Introduction
The long-term unemployment rate is a killer of economic growth. Its impact on the individual and society as a whole cannot be ignored, particularly in emerging economies. Understanding long-term unemployment trends can help us identify increases and decreases in the dependent economic indicators and their overall impact.
What is Long Term Unemployment Rate?
Long-term unemployment
It occurs when a worker actively seeking employment is unable to find a job for 27 weeks or more. To be included in the statistic, the participant should have actively sought employment in the last four weeks. To be recorded in the statistic, the worker should have been actively seeking employment even after being unemployed for six or more months. Hence, it is probably undercounted as most people do not continuously seek employment for six straight months out of discouragement.
Hence, the long-term unemployment rate is then the percentage share of the labor force that is unemployed for six or more months, given that they have actively sought employment in the last month.
How can the Long Term UR numbers be used for analysis?
Long-term unemployment is majorly caused by cyclical and structural unemployment. Cyclical unemployment occurs due to the natural business cycles that companies go through. Most businesses have specific quarters when business is low, where they might downsize and lay off employees. Seasonal hiring and firing constitute cyclical unemployment. Cyclical unemployment also occurs during economic slowdowns and recessions.
Structural unemployment occurs when unemployed labor skills do not match the available job requirements. Unlike cyclical unemployment, it is not dependent on business cycles. Structural unemployment is more challenging to address than cyclical unemployment. It keeps the unemployment rates high long after the economy’s recovery out of recession. It occurs when business and technology shifts during the time of unemployment make unemployed labor skills outdated.
Long-term cyclical and structural unemployment has a positive feedback effect on each other making things worse. Cyclical unemployment during business slowdowns increases the unemployment rate. When they are unemployed long enough, their skills become outdated and gives rise to structural unemployment. This overall reduces consumer spending for the unemployed and indirectly affects consumer sentiment of the employed. When consumer spending drops, other industries also observe the same cyclical and structural unemployment, spiraling the economy downward.
Long-term unemployment can lead to people working in underpaid jobs or find work not relevant to their skills out of desperation. It reduces economic productivity as skilled laborers are not being utilized for what they know best. Secondly, long-term unemployment places a financial crunch that can have a demoralizing effect on happiness, mental state, and job satisfaction. It is also observed that long unemployment periods tend people to self-isolate from the community. Anti-social behavior and hooliganism are also benefited from long-term unemployment.
While the government gives out unemployment benefits, which may encourage them to hold off to find better paying and more suitable jobs to their skills, it decreases public spending. When the unemployment rates are high, public spending takes a direct hit, crippling the government from spending their revenue on activities that help economic growth. As the government keeps giving out benefits, it has led to a rise in long-term unemployment rates. While benefits are necessary to mitigate financial impact during unemployment, it also tends to increase unemployment duration, which is terrible for economic growth.
As long as long-term unemployment is prevalent, improving the living standards of people is hard to accomplish. People cannot apply for loans or buy a house on a mortgage if they frequently lose jobs and take a long time to find new jobs. Financial insecurity and strained personal finances discourage people from spending and encourage saving for another jobless quarter or two. Long-term unemployment has a severe effect on householders, with only one working individual who provides for the family.
Long-term unemployment is bad for the economy. On the flip side, 50% of the long-term unemployed find a job in six months, and 75% do within a year. Within 18 months, the remaining also does find something or the other if they keep looking.
