Introduction
The Piercing Line is a simple and effective candlestick pattern, and it is used to trade the bullish reversals in the market. This pattern typically appears in a downtrend. Also, when it appears in a significant support area, we can consider it more reliable. Piercing Line is a two candlestick pattern where the sellers influence the first candle, and the second candle is responded by enthusiastic buyers. Piercing Line essentially indicates the bears losing control, and bulls taking over the market.
- First of all, in a downtrend, the first candle of the pattern should be bearish.
- The second candle should be bullish, and it should open lower than the closing of the previous candle, and it must close above the midpoint of the bearish candle.
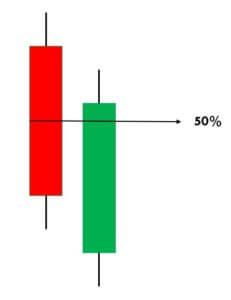
This indicates that buyers now overwhelmed the sellers. In terms of supply-demand, this pattern shows that the supply is depleted somewhere, and the demand for buying has increased. Remember not to trade this pattern alone. Always use it in conjunction with some credible indicators or other trading tools to further enhance the probability of winning.
Piercing Line Pattern Trading Strategies
Piercing Line Pattern + Percentage Price Oscillator
In this strategy, we have paired the Piercing Line pattern with the Percentage Price Oscillator to generate credible trading signals. The Percentage Price Oscillator is a momentum indicator. It consists of a centerline, histogram, and the two moving averages. Just like the MACD indicator, the PPO also represents the convergence and divergence in price action. This indicator gives a crossover at the overbought and oversold market conditions.
When price action crosses the centerline, it means that the bullish or bearish momentum is super strong. We want to let you know that PPO is not that popular in the industry. Also, it is not available in the MT4 terminal. However, you can download this indicator from this link and add it to your MT4 terminal. If you are a Tradingview user, search the PPO indicator in the indicators tab, and you should be able to find it.
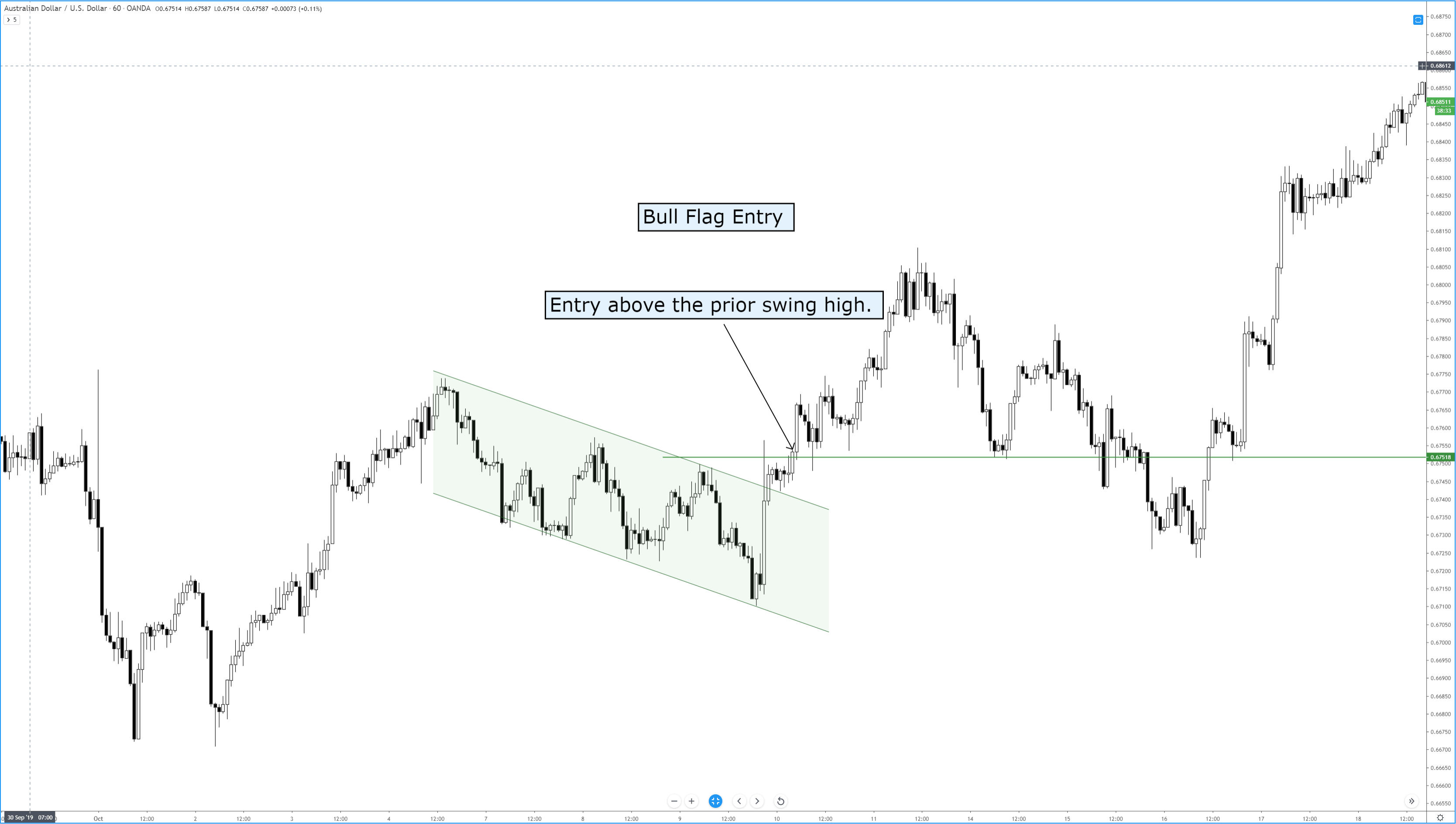
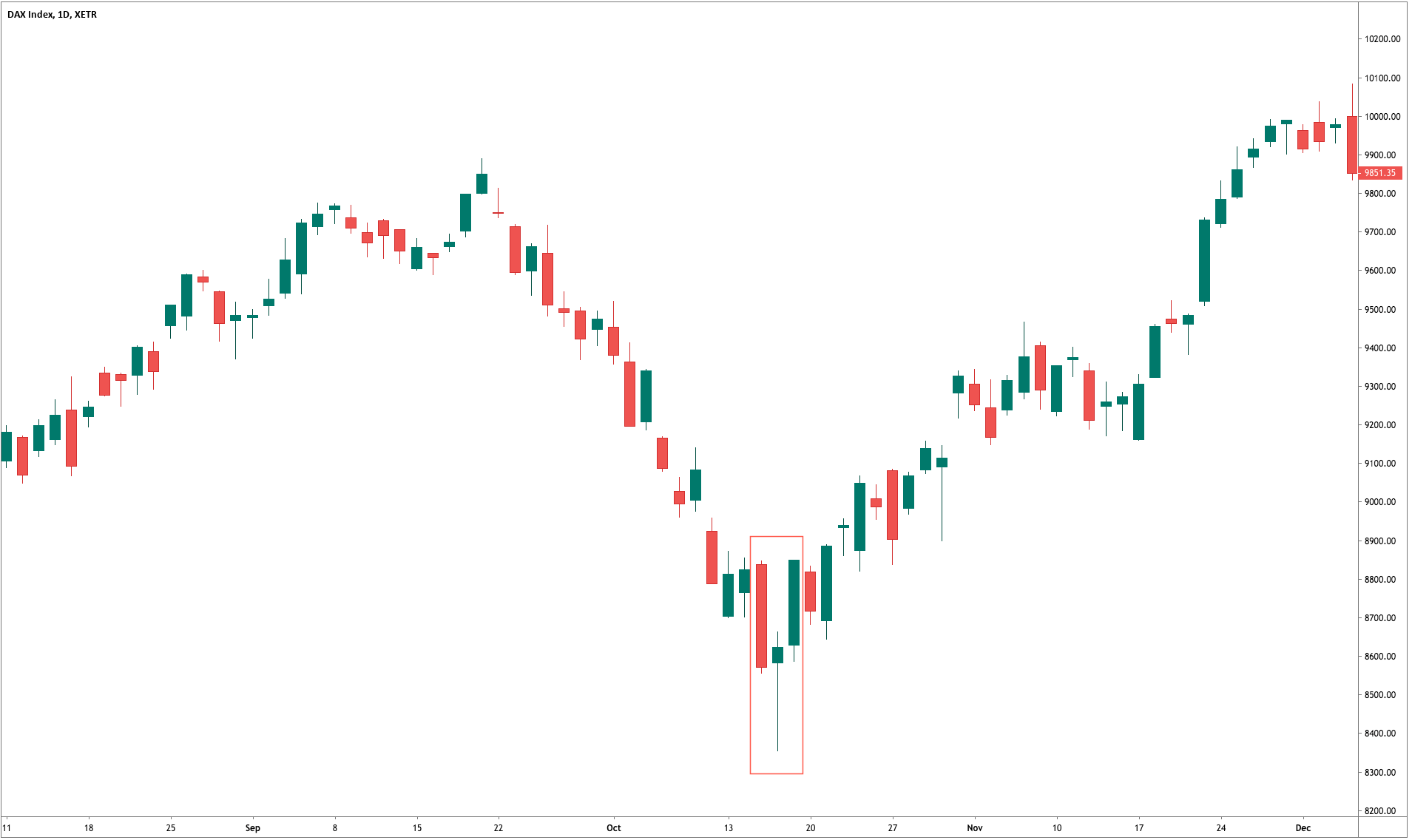
Step 1 – Find out the Piercing Line pattern in a downtrend.
