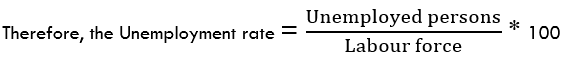Introduction
In this analysis, we’ll focus on endogenous economic growth factors in the EUR and the US. We’ll also analyze the exogenous factors that will help us compare the economic performance in both regions.
Endogenous economic factors are inherent within the domestic economy and are primarily driven by domestic demand. On the other hand, exogenous factors are external economic factors that result from a country’s participation in the international markets. Both of these factors influence the fluctuation of the currencies from both countries.
Ranking Scale
We will rank both the endogenous and the exogenous economic factors on a scale of -10 to +10. A negative ranking shows that the economic factor had a deflationary impact on the currency. Conversely, a positive ranking implies that it had an inflationary impact.

USD Endogenous Analysis – Summary
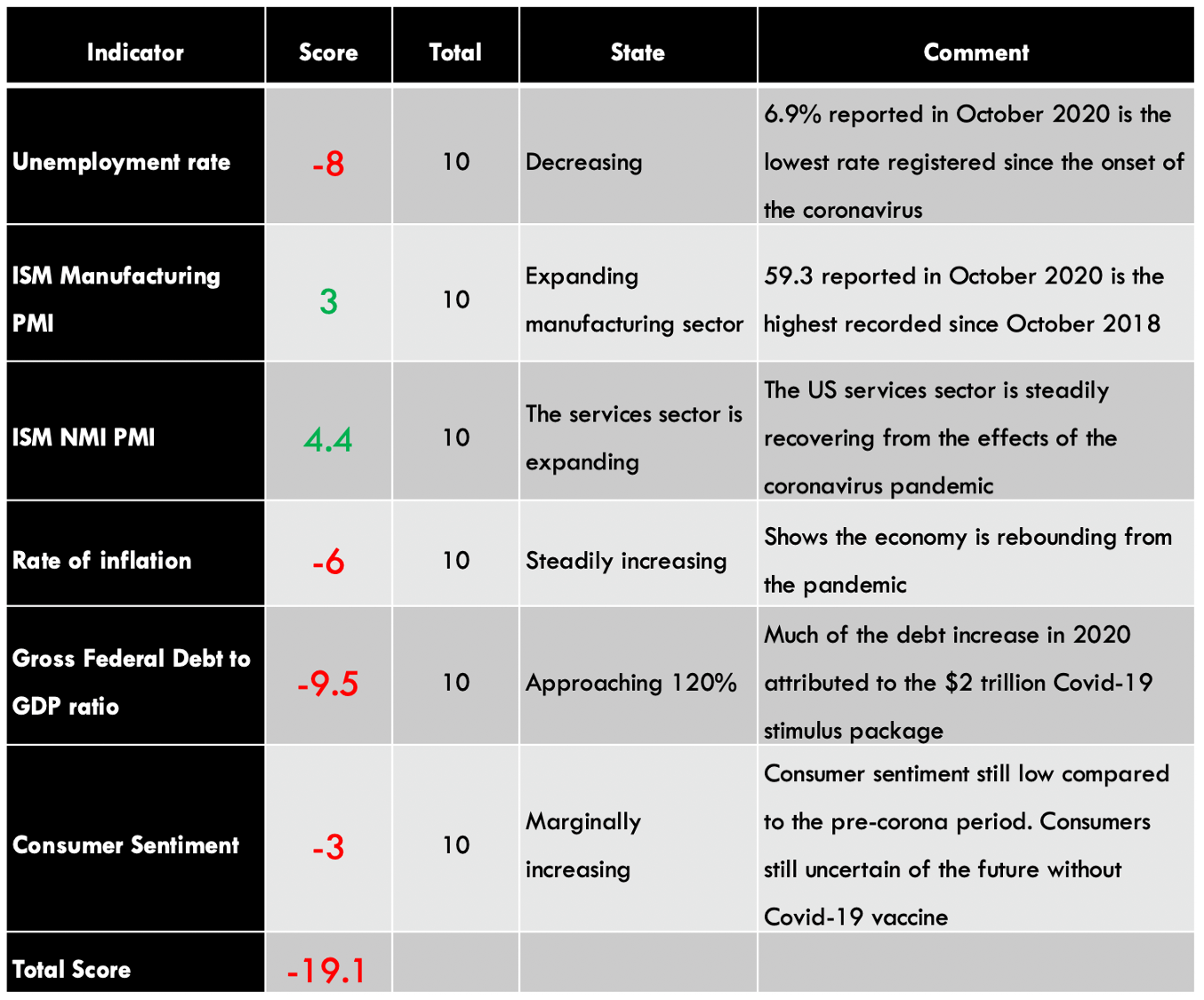
The USD endogenous factors recorded a score of -19.1, implying a deflationary effect on the USD. This essentially means that according to these indicators, the USD has lost its value since the beginning of this year.
