Introduction
The market does not move in random directions. It either trends or consolidates. As many would not know, the market is like a closed circle, and the same states keep repeating over and over again. Thus, in trading, one must learn how to become pro at reading these market states.
On that same note, we shall be going over an effective strategy when the market is in a consolidation/ranging state. However, before jumping right into the strategy, it is important to understand the basics and related concepts.
What is a consolidation phase in a market?
There are several ways to comprehend the consolidation phase of the market. There is logical reasoning behind the occurrence of this state, and is not simply a random pattern that shows up quite often.
The consolidation state is that phase of the market when the market moves in a sideways direction. This state is also referred to as a range. The reason for its occurrence is related to the strength between bulls and bears.
Comprehending a Range
There are two parties in the market – the bulls and the bears. Their strength is what describes the state of the market. In a trending market, either of the parties is powerful. For instance, if the market is going up, it simply means that the bulls control the market. In a consolidation state, both bulls and bears show equal strength. The bulls show strength by pushing the market higher, while the bears show power by taking the price right back down. As a result, the prices in both directions – which we refer to as a range.
How to draw a range?
To trade this range strategy, it is vital to understand how a range is drawn. A range is made up of two levels:
- Support
- Resistance
Thus, drawing the correct support and resistance levels will result in a perfect range.
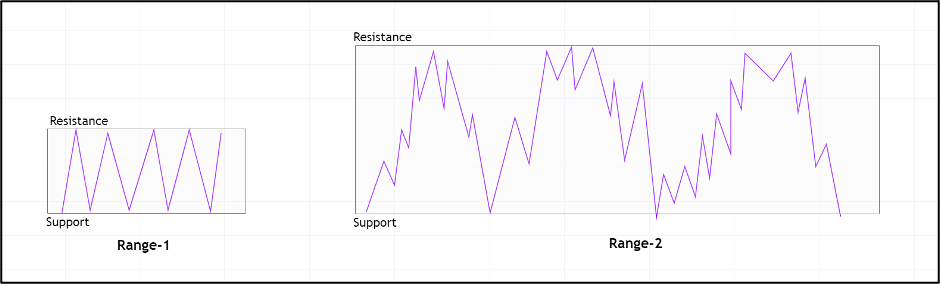
Another point considered is the size of the range. The larger the range, the better. The other small consolidations in the market are ignored. Following is an example of how we pick an ideal range.
In the above example, both are ranges as the market is moving in a sideways direction. However, we do not consider range-1 as a range for our strategy. This is because a single line going up and down fails to depict the market’s price action.
Supply and Demand Range Strategy
What is the usual approach to trading a range? It is to buy at the support and sell at the resistance. But we’re going to step the game a little bit. The supply and demand range strategy uses the same principles of a typical range, in addition to other factors.
Step by step procedure to trade the Supply and Demand Range Strategy:
- Find a legitimate range in the market. Mark the Support and Resistance levels appropriately.
- Determine the direction of the market prior to the range.
- Find a potential supply/demand level.
- Get in when the market breaks through the range and reaches the supply/demand zone.
Buy Example
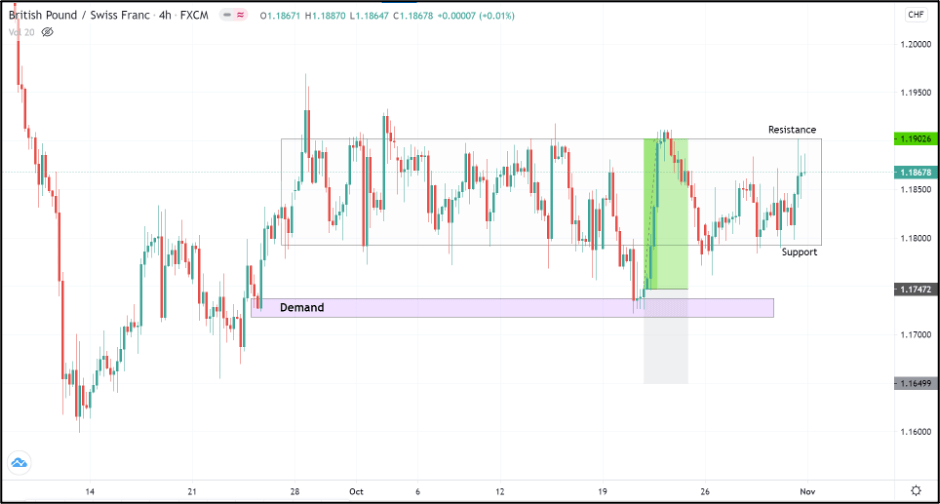
Consider the below chart of GBPCHF on the 4H timeframe. We see that the market has been ranging between 1.1902 and 1.1800. Observe that the support and resistance levels have been marked by cutting off the false market breakouts.
