Introduction
In conducting the global macro analysis of the EUR/CHF pair, we’ll focus on endogenous economic factors that contribute to the growth of GDP in the EU and Switzerland. Exogenous factors that influence the exchange rate of the EUR/CHF in the forex market will also be analysed.
Ranking Scale
A sliding scale of -10 to +10 will be used to rank the impact of endogenous and exogenous factors.
The ranking of the endogenous factors will be based on their correlation analysis with the GDP growth rate. A negative score implies that they resulted in the contraction of the economy hence depreciating the domestic currency. A positive score implies that they led in economic expansion hence appreciation of the domestic currency.
The exogenous factors are ranked based on their correlation with the EUR/CHF exchange rate. A positive score means that the pair lead to an increase in the exchange rate, while a negative ranking means that the exchange rate has decreased.
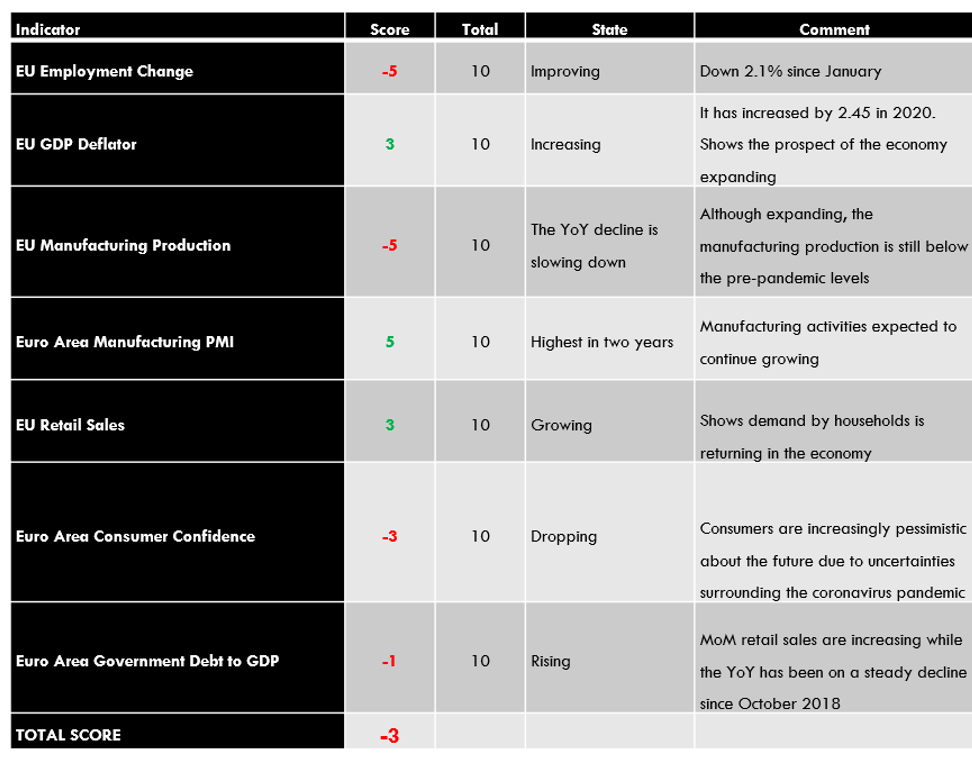
EUR Endogenous Analysis – Summary
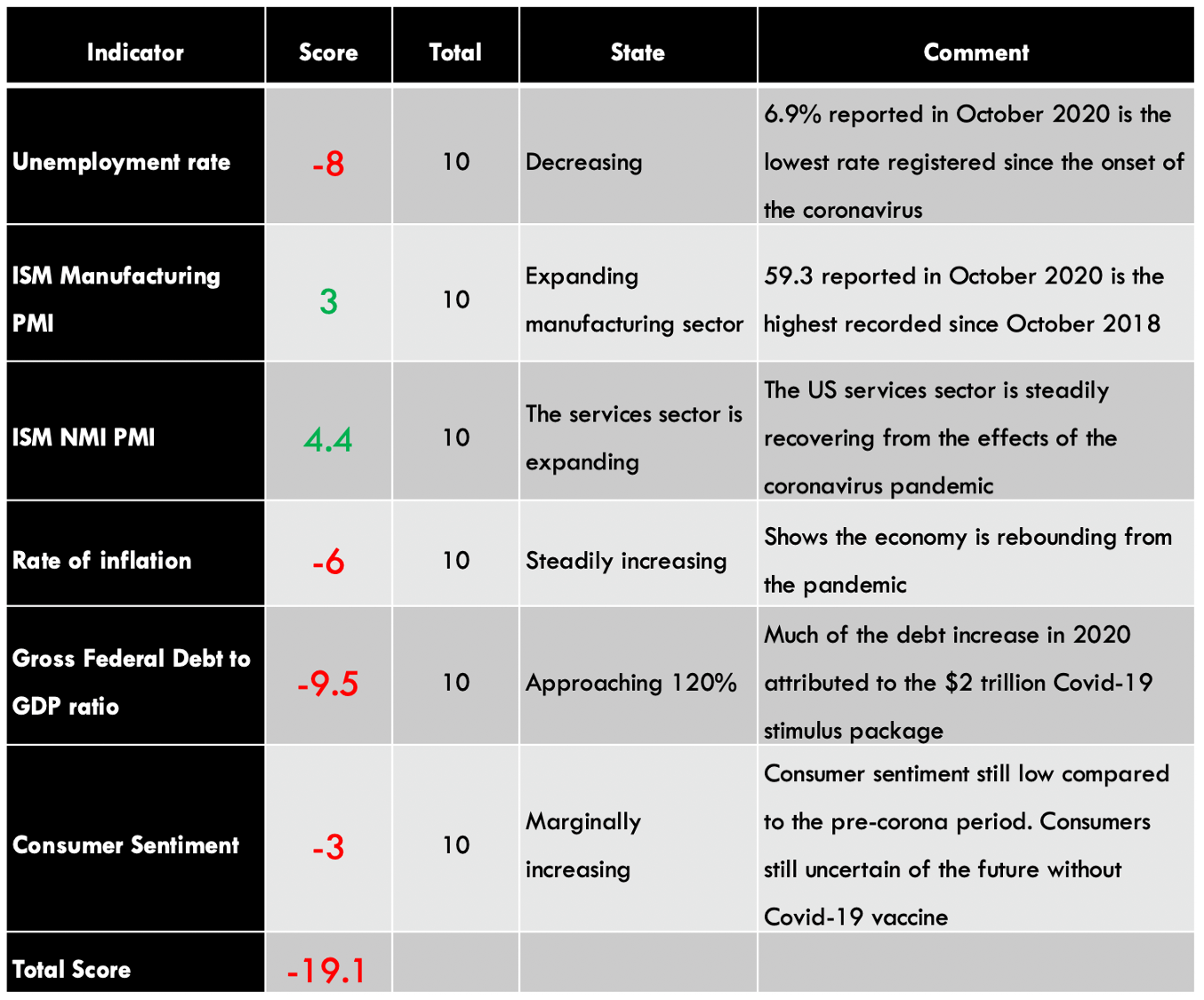
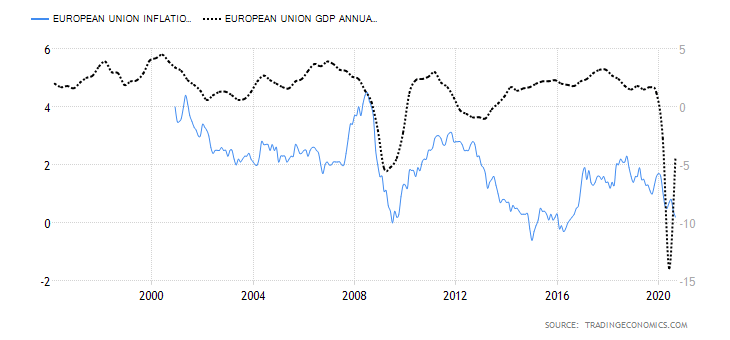
The EUR’s endogenous analysis has a score of -3. This implies that the Euro had marginally depreciated in 2020.
