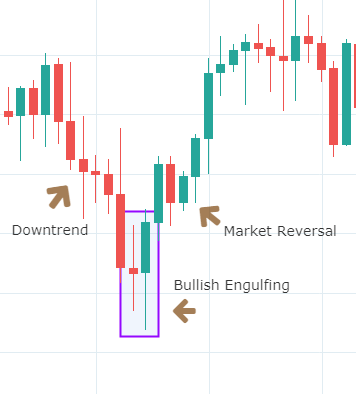
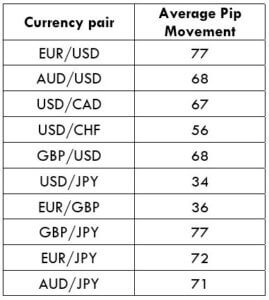
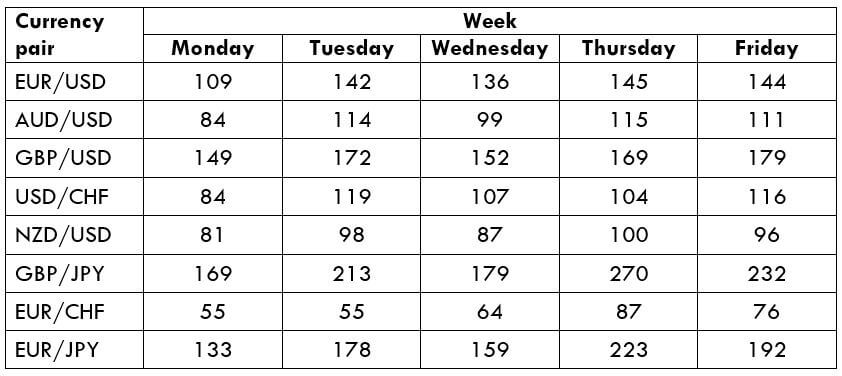
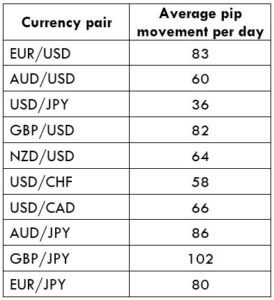
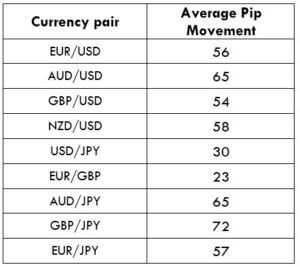
What is a Pivot Point?
The pivot point is a technical indicator that shows the levels typically used to determine the overall trend of the market in different timeframes. These points are essentially used by professional traders to identify support and resistance levels. As a retail trader, one must keep an eye on these levels to identify potential buy/sell signals. To put in simple terms, the pivot points and its corresponding support and resistance levels are places at which markets can possibly change its direction.
The reason this indicator is very enticing is because of its objective. Unlike other technical indicators, there is no decision making involved. The Pivot Points are very similar to the Fibonacci levels. This is because these levels are pretty much self-fulfilling. However, there are some differences in some respects, which shall be discussed in the next section.
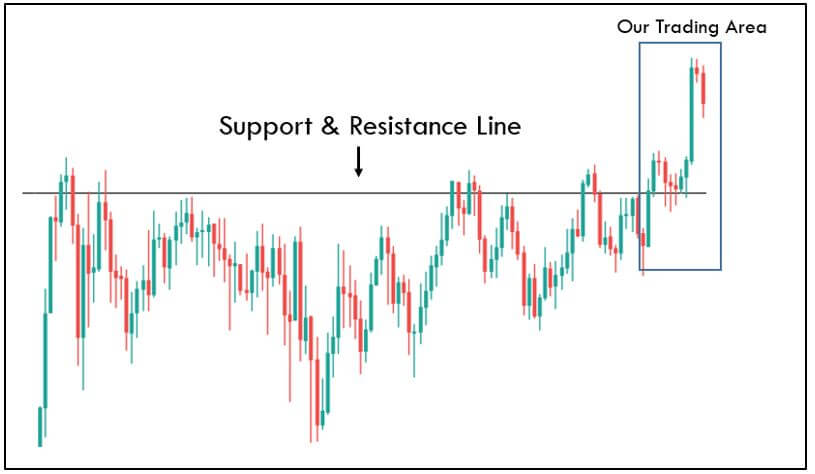
It is important to know that the pivot point indicator is mostly designed for short-term traders who wish to take advantage of small price movements. The technique to trade this is similar to that of trading support and resistance, where we participate in the market on a break or bounce from these levels.