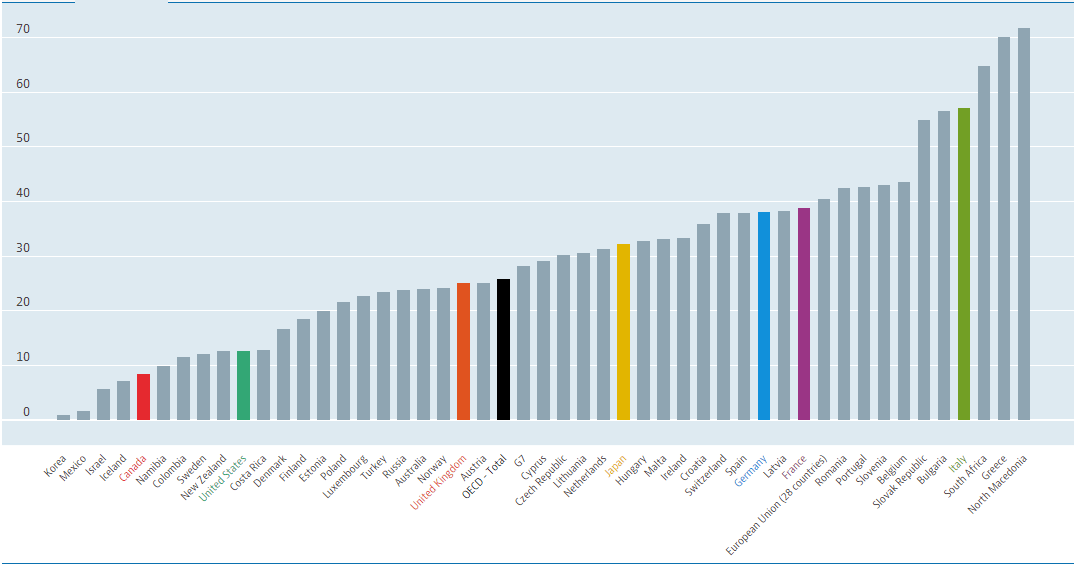
Chart Credit: OECD
Overall, it is more challenging to reduce long-term unemployment than short-term cyclical unemployment. It is a critical hindrance to achieving high growth rates for any country. The above statistic shows how it is an international issue and not any particular set of countries.
Impact on Currency
Long-term unemployment rates are not as important as unemployment rates, jobless claims, non-farm payroll numbers. As unemployment rates itself include the long and short-term ones, it is not an important economic indicator for currency markets.
Hence, it is a lagging low-impact indicator. It is an inversely proportional indicator, meaning high long-term unemployment is bad for the economy and currency.
Economic Reports
In the United States, The Bureau of Labor Statistics publishes monthly employment and unemployment reports under the Employment Situation Report. Table A-12 in it details the long-term unemployed figures. The figures are seasonally adjusted for month-over-month, and year-over-year comparisons are also provided.
Long-term unemployment reports are also maintained by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). It defines long-term unemployment if a person is unemployed for 12 or more months.
Sources of Long Term Unemployment Rate
The United States Bureau of Labor Statistics’ Long-term Unemployment data is available here. The Bureau of Labor Statistics publishes monthly employment and unemployment reports on its official website for our analysis. The OECD also maintains long-term unemployment data. Consolidated reports of long-term unemployment rates of most countries can also be found in Trading Economics.
Impact of ‘Long Term Unemployment Rate’ News Release on the Forex Price Charts
The long term unemployment refers to those persons who have been unemployed for more than 52 consecutive weeks. Very long term unemployment rate refers to those persons who have been unemployed for more than 104 consecutive weeks. This data is essential for the government and economists who analyze quarterly and yearly trends of unemployment.
It helps them in understanding the long term employment situation of the country. However, the monthly numbers are significant to the market players when it comes to the forex market. Therefore, the impact of long term unemployment is not realized immediately on the currency pair.

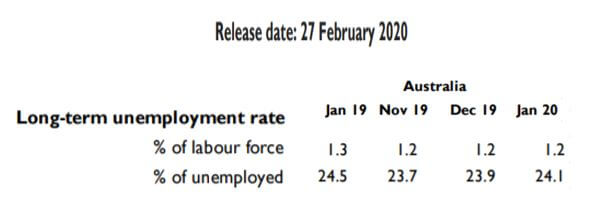
The below image shows the latest long term unemployment data of Australia that was released in February. We can see the unemployment rate was the same compared to the previous year, but there was a reduction in the percentage of the labor force. In the following sections, we will observe the change in volatility due to the news release.
