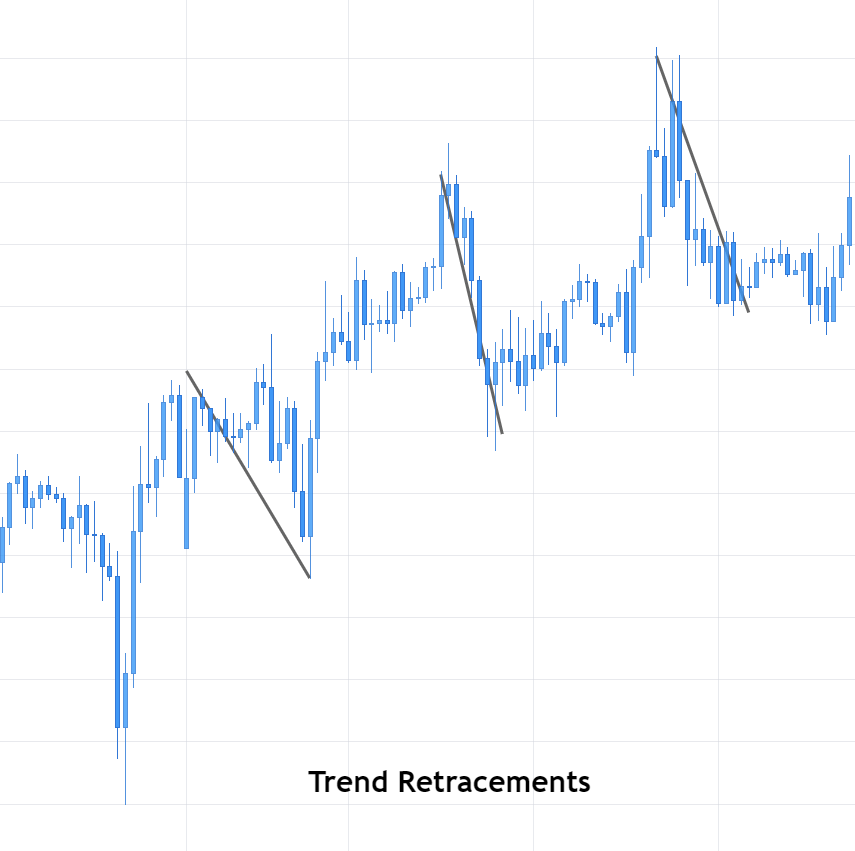
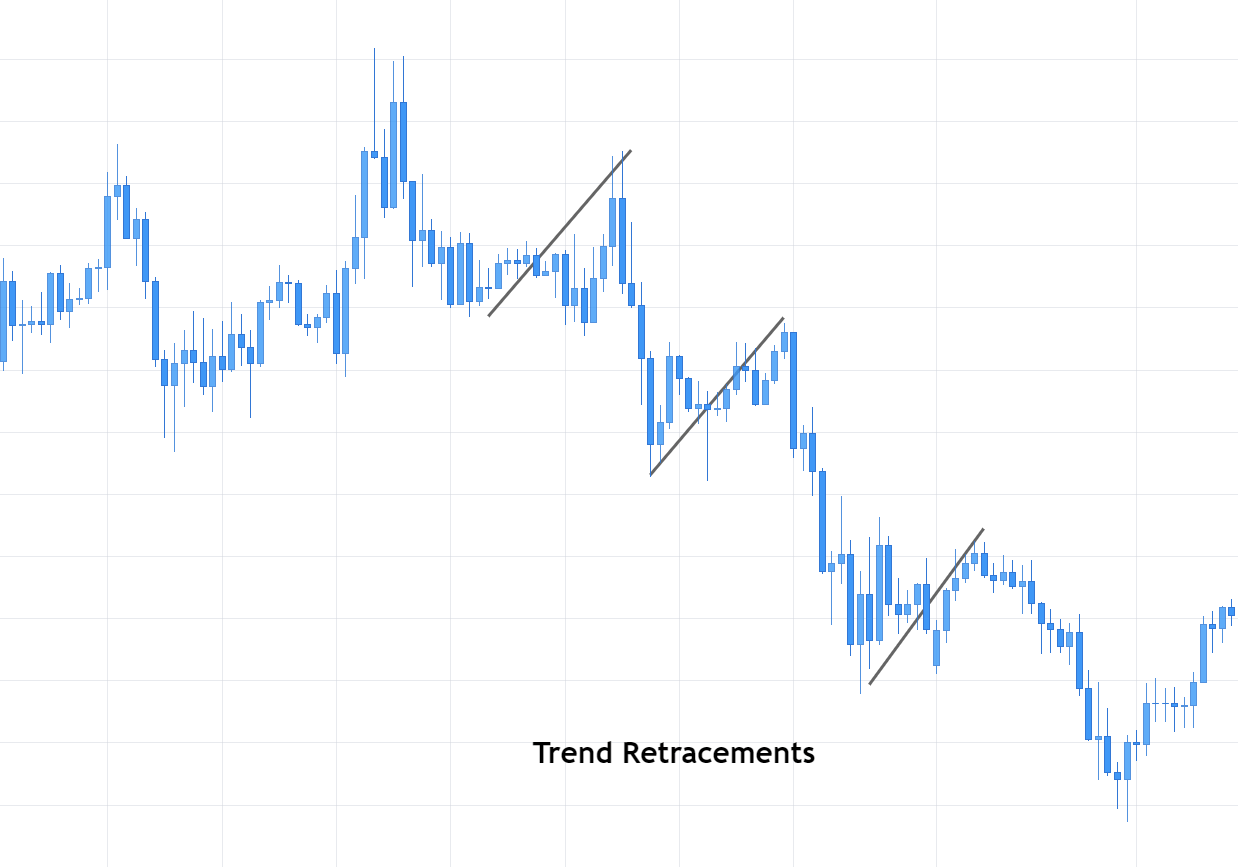
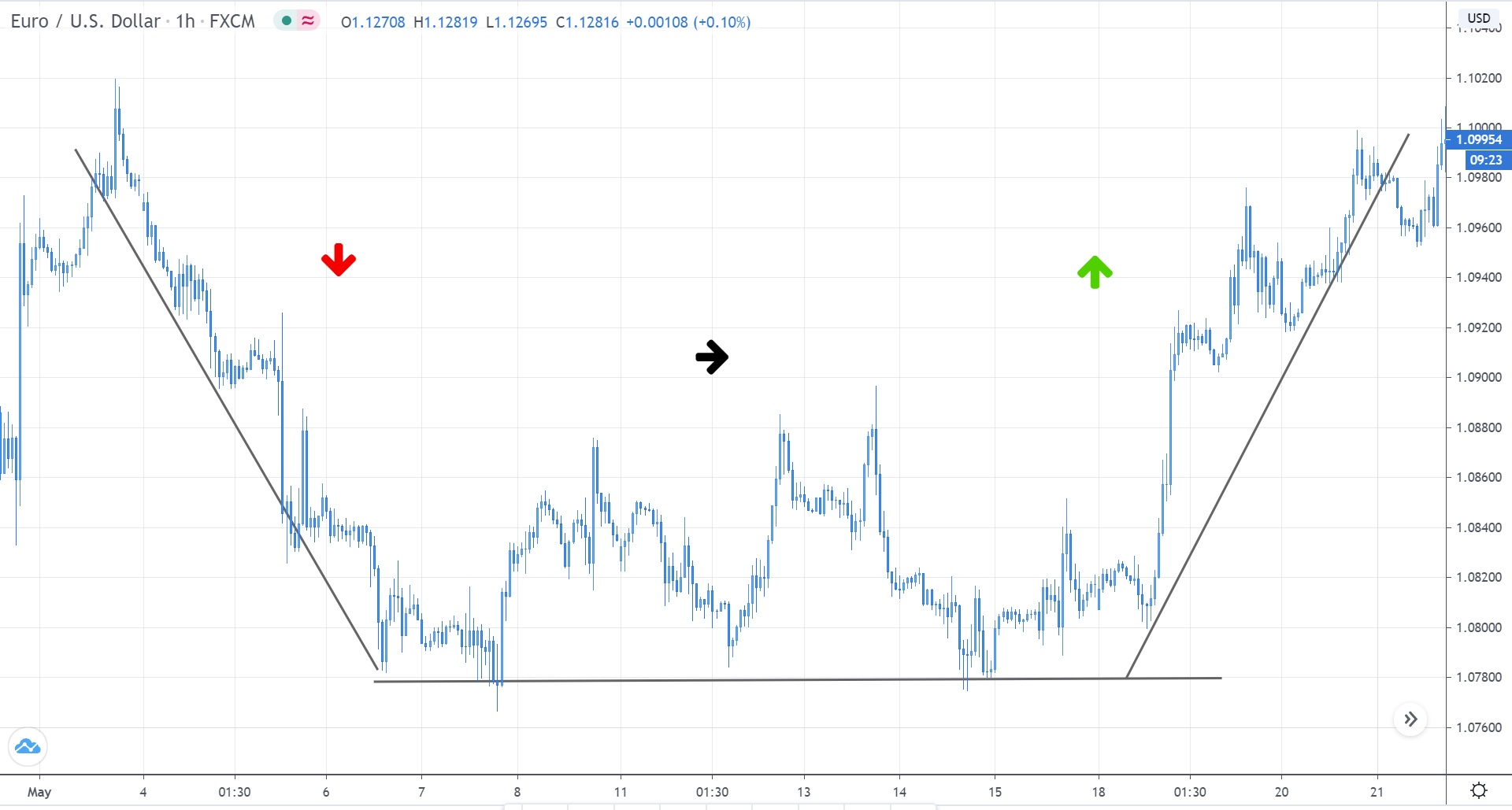
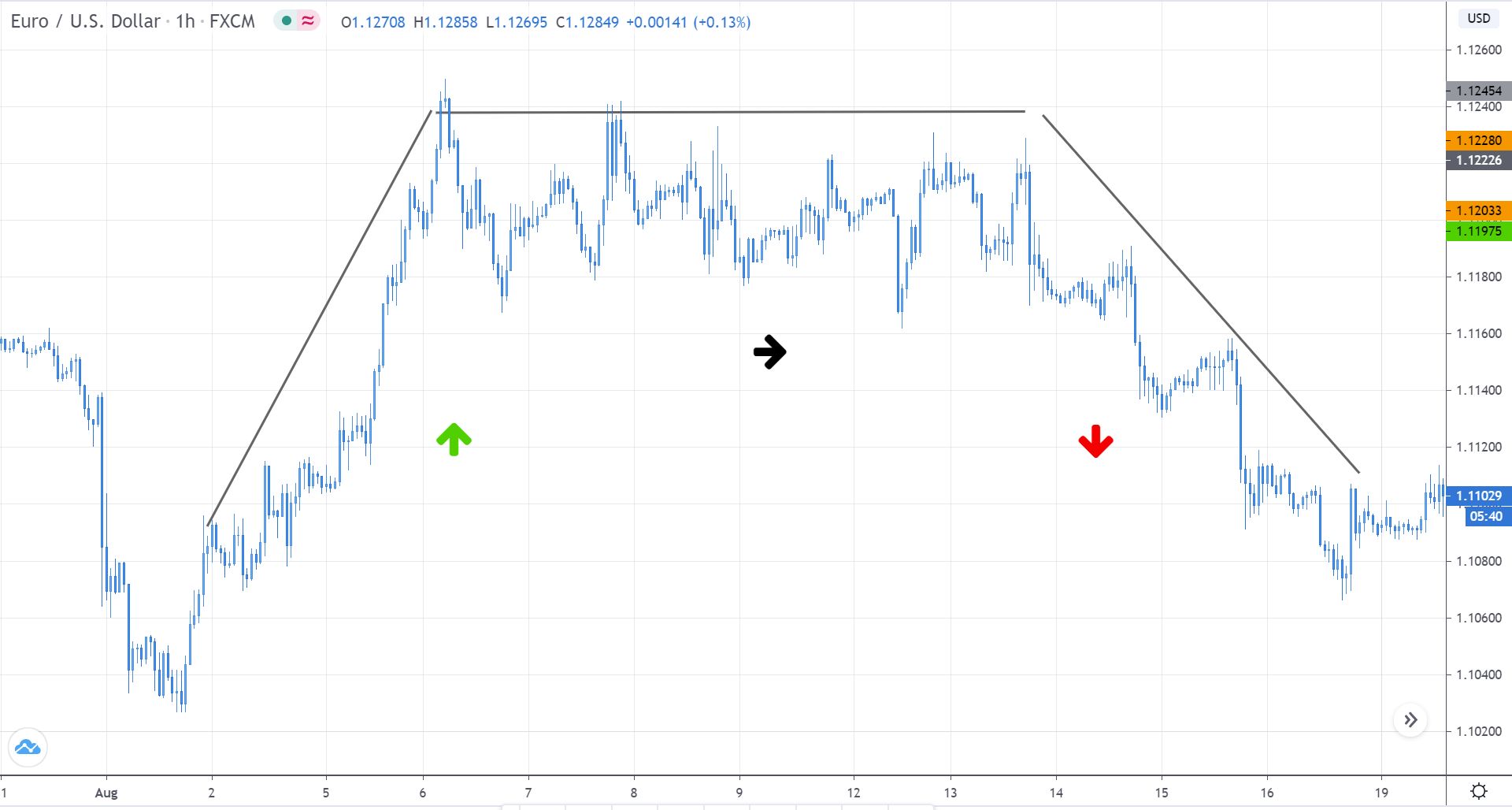
