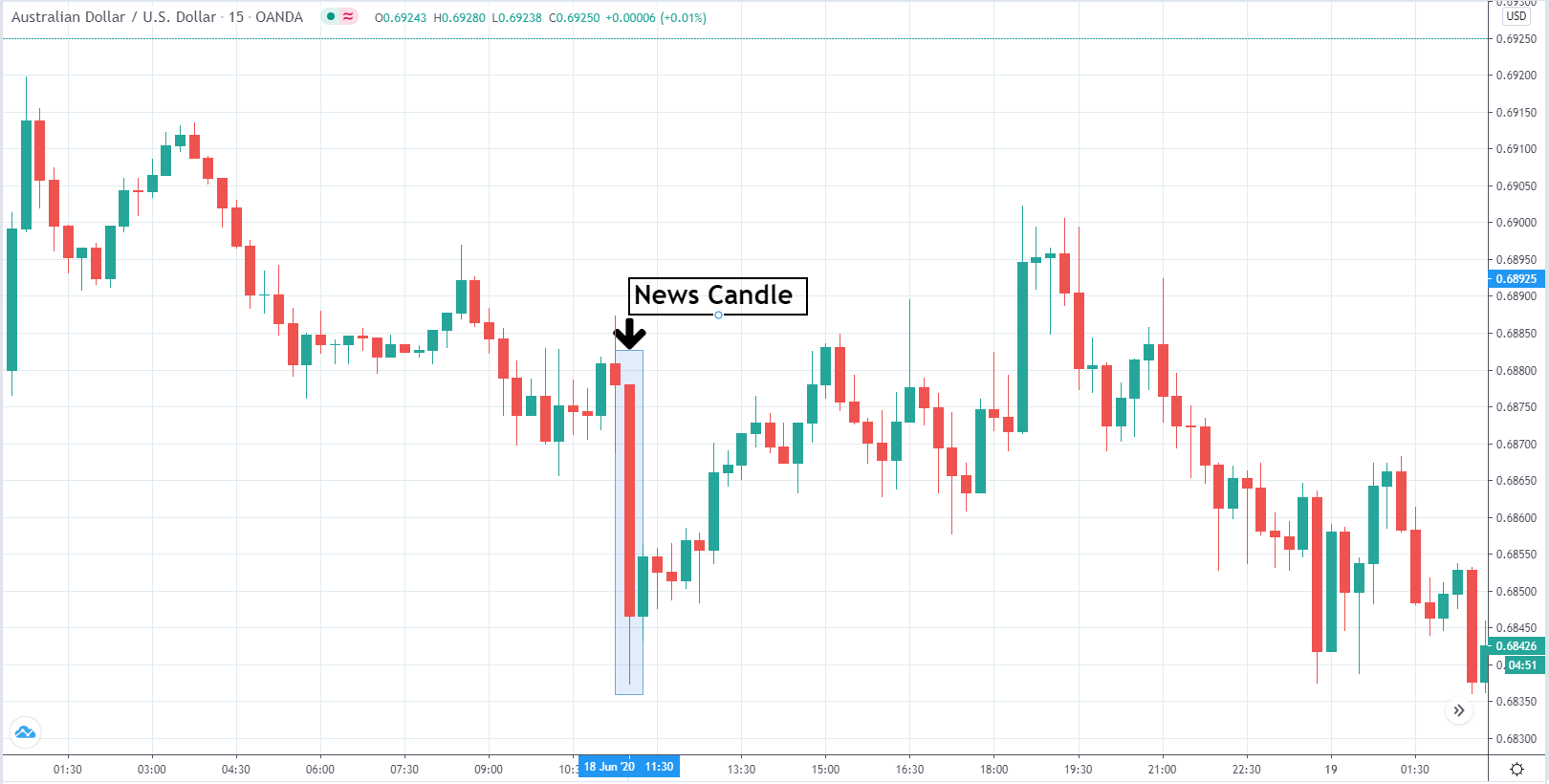
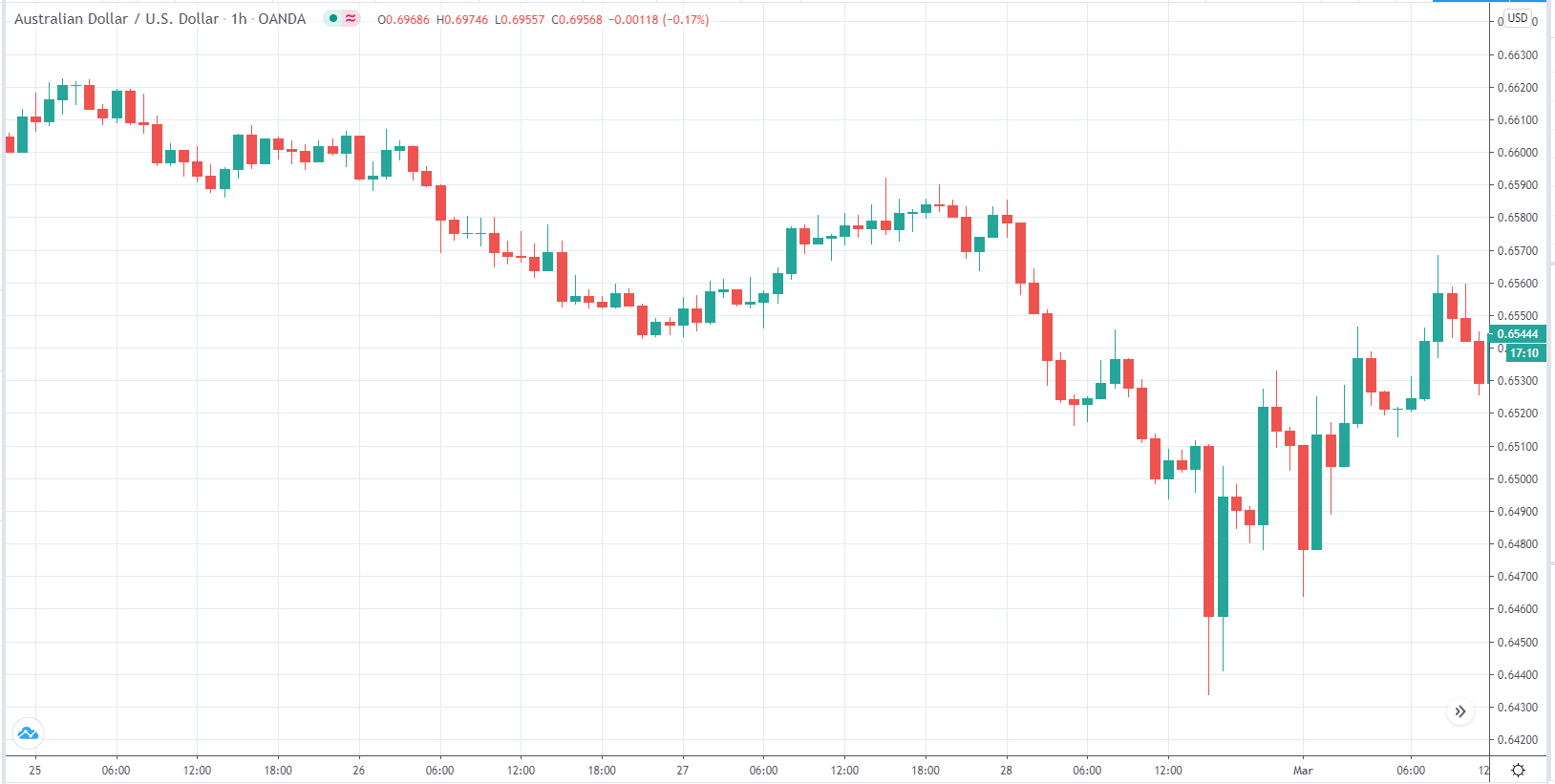
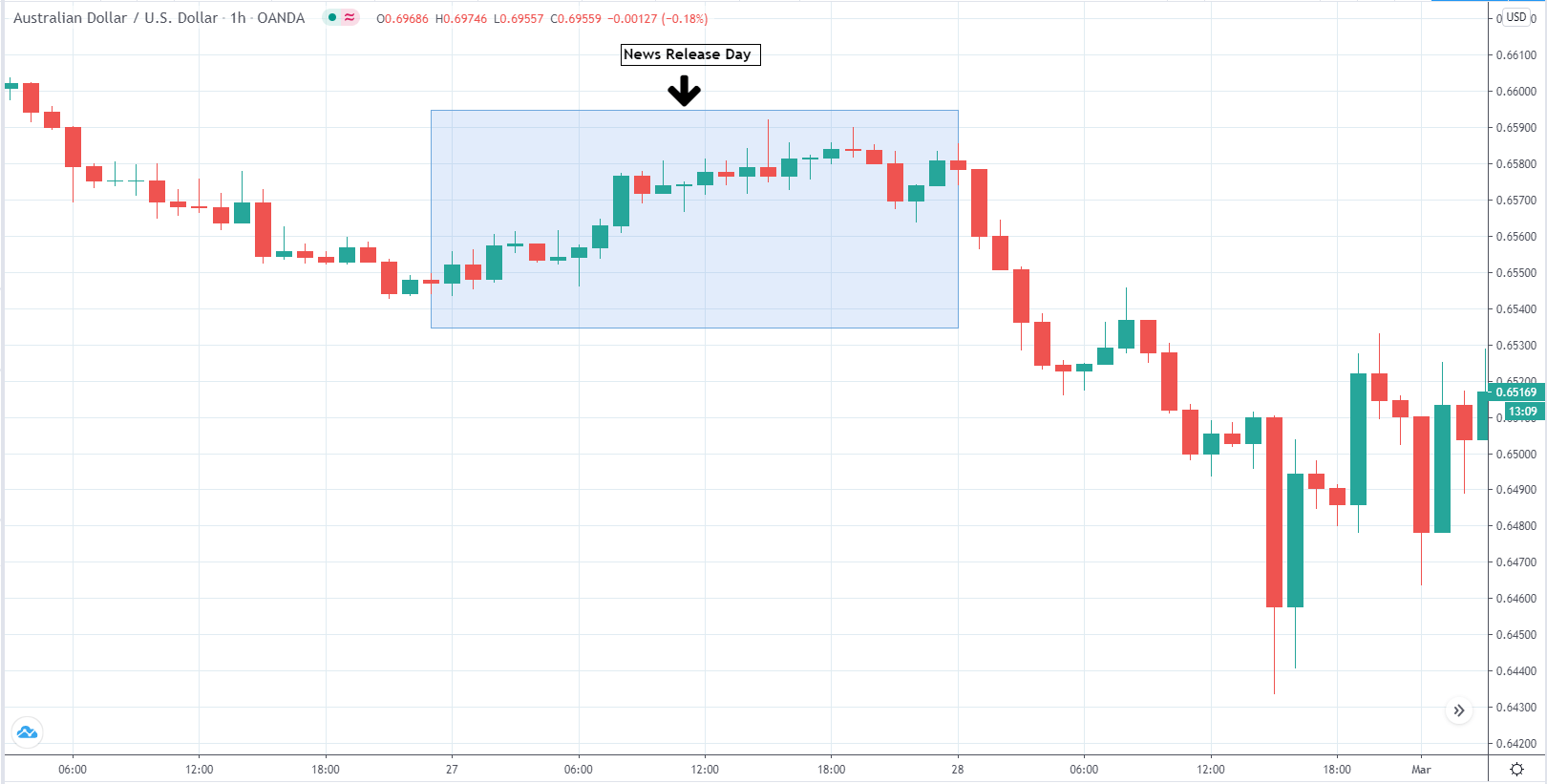
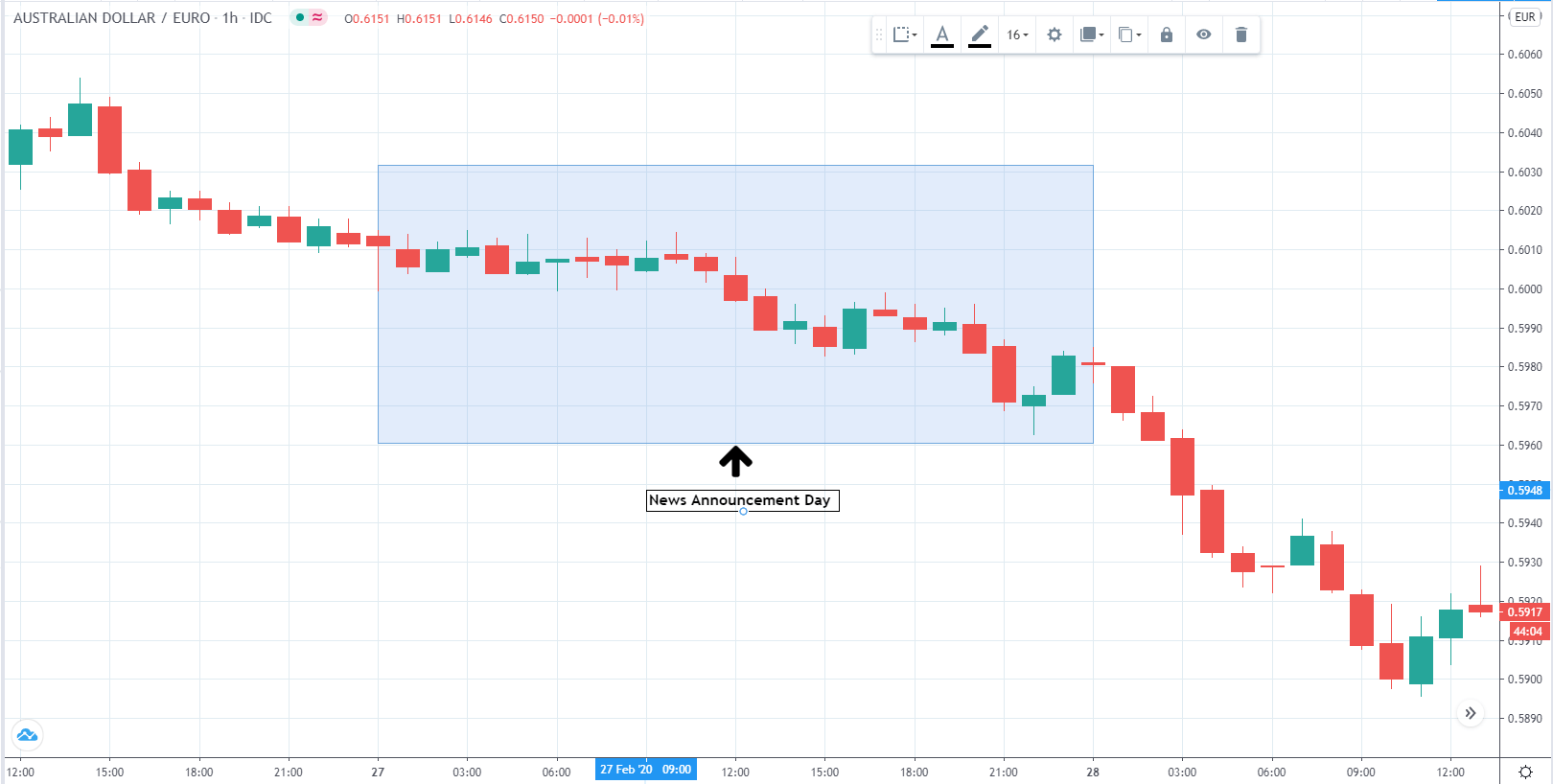
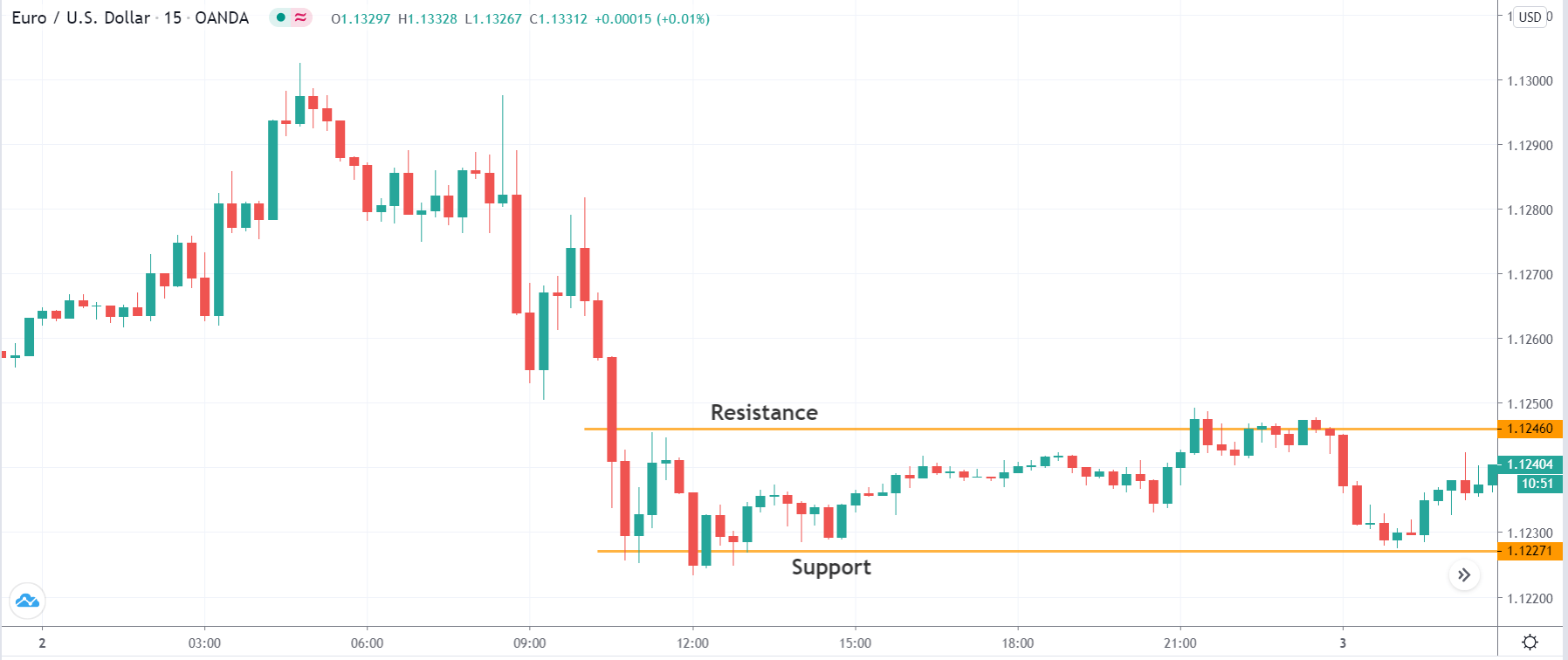
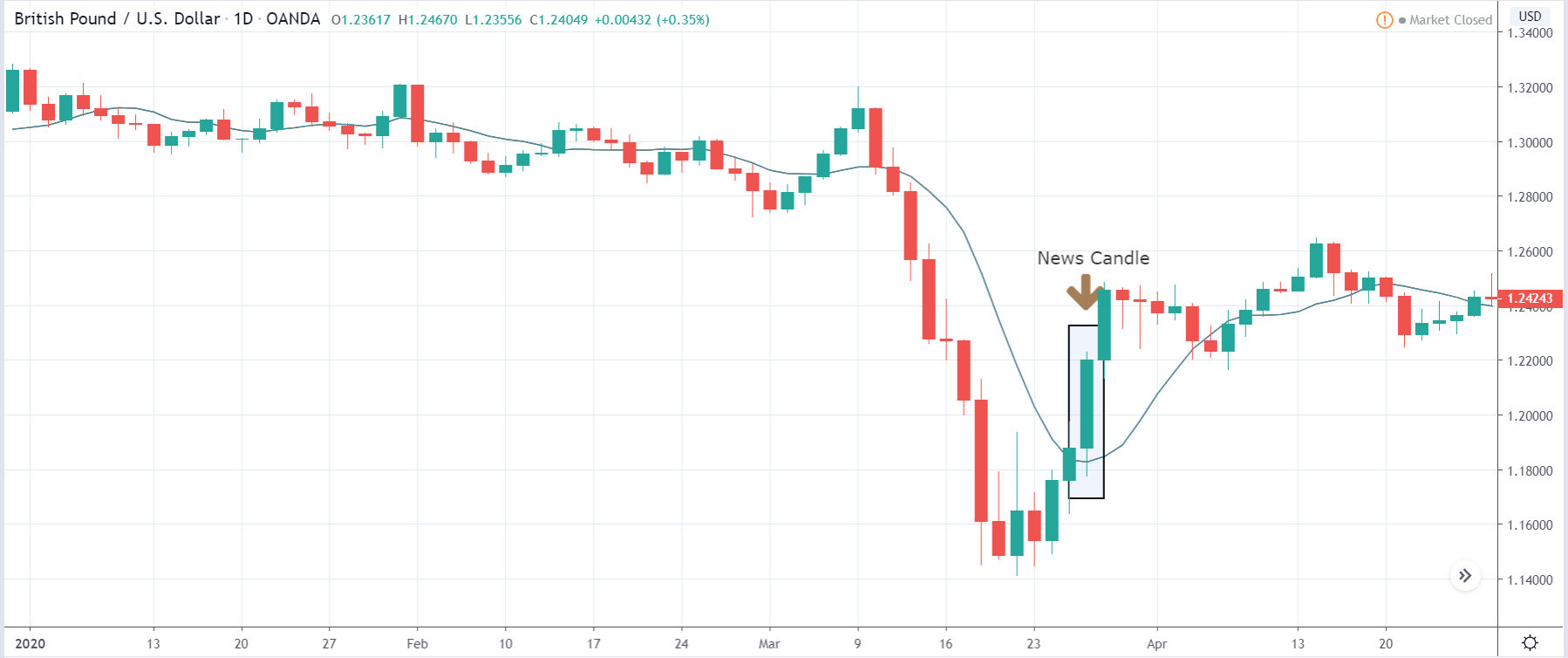
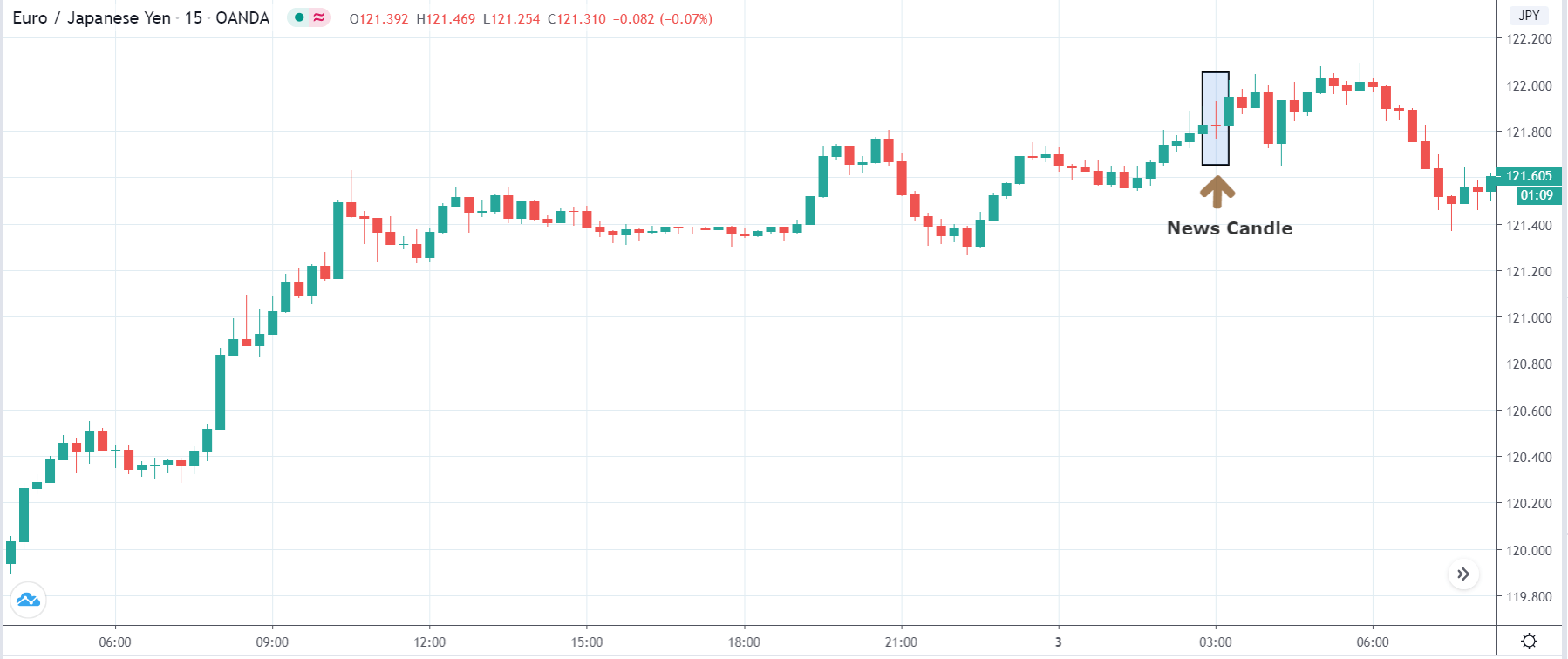
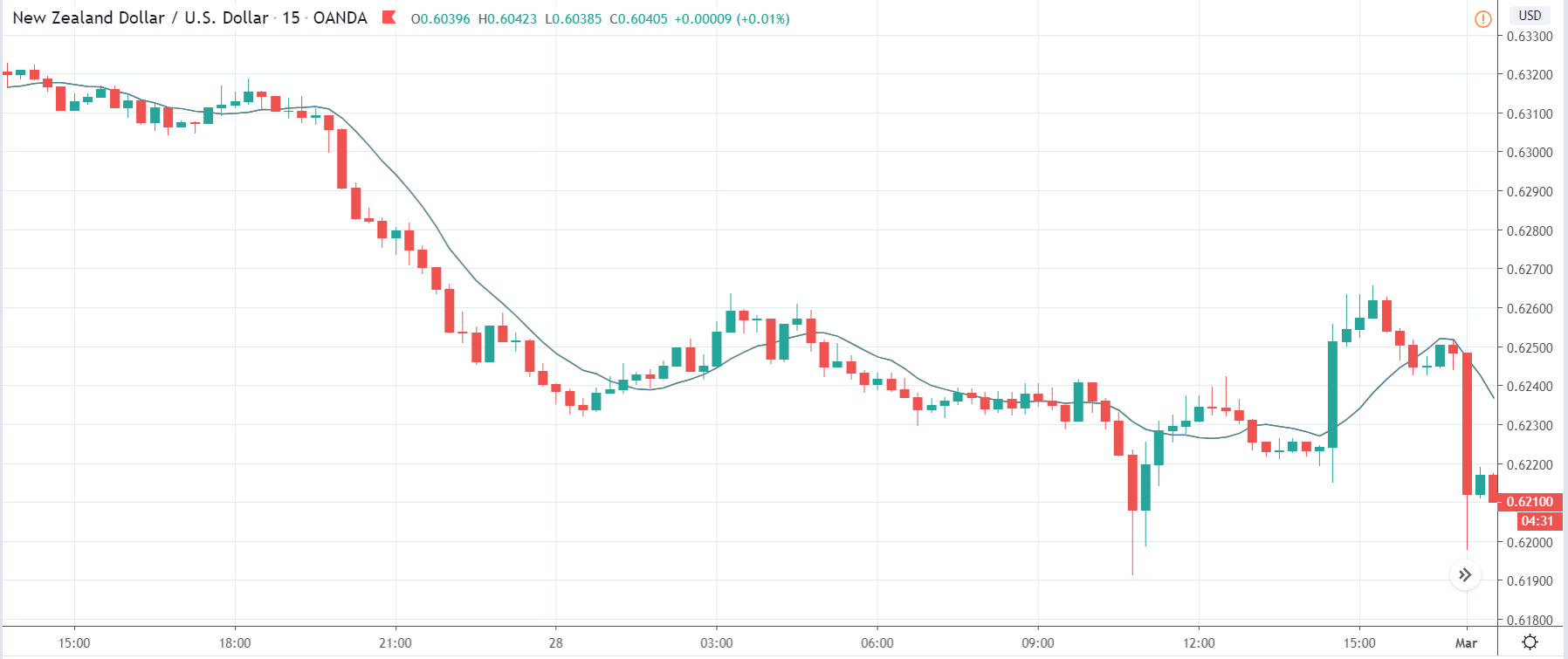
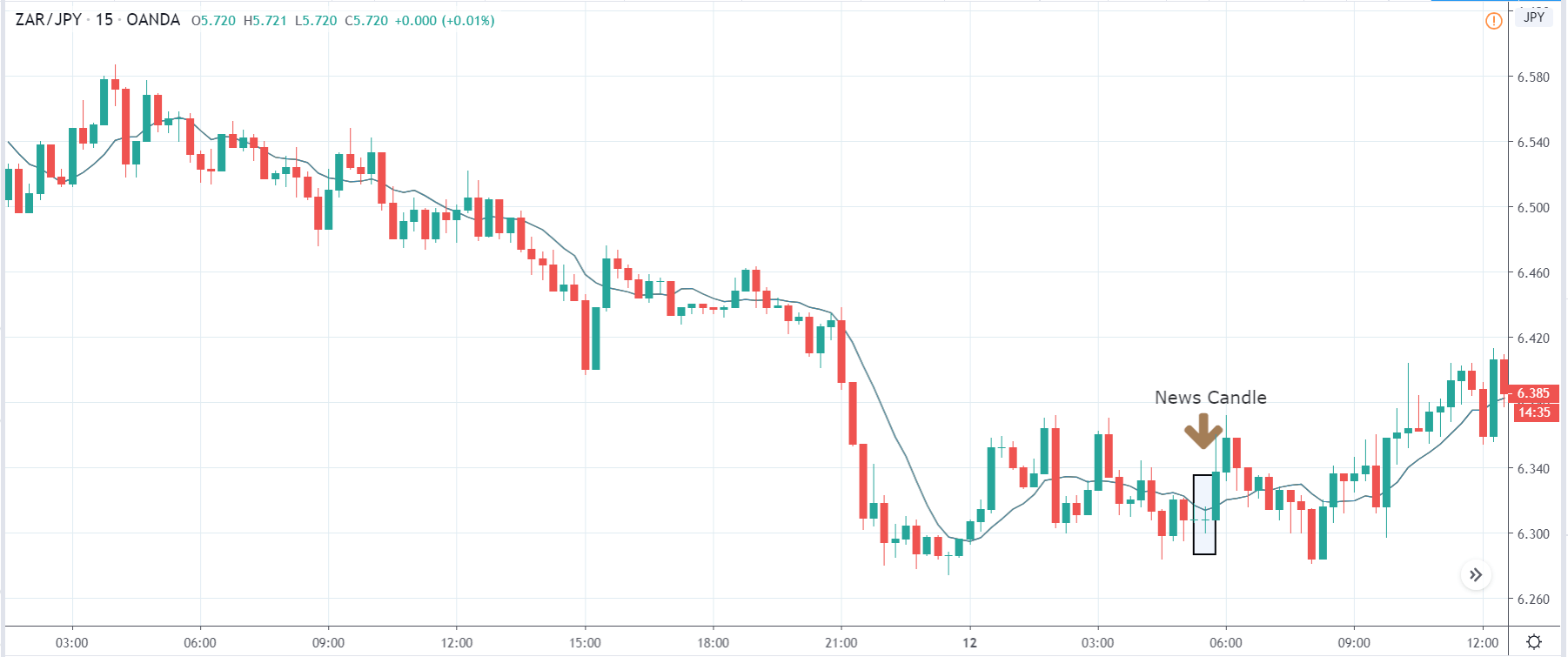
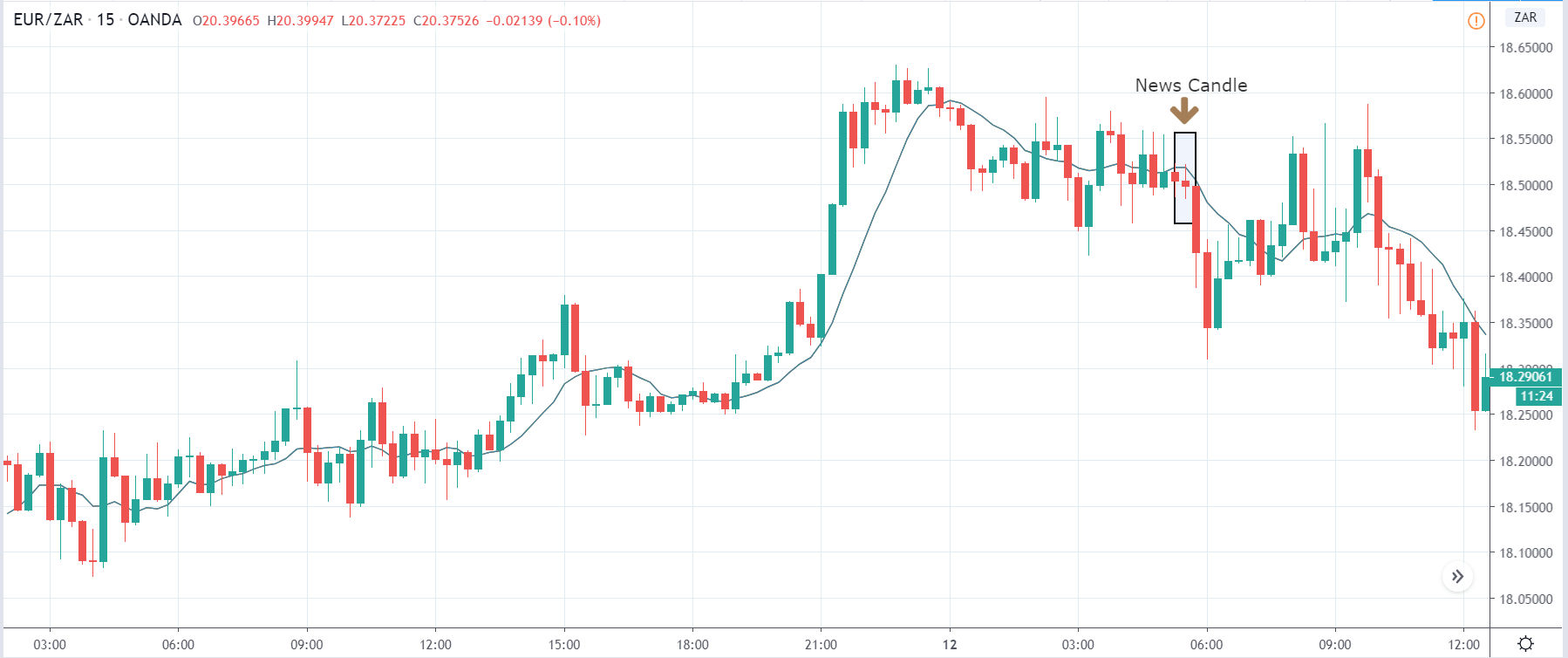
You may have read or thought that trading with the news can be very easy if you place a purchase order and a sales order. This hypothesis starts from the idea that price moves without setbacks. Most of the time this is not the case, since the price can be directed without a trend, either in its initial phase or during the entire period.
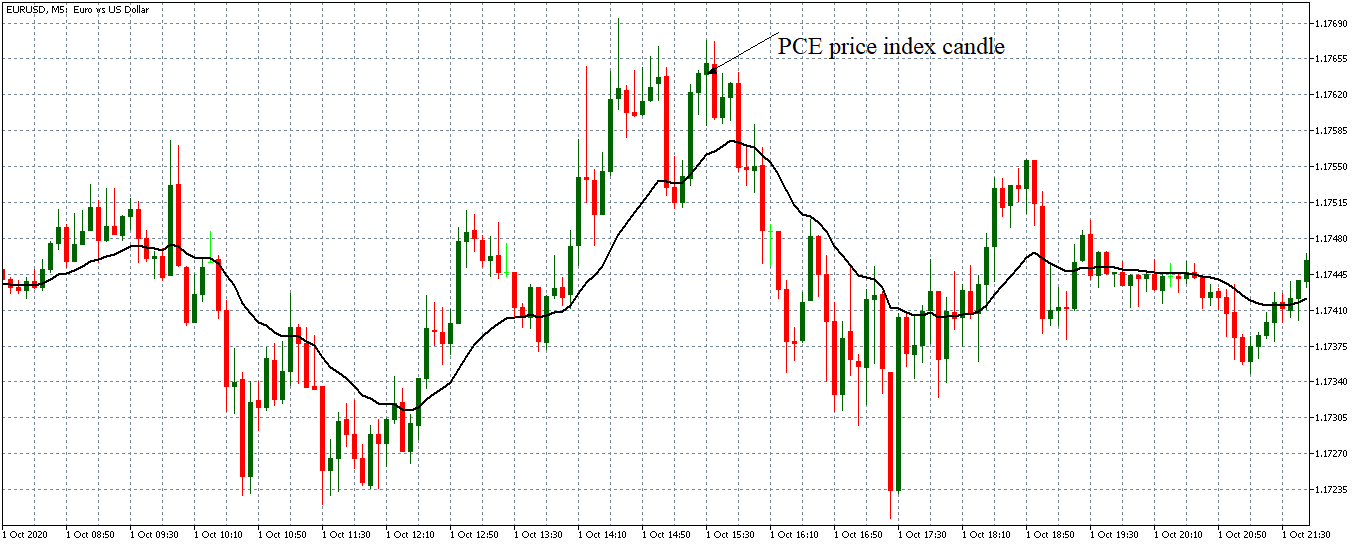
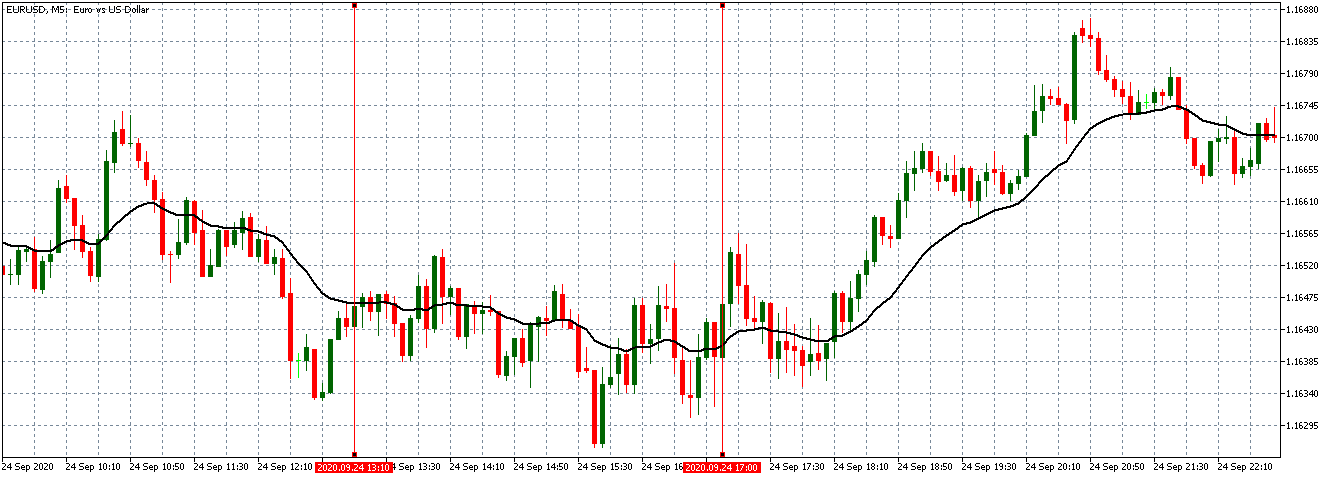
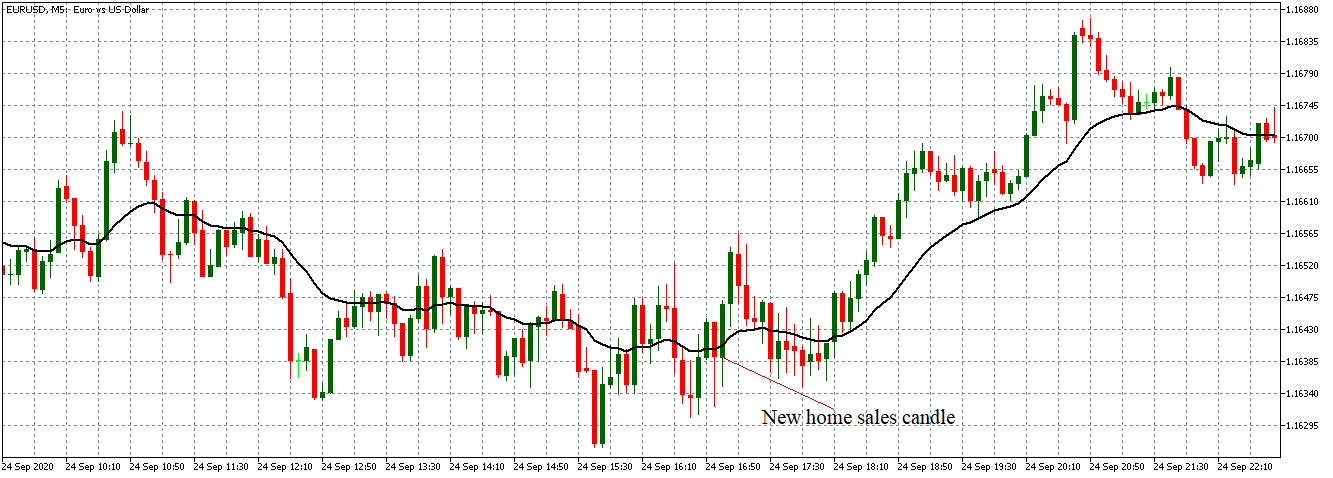
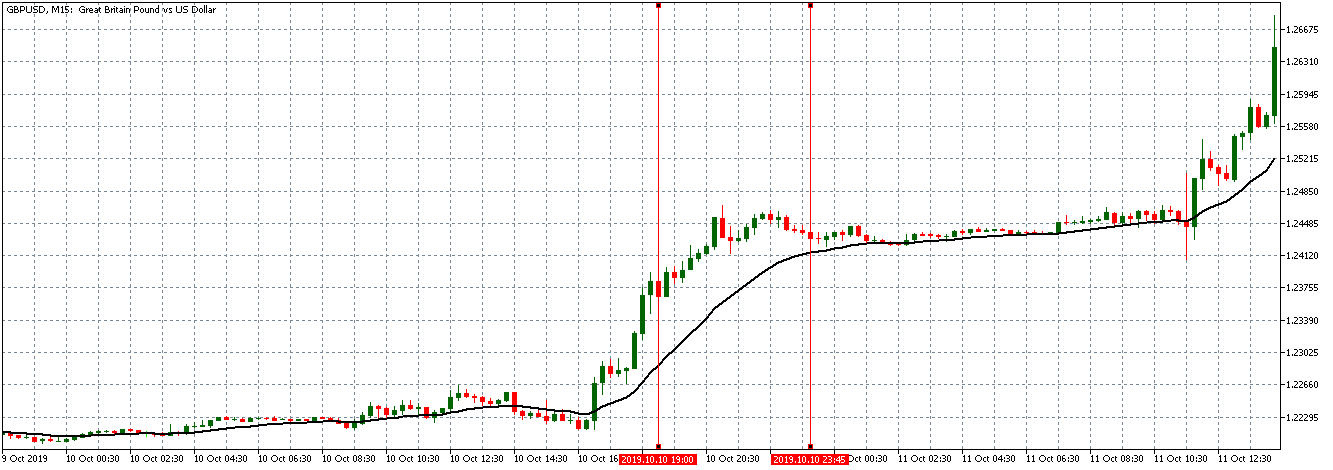
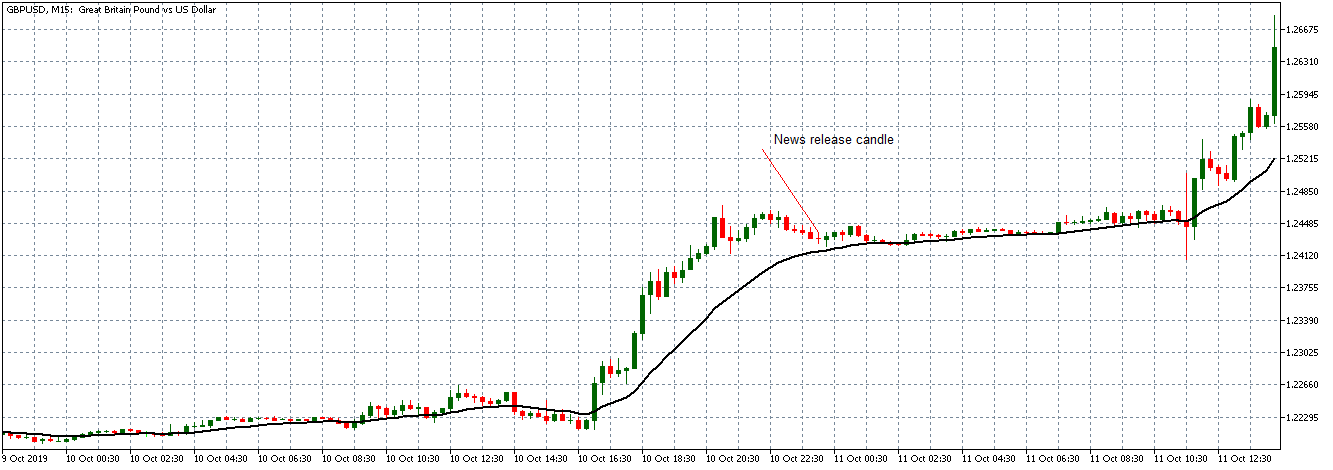
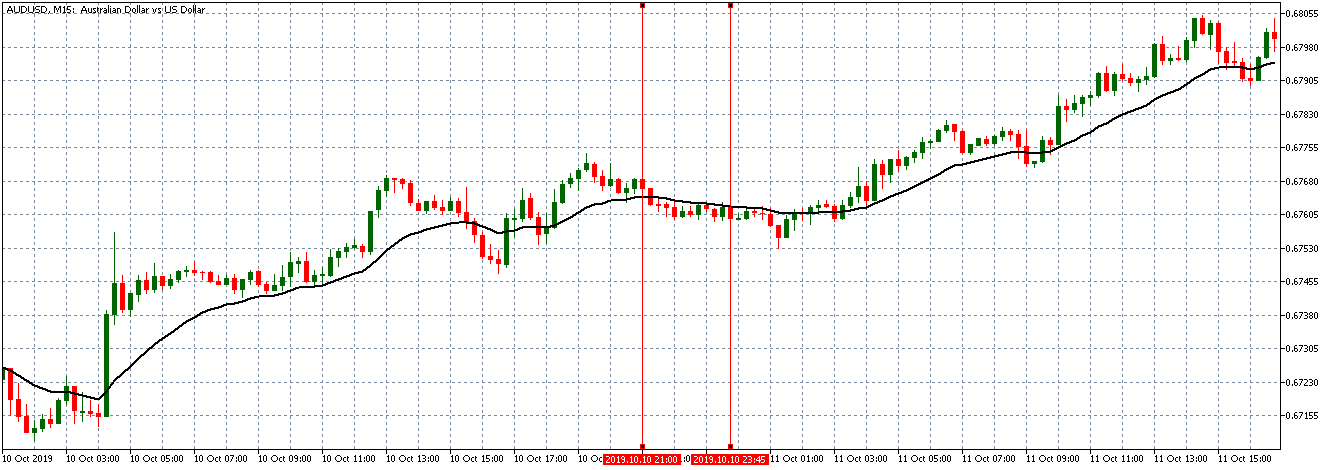
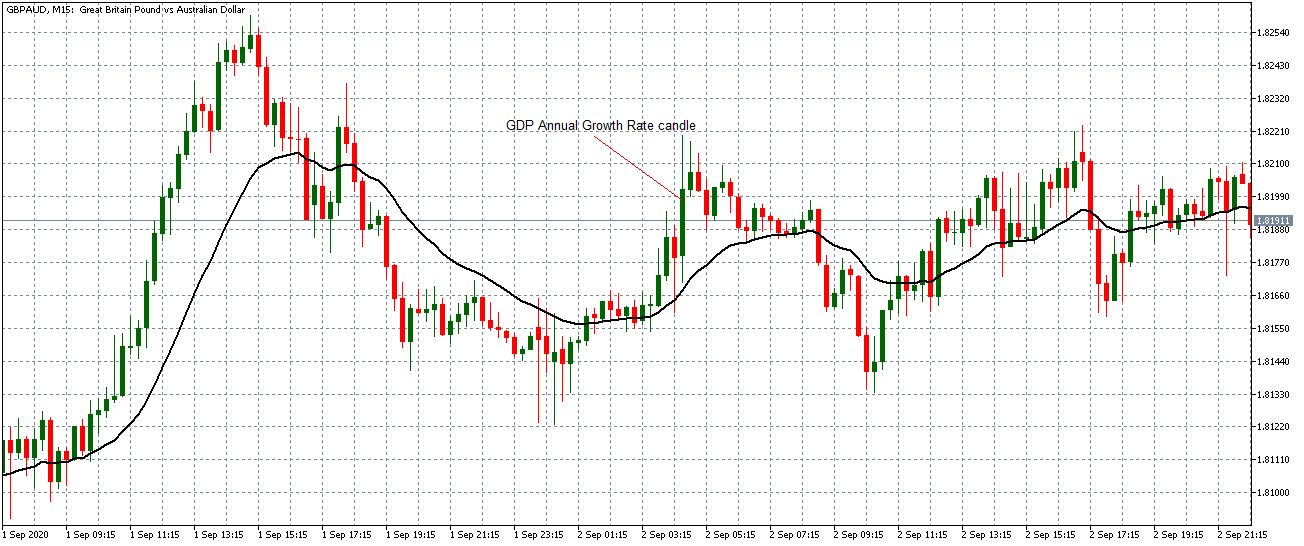