The Difference between Pivot Points and Fibonacci Retracements
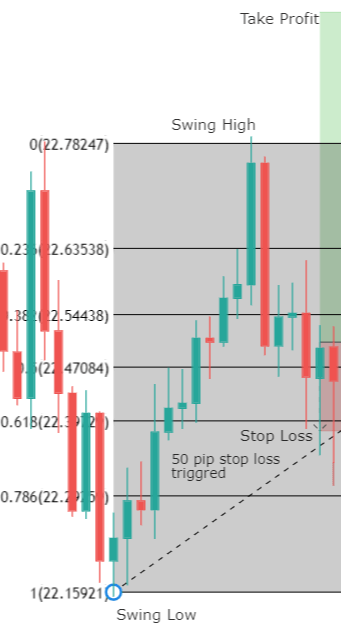
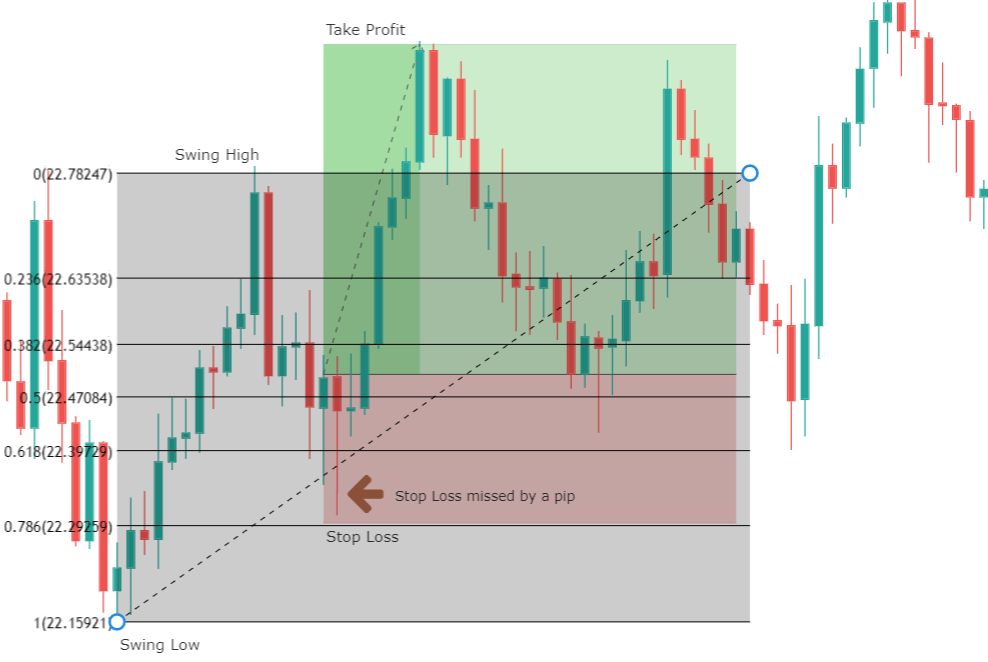
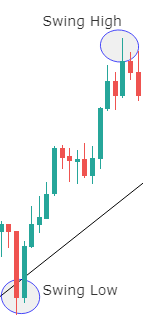
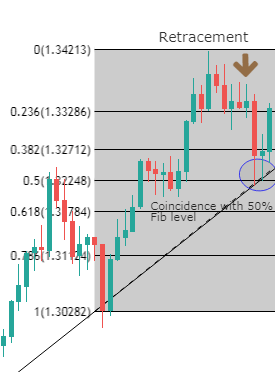
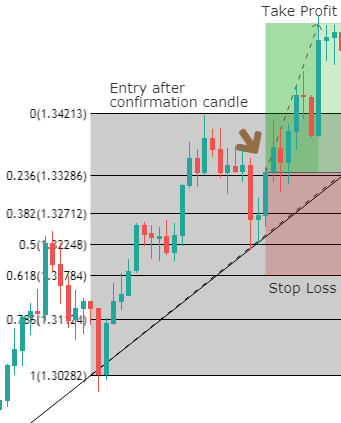
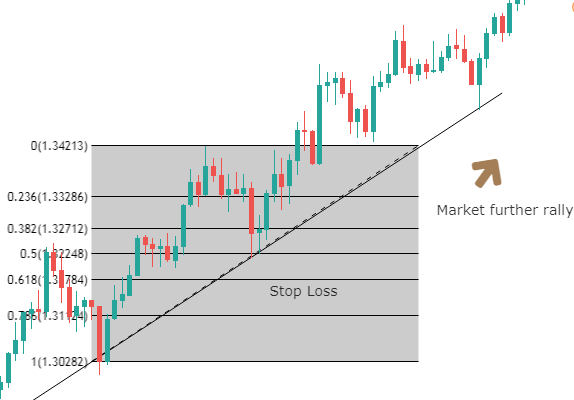