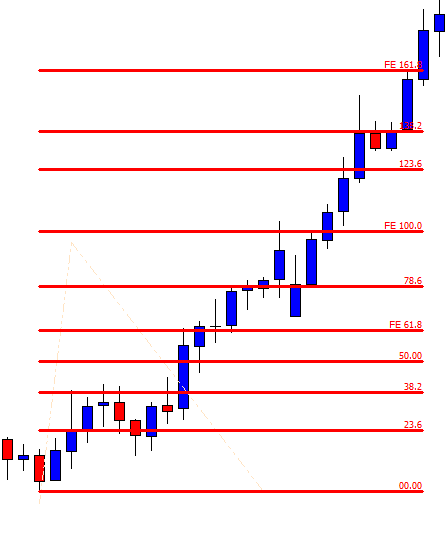
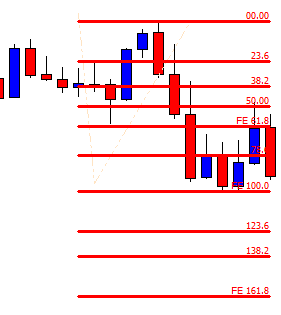
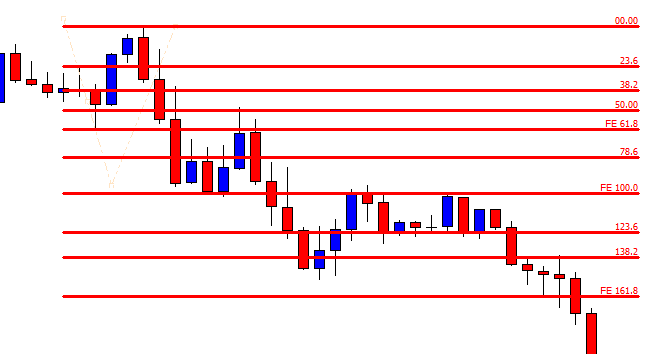
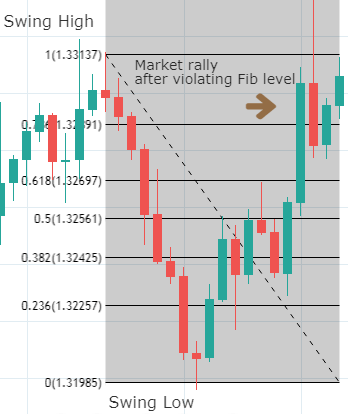
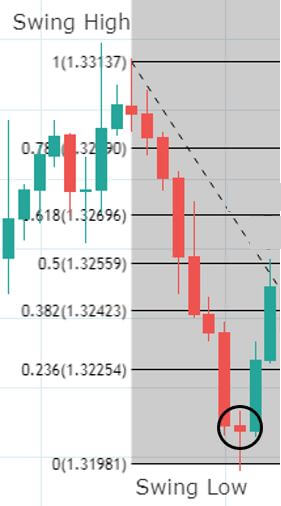
As it shall be further developed throughout this article, the first step when applying the Fibonacci method to construct support and resistance levels of a broader price trend is to identify and connect lower and higher points of wave impulses before a bullish move, and higher and lower points when the move is bearish.