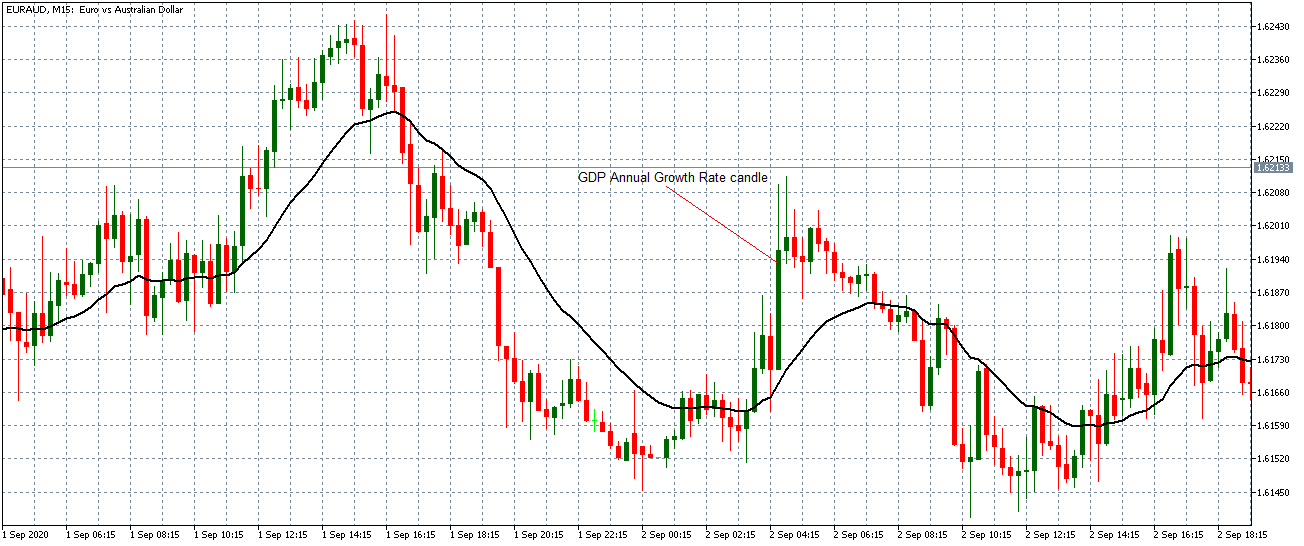
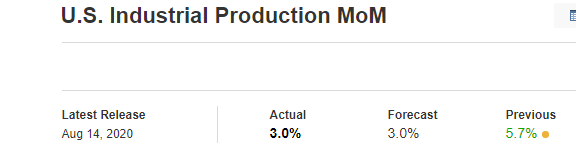
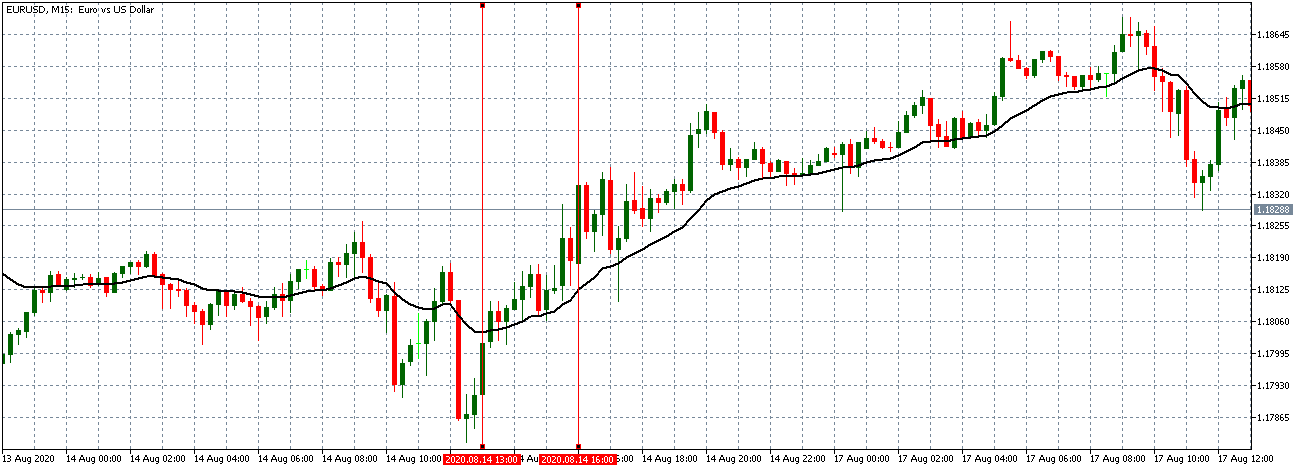
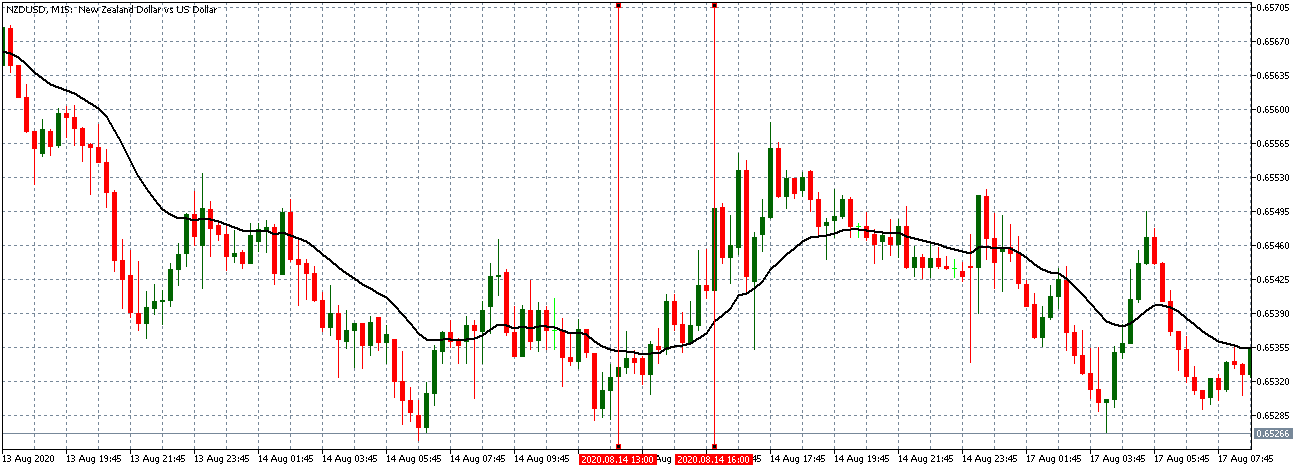
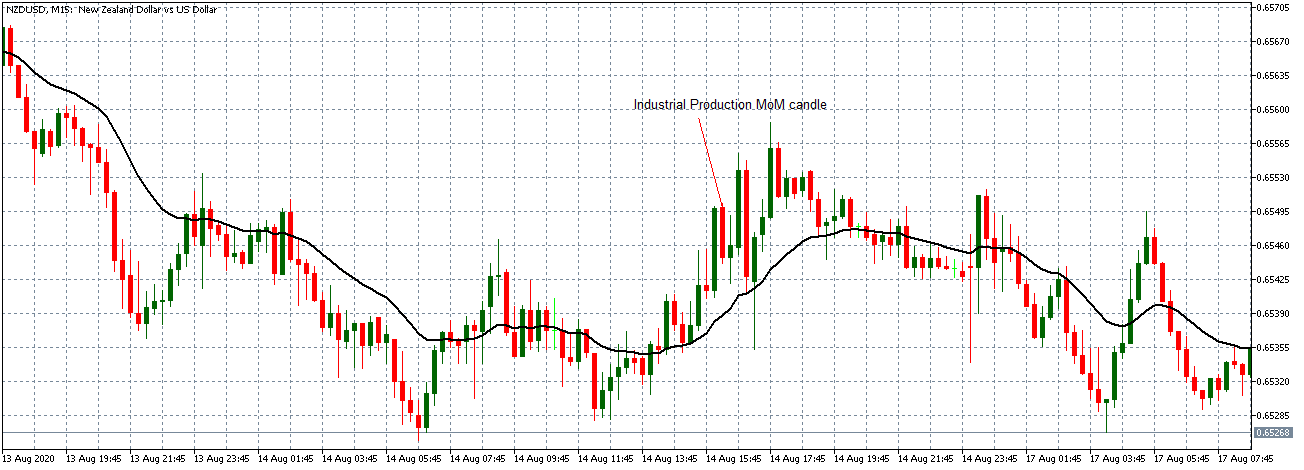
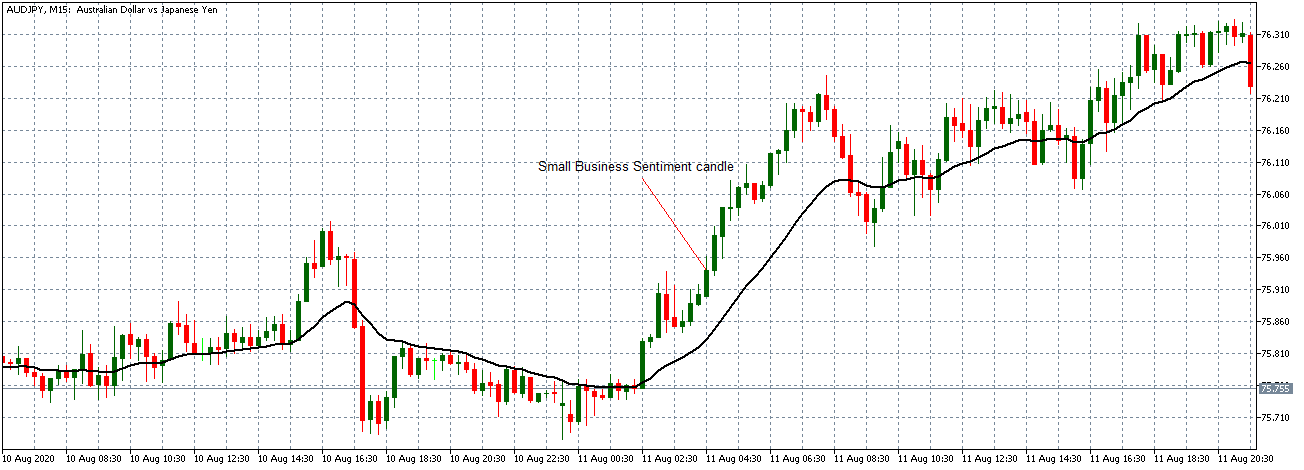
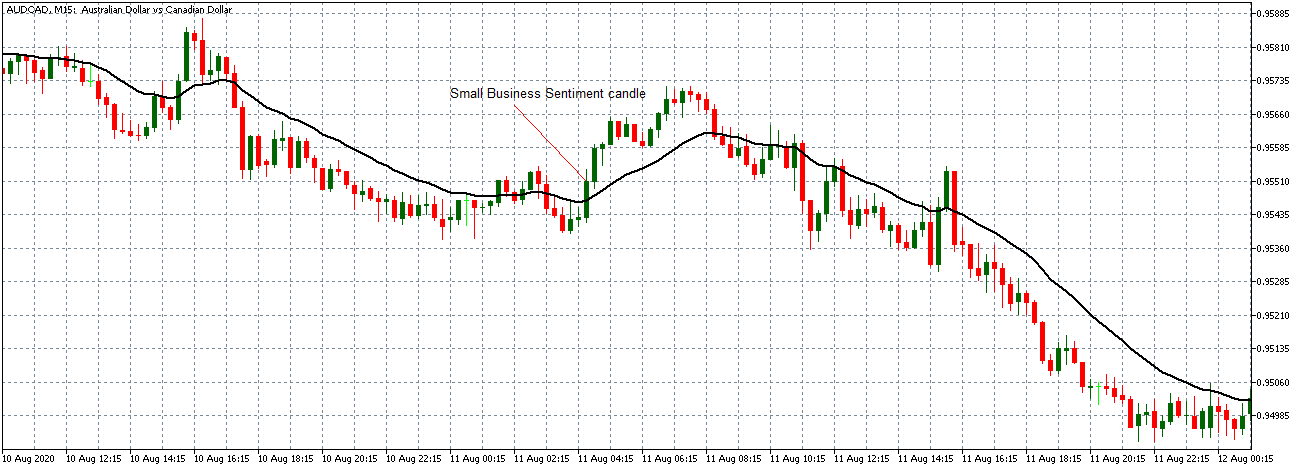
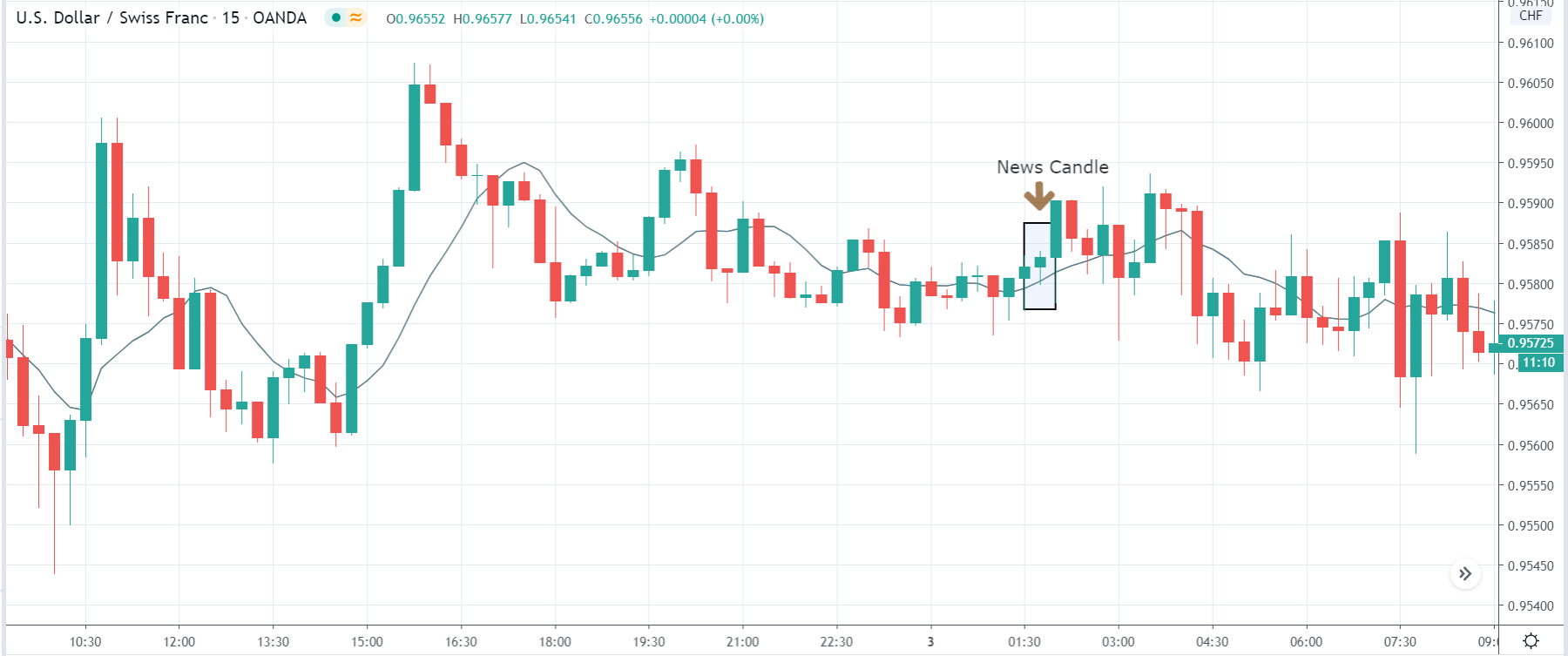
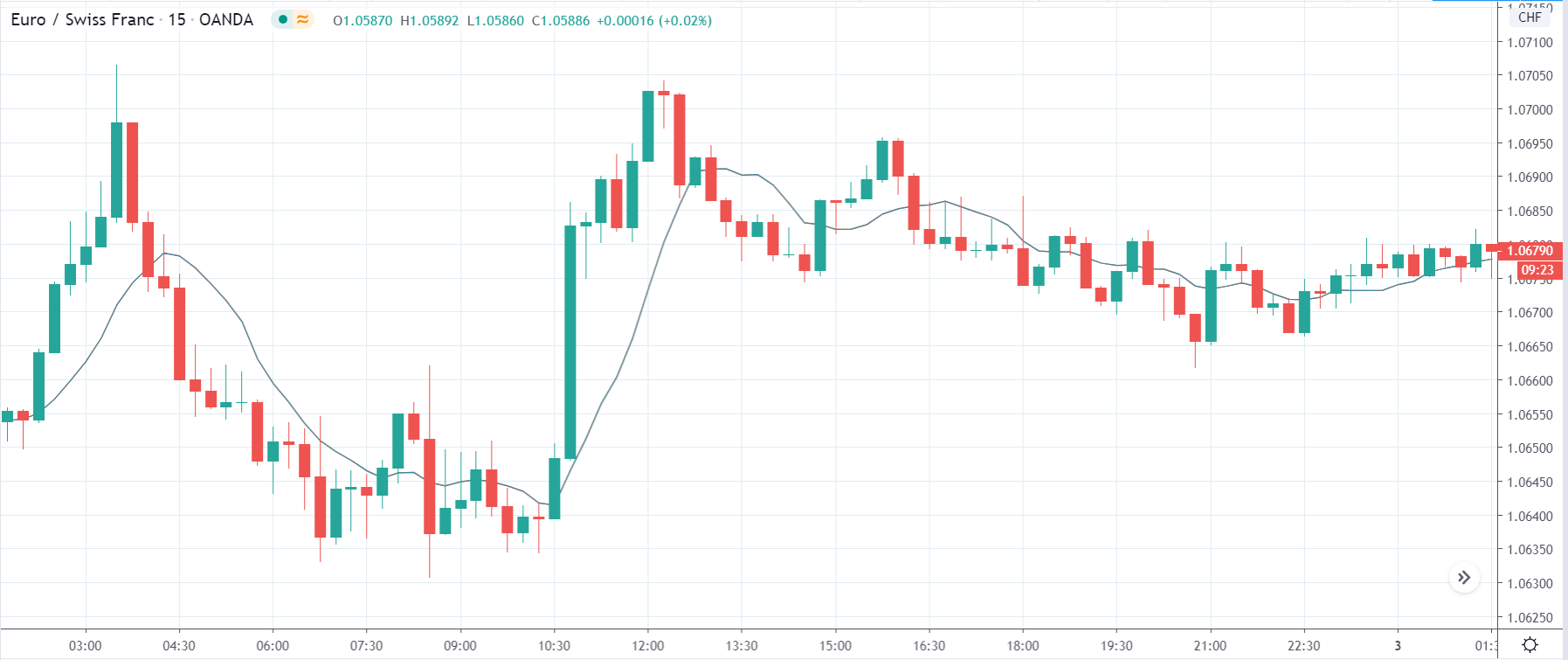
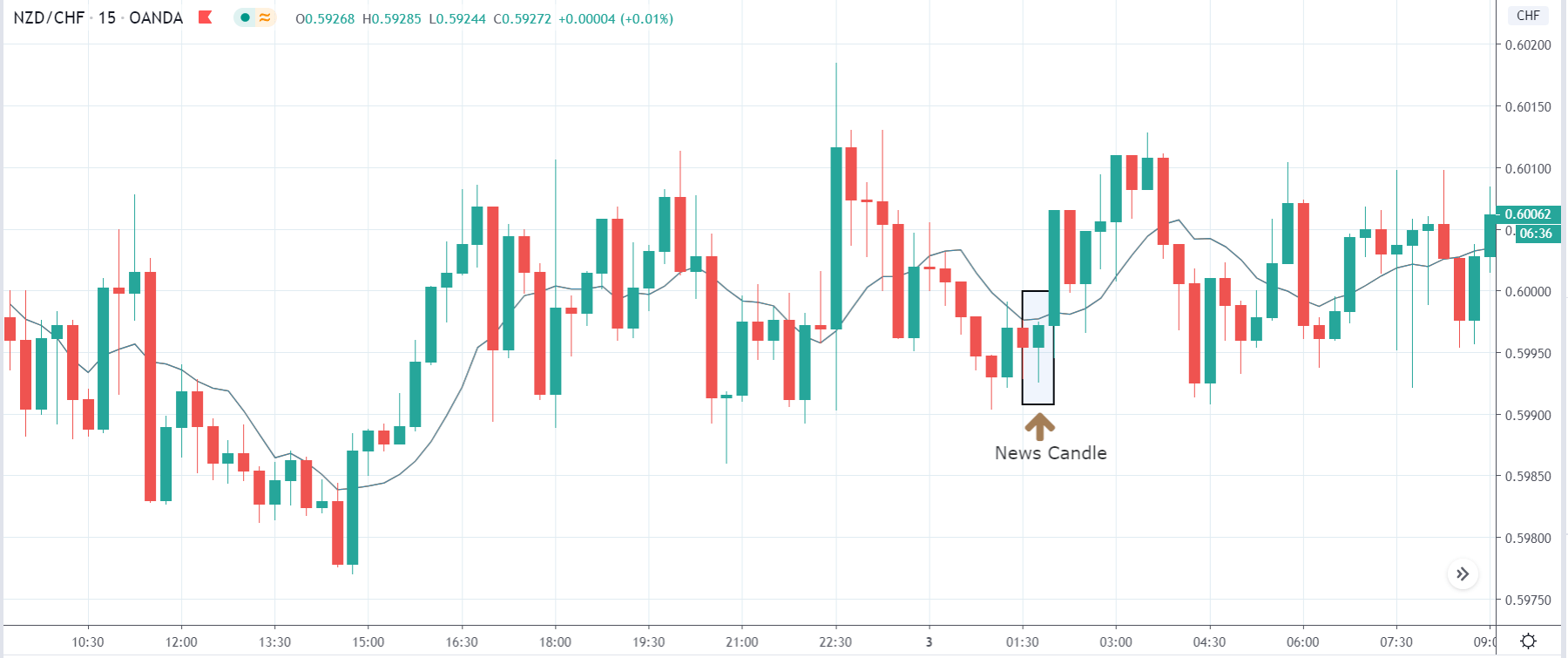
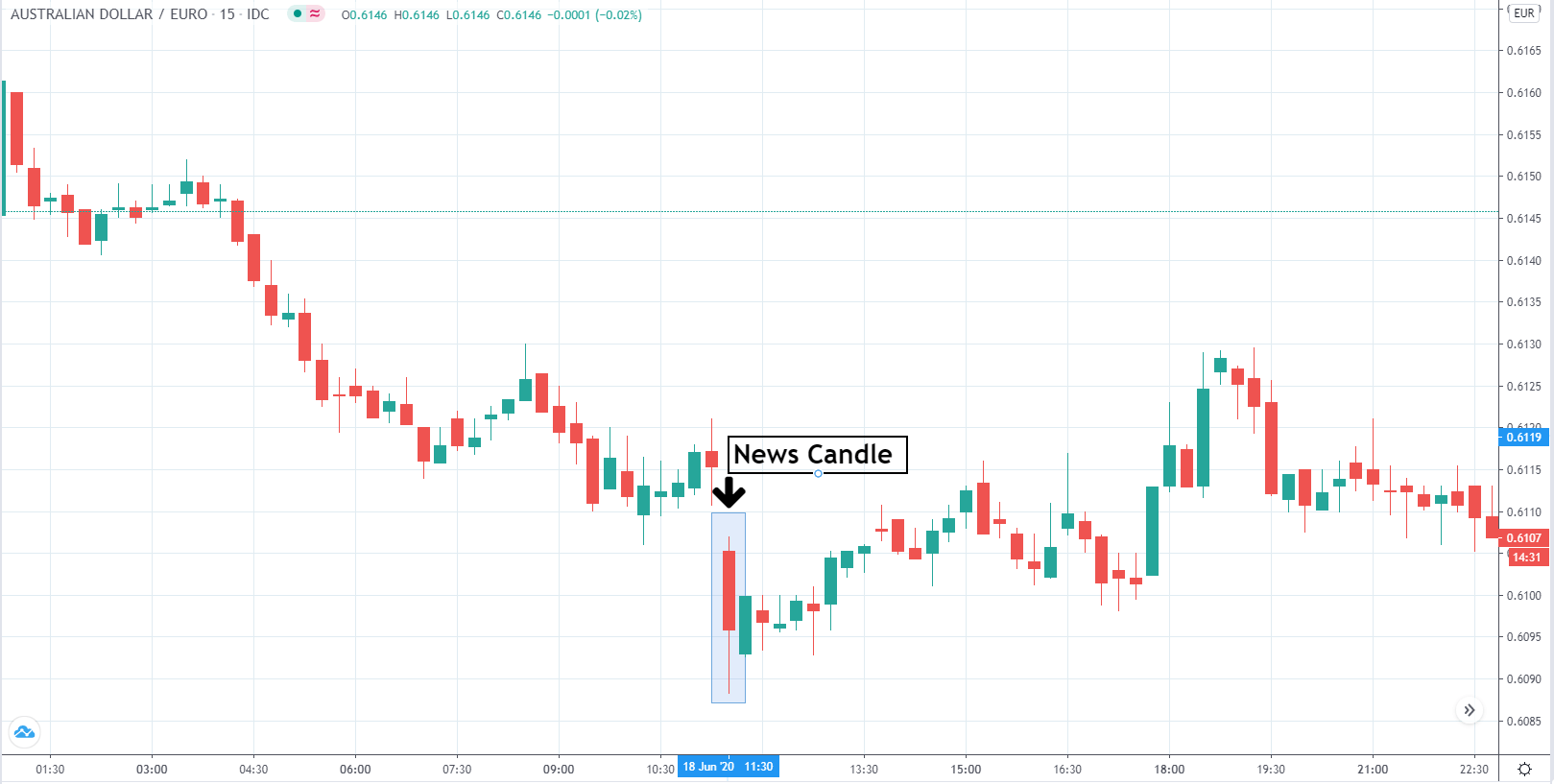
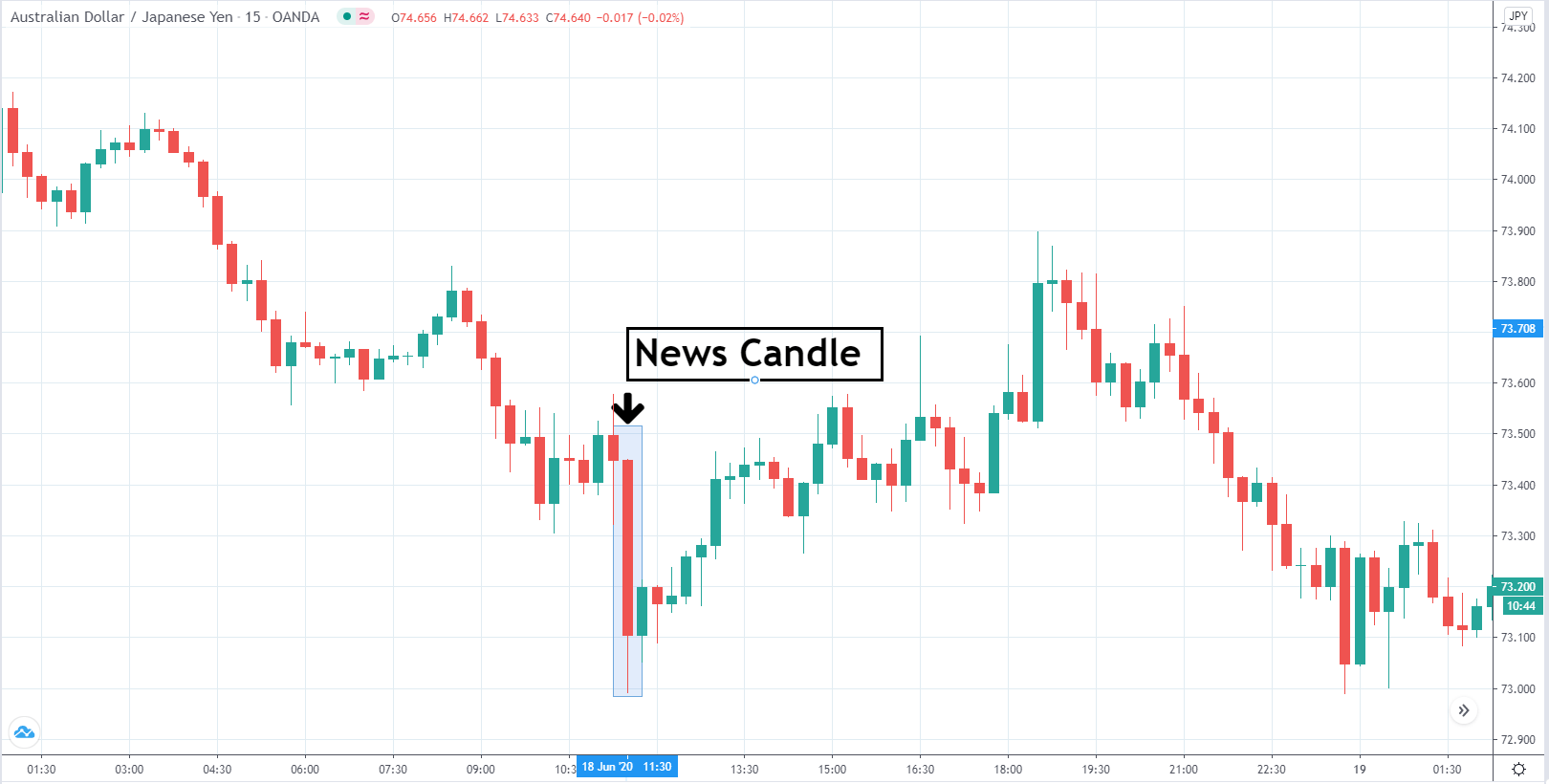
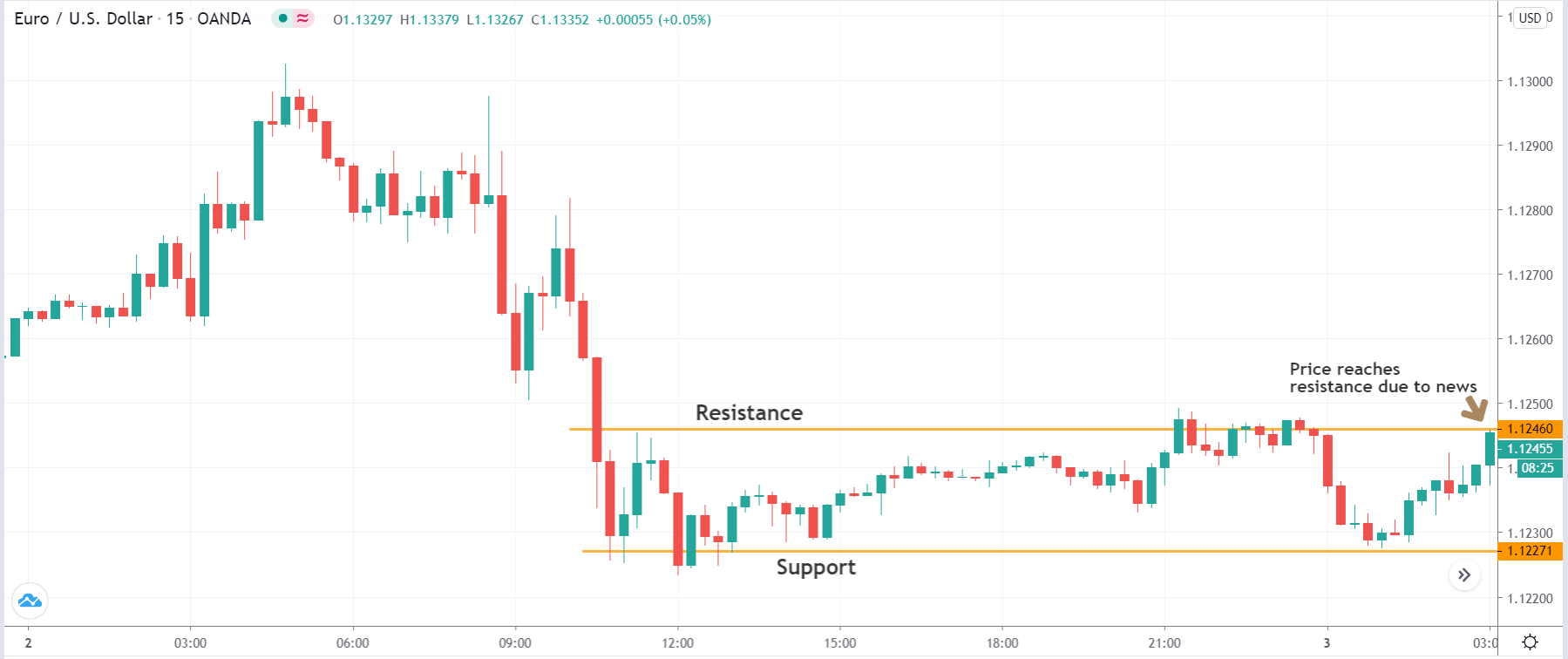
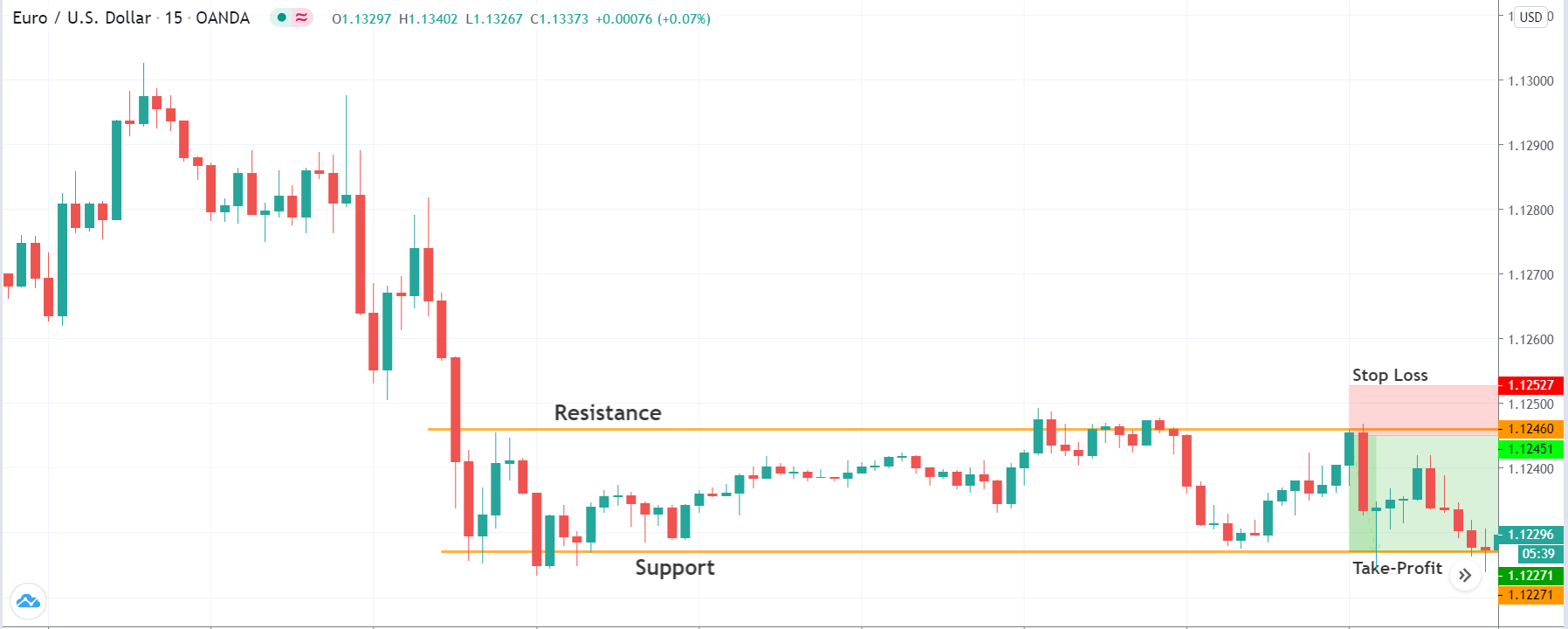
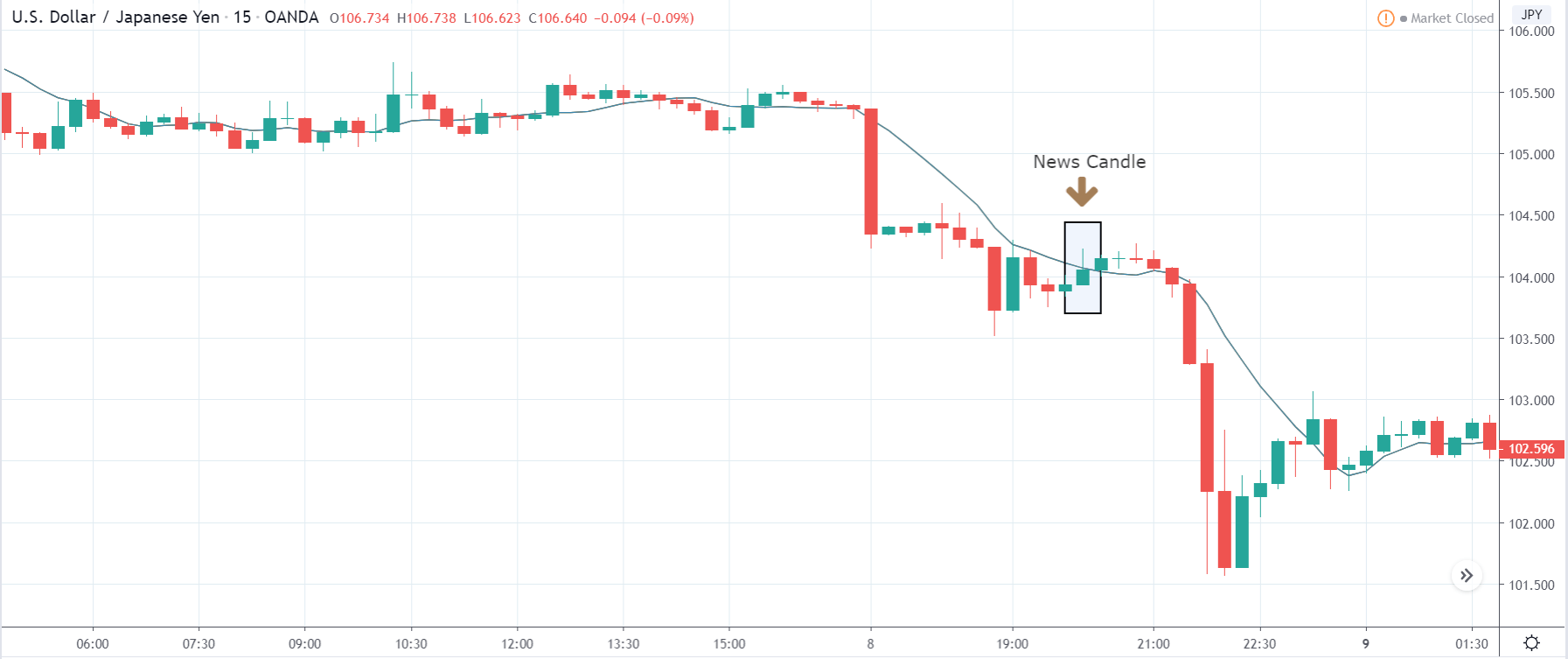
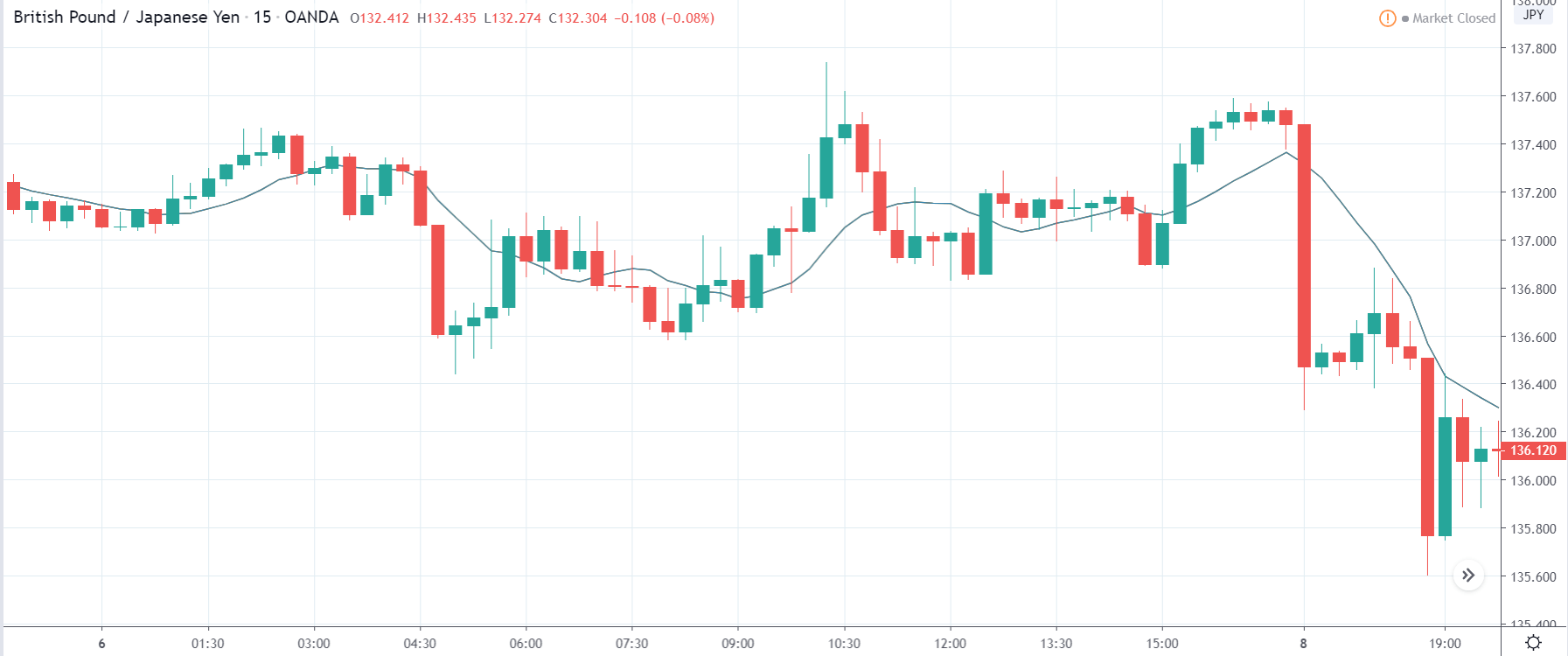
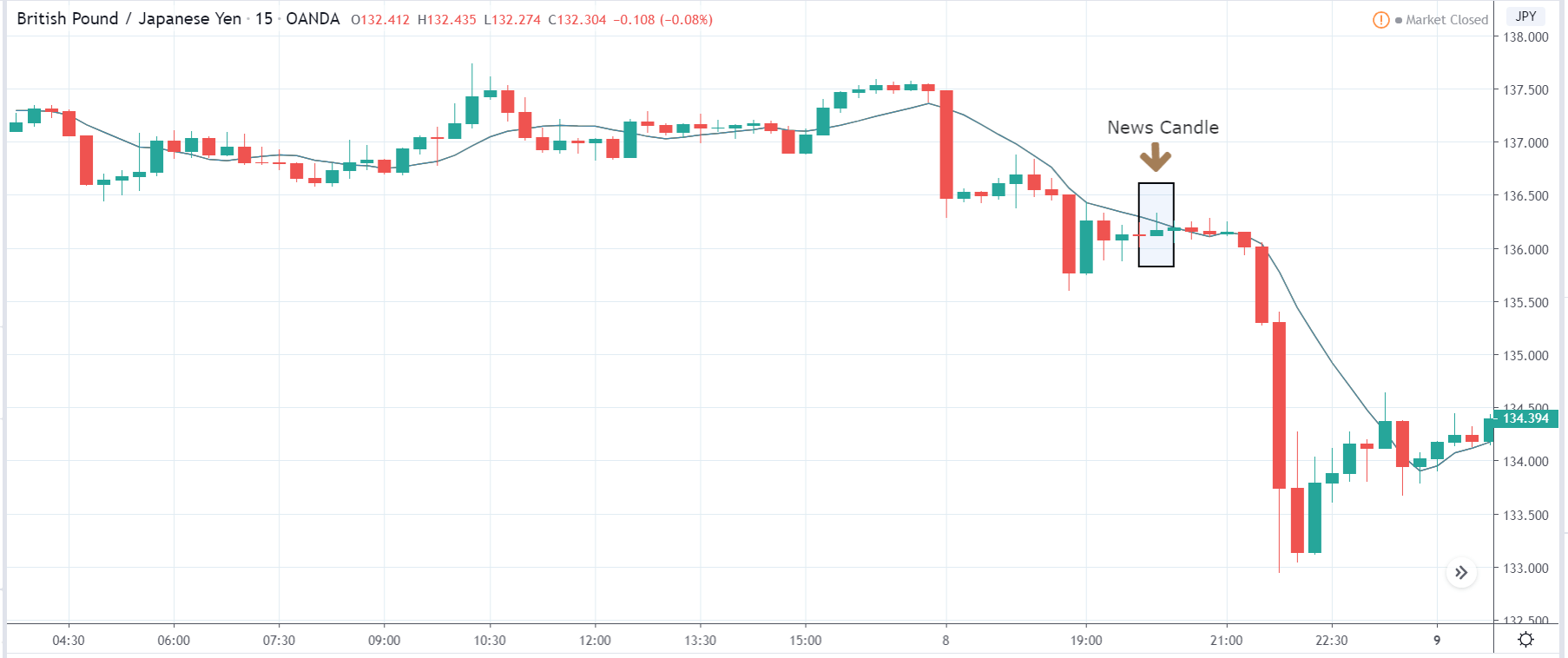
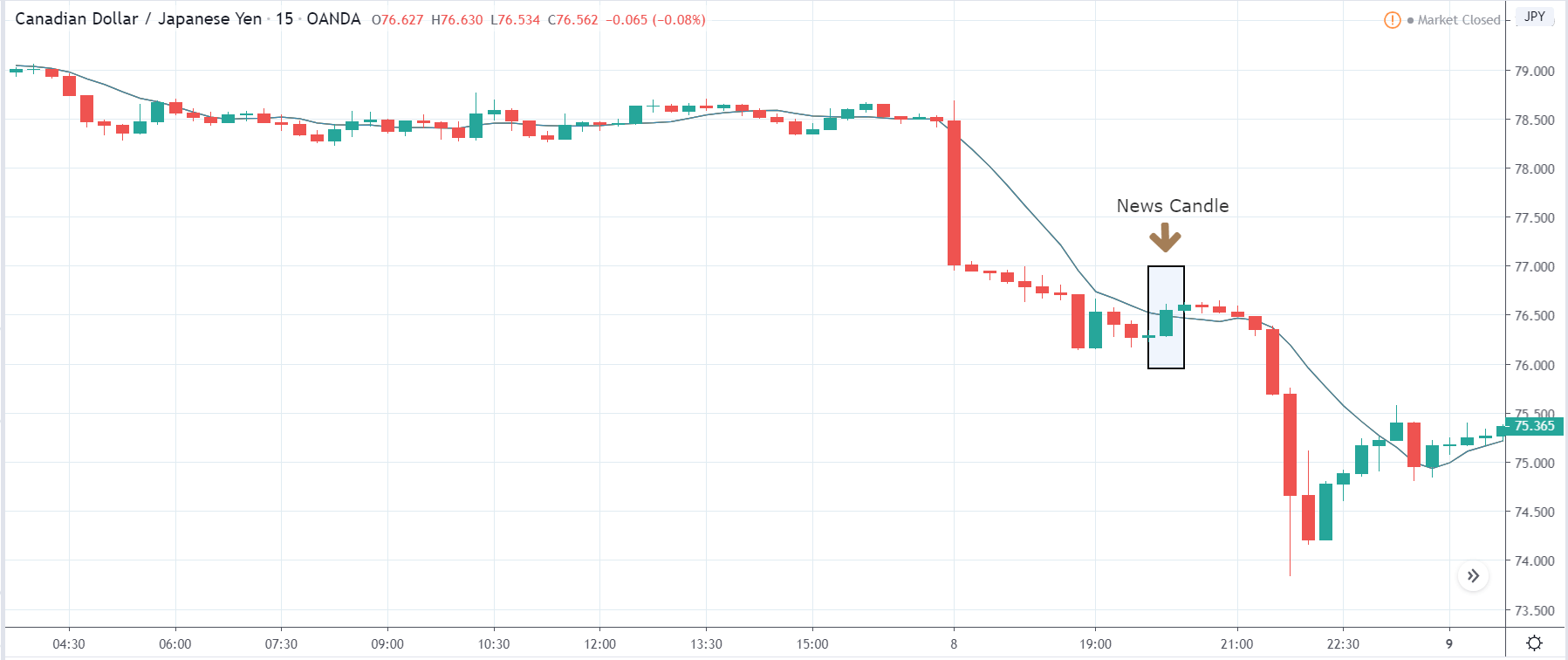
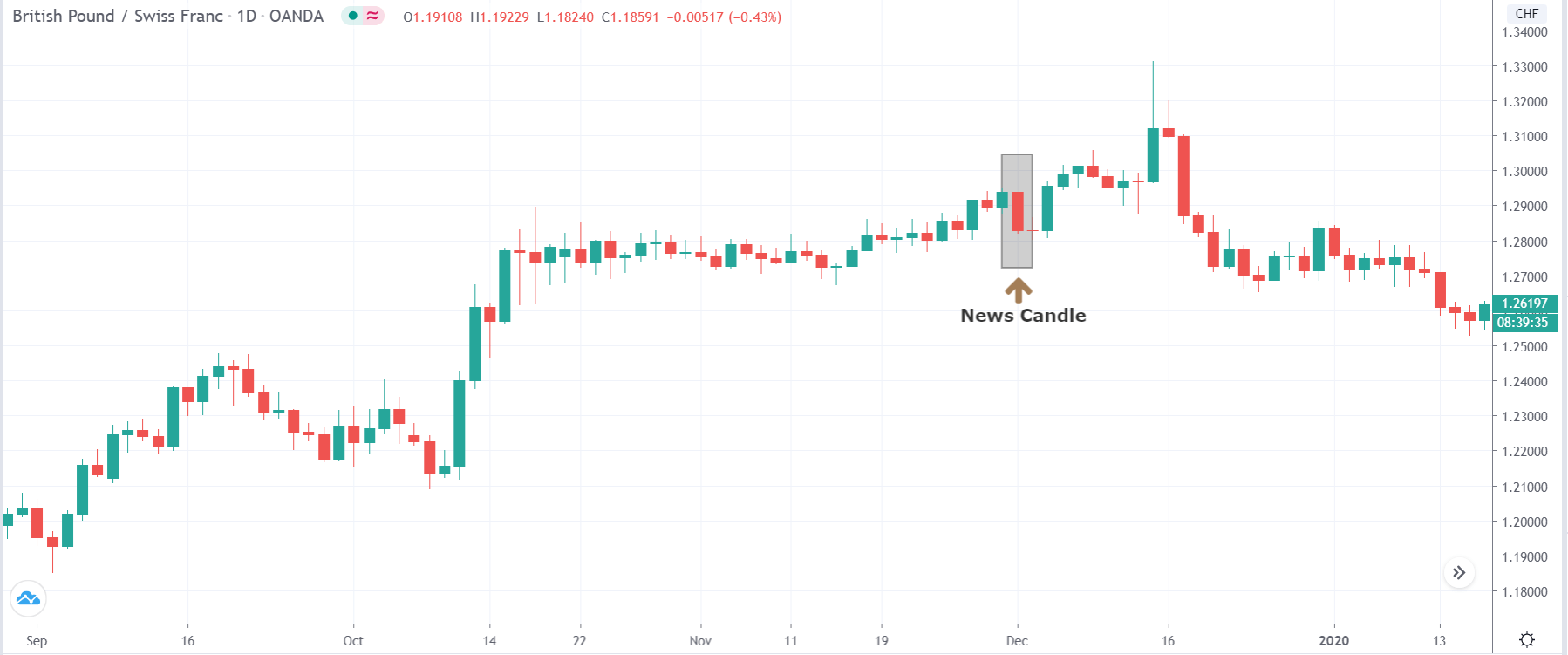
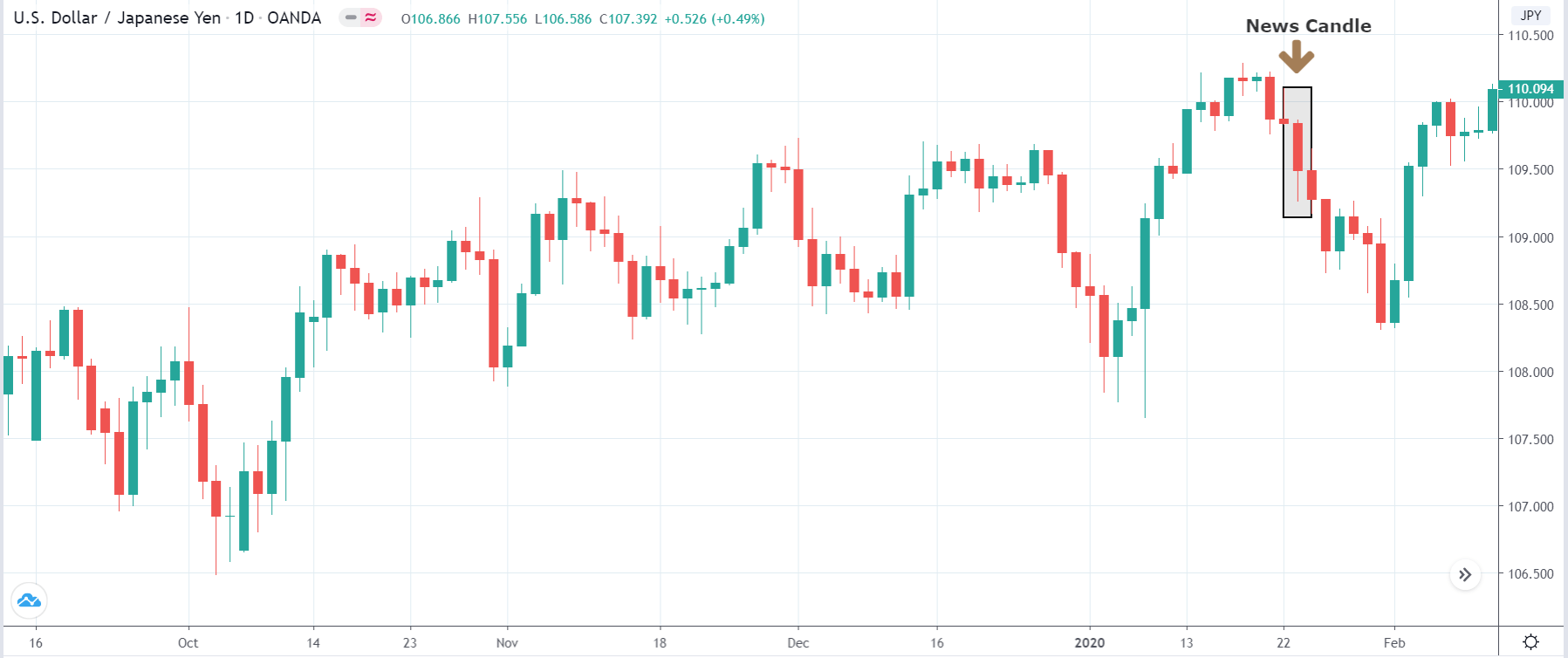
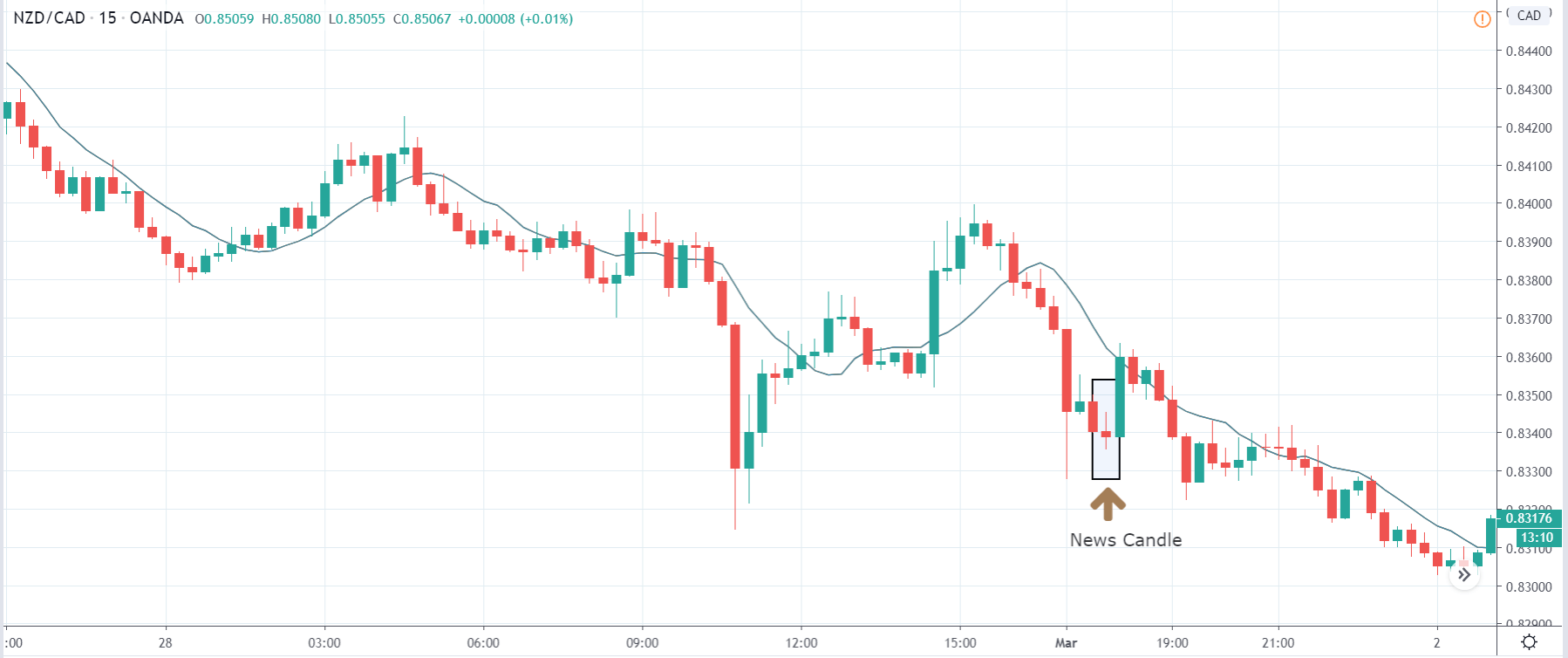
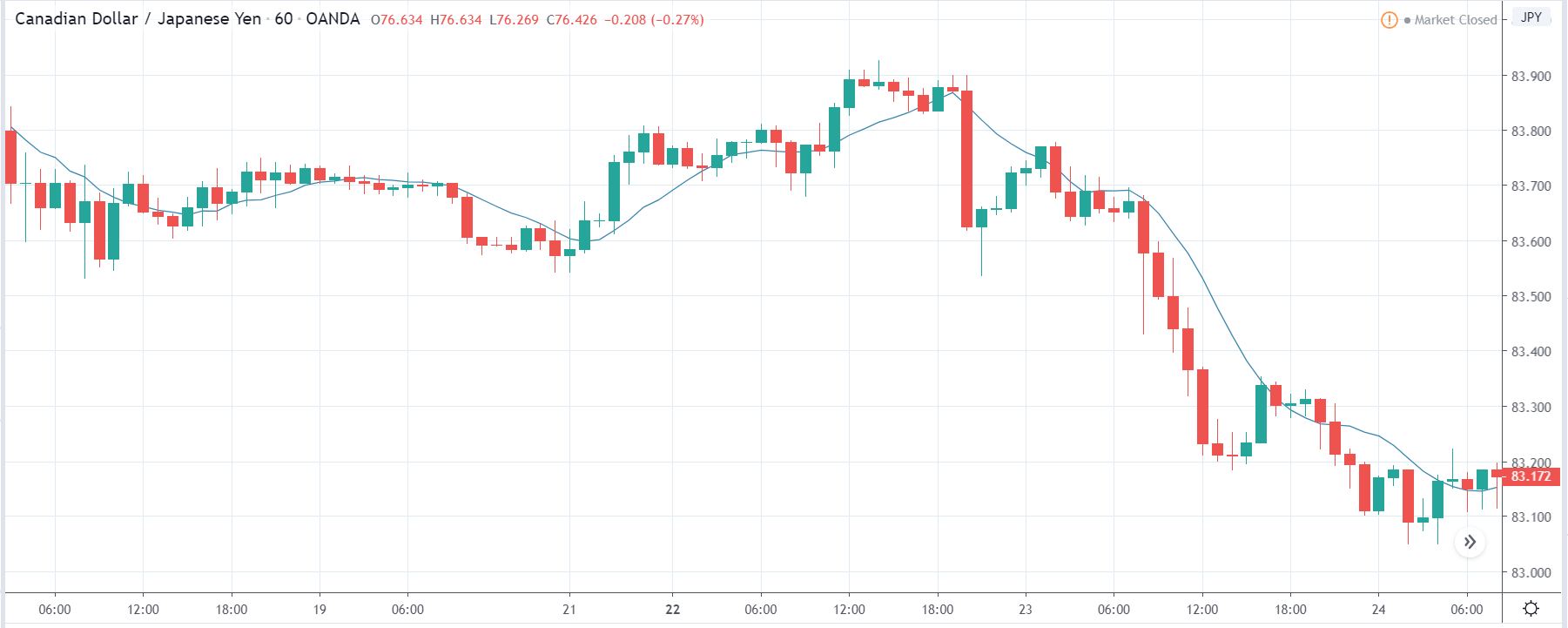
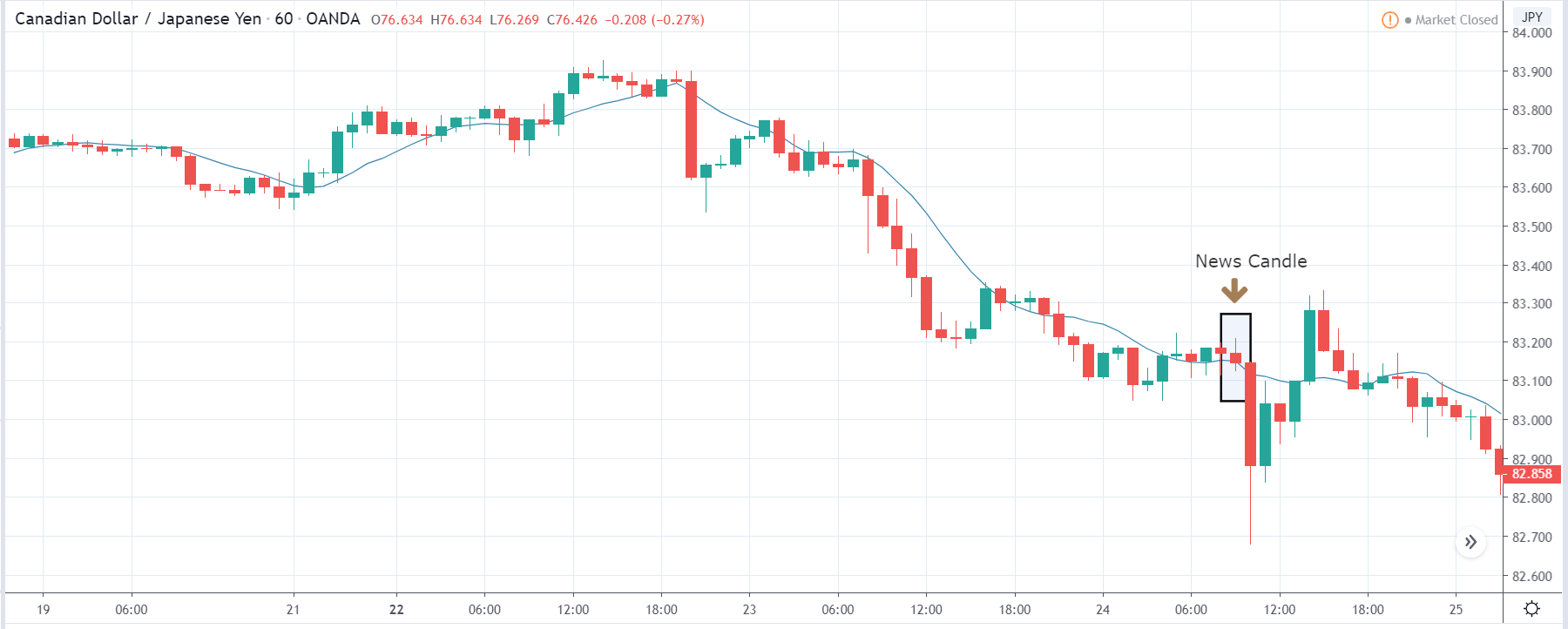
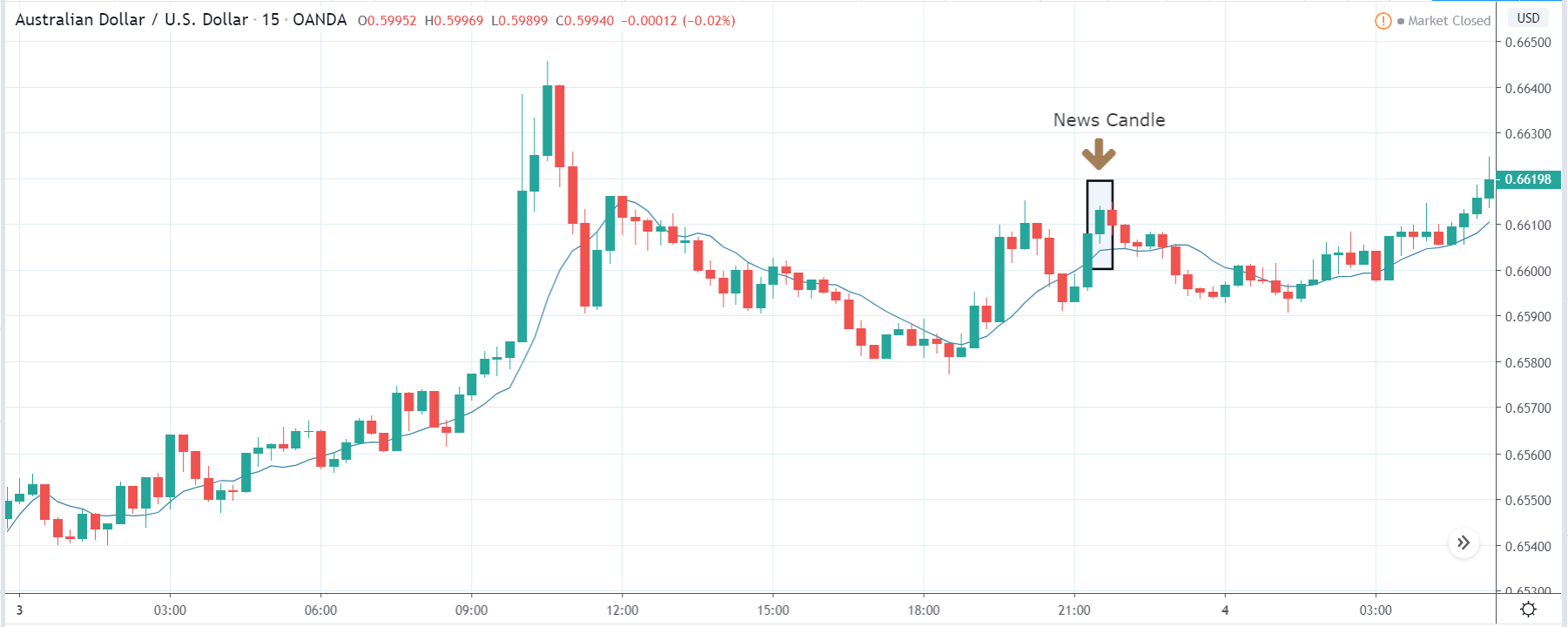
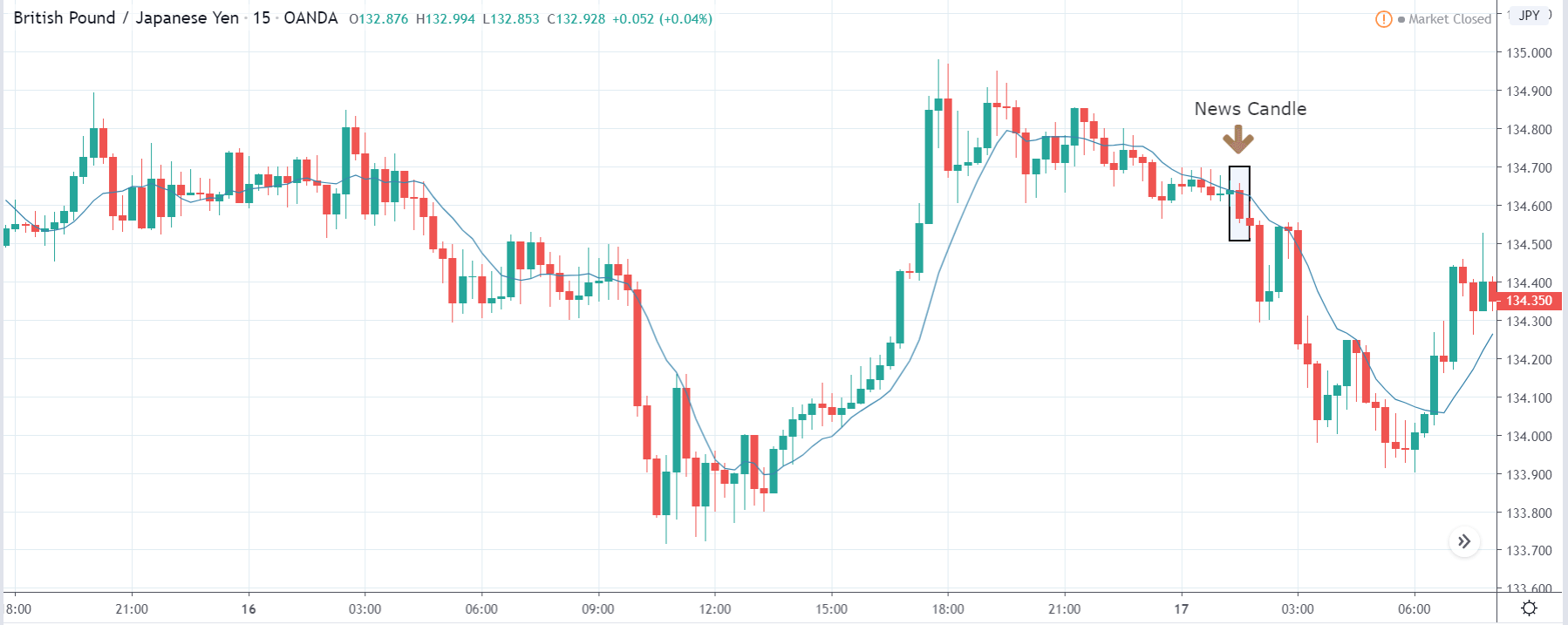
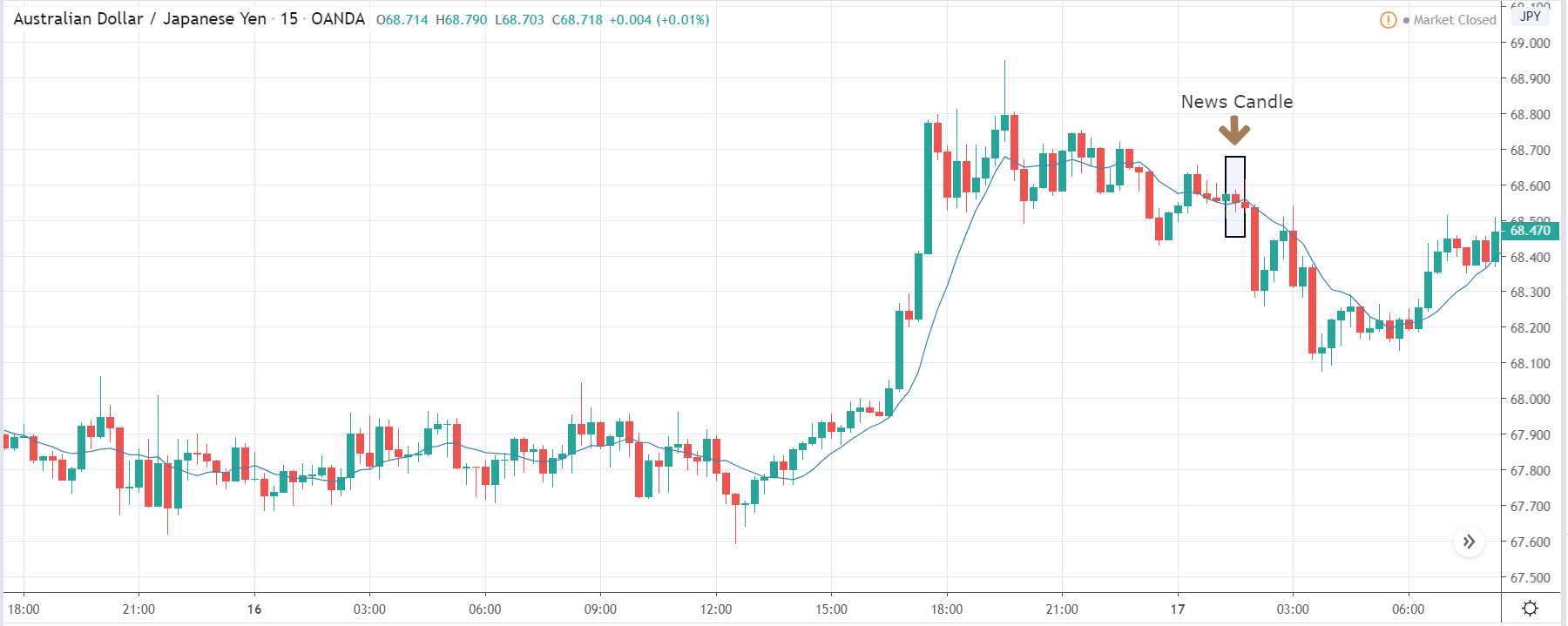