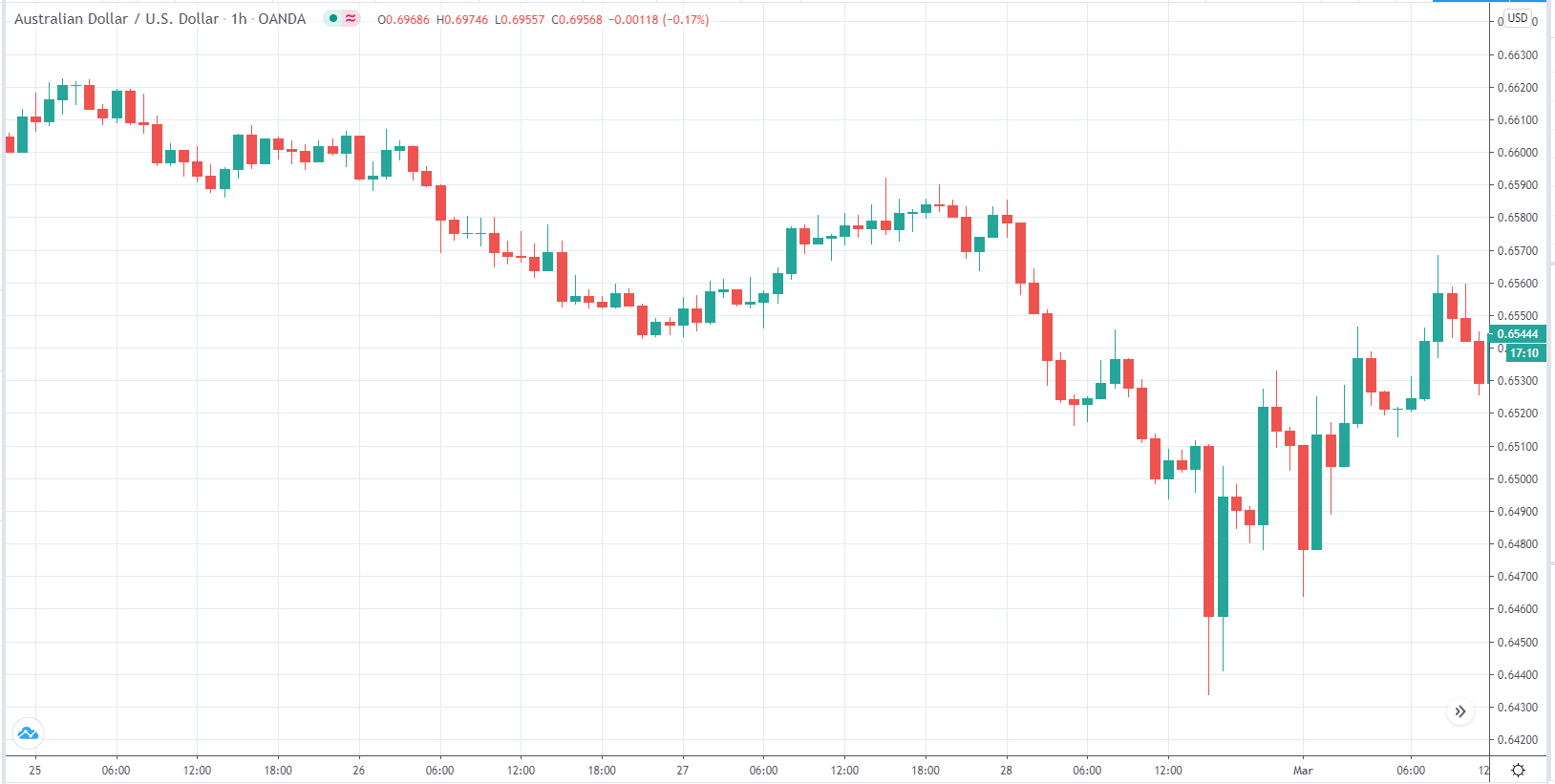
AUD/USD | Before the announcement
The above image is a 1-hour timeframe AUD/USD chart showing the moves from February 25th to March 1st, 2020. The currency has been slowly moving down and picks up a little momentum in its drop-down after February 28th.