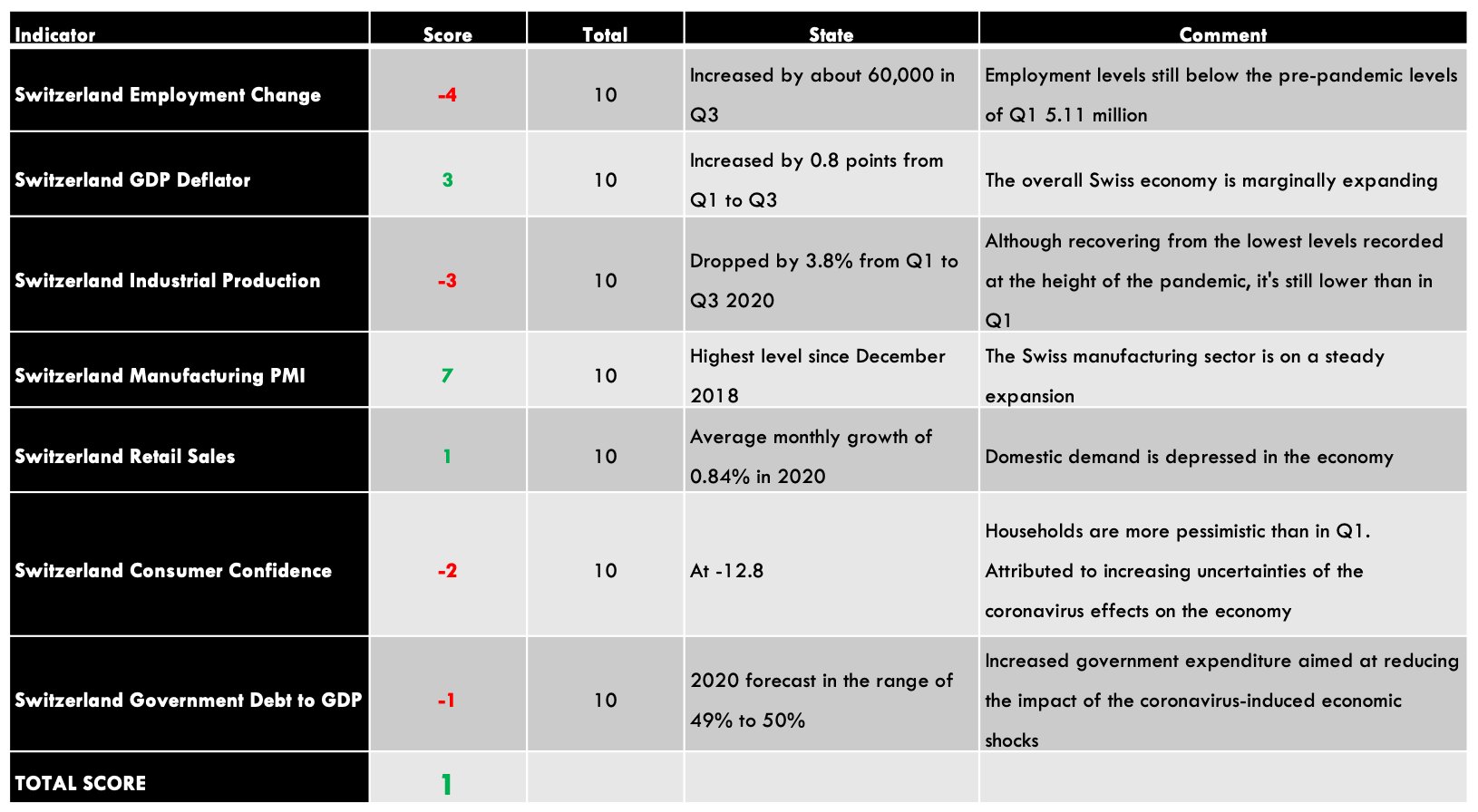
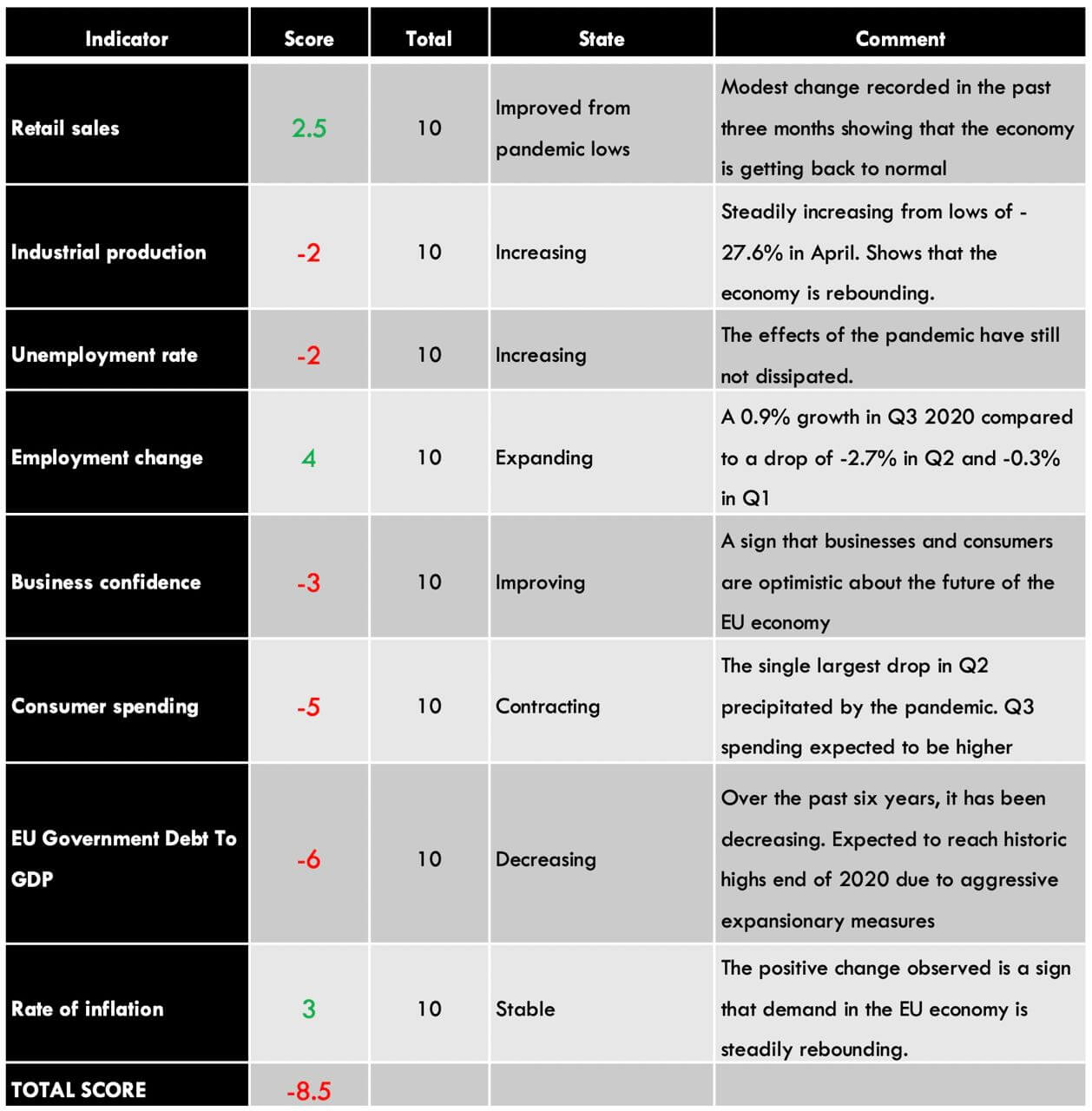
CHF Endogenous Analysis – Summary
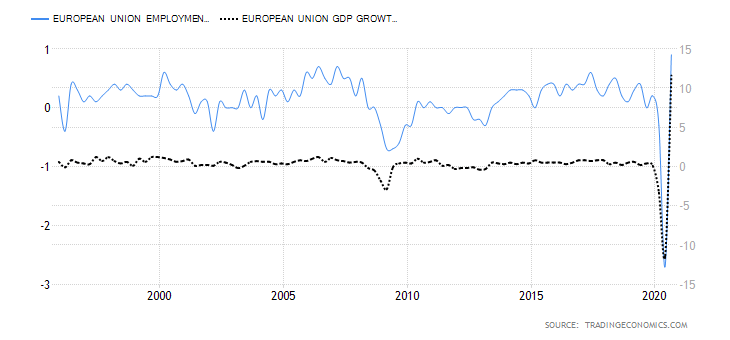
- Switzerland Employment Change
The change in the level of employment covers the quarterly developments in the labour market in Switzerland. The statistic includes the changes in both fulltime and parttime employment. Typically, changes in employment is a result of changes in business activities.
In Q3 of 2020, 5.08 million people were employed in Switzerland compared to 5.02 million in