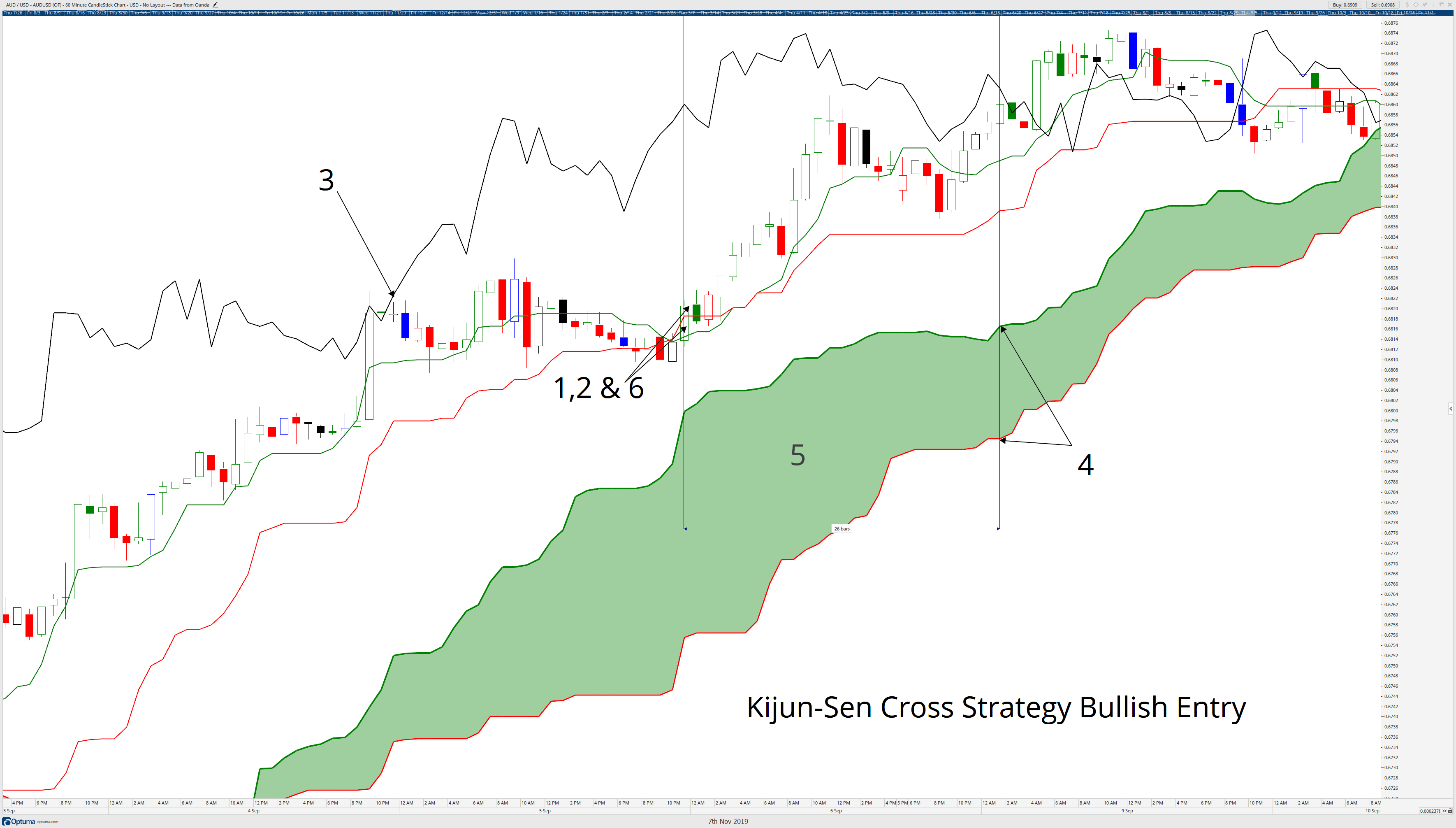
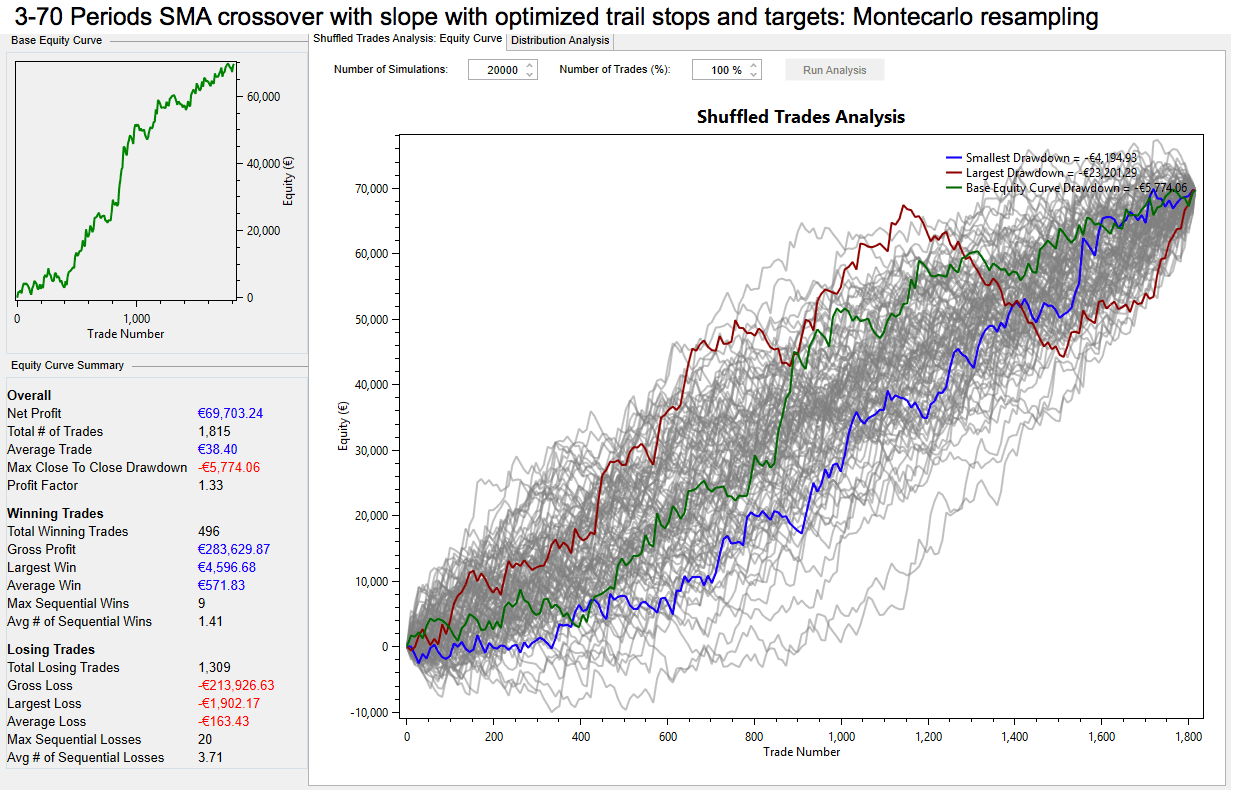
When the fundamentals lag behind the technicals
In recent weeks you will have noticed that the financial markets are in complete turmoil, with extreme volatility in all sectors, but especially in the oil markets more recently, and where stock markets seem to be propped up by hope more than fundamentals; after all, many indices have been rallying while the world economies have ground to a halt. And where volatility has also spilled over into the currency market.