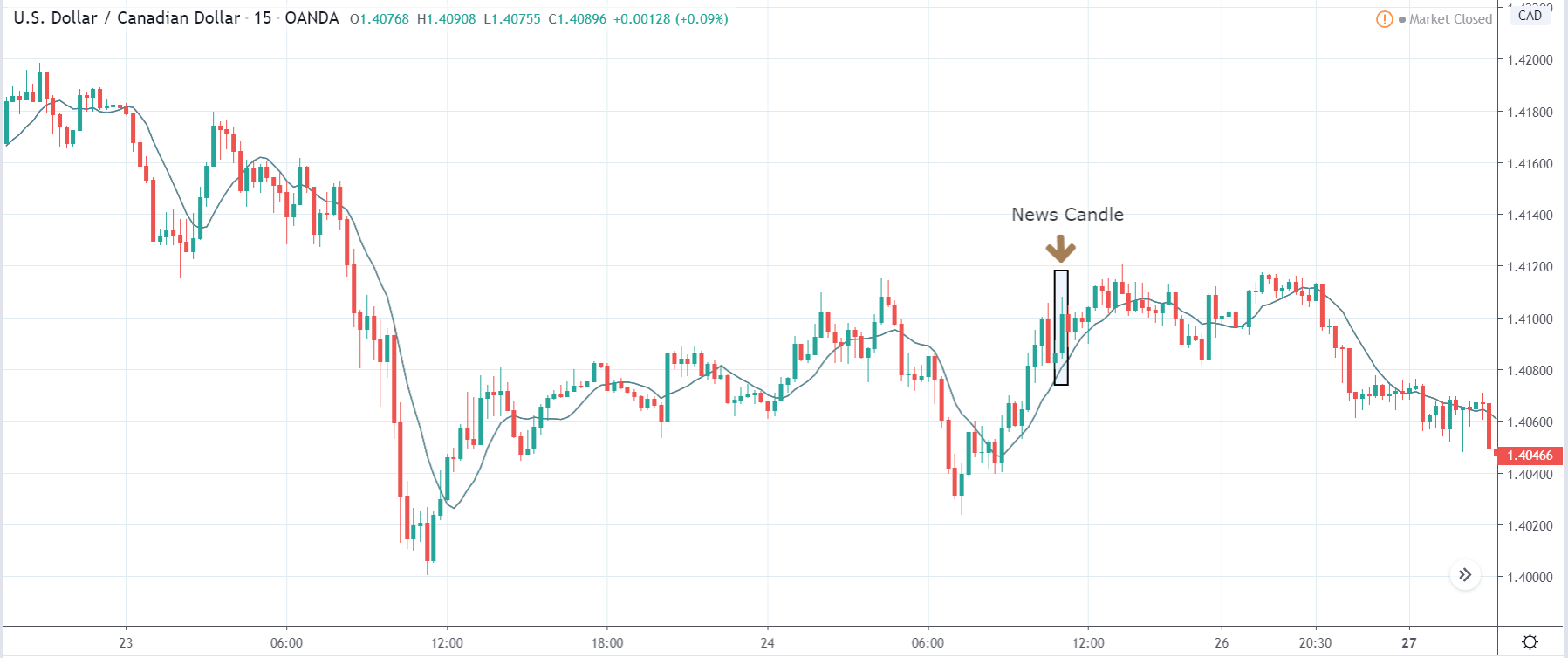
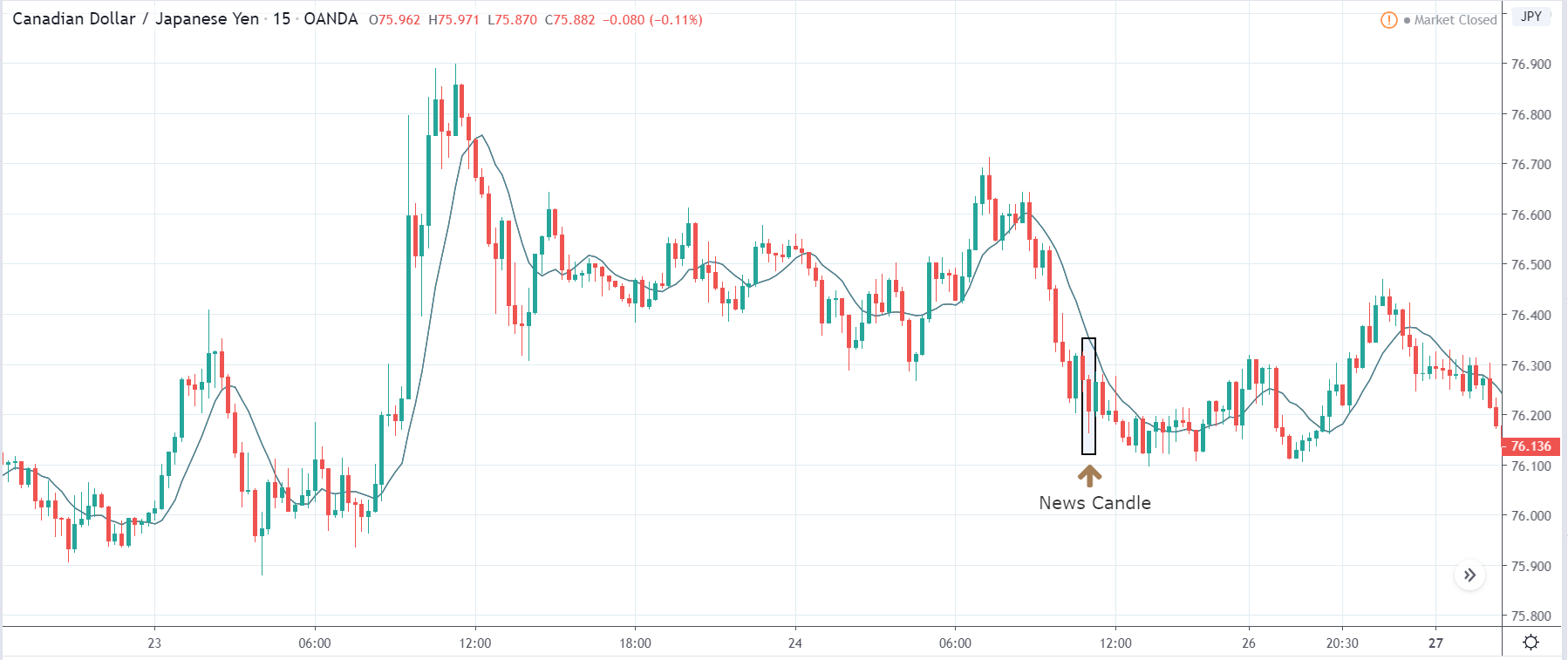
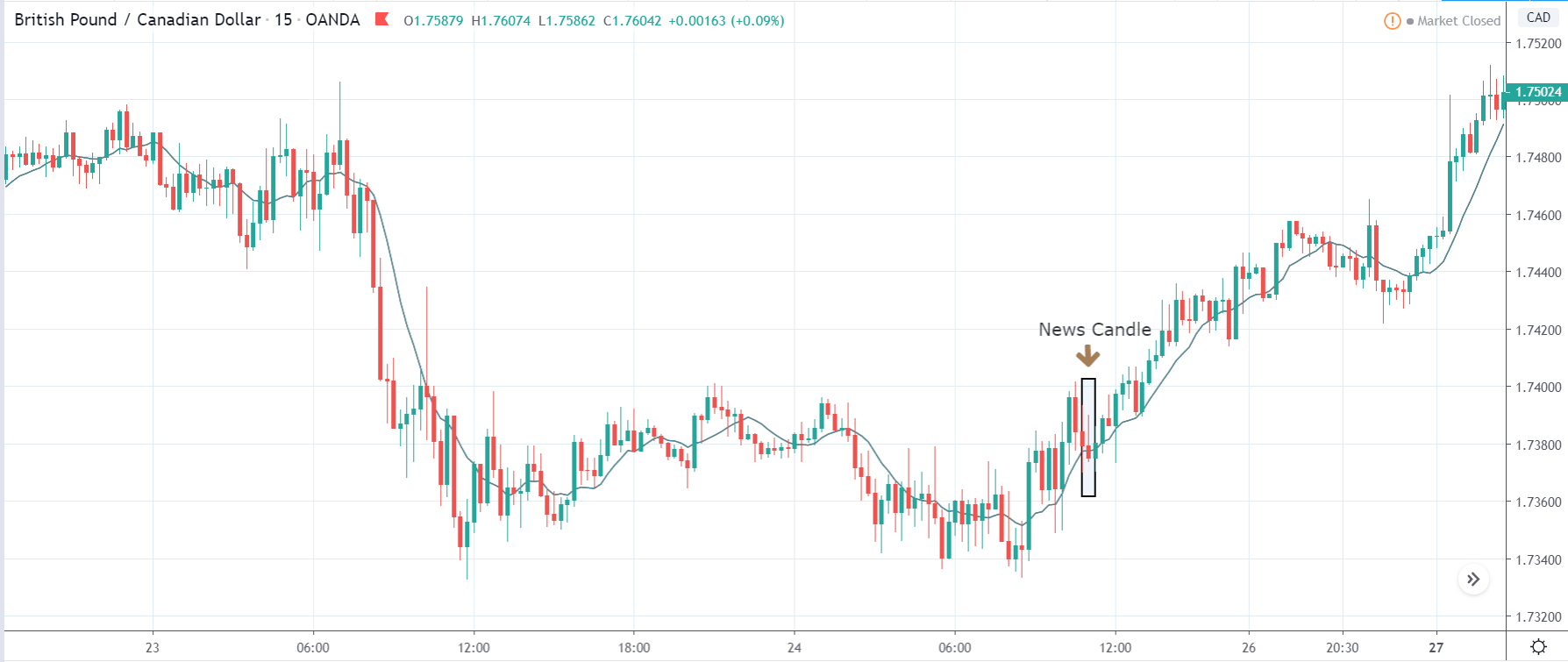
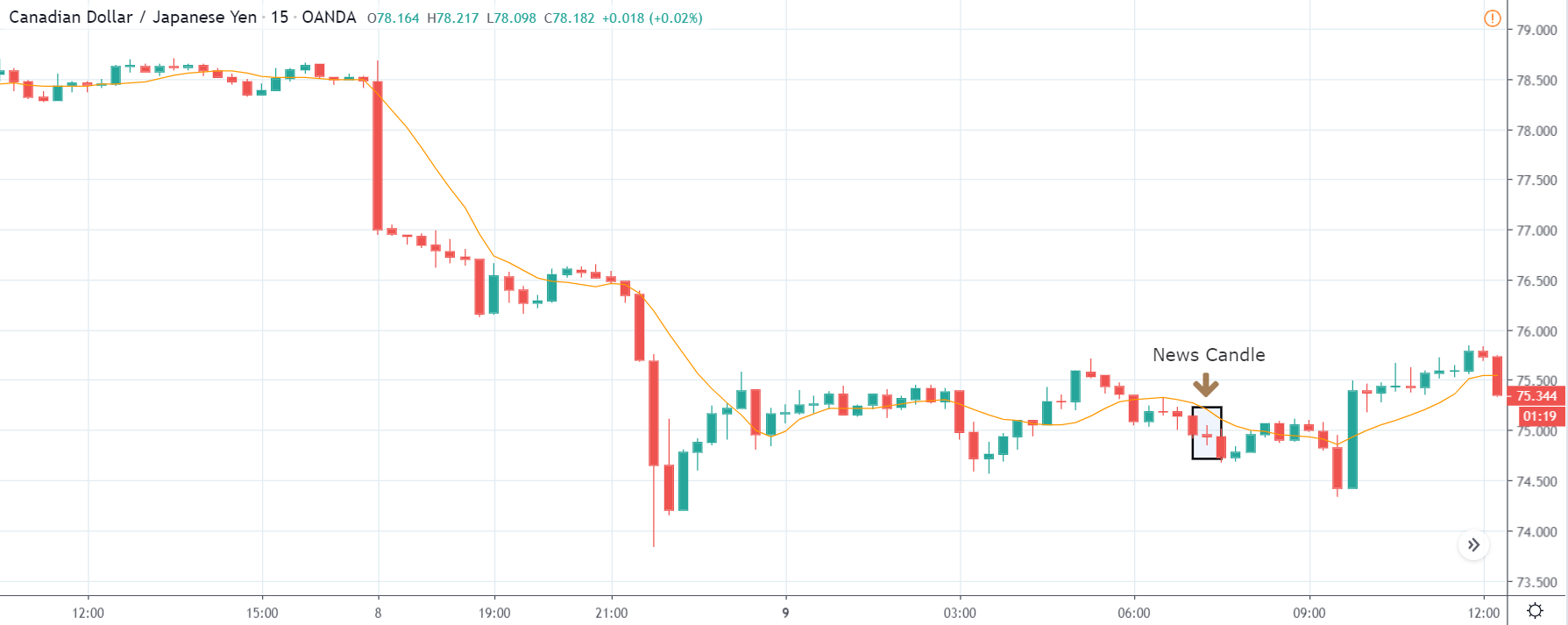
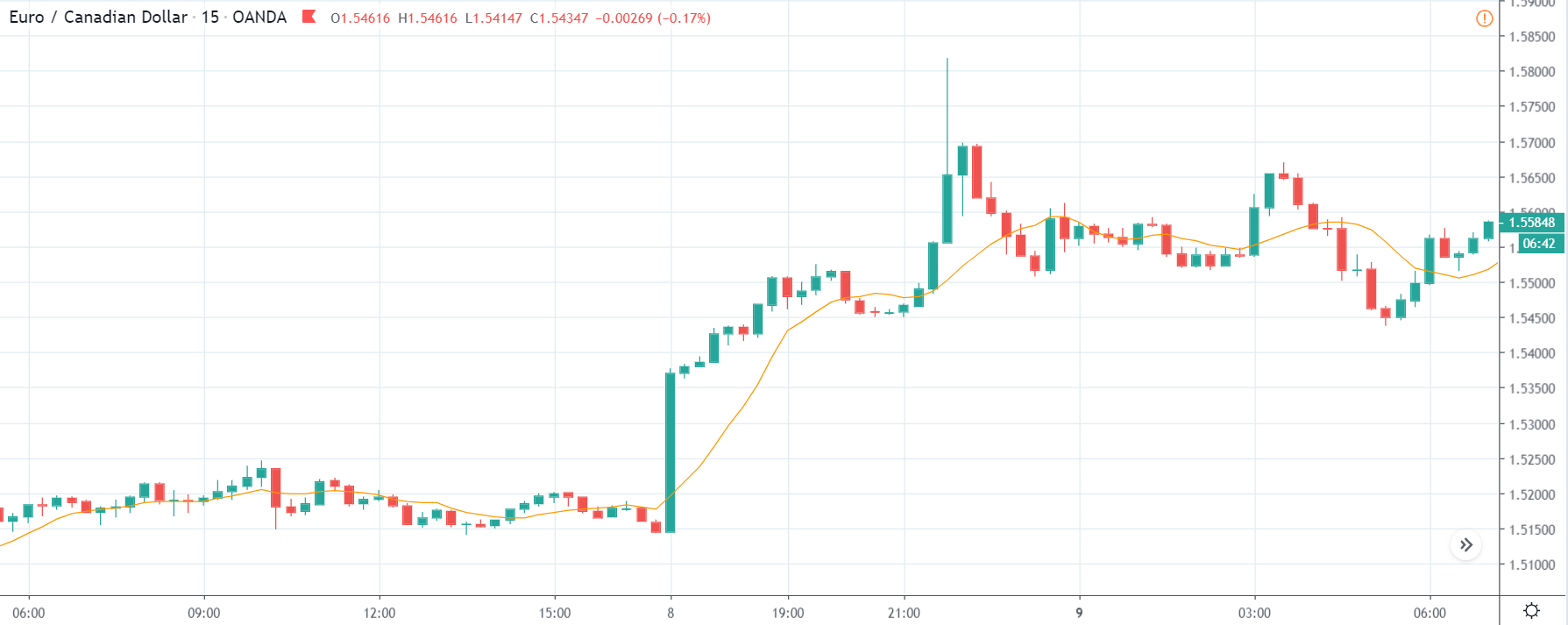
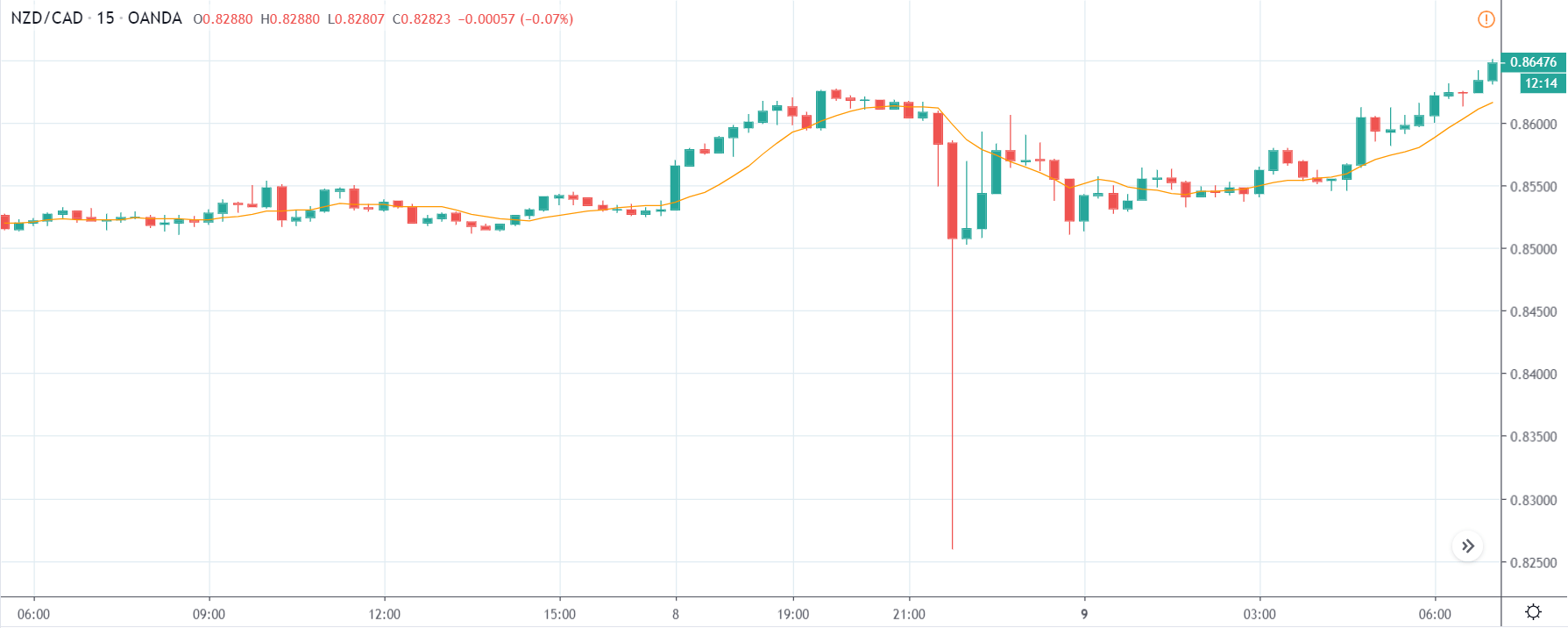
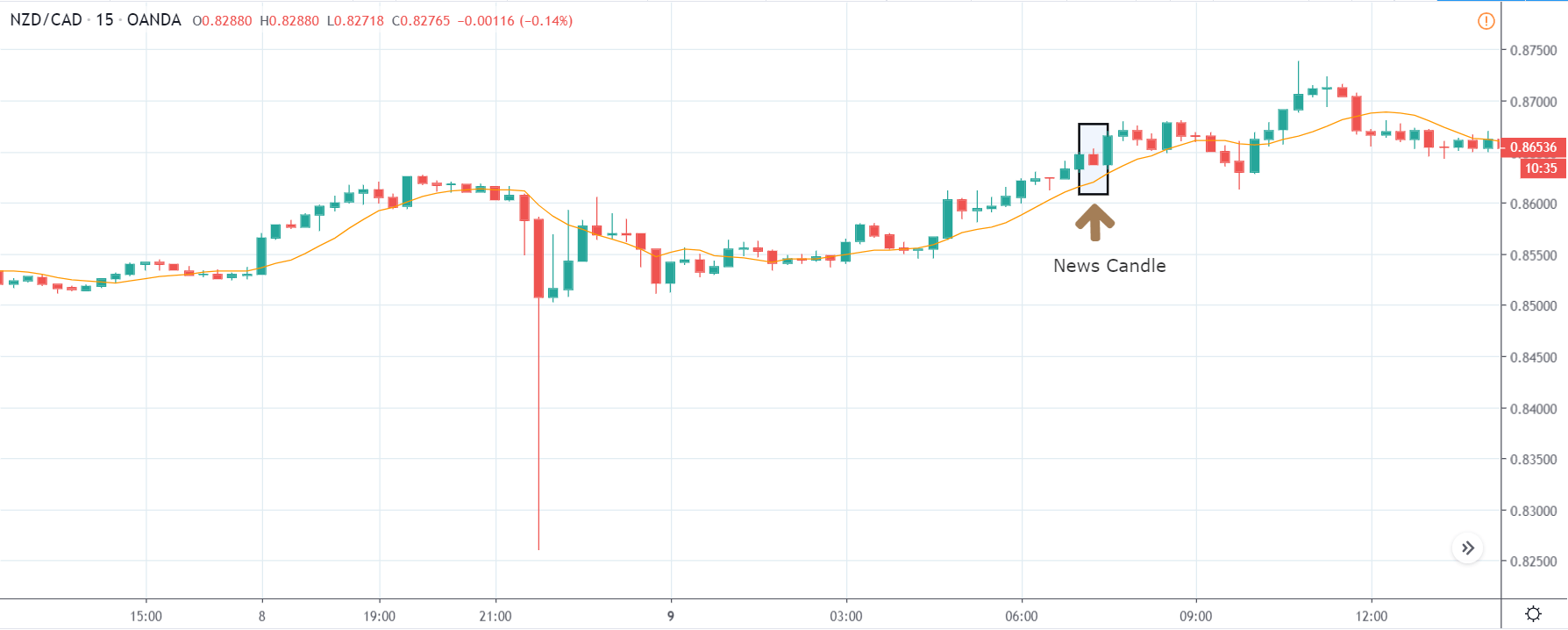
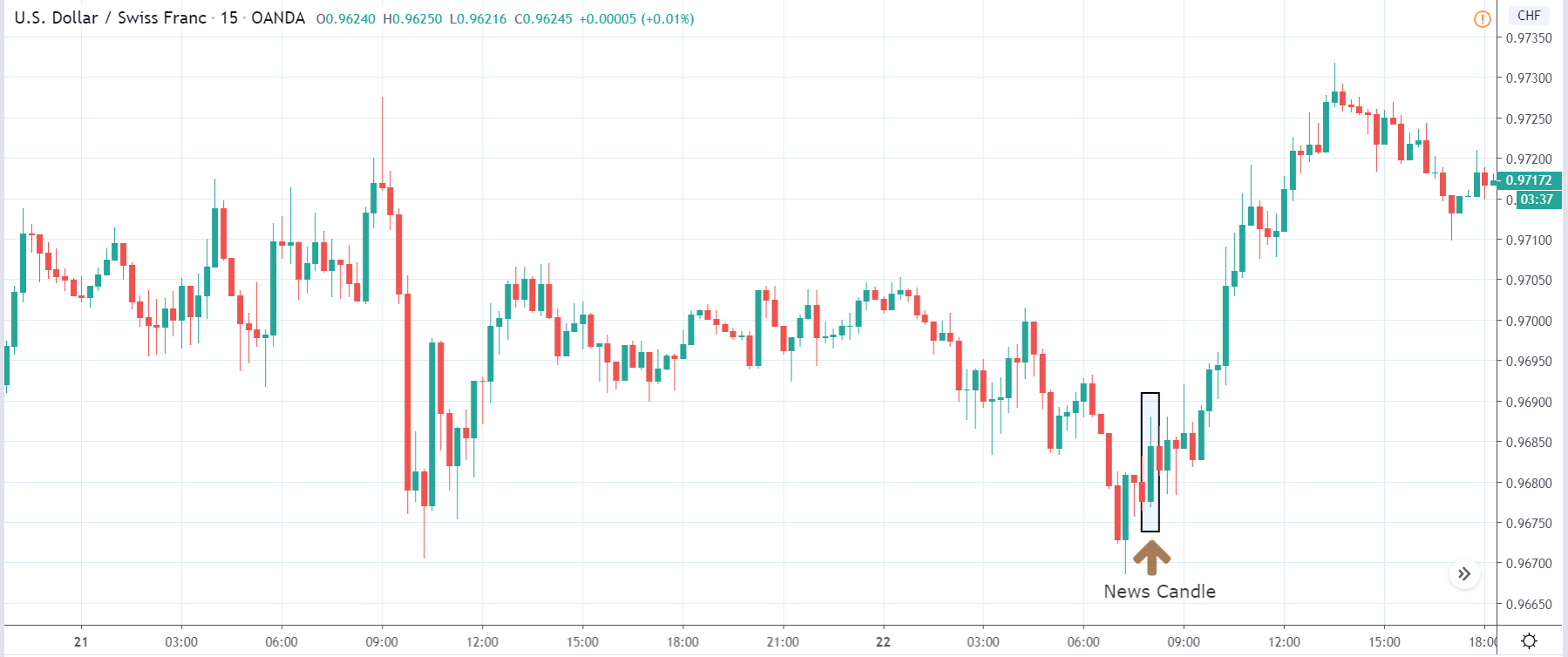
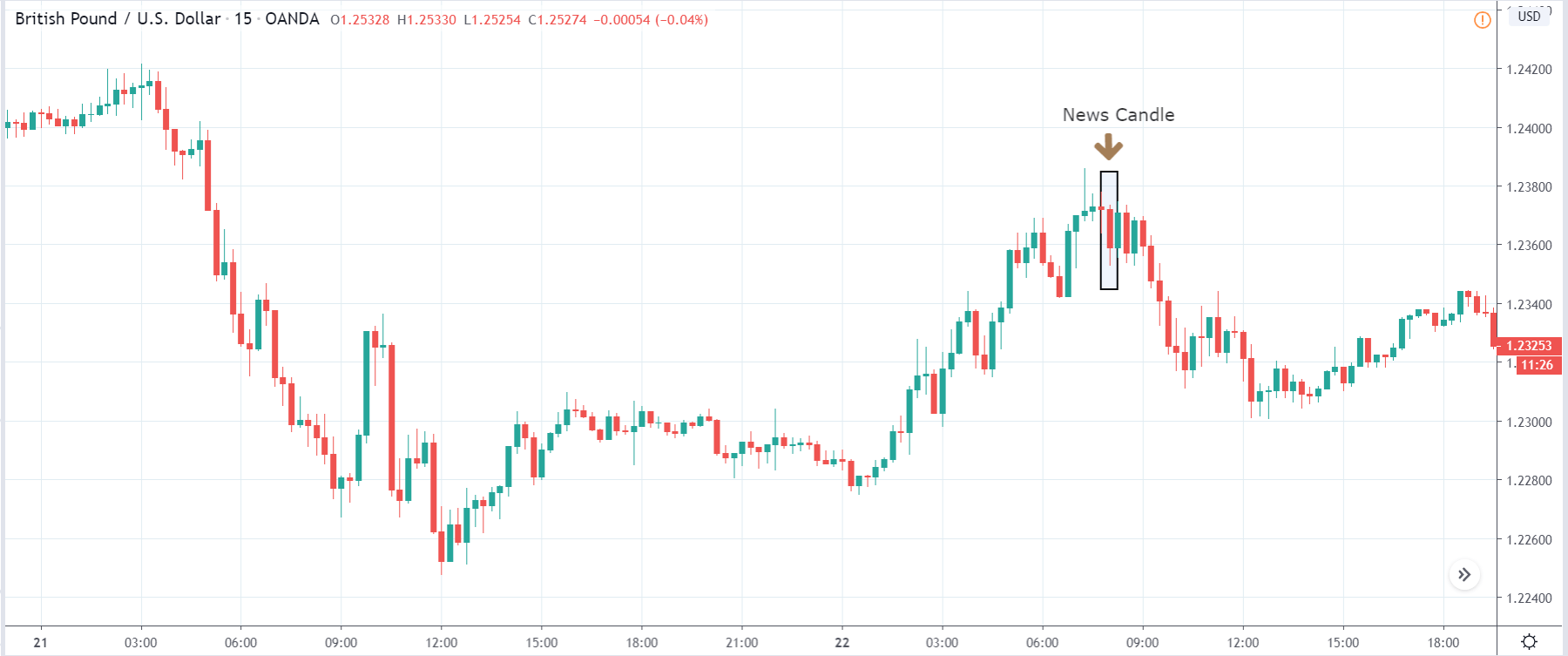
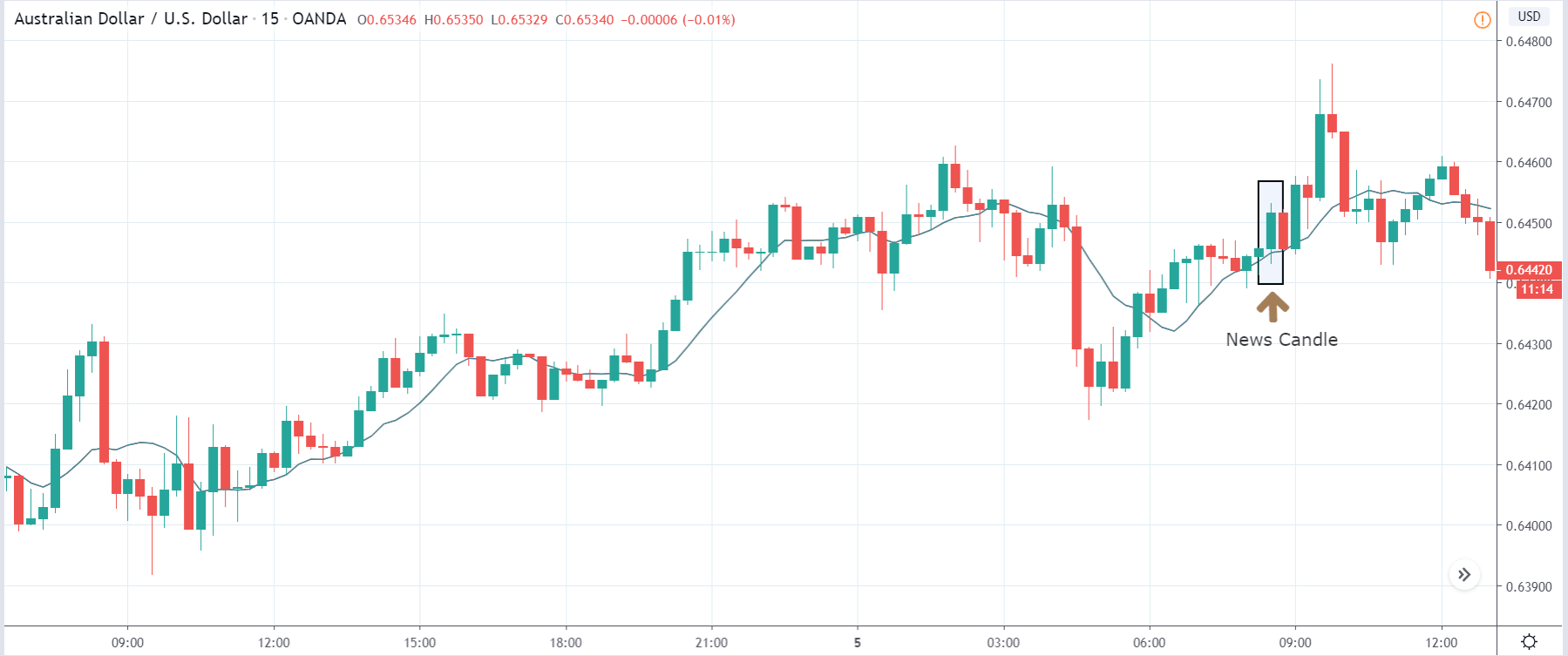
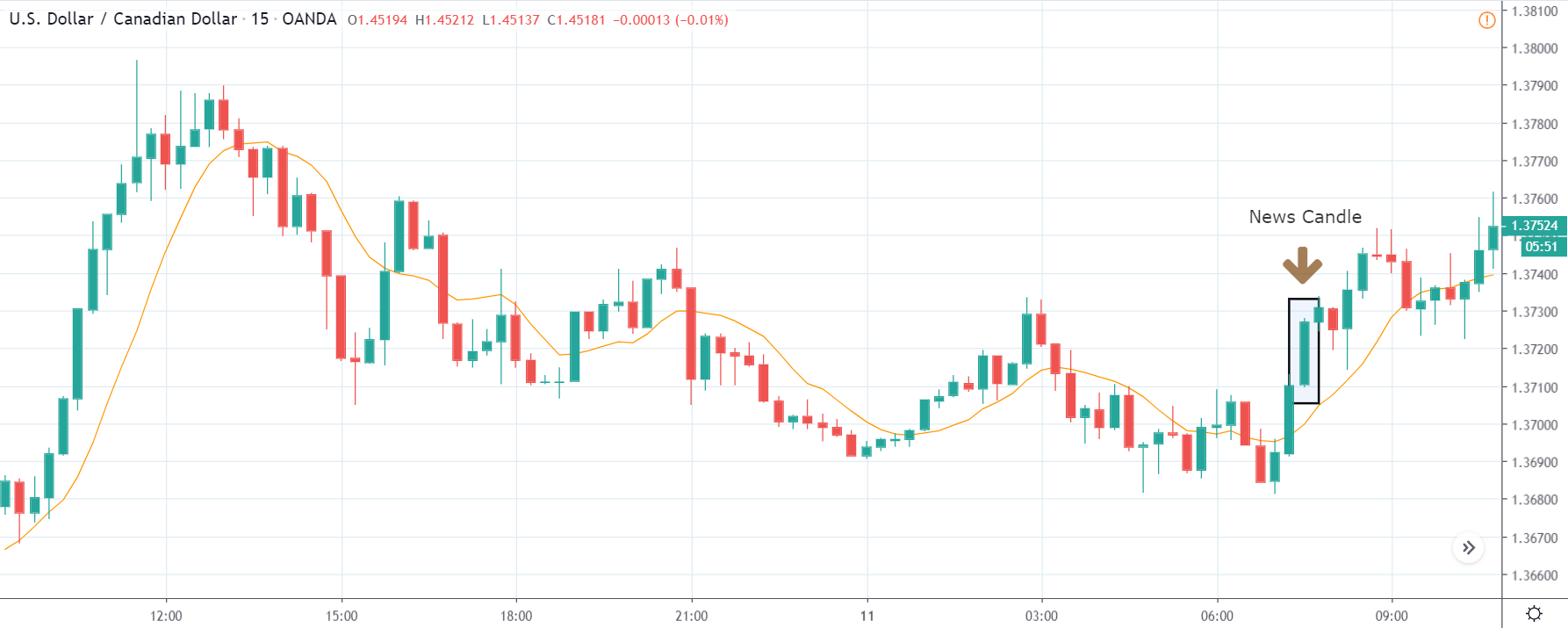
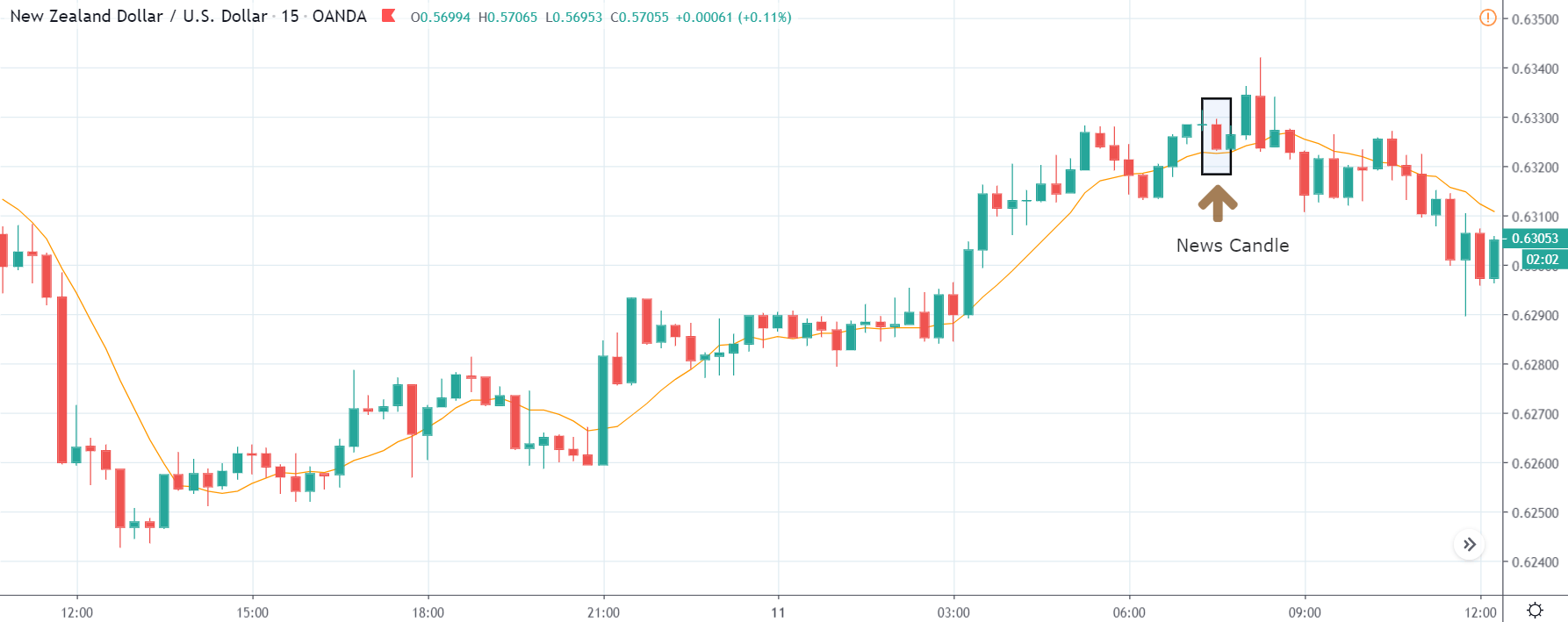
The price moves aimlessly before the news. We place a purchase order (above) and a sale order (below). Do not take into account the zones, it is just an example to see it.
Suppose we leave them as they are. They activate both and we lose the difference. Suppose now that when the first is activated we cancel the other. In this case, we also lose because we opened activated the purchase and subsequently the price falls. This doesn’t have to be like this forever, I just give you this example to you realize that what we’re dealing with isn’t as wonderful as appears in your mind.