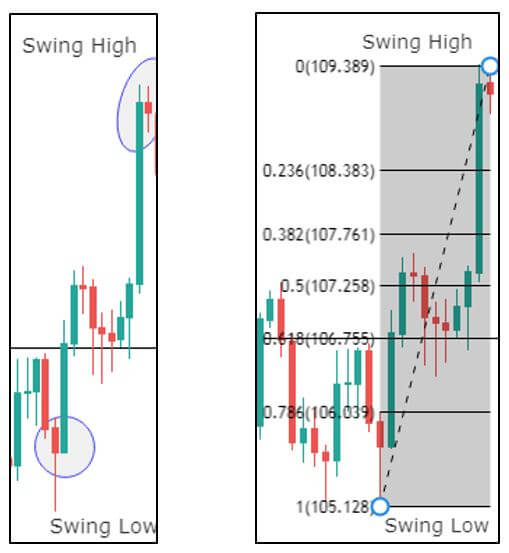
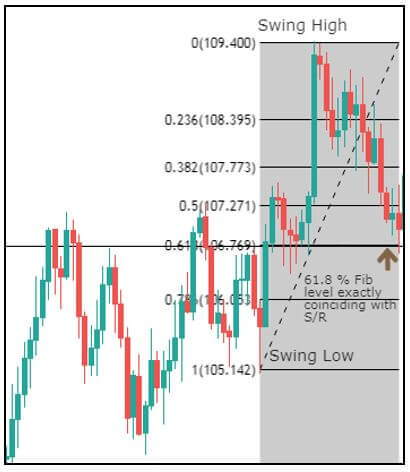
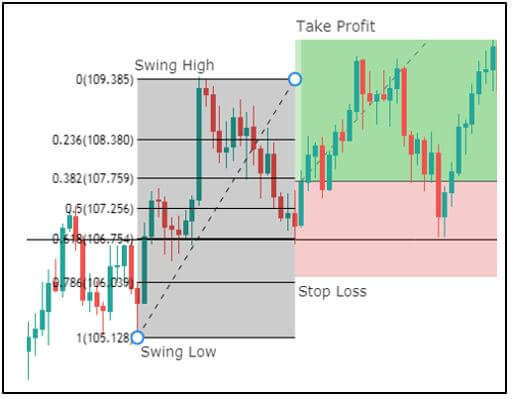
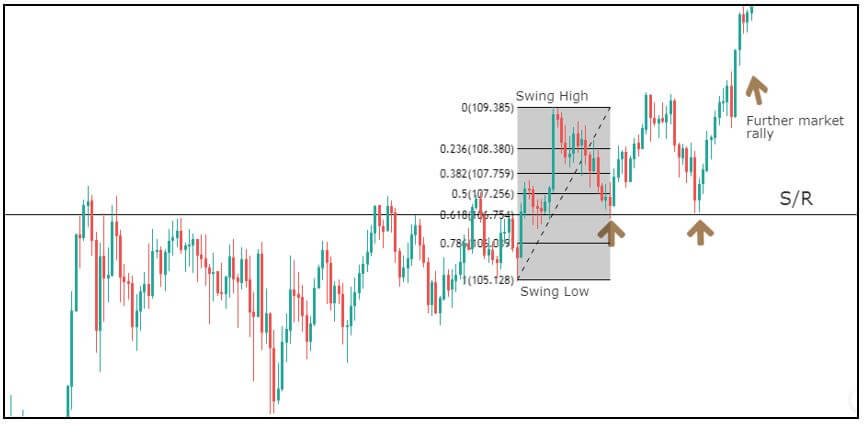
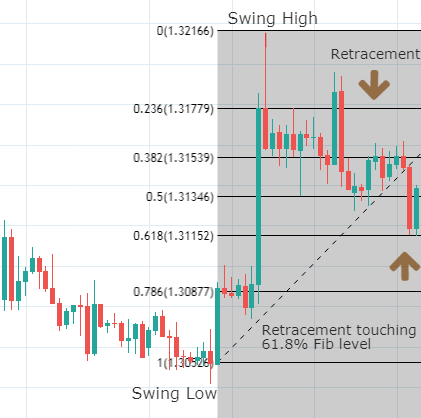
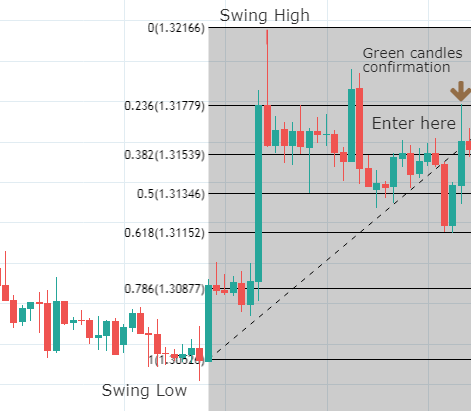
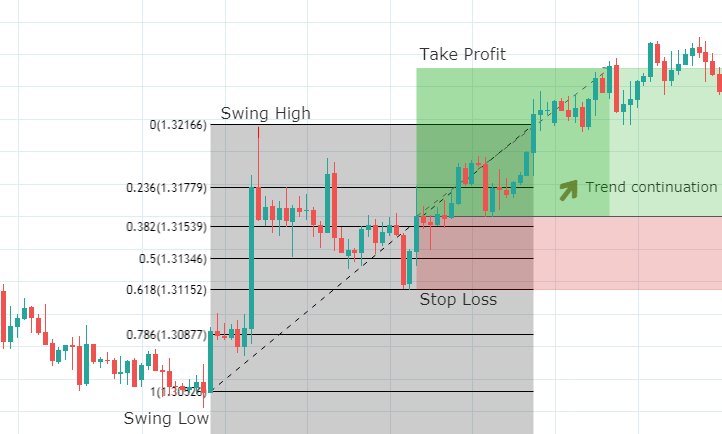
Though Pivot points and Fibonacci retracements are made by drawing horizontal lines to depict potential support and resistance levels, there vary in few aspects. In Fibonacci levels, there is subjectivity involved in picking the swing lows and highs. But, in pivot points, there is no discretion involved.