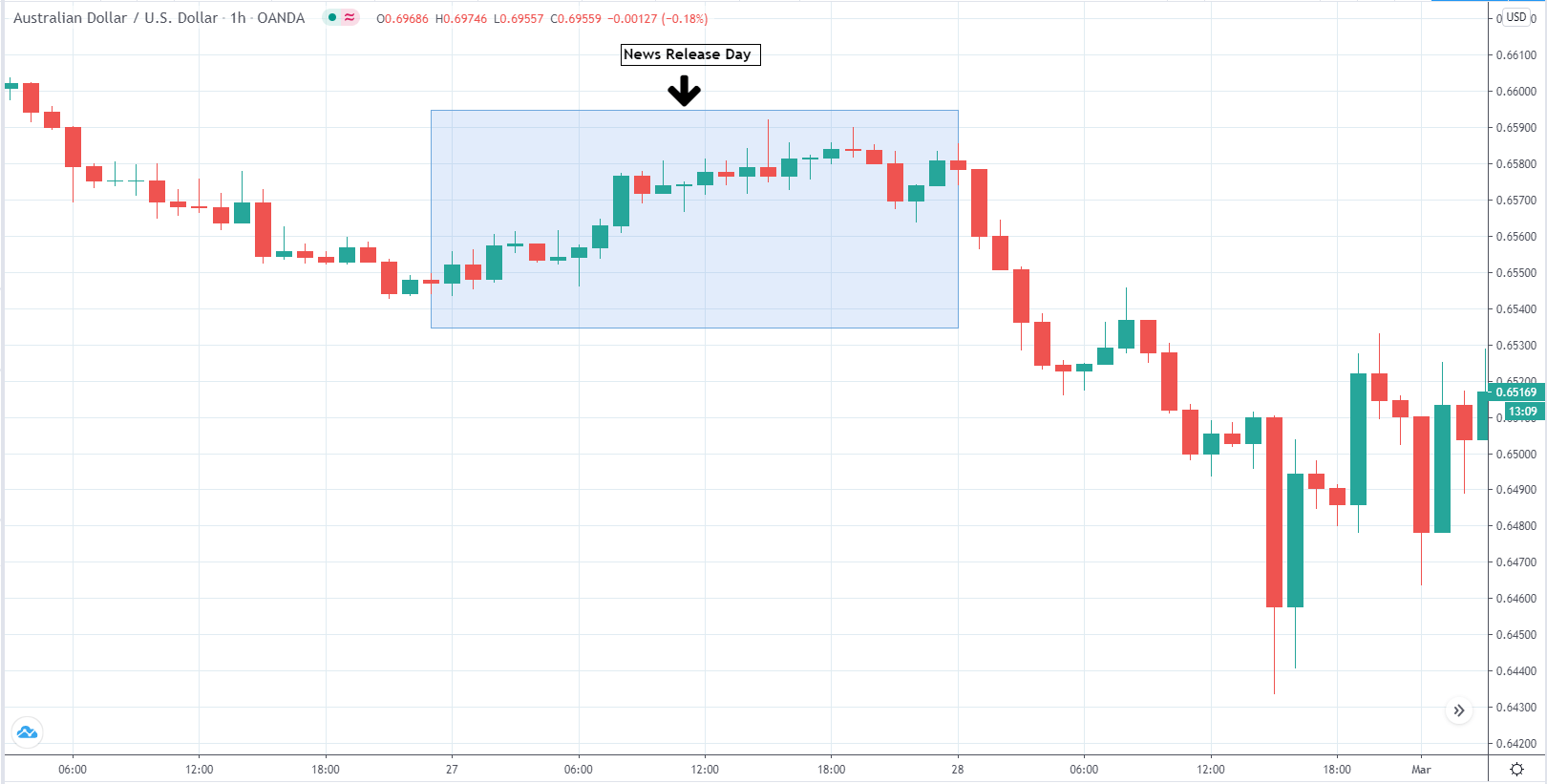
AUD/USD | After the announcement
The above image is a snapshot of AUD/USD on the day of long-term unemployment rates in Australia news announcement on February 27th, 2020. The report published by the treasury department of Australia showed lower unemployment rates than the previous year. The favorable figures for AUD did not reflect in the pair’s non-volatility.