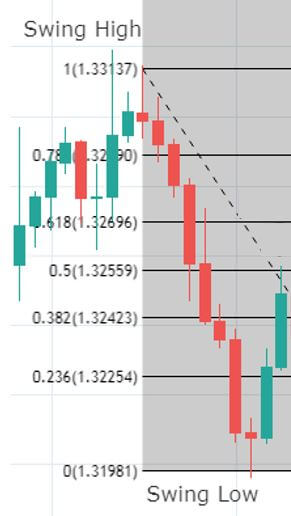
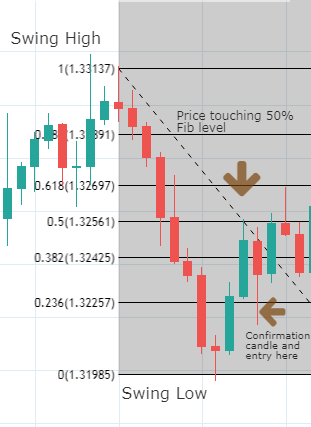
It is important to notice that Fibo percentages of any range when taken from high to low and from low to high correspond to 100. For example, as it is shown in the graph below, if one connects the higher and lower price levels of a bearish wave, the distance between the highest point and the 61.8% retracement equals 38.2% retrace if the connection was to be made from the lowest to the highest points in an inverted symmetric wave. In other words, Fibonacci retracements determine portions of the wave that coincides to 100 when summed up, so that the high price is to 61.8% as the lowest price is to 38.2%. The observation described above has immense implications when attempting to predict the strength of price after a breakout of a given cluster in concordance with other analytical tools. For instance, a 61.8% retracement would indicate that the counter-move is deep enough for us to regard price as losing steam in a broader trend so that a break higher or lower is more likely to complete the 38.2% extension. After all, Fibo ratios are, like any other technical tools, instruments of price prediction and not written-in-stone dogmas.

The graph above is taken on the USD/CAD and shows the simplest process of connecting the highest and lowest price points of a bearish wave in order to determine resistance levels of a possible retracement move.
When applying Fibo techniques to determine support and resistance price levels, it is important to avoid the following very common mistakes:
- Not any High or Low should be plugged with every Low or High to construct resistance or support levels respectively. The reason for this is that;
- Not every time interval has the same robustness, i.e., faster time-frames could see the complete counter-move as profit-taking without negating the impulse of a broader trend while a smaller counter-move of a broader time-frame could also be the completing of a broader wave.
- Depending on the chosen time-frame of the graph, a wave can be completed or not, thus the Fibo levels are correctly or incorrectly constructed. For example, some authors suggest that it is best to build Fibonacci retracements levels in ranges that include strong price impulses; or ranges when a subsequent sub-wave marks the final thrust of the price.
- The time validity of any Fibo setup depends on both the underlying time-frame of the graph and the degree with which a charted range has developed. Put it differently, when considering price as a “living entity”, it is relevant to notice that every technical setup is valid to a certain point and time.
Consequently, constructing Fibo retracement is far more complex than simply connecting some random Highs with Lows or Lows with Highs. Albeit the popularity of Fibo techniques, mainly due to its predictability power, they are only a method that should, in fact, be combined (better to say, completed) with other techniques. The cornerstone of Fibo retracement (and extensions) relates to the degree of robustness of the resulting pivots in terms of the strength with which such price levels succeed in preventing price breakouts, i.e., how well they serve as thresholds that manage to “hold” price within a given range in time and frequency.