In Fib retracements, the levels can be constructed by connecting any price points on a chart. Once the levels are determined, the lines are then drawn at percentages of the selected price range. In the case of pivot points, fixed numbers are used instead of percentages. And the fixed values are the high, the low, and the close of the prior day.
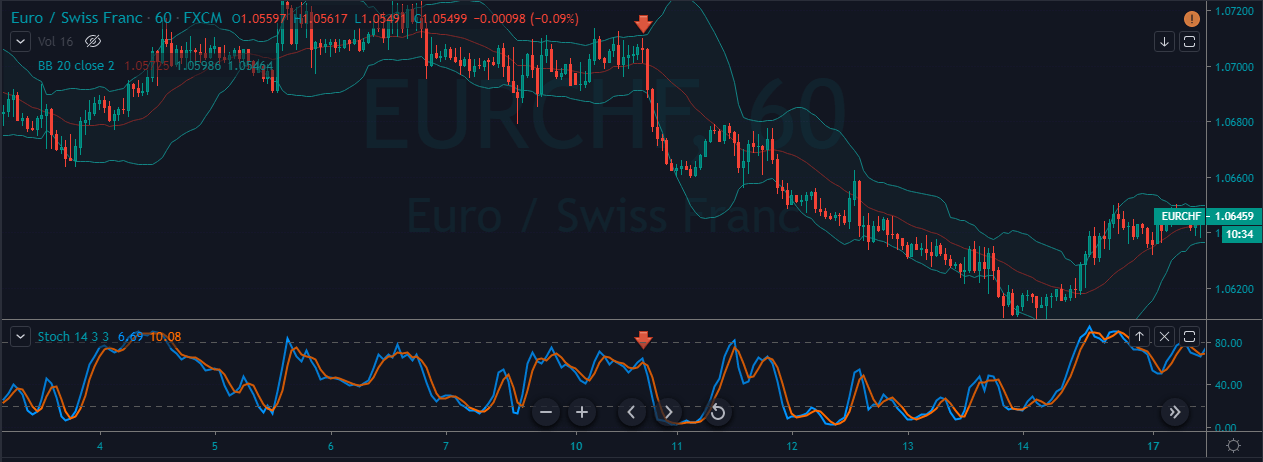
Interpreting Pivot Points
Pivot points indicator is typically used by traders who trade the market using technical analysis. This indicator can be applied to the Stock, Forex, Commodity, Futures as well as the Cryptocurrency market. This