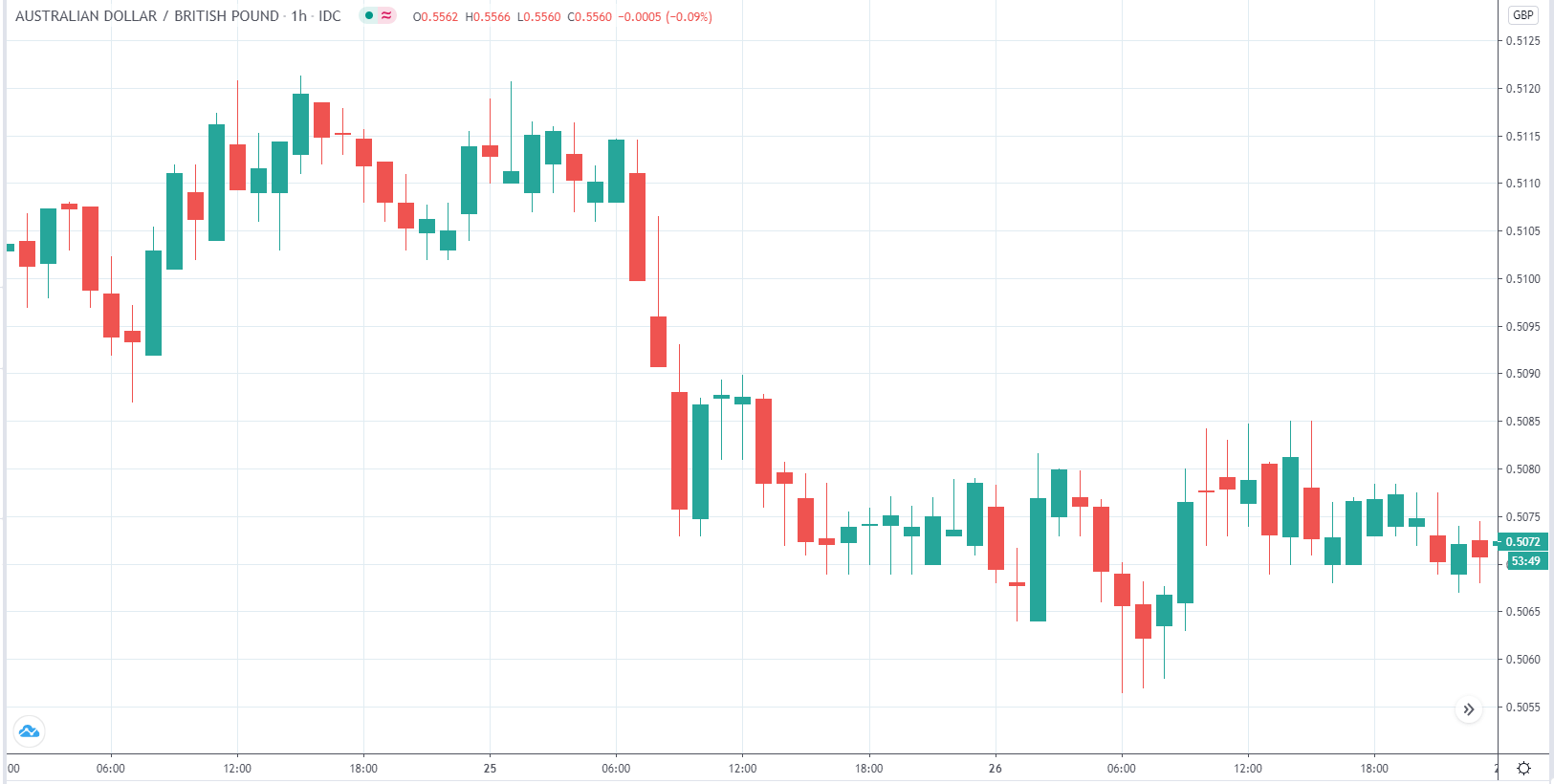
AUD/GBP | Before the announcement
The above image is a 1-hour timeframe AUD/GBP chart showing the moves from 25th to February 26th. The currency has not shown any clear down or uptrends till now.
AUD/GBP | After the announcement
The above image highlights the currency pair move throughout the news announcement day. We can see that there was only about a 40-pip maximum move, which is minimal movement and typical for such a pair. The news did not build any rallying up for AUD against GBP.
