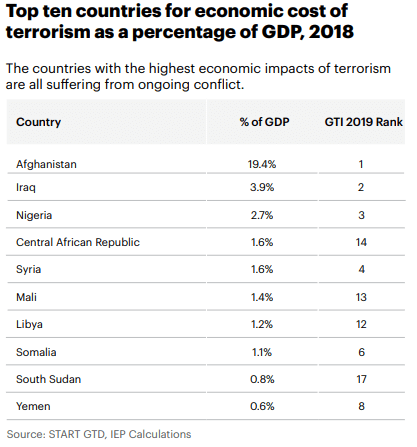
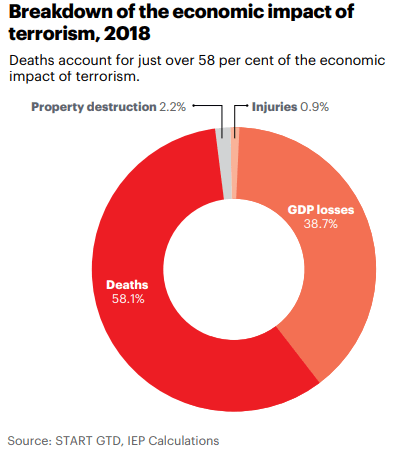
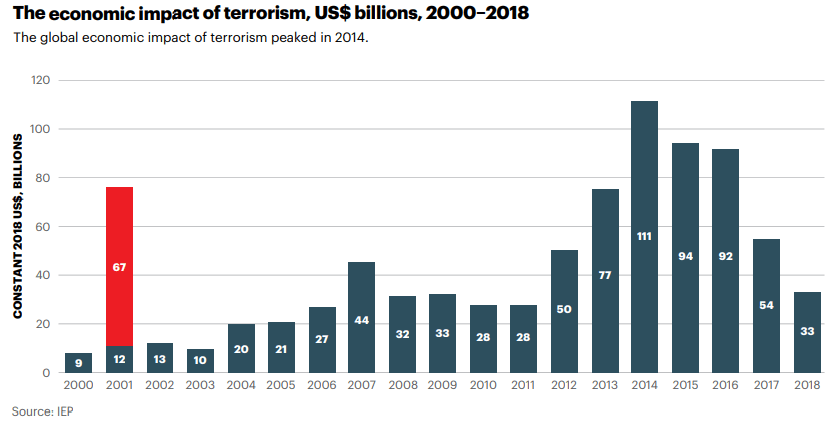
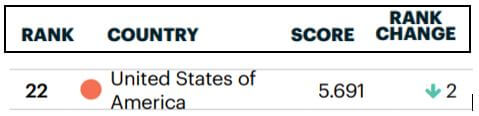
Introduction
Mining Production is a key economic indicator as the final output of Mining Production is the primary input for many industries. Therefore, it is the core part of many industries’ business activity.
Fluctuations in the Mining Production figures are bound to translate to all the dependent industries that use the Mined resources as input in their production process. The knock-on effect can be many-fold, and hence it is a vital economic indicator for investors, economists, and government authorities.
What is Mining Production?
Mining Production refers to the entire process of searching for, extraction, beneficiation (purification), and processing of naturally occurring minerals from the Earth. Mining is the process of extracting useful minerals by excavating into the Earth as these minerals cannot be produced on the surface. Minerals are essential for running society to a large extent.
Minerals typically drilled can be Coal, metals like Copper, Iron, Zinc, or industrial minerals like limestone, potash, and other crushed rocks. Coal remains one of the most significant sources of energy throughout the world. Metals like Iron, Copper have a wide range of usage in industries, from small chips in computers to construction of giant buildings. Limestone, Sand, and other rocks have used in cement industries, which all contribute to the construction and housing industries.
In the United States, the Mining Production figures are released as part of the “Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization – G. 17” report by the Federal Reserve. This report is also called the Industrial Production Index (IP Index) or Factory Output.
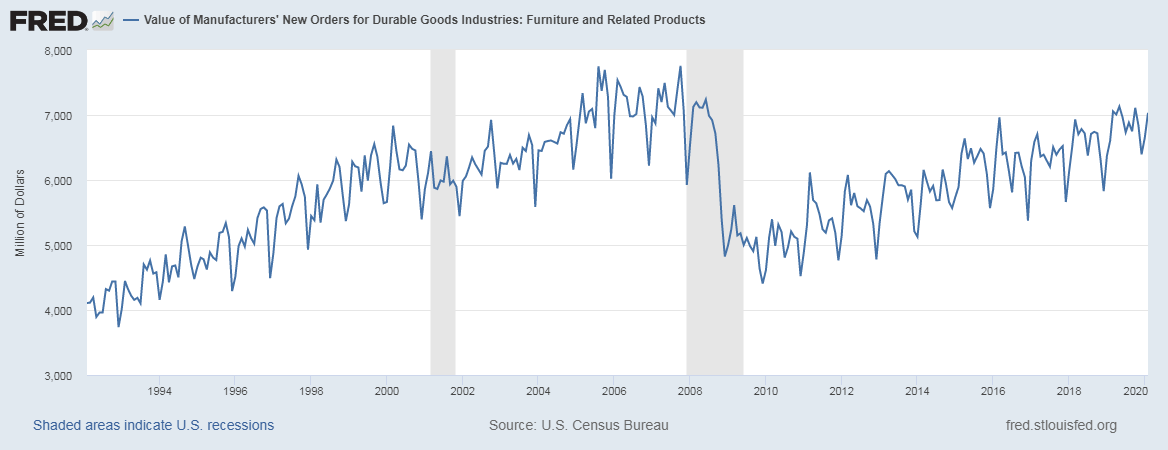
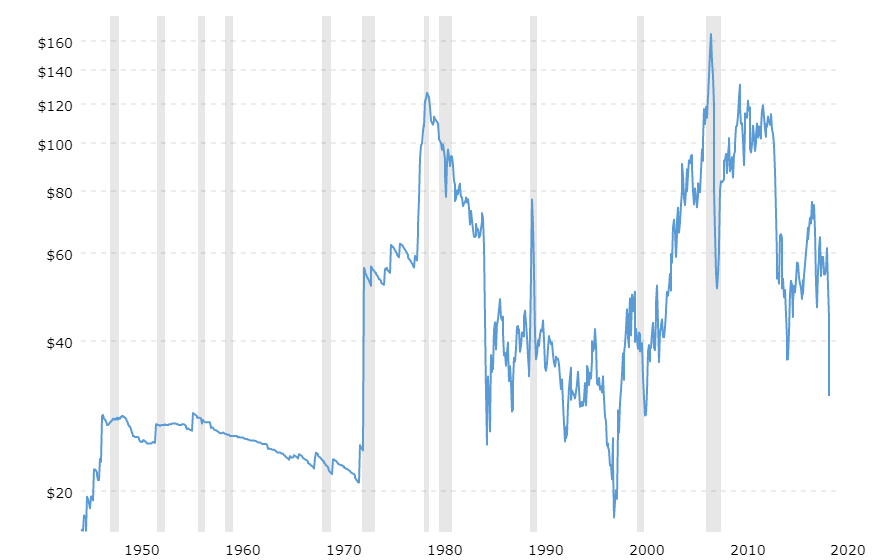
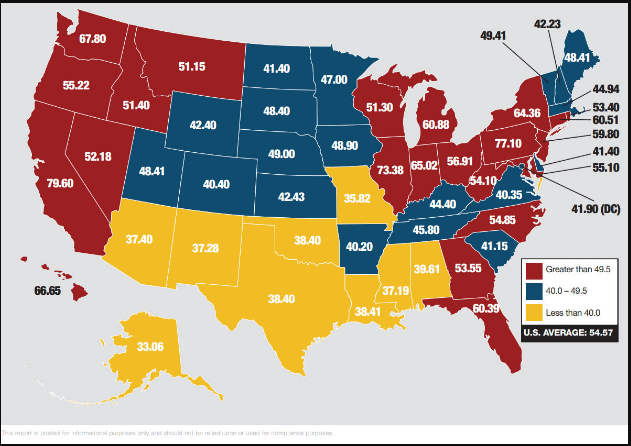
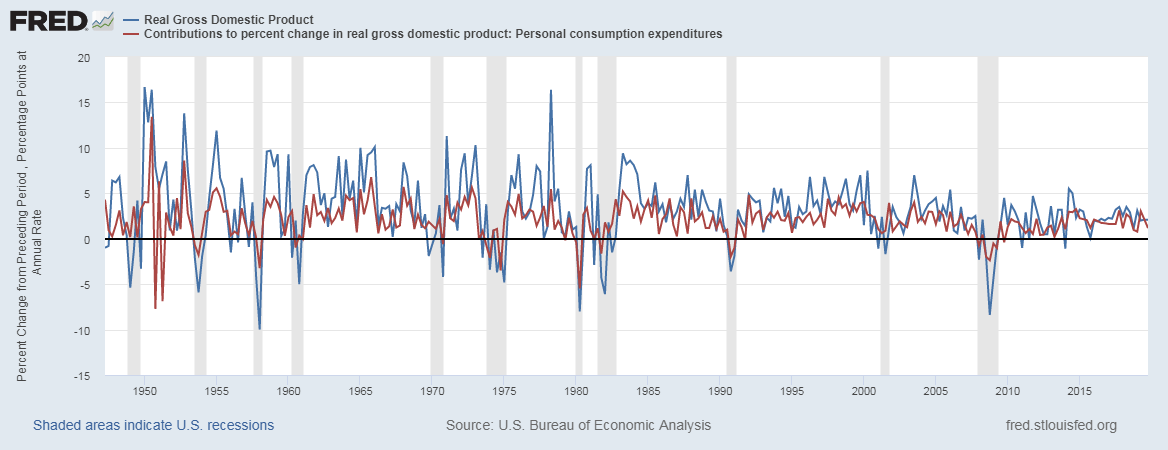
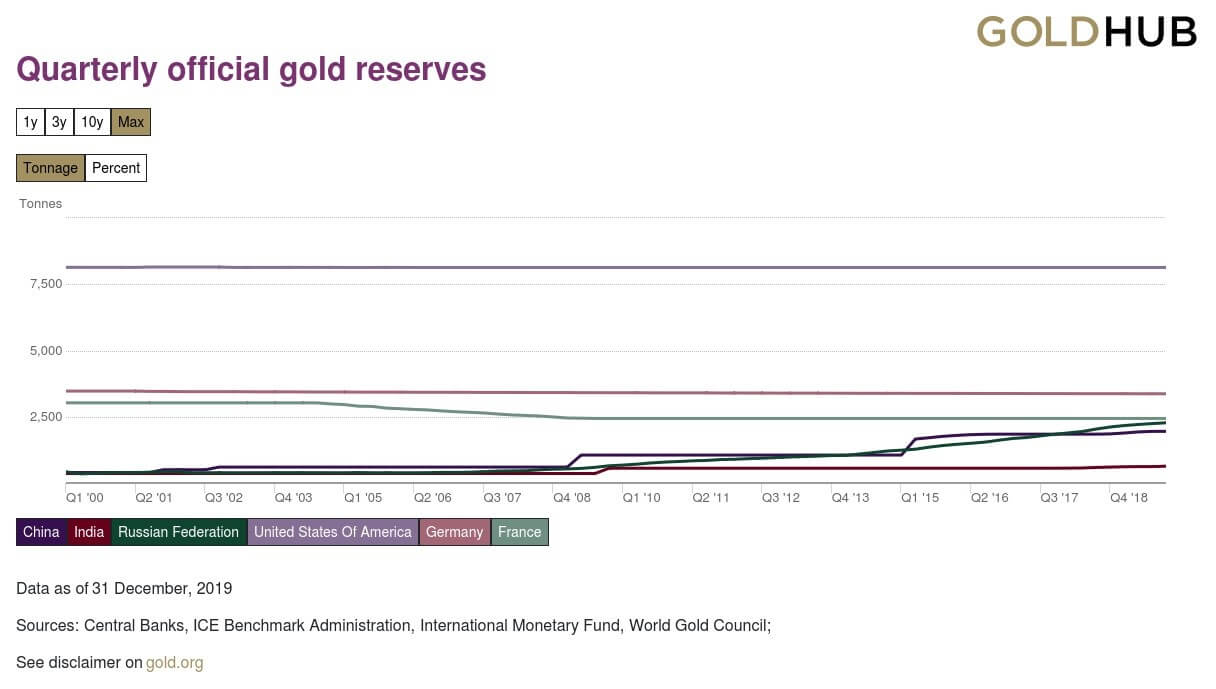
The Mining Production numbers are expressed in index and percentage change formats. The base year for the reference index period is 2012, for which the score is 100. Every month the Mining Production numbers are published according to this index. For example, an index figure of 130 indicates that Mining Production has increased in contrast to 2012 statistics. The percentage change compares the figures to the previous month. It is a seasonally adjusted statistic. The figure below illustrates the Mining figures dating back to 1920.
How can the Mining Production numbers be used for analysis?
Hence, it is apparent that Mining lies at the heart of all industrial activities. A decrease in Mining production can adversely affect all the dependent industries, and correspondingly the effects will pass onto unemployment, layoffs, wages, economic slowdown, etc.
Since the end products of the Mining Industry act as the starting input for many industries, it serves as a leading indicator for the economy. It lies at the very start of the economic activity chain, and the ripple effect through fluctuations in Mining Production figures will effect dependent industries with 1-6 months’ time lag depending upon the nature of dependent business.
Investors, government authorities, and economists extensively use the IP Index report for their purposes. Mining is the extraction of minerals that are essential for the economy; the government monitors and provides the necessary support to improve Mining Production. In 2006, the mining industry alone produced shipments worth 78.65 billion dollars, and that is excluding oil and gas. Coal accounts for 50% of electric power generated in the United States.
Mining Production is susceptible to some of the following:
Resource Availability – Since minerals are non-renewable resources, which means they are exhaustible. Once a region is depleted of the particular resource, search for new mining areas, relocation, and Mining again is expensive to process.
Weather – Bad weather conditions can interrupt Mining Production as it typically involves explosions and heavy drilling equipment. Heavy rains can close down mines and access roads. Lightning can put the massive equipment operations, explosion handling personnel at risk. Strong winds disrupt blasting. High temperatures can affect Mining workers.
Technology – The amount of latest and advanced mining technologies that are available at the disposal of the country determines the Mining Production cost and total output.
Terrain – The type of terrain that needs to be mined can also affect Mining costs and Production levels. Mining Industries are the leading employers at the place of their operation. Mining supports more than 500,000 jobs directly and an additional 1.8 million jobs indirectly through its dependent industries. Hence, wages, employment, economic activity, revenue generation, exports, energy consumption are all affected by Mining Production.
Impact on Currency
The Mining Production figure is a proportional and leading economic indicator. An increase in Mining production figures translates to stimulated business activity in the dependent industries, higher employment, wages, and improvement in economic activity. It will also generate higher revenue for the nation through exports of Mining Produced goods like Coal, Iron, etc. All this has a positive effect on the currency, and the currency appreciates. The reverse also holds.
Economic Reports
The Mining Production report is a part of the IP report that is published by the Fed every month. This report is published in the form of estimates with subsequently revised estimates. The first version/estimate is released on the 15th day of every month, and this shows the Mining data of the previous month. This is the major report as it factors in about 75% of the data. The next four estimates account for 85%, 94%, 95% & 96% respectively as the source data becomes available after each passing month.
Sources of Mining Production
The monthly Mining Production statistics are available on the official website of the Federal Reserve for the United States. The St. Louis FRED provides a comprehensive list of Industry Production, and Capacity Utilization reports on its website with multiple graphical plots. You can find this information here and here. We can also find global Manufacturing Production figures for various countries in statistical formats here.
Impact of the ‘Mining Production’ news release on the price charts
In the previous section of the article, we learned the Mining Production economic indicator and understood it’s significance in an economy. The mining industry is critical to a nation’s economic well-being. It influences the country on a regional and individual level, with significant dependence on the resources under development as well as government policies. The mining industry is today is opening up new opportunities for foreign investments and technical assistance. Mining also impacts employment opportunities and income generation. Governments and mining companies are working together to achieve these goals.

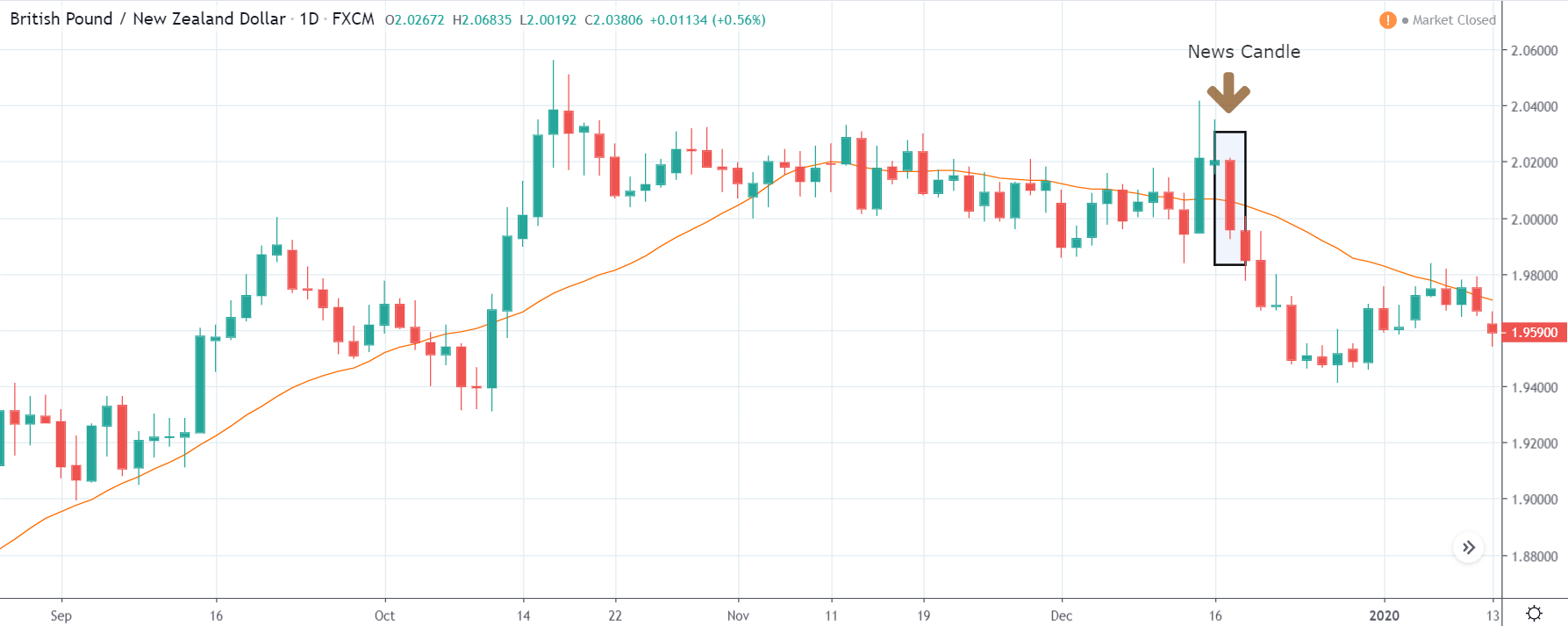
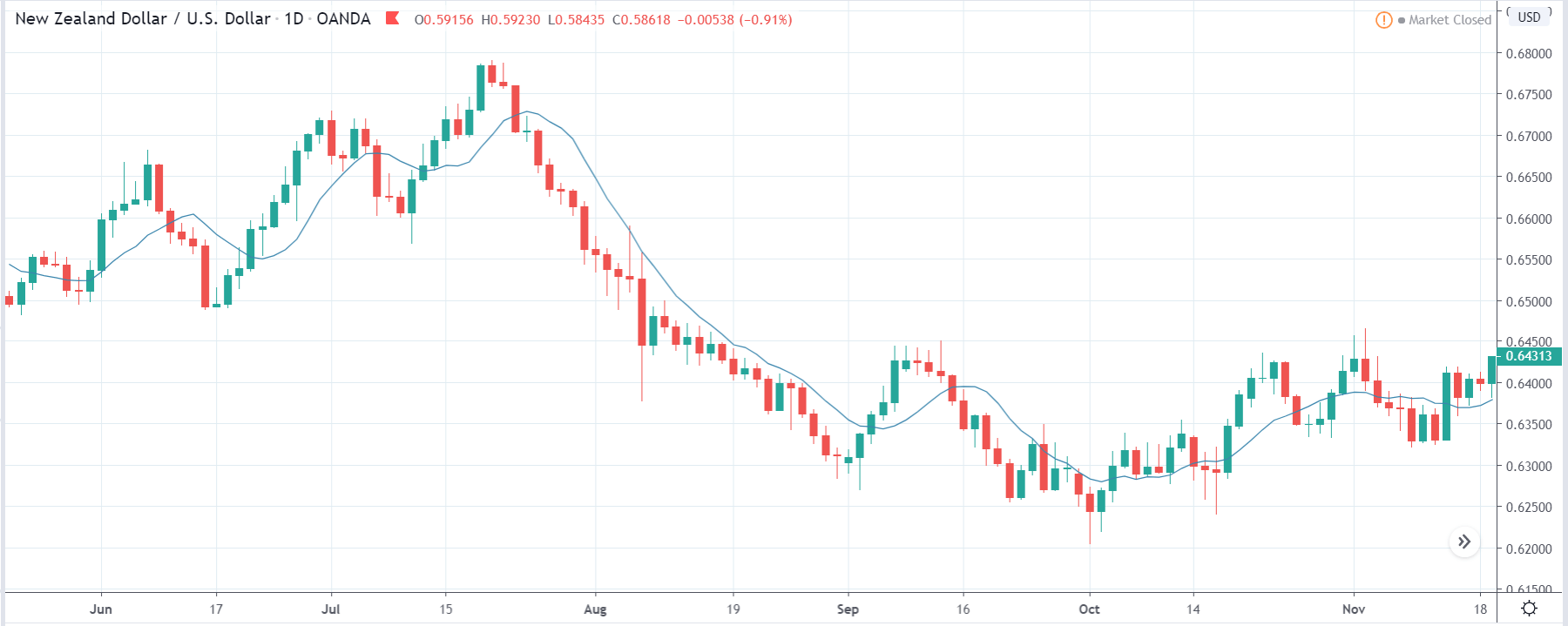
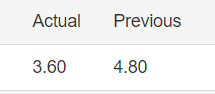
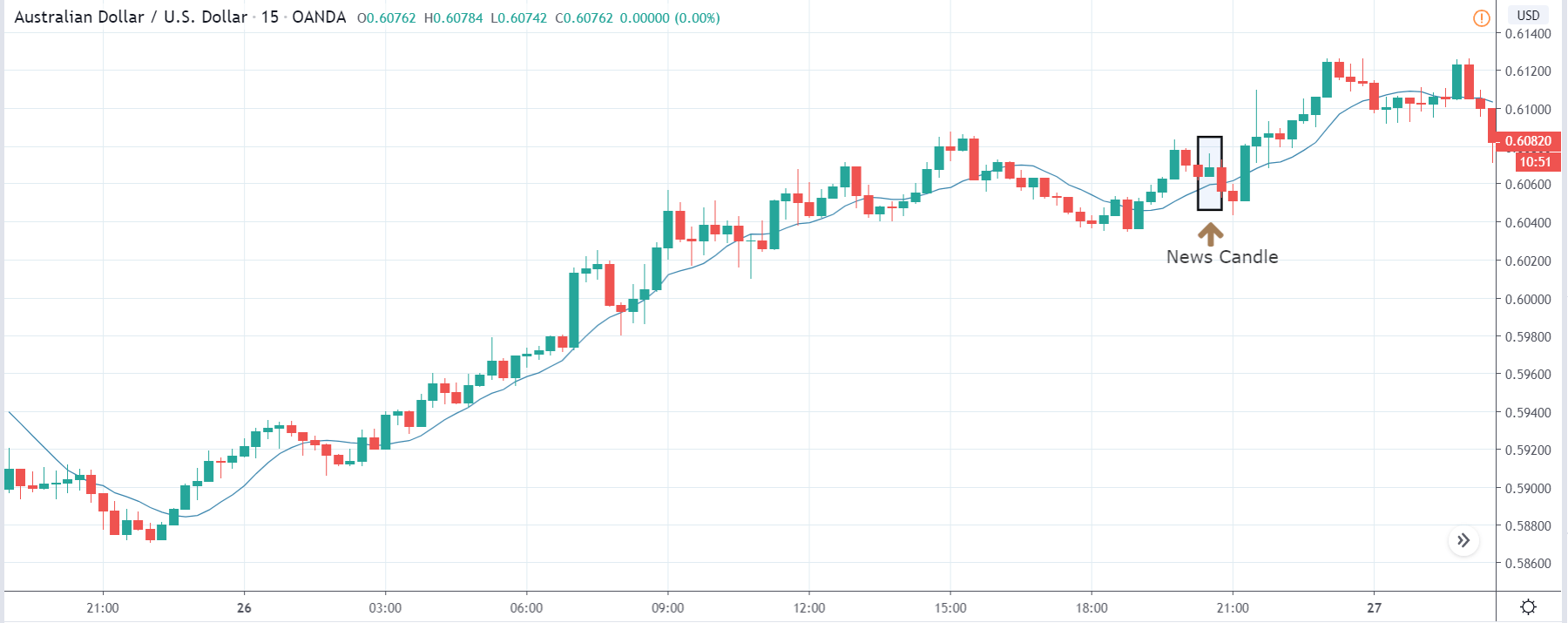
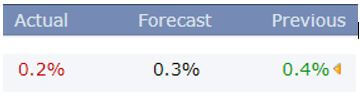
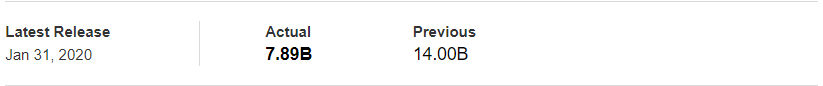
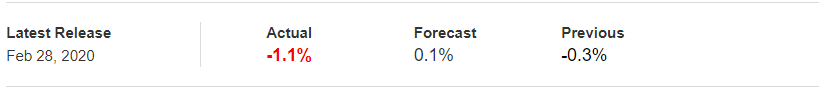
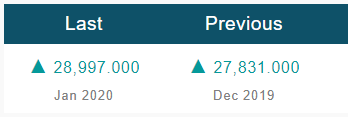
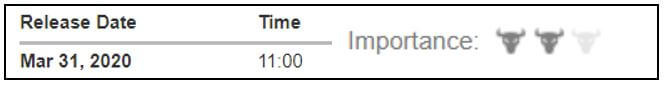
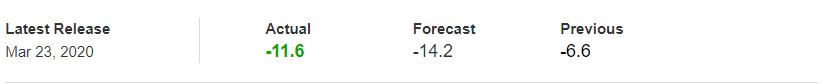
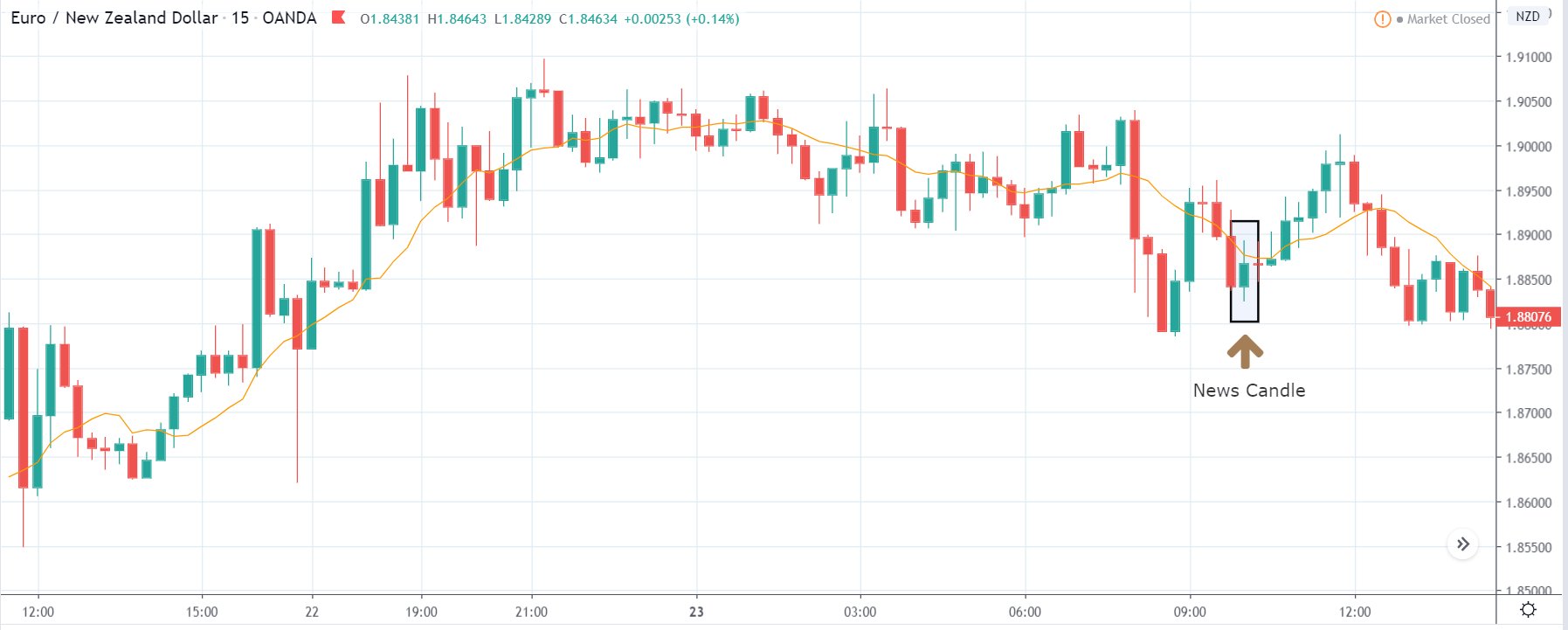
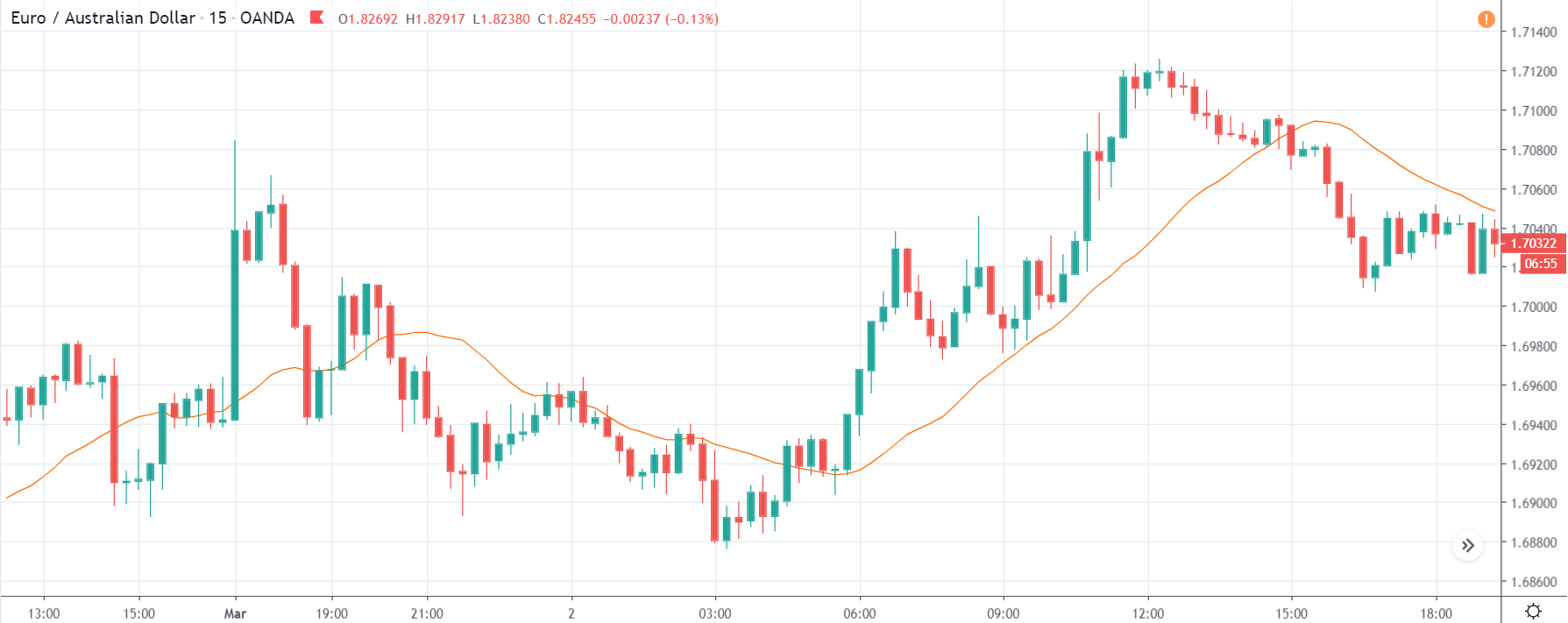
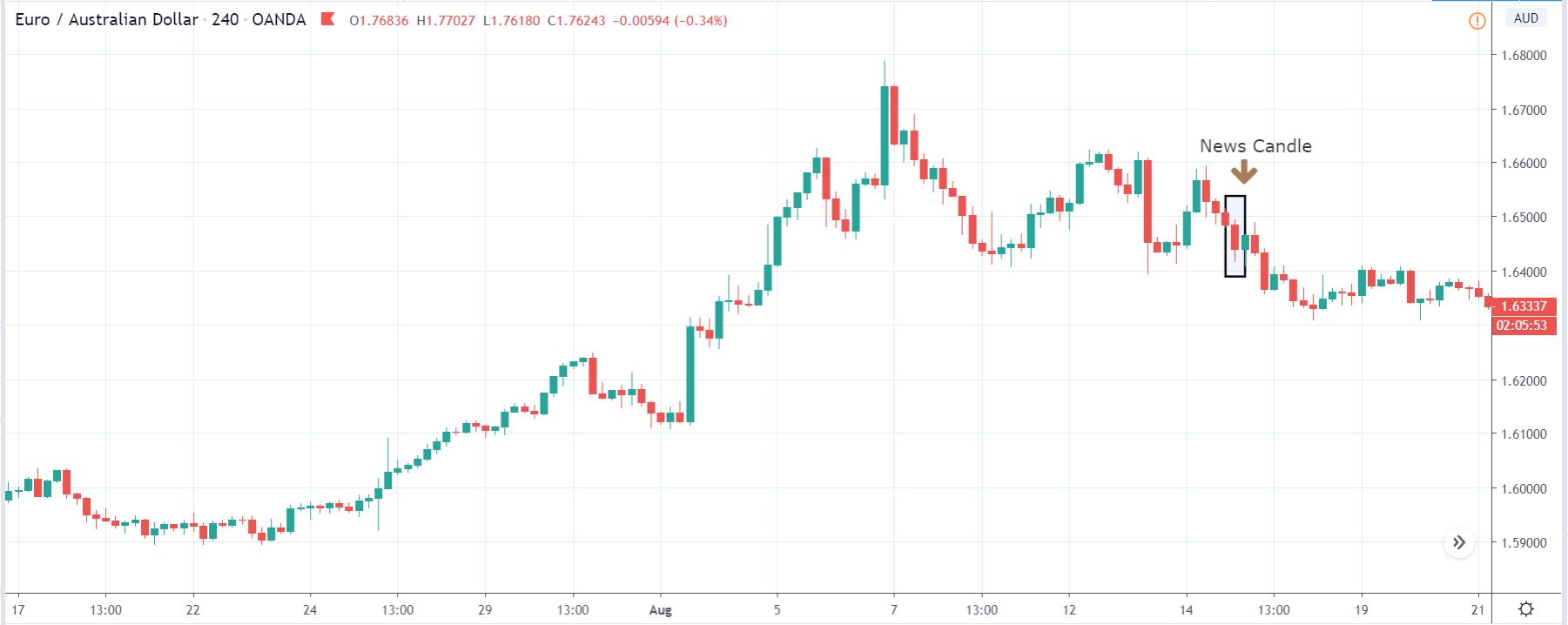
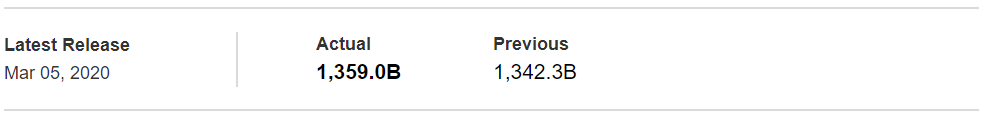
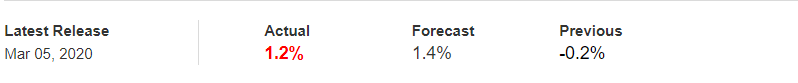
In today’s example, we will analyze the impact of Mining Production South African Rand and witness the change in volatility because of the news announcement. The below image shows that the Mining Production in South Africa increased 7.5% year-on-year in January 2020, following a 0.1% gain in the previous month and beating market expectations by a huge percentage. Let us see find out how the market reacts to this data after the news release.