You can find the complete USD Endogenous Analysis here.
EUR Endogenous Analysis – Summary
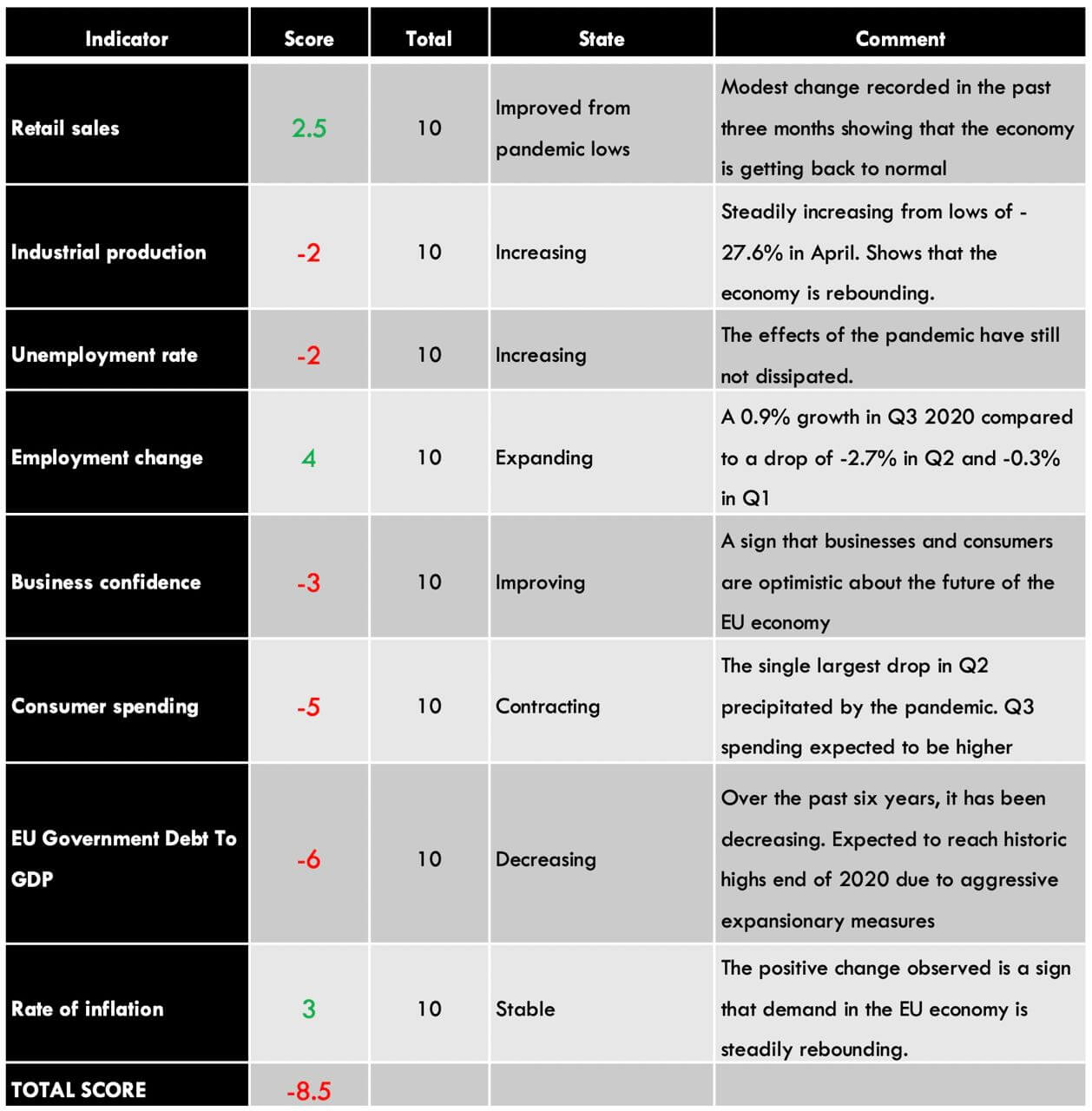
The endogenous analysis of the EU economy shows a modest deflationary score of -8.5. This means that in 2020, the Euro has shed some of its inherent value.
The endogenous economic indicators in the Eurozone are an aggregate of the 27 member countries in the EU.
- Monthly retail sales
It measures the inflation-adjusted value of retail sales. About 40.1% of all retail sales in the EU are from food, drinks, and tobacco. Electronics and furniture account for 11.5%, while computer equipment accounts for11.4%. 