Be careful with it. Try it, but be very careful and check results with backtesting. Logic makes us think that this can go well but then when we see the results we realize that often this is not so. These types of operations are usually displayed by brokers and platforms so that you operate when there is a lot of volatility and with a lot of money. Then they do their business, earn commissions and win when the customer loses. As a trader, you must be above these things and concentrate on your business and your operation.
Trading with Volatility and News
 It is normal that you can think after all this when you open your trading platform “what if the flute sounds? what if it does?”. We’ve all read the typical news in the newspaper where it tells you that x person won an incredible amount of money with x event. Quick and easy. Here the survival bias is very high. Don’t tell you that that could be 0.0001%
It is normal that you can think after all this when you open your trading platform “what if the flute sounds? what if it does?”. We’ve all read the typical news in the newspaper where it tells you that x person won an incredible amount of money with x event. Quick and easy. Here the survival bias is very high. Don’t tell you that that could be 0.0001%
Actually, with all this, I’m not telling you that you can’t trade when news comes in, I’m telling you to get your mind off the fact that you make a lot of money luckily. If you do not use high leverage and for example apply swing trading strategies or you have a % risk in each small trade if you diversify. this news will not affect to a greater extent.
In fact, be clear that most of the time there will be a complicated situation in the market: currency wars, economic crises, political decisions. Volatility in the market can occur when you least expect it and you should be a trader who knows how to manage this well.
Mind-Set to Trade News Trading
Many traders think that news is the axis of their ills and that all their losses are due to this or the other. It’s not like that. These are just excuses. You may also have heard something like “but if the data is good, why does the price drop?”