indicator is unique from the other indicators because it doesn’t move with the price action.
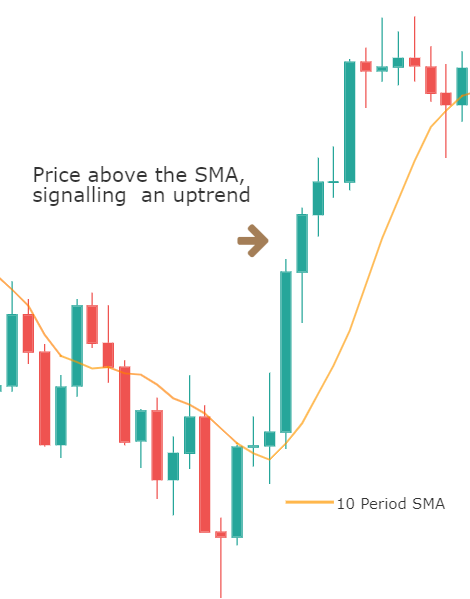
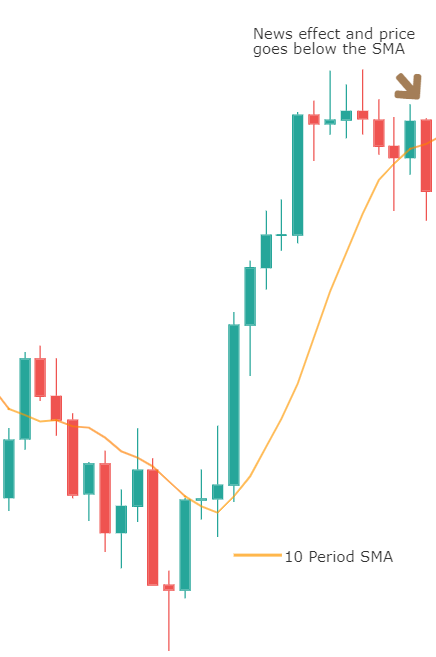
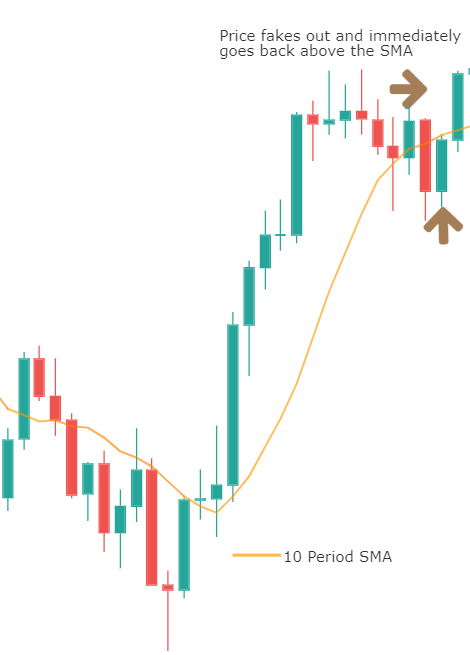
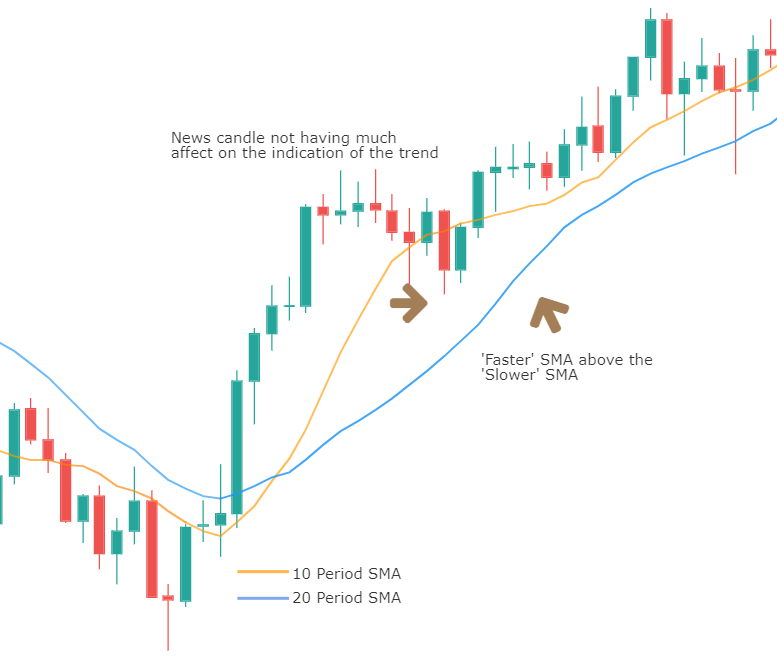
It is static, and the levels drawn remain at the same prices throughout the day. This means that traders can plan their strategy much in advance. For example, in most of the approaches, if the price falls below the pivot point, traders will go short on the security. And similarly, if the price goes above the pivot point, they will look for buying opportunities.