To trade this market, our job is not simply to hit the buy at the support and sell at the resistance. As mentioned, we take into account the preceding direction and the supply and demand levels around it.
The direction of the market prior to the range was an upside, indicating that the bulls were in control previously. A point to note is that, despite the market being in a range, it does not change the fact that the bulls are still powerful. Thus, we rather look for buying opportunities than shorting signals.
To do so, we wait for the price to drop below the bottom of the range and hold at any one of the demand zones. Once the market begins to reverse its direction from south to north around the demand zone, we can go long. The same scenario has been illustrated in the chart below.
Placements
Stop Loss – Well below the demand zone would be decent.
Take Profit – Top of the range would be an ideal spot to take profits.
Sell Example
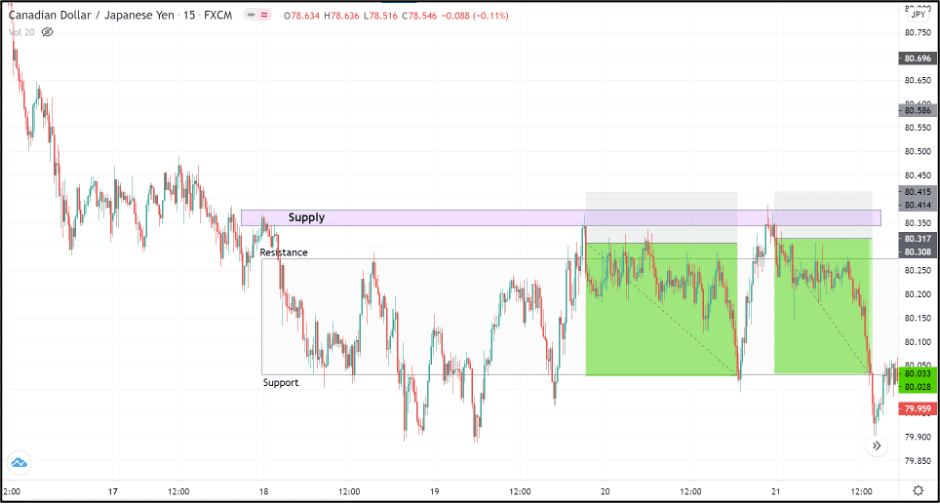
Consider the chart of CAD/JPY on the 15min timeframe shown below. The recent market price action depicts that the market is moving sideways. The market’s overall trend is down, indicating that the bears are in control of the market.
Since the scenario is opposite to the previous example, we wait for the market to break through the resistance and reach any potential supply level. In the below example, we can see that the price broke through the resistance twice reacted off from the supply, as shown. Thus, we can look for entries when the market begins to switch direction to the downside.
Placements
Stop Loss – Above the supply zone
Take Profit – Bottom of the range
Conclusion
The only way to trade a range is not by buying and selling from the top and bottom of the range. It can be professionally traded with the application of other factors. And this range strategy particularly dealt with the strength of the bulls and bears and the concept of supply/demand.
We hope you were able to comprehend our Supply and Demand Range strategy. Do test them out for yourself and let us know your results in the comments below. Happy trading!