. Simply because in the financial markets prices are driven by expectations. That is, the price at which an asset is quoted includes what is expected of that asset in the future. So that’s why when you publish a piece of information that you assume is good, some institutional investors had already taken it into account and even though it would be even better.
You have to have a micro mindset (each operation counts) and a macro mindset (what is really important in the long term and its consequences). So if you play a card with a piece of information or a piece of news, you’re sending the macro to take it for granted. Keep this in mind or you’ll learn it by taking out your wallet and burning accounts.

New Is Not the Solution (or Problem)
Why, instead of focusing on speculation or news, don’t you focus on what you have objectively? That is data-based trading systems. When investing in the long term it makes sense to read and soak up some company and industry news. But by trading, we look for short-term moves. Do you really think you can from home predict a story that is public in a market as big as the currency market?
What you could do is concentrate on creating systems that have a positive statistical advantage and apply them rigorously. If it’s the news and it works well, great. But don’t get obsessed with the idea that news is the origin of everything. Focus on what you can control.
All this being said, in my case what I do is I keep in mind the news to keep in mind the moments where the market can move aggressively. If there is a moment (very punctual) where a lot of news (very important) will be published or a weekend where there is some decision that can make the markets shake, I try to close everything and be out. But this is at very specific times, perhaps less than 1%. Most of the time I take on this volatility and adapt my systems to them.
Ignoring News In the Press