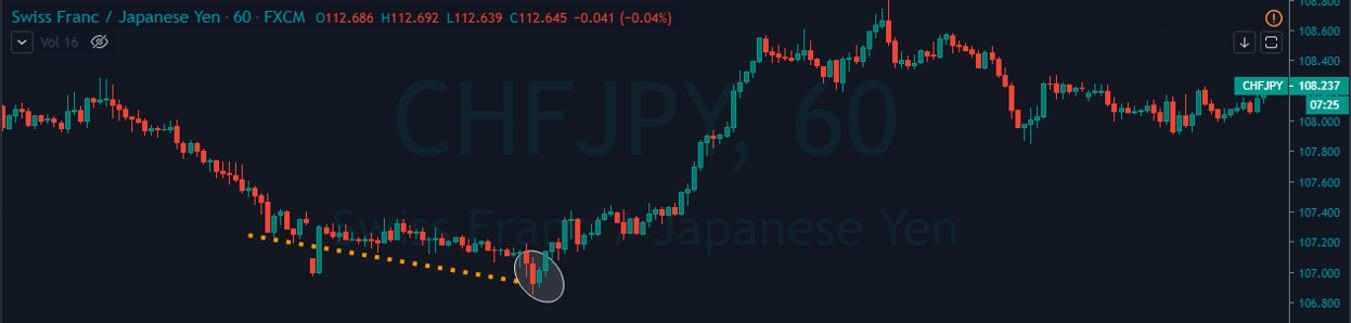
Step 2 – Once you find the Piercing Line pattern, the next step is to wait for the reversal to happen on the PPO indicator at the oversold market conditions.
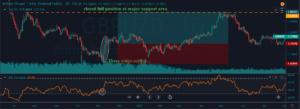
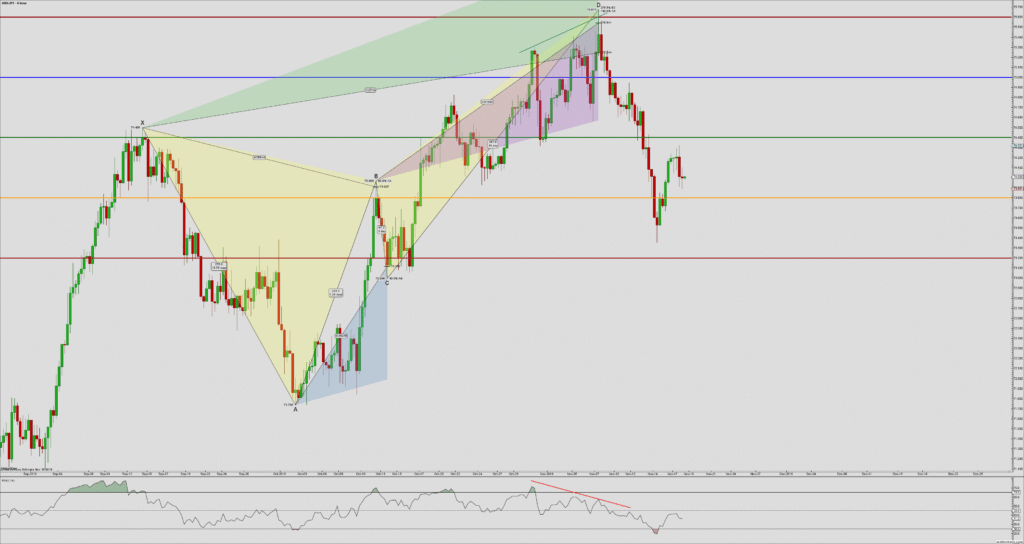
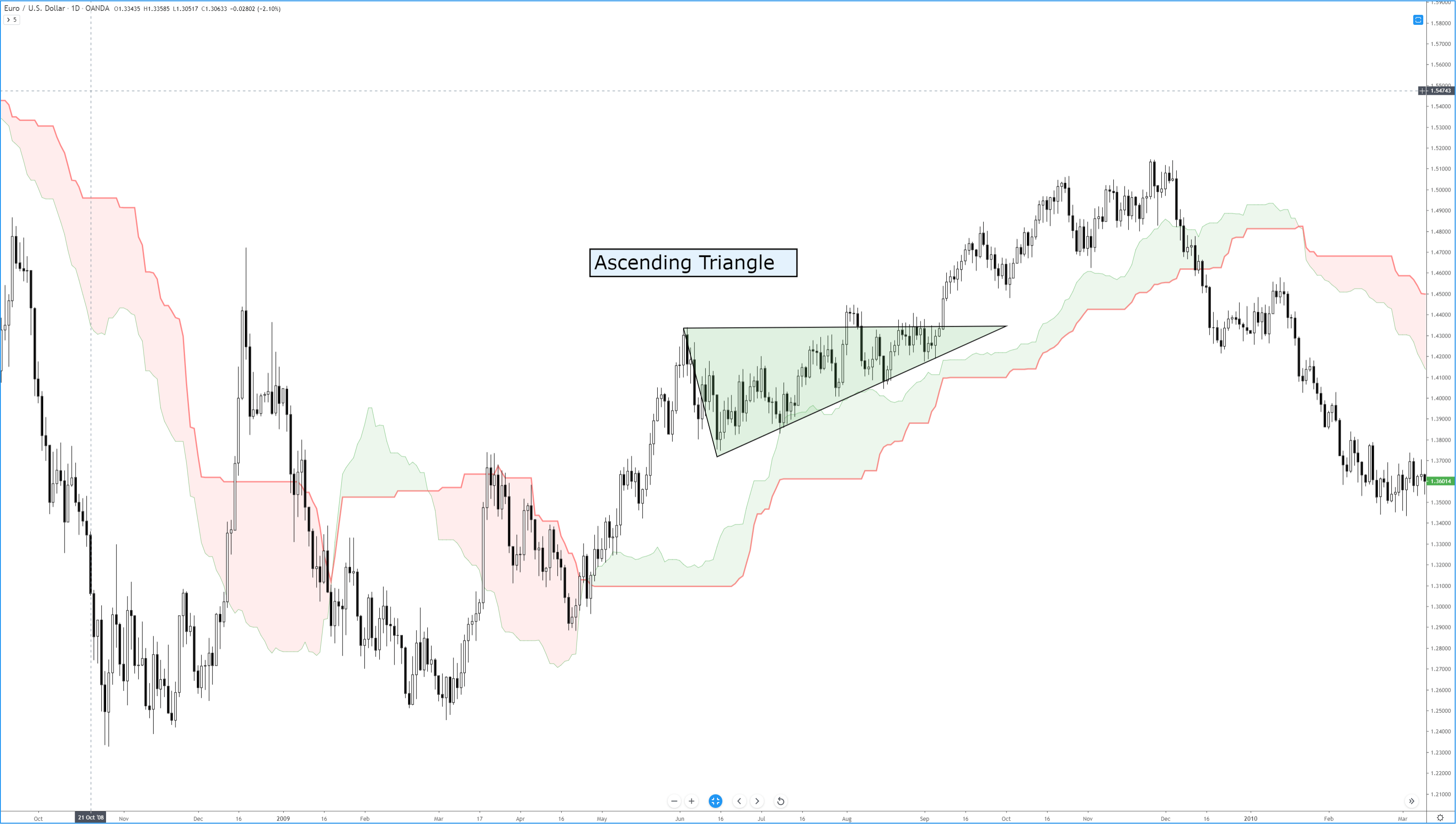
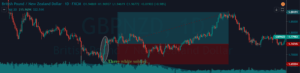
In the below CHFJPY chart, the market was in an overall downtrend. We can see the market printing Piercing Line pattern, and that is an indication of a trend reversal. We can also see the PPO indicator giving crossover in the overbought area at the same time. Both of these clues indicate a clear buy signal in this pair. We can also see the price action showing divergence, which is another clue