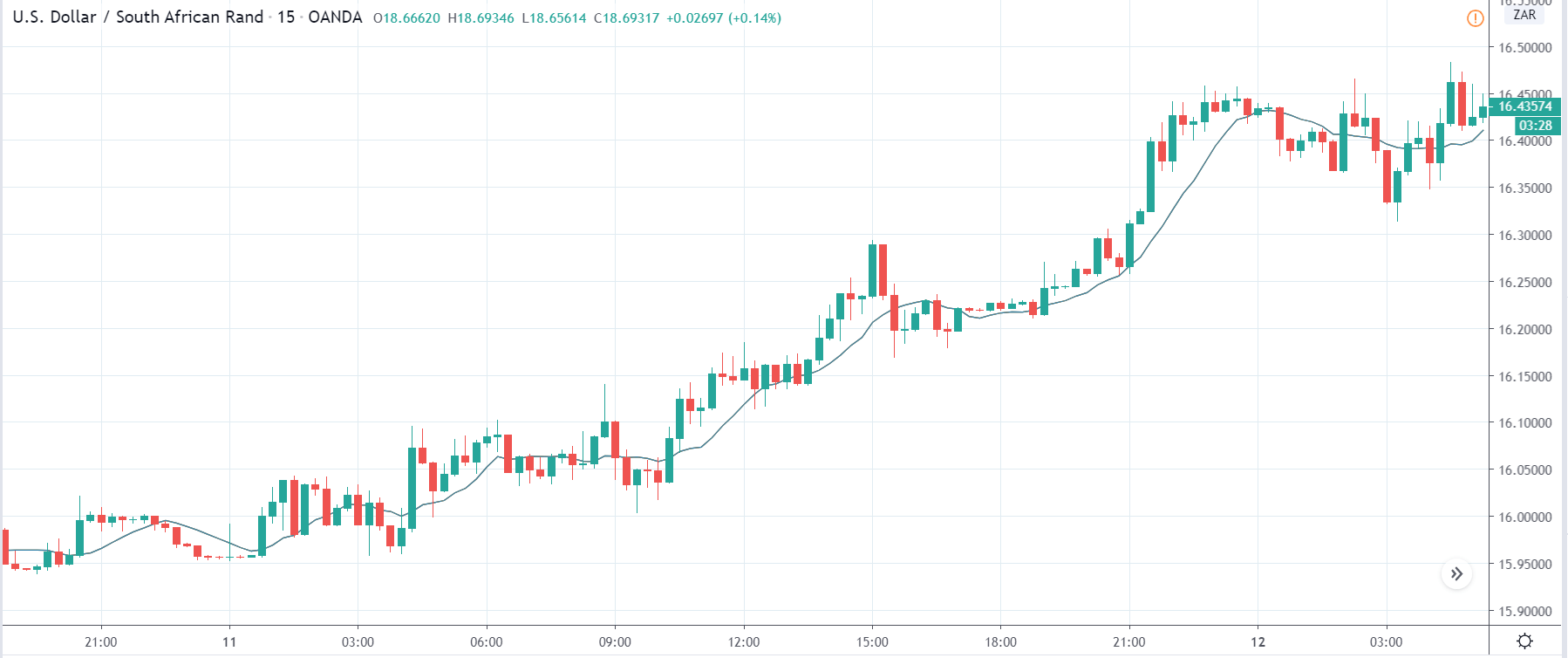
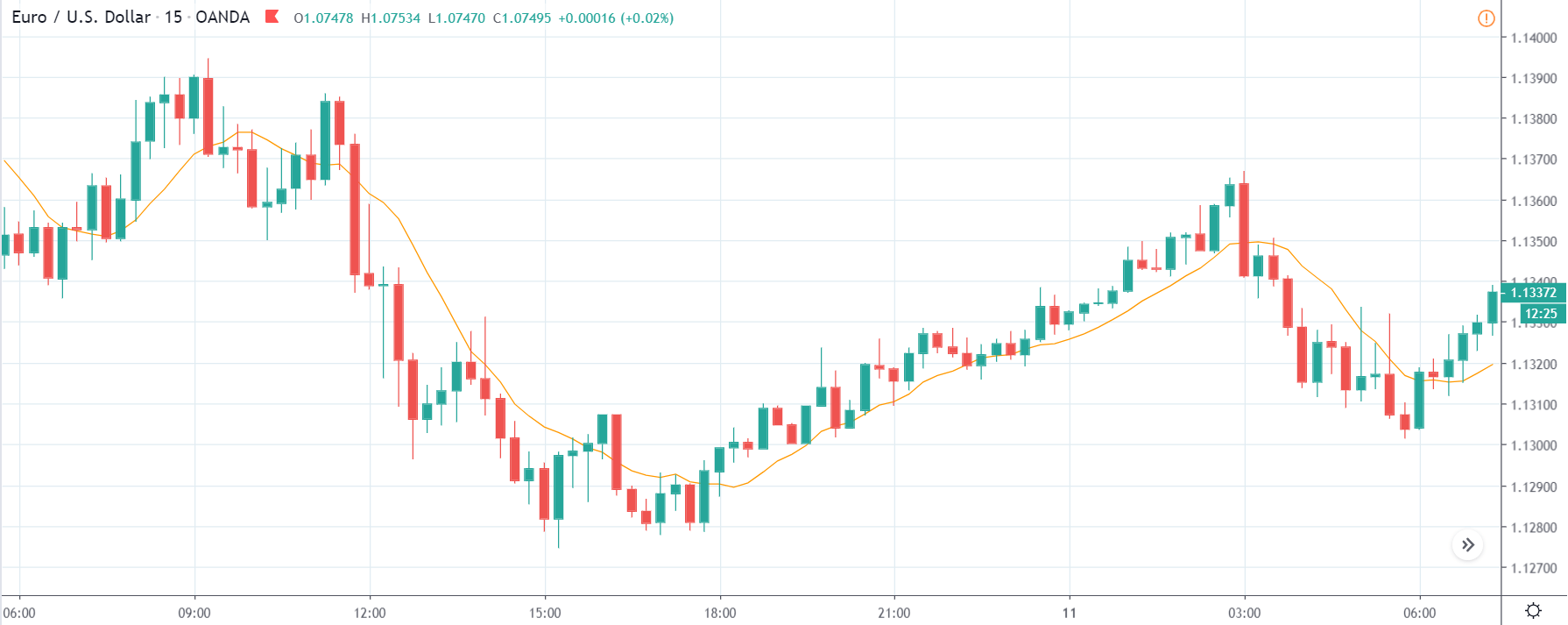
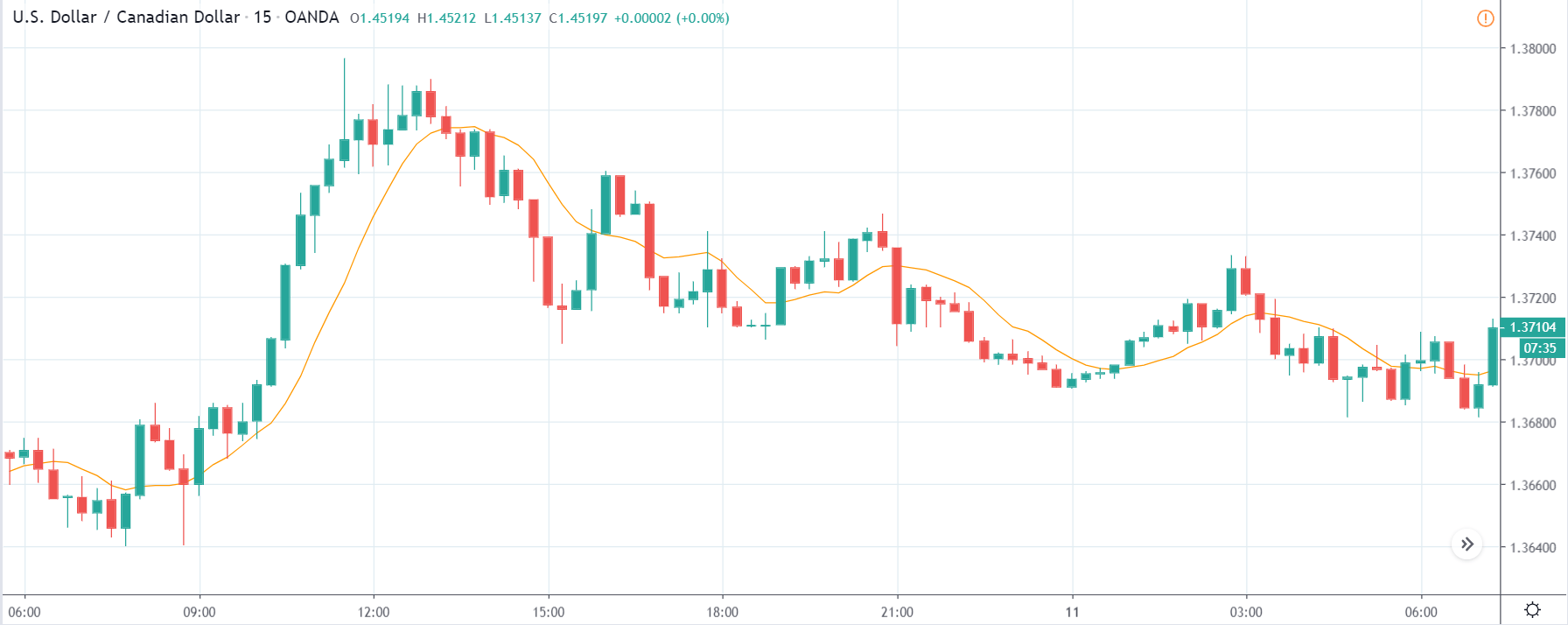
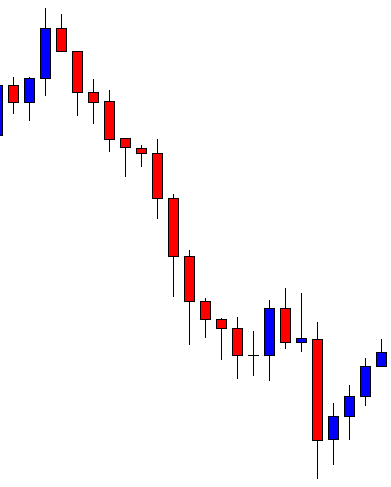
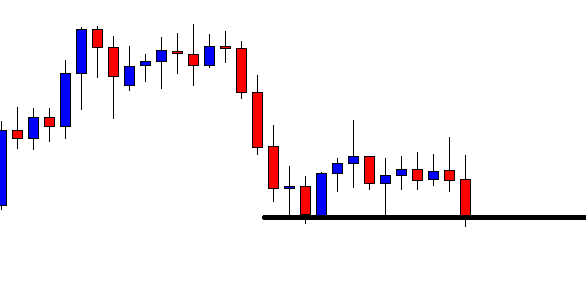
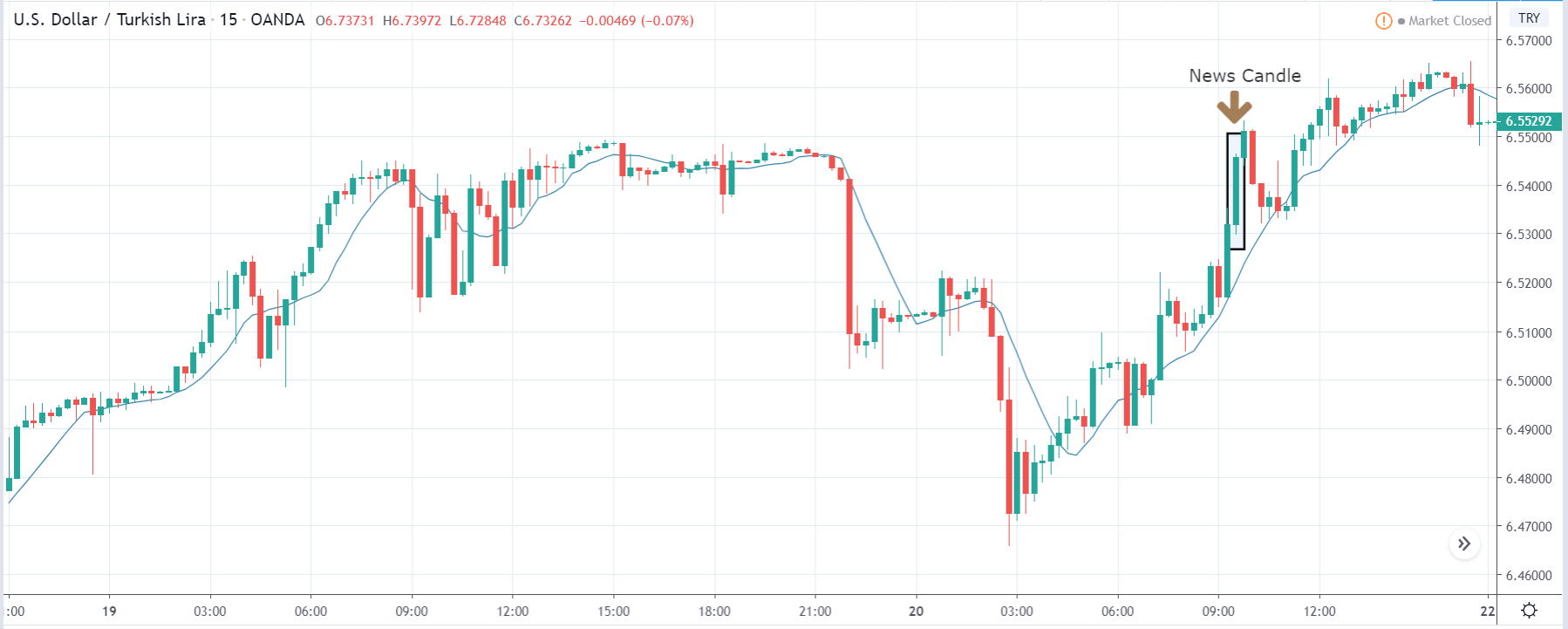
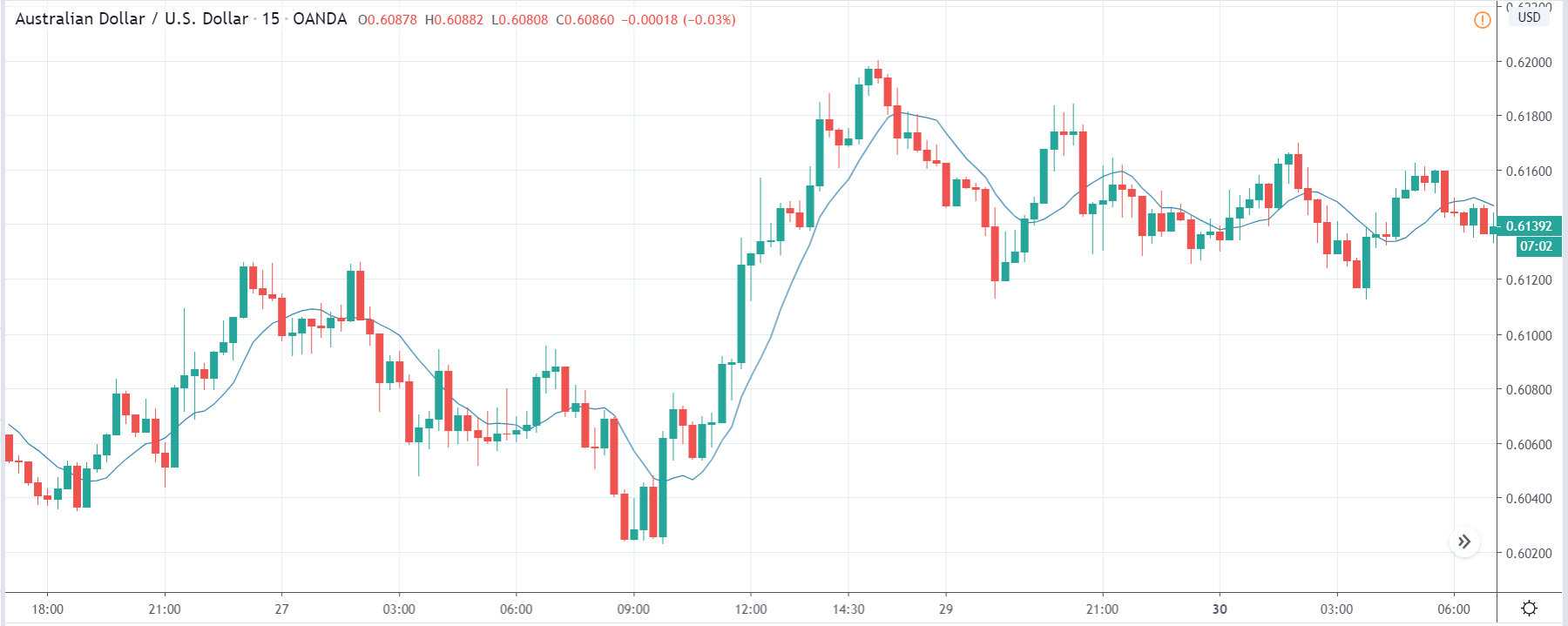
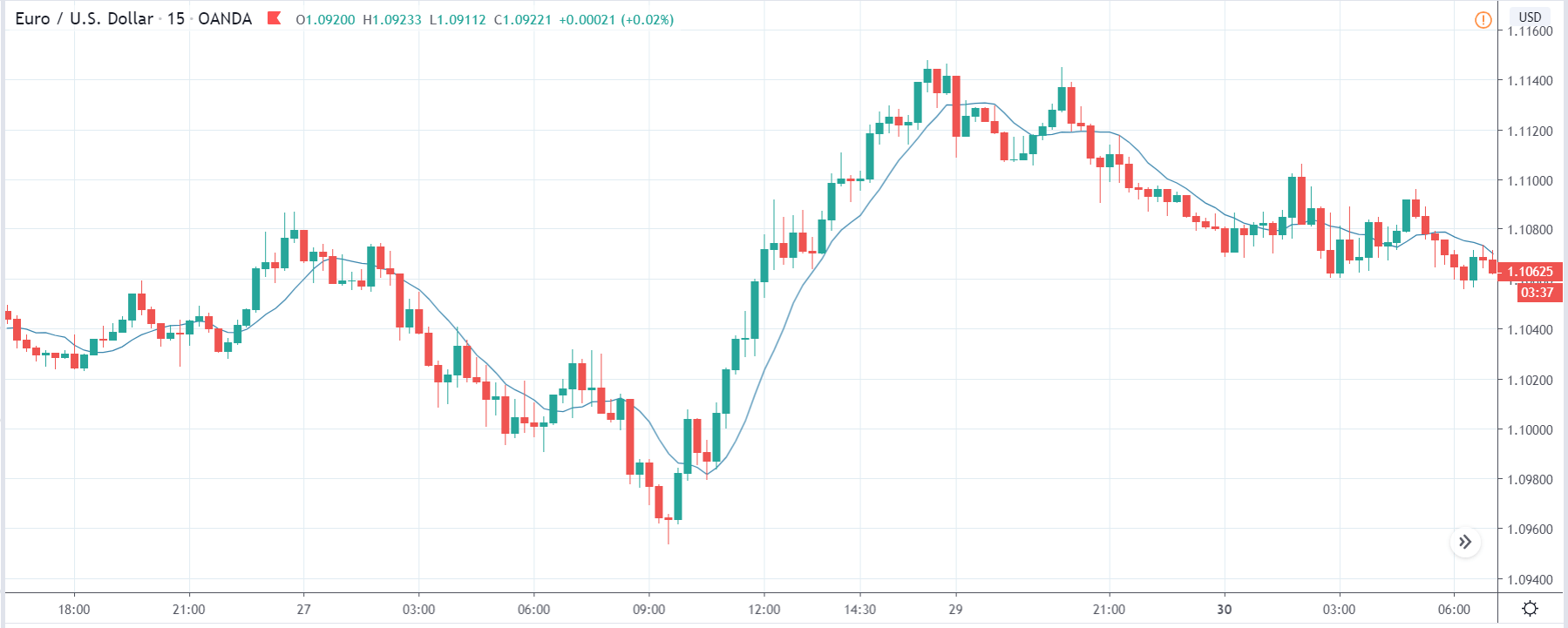
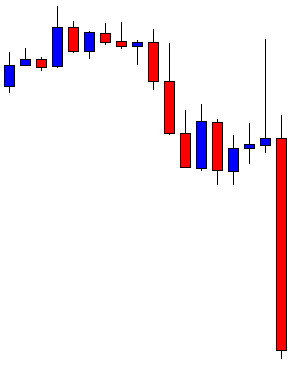
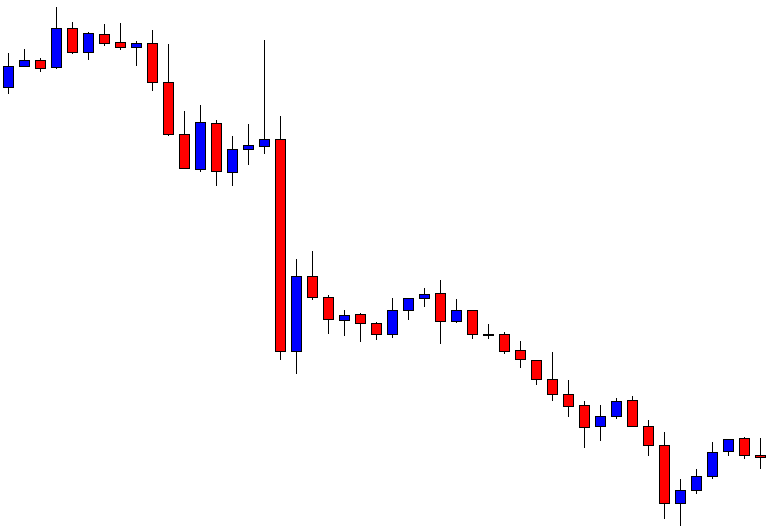
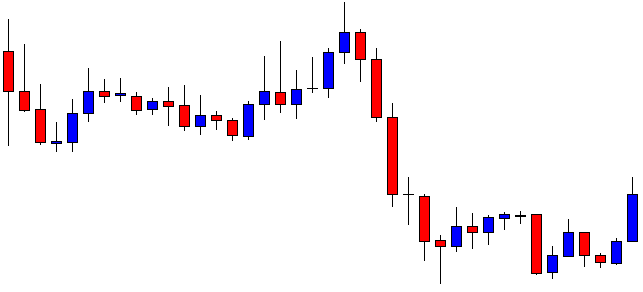
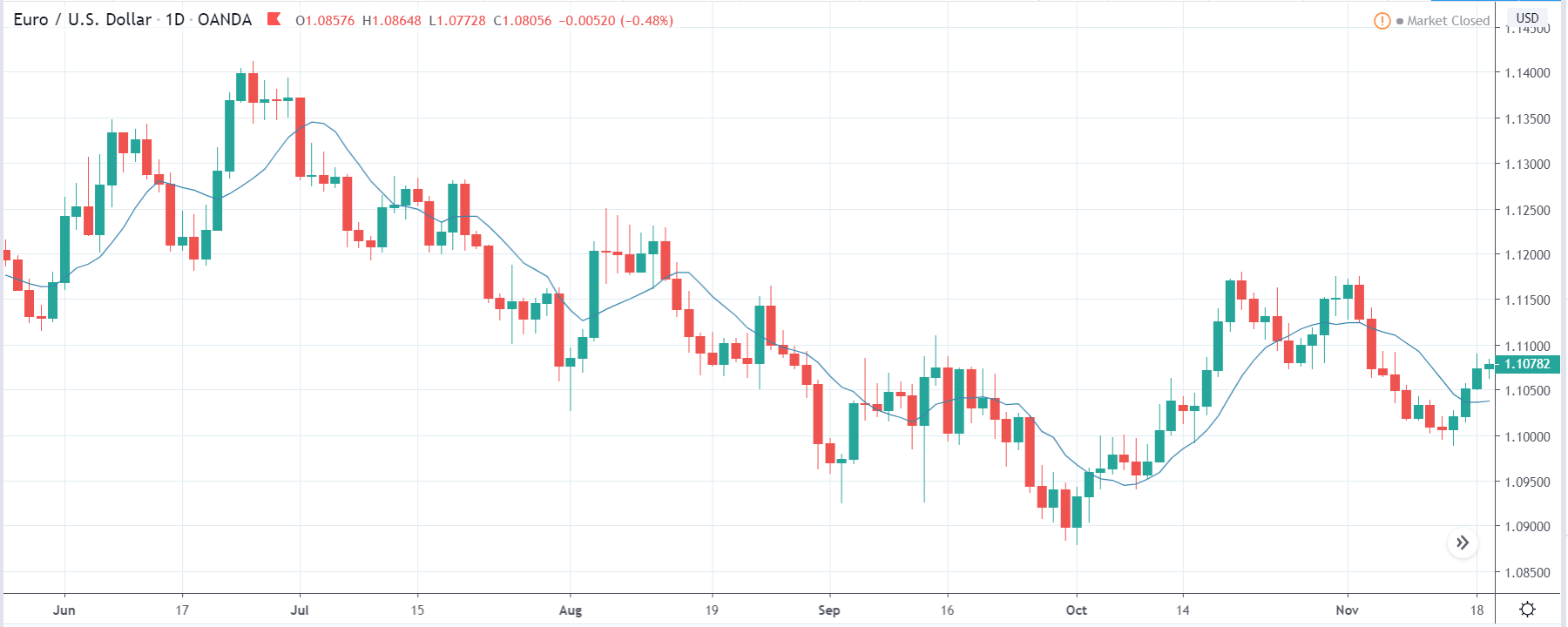
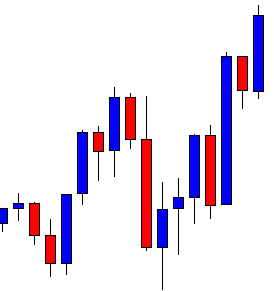
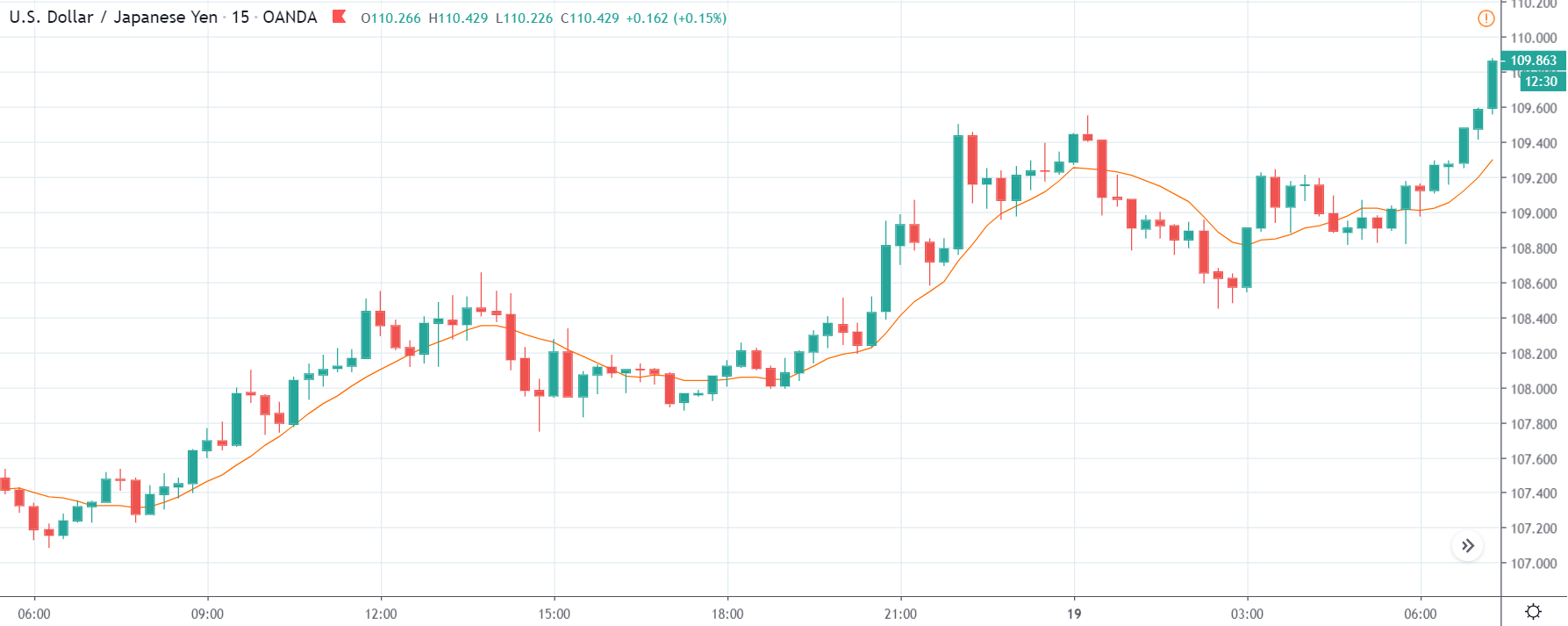
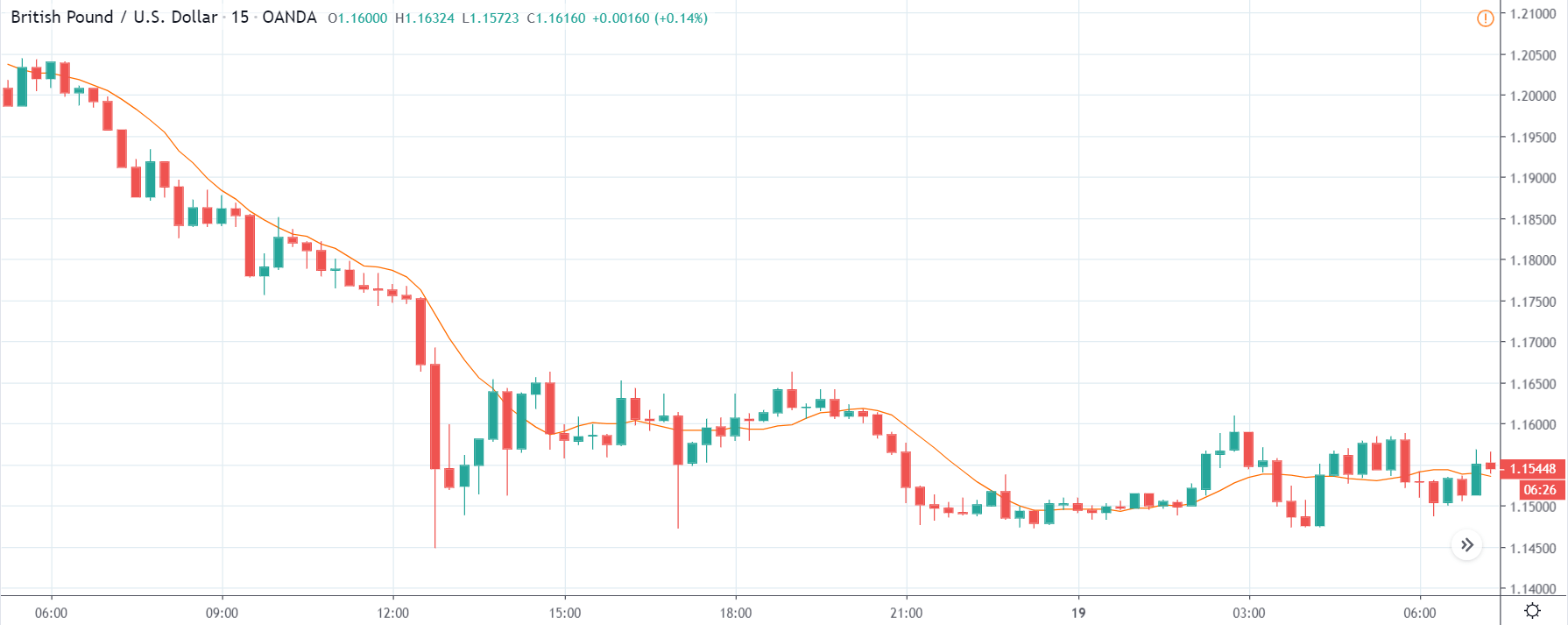
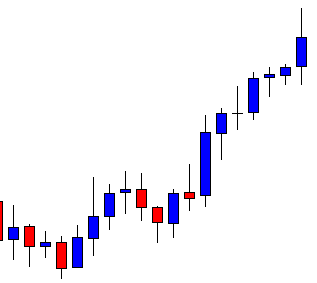
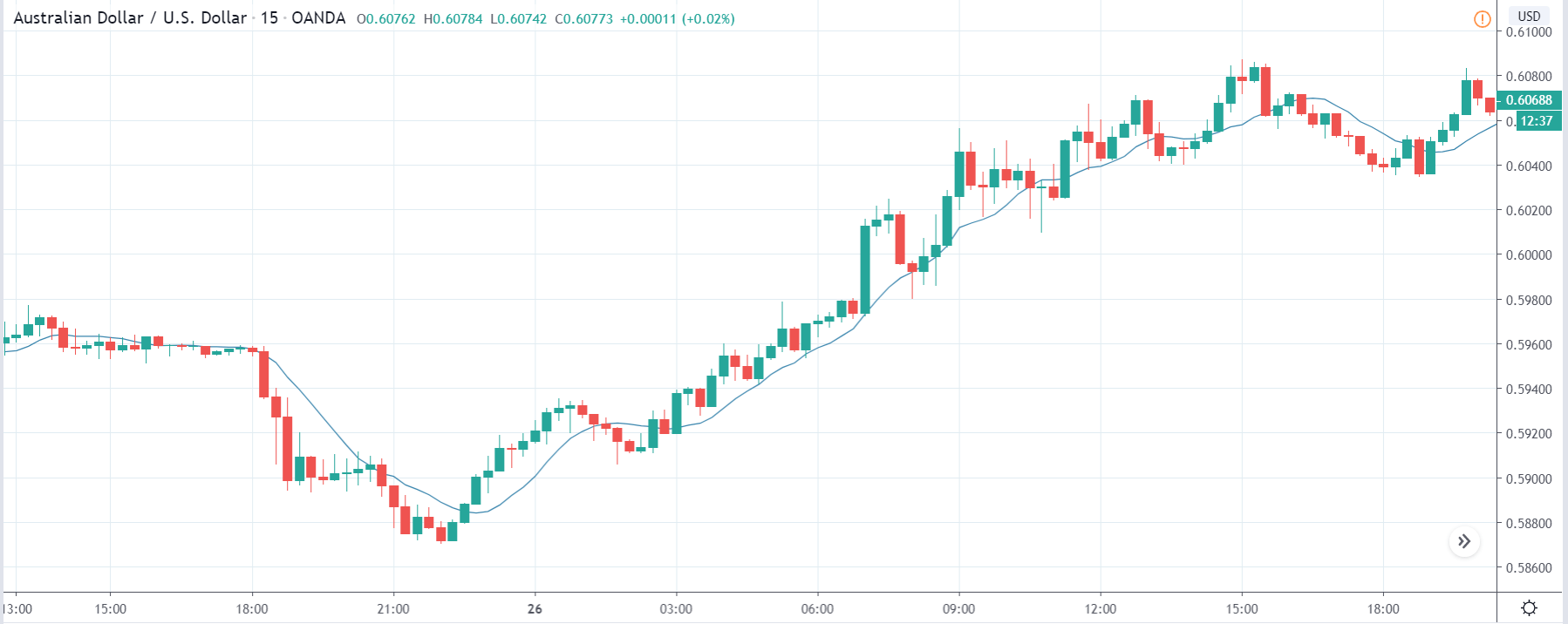
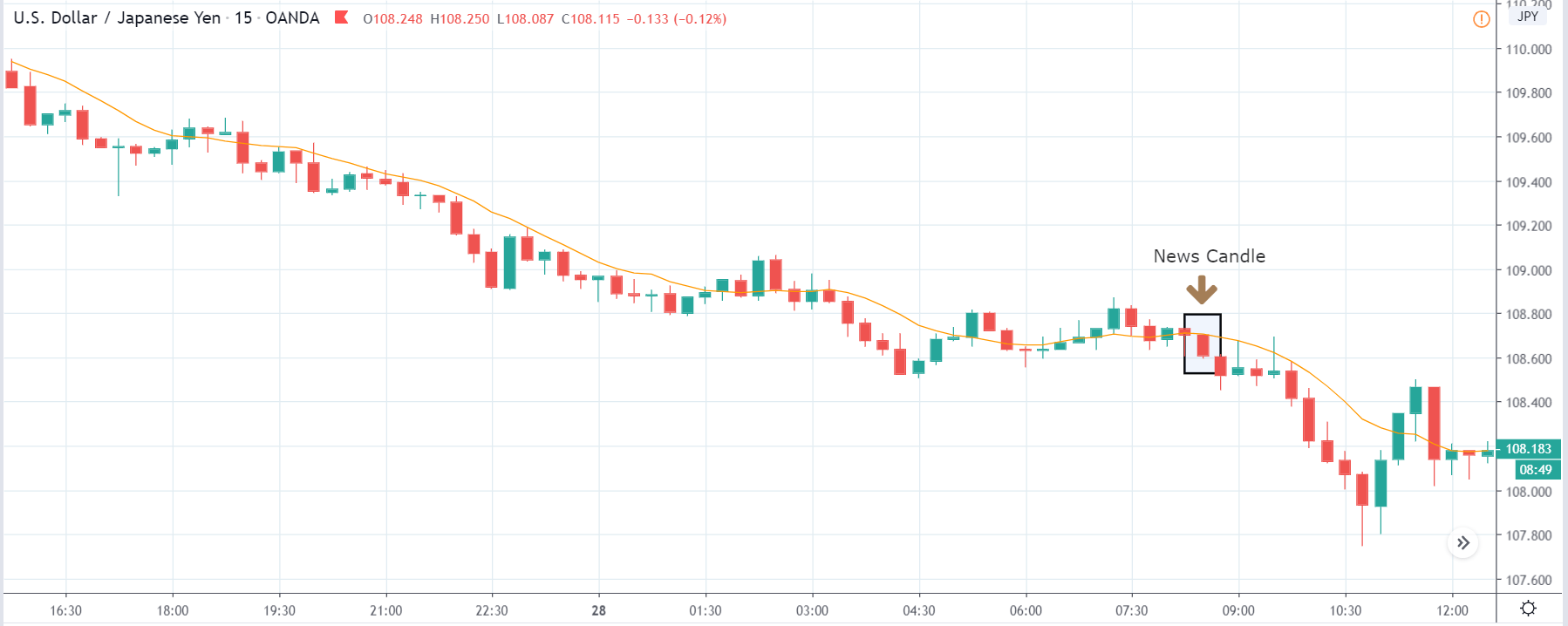
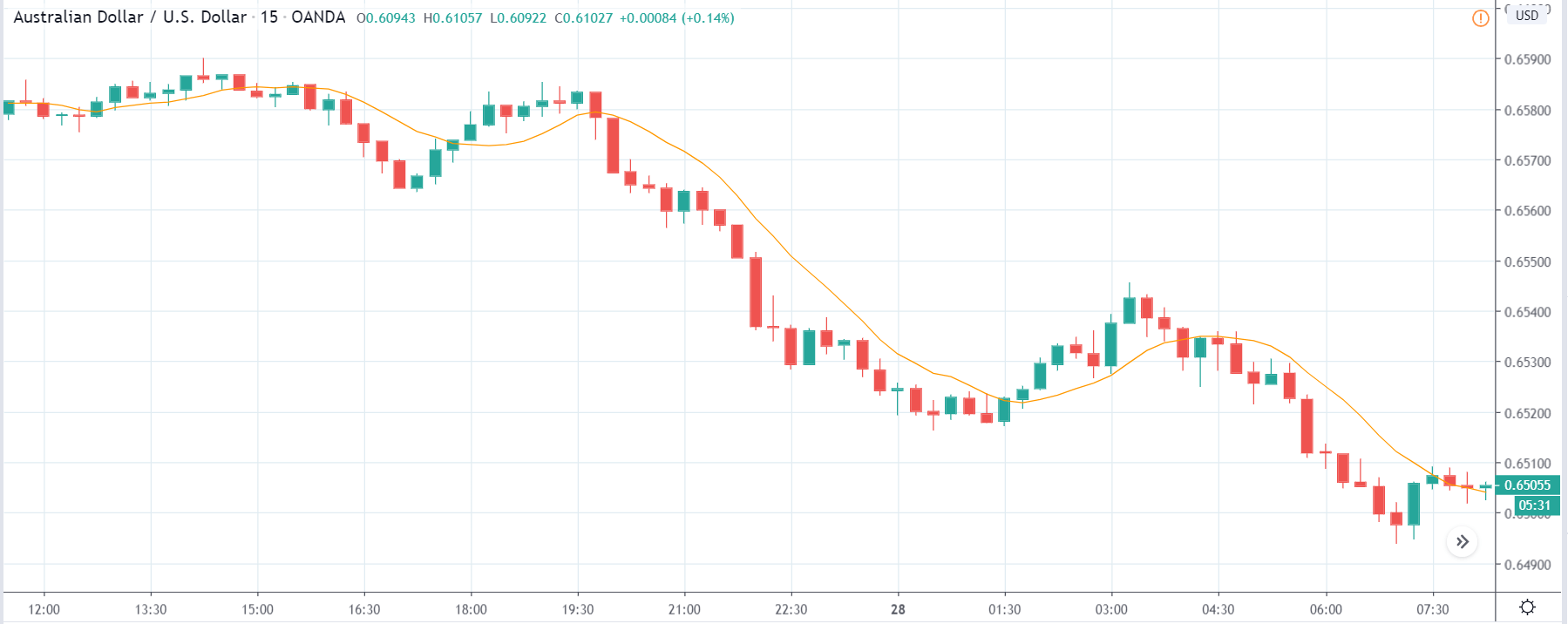
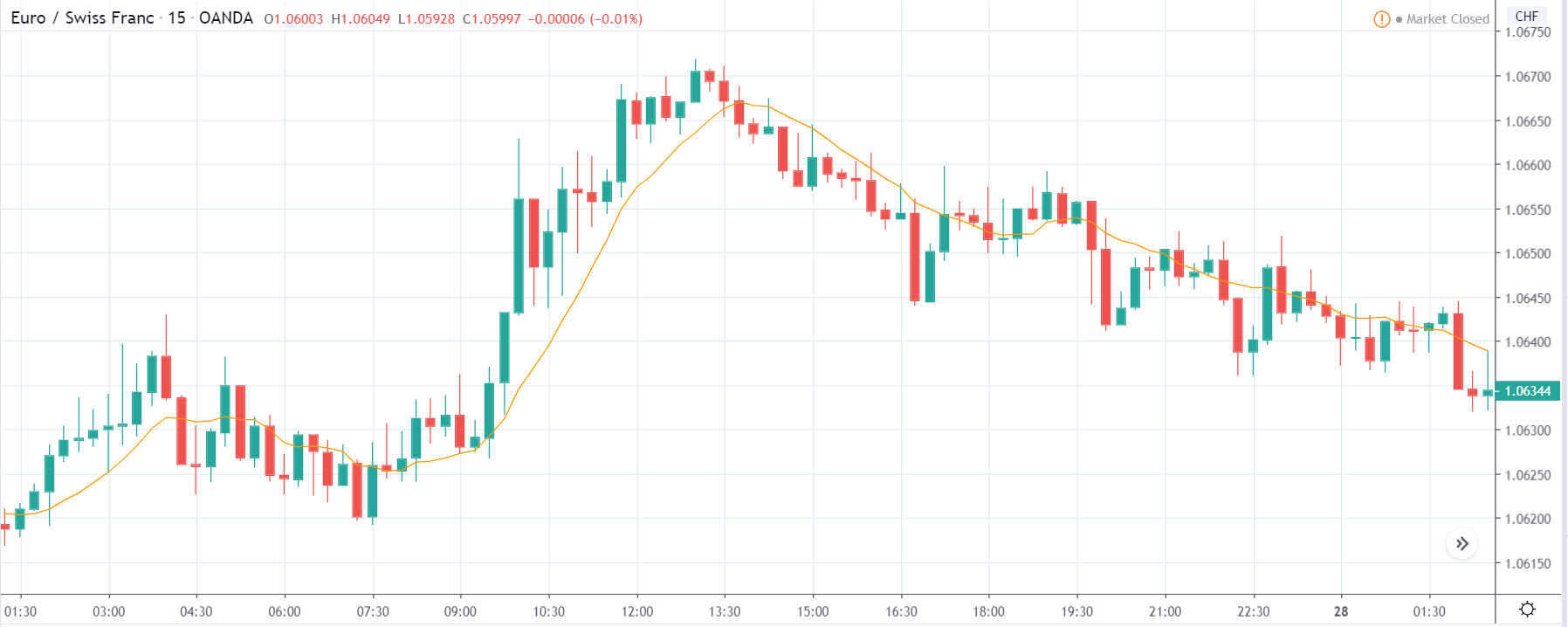
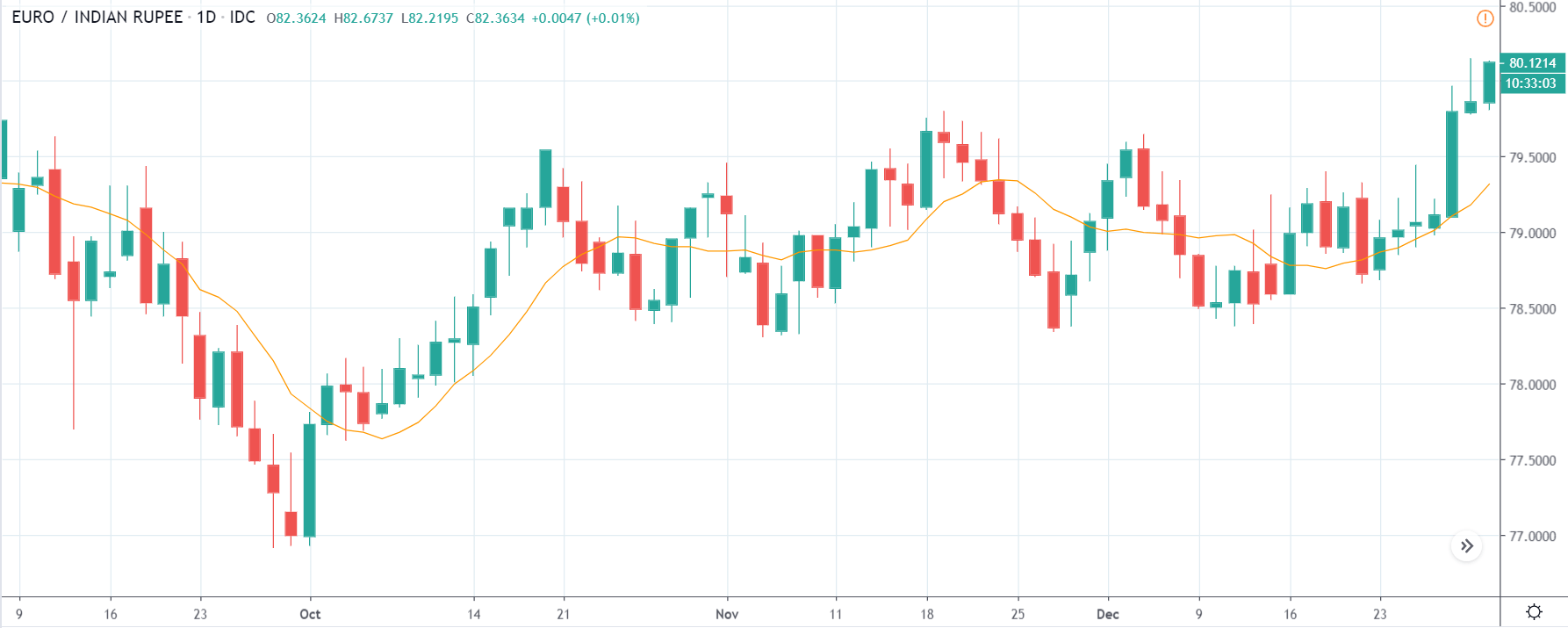
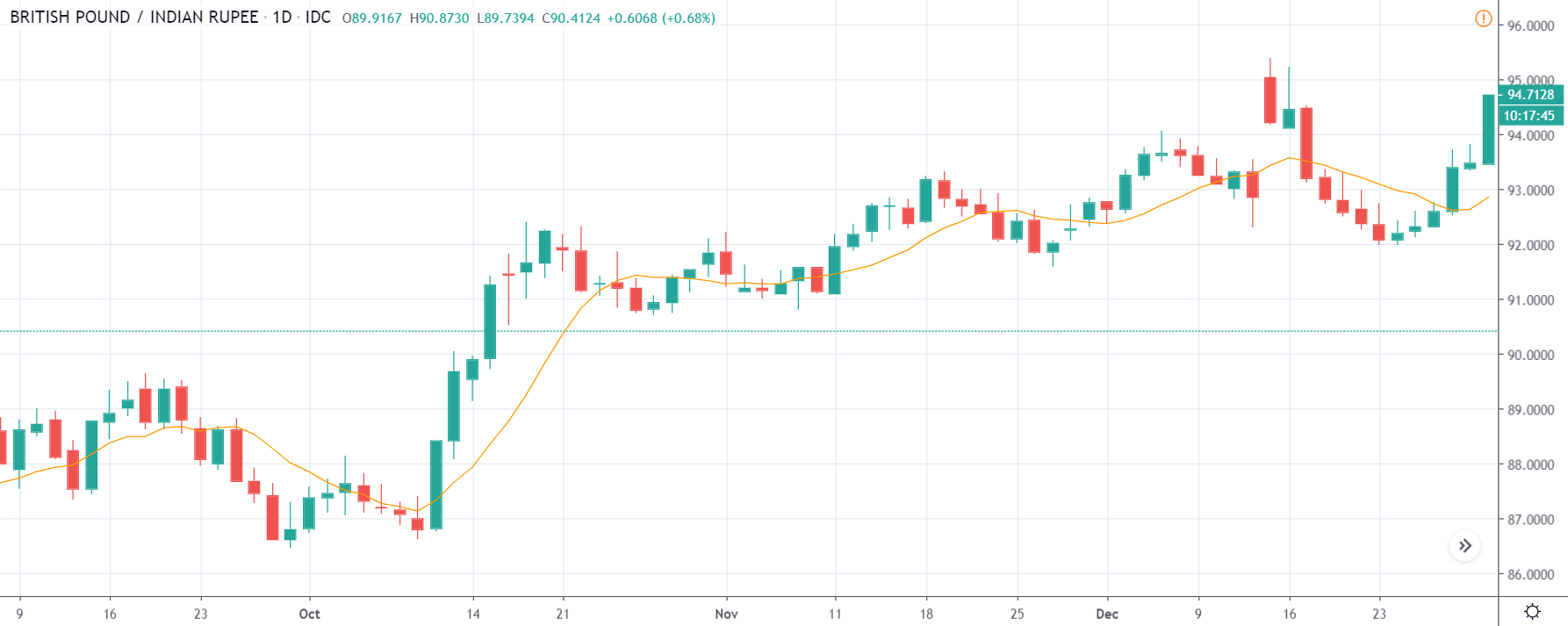
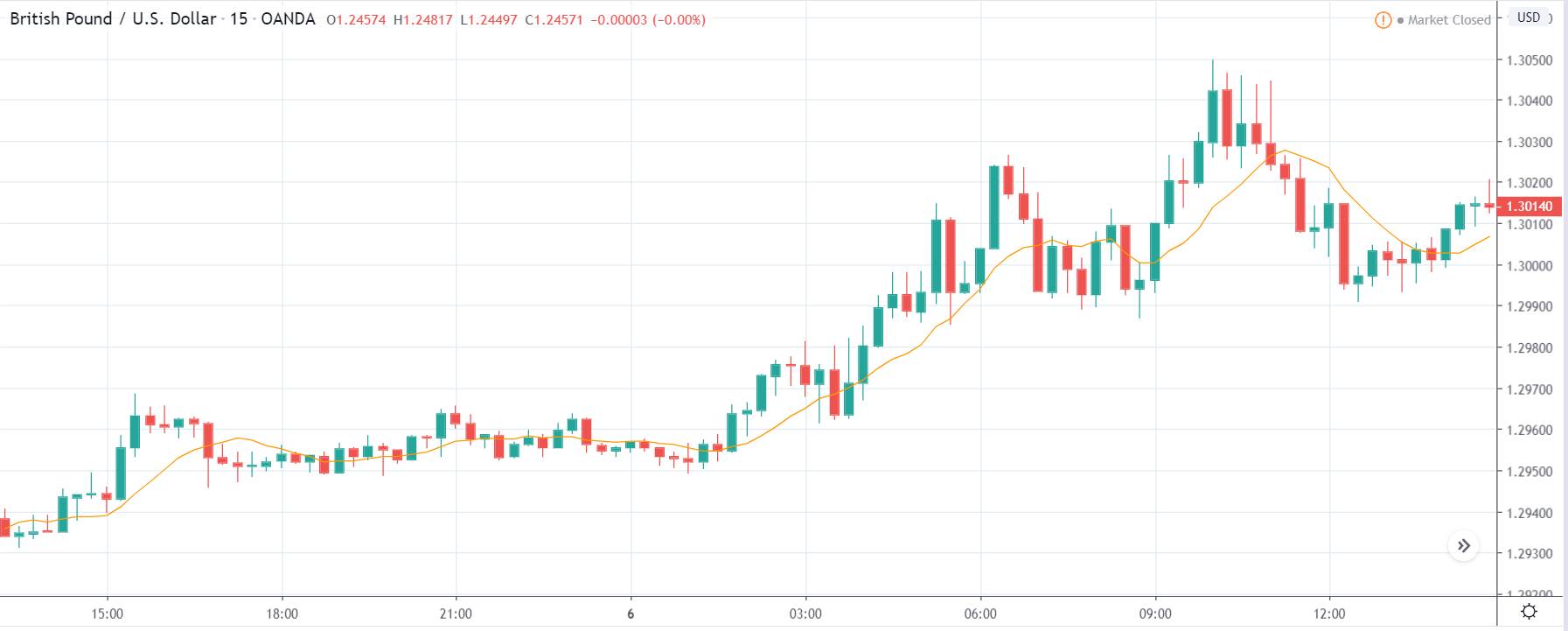