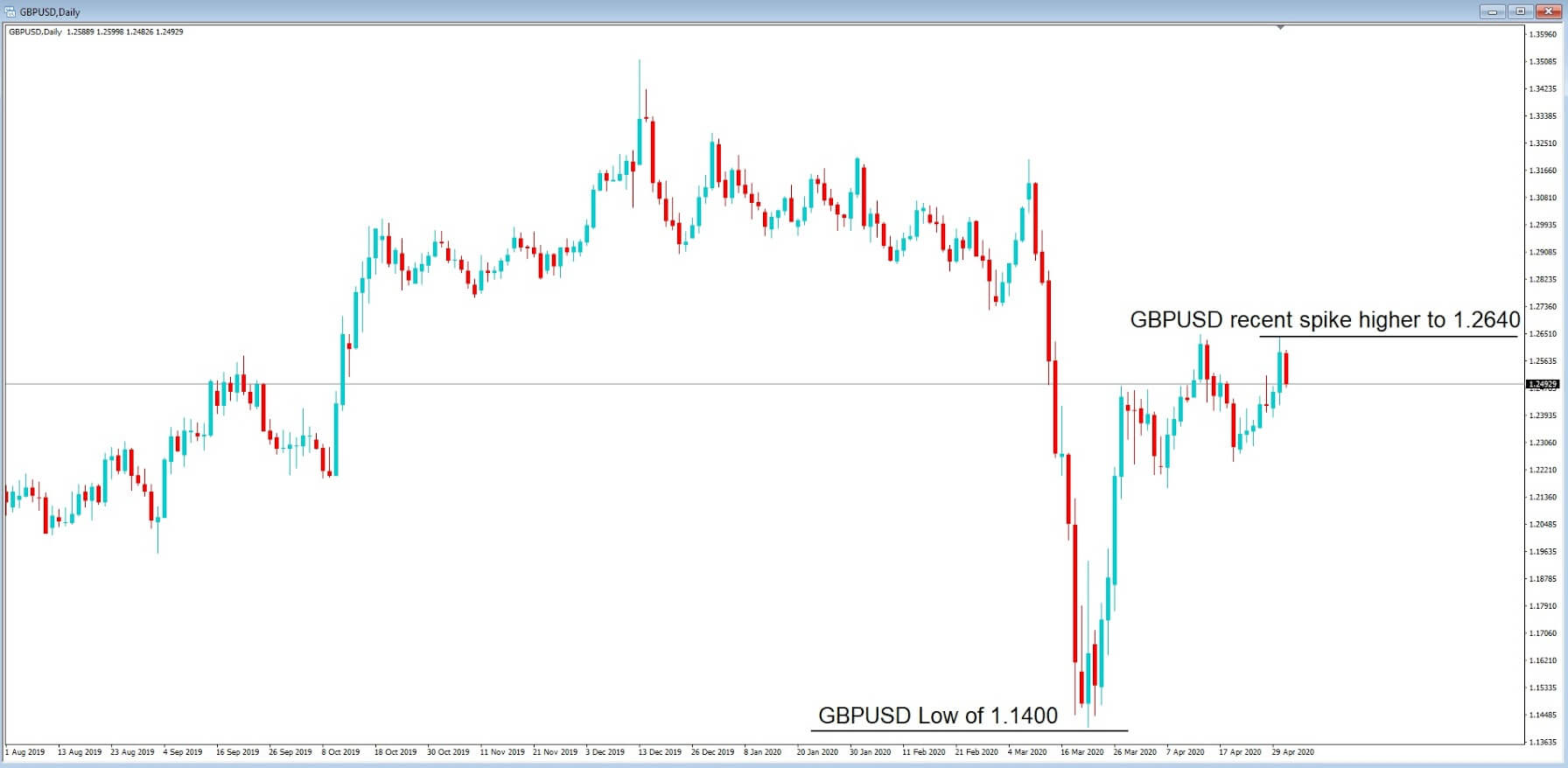
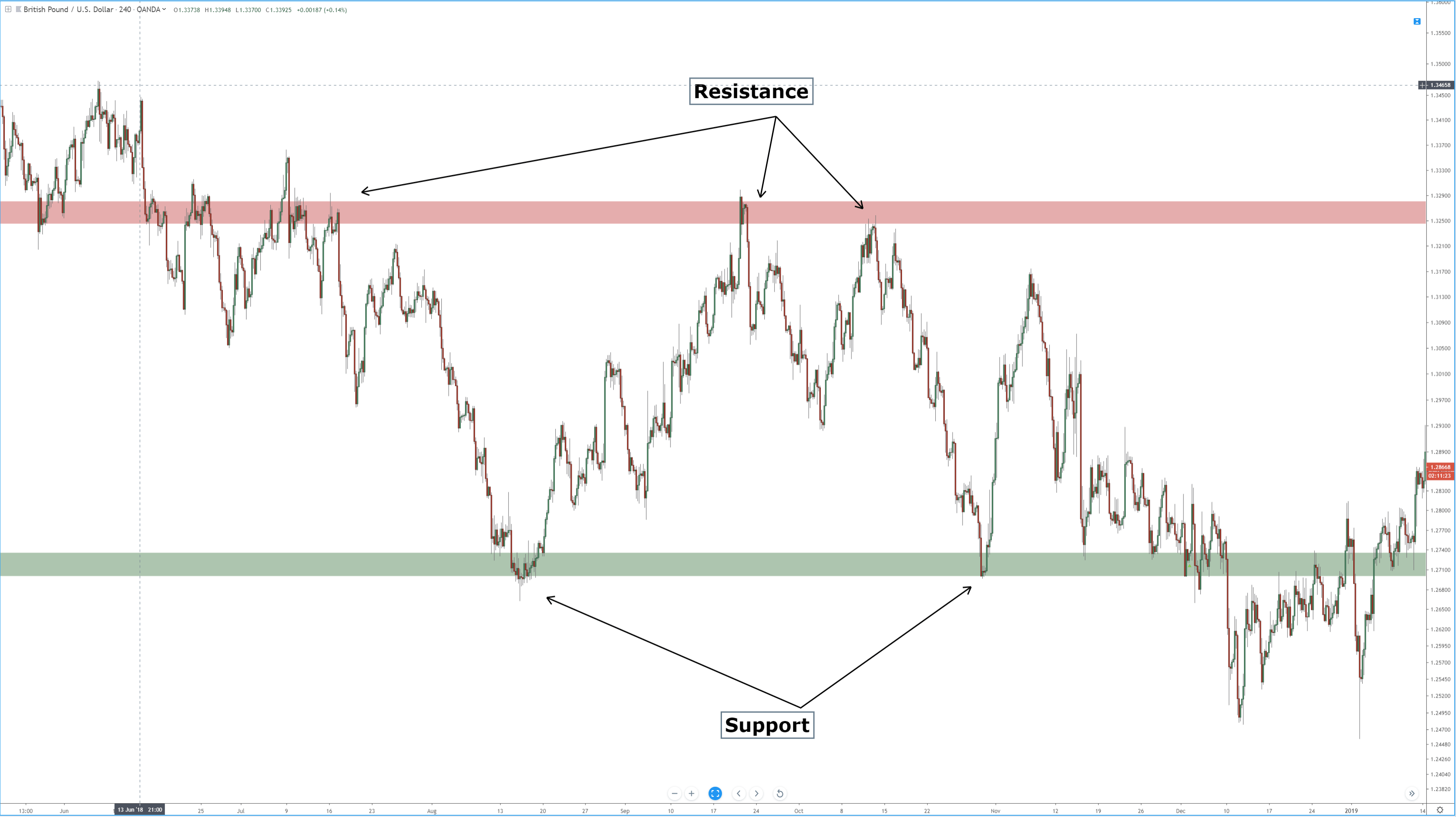
At the end of March 2020, we saw huge moves in currency pairs including a spike in cable, which only a few short weeks ago was trading at 1:14 and yet has recently spiked up to 1.2640, and where fundamentals for the British economy do not support this huge increase in the value of the pound.
So what is going on? Well, one thing is for sure, British economic data releases are not really showing the true extent of the fallout of the Covid-19 pandemic yet. And so, the fundamentals are lagging the technicals. In other words, the markets are being driven by technical analysis rather than fundamental analysis, in some circumstances.
Something that has stuck out like a sore thumb with regard to fundamentals lagging technicals is the USDCAD pair’s recent choppy price action. Let’s drill down in a little more detail to try and establish what is going on.