9.2% of the retail sales are attributed to clothing and footwear, while pharmaceutical and medical products account for 8.9%.
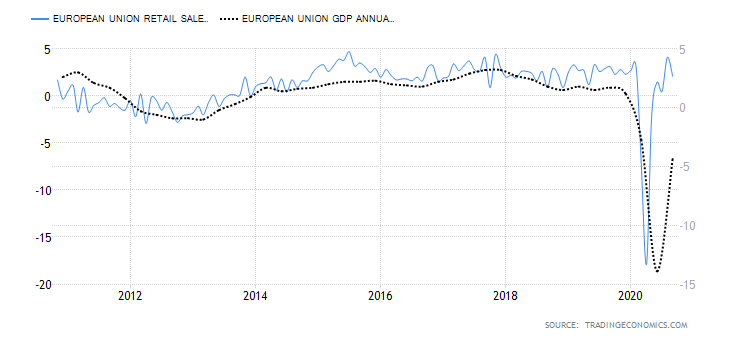
In September 2020, retail sales in the EU dropped by 2%. Given that retail sales account for about 70% of the GDP, our correlation analysis, we assign the EU retail sales an inflationary score of 2.5.
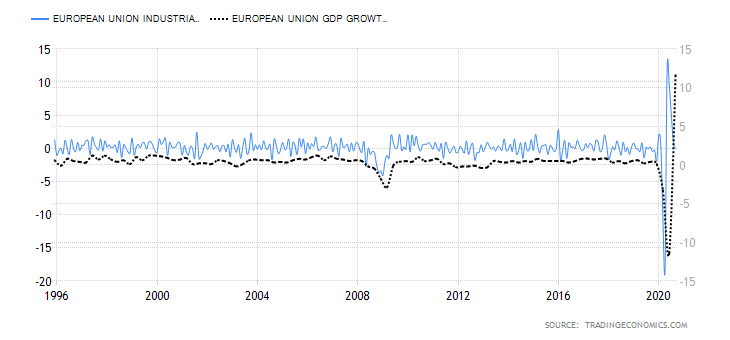
- Industrial production
This indicator measures the total output by manufacturers, mines, and utility industries in the EU. The value is adjusted for inflation. Note that the industrial sector in the EU is among the top employers.