to go long. If we are able to find all of these clues on a single price chart, we shouldn’t mind placing bigger trades.
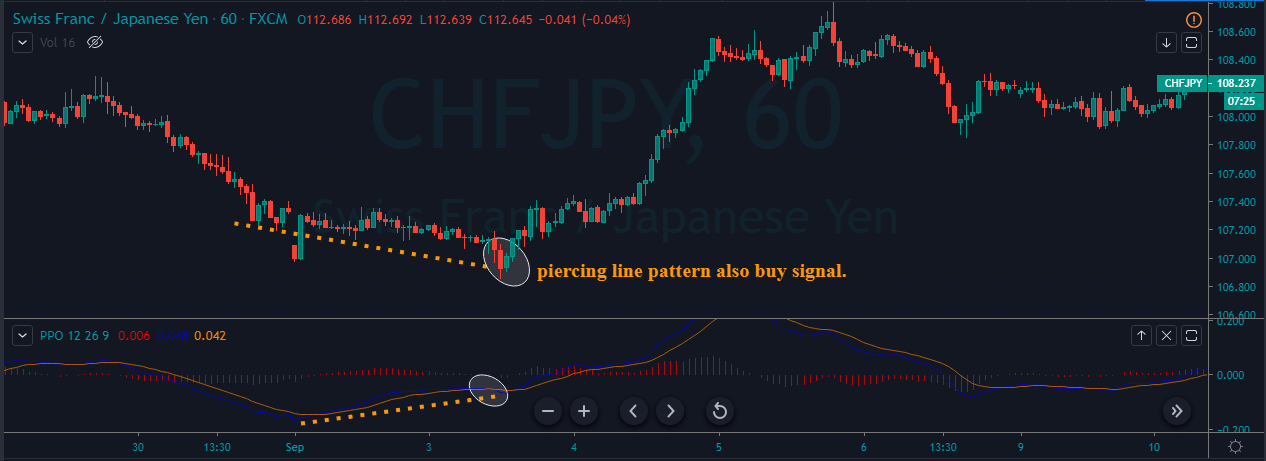
Step 3 – Stop-loss and Take Profit
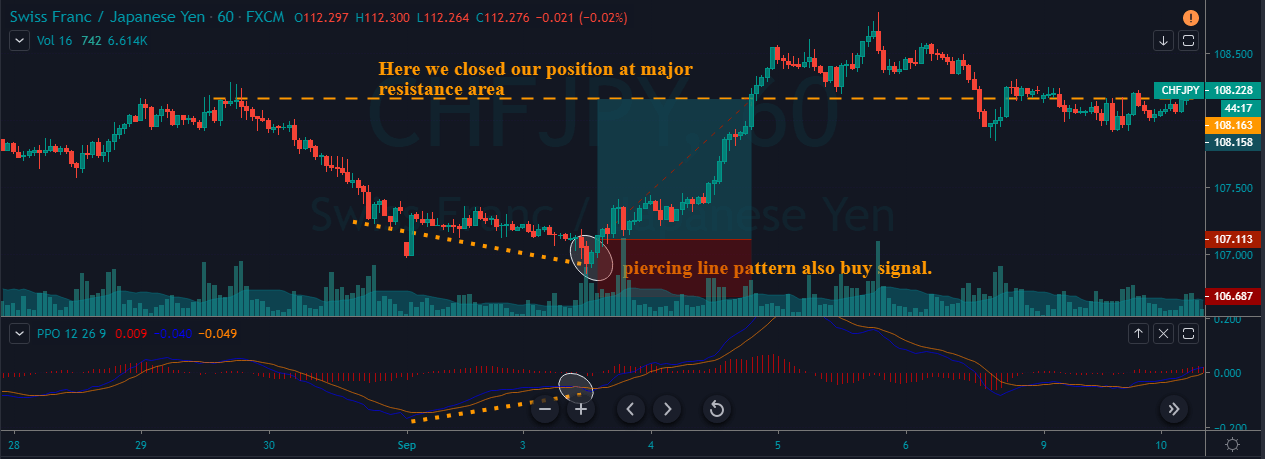
PPO indicator quite often gives high probability trading signals. So when we take trades of that kind, most of the time, we must place the stop loss just below the first candle of the Piercing Line indicator.
There are several ways to book profits. For this particular strategy, we can close our position when the PPO reversed at the overbought area or when the market starts printing the opposite pattern. If you plan to make more money in a single trade with extra risk, it is advisable to book the profit at the higher timeframe’s major resistance area.
