Introduction
USD/CHF is the abbreviation for the US dollar and the Swiss franc. This pair is a major currency pair. USD is the base currency, while CHF is the quote currency. The pair as a whole tells how many units of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. Trading USDCHF is as good as saying, trading the ‘Swissie.’
Understanding USD/CHF
The exchange value of USDCHF represents the number of Swiss francs required to buy one US dollar. For example, if the value of USDCHF is 0.9820, to purchase one USD, the trader must pay 0.9820 Swiss francs.
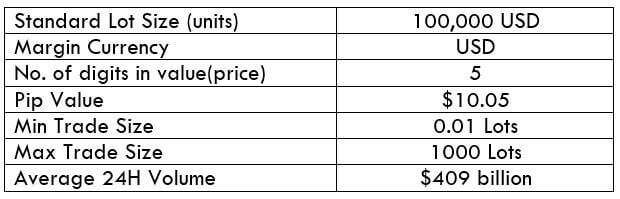
USD/CHF Specification
Spread
Spread in trading is the difference between the bid price and the ask price offered by the broker. It is measured in terms of pips and varies on the type of account and type of broker.
Spread on ECN: 0.8
Spread on STP: 1.6
Fees
There is a small fee or commission charged by the broker for every trade a trader takes. This depends on both types of accounts and broker. For our analysis, we have kept the fee fixed at one pip.
Slippage
Due to volatility in the market, a trader does not usually get the price that he demanded. The actual price differs from the demanded price. This difference is referred to as slippage. For example, if a trader executes a trade at 0.9890, the real price received would be 0.9892. This difference of two pips is known as slippage.
Trading Range in USD/CHF
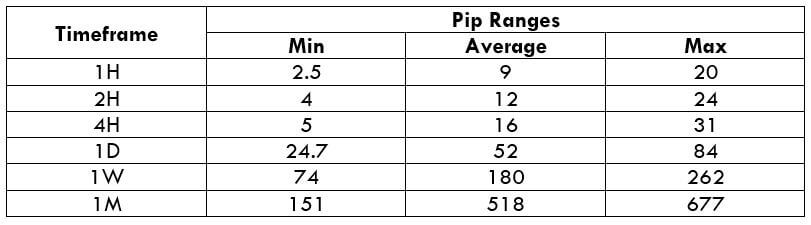
The trading range is a tabular representation of the minimum, average, and maximum pip movement on a particular timeframe. Having knowledge about this is necessary because it helps in managing risk as well as determining the right times of the day to enter and exit a trade with minimal costs.
Below is a table that depicts the minimum, average, and maximum volatility (pip movement) on different timeframes.
USD/CHF PIP RANGES
Procedure to assess Pip Ranges
- Add the ATR indicator to your chart
- Set the period to 1
- Add a 200-period SMA to this indicator
- Shrink the chart so you can assess a large time period
- Select your desired timeframe
- Measure the floor level and set this value as the min
- Measure the level of the 200-period SMA and set this as the average
- Measure the peak levels and set this as Max.
USD/CHF Cost as a Percent of the Trading Range
The number of pips the currency pair move in each timeframe is shown in the above table. Now, we apply these values to find the cost percentage when the volatility is minimum, average, and max. This cost percentage will then help us filter out the most optimal time of the day to take trades.
The comprehension of the cost percentage is simple. If the percentage is high, then the cost is high for that particular timeframe and range. If the percentage is low, then the cost is relatively low for that timeframe and range.
Note that, the total cost on a single trade is calculated by adding up the spread, slippage, and trading fee.
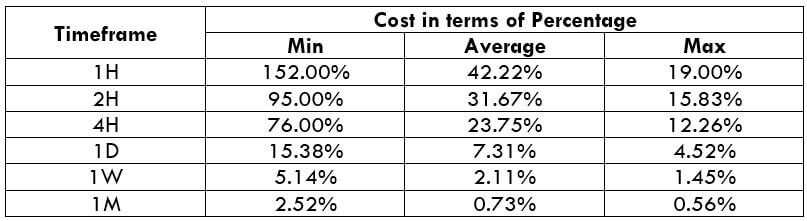
ECN Model Account
Spread = 0.8 | Slippage = 2 | Trading fee = 1
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 2 + 0.8 + 1 = 3.8
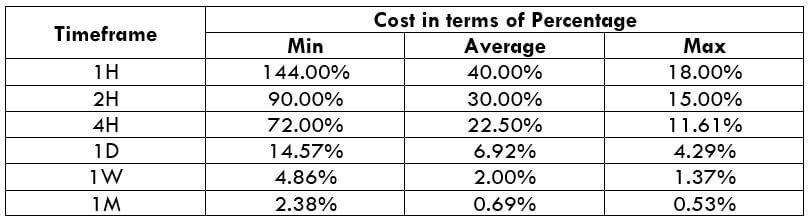
STP Model Account
Spread = 1.6 | Slippage = 2 | Trading fee = 0
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 2 + 1.6 + 0 = 3.6
The Ideal way to trade the USD/CAD
Entering and exiting trades during any time of the day might not be the smartest move. There are particular times of the day a trader must manage their trade to reduce both risk and cost on the trade. This can be made possible by comprehending the above two tables.
The percentages are highest in the min column. Meaning, the cost is pretty high when the volatility of the market is low. For example, on the 1H timeframe, when the volatility is 2.5 pips, the cost percentage is 152%. This means that one must bear high costs if they open or close trades when the volatility is around 2.5 pips. So, ideally, it is recommended to trade when the market volatility is above the average mark.
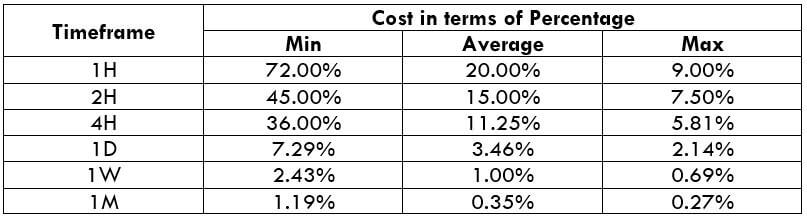
Apart from that, it is much better if one trades using the limit orders rather than market orders, as it nullifies the slippage on the trade. In doing so, the costs of each trade will reduce by about 50%.