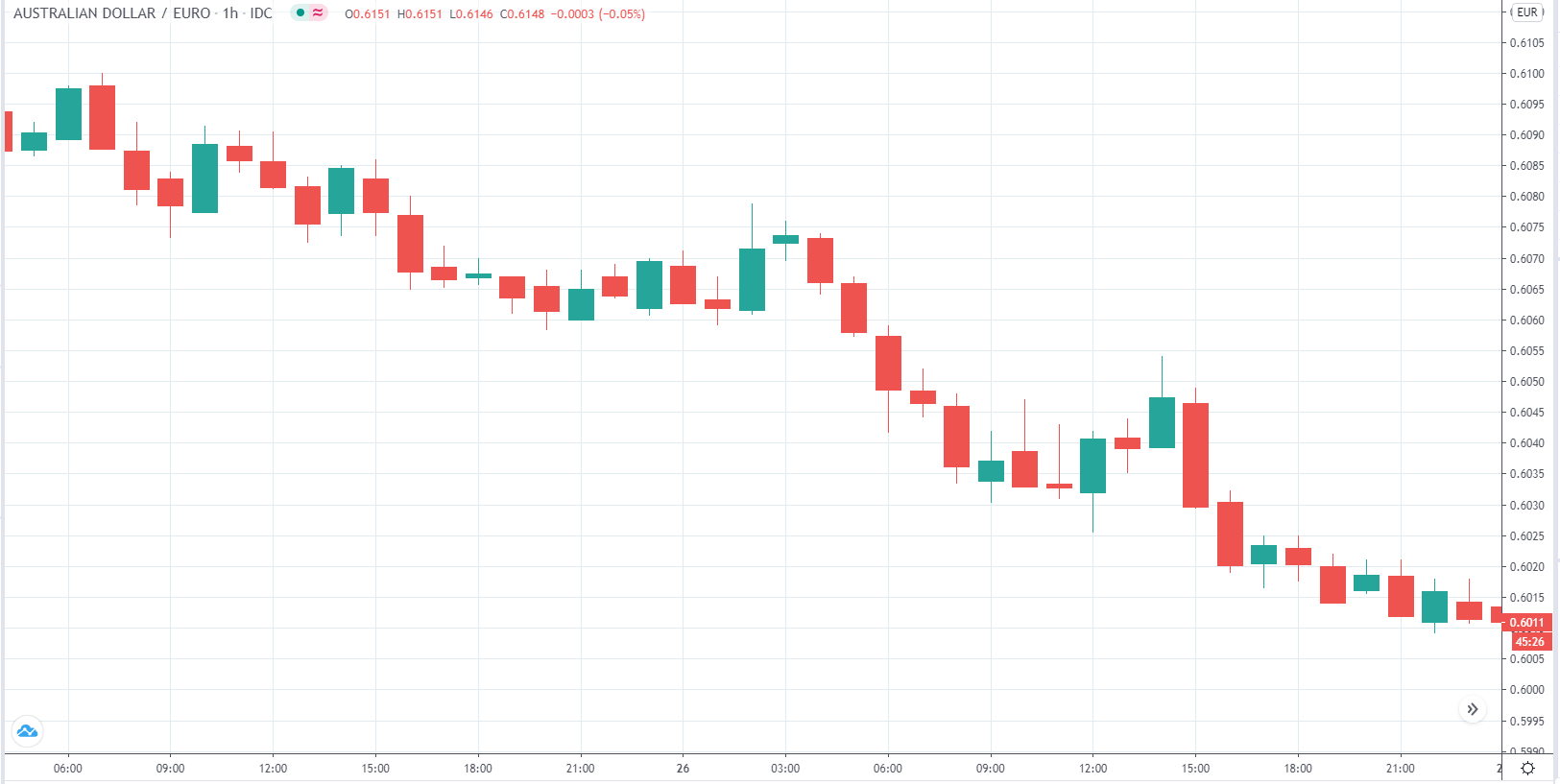
AUD/EUR | Before the announcement
The above image is a 1-hour timeframe AUD/EUR chart before February 27th, 2020. As we can see, AUD has been losing its value slowly against EUR in the last two days.