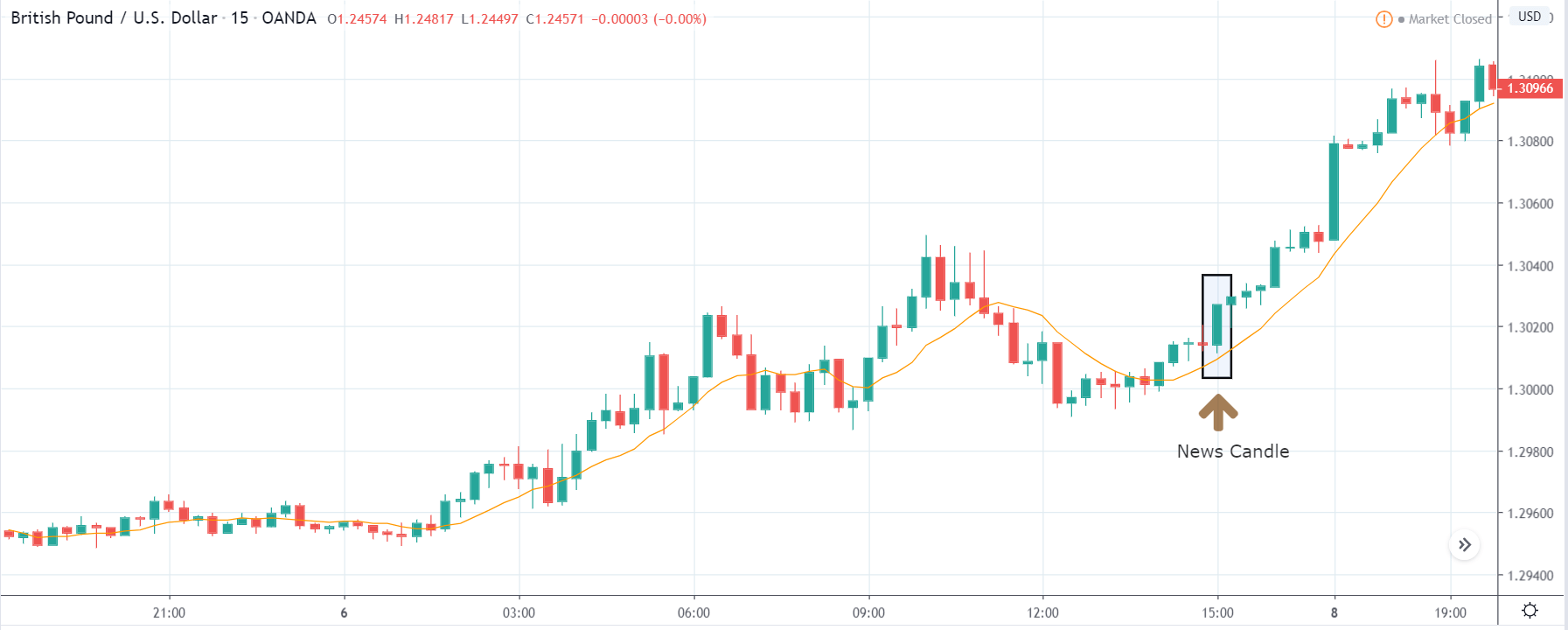
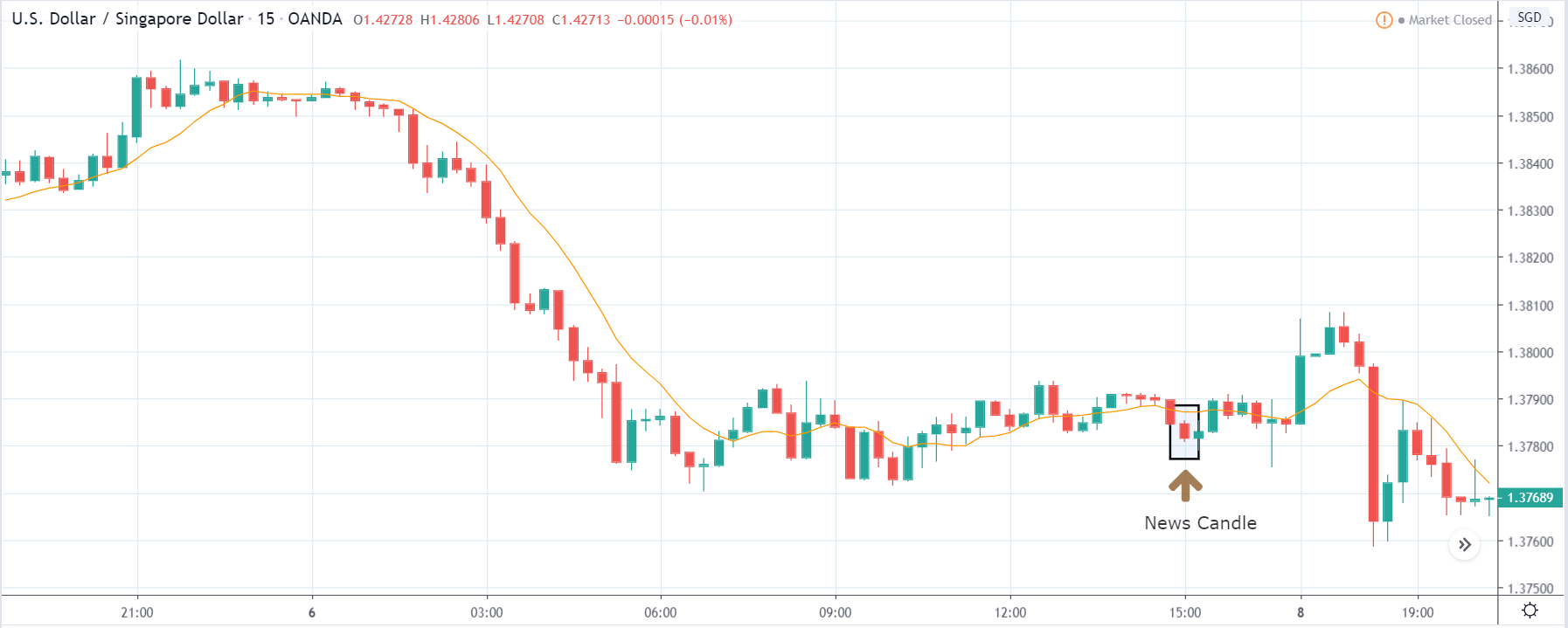
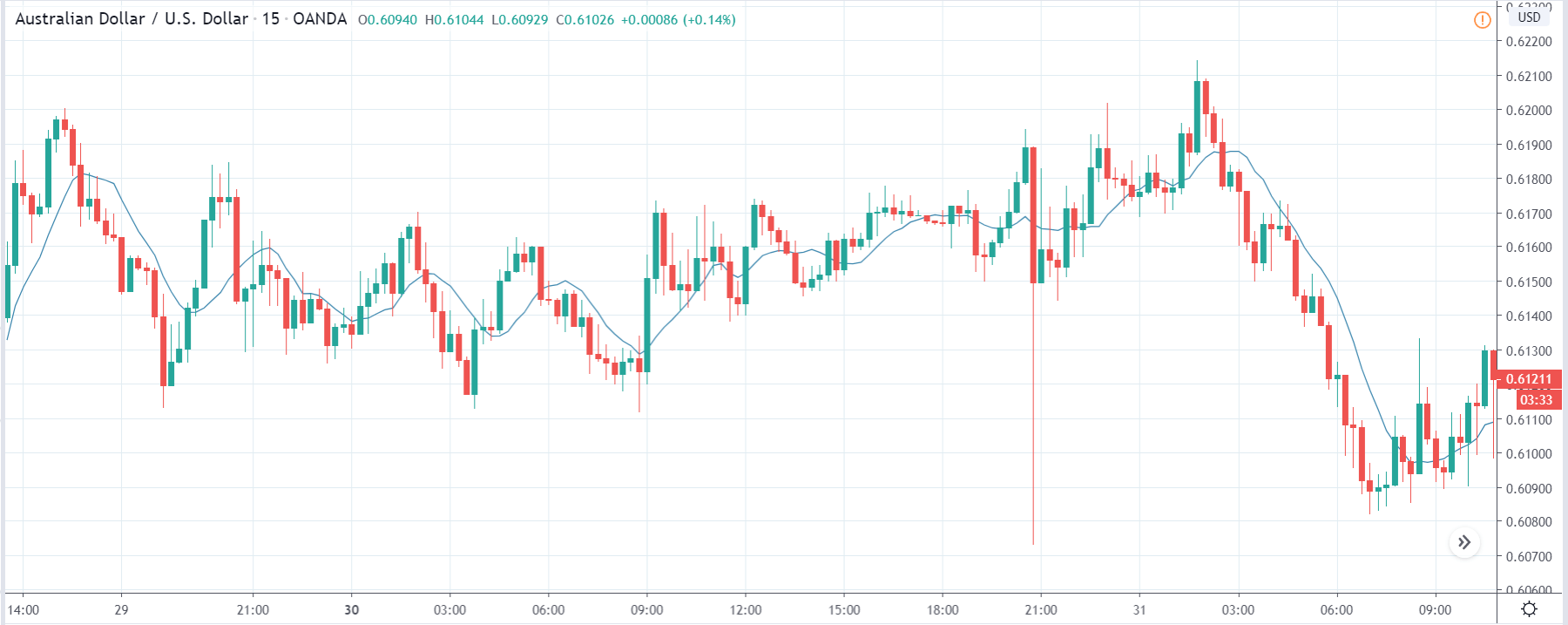
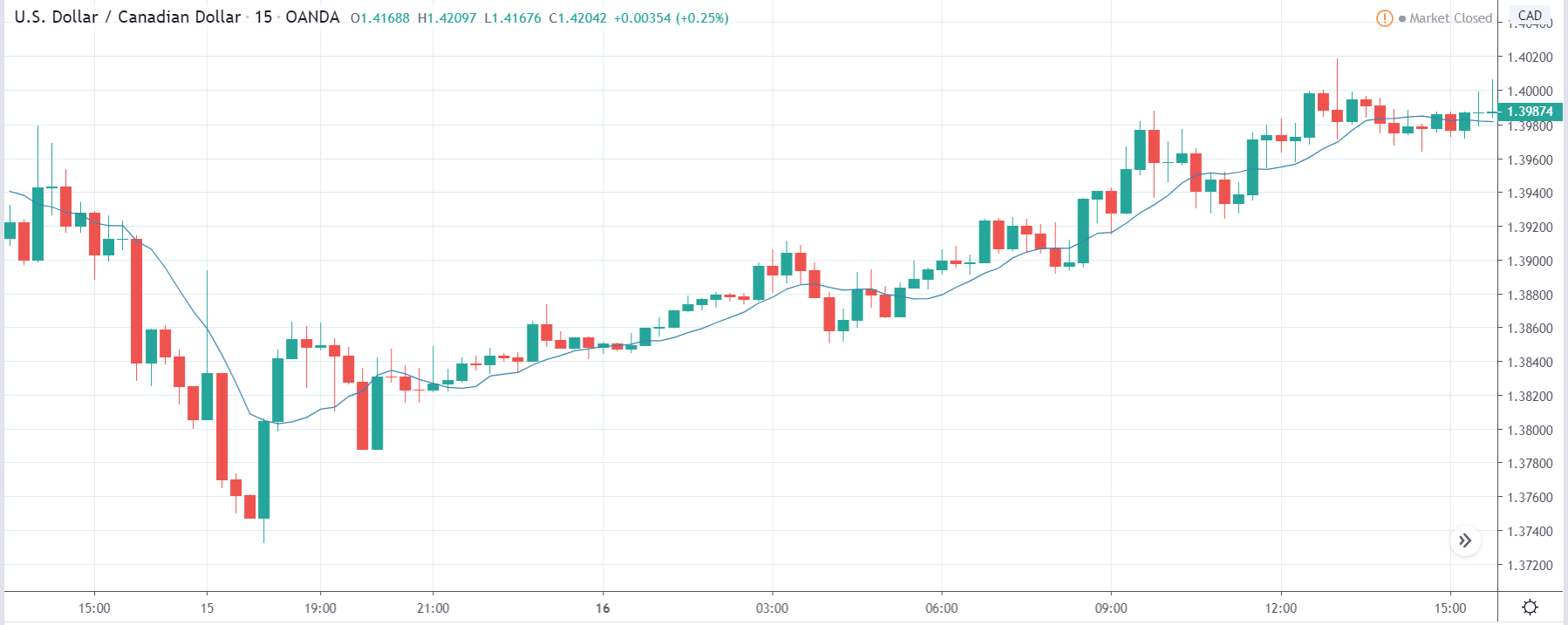
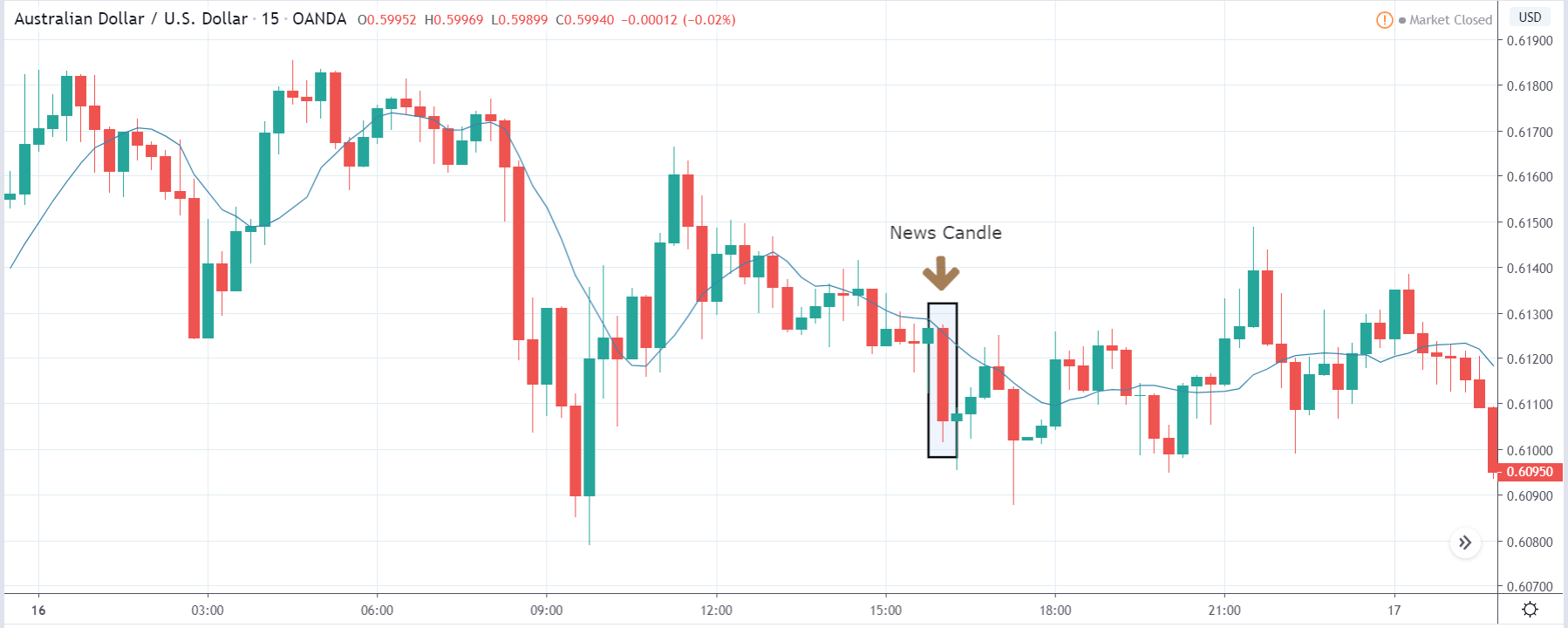
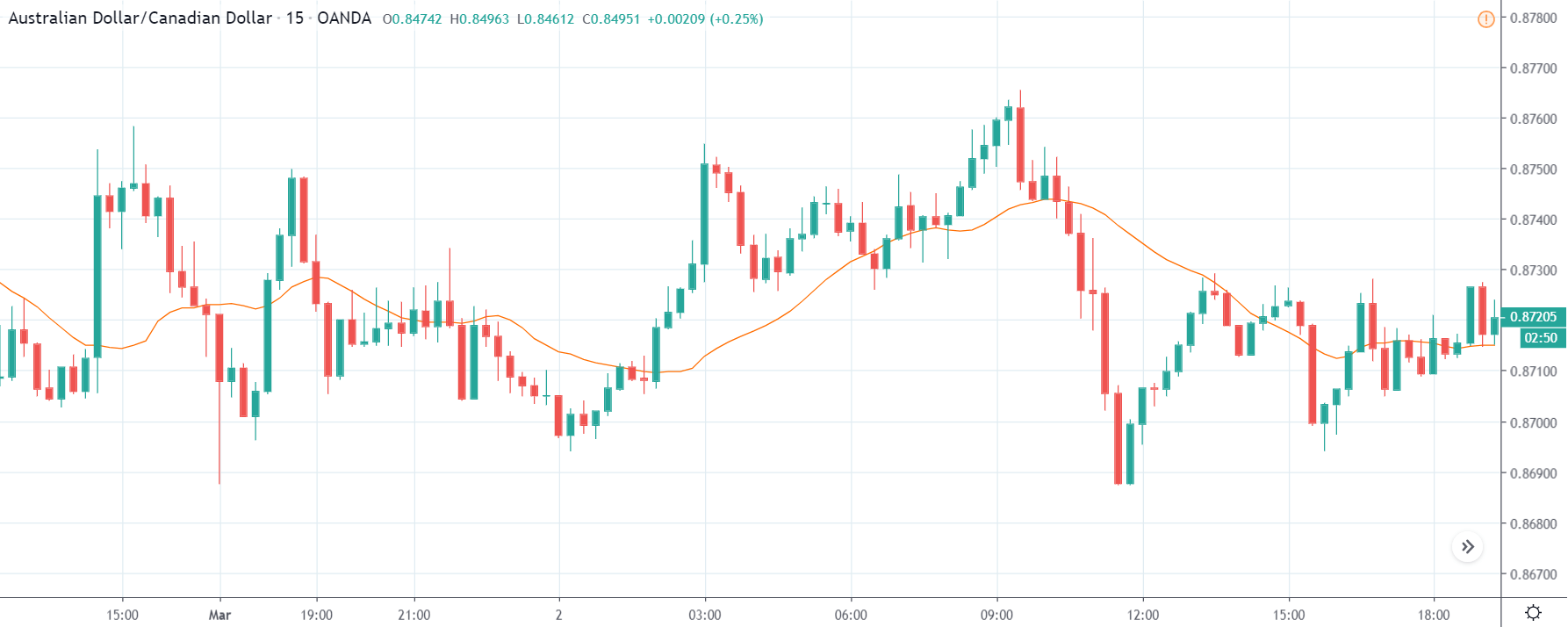
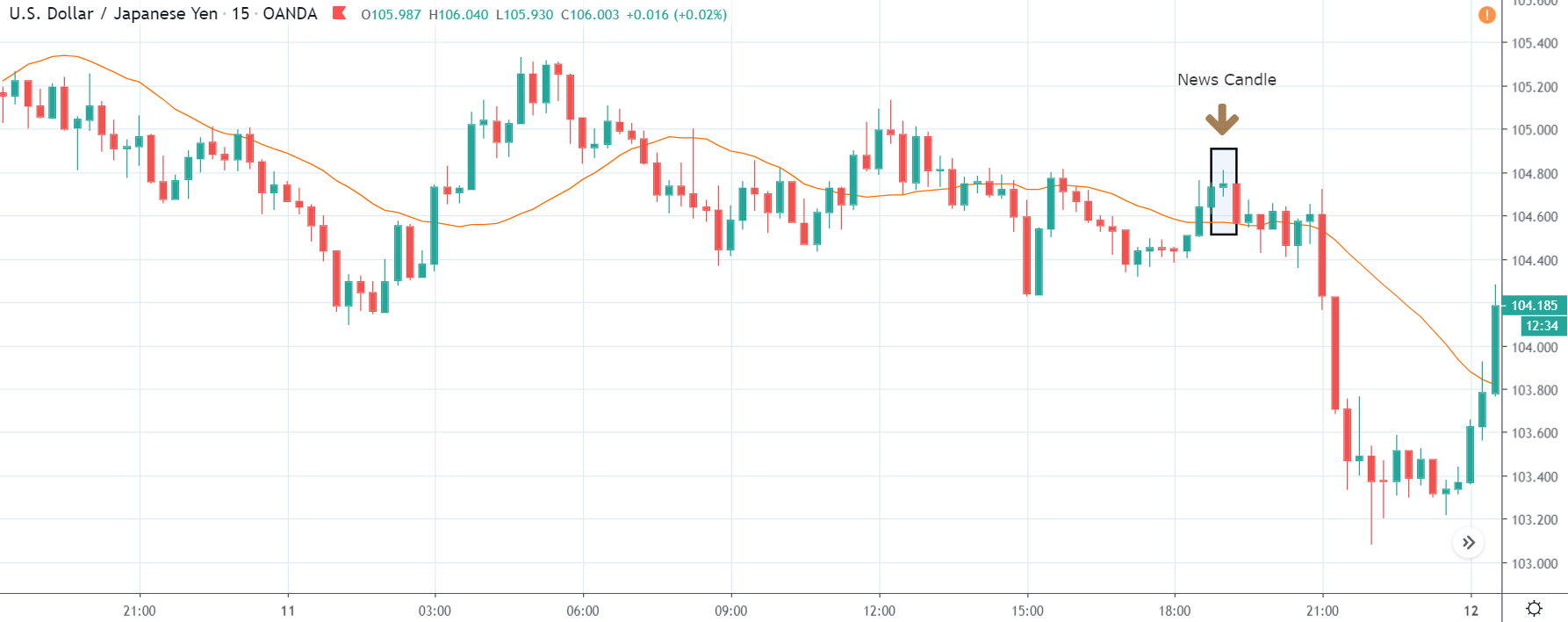
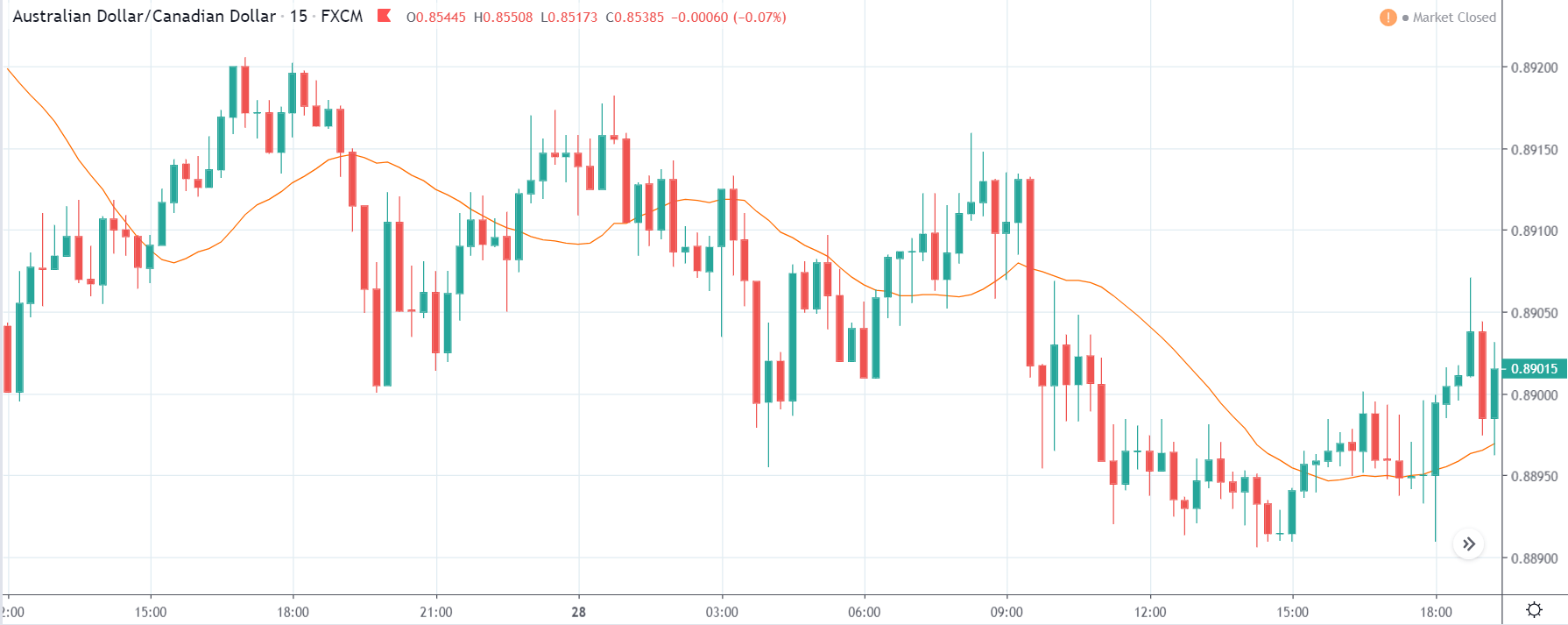
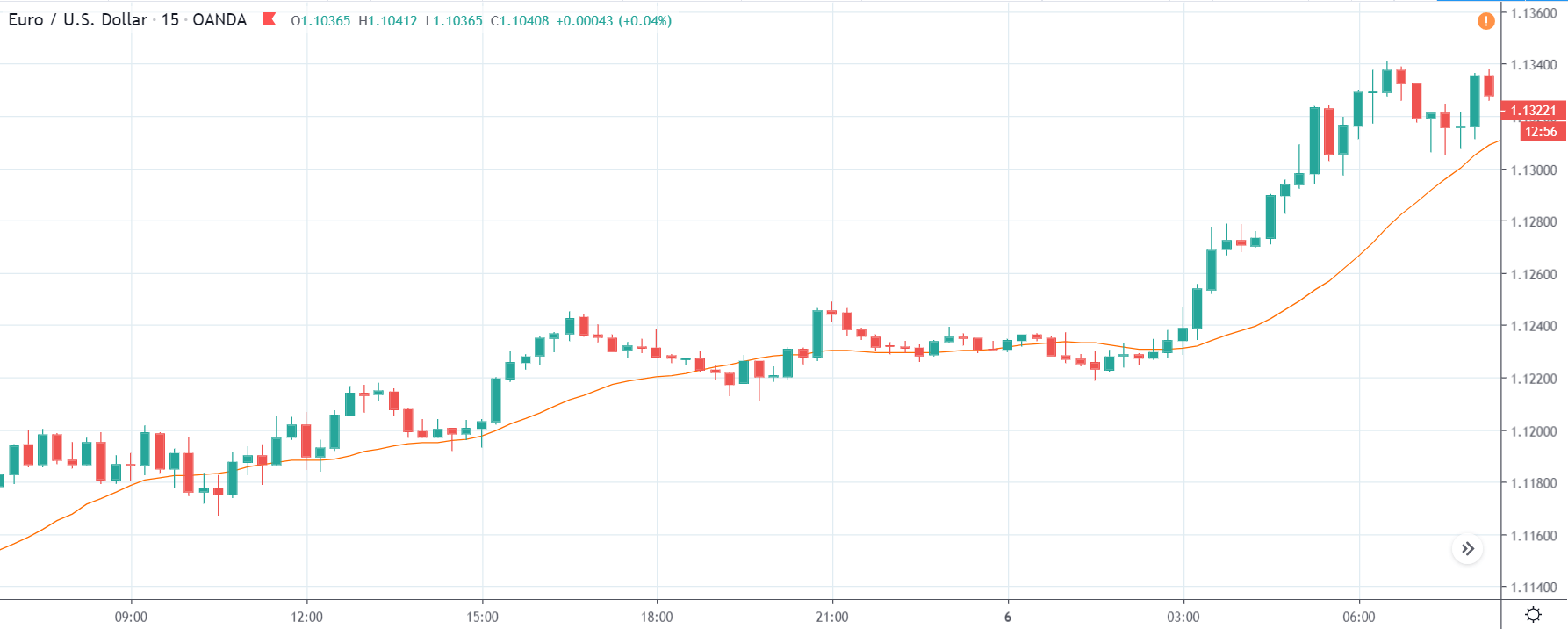
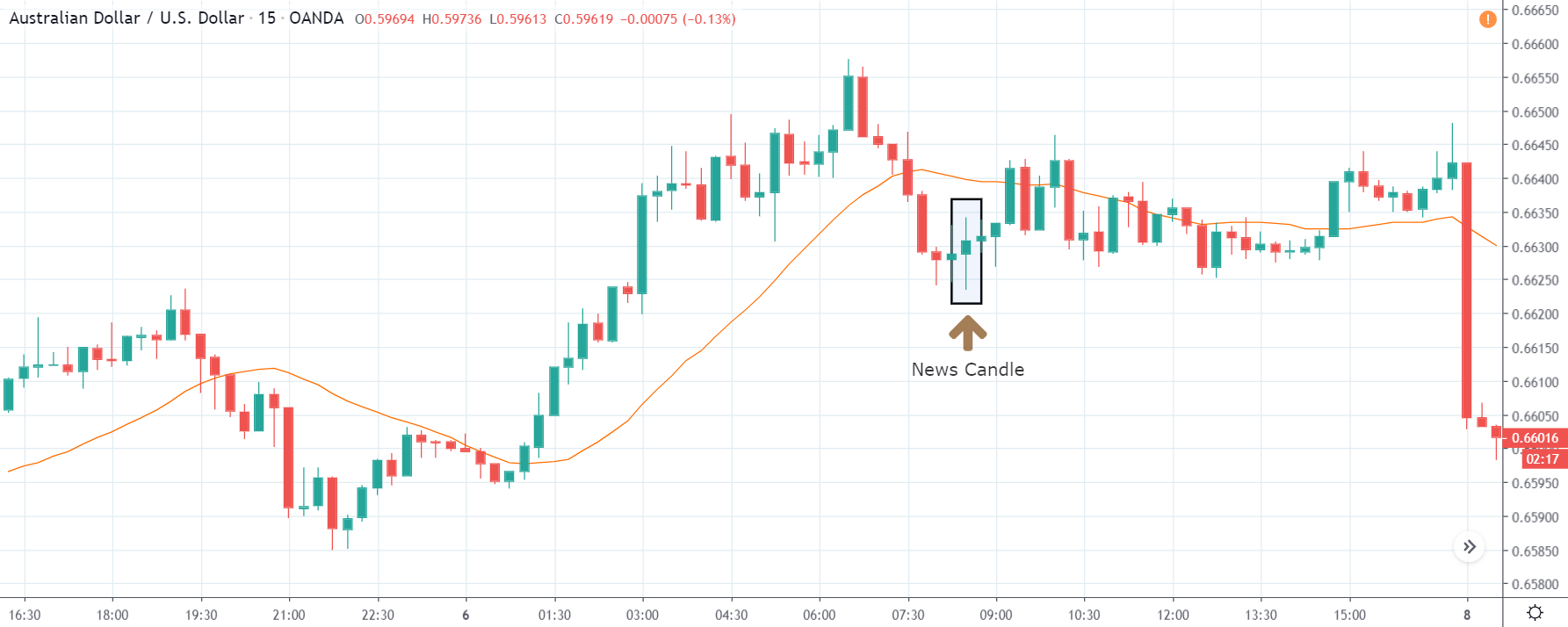
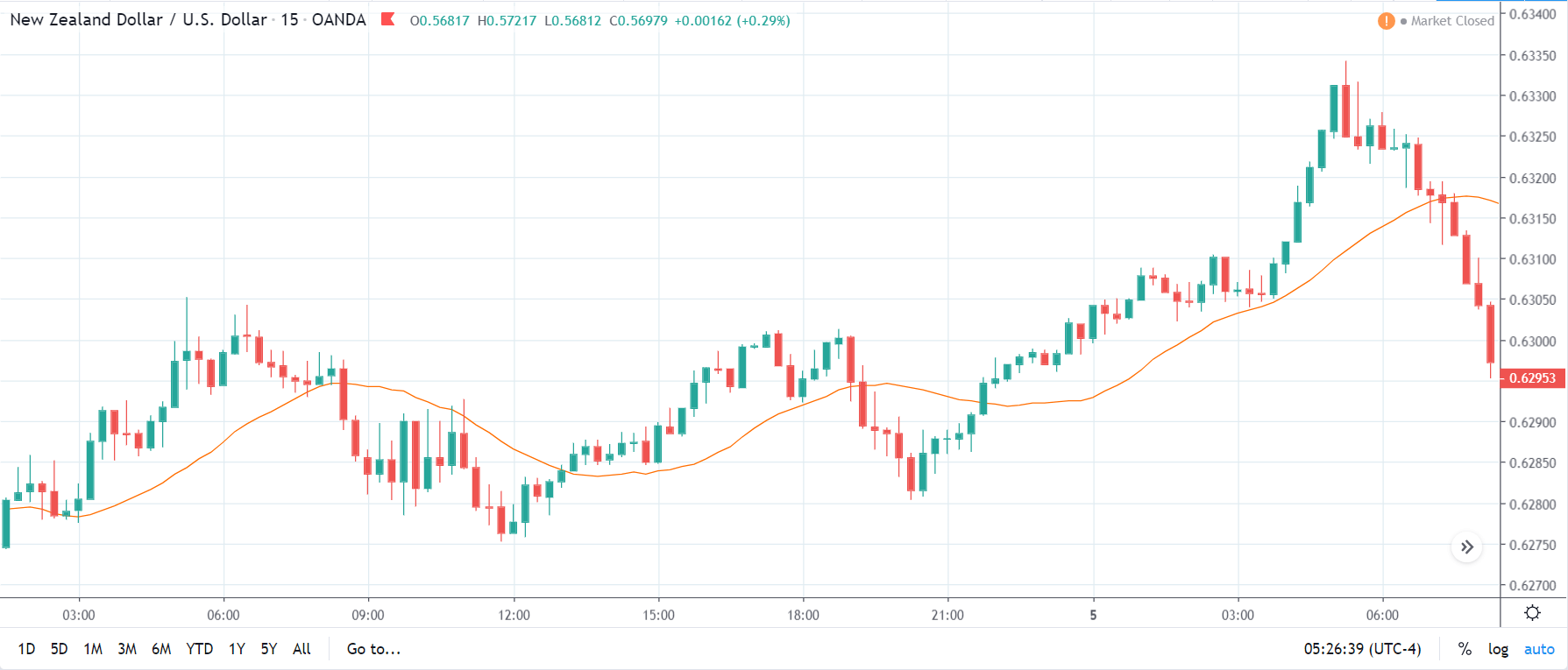
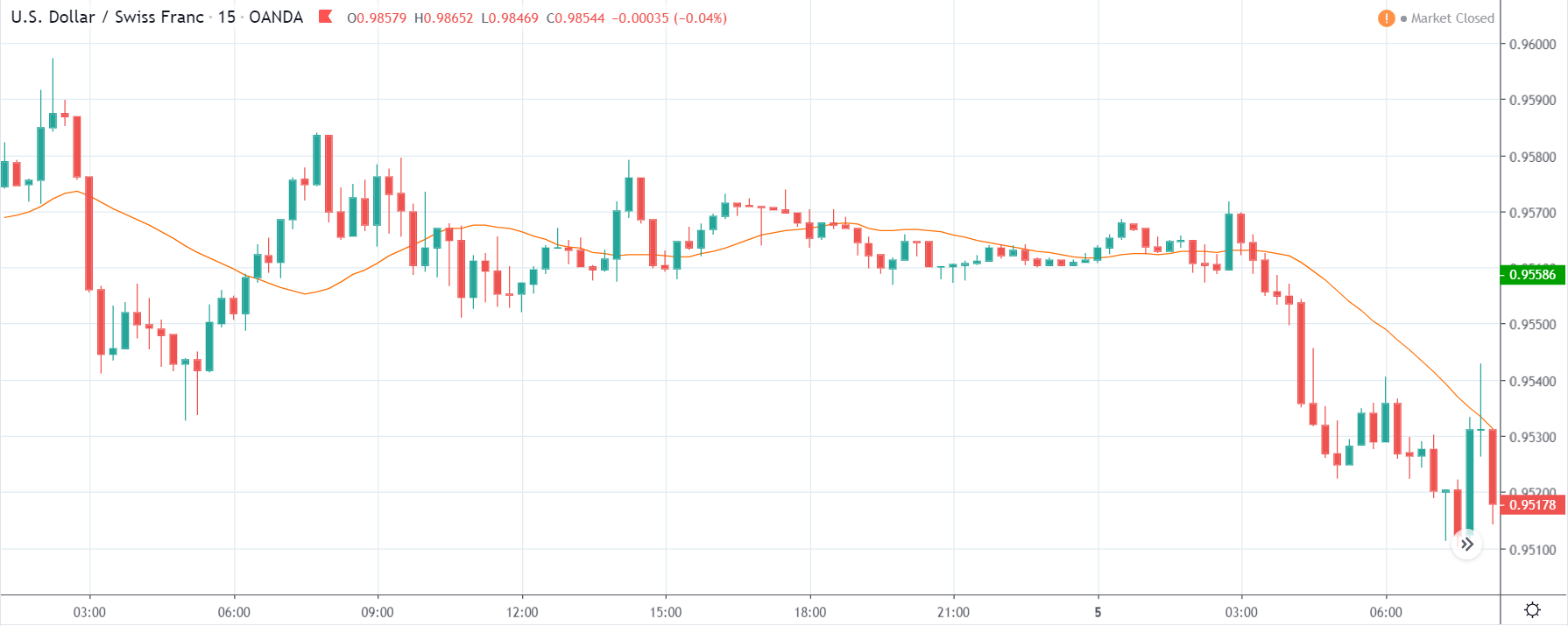
USD/ZAR | Before the announcement:
The first pair that will be discussed is the USD/ZAR currency pair. Here, we see that the market is in a strong uptrend before the news announcement, as shown in the above image. As the impact of Mining production is less on the value of a currency, we will wait for the price to retrace near a ‘support’ area and then take a ‘buy’ trade. Until then, we have to watch if the price crashes below or shows signs of reversal.