In September 2020, industrial production dropped by 0.4%, which is an improvement from the drop of 17.1% recorded in April. However, the change in industrial production has been steadily falling from a peak of 12.4% in May.
Based on our correlation analysis, we assign the EU change in monthly industrial production a deflationary score of -2.
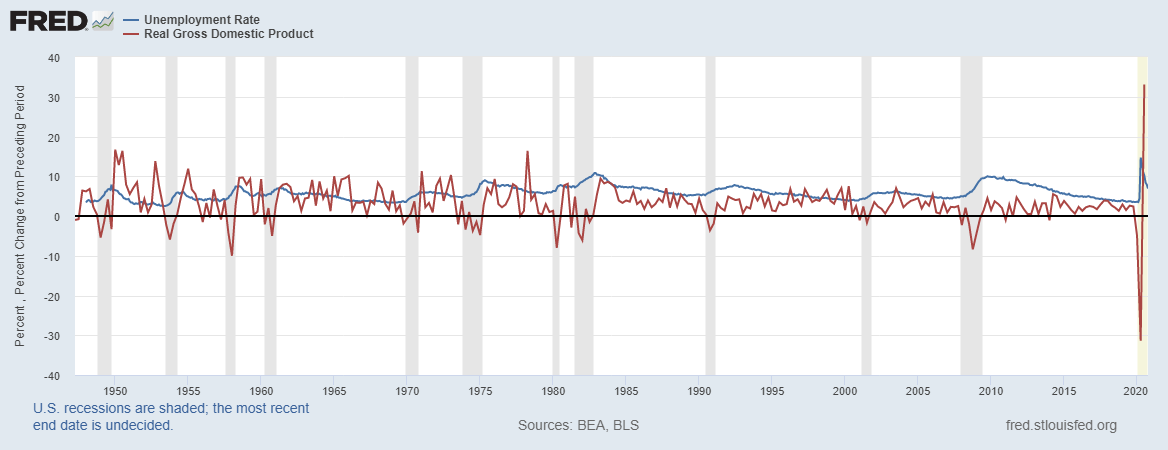
- Unemployment rate
This indicator shows the percentage of the total workforce in the EU who are seeking gainful employment. The data shows the monthly change.
In September 2020, the unemployment rate in the EU was 8.3%. Throughout the year, the EU has experienced a steady increase in the unemployment rate. This is due to the economic effects of the coronavirus pandemic. However, our correlation analysis shows the minimal impact of the unemployment rate on the EU GDP. Therefore, we assign it a deflationary score of -2.
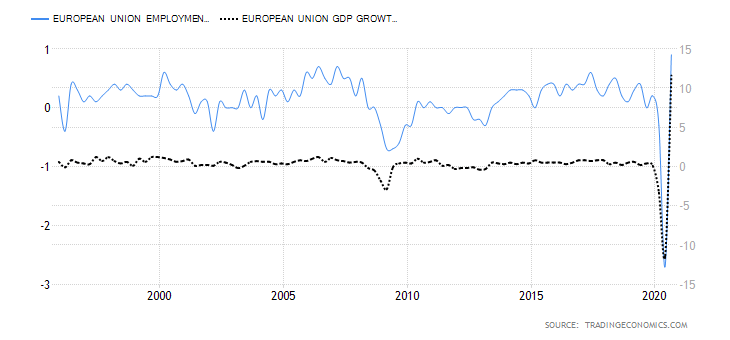
- Employment change
As an economic indicator, employment change shows the quarterly change in the number of EU citizens who are gainfully employed. This indicator can also be used to show the ability of the economy to create more jobs. It measures both full-time and part-time employment.
In the third quarter of 2020, the EU employment change increased by 0.9%, showing that the EU economy is recovering from the slump of Q2 2020. Our analysis shows a higher correlation of the employment change with the changes in GDP. Hence, we assign it an inflationary score of 4.