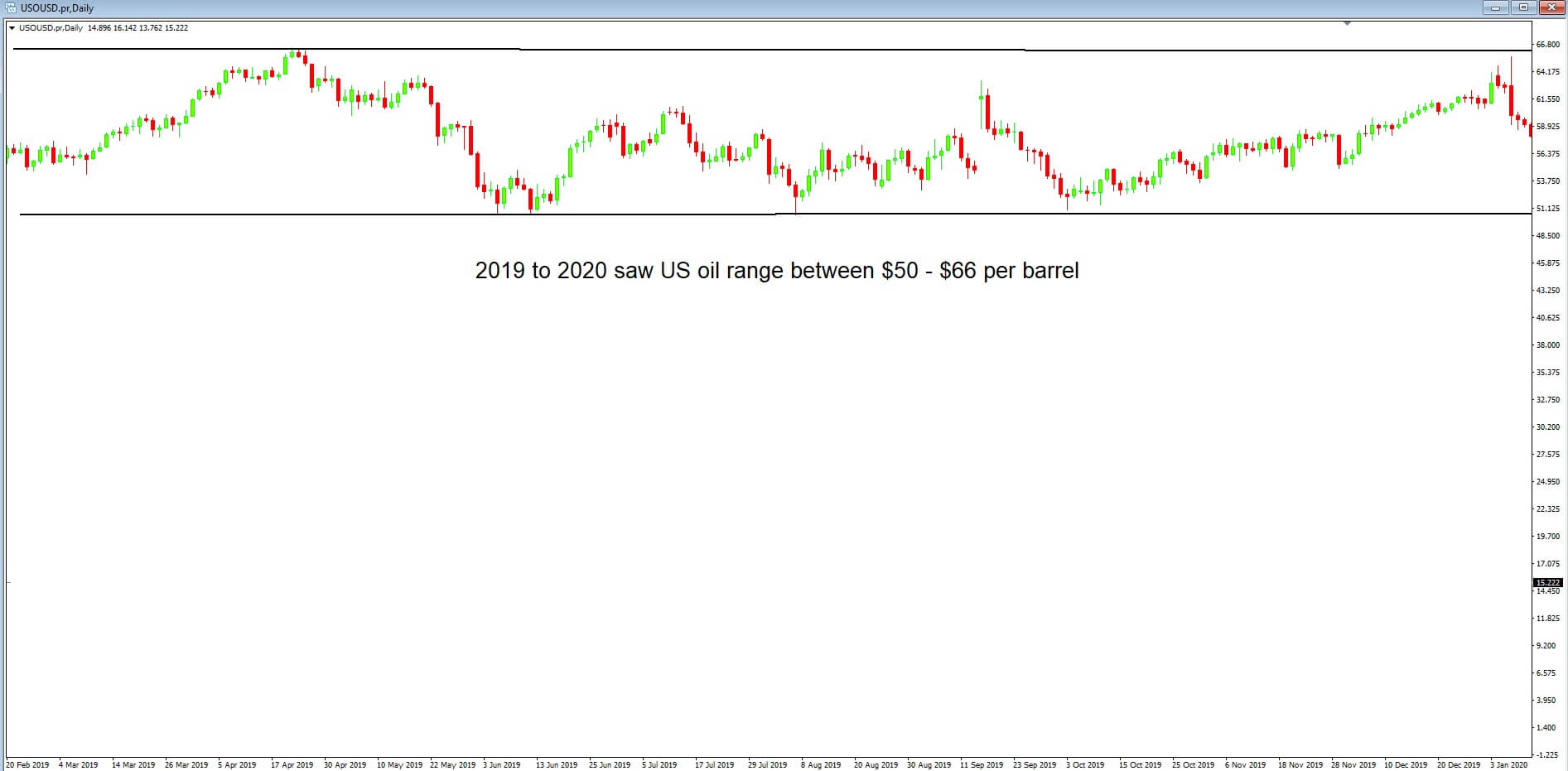
Before we do that, let’s take a look at the West Texas Intermediate or WTI, price action chart of the last 12-months. WTI is the benchmark for crude oil, and from 2019 to 2020, the price of a barrel of crude oil ranged between $50 to $66. West Texas Intermediate is a specific grade of crude that is used around the world and is seen as a benchmark in pricing oil.