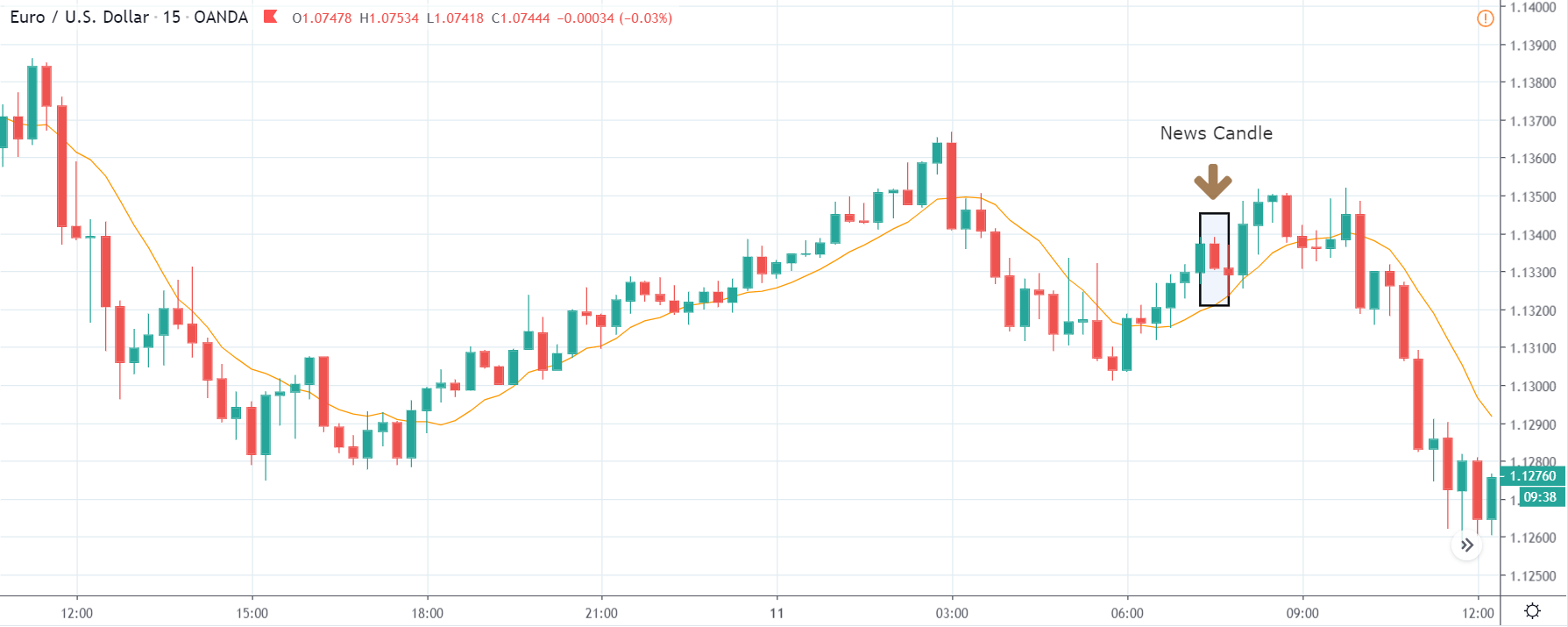
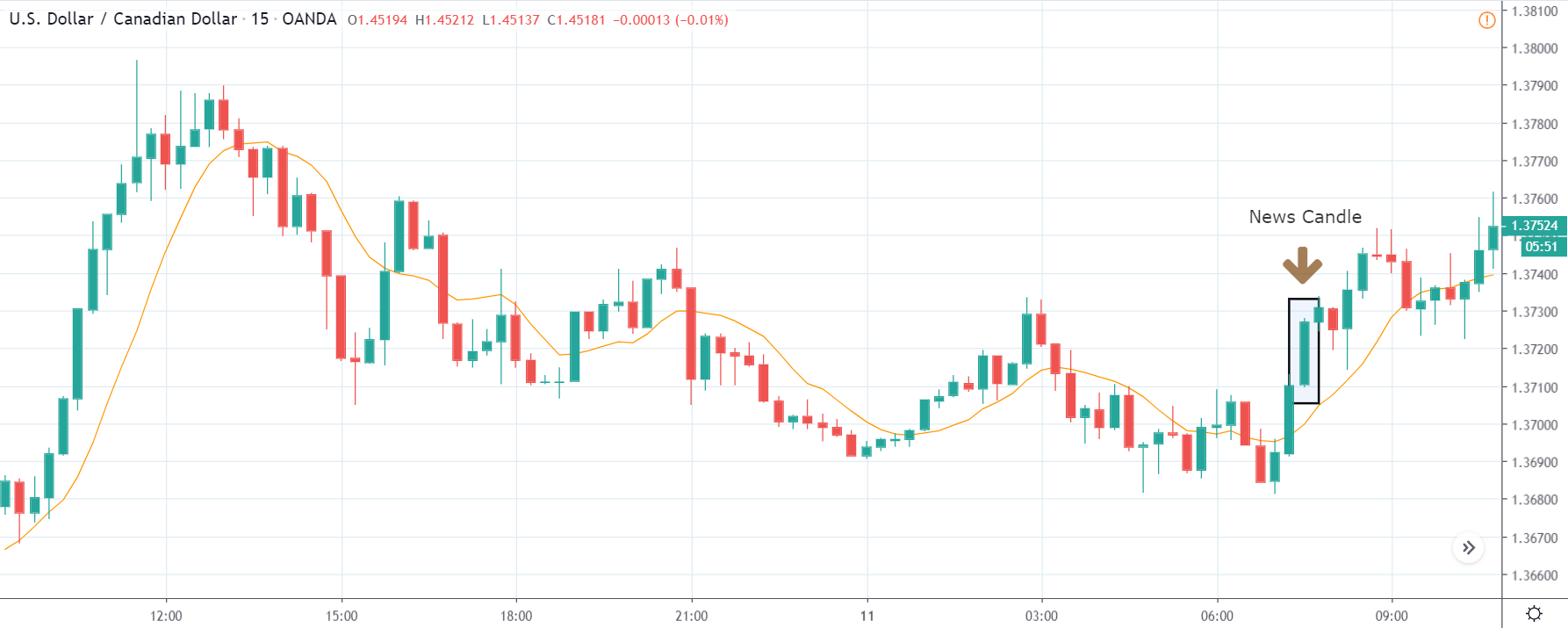
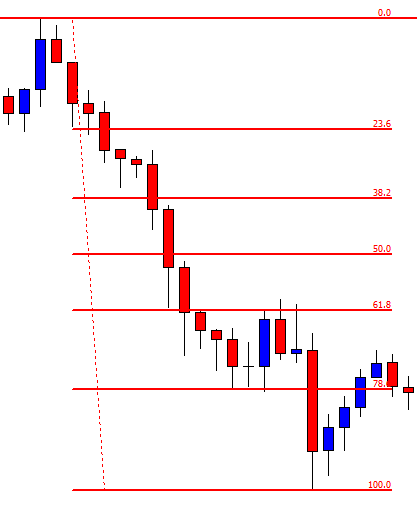
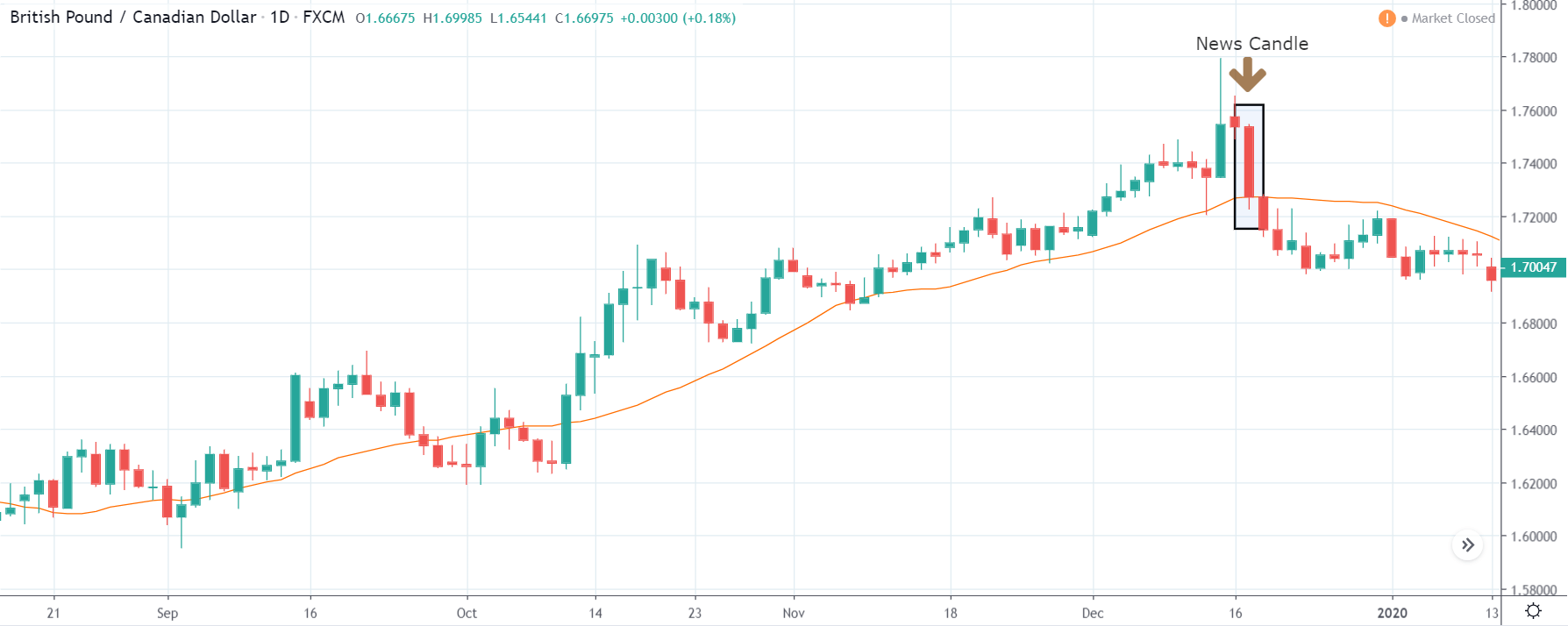
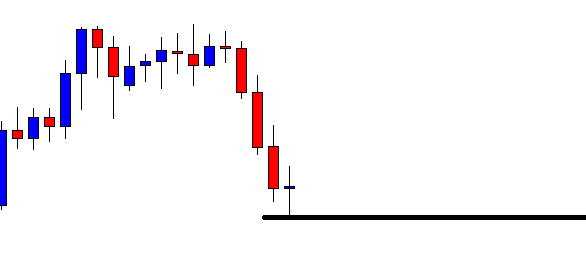
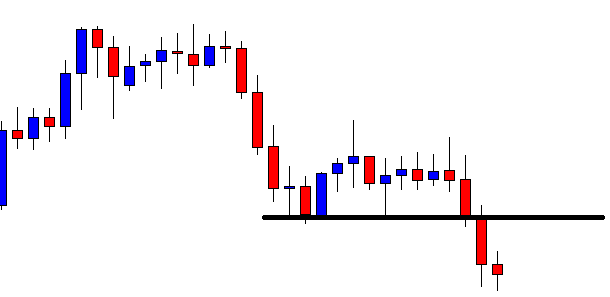
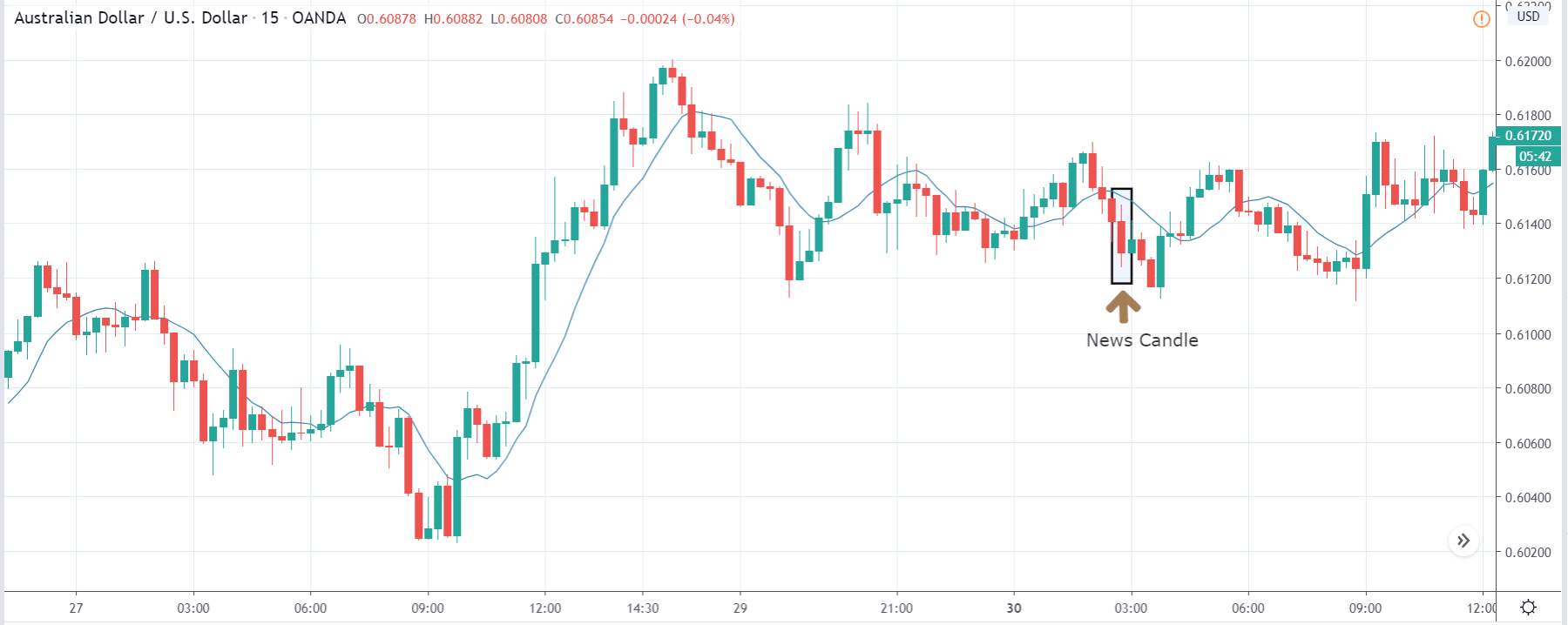
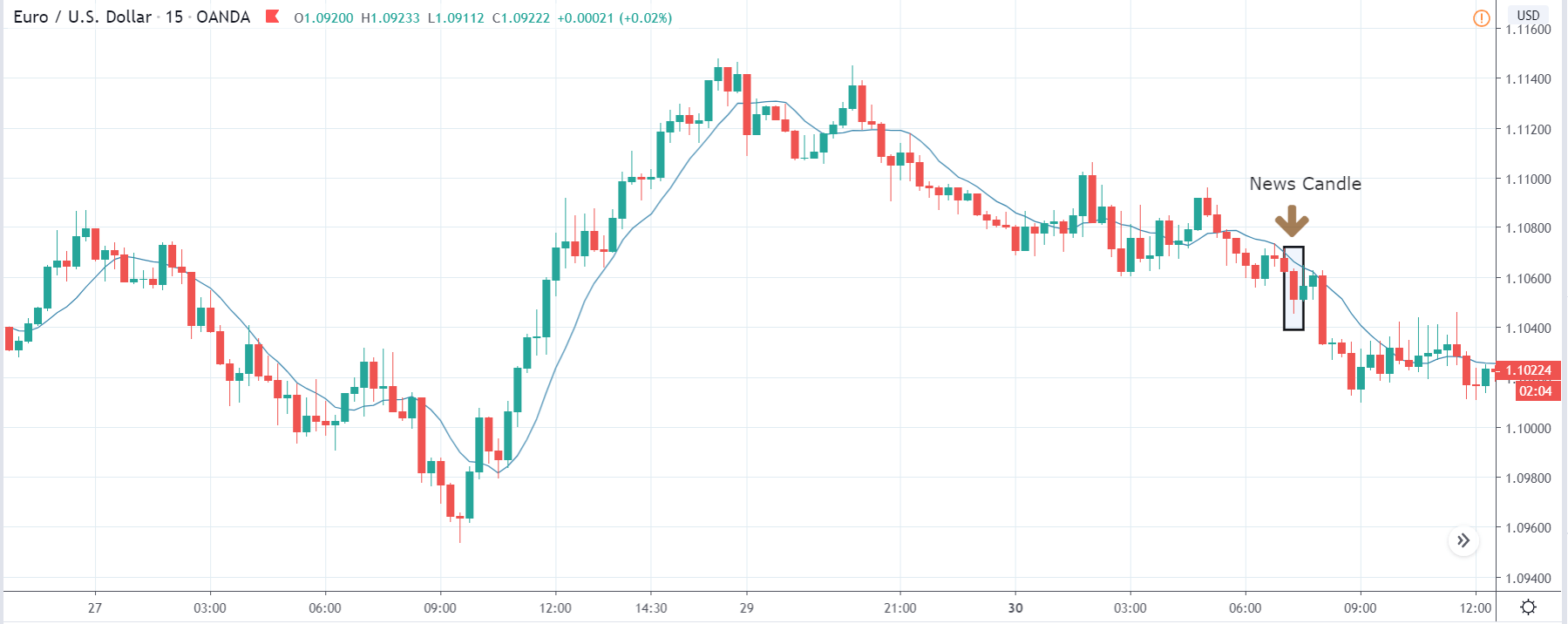
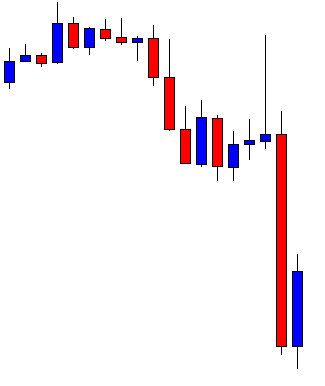
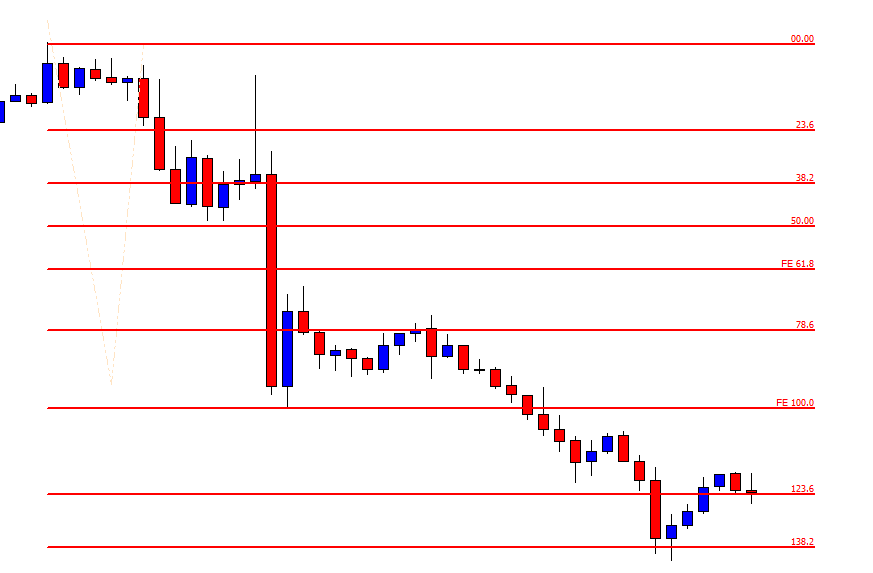
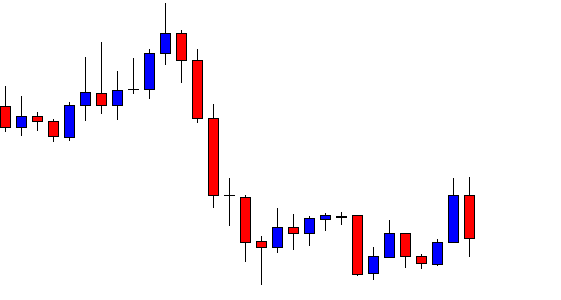
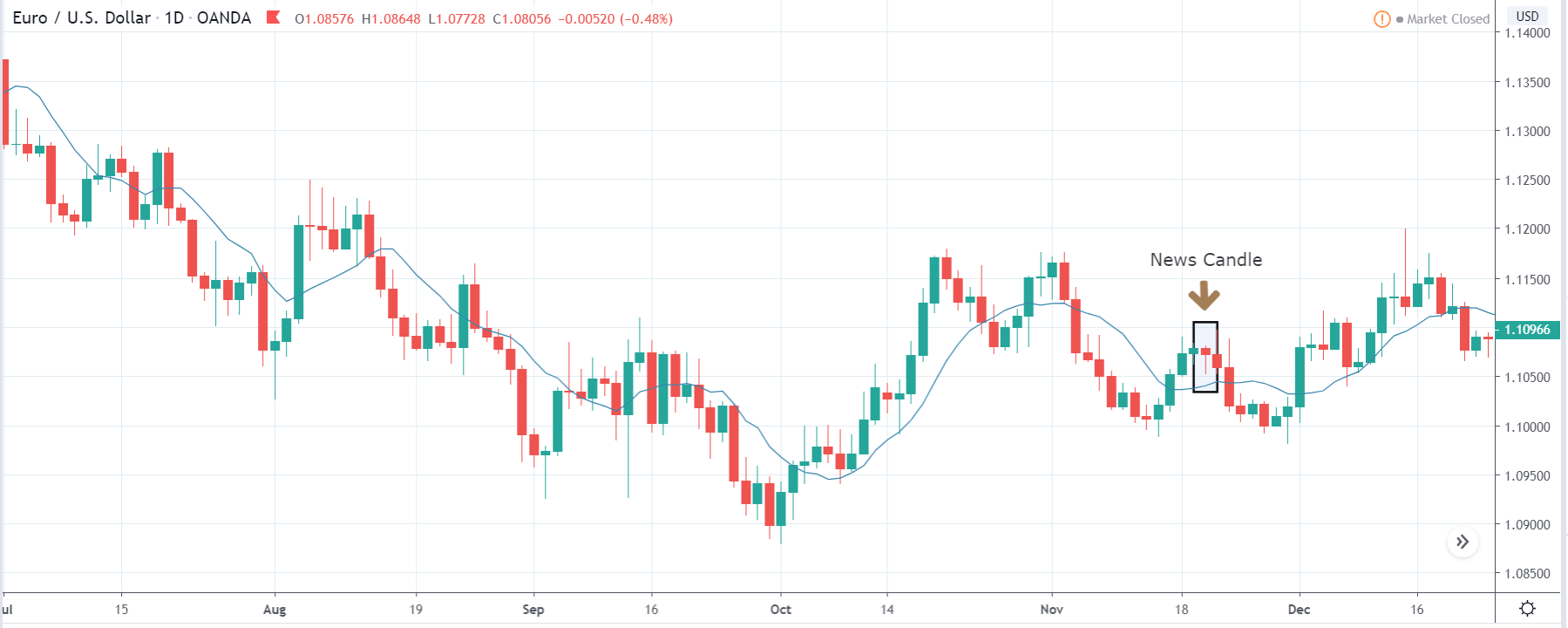
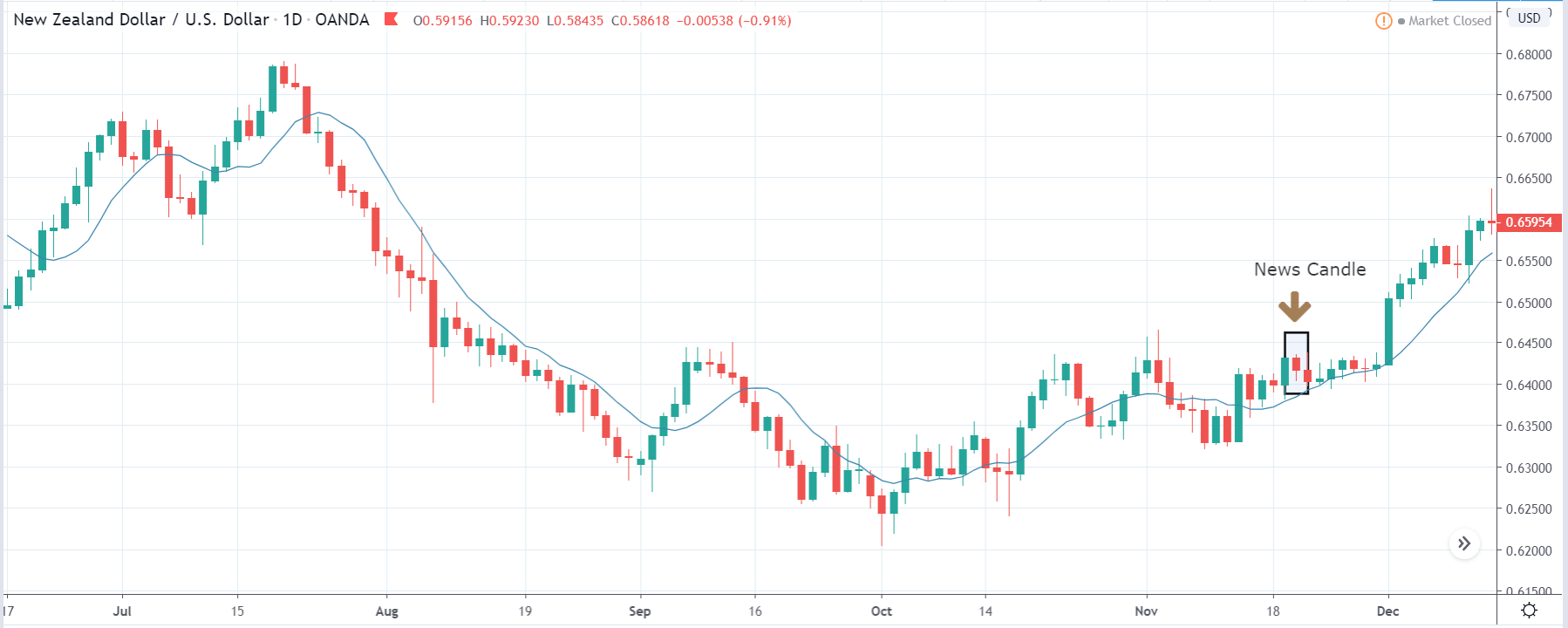
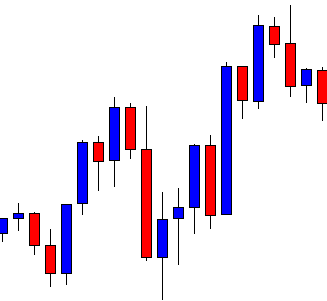
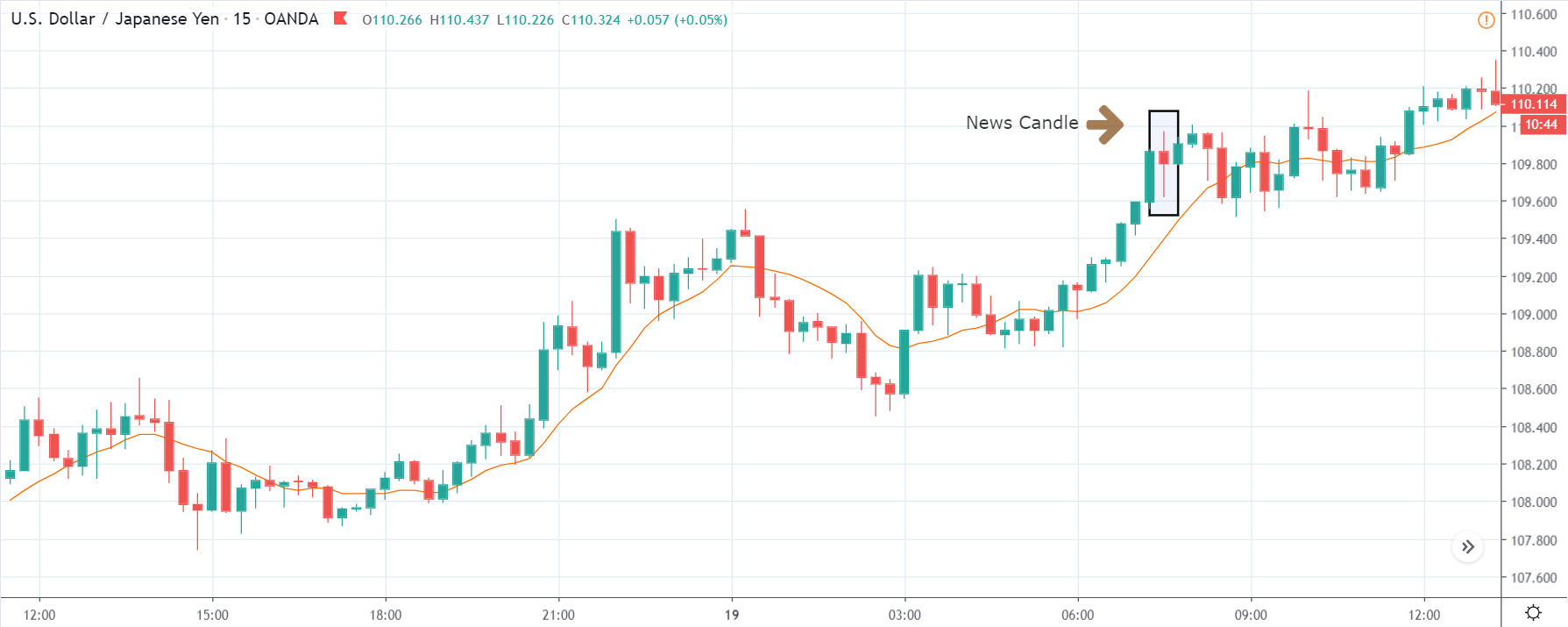
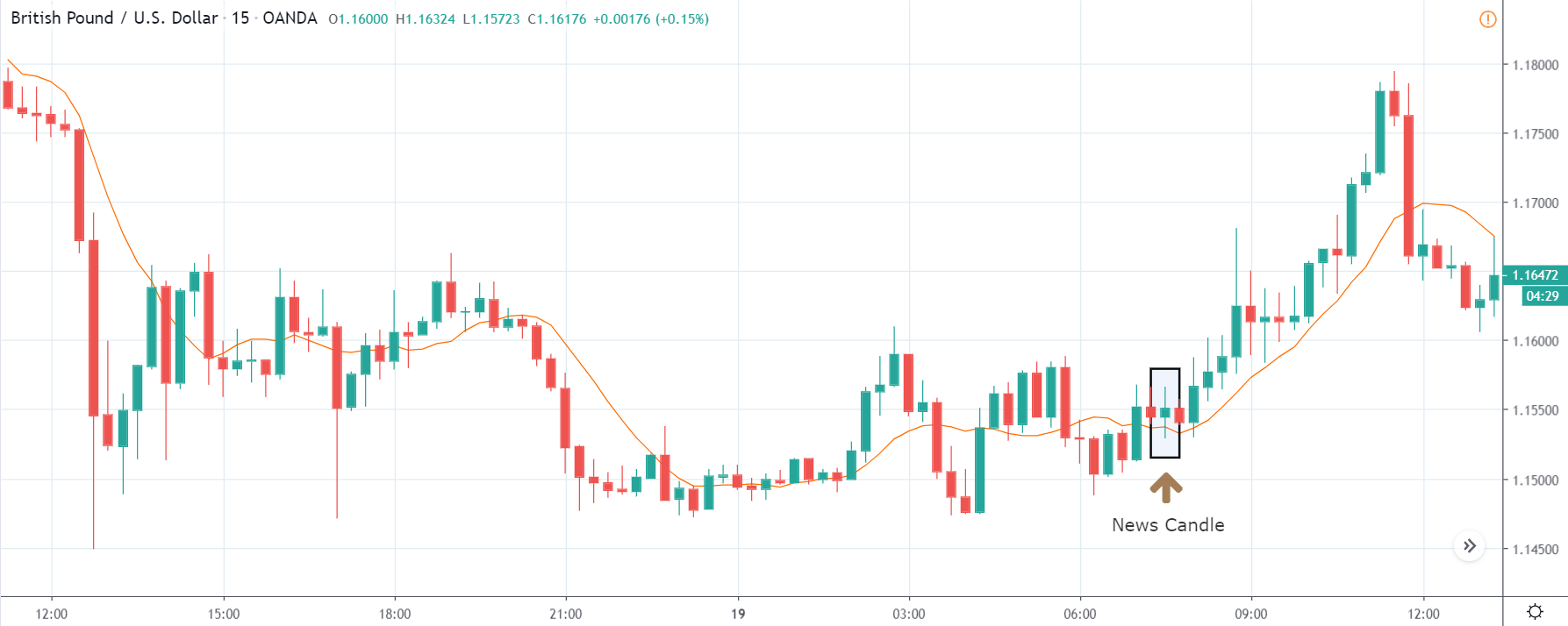
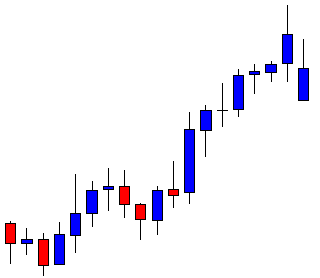
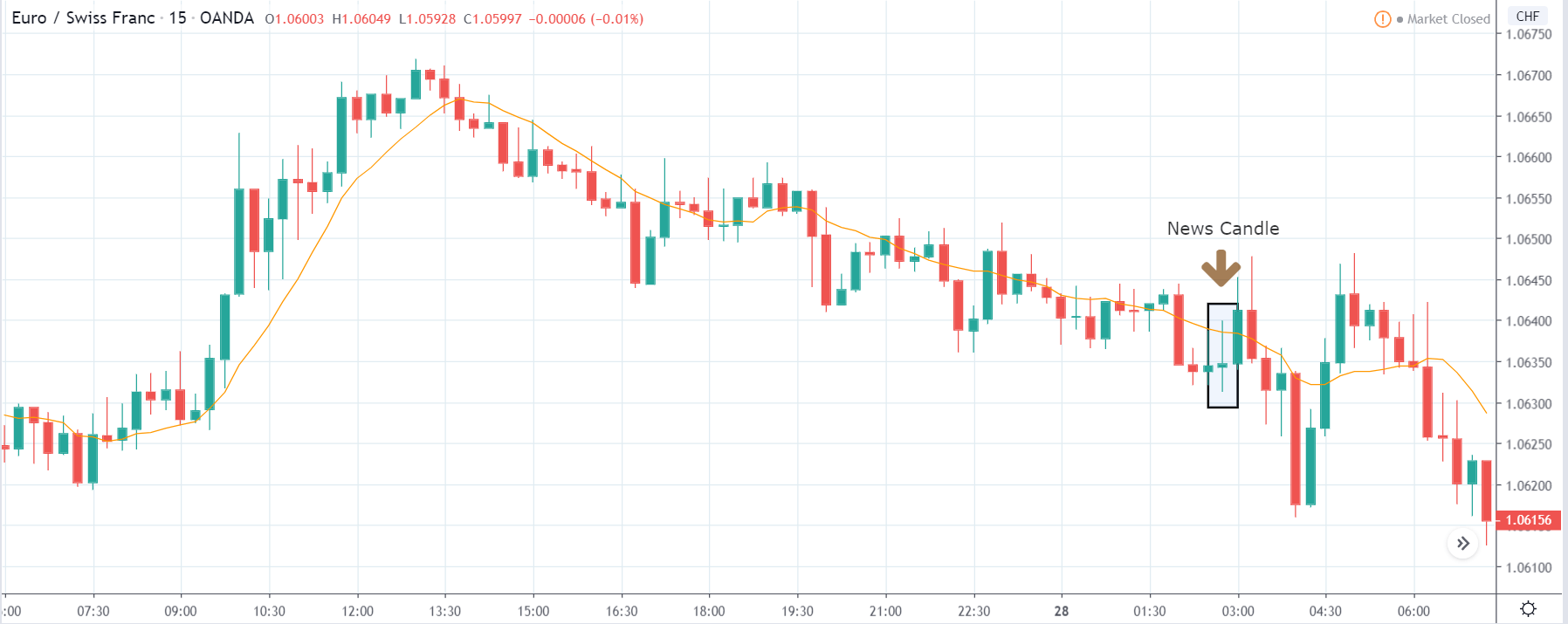
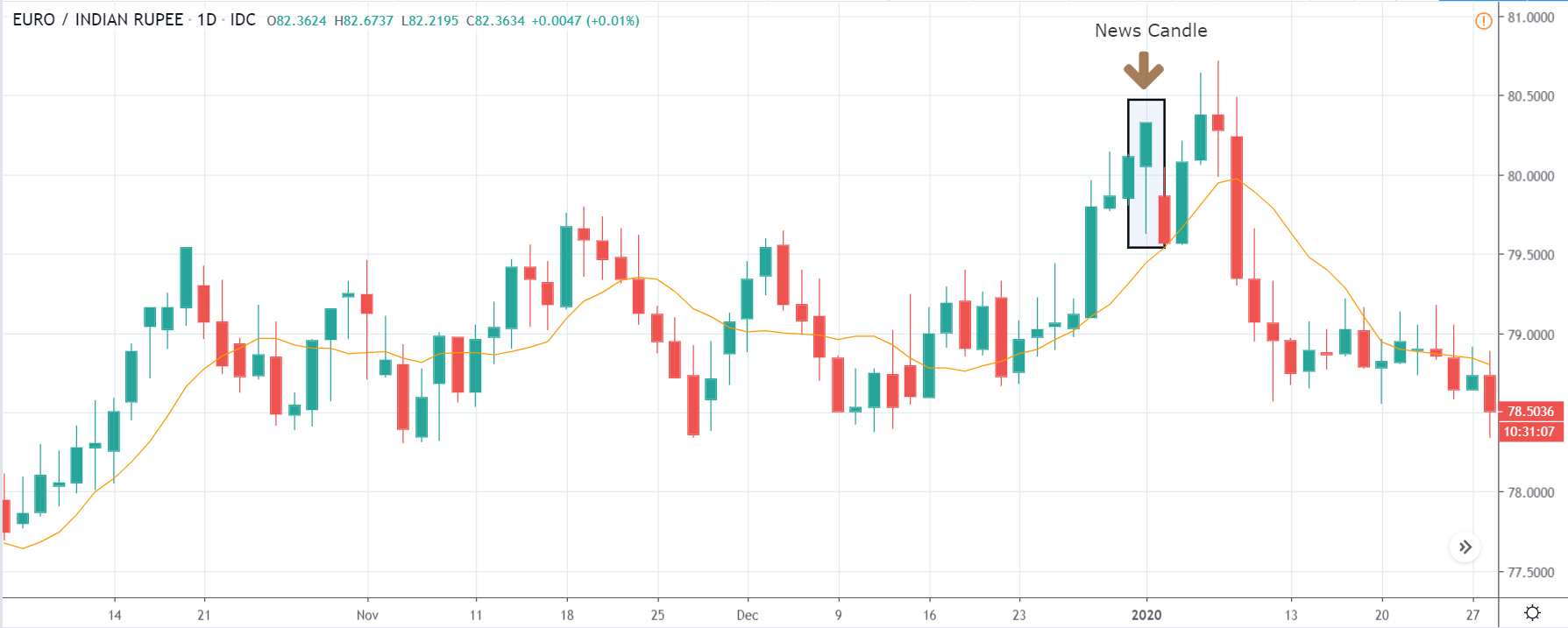
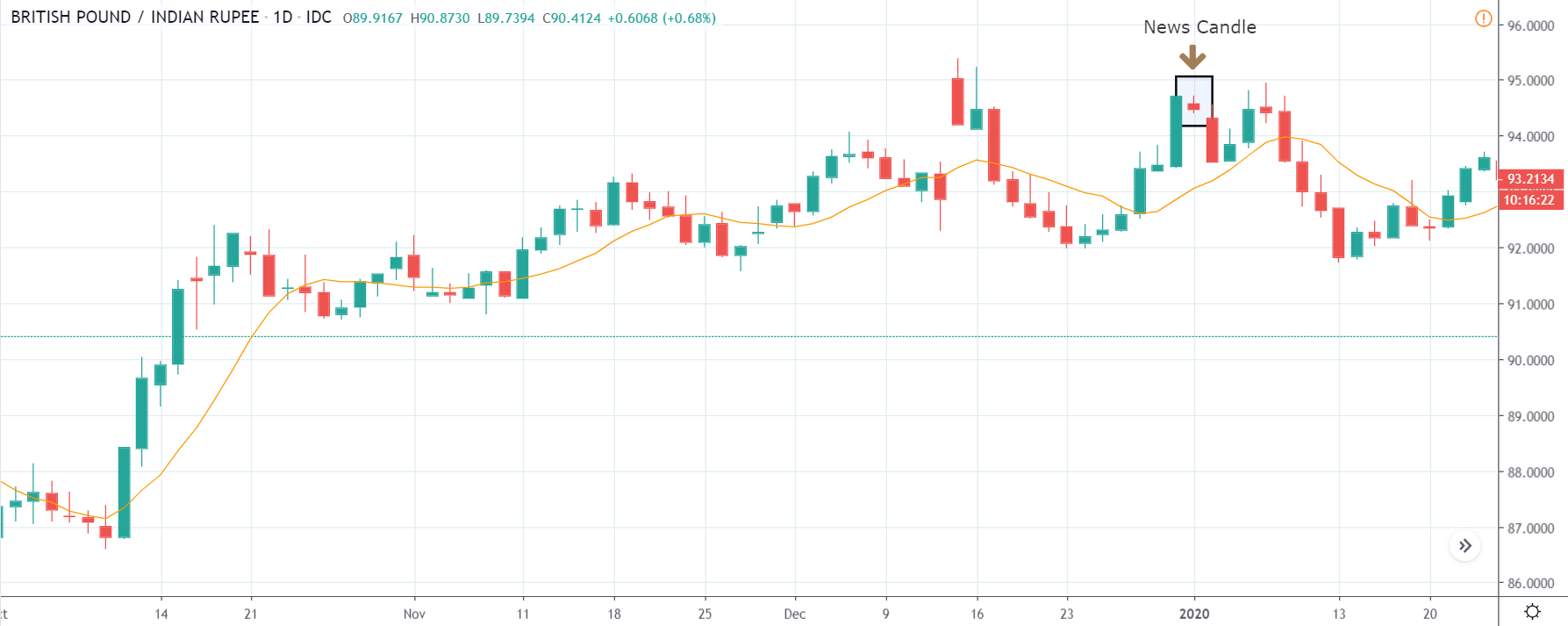
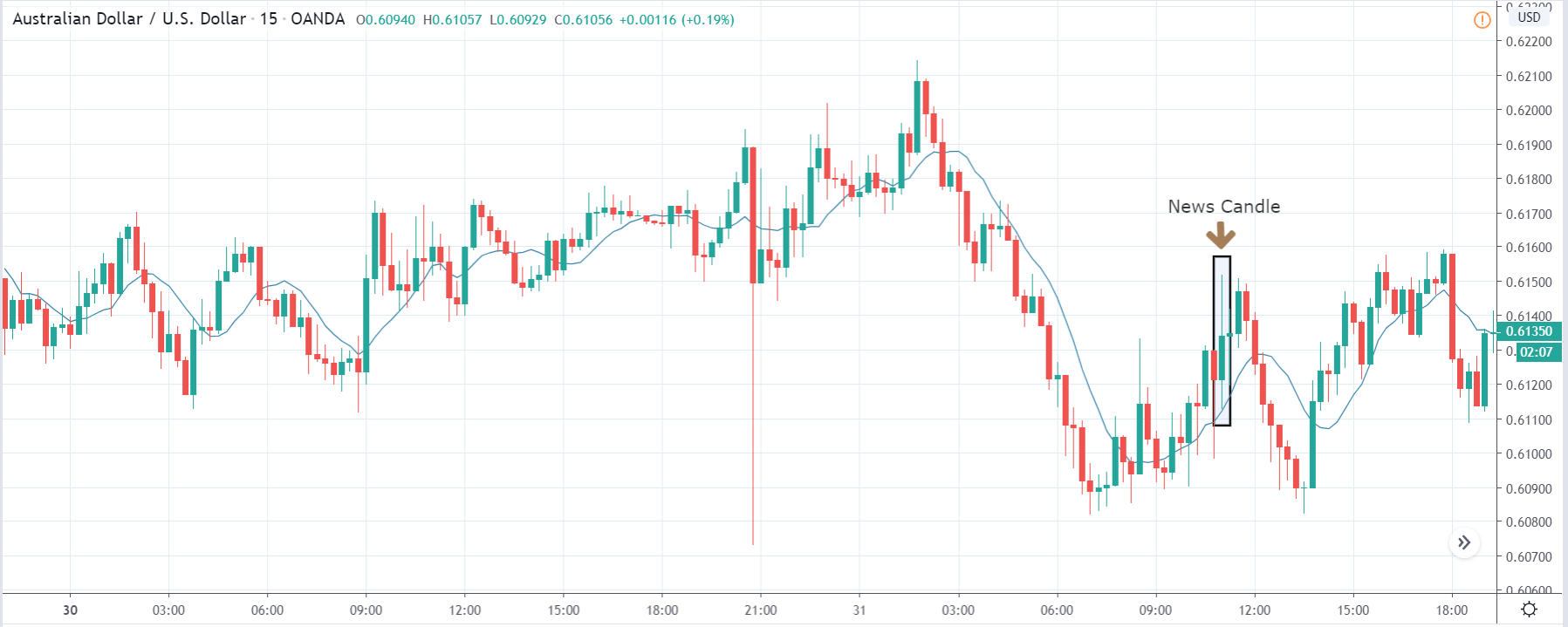
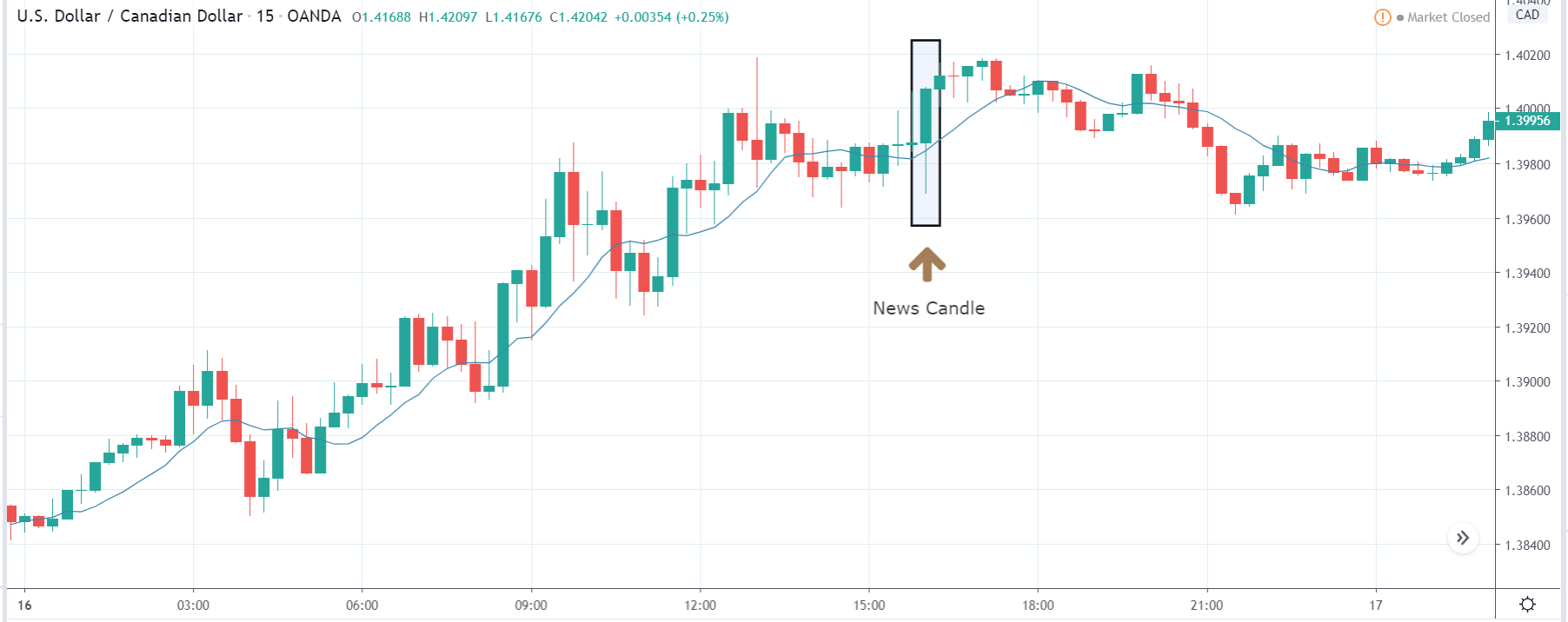
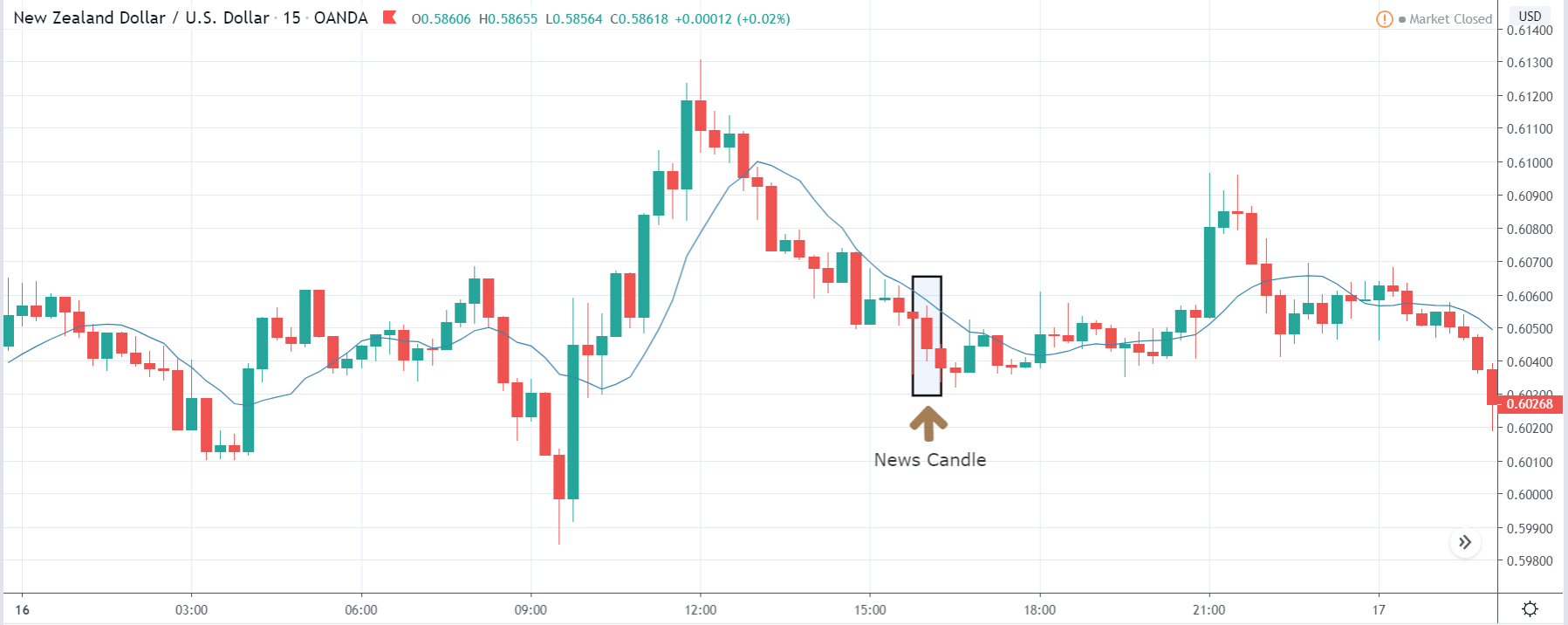
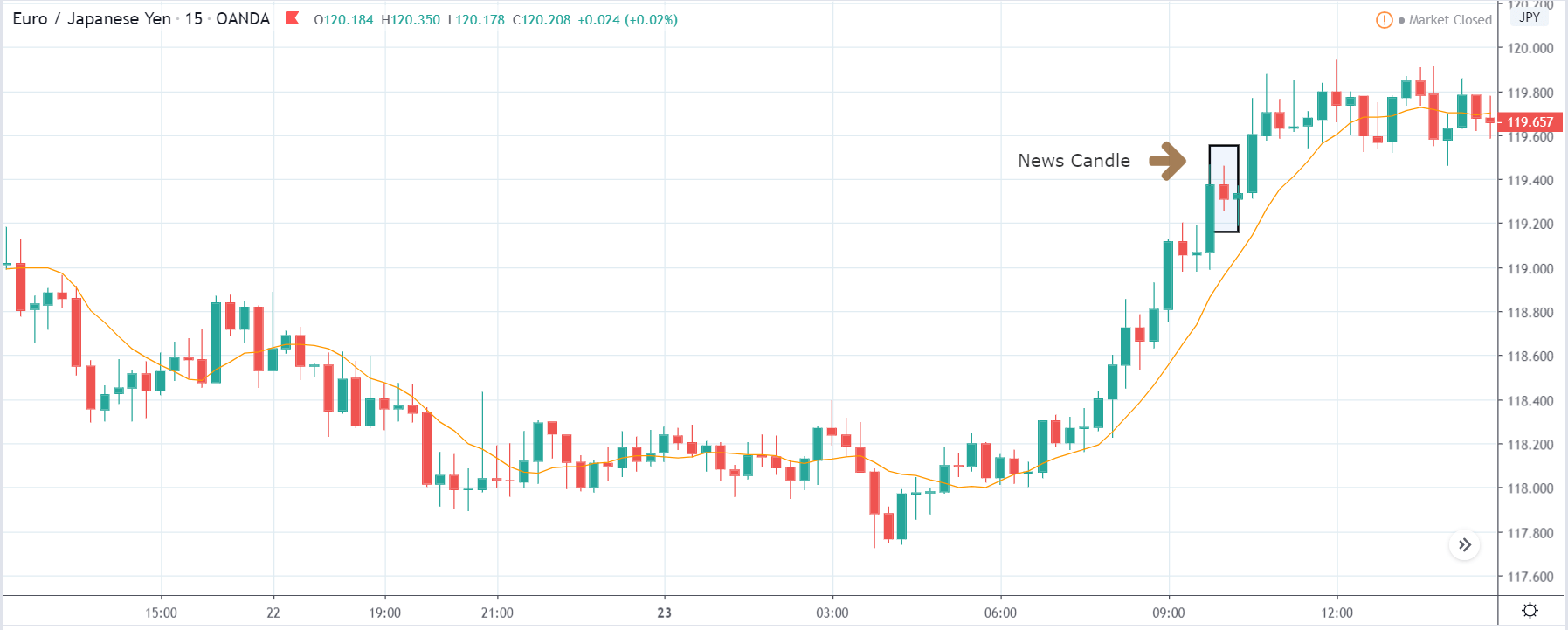
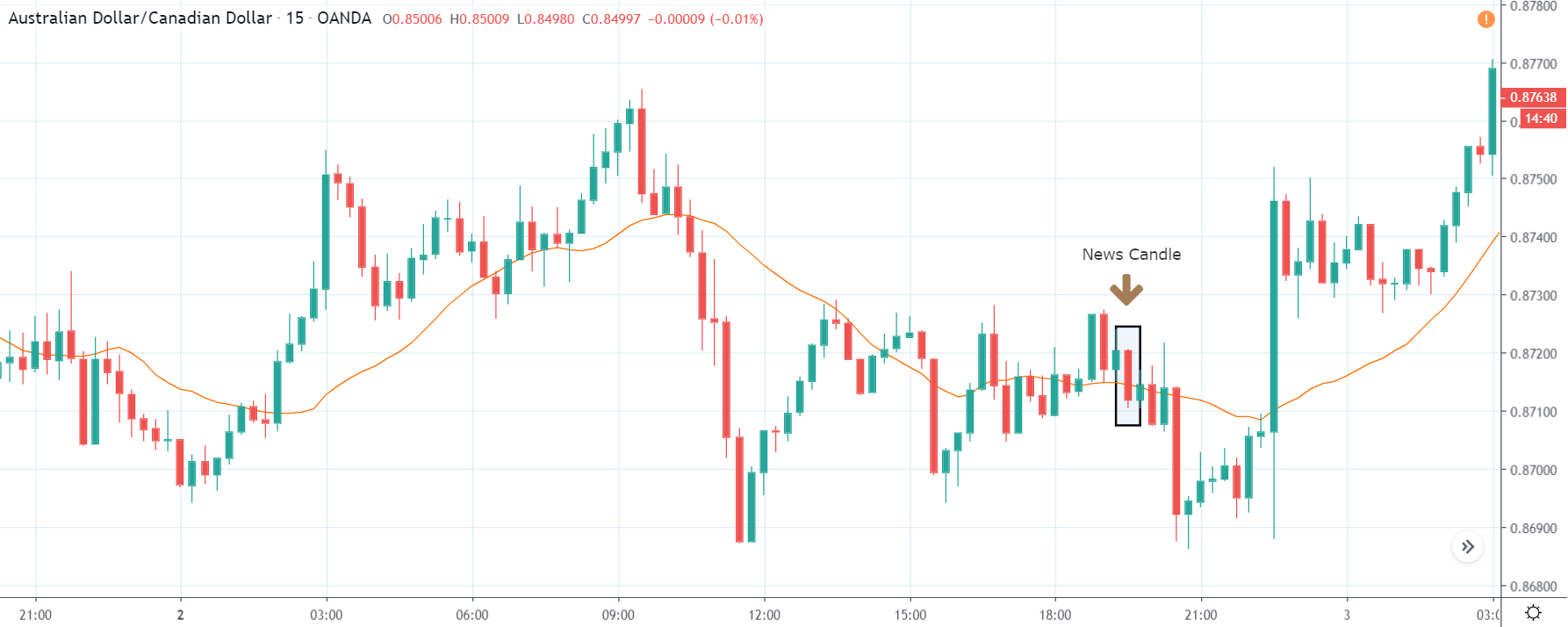
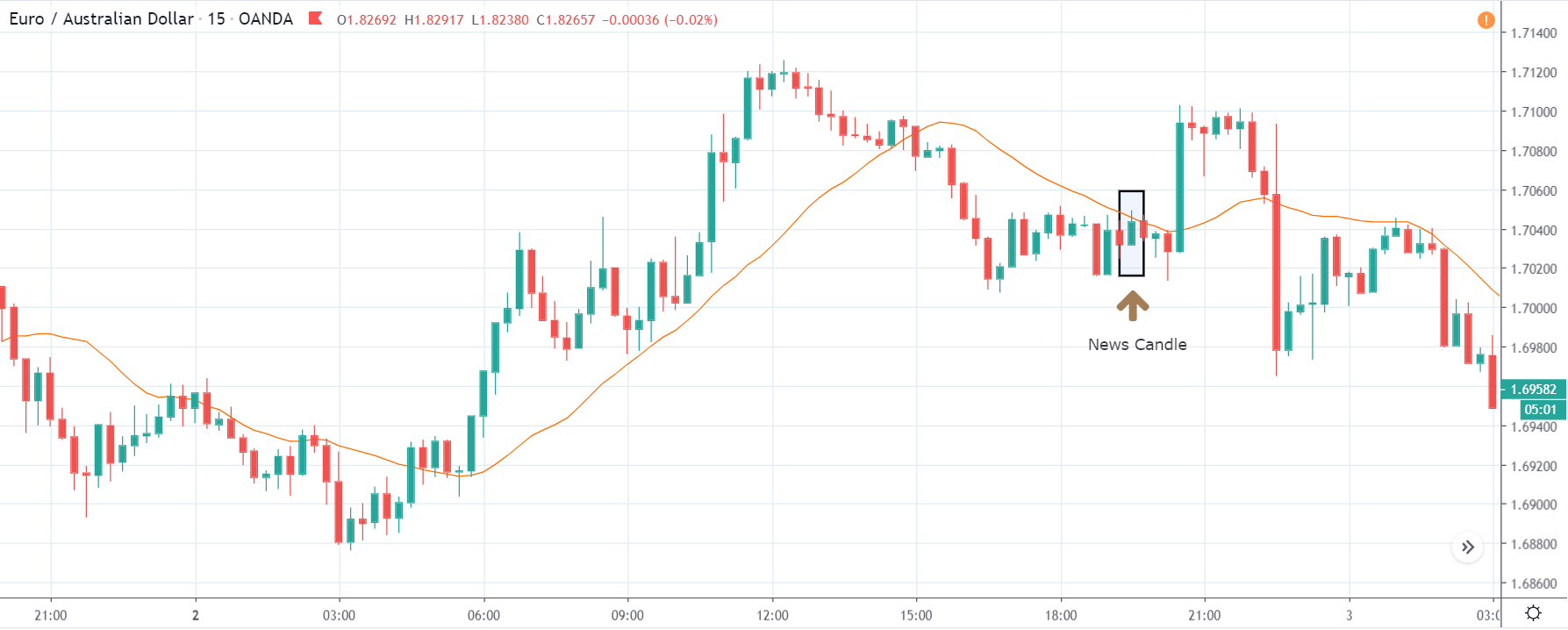
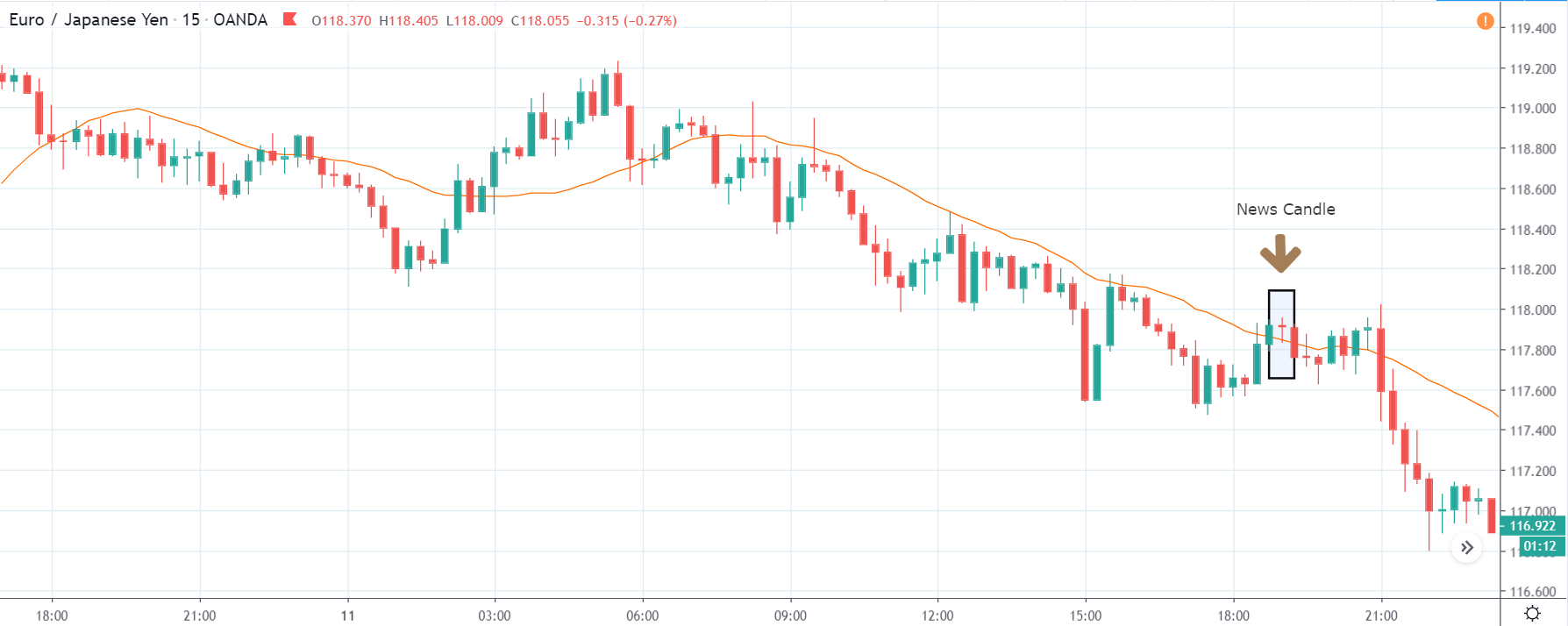