Q2. The employment level is still below the 5.11 million registered in Q1. We assign a score of -4.
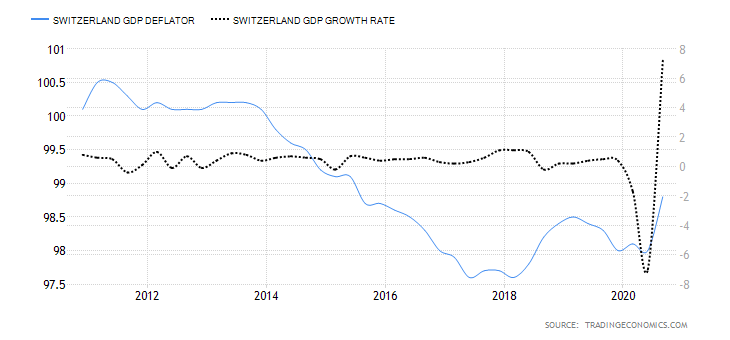
- Switzerland GDP Deflator
Switzerland GDP deflator is used to calculate the change in real GDP in terms of prices of all goods and services produced within the country. This is a comprehensive measure of inflation compared to measures like CPI and PPI, which only focus on a small portion of the economy.
In Q3 2020, Switzerland GDP deflator rose to 98.8 from 98 in Q2. Up to Q3, the GDP deflator has increased