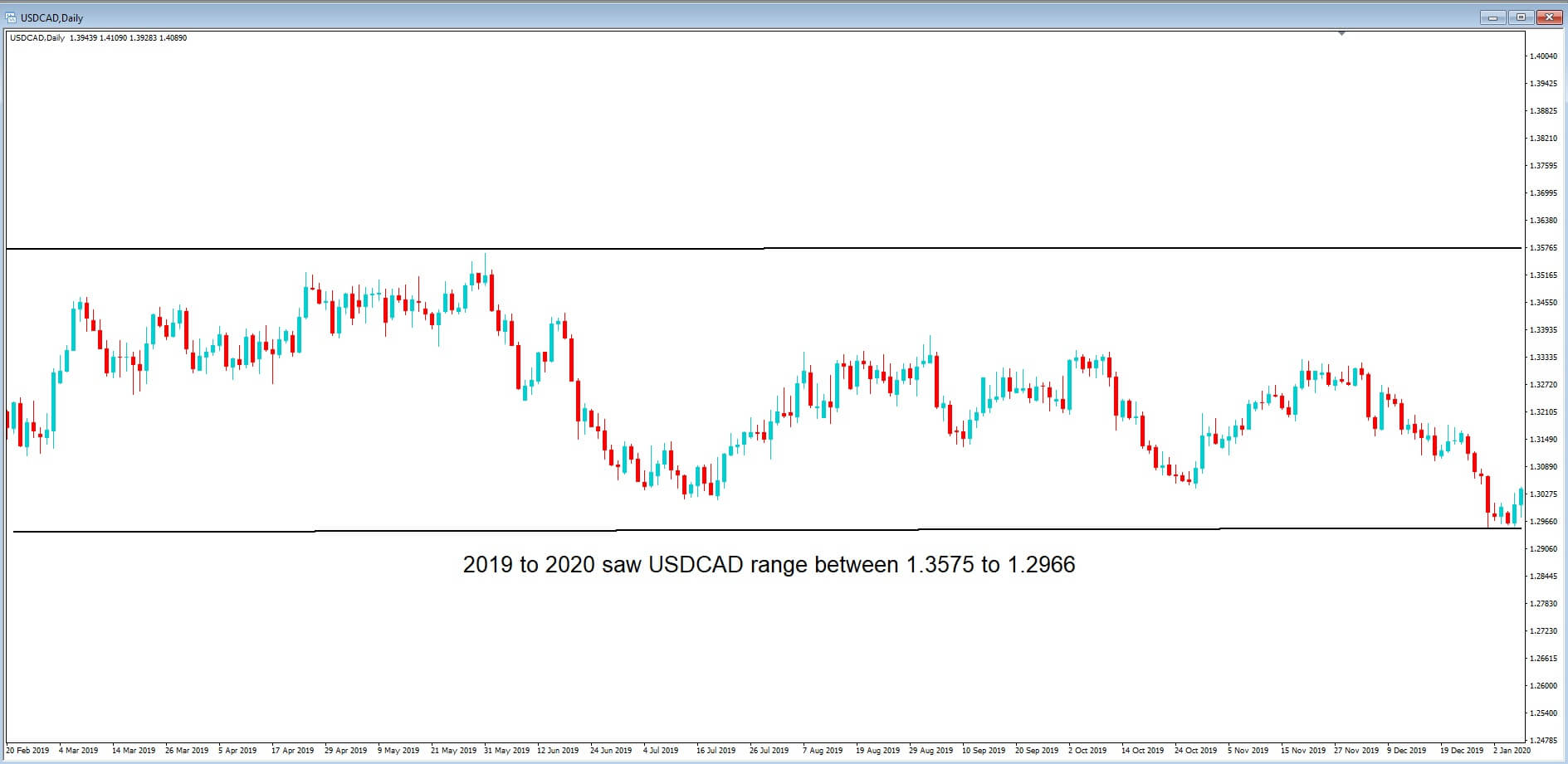
In this chart, we can see that in the same 12-period, USDCAD ranged between 1.2966 to 1.3575. Obviously, this was just before the virus pandemic. But in case you didn’t know, Canada is the fourth-largest producer and fourth-largest exporter of oil in the world, with 96% of Canada’s oil exports going to the United States.
Production and exportation of all products, including gas and electricity in Canada, contributed to around 170 billion in Canadian Dollars to it’s 1.8 trillion dollars of gross domestic product, which equates to around about 10% of GDP. And so oil is big business in Canada. And anything that upsets the production and exportation of oil will have a dramatic effect on Canada’s gross domestic product, and a spillover will, of course, be the value of the Canadian dollar, where we would expect price action volatility.
In fact, Canada has huge reserves of crude oil in Alberta’s Oil Sands and large deposits off the coast of Atlantic Canada. Oil is such a big business here, including exploration, drilling, production, field processing, as well as storing and the transportation of oil.
The Canadian dollar is sometimes referred to as the Loonie because of the loon bird, as depicted on the Canadian $1 coin. The Canadian dollar is one of the major currency pairs. It is widely traded in the financial markets and has been subject to extreme volatility during the current crisis.
However, we have also noticed that the USDCAD price action has become out of kilter recently, and this can be attributed to price action falling out of line with fundamental analysis and where traders have been preferring to trade on the basis of technical analysis. But be warned, fundamental reasons will catch up eventually and make the relevant corrections.