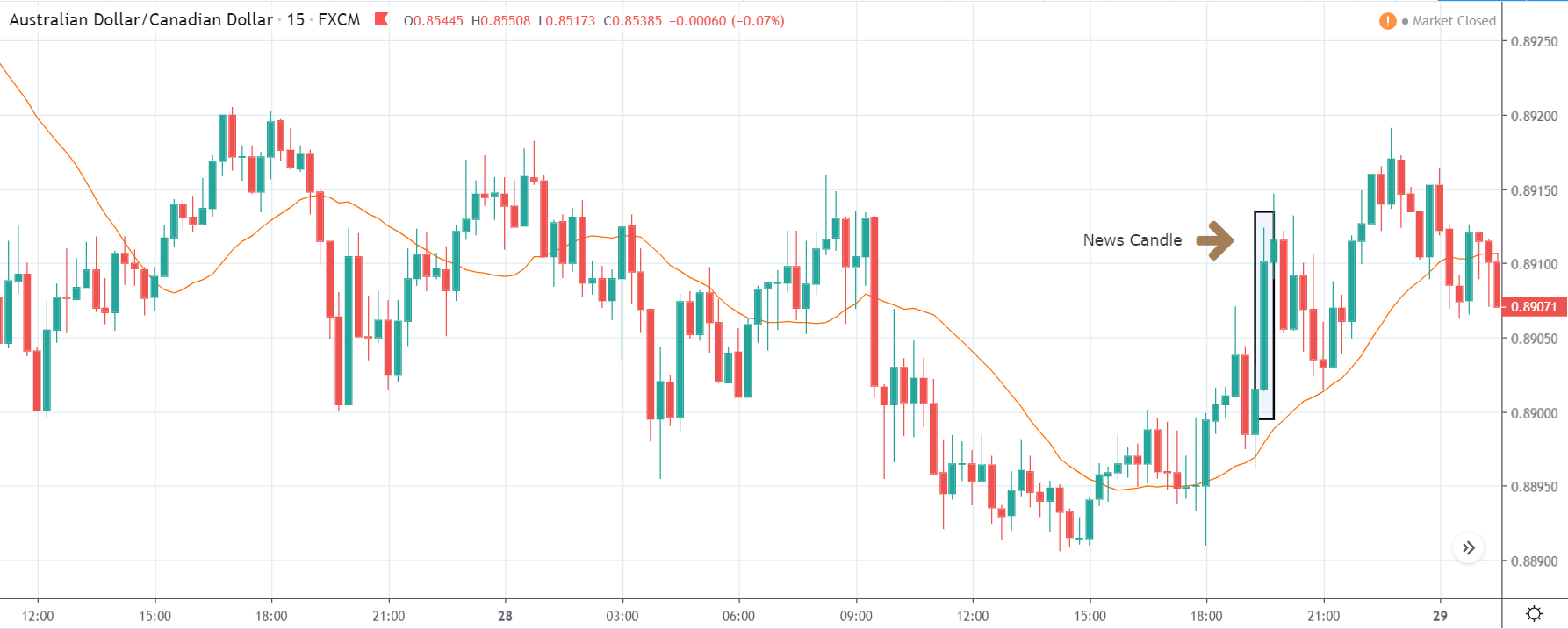
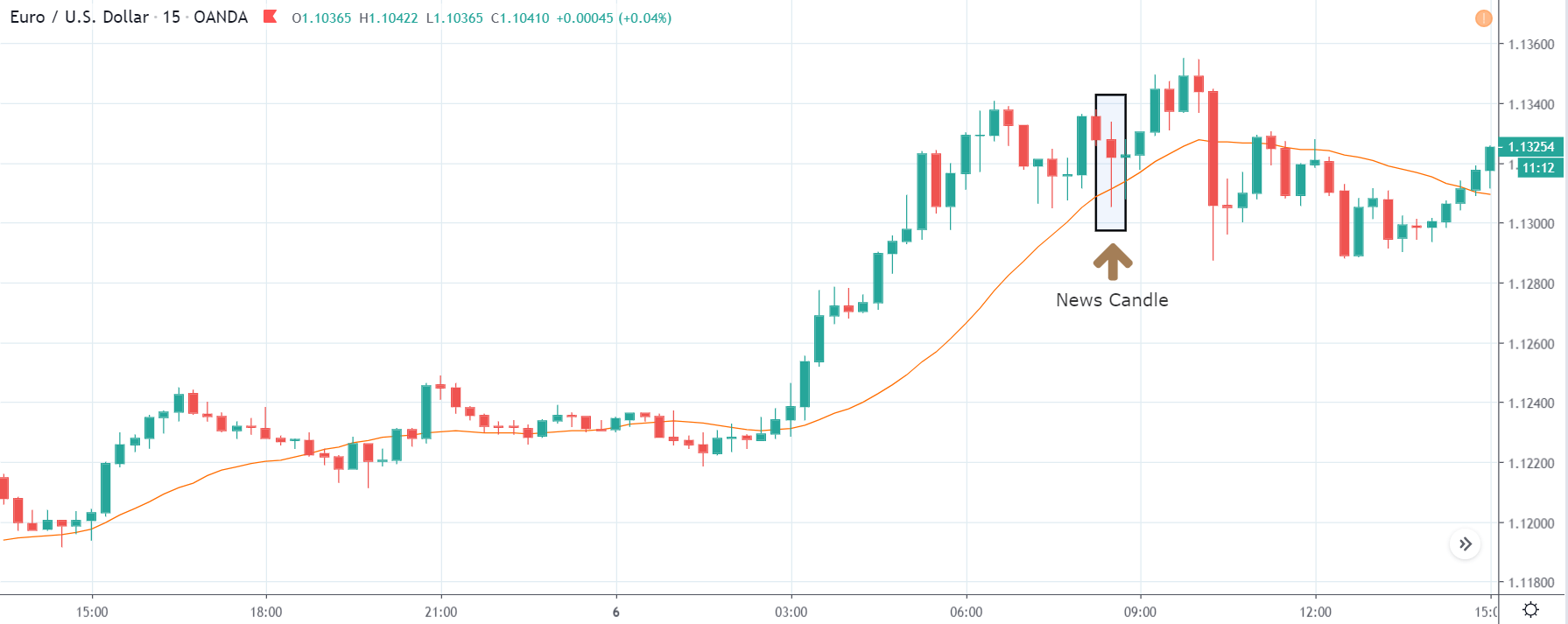
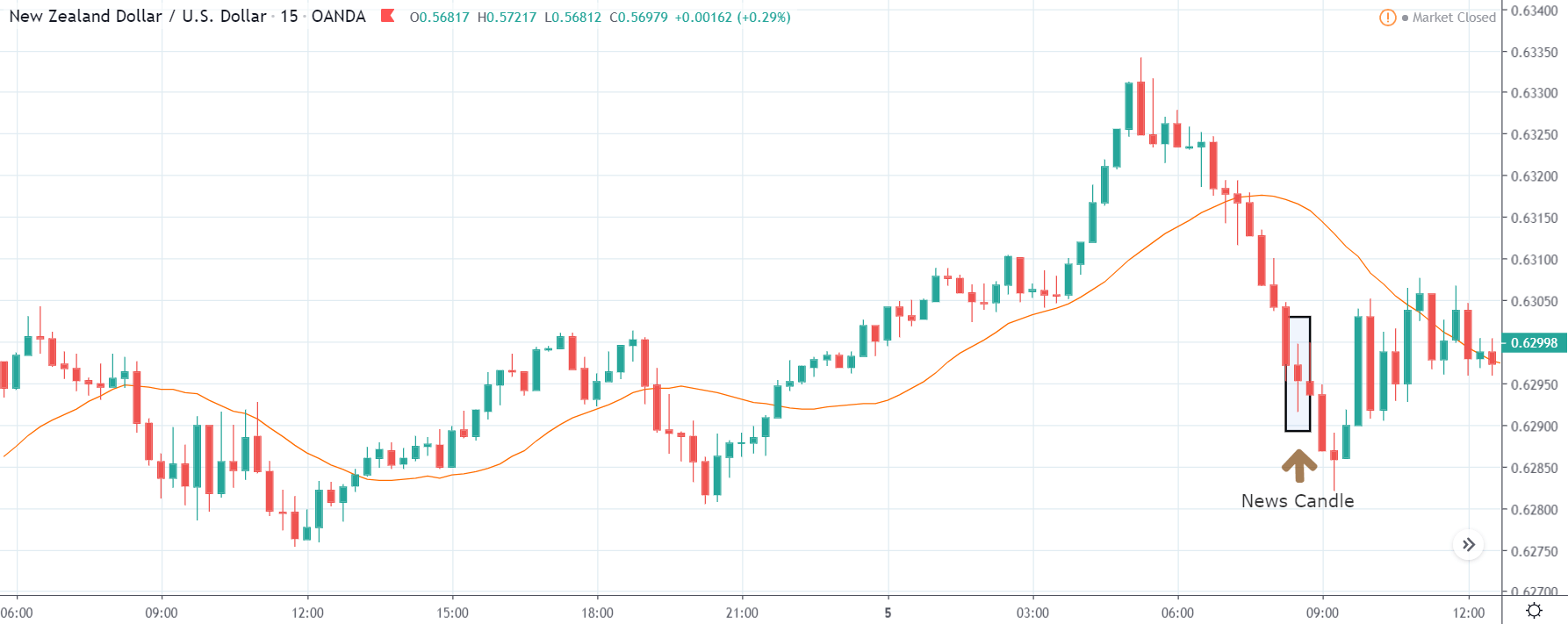
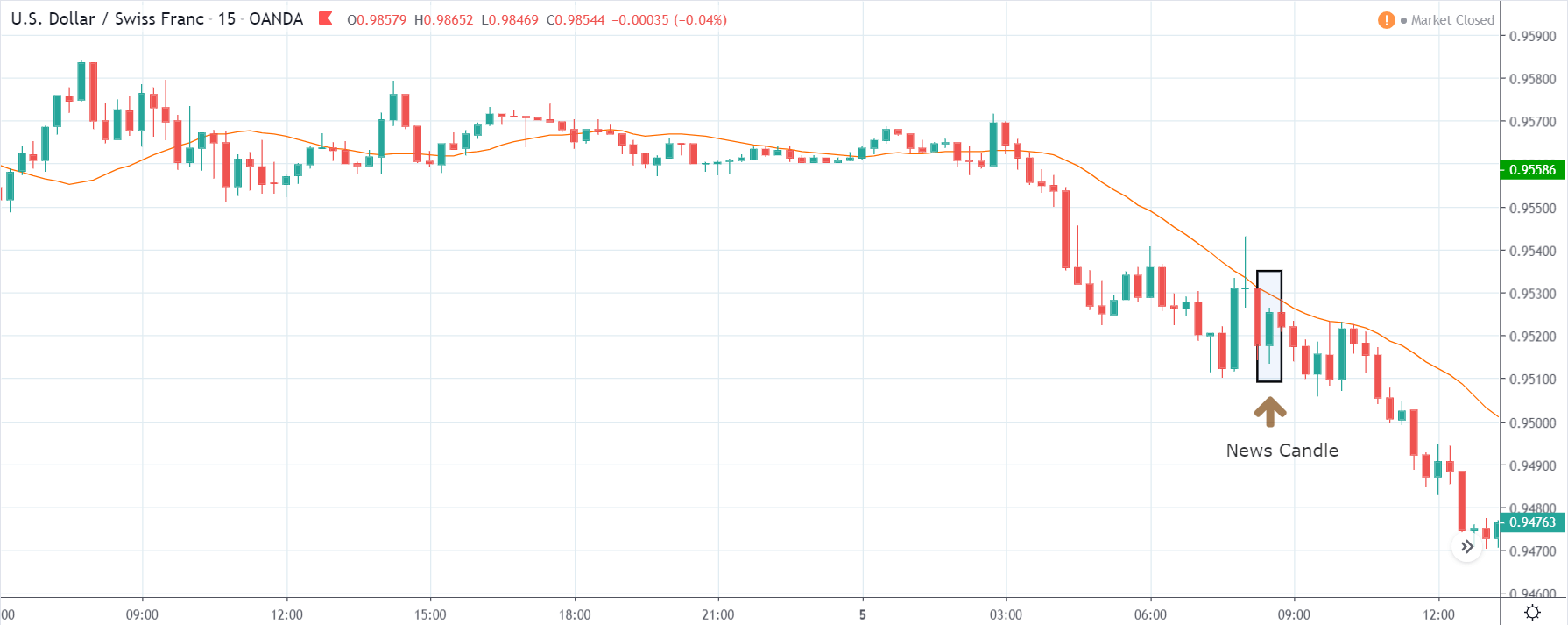
USD/ZAR | After the announcement:
After the news announcement, the market hardly reacts to the Mining Production data keeping the volatility at the bare minimum. Later we see that volatility increases to the downside, which causes the strengthening of South African Rand. The market shows positively to the news release after the close of the ‘news candle.’ As the Mining Production data was bullish, traders are seen going ‘short’ in the currency pair and strengthening the South African Rand, immediately after the ‘news candle.
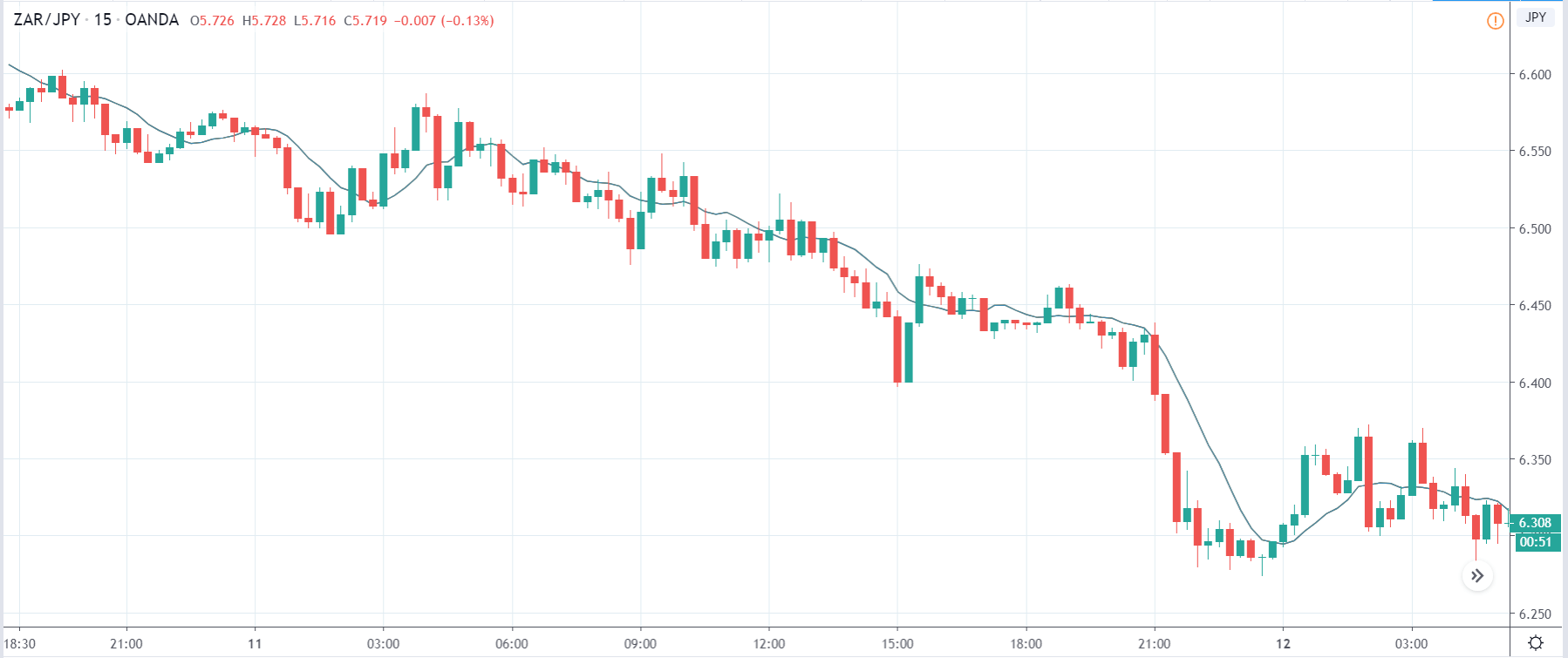
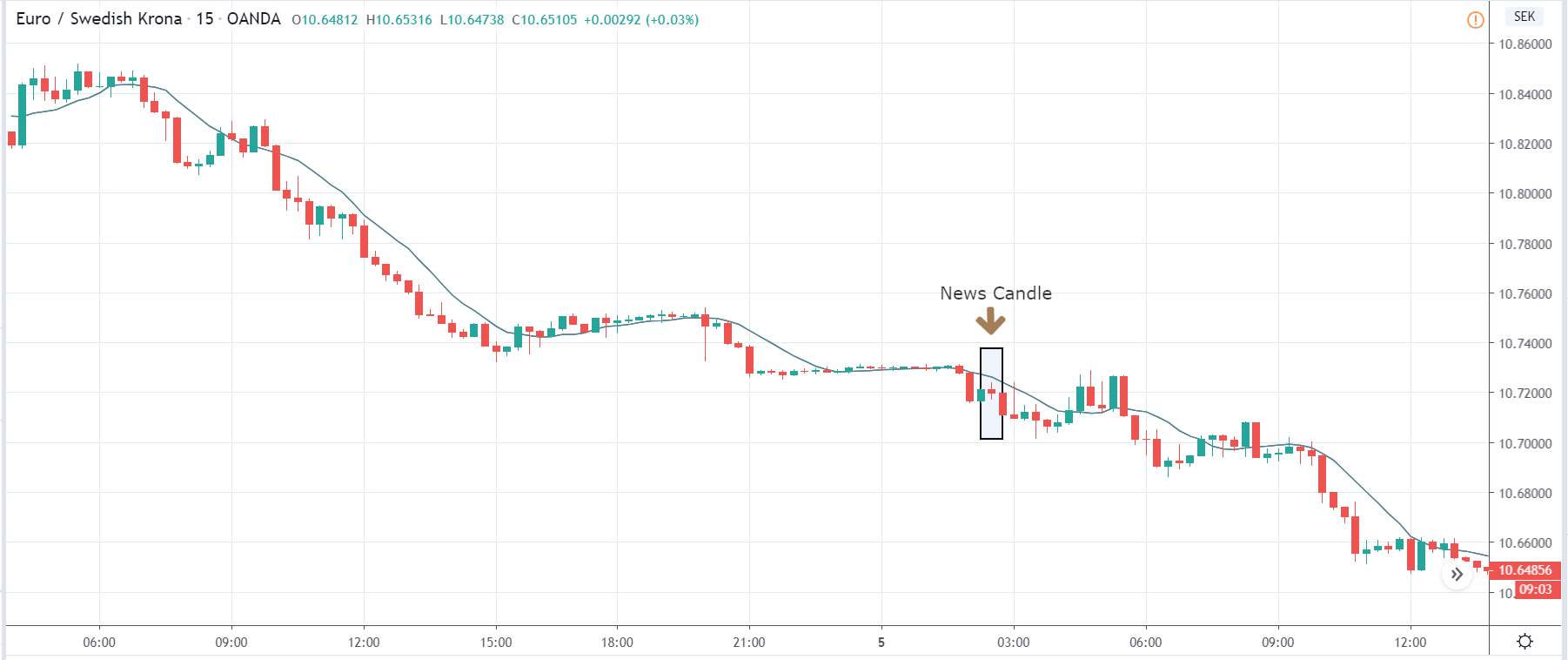
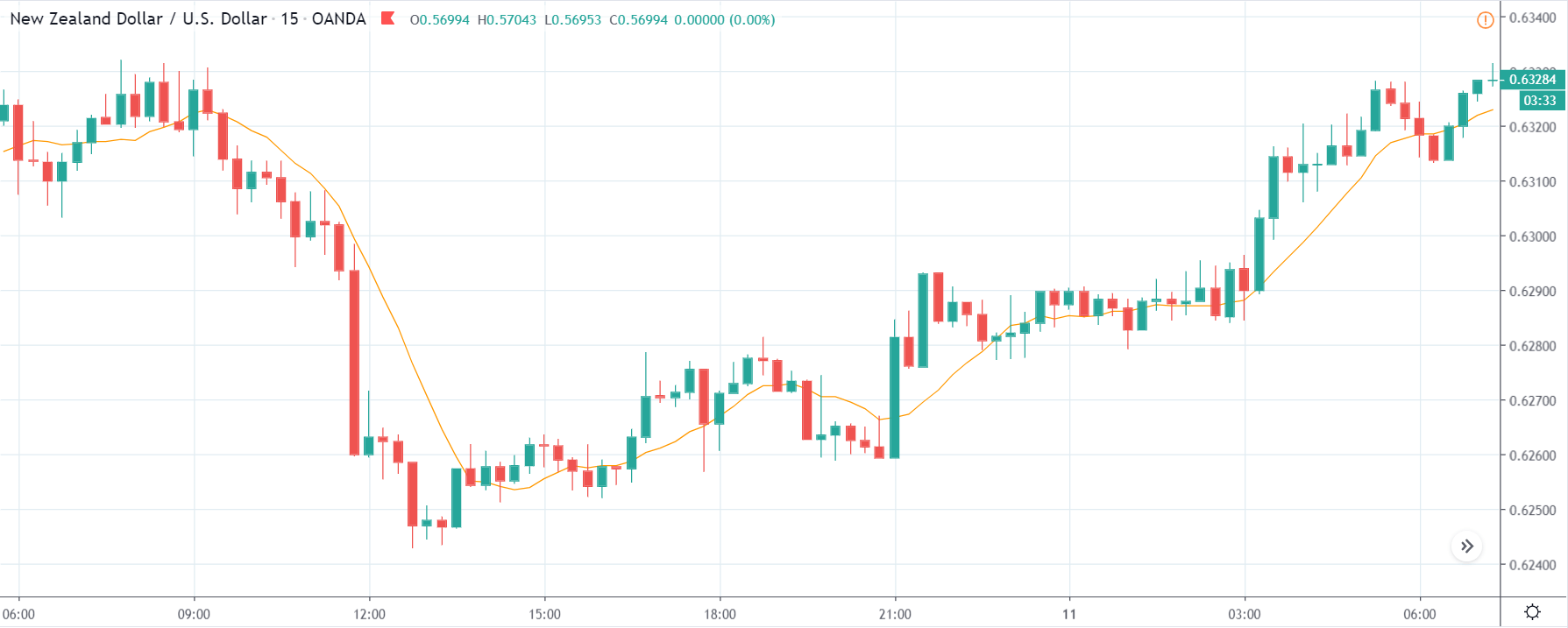
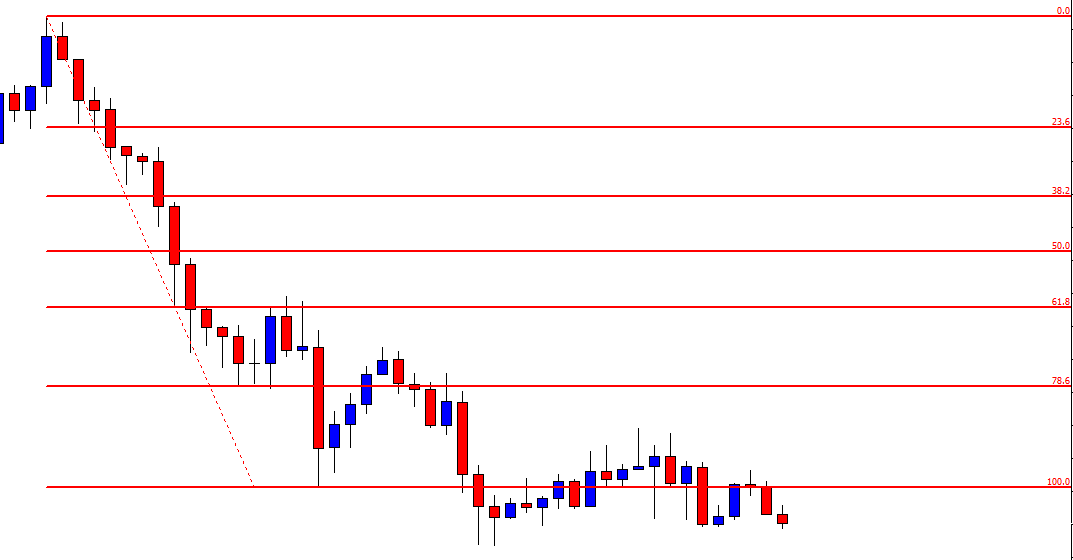
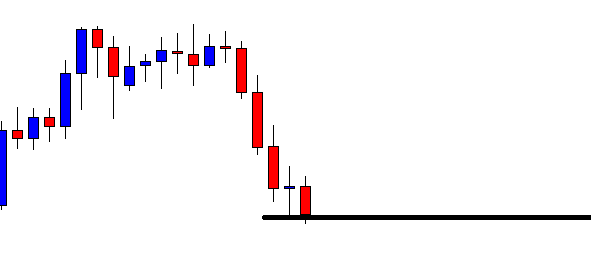
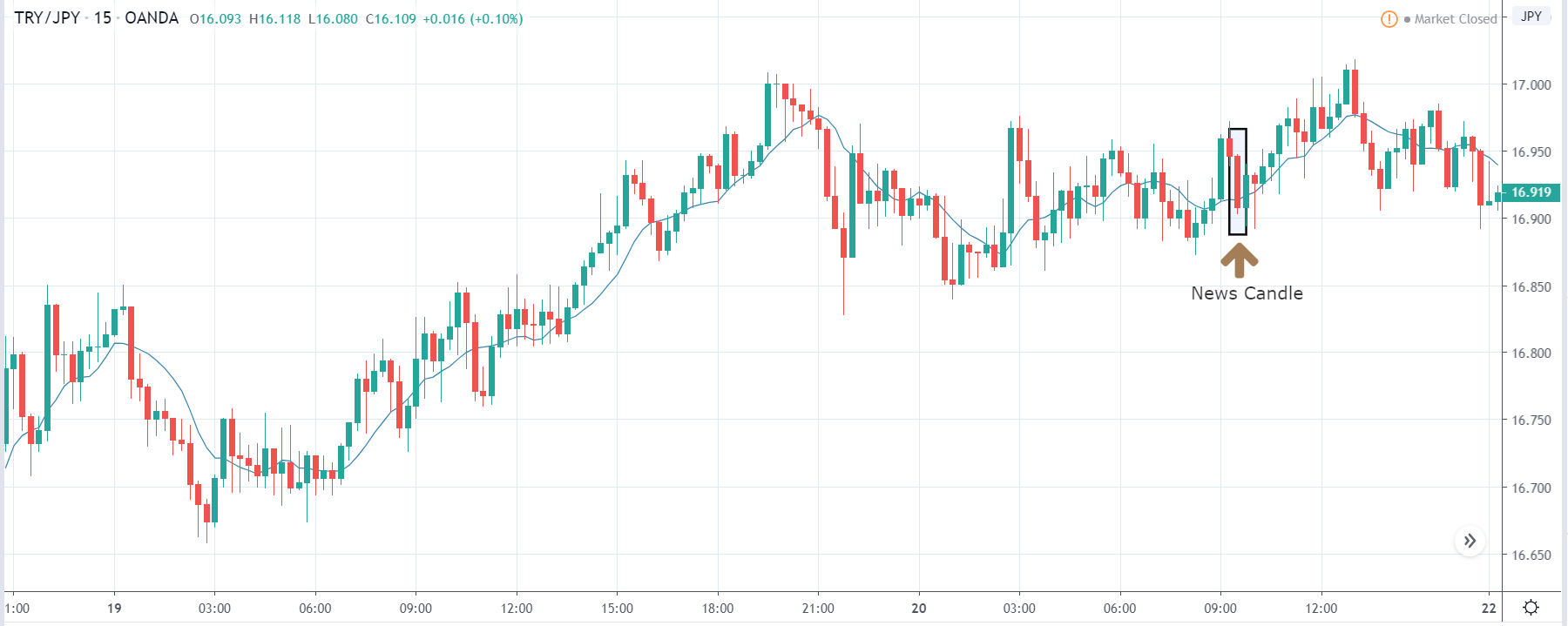
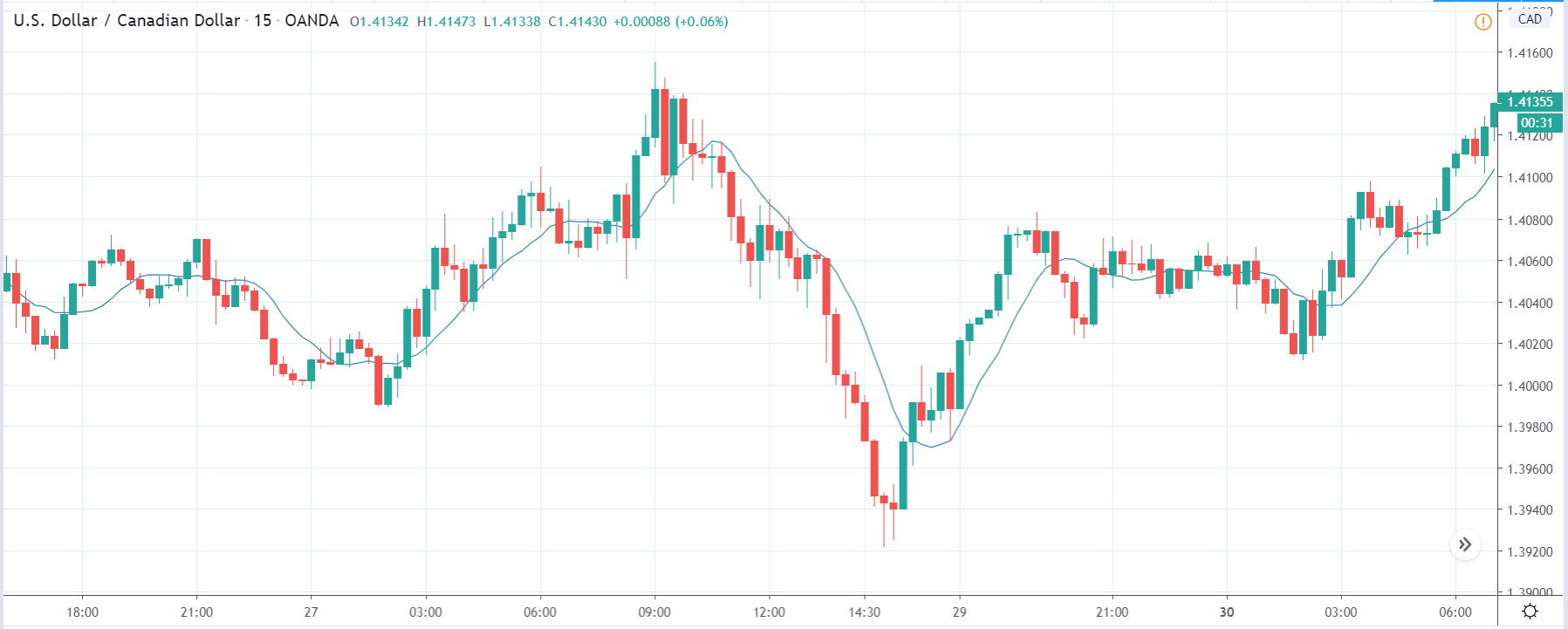
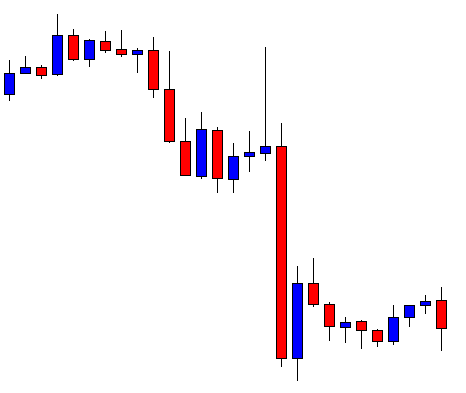
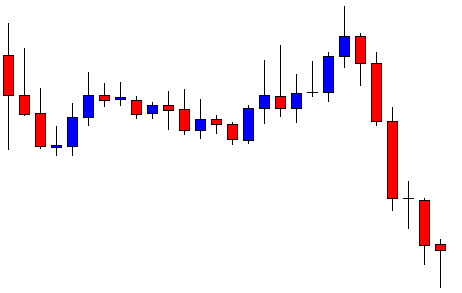
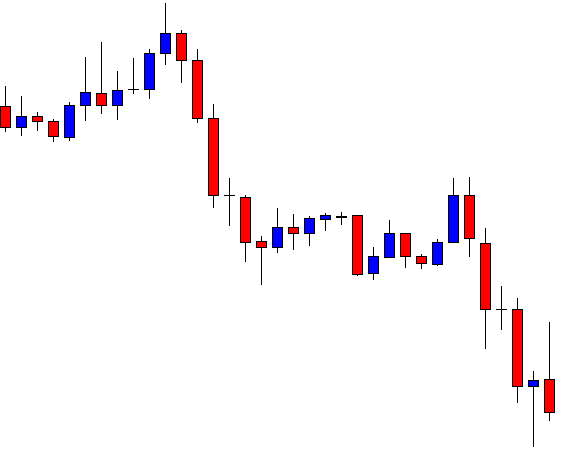