In recent months, for example, a lot of news has been published about Brexit and most of it seemed definitive. The bottom line is that a year has passed and nothing has changed. Another situation: Trump’s ongoing tweets. You can’t predict that. Face it. It’s part of the equation of trading. And it also makes it different.
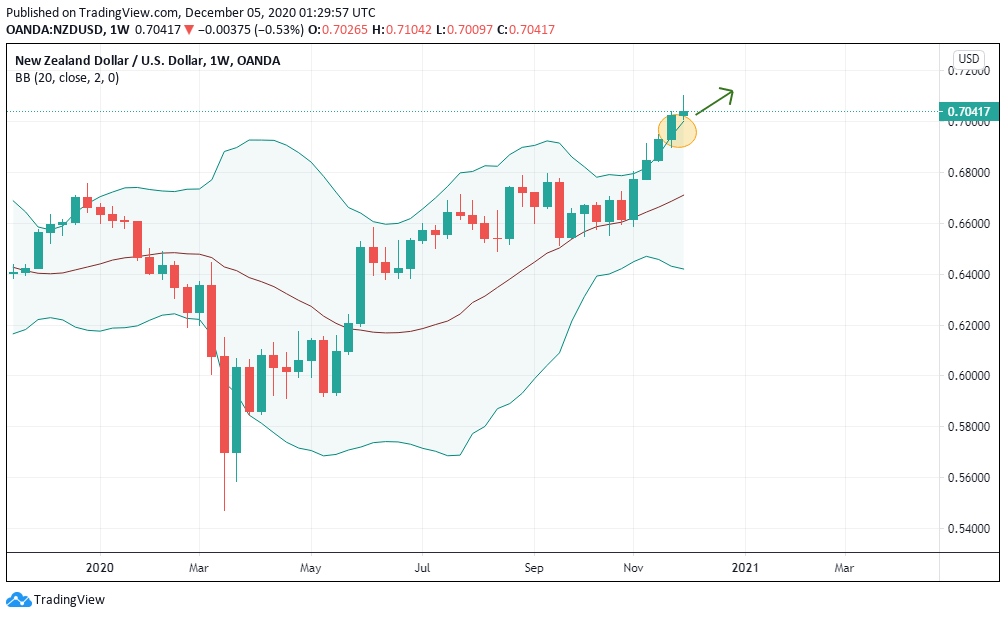
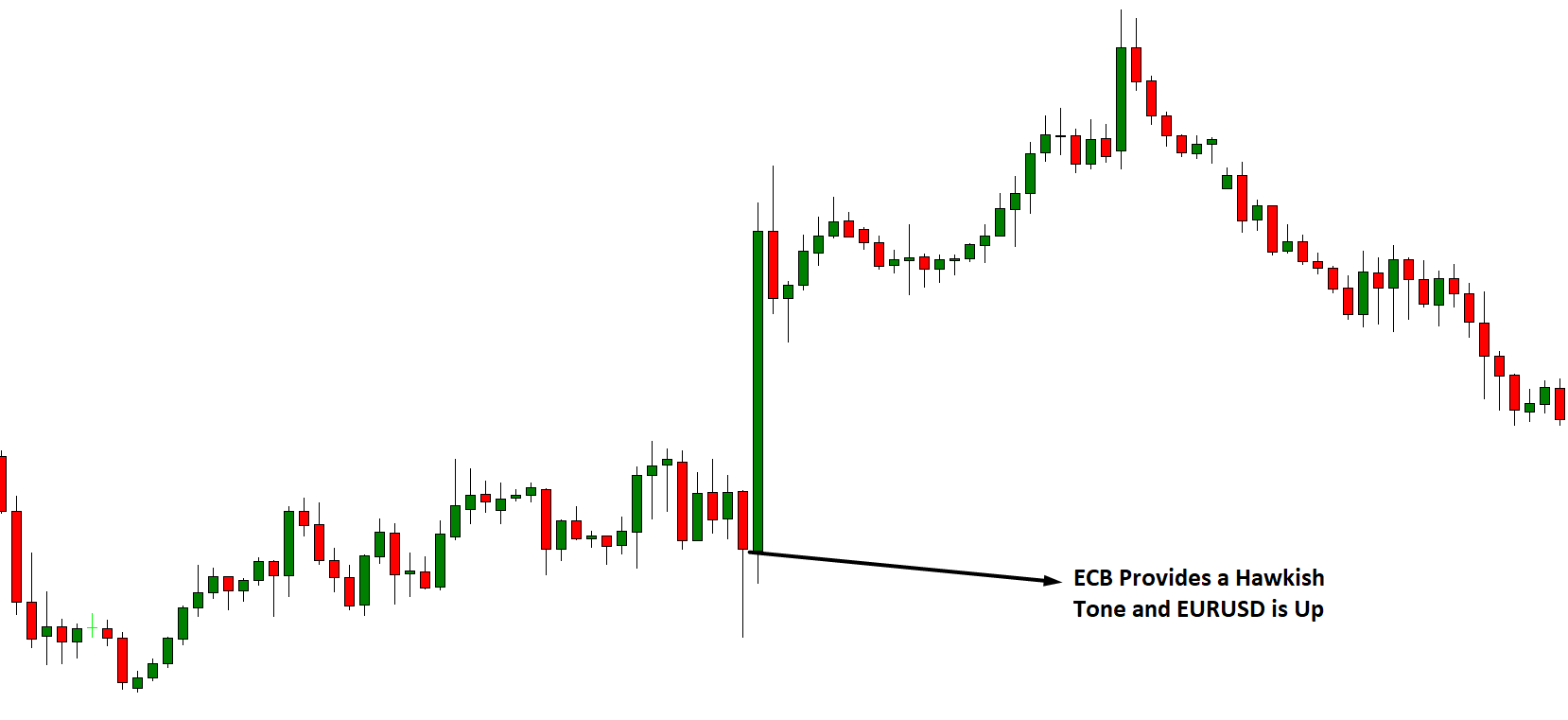
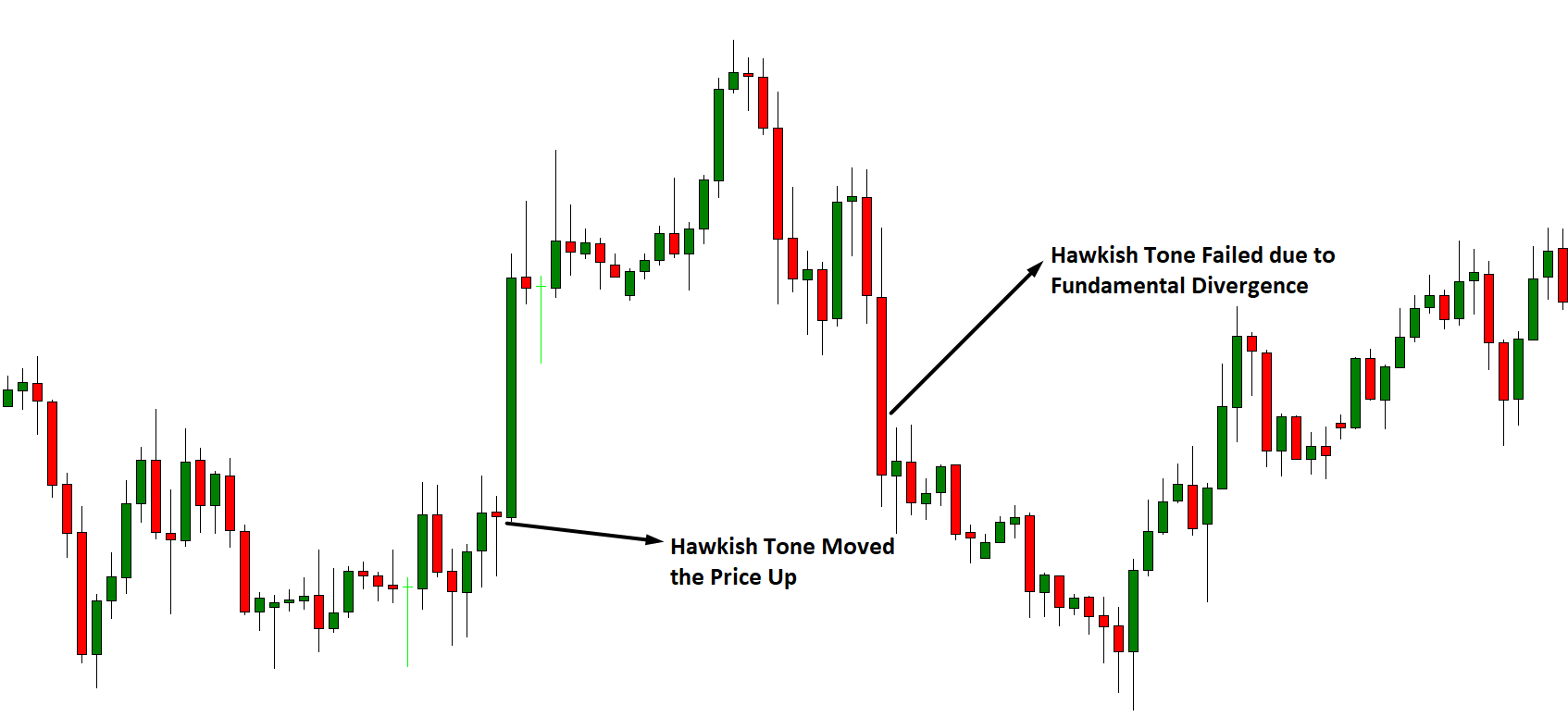
The press always has a good headline to justify what is happening. For example, after an event, the EUR/USD pair goes up. You can read or listen in some media: “The EUR/USD crossing goes up despite the measures of the European Central Bank.” However, if after that same event the pair falls you can read something like: “The EUR/USD crossing drops due to the measures of the European Central Bank.”
It’s kind of like knowing the end and creating an argument that makes sense to get to that end. We as traders are interested in the behavior in the price market, the rest is just noise that gives us little good. This is another of the big arguments why I trade through systems, they don’t get carried away by this kind of thing.