let’s set out our reasoning behind this theory:
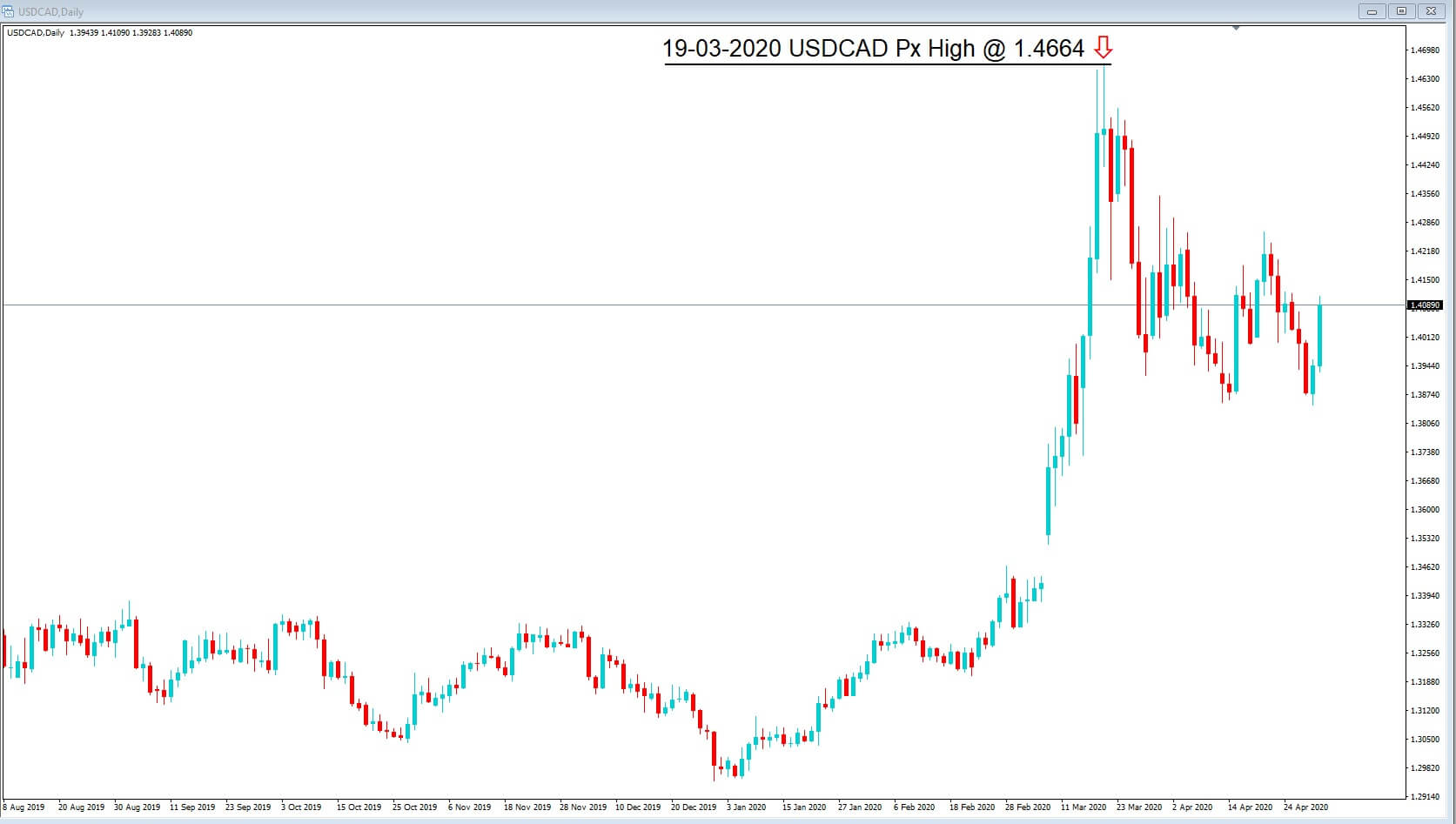
In this daily chart of the USDCAD, pair we can see that the price action, which had previously been contained within the 1.2966 to 1.3575 area, has spiked higher to reach a multi-year high at 1.4664 on the 19th March 2020. There are several reasons for this, including the perceived Covid-19 related hit to the Canadian economy, which affected and devalued the Canadian dollar.
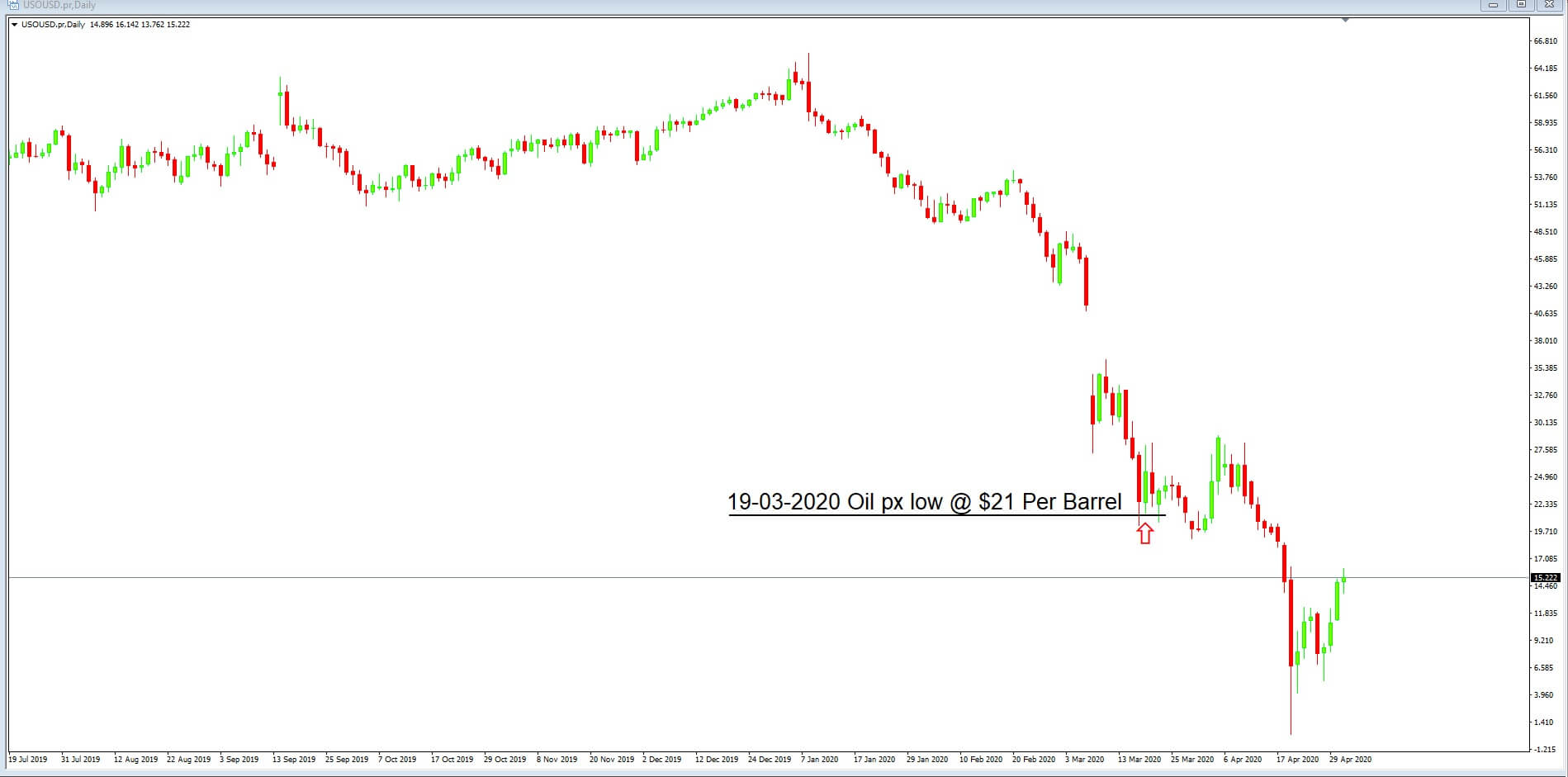
But if we take a look at this chart of WTI, we can also see that the 2019 to 2020 price of a barrel of crude oil range of $50 to $66 has spiked lower to $21 per barrel and therefore this would have been the main contributor for the Canadian dollar spiking higher because traders envisaged that the low price of oil, which is attributed to a global slowdown and a lack of demand, would devalue the Canadian dollar and that is exactly what happened; Oil price lower, Canadian Dollar value lower.