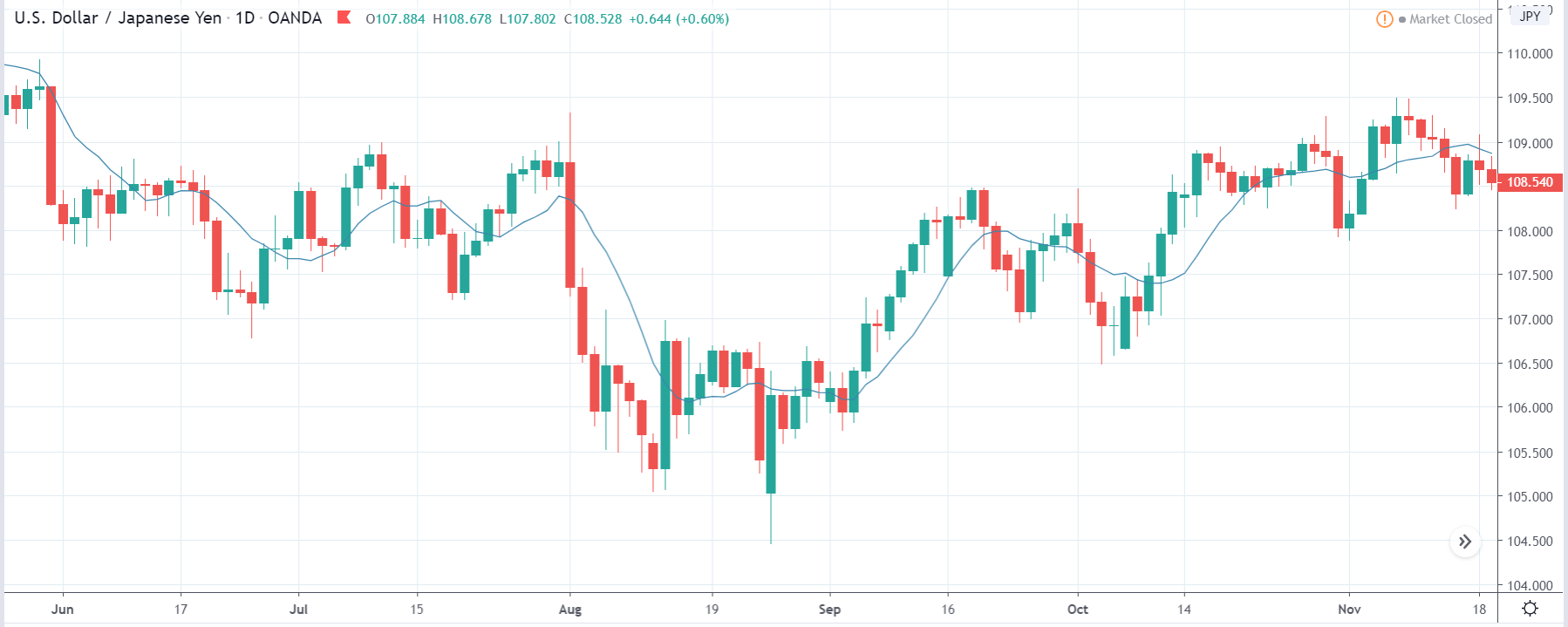
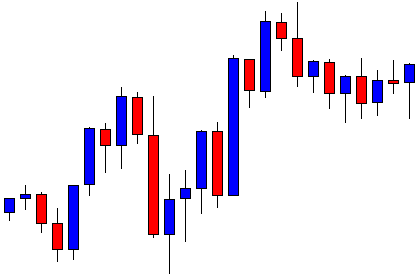
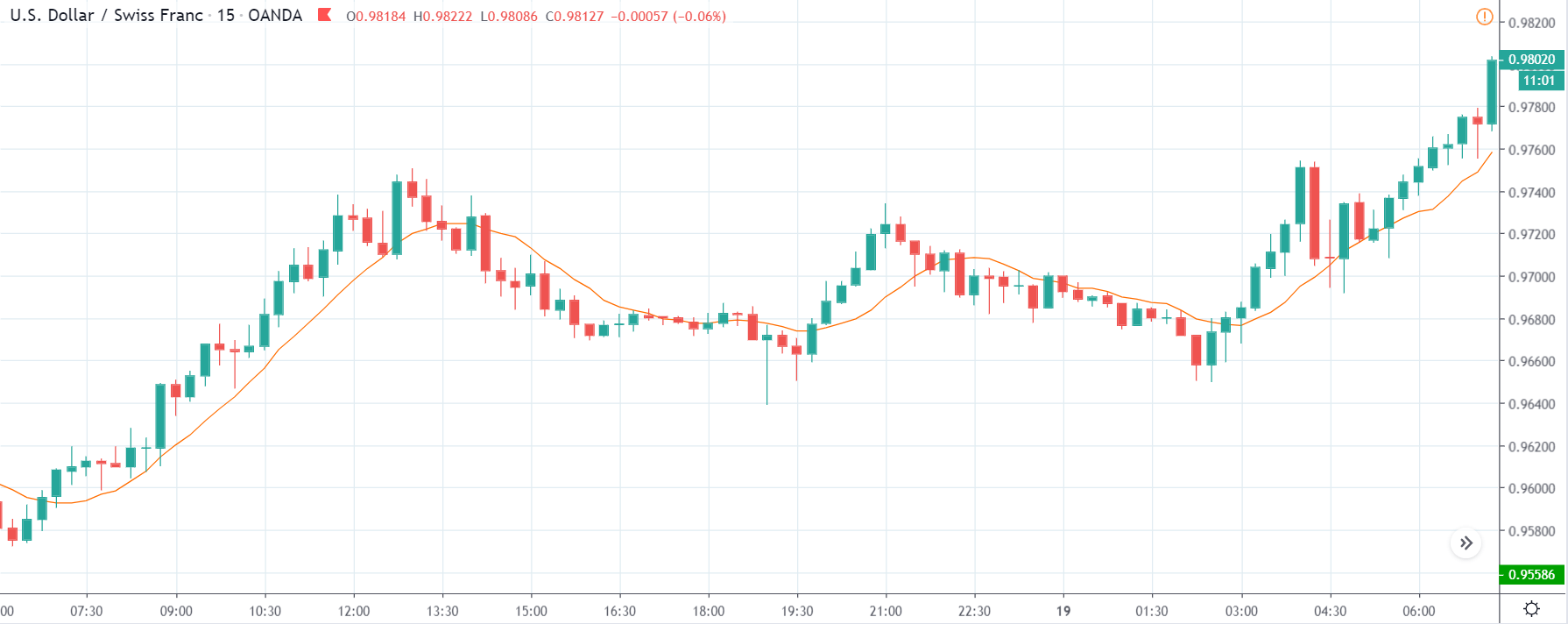
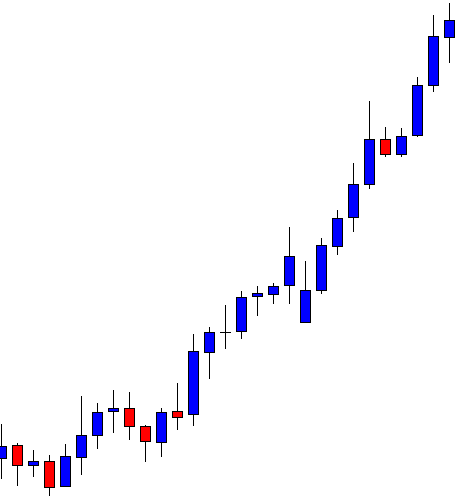
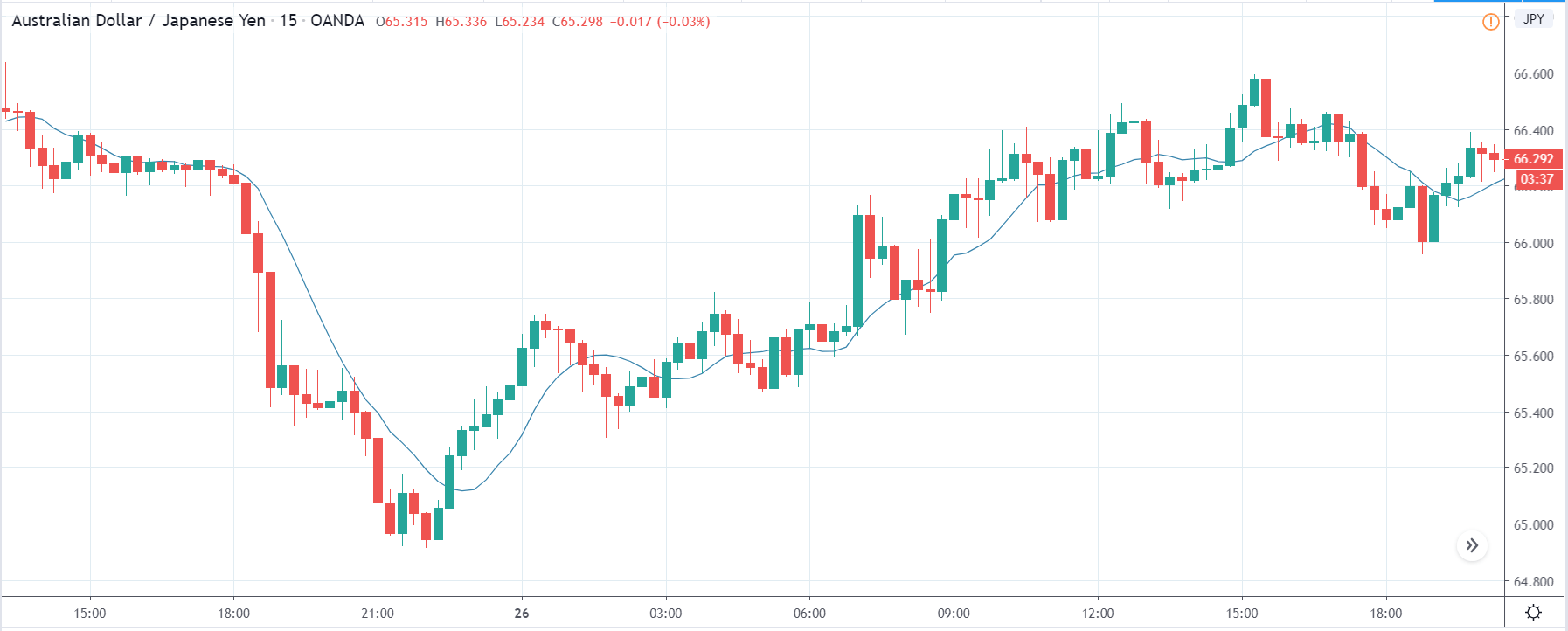
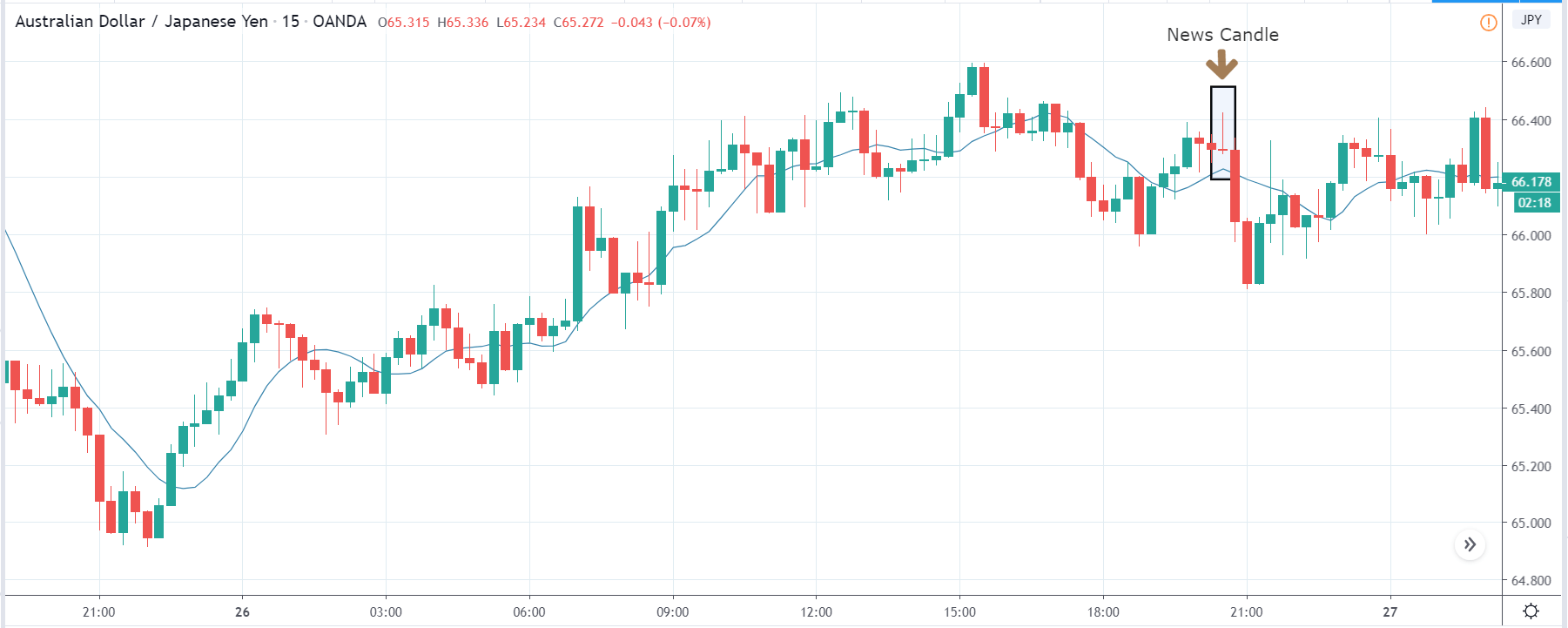
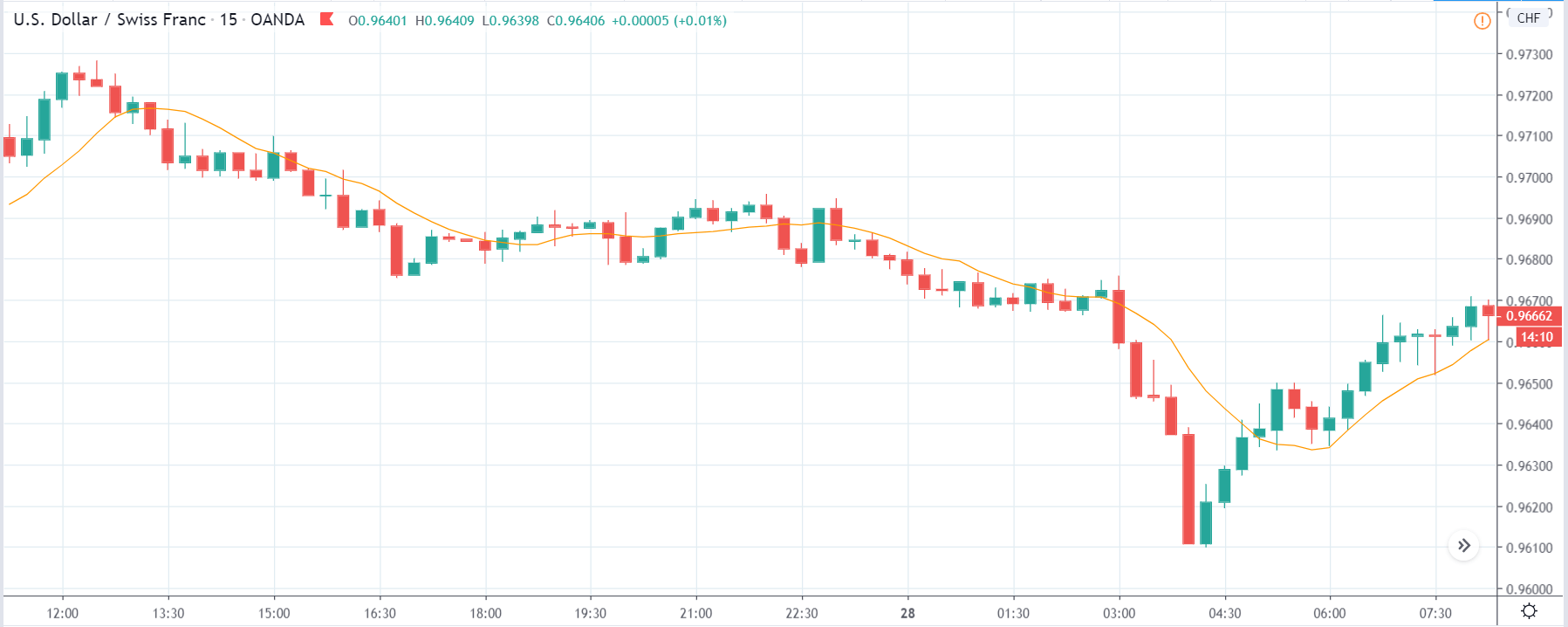
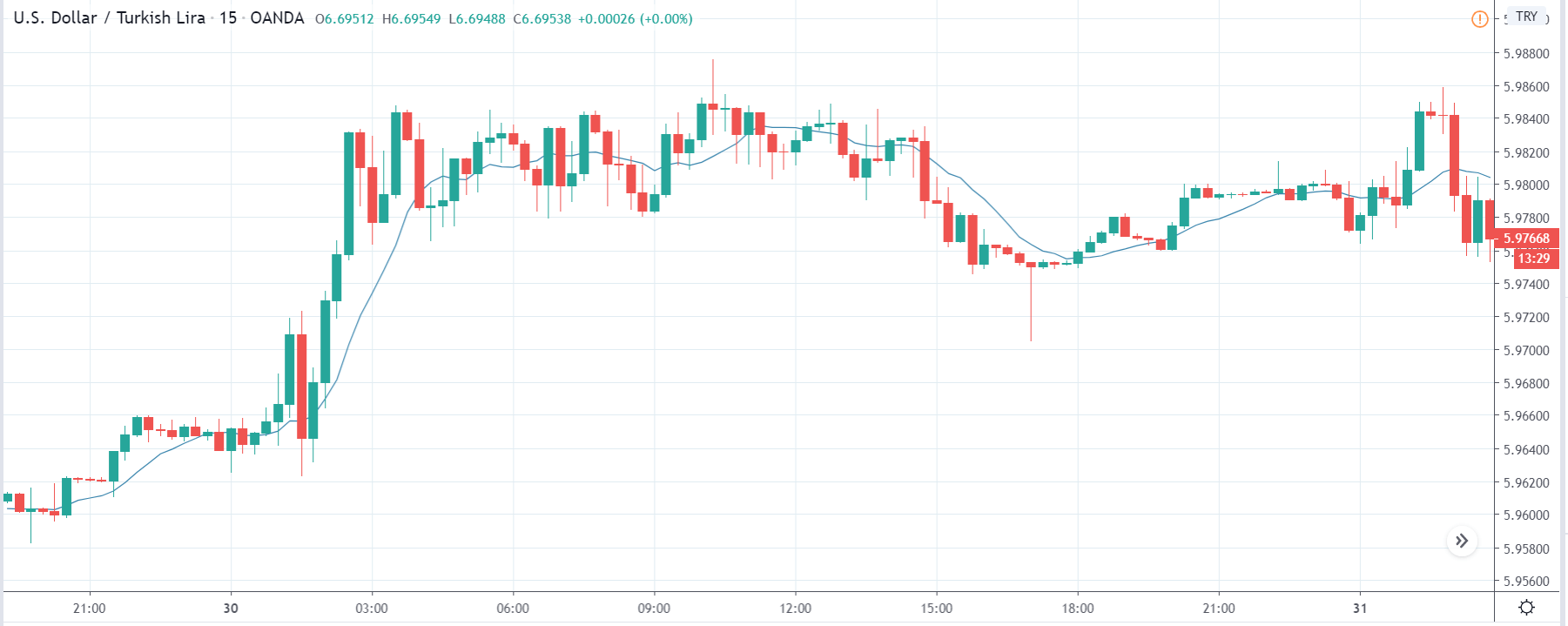
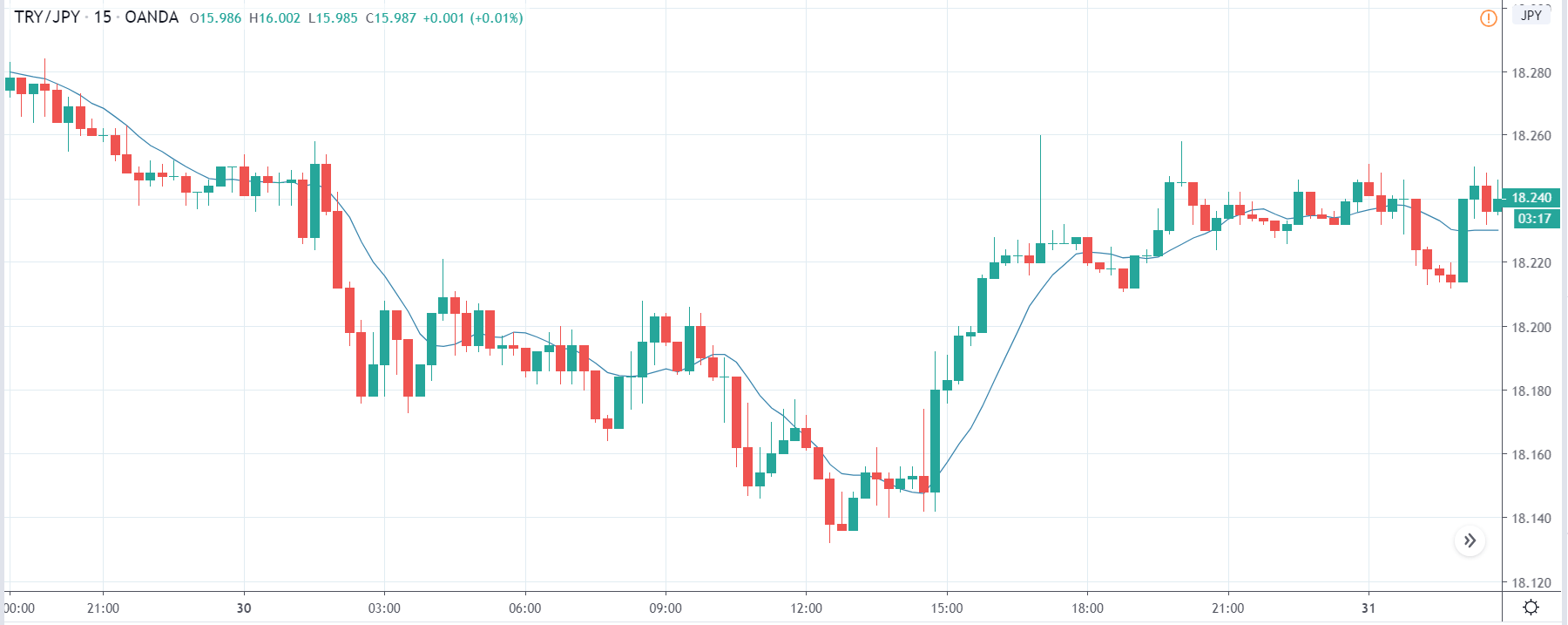
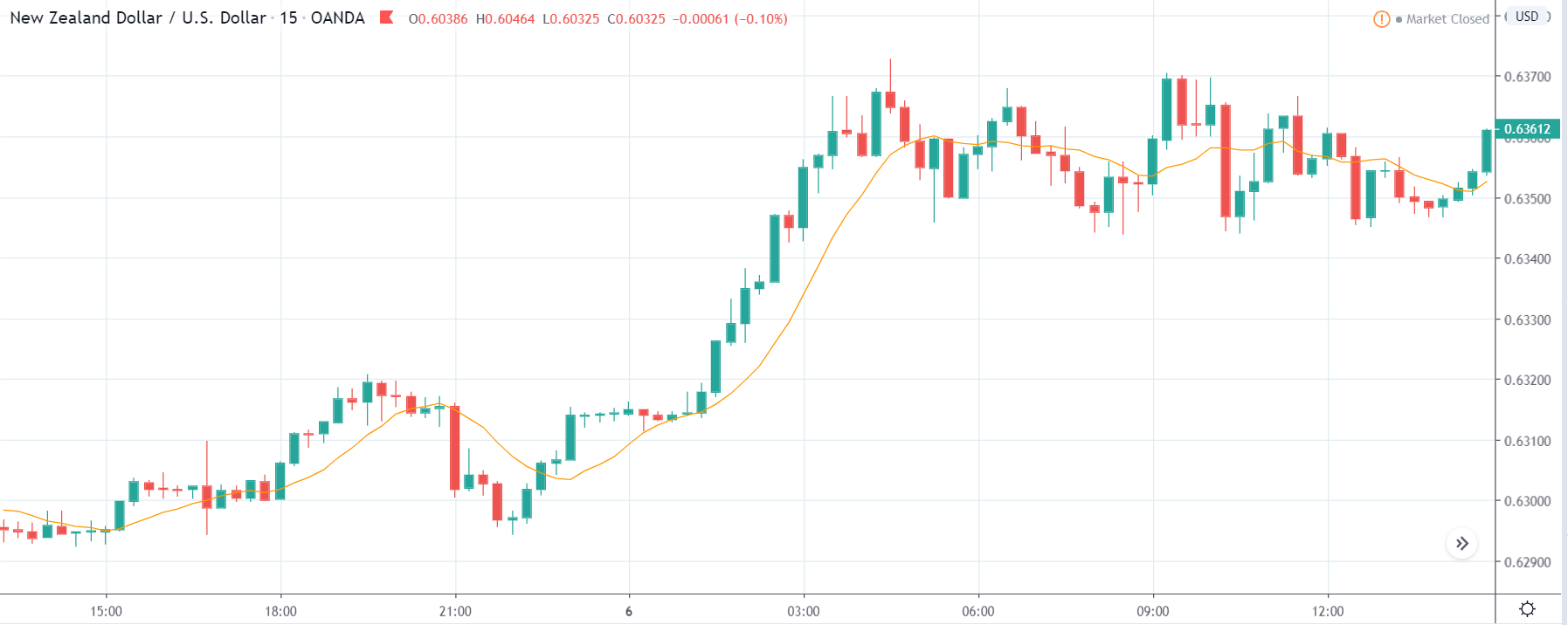
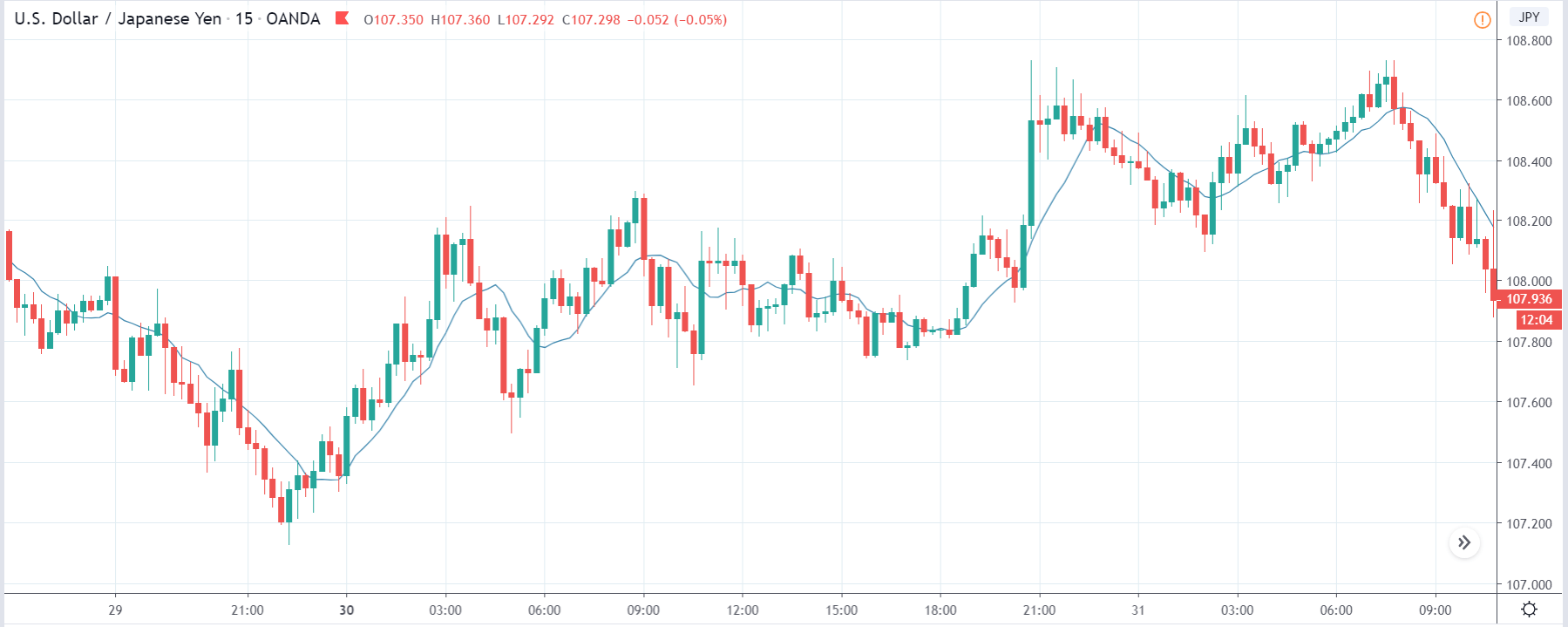
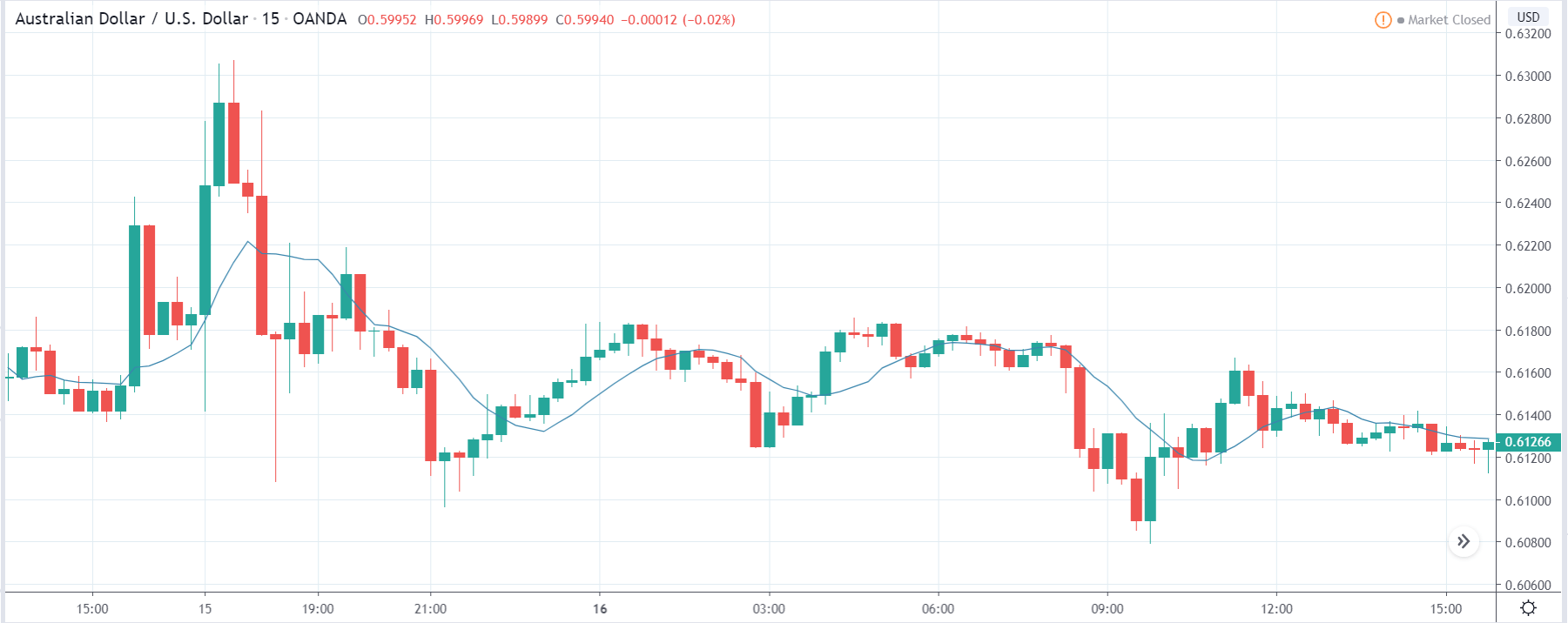
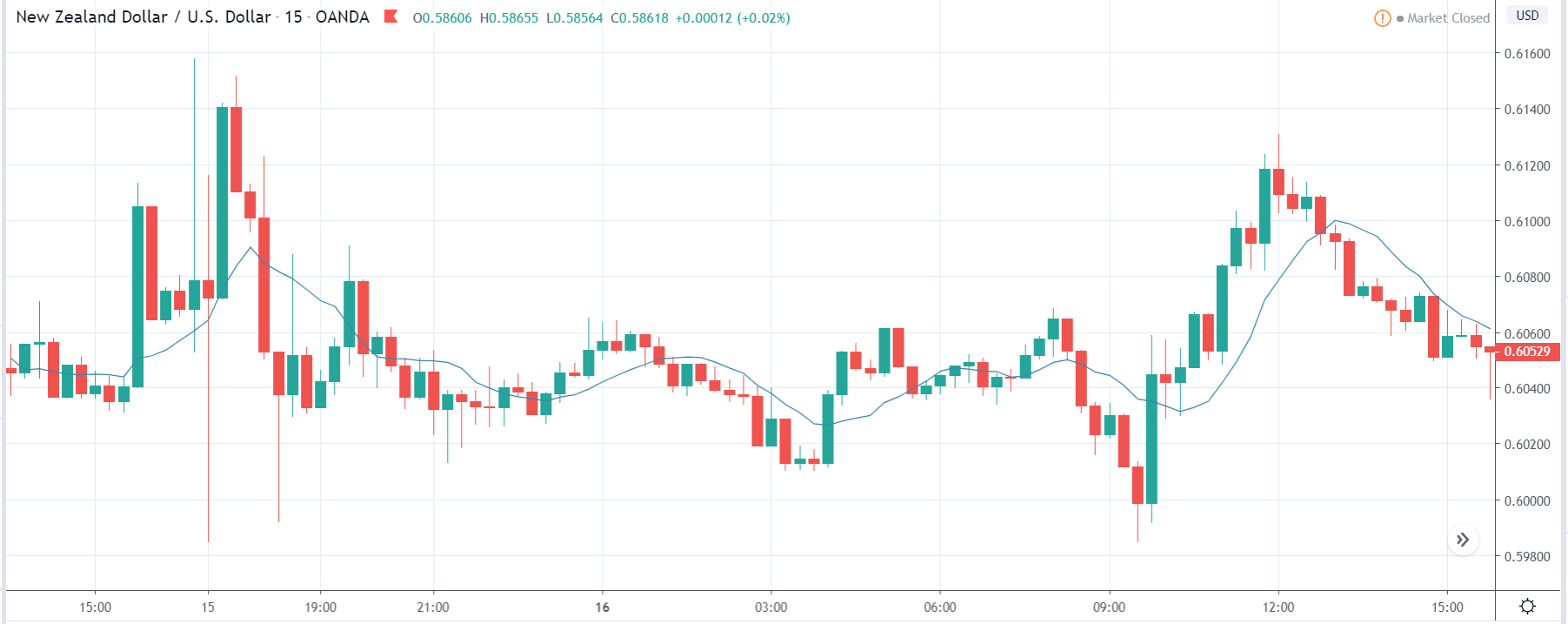
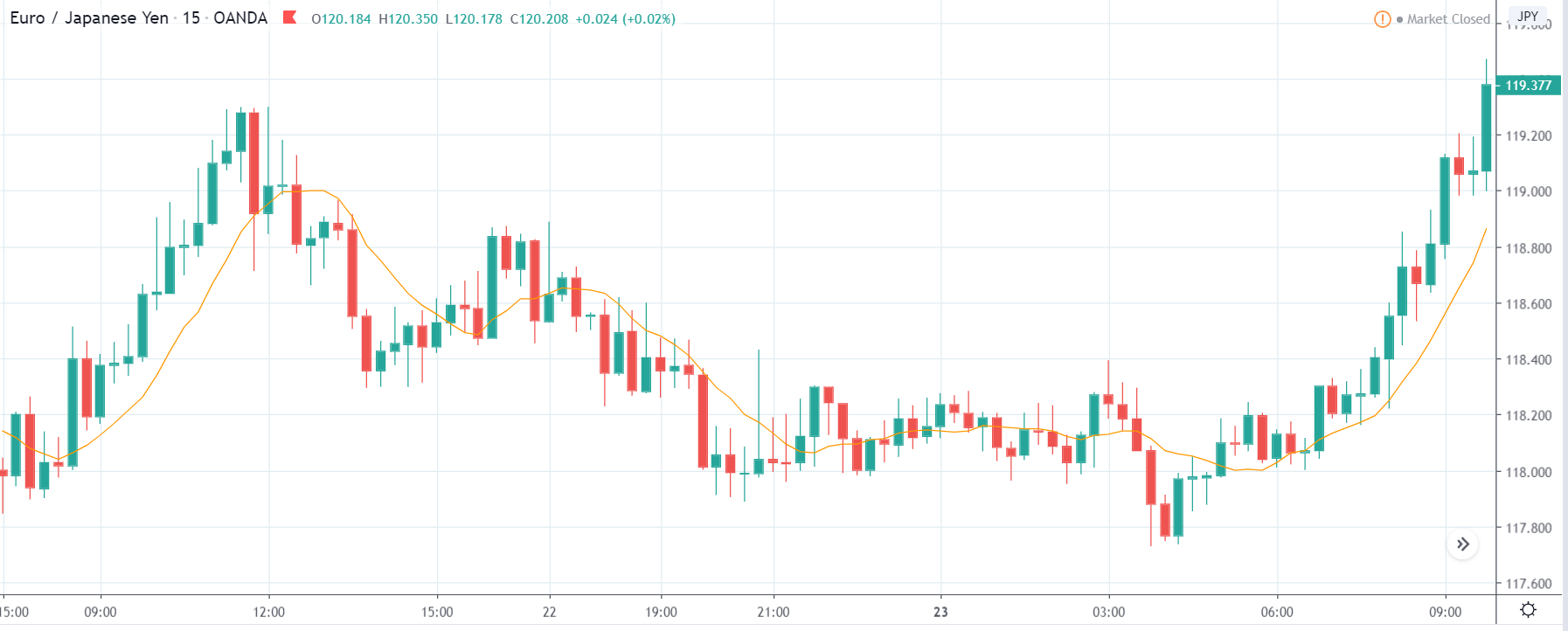
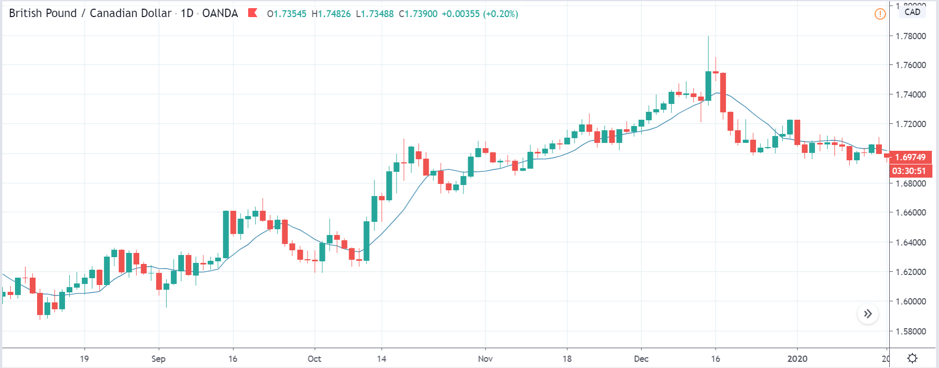
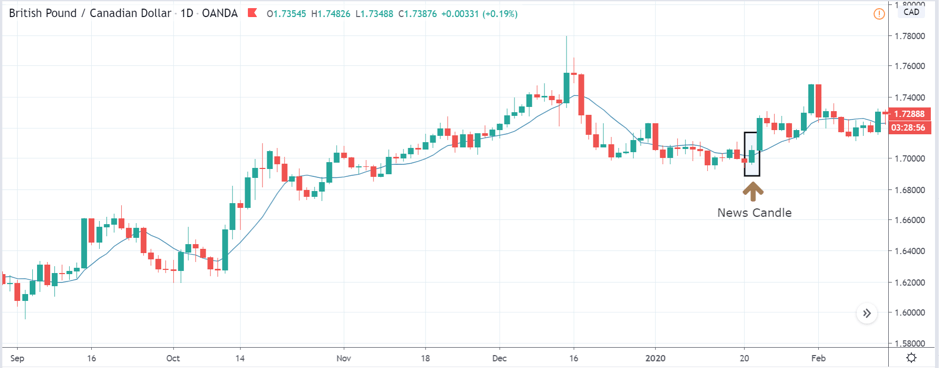
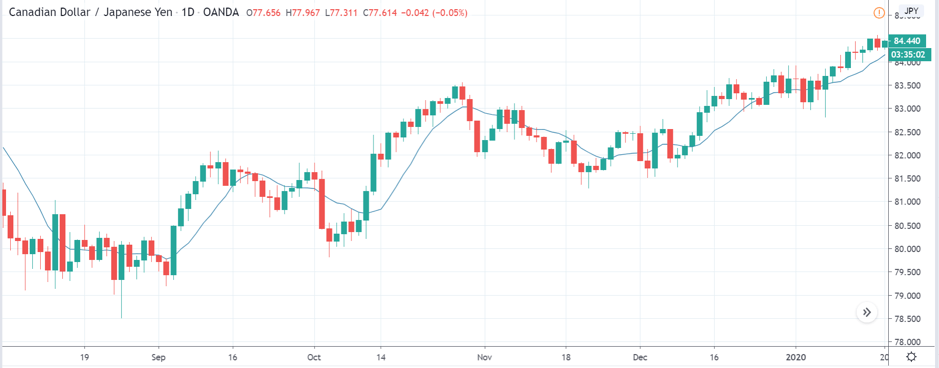
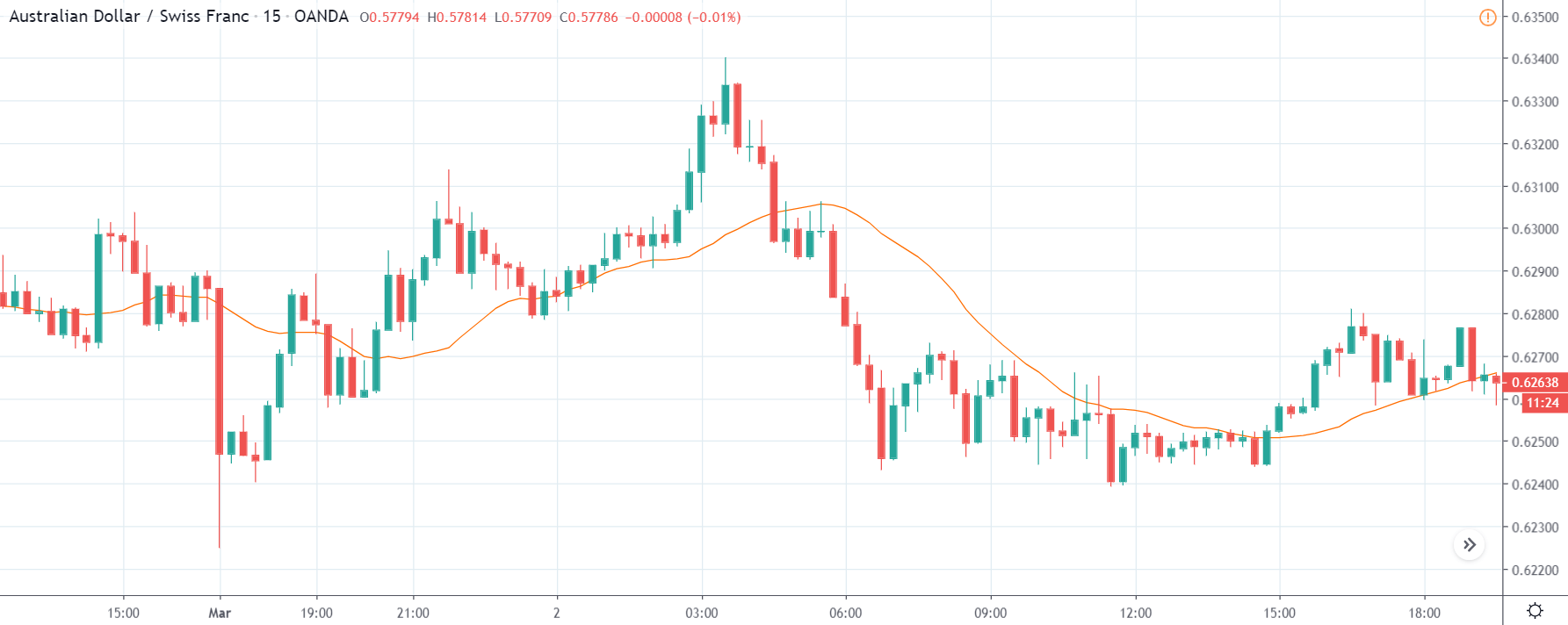
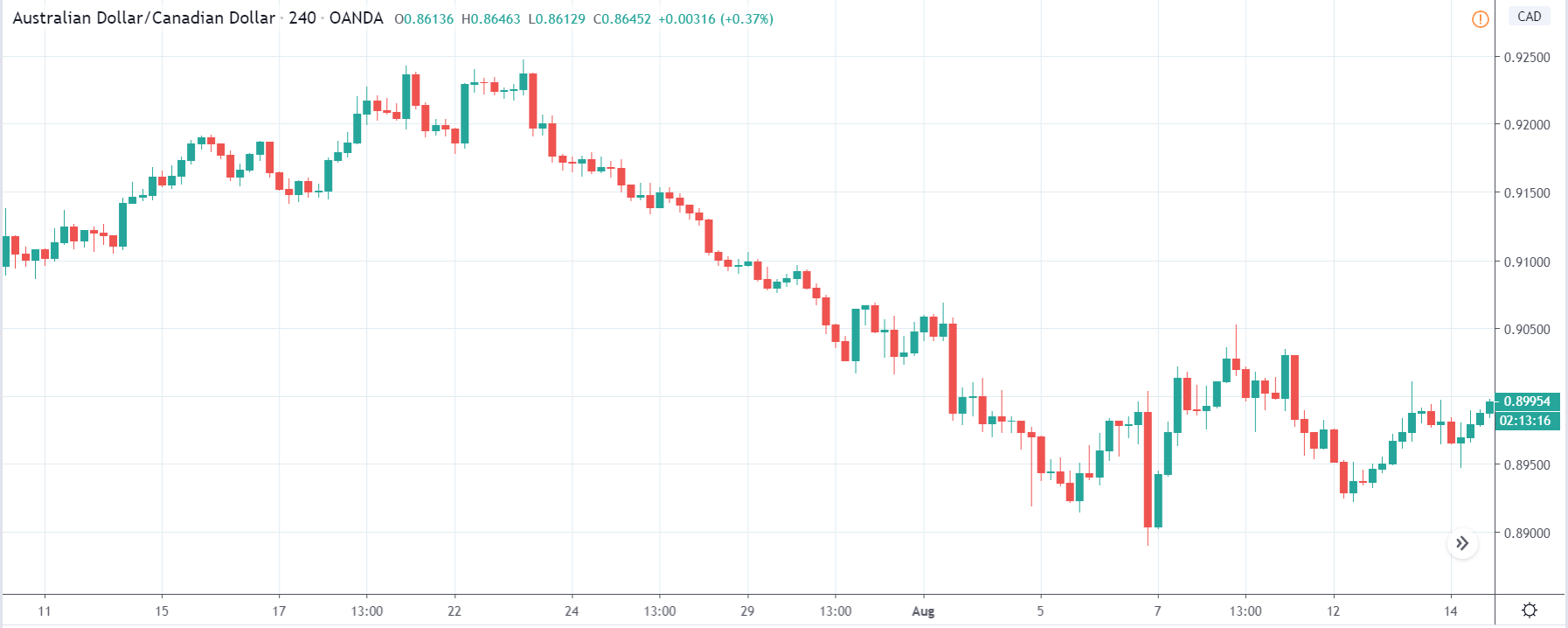
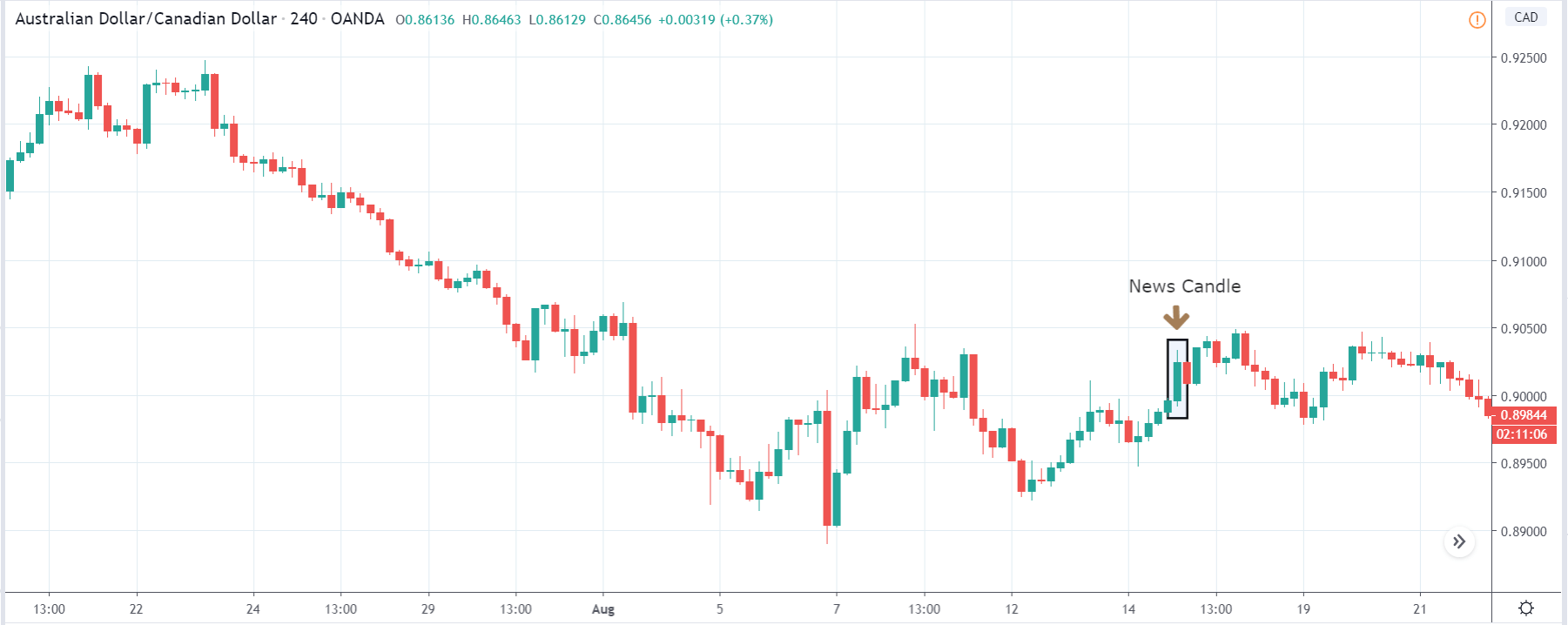
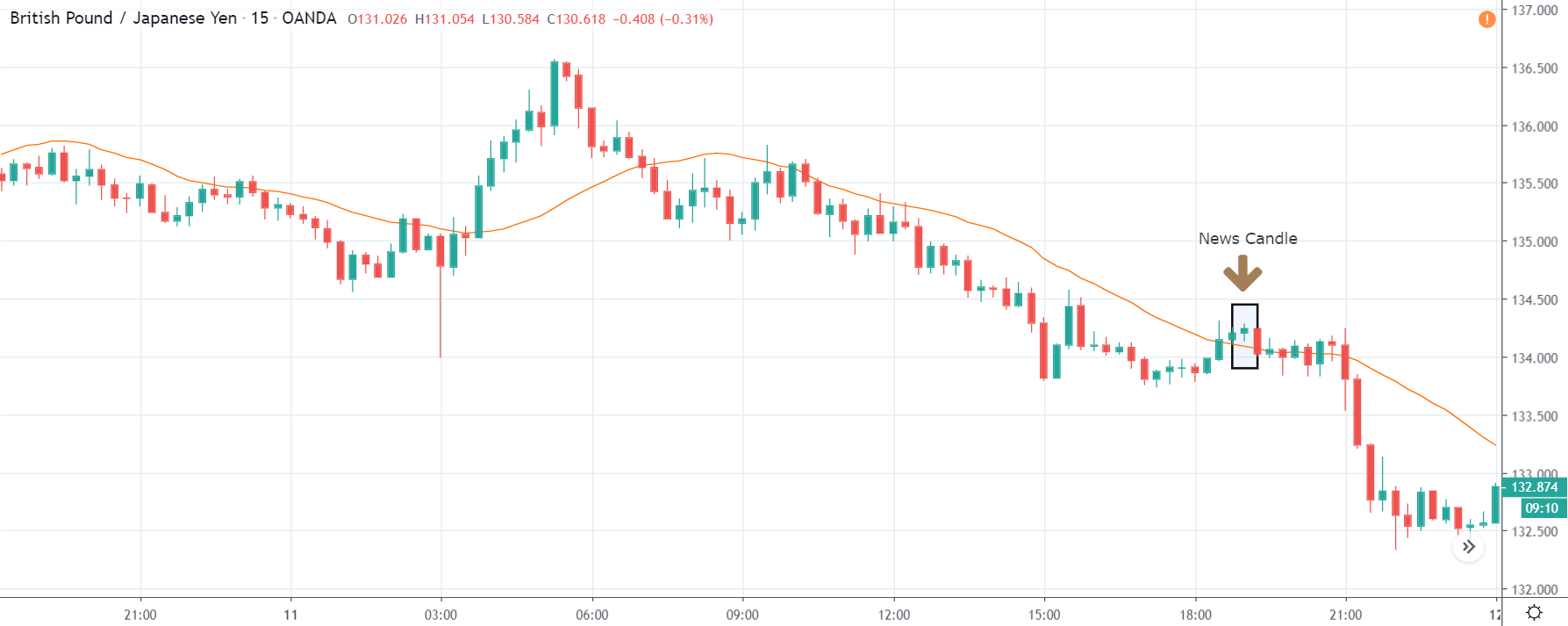
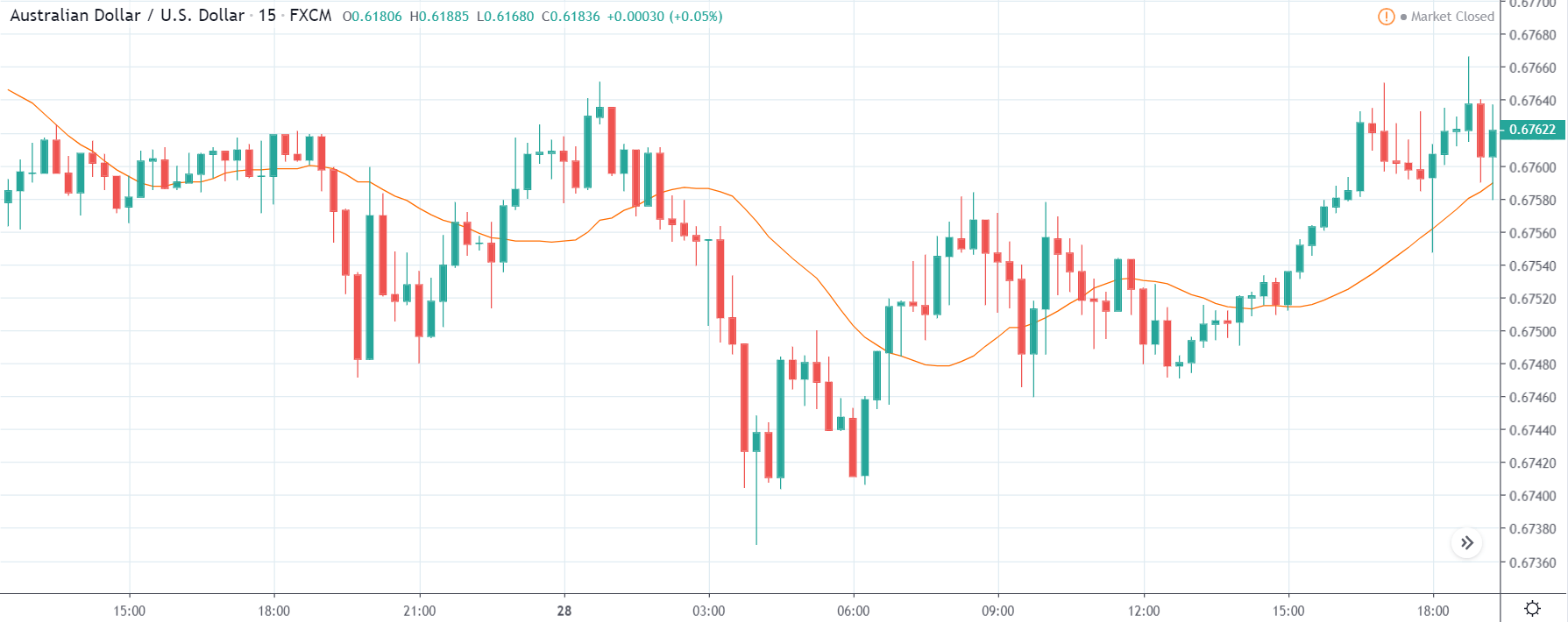
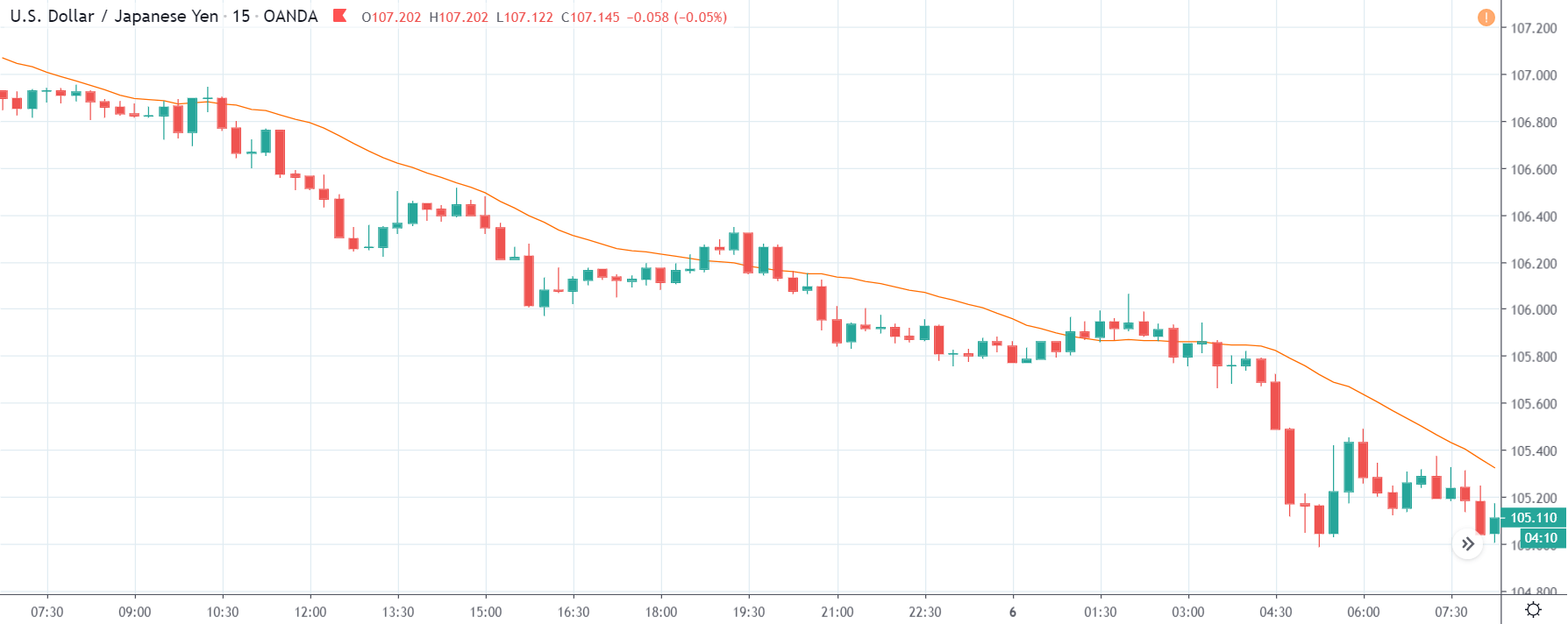
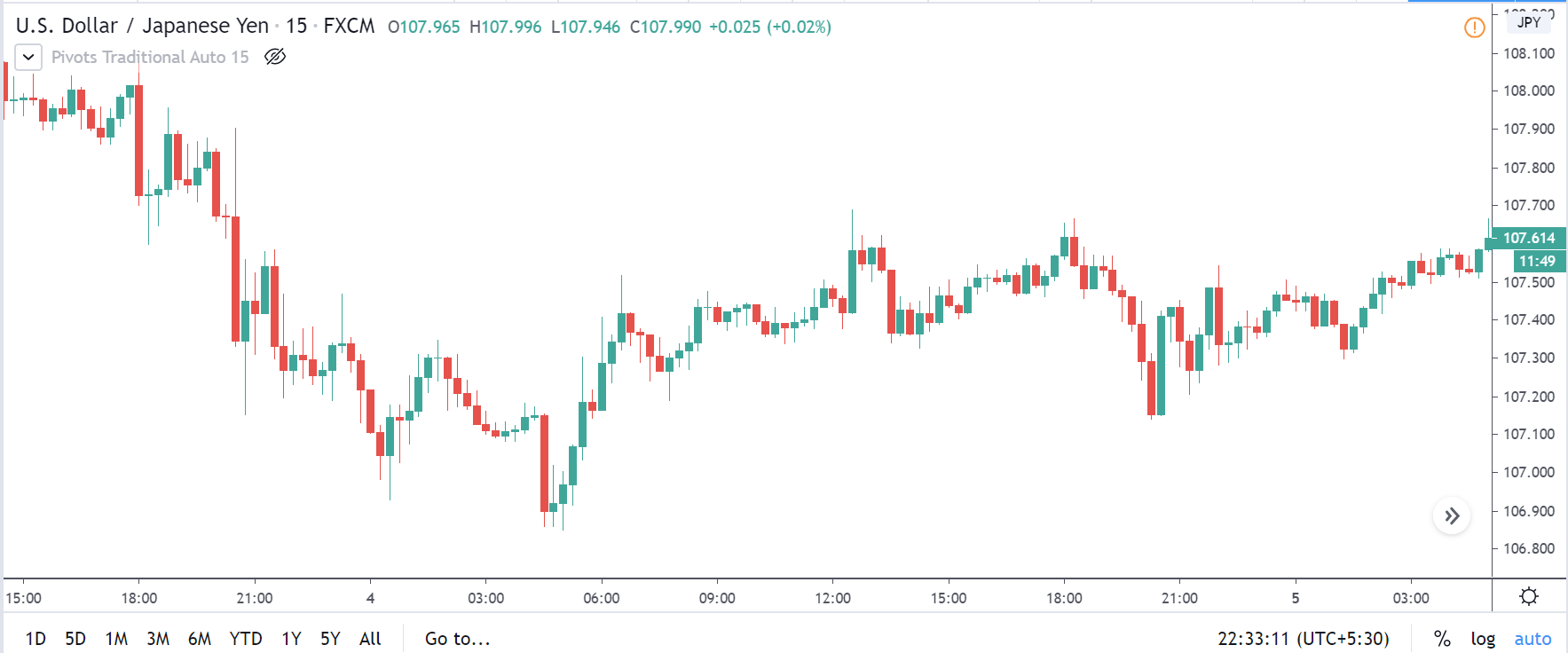
ZAR/JPY | Before the announcement:
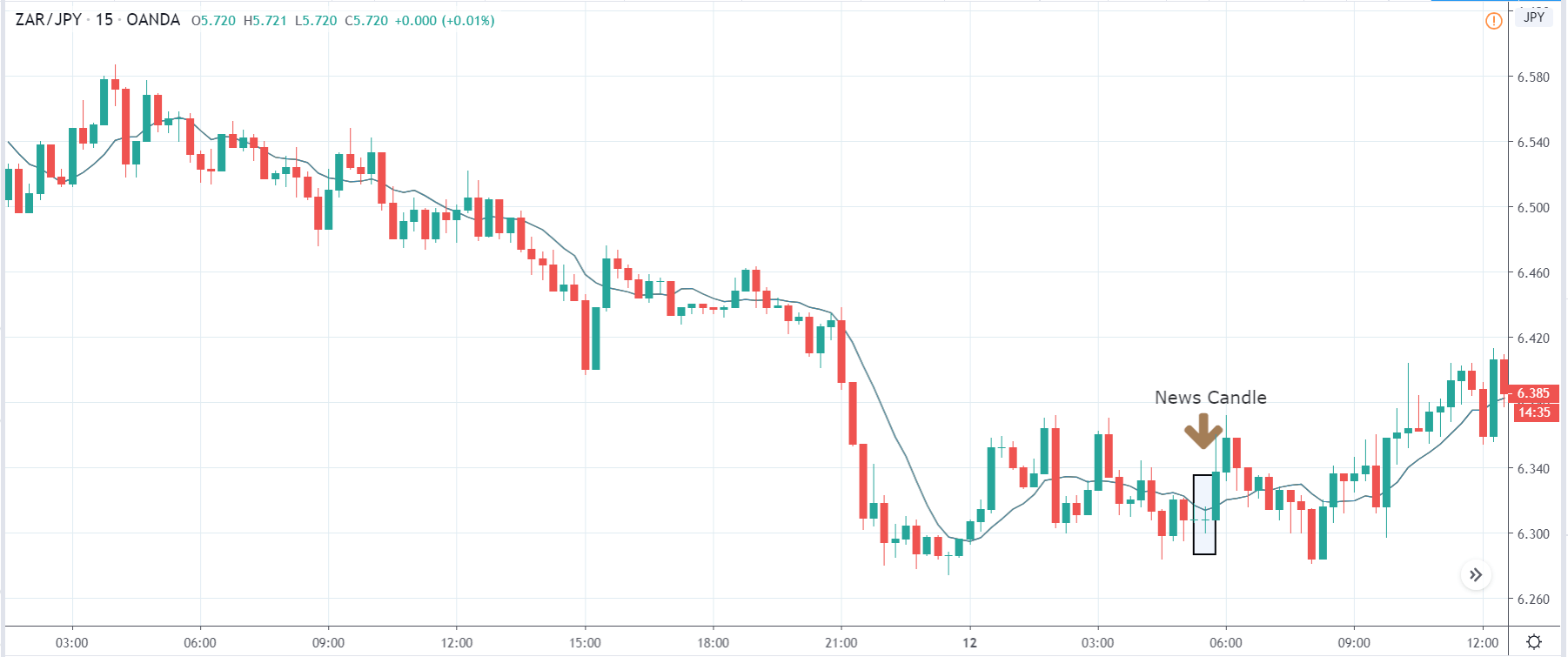
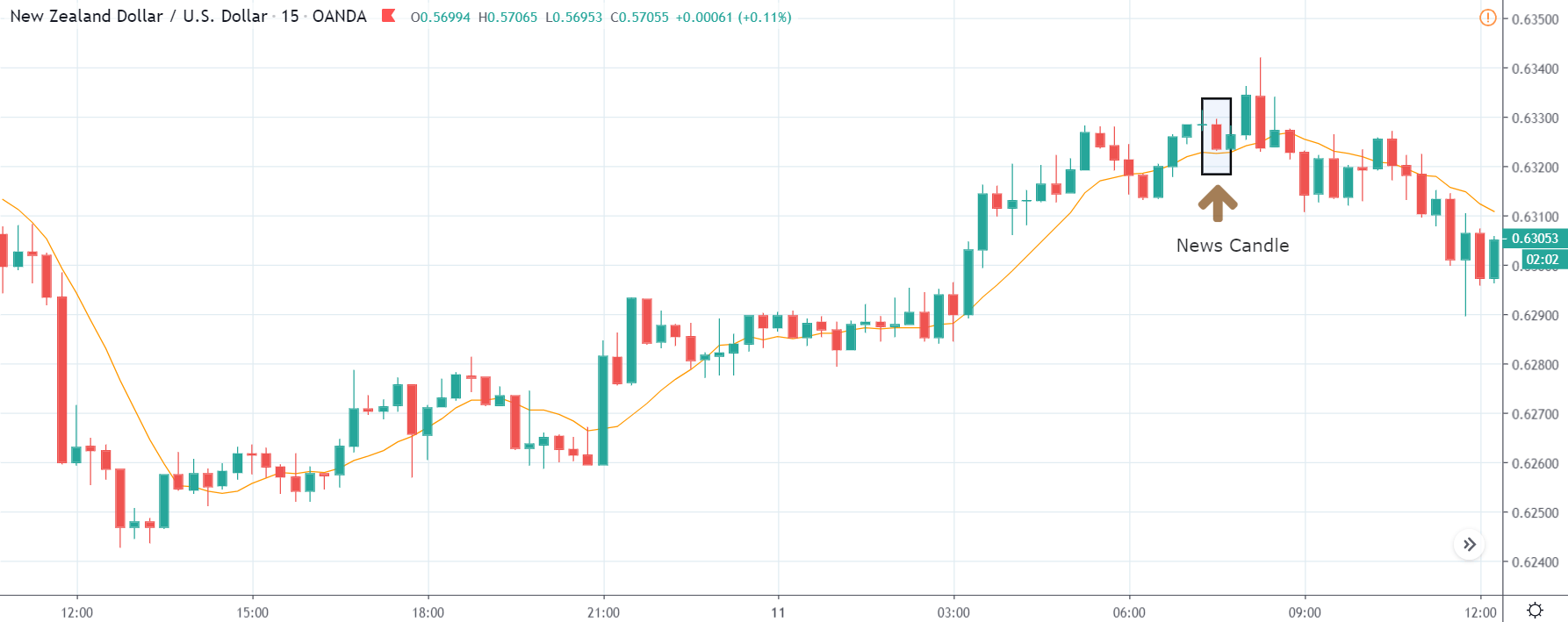
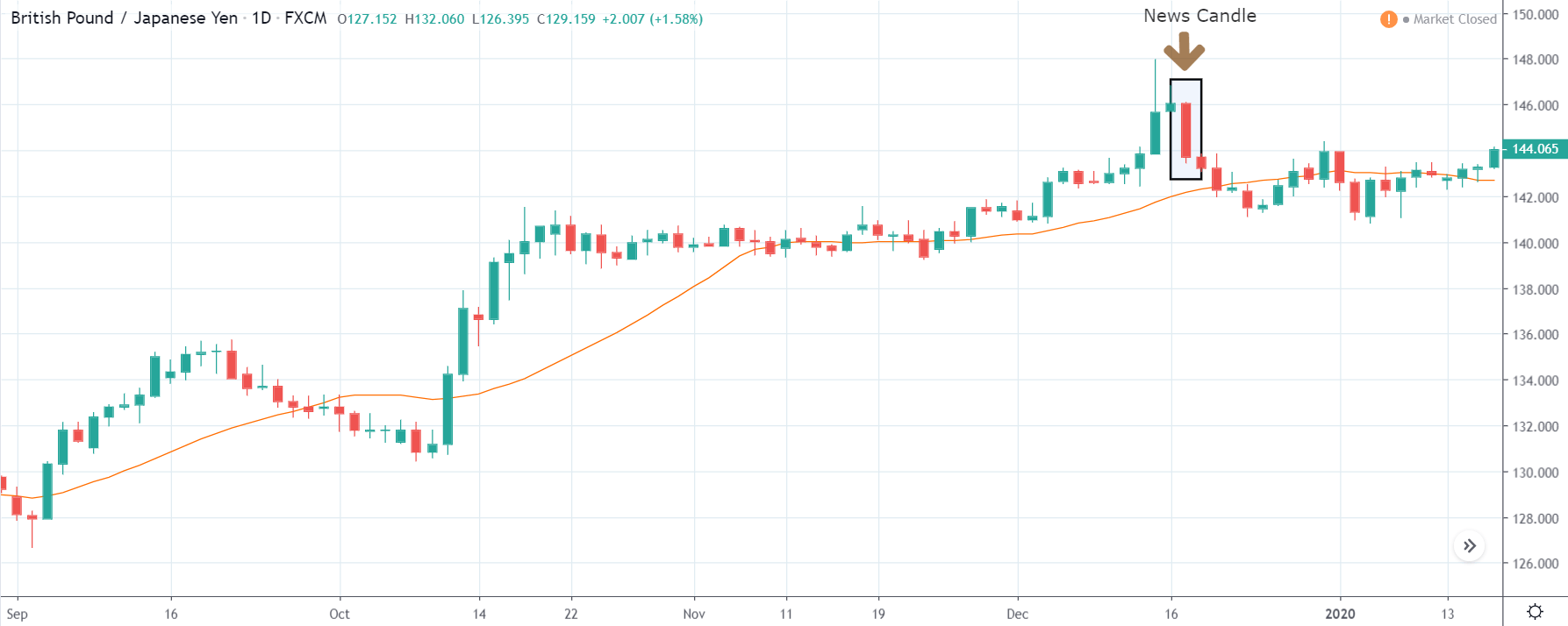
