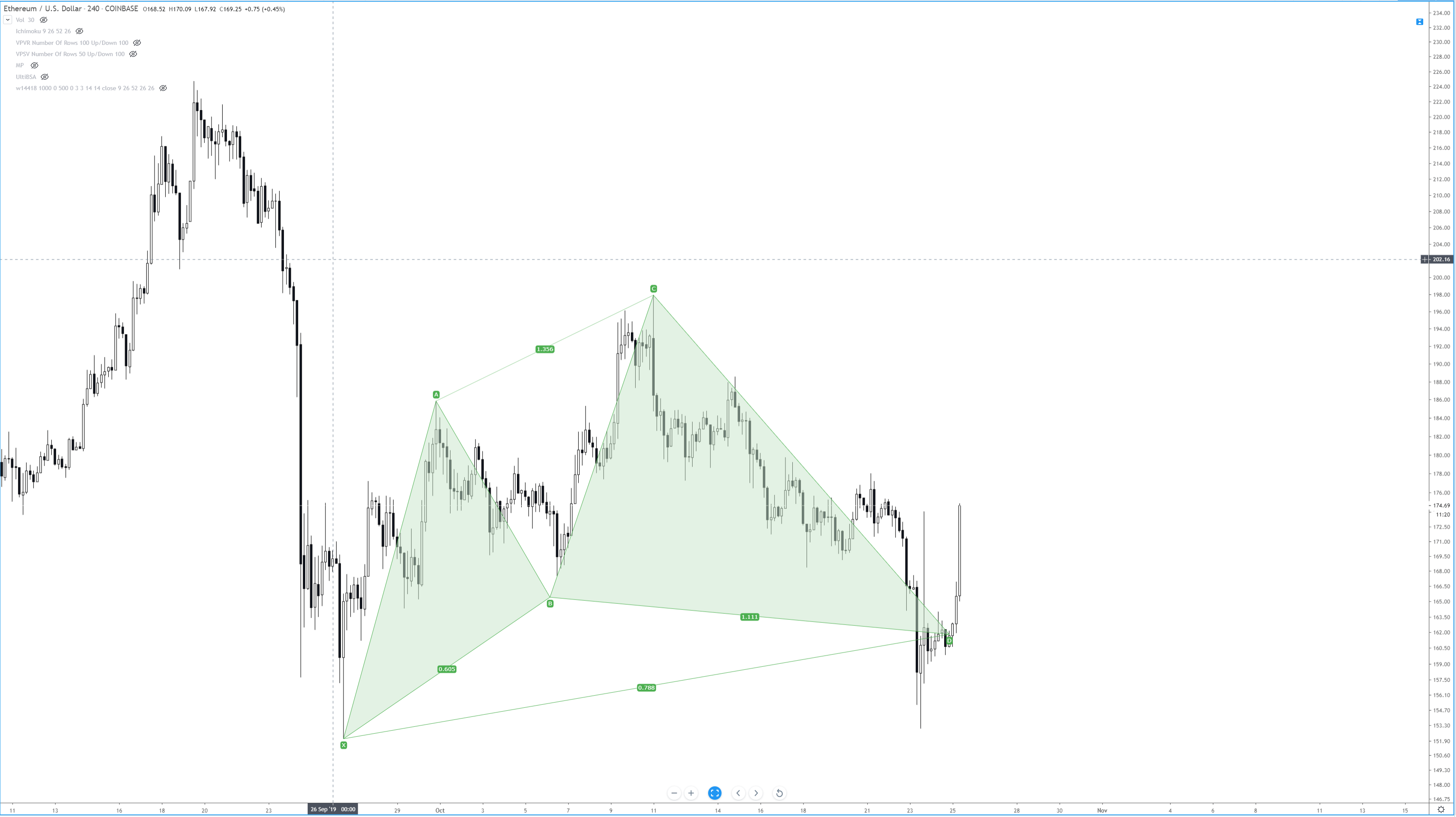
The Cypher Pattern
The Cypher Pattern is another type of Harmonic Pattern – except it isn’t – but it is. This is one of the few patterns not identified by Scott Carney. Darren Oglesbee discovered this particular pattern.
This pattern is very similar to the Butterfly in both it’s construction and where it typically will occur (near the end of trends). However, the Cypher Pattern is a rare pattern and not one that shows up with a high amount of frequency. Don’t confuse rarity with being more powerful or profitable. I do not know enough about this pattern, nor have I had the opportunity to trade it enough to gauge it’s ‘power’ versus its peers. All I do know is that in the times I have traded it, its positive expectancy rate is high, no different than a Bat or Alternative Bat in my experience. The same goes for the Crab and Deep Crab, for that matter. Just like all of the other Harmonic Patterns that you will have learned about, the Cypher has specific rules and conditions that must be met for it to be a specified Cypher pattern.
Cypher Confirmation Conditions
- B must retrace to an expansive range between 38.2% and 61.8% of XA. At least 38.2% but not exceeding 61.8%
- C is an extension leg and moves beyond A – but must move to at least 127.2%, but it is normal for it to go as far as the 113% – 141.4%. It is considered invalid if it moves beyond the 141.4%
- CD leg should break the 78.6% level of XC.
- The PRZ (Potential Reversal Zone) of D is a wide range where the price must get to. Price can move anywhere between 38.2% to 61.8%.
I’ve created a simplified approach to how to ‘see’ this pattern.
Simplified Approach (Bullish Cypher)
- C must be higher than A.
- D must be less than B but greater than X.
- We should see a higher high (C > A) and a higher low (D > X).
Simplified Approach (Bearish Cypher)
- C must be less than A.
- D must be more than B but less than X.
- The same approach as above, reverse: lower high (D < X) and a lower low (C < A).
This pattern can be confusing (all harmonic patterns can be complicated), but in a nutshell, what we see happening with the Cypher pattern is the first pullback/throwback of a trend (B). After B, the small pullback/throwback of B occurs with the C leg. From a bullish perspective, when we see prices making lower highs and lower lows, but there is no follow-through shorting pressure, we should be on the lookout for some powerful and influential moves to occur in a very short period of time. It is not uncommon to see a bullish candle engulf several days of consolidation with this pattern.
Sources: Carney, S. M. (2010). Harmonic trading. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Financial Times/Prentice Hall. Gilmore, B. T. (2000). Geometry of markets. Greenville, SC: Traders Press. Pesavento, L., & Jouflas, L. (2008). Trade what you see: how to profit from pattern recognition. Hoboken: Wiley.