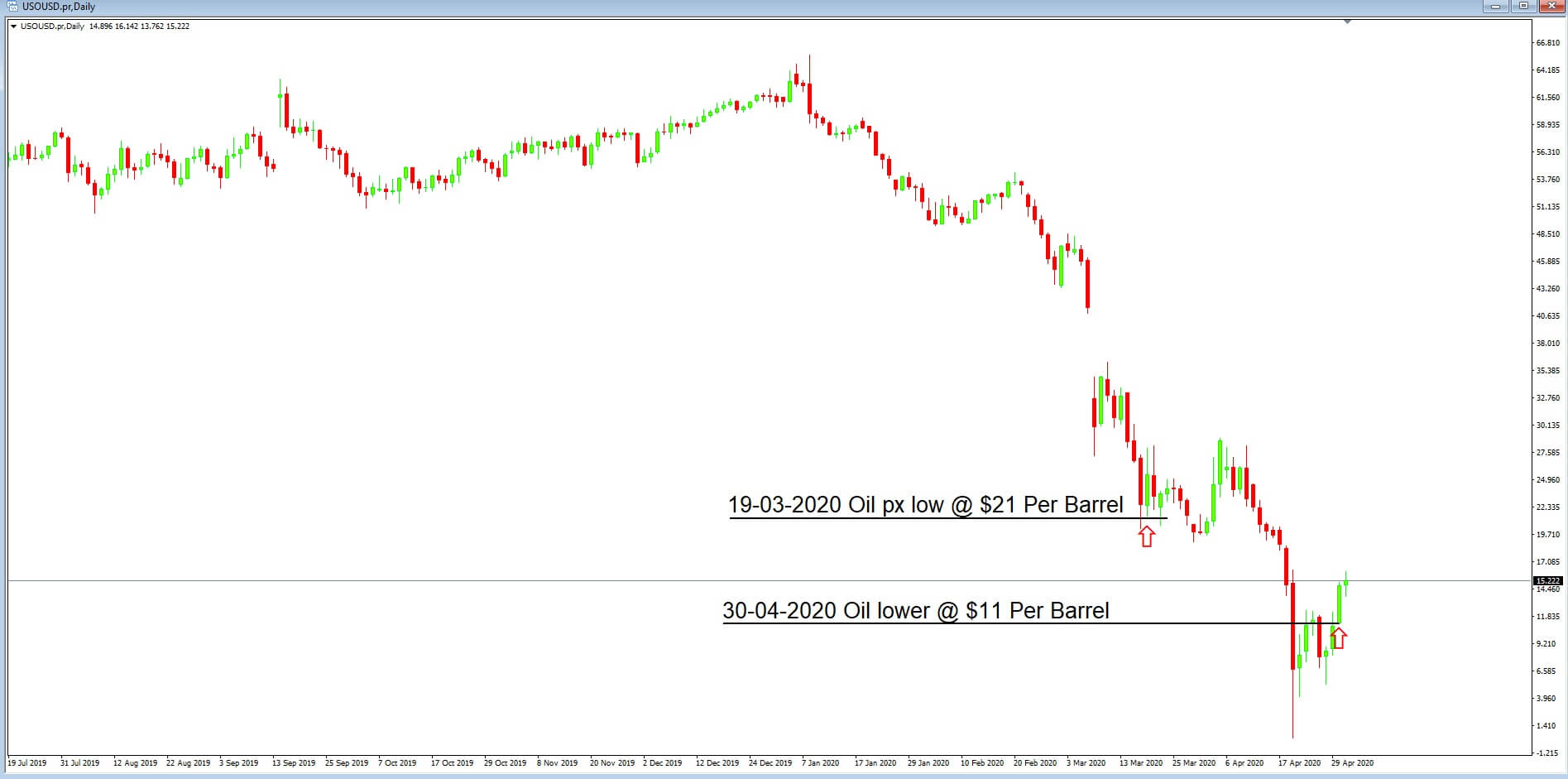
Let’s move forward to 30th April where the price of oil has continued to collapse, at one point going into negative territory to – $40 a barrel for WTI for May’s futures contract, which is the first time in history that this has ever happened. But at this point, we can see that price has somewhat recovered to $11 dollars per barrel. And we might, therefore, expect that the Canadian dollar has also weakened.