by 0.8 points. The increase in inflation can be taken as an indicator that the economy is bouncing back from the economic shocks of the coronavirus pandemic. We assign a score of 3.
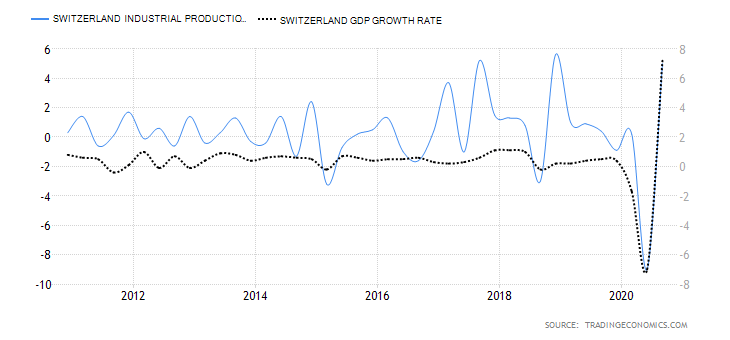
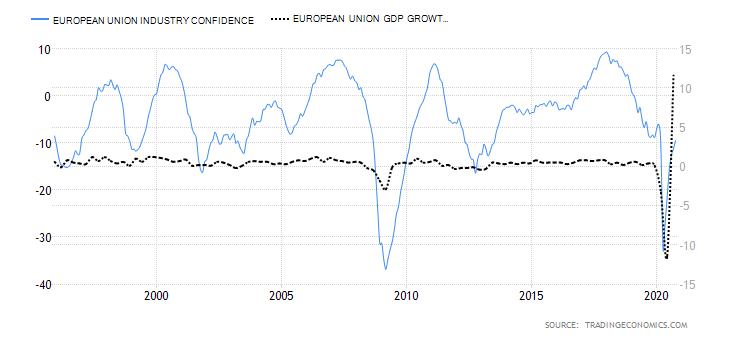
- Switzerland Industrial Production
This indicator shows the changes in output for firms operating in the manufacturing, mining, quarrying, and electricity production. Although Switzerland is not heavily dependent on industrial production, it is still an integral part of the economy.