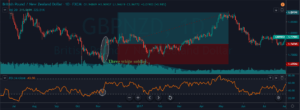
In the below chart, we can see that we have closed our whole position at the major resistance area and the stop-loss order was just below the recent low.
Piercing Line Pattern + Double Moving Average
In this strategy, we have paired the Piercing Line pattern with the Double Moving Average. Moving Average is a very well-known indicator in the industry. Many average indicators are available in the market. If you are using the lower period average, expect more trading signals. Contrarily, if you are using the higher period average, expect fewer but accurate signals.
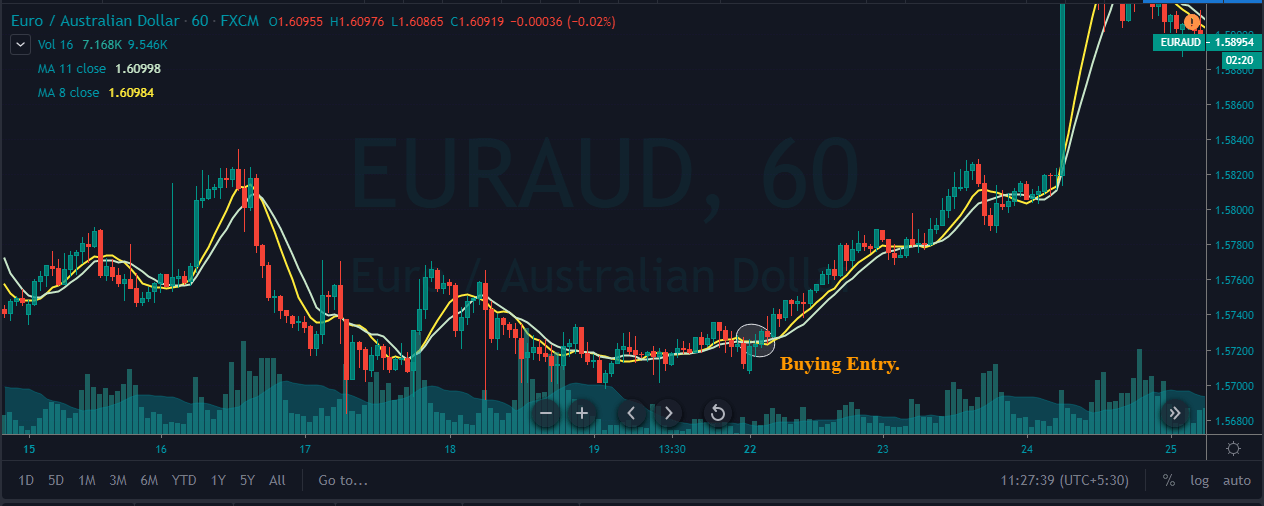
Step 1 – First of all, find out the Piercing Line pattern in a downtrend.