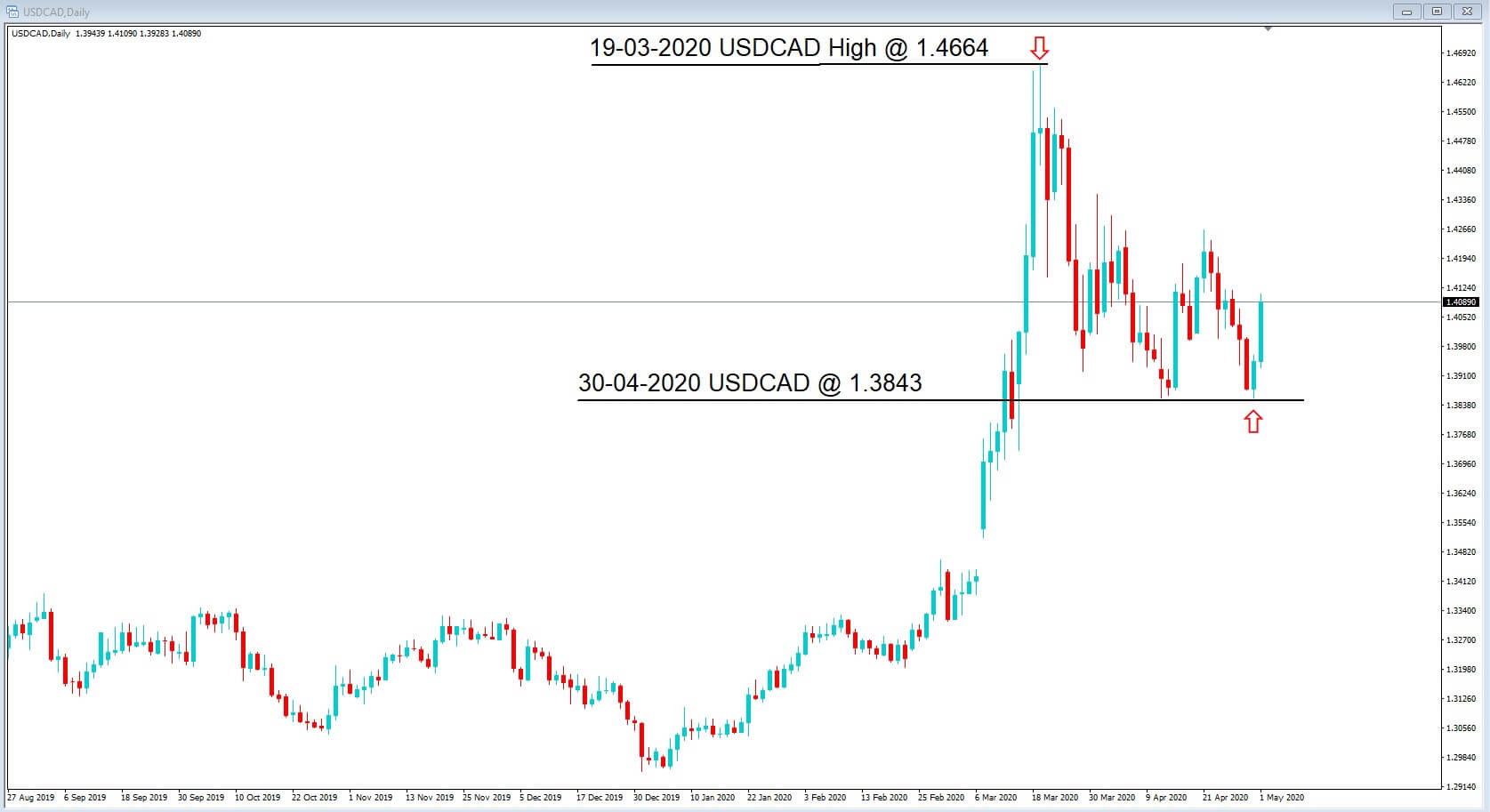
However, on the same day of the oil low, 30th April, the Canadian dollar has rallied higher in value, with the USDCAD showing a low of 1.3843, its highest level in six weeks. Before moving higher again to 1.4100 where it currently sits.
While some of the increase in the value could have been attributed to the oil price coming off of its low, especially the minus figures, on hopes of a fuel demand recovery, the prospects of further economic stimulus by the Canadian government, and the gradual reopening of western economies, we can be in no doubt that there has been a lag in fundamental analysis, and where traders have preferred to move with technical analysis, during the period of 19th March to 30th April.
However even if things began to get back to normal, this is going to be an extremely long process, and yet many oil-producing countries such as Saudi Arabia and Russia keep pumping out oil in a high volume regardless of the slowdown in global economic growth and where the
surplus of oil in storage all around the world is not likely to be consumed until 2022, according to some analysts.
Therefore no matter what type of recovery we see, and it won’t be rapid until there is a cure for Covid-19, on the basis of supply and demand, we will see low oil prices for a long time to come. Therefore we should expect the US dollar CAD to continue to rise, perhaps to previous highs of $1.46, as the fundamentals catch up with the technicals.