In Q3 2020, the industrial production in Switzerland increased by 5% from a drop of 9% in Q2. The YoY industrial production for Q3 was down 5.1%. For the first three quarters of 2020, the industrial production is down 3.8%. We assign a score of -3.
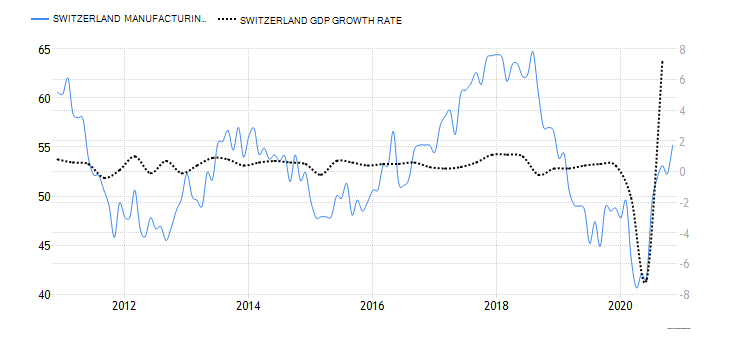
- Switzerland Manufacturing PMI
This is an indicator of the economic health of the Swiss manufacturing sector. The purchasing managers are surveyed based in a questionnaire which covers the output in the sector, suppliers’ deliveries, inventories, new orders, prices, and employment. A PMI of above 50 shows that the Swiss manufacturing sector is expanding, while below 50 shows that the sector is contracting.
In November 2020, Switzerland manufacturing PMI rose to 55.2 from 52.3 in October. This is the highest reading since December 2018 and the fourth consecutive month of expansion since July. We assign a score of 7.
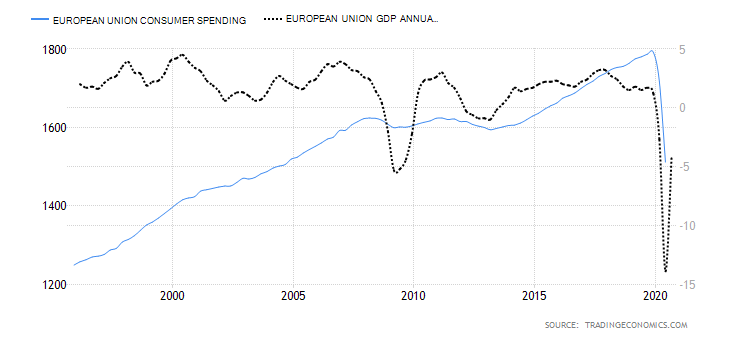
- Switzerland Retail Sales
The retail sales measure the consumption of final goods and services by households in Switzerland. The expenditure by households drives the aggregate demand in the economy, which results in the changes in GDP.
In October 2020, Switzerland retail sales increased by 3.2% from a drop of 3.2% in September. YoY retail sales increased by 3.1% in October from 0.4% in September. Up to October 2020, the average retail sales has increased by 0.84%. We assign a score of 1.