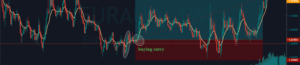
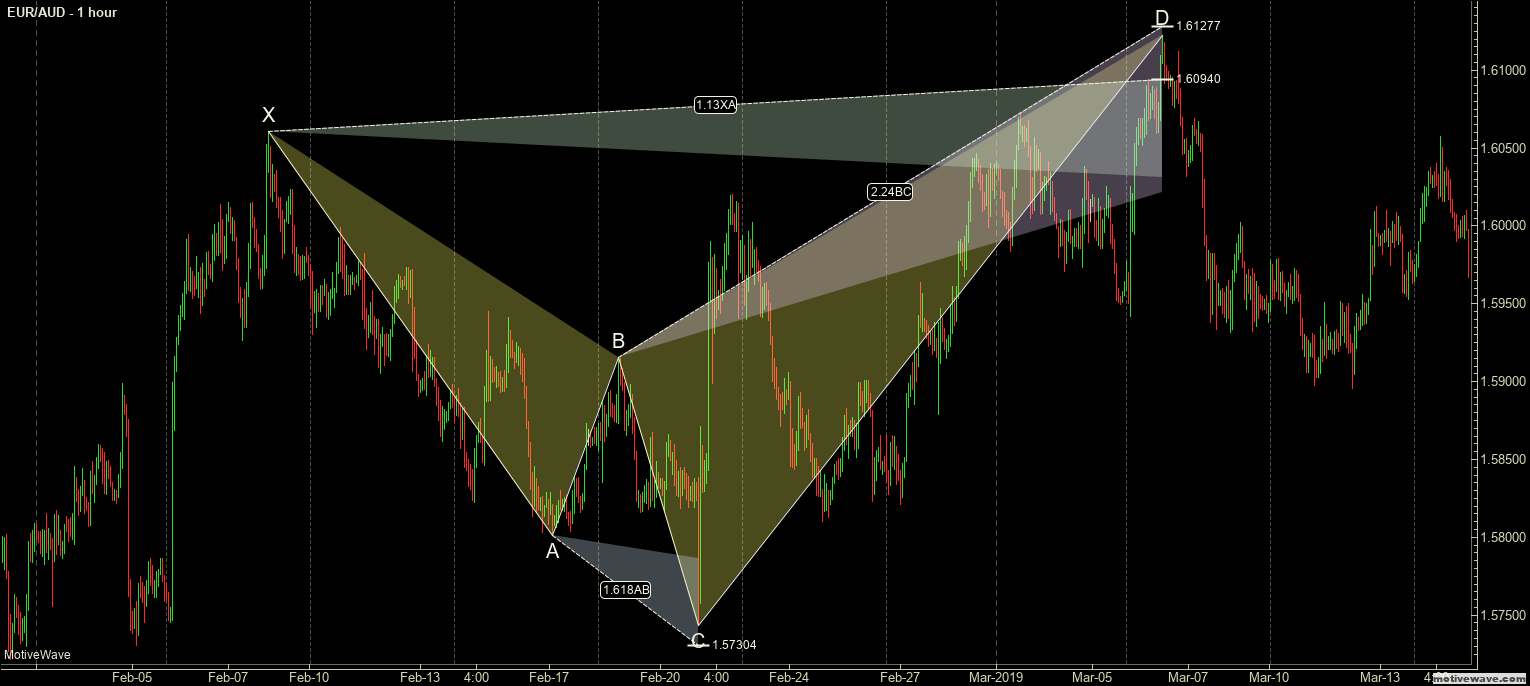
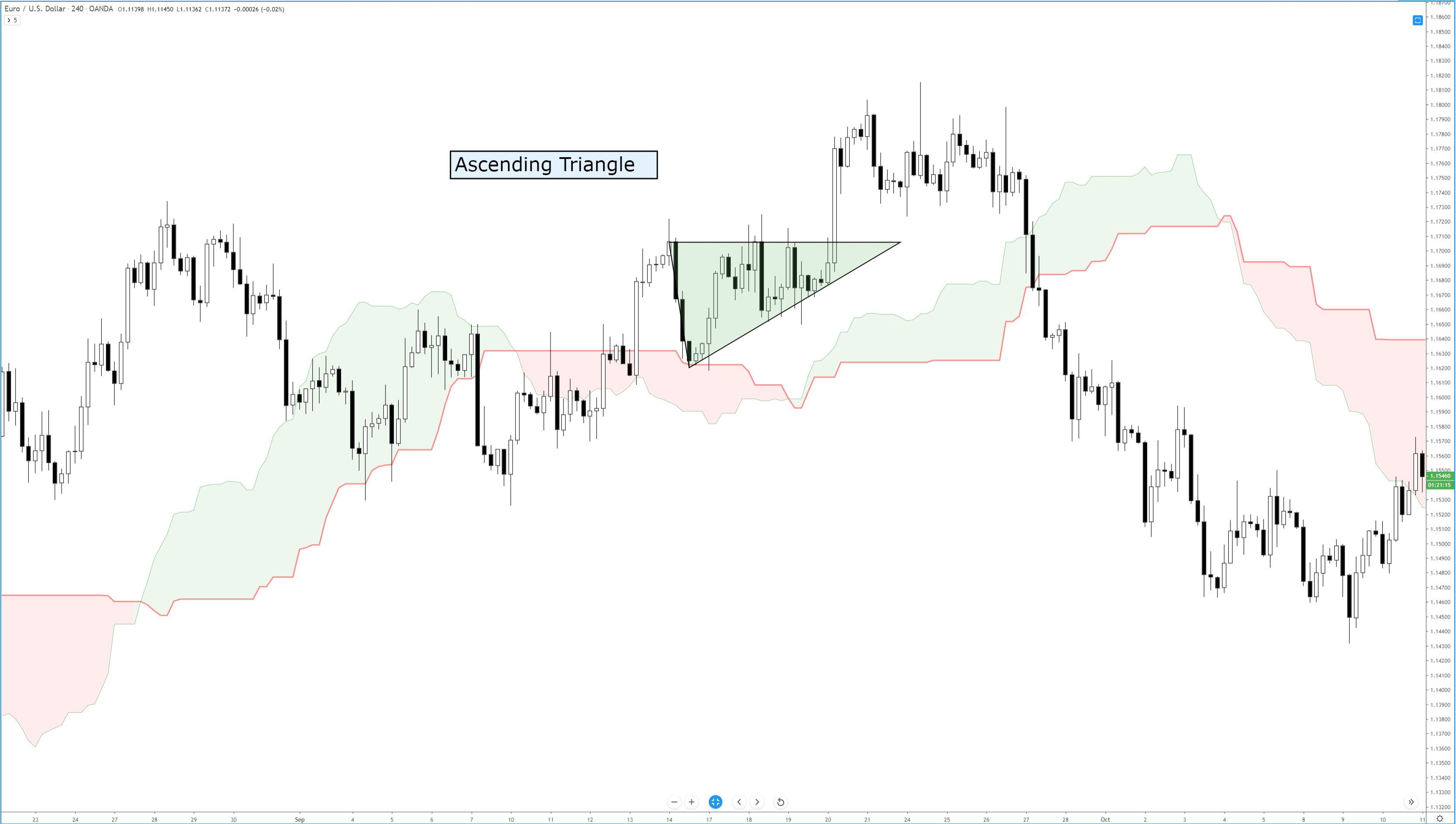
Step 2 – Activate the buy trade when the lower period MA crosses the higher period MA. In the below EURAUD Forex chart, the price action was in a downtrend, and around the 22nd of December, the market prints the Piercing Line pattern. This means that the sellers now have a hard time to go lower, and buyers took over the market. Furthermore, when a lower period moving average crosses the higher period moving average, it is a clear indication to go long. After our entry, price action immediately prints a brand new higher high.