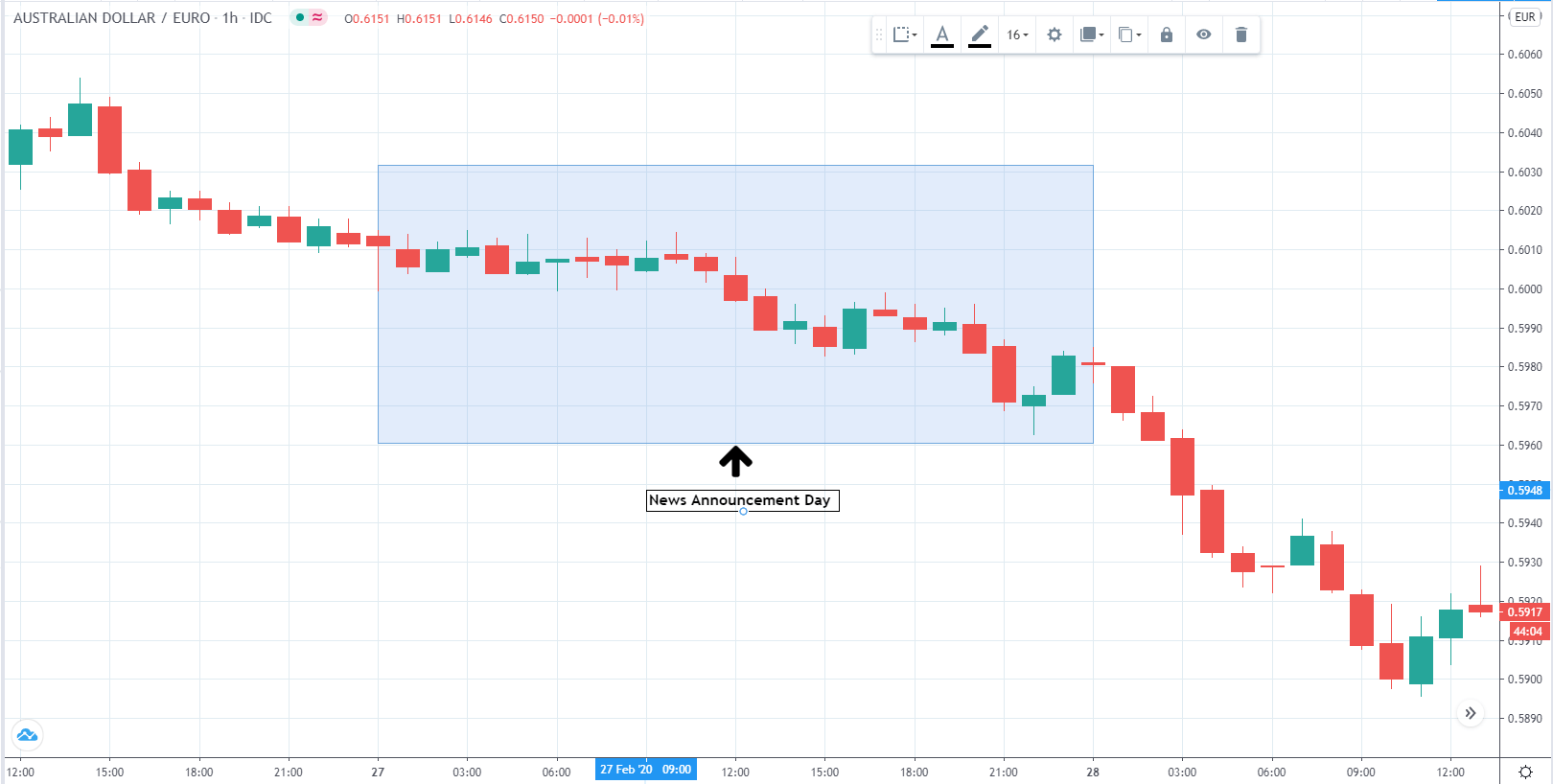
AUD/EUR | After the announcement
The above image highlights the news announcement day. We can see that despite the long-term unemployment rates came in favor of AUD, the market ignored and continued selling AUD and purchased EUR. The downward trend before continued during and after the news announcement day without any effect.
In conclusion, as we have seen, the long-term unemployment economic indicator was almost entirely ignored by the market. The market knows it is a lagging indicator, and the effects have already been priced into the market, therefore showing no volatility during the news announcement. Hence, the above trend analysis confirms our fundamental analysis of the economic indicator as a low impact lagging indicator that is overlooked by the currency market.