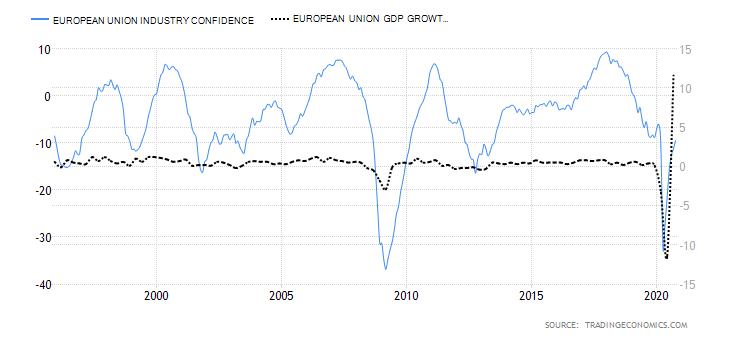
- Business confidence
The business sentiment is also referred to as the Industry Sentiment. It measures the economic sentiment among manufacturers, consumers, and employers in the EU by rating the current and future economic conditions.
The lowest business confidence recorded in 2020 was -32.3 in April 2020. Since then, the indicator has been steadily improving to -9.5 in October. Based on the correlation analysis with the EU GDP, we assign business confidence a deflationary score of -3.
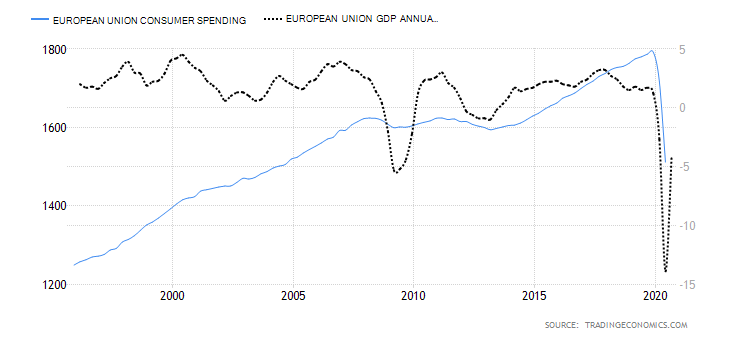
- Consumer Spending
Consumer spending measures the quarterly amount that households spend on goods and services for personal consumption. As an economic indicator, it can be used to show households’ welfare and the prevailing economic conditions. Since consumer expenditure accounts for about 70% of the EU GDP, any changes in the quarterly expenditure are bound to impact the GDP levels directly.
In Q2 of 2020, consumer spending dropped to € 1511.14 billion from € 1716.59 billion in Q1 of 2020. It is the largest drop ever recorded in history and can be attributed to the pandemic-induced economic recession.
Due to its high correlation to the change in GDP, we assign consumer spending a deflationary score of -5.
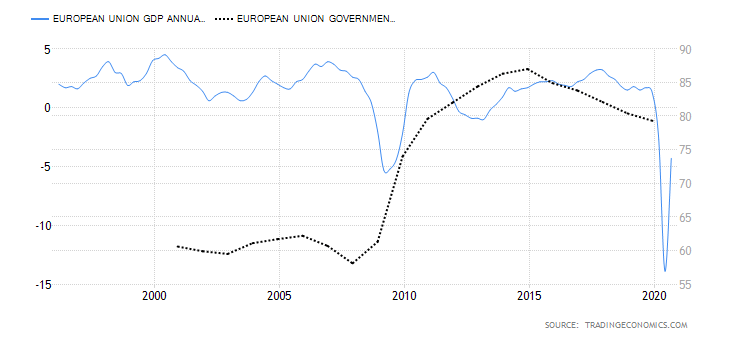
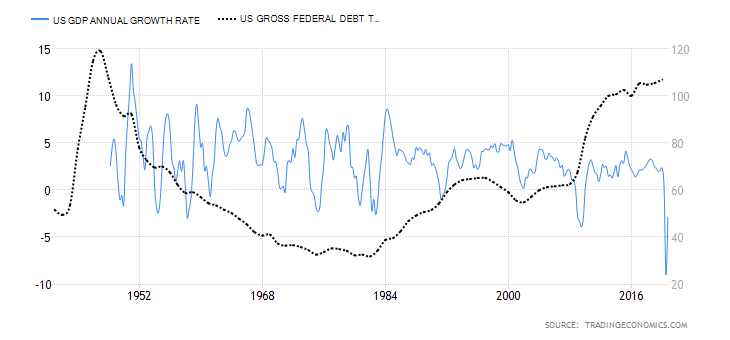
- European Union Government Debt To GDP
This ratio compares what the EU economy produces and what it owes. It shows the efficiency of the economic process and the capability of the government to service its debts without overstretching the available resources. Investors can use this ratio to gauge whether the debt in an economy is becoming unsustainable.