Step3 – Stop-loss and Take Profit
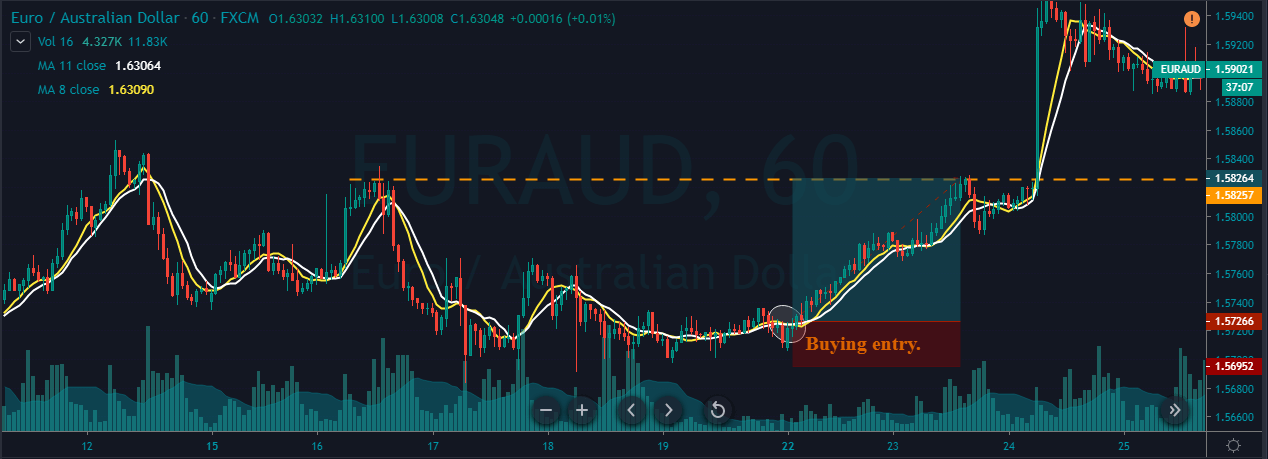
If you are an aggressive trader, use the recent low for stop loss. But if you are a conservative trader, make sure to place wider stop losses. If you plan to ride the longer moves, wait for the price action to hit the daily support area. But if you plan to go for intraday trades only, we suggest you exit your position when the double MA gives the opposite signal.
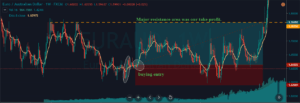
In the below chart, we can see that we have closed our full positions at the higher timeframe major resistance area, and stop-loss was just below the recent low. Overall, it was a 3R trade.