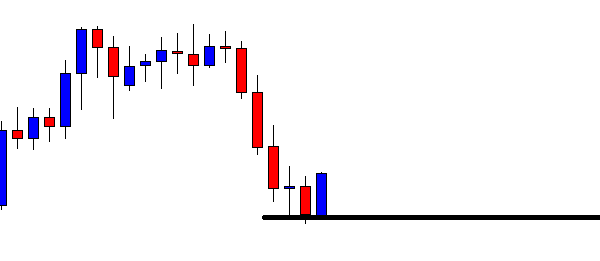
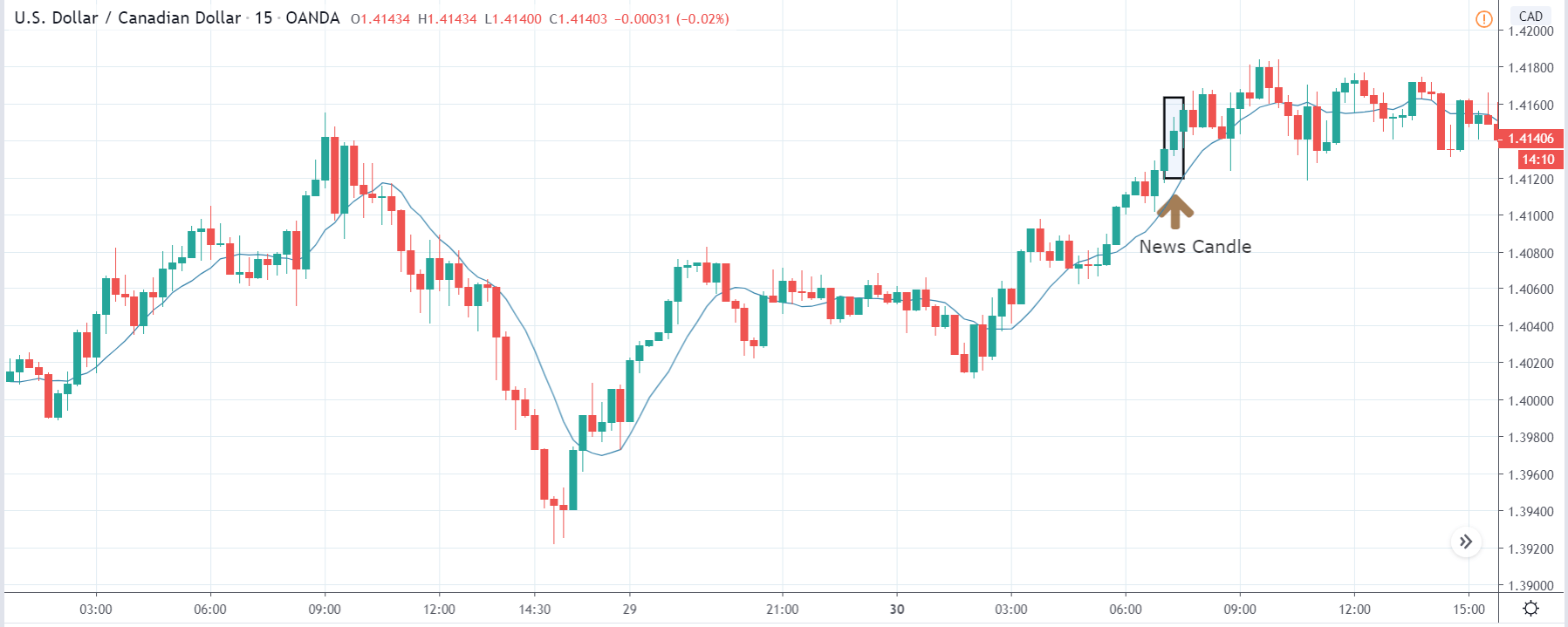
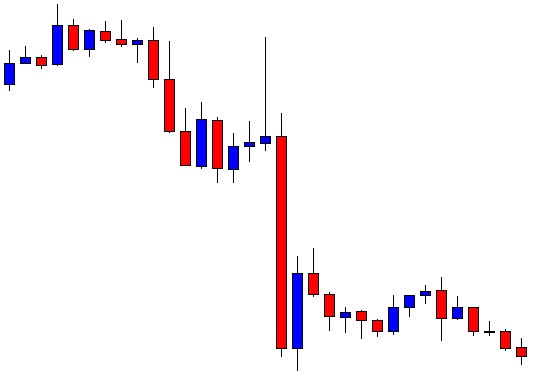
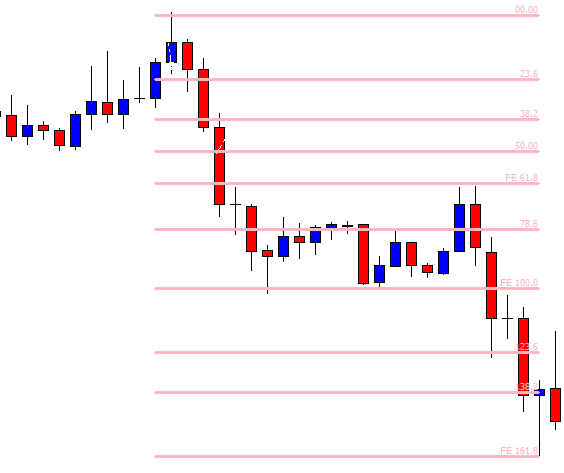
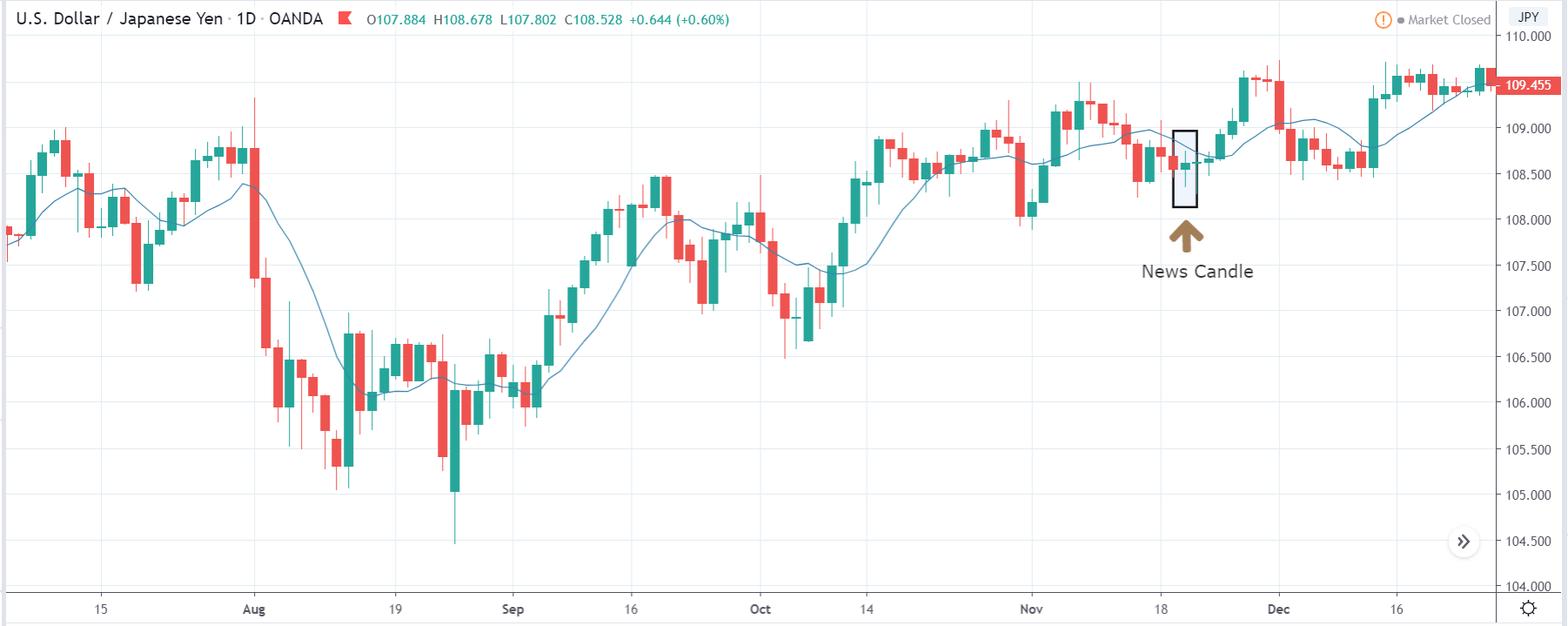
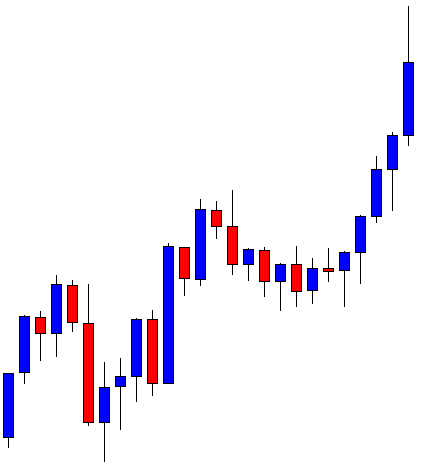
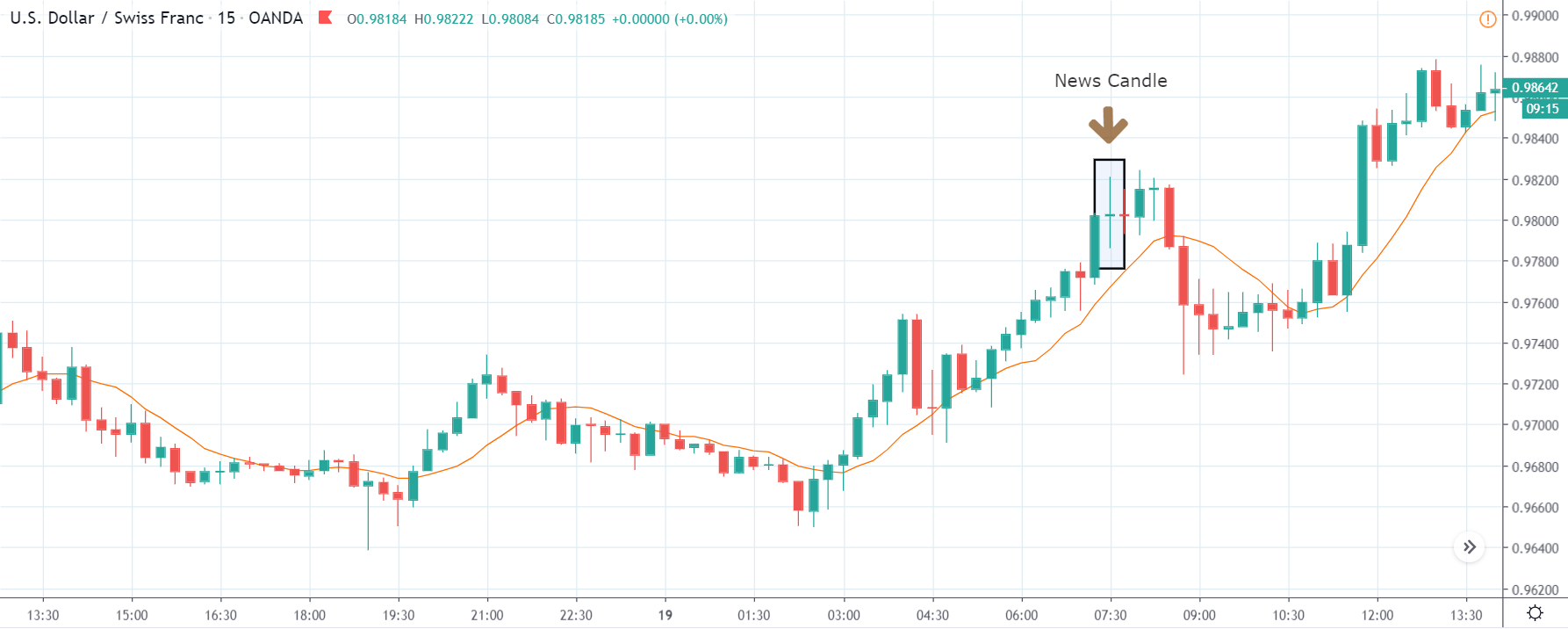
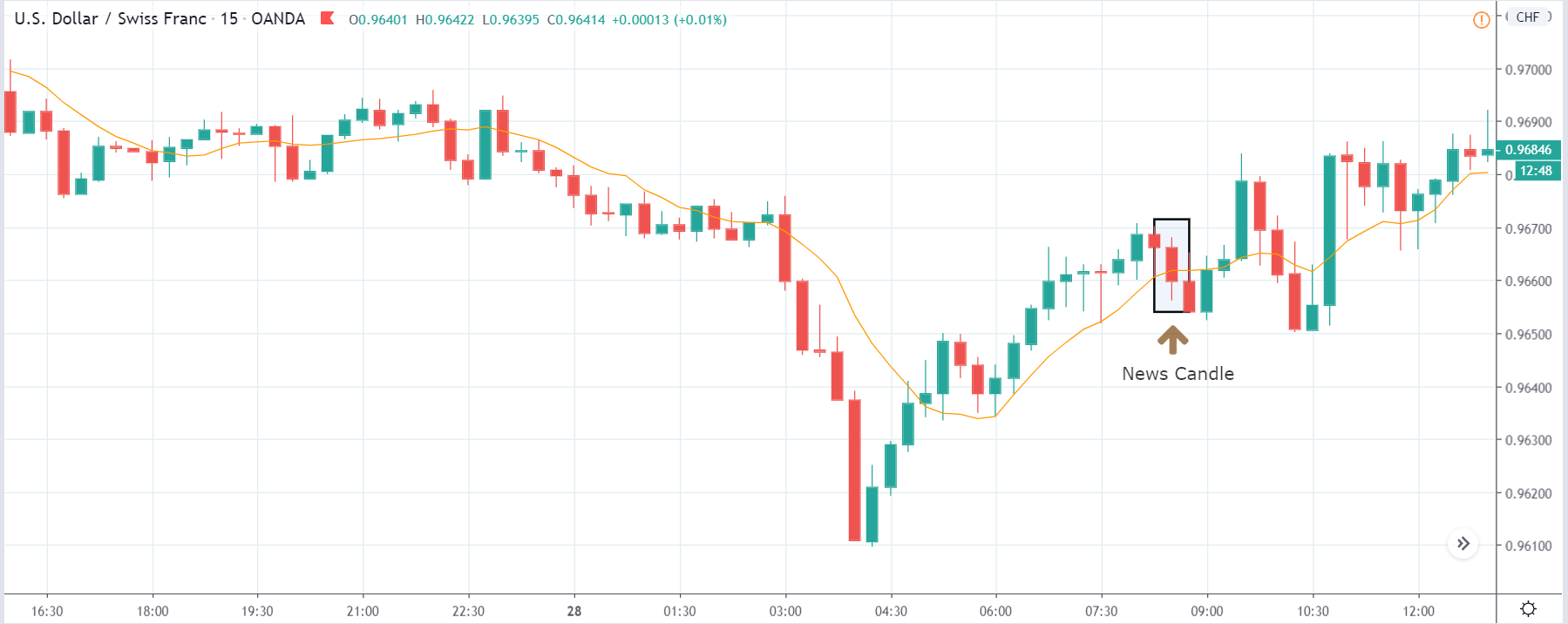
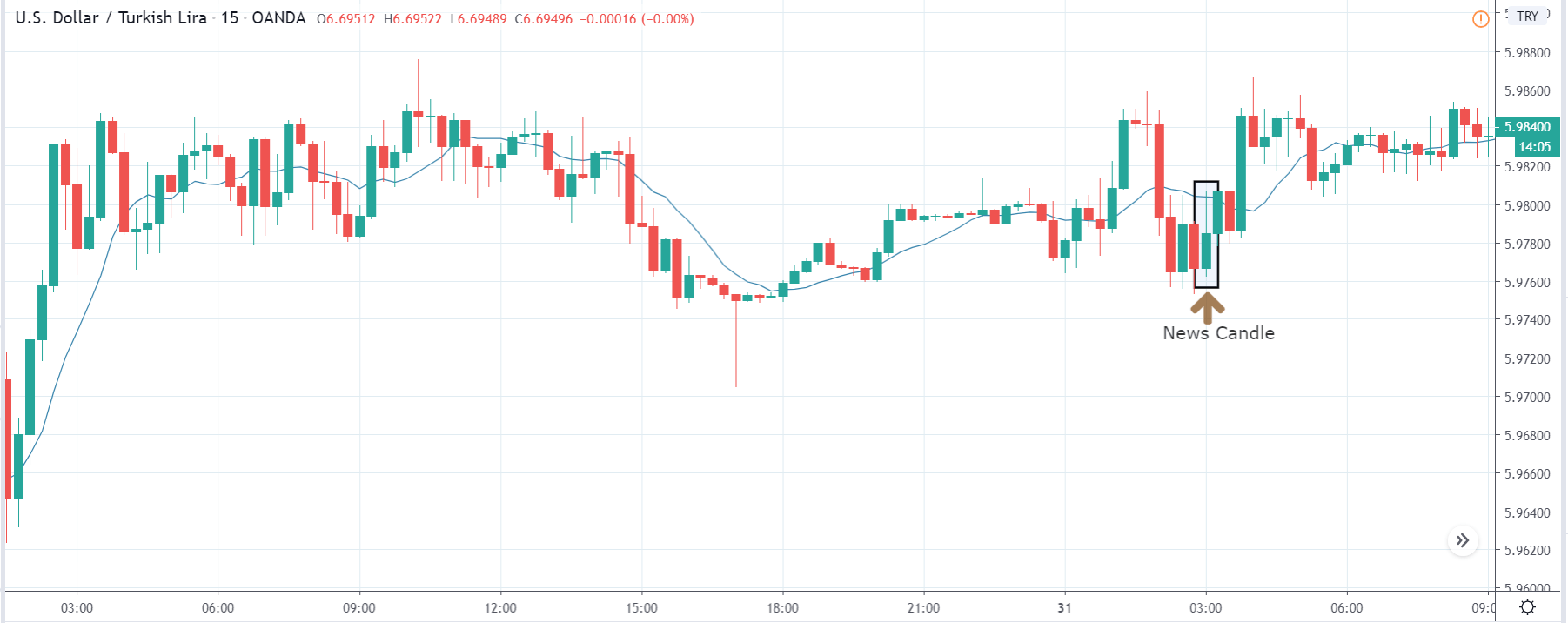
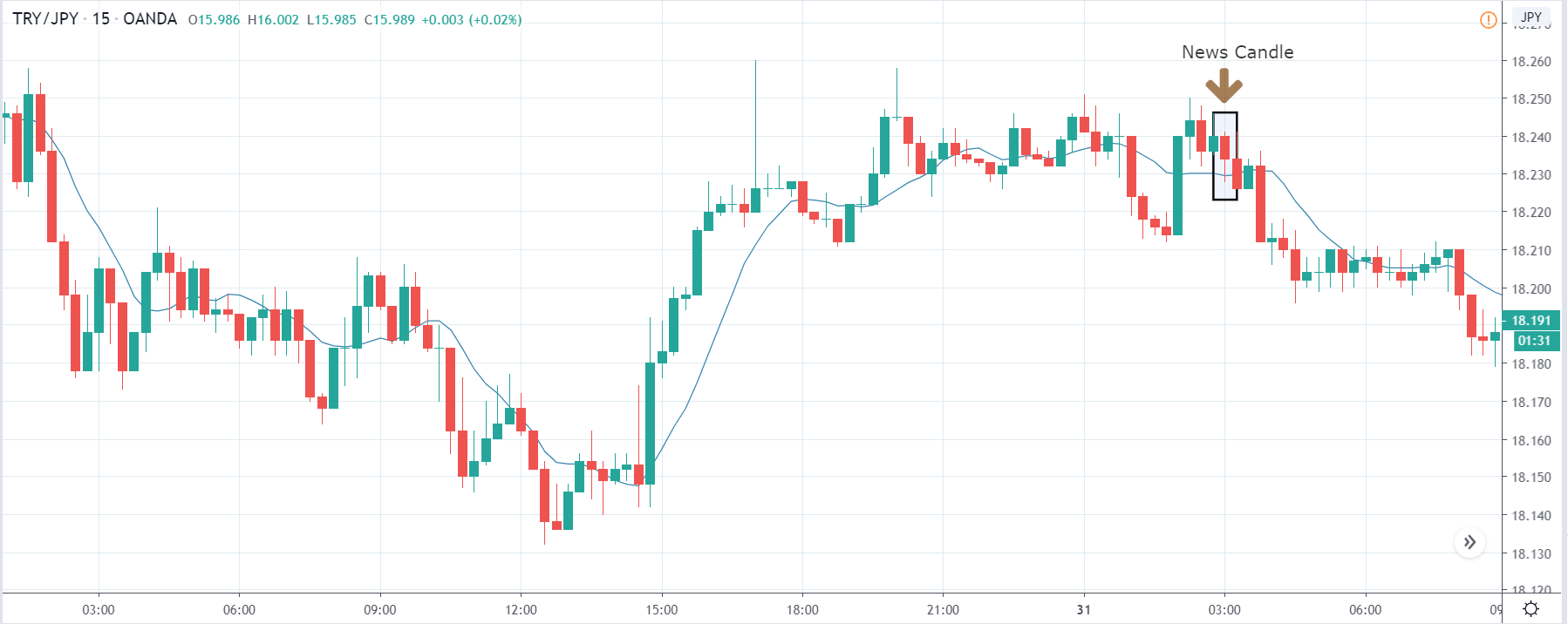
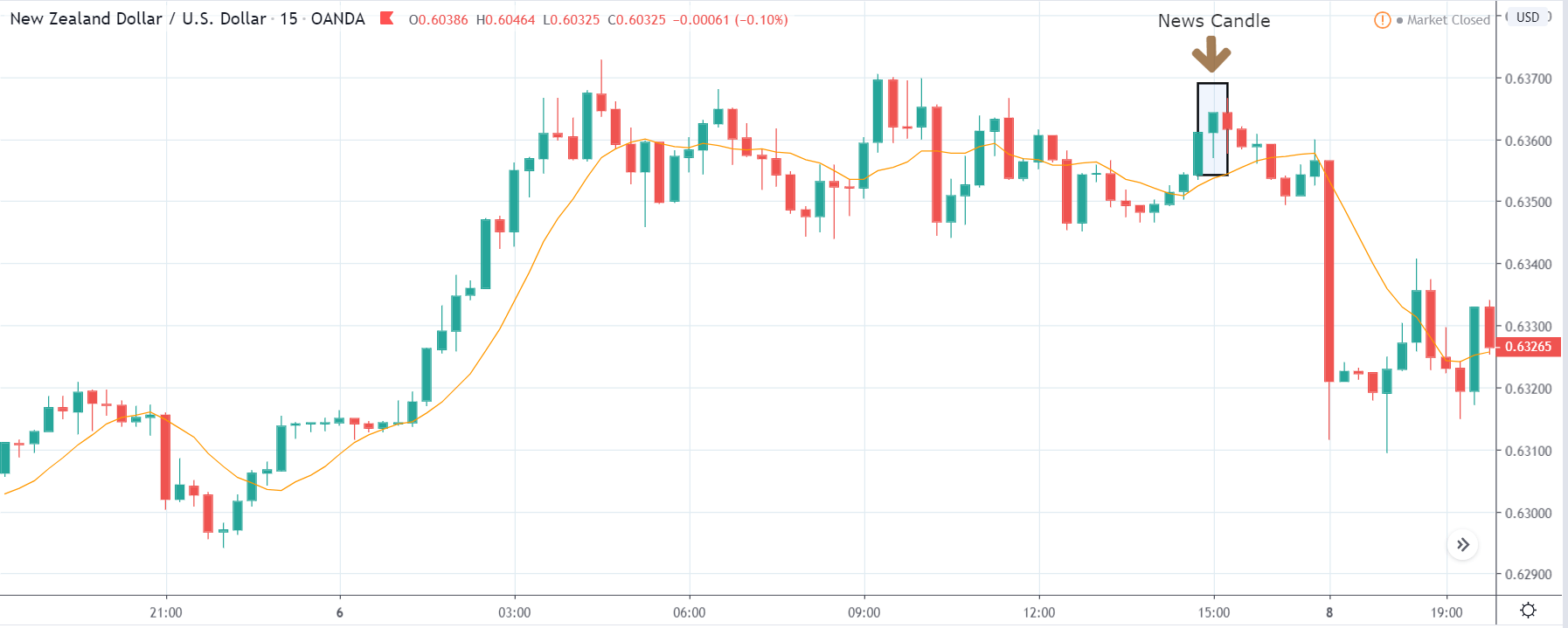
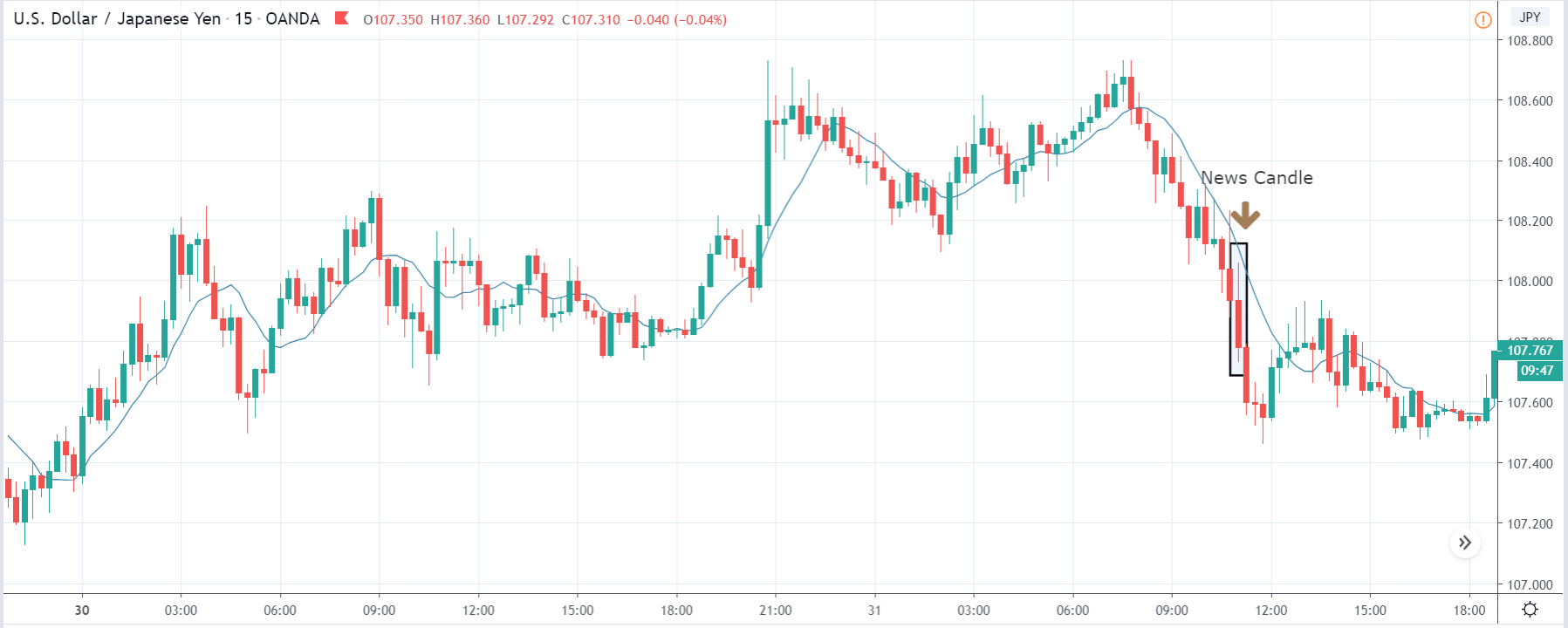
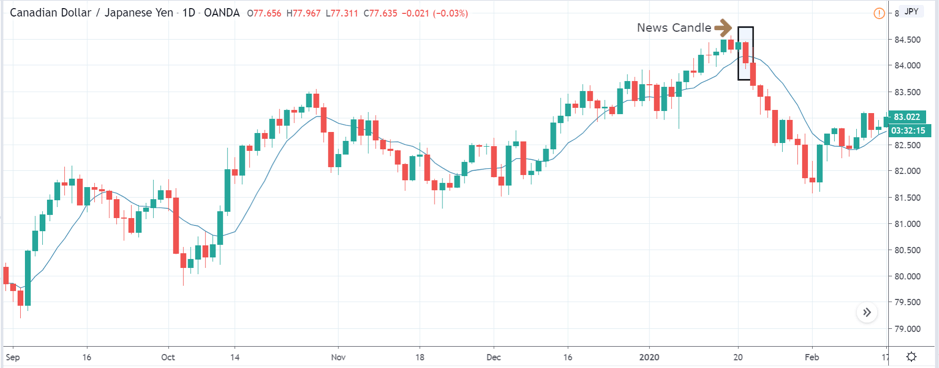
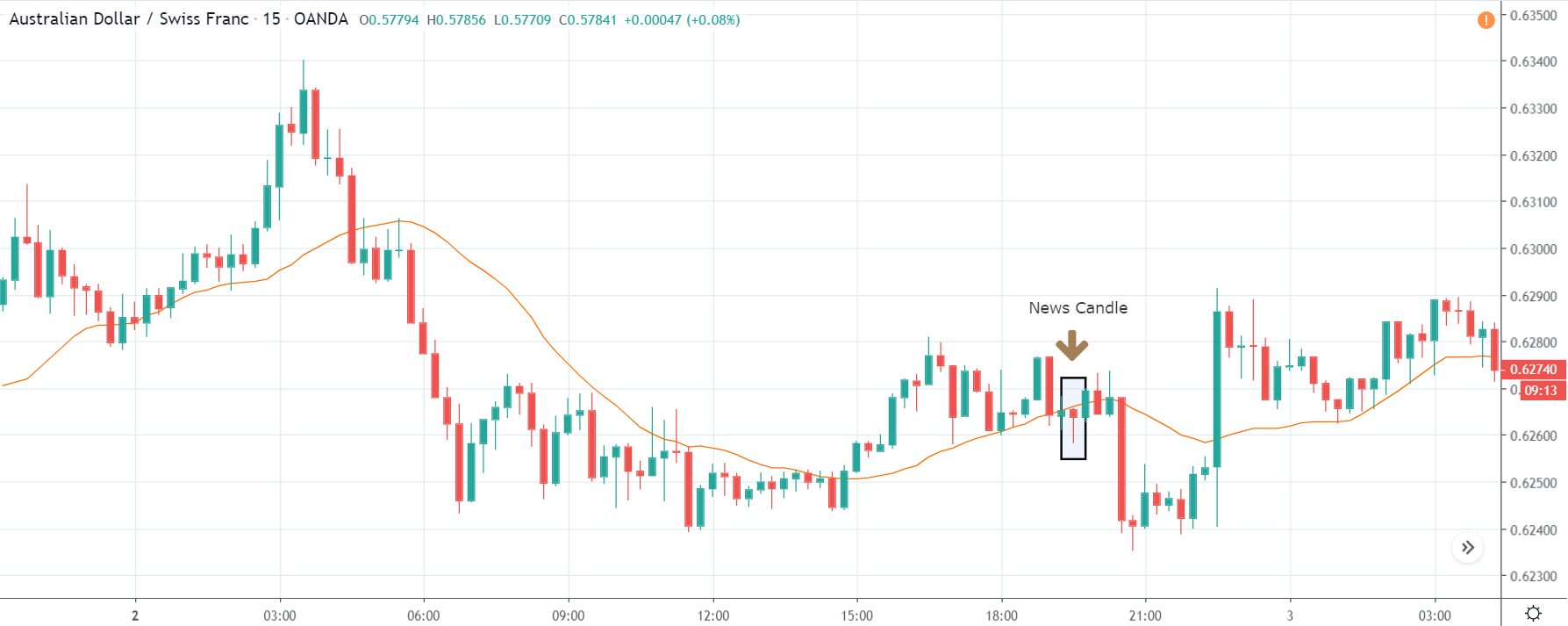
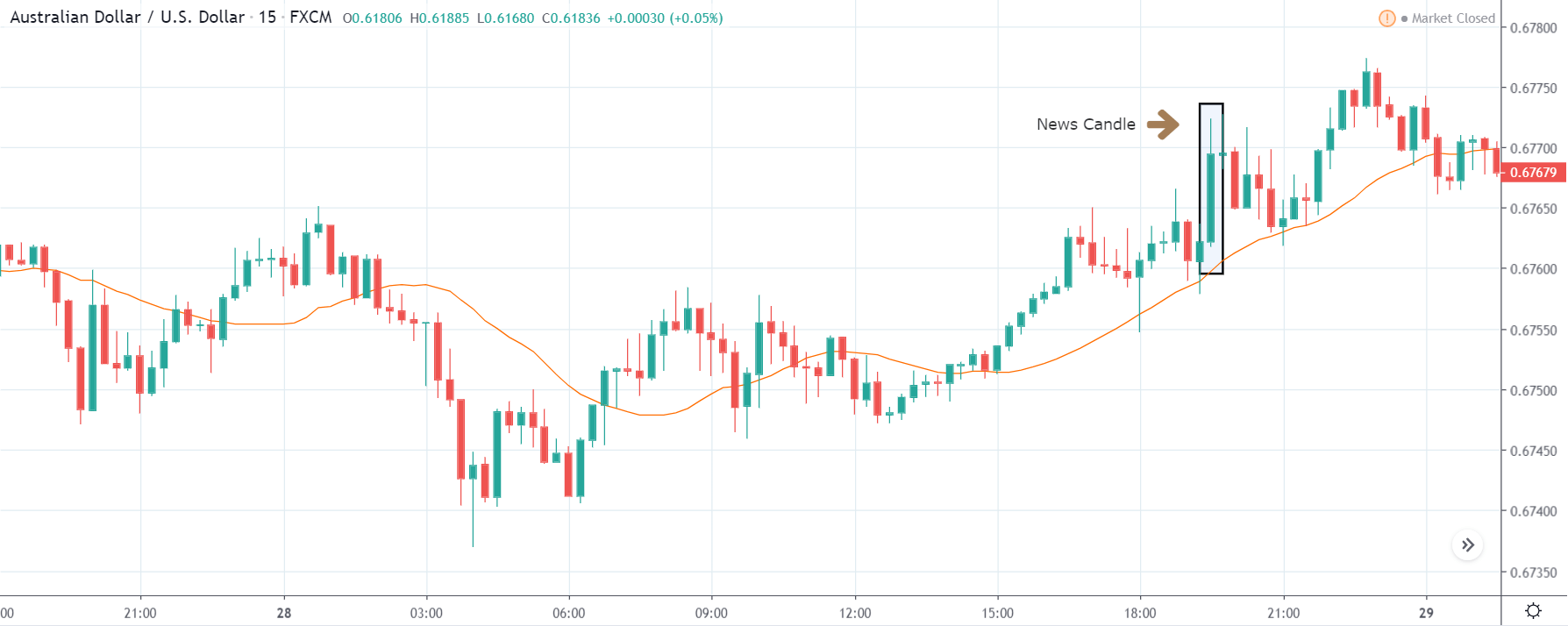
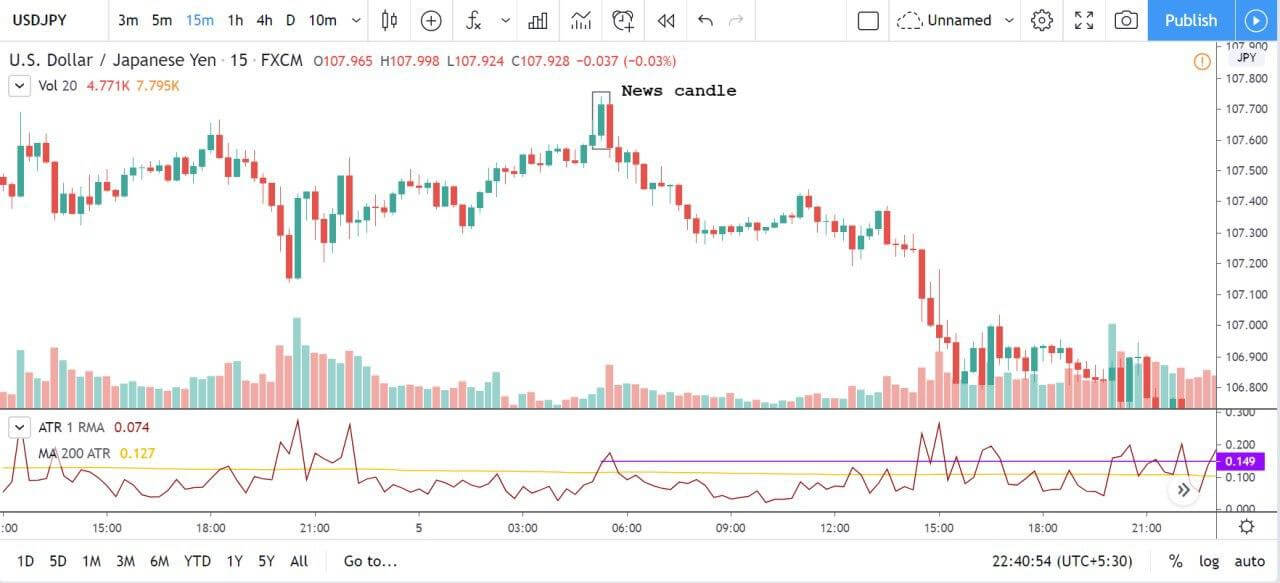
ZAR/JPY | After the announcement:
The above images represent the ZAR/JPY currency pair, where the first image shows the characteristics of the chart before the news announcement. We see that the market is a strong downtrend, and since the South African Rand is on the left-hand side of the pair, it signifies extreme weakness in the currency. Presently, the price seems to have formed a ‘range,’ and right now is at the bottom of the ‘range.’