Increasing levels of government debt and a stagnating GDP results in a deflationary effect for the domestic currency.
By the end of 2020, the EU government debt to GDP is expected to reach 95% from 79.3% recorded in 2019. The higher government debt to GDP in 2020 is a direct result of the aggressive measures out in place to curb deep recessions from the coronavirus pandemic.
Based on our correlation analysis, we assign a deflationary score of -6 to the EU government debt to GDP.
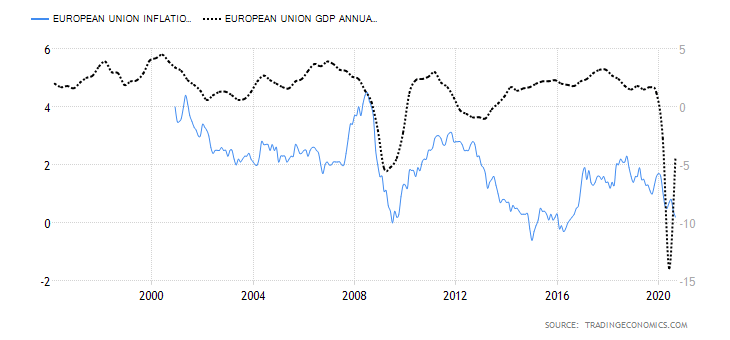
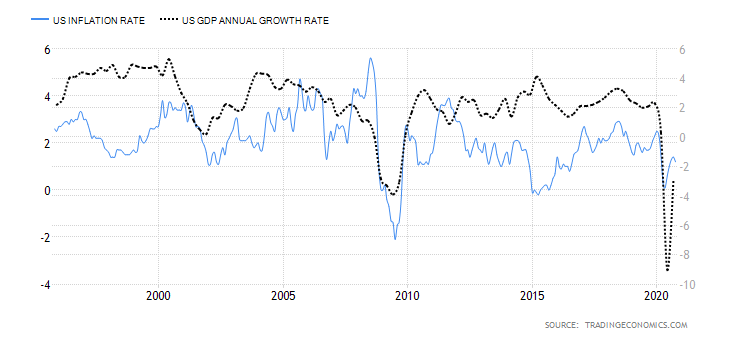
- EU Rate of inflation
In the EU, the inflation rate is best measured using the consumer price index (CPI). It measures the overall monthly change in the prices of consumer goods and services. The rate of inflation can be used as gauge the purchasing trends among households.
In theory, a rise in inflation implies that consumers’ demand for goods and services is increasing. Conversely, a drop in inflation implies that demand is shrinking hence corresponding to lower GDP levels.
In September 2020, the rate of inflation in the EU decreased by 0.2%. It is, however, an improvement from the -0.4% recorded in July and August. Based on its correlation with GDP, we assign the EU rate of inflation a score of 3.
In the next article, we have posted the Exogenous Analysis of the EUR/USD pair to have a clear idea of whether this pair is bullish or bearish market conditions.