It is typically assumed that robust support and resistance levels are the results of using Fibo tools from different divisions and sub-divisions of a certain price range. In other words, any price wave (i.e., oscillation) can be circumscribed in broader waves when observing the chart in a slower time-frame. For example, an 800-pips wave on a monthly chart could easily contain 10 sub-waves on a daily chart and 100 mini-waves. By incorporating slower charts, i.e., wider ranges, we achieve more robustness to the analysis. Adding multiple time-frames allows us to transform simple price levels into clusters and when such areas prove to consistently contain price, they become pivots.
A multi-dimensional approach is belonging (in its simplest form) to a third analytical methodology known as relational. Every trader must print robustness to the price levels he constructs so that a faster and more frequent scalper would combine the 5, 15 and 60 minutes charts while a long-term and more fundamental oriented trader would consider the 4 hours, daily and weekly charts. That leads us to the assumption that there is no “correct” or “incorrect” way to apply Fibo when building up supports and resistance levels; a construction is better or worse depending on how much it fulfills the needs of the trader.

In the graph, you can see how the Fibonacci retracements should be applied if you want to find market resistance. Also, you can see that the market respects on several occasions important Fibonacci percentages such as 38.2%, 50% and 61.8% over the monthly period.
In the second example, you can see how Fibonacci retracement should be plotted to find market supports. The range was drawn from the bottom to the top of a bullish trend before subdividing the range to find market supports.

How to find the range to apply Fibonacci if the market is constantly expanding and shrinking continuously and the oscillations are not symmetrical? To start creating the ranges, there are occasions where the market gives the starting points to locate these ranges. For example, when there are gaps in a bearish market, you can locate the 50 Fibonacci percentage right in the middle of the gap trying to get it aligned. But it is not enough to align the line of 50% with the gap, it is necessary to observe that the high and low prices and the subdivisions are respected by the market in different horizons of time. For this, the subdivisions must be plotted to the axis so will be easier to see if the market has respected these points in its various oscillations. In addition, some points of the subdivision although they have not generated a rebound of the market, can be areas where it begins to develop a strong trend whether bullish or bearish.
After the correct range is selected, the question arises as to whether Fibonacci subdivisions within the range are major resistances or supports. To answer this, you must define a second range with the same starting point of the previous range, but with a different length. When these two ranges have been created, an entry goal will be generated that is called a confluence zone (i.e., price cluster). This area of confluence is formed when different Fibonacci ratios of several ranges overlap each other, showing that there are areas where Fibonacci levels fall at the same market price, it should be clarified that they are not necessarily the same percentages of the ranks.
The confluence areas are tipping points in the price and these areas determine higher supports or resistances. Already knowing the areas or prices that are major resistances or supports, it will be possible to project the direction of the market in the future because it will be known which areas will generate a rebound in the market, or if it is the case that the market breaks it will trigger a strong movement when the market continues its tendency without rebounding. With this knowledge of important points, you can put stop loss points if the market rally takes an unexpected direction or if it exceeds areas of confluence.
To be more confident which will be the correct direction of the market, we need to create a third rank with their respective subdivisions. When the third rank is made in the market, we must be sure that its subdivisions have been respected by the market in the past more than once to ensure that they are not minor resistances or supports. With the third range already made, it will be possible to see sometimes that there is more than one zone of confluence between the subdivisions of the ranks. A key element will be to locate the stop-loss outside of the confluence zones because if it is located between these will not achieve the goal of stopping the losses but possibly stop the gains if a rebound is generated in the areas of confluence. It is also important to mention that Fibonacci ranges should be larger when the trade is long term to be able to observe the entire market panorama than in a short-term position and therefore also the stop loss point will be farther away in long-term horizon operations.
For example, the following graph shows the EUR/USD with three ranges traced with Fibonacci retracements. As you can see, there is a confluence zone around the price 1,19949 since several of the subdivisions of the ranks coincide at this point, forming a major resistance as it began to trace from a low price to different high prices. Another example to see the stroke of the three ranges and their confluence zones is the next graph of the AUD/USD, where you can see several areas of confluence that will be major supports given the way the ranges were plotted from a high price to different low prices. Below the area of 0.89870, there is a major support as well as the level of 0.69470.


©Forex.Academy