Bottom Line
Piercing Line pattern is a bottom reversal pattern, and it is one of the very well-known bullish reversal patterns. We can say that this pattern is exactly the opposite of the Dark Cloud Cover pattern. We won’t be able to see this pattern very frequently on the price chart, but when it appears, a trend reversal is guaranteed. Sometimes you will find this pattern in the consolidation phase, but it’s not worth your time to trade it in ranges. So it is always recommended to find this pattern in a clear trending market because that’s where we can generate more effective signals. The only limitation of this pattern is that it requires the use of other technical tools to confirm the signal and cannot be used stand-alone. But that’s the case of most of the candlestick patterns, so that’s not a major limitation.
That’s about the Piercing Line candlestick pattern. Let us know if you have any questions in the comments below. Cheers!

 As the case of the Morning Star, a gap up on the second small-bodied candle followed by a gap down on the third black candle is further confirmation of a reversal, but that seldom happens in the Forex Market. Also, the third candlestick is asked to close below 50 percent of the body of the first white candle.
As the case of the Morning Star, a gap up on the second small-bodied candle followed by a gap down on the third black candle is further confirmation of a reversal, but that seldom happens in the Forex Market. Also, the third candlestick is asked to close below 50 percent of the body of the first white candle.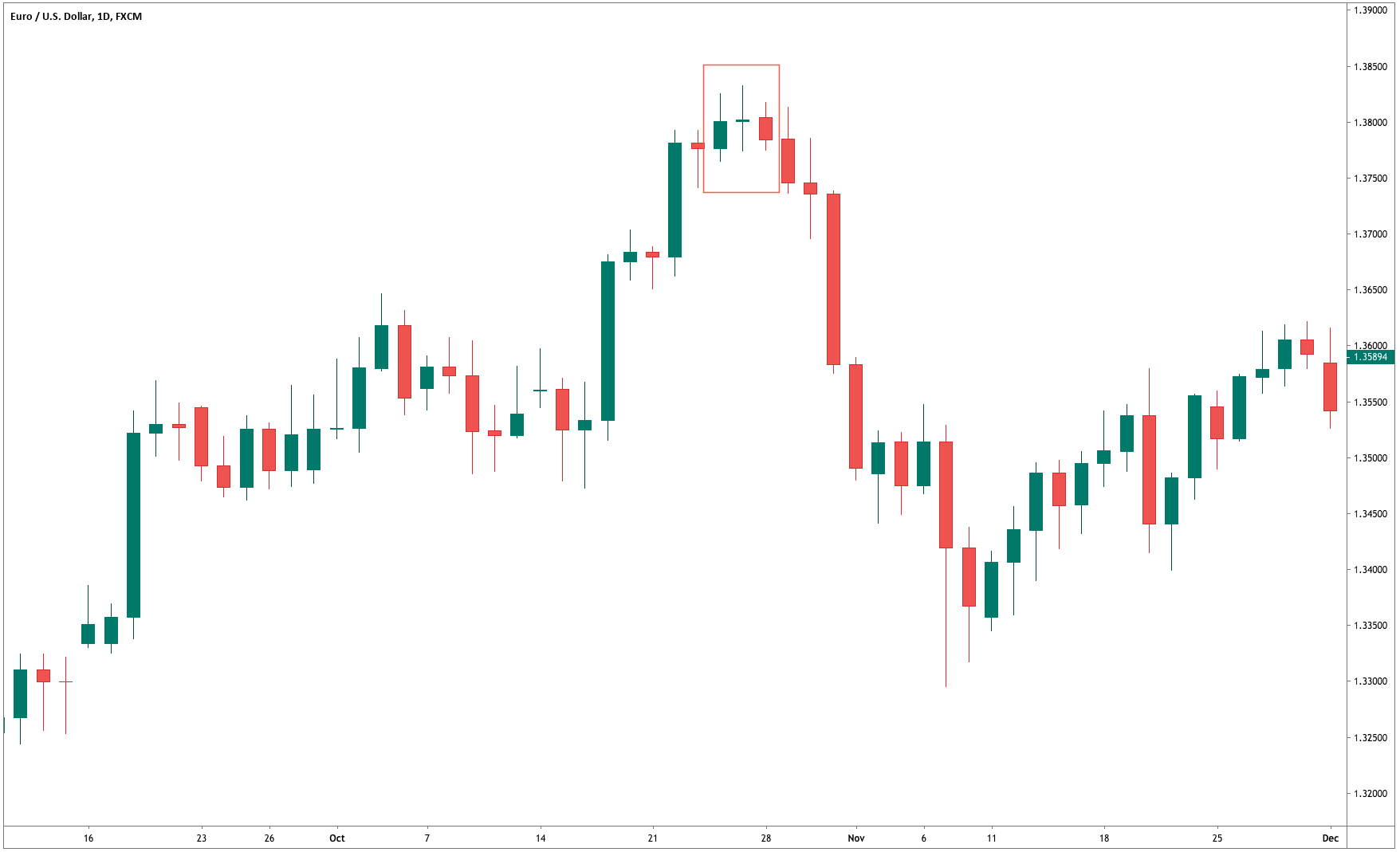










 Step 3 – Step Loss & Take Profit
Step 3 – Step Loss & Take Profit