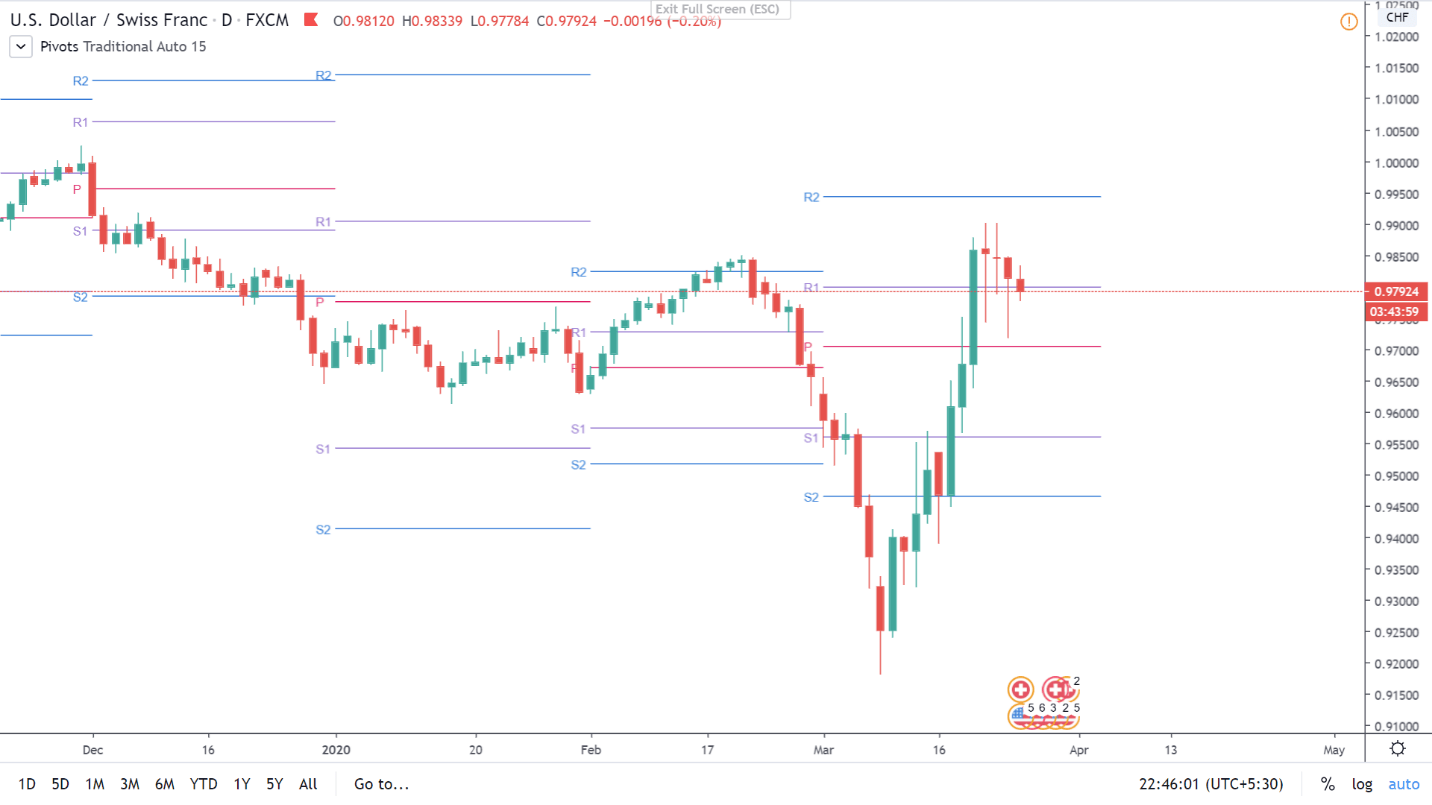
How do Pivot Points look?
When the standard pivot points are applied to the charts, it will look something like this (as shown below).
In the above chart, P stands for Pivot Point | S stands for Support | R stands for Resistance
There are R1, S1, R2, S2, etc. as well, but it shall be explained in the upcoming lessons. Stay tuned!
[wp_quiz id=”69068″]