Thus, we can expect buyers to get active at any moment. We cannot take any position in the market at this moment. After the news announcement, volatility remains at the same level as before, and the price does not respond to the news data as expected. The ‘news candle’ forms a ‘Doji’ candlestick pattern where the price closes almost at the opening price. Since the Mining Production data does not have a major impact on the currency, traders should analyze the currency pair from a technical perspective and take suitable positions.
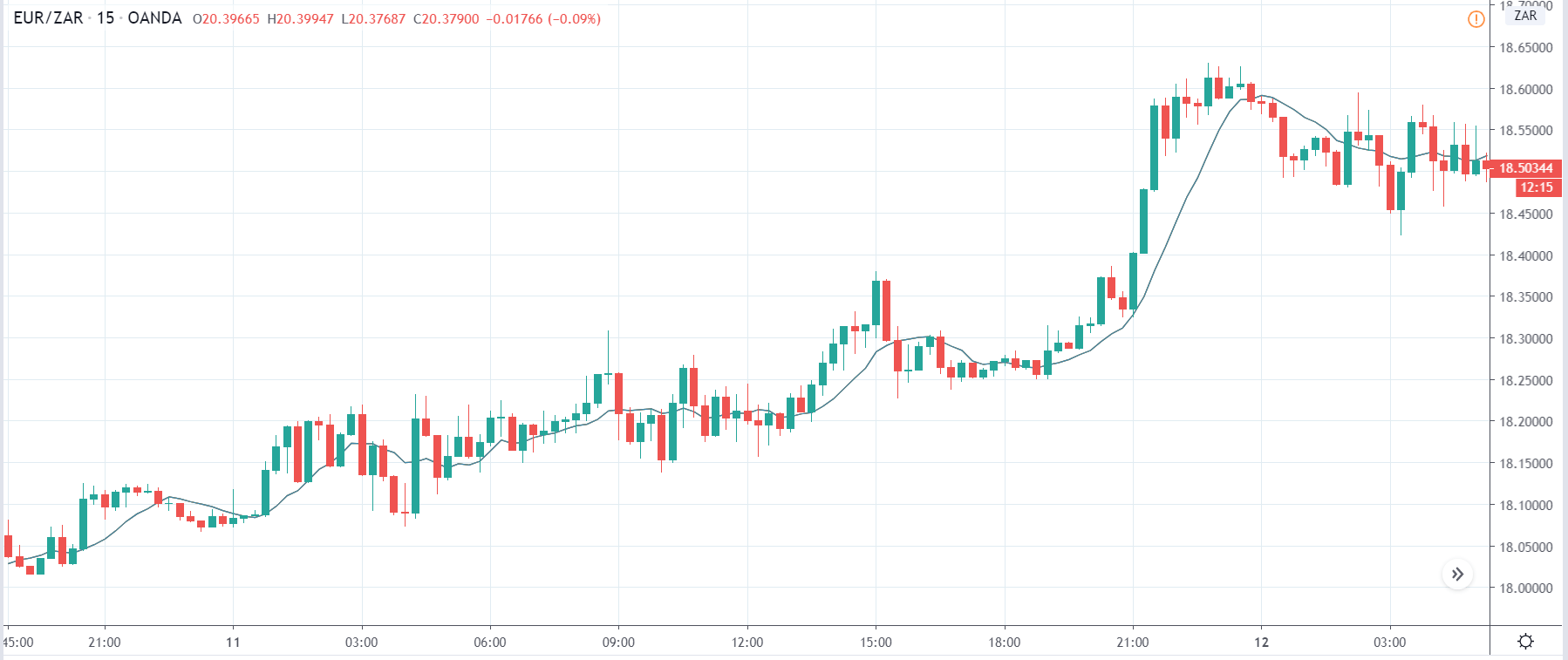
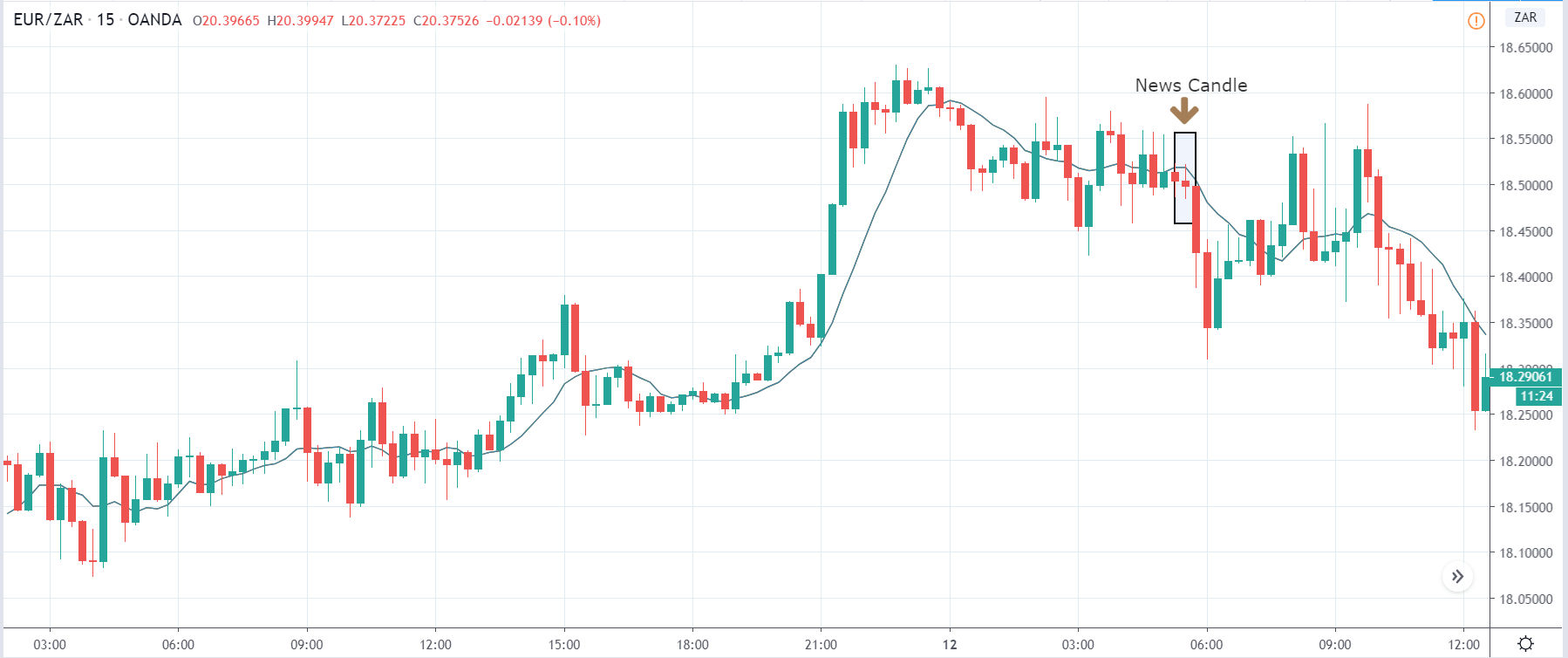
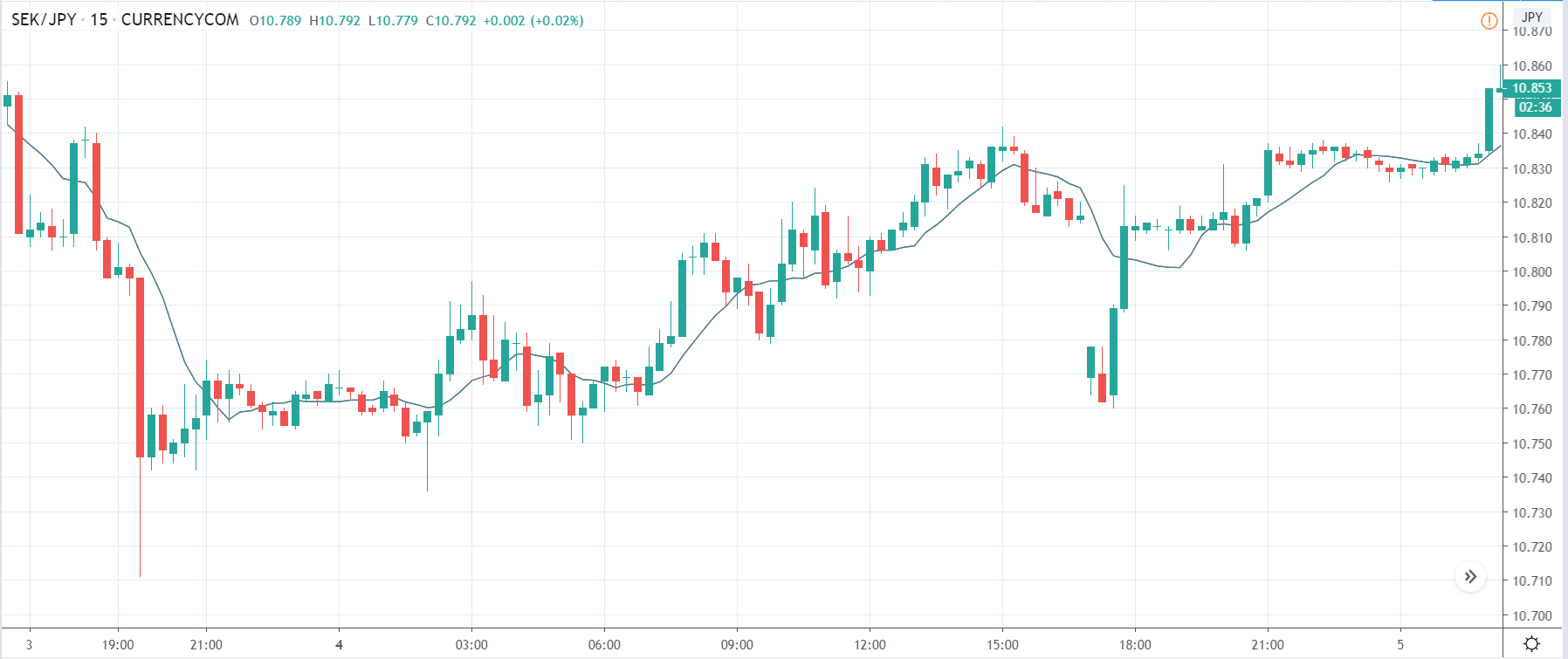
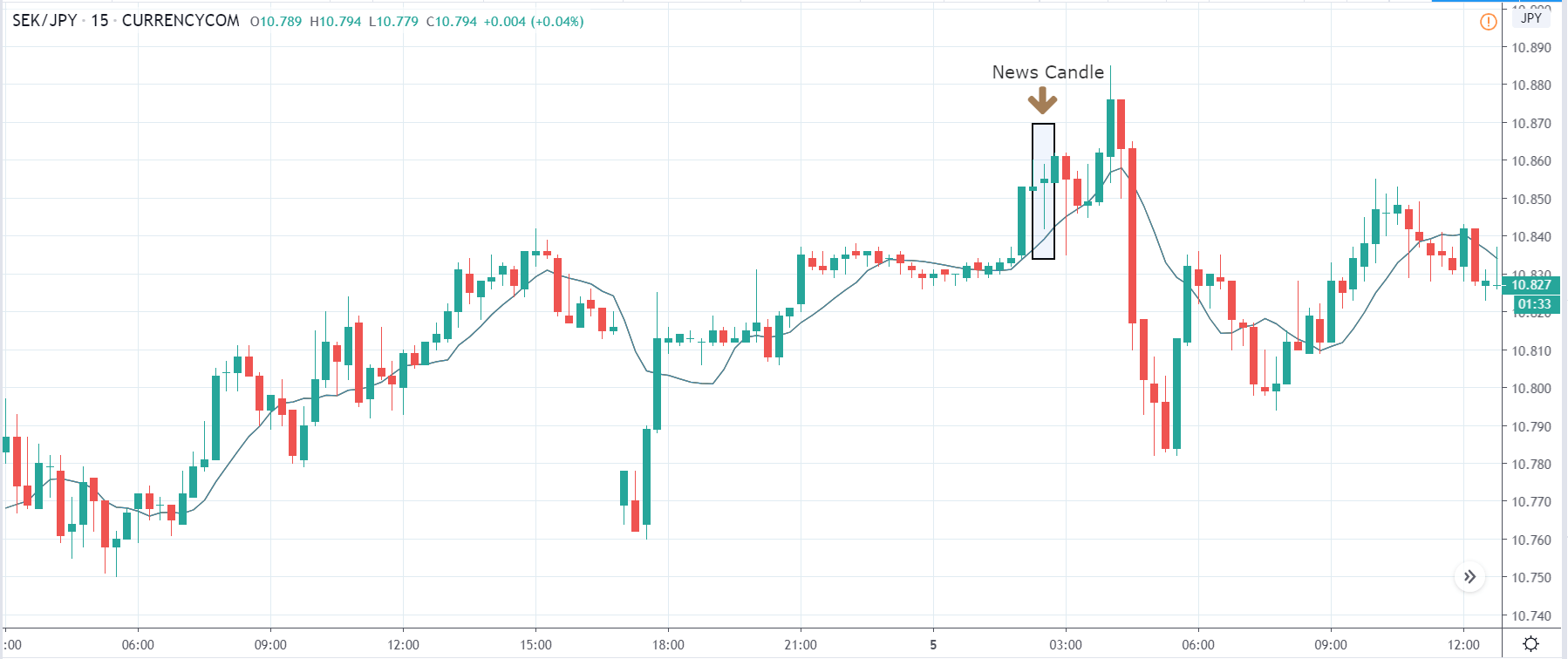
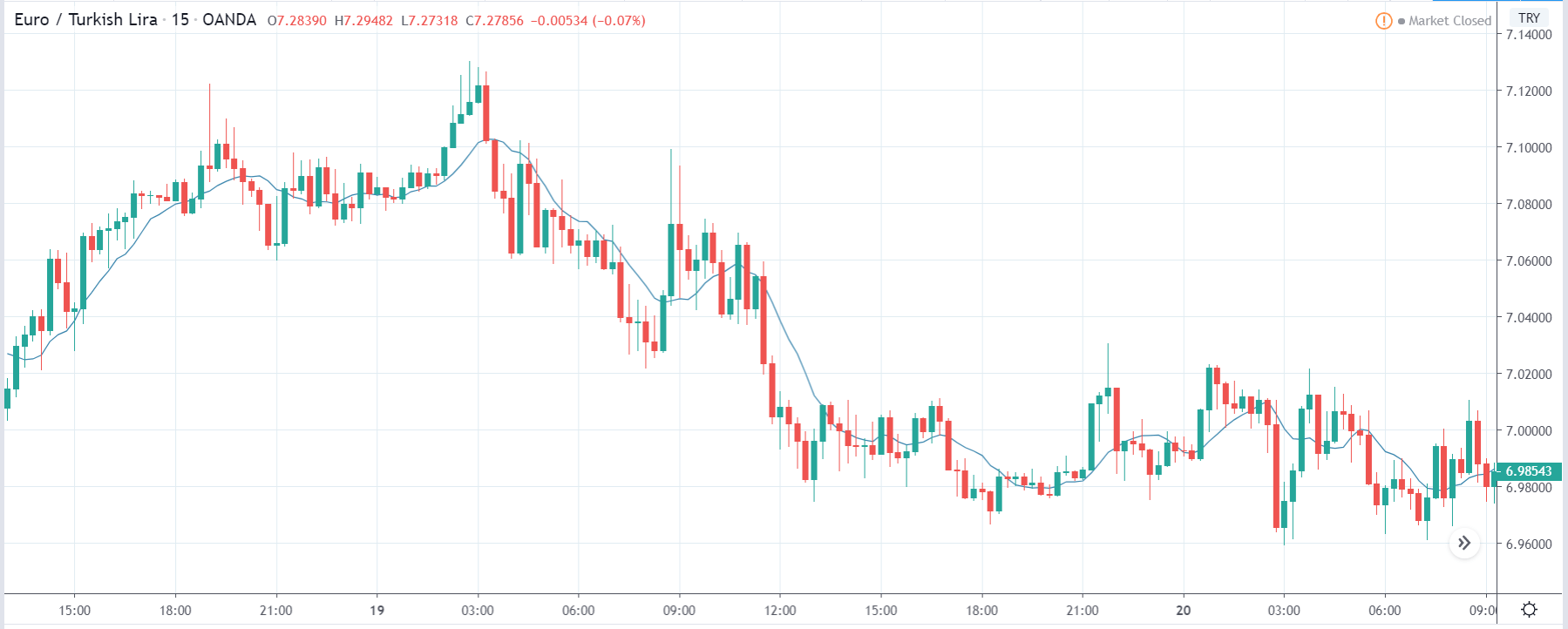
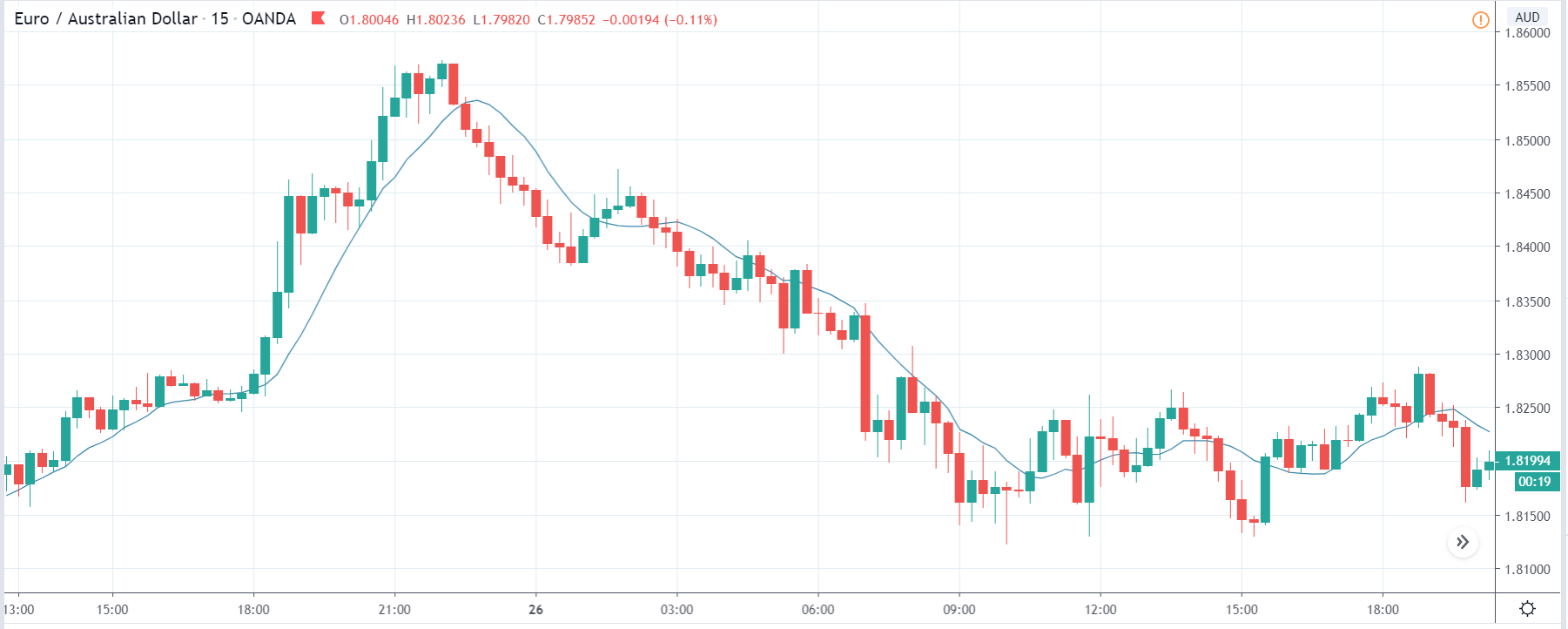
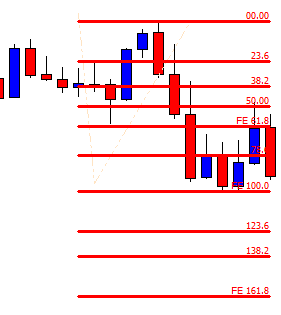
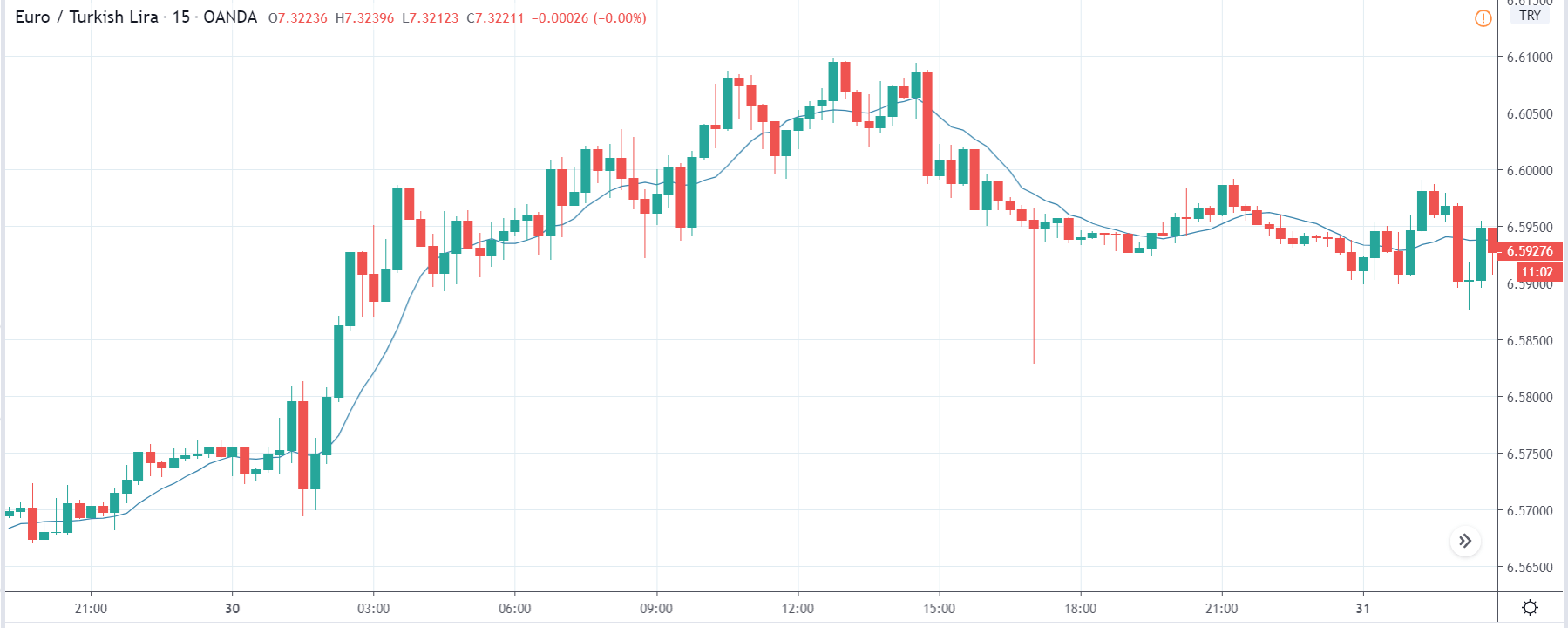
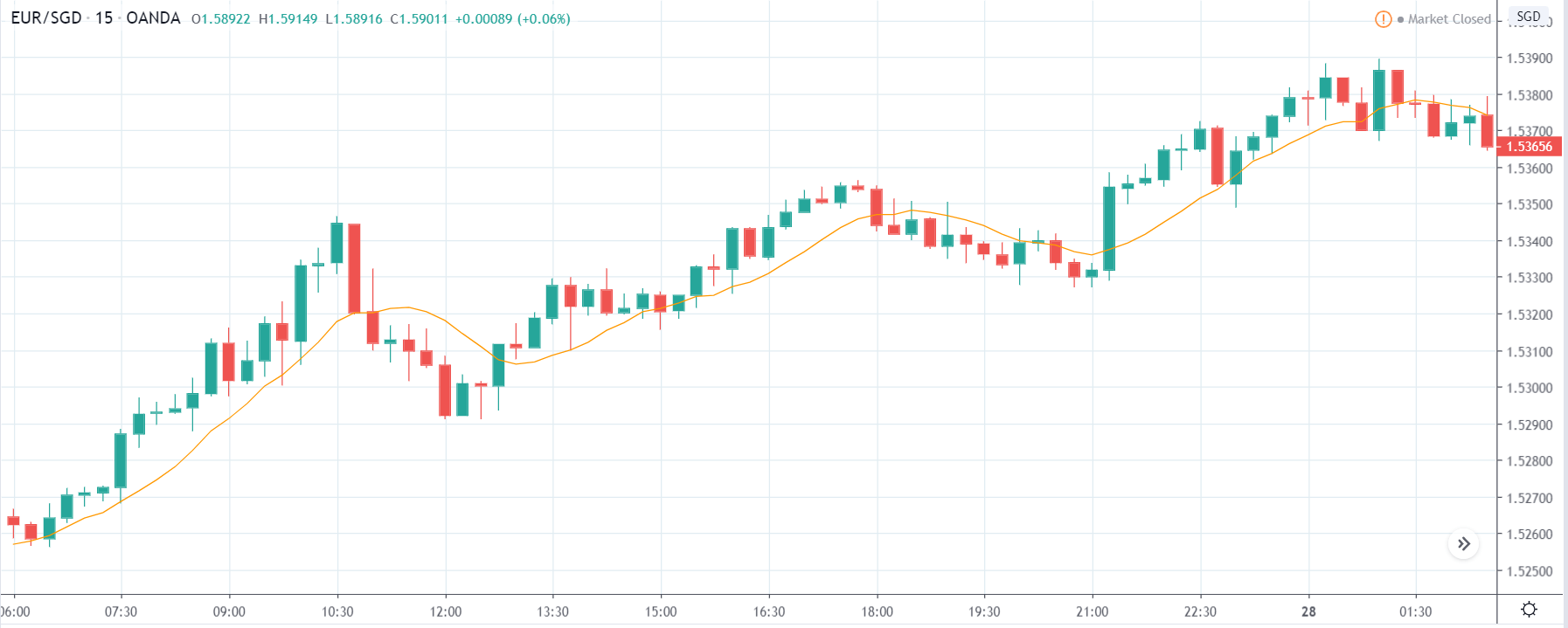
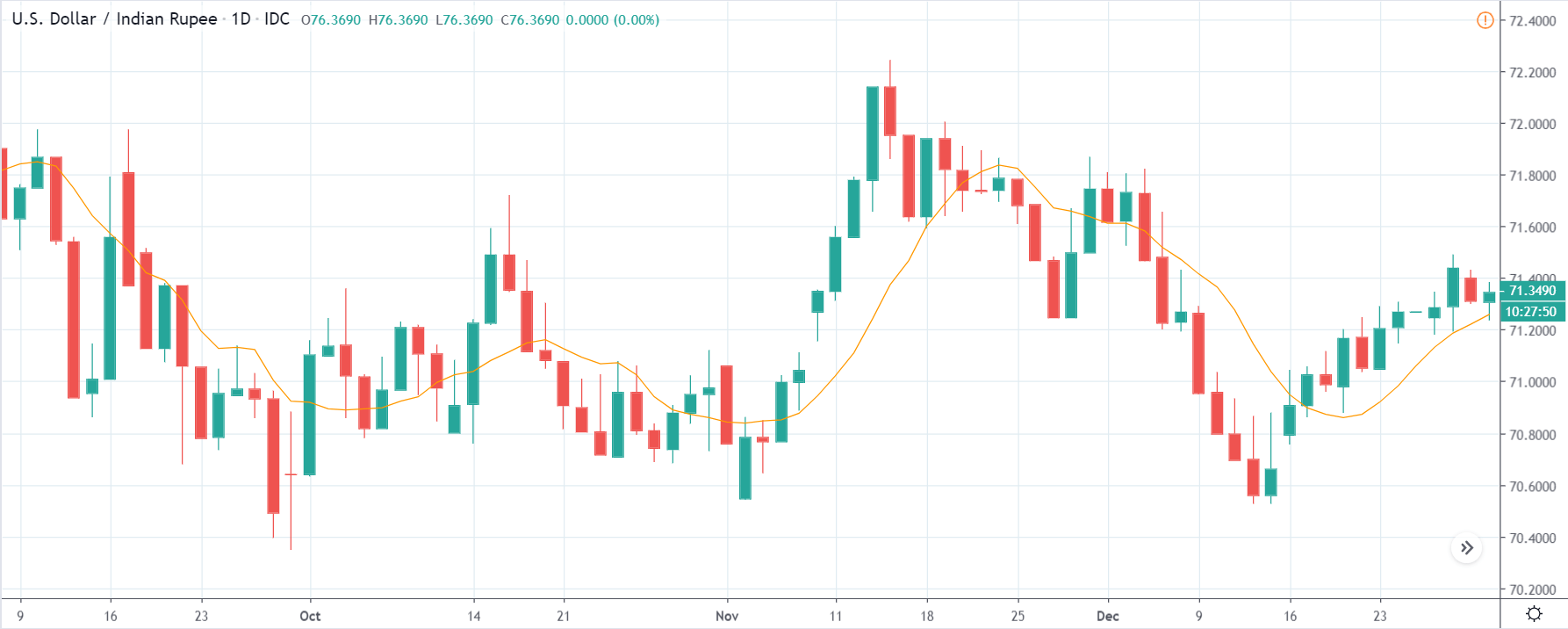
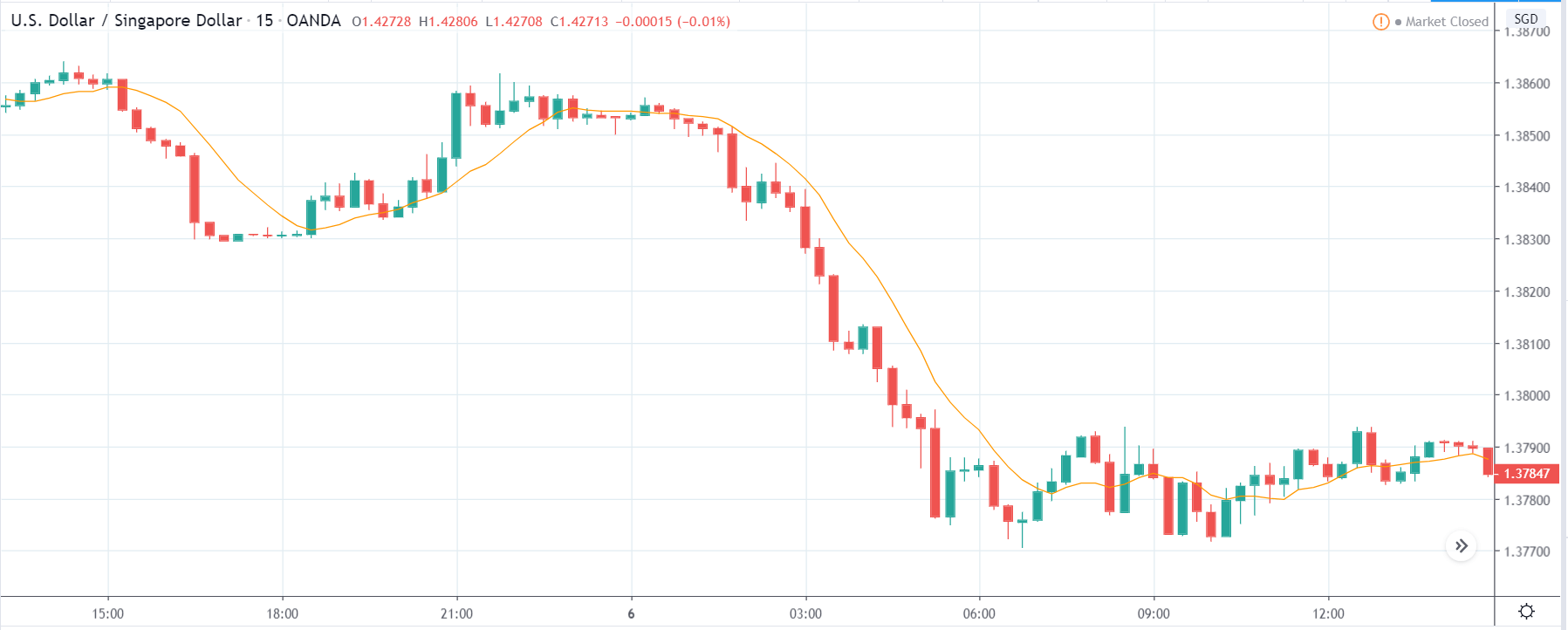