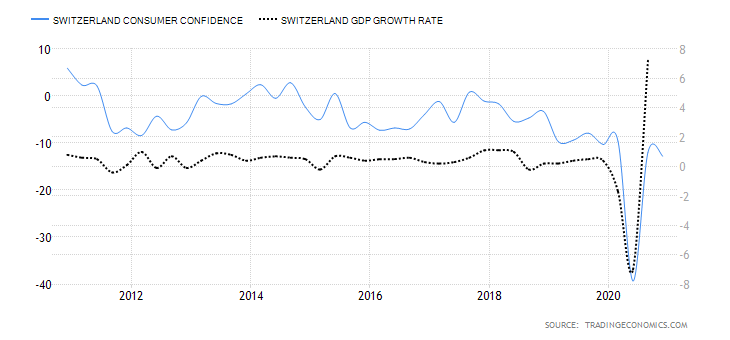
- Switzerland Consumer Confidence
About 1000 Swiss households are surveyed in January, April, July and October. They are evaluated based on their opinions about the economy, job security, financial status, inflation, and purchases. Consumer confidence tends to be higher when the economy is expanding and low during recessions.
In Q4 2020, the Swiss consumer confidence dropped to -12.8 from 12 in Q3. Although it is higher than it was in Q2 at the height of the pandemic, it is still lower than in Q1. The expectations on households’ financial situation also dropped to -6.6 from -4.2 in Q2. Households were increasingly pessimistic about the labour market and their job security. this can be attributed to the uncertainties that surround the ongoing coronavirus pandemic. We assign a score of -2.
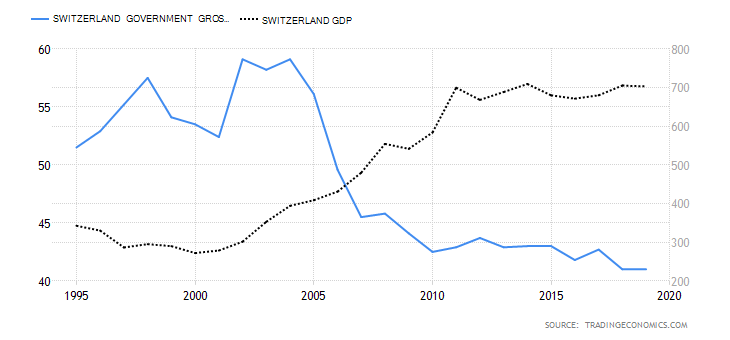
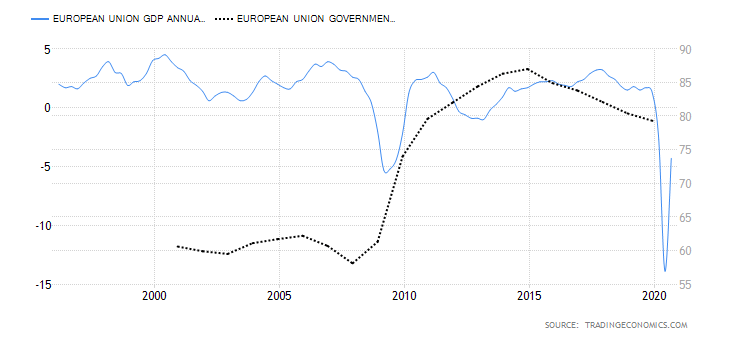
- Switzerland Government Gross Debt to GDP
This is the total amount that the Swiss government owes to both domestic and international lenders is expressed as a percentage of the GDP. It helps us to understand and evaluate the size of the debt relative to the size of the economy. At below 60%, the government is seen as being able to service its debt obligations and have room to acquire more debt without straining the economy.
In 2019, the Switzerland government gross debt to GDP was 41% same as in 2018. In 2020, it is expected to range between 49% and 51% due to aggressive expenditure to alleviate the shocks of coronavirus pandemic. We assign a score of -1.
In the very next article, you can find the exogenous analysis of the EUR/CHF Forex pair. Please check that and let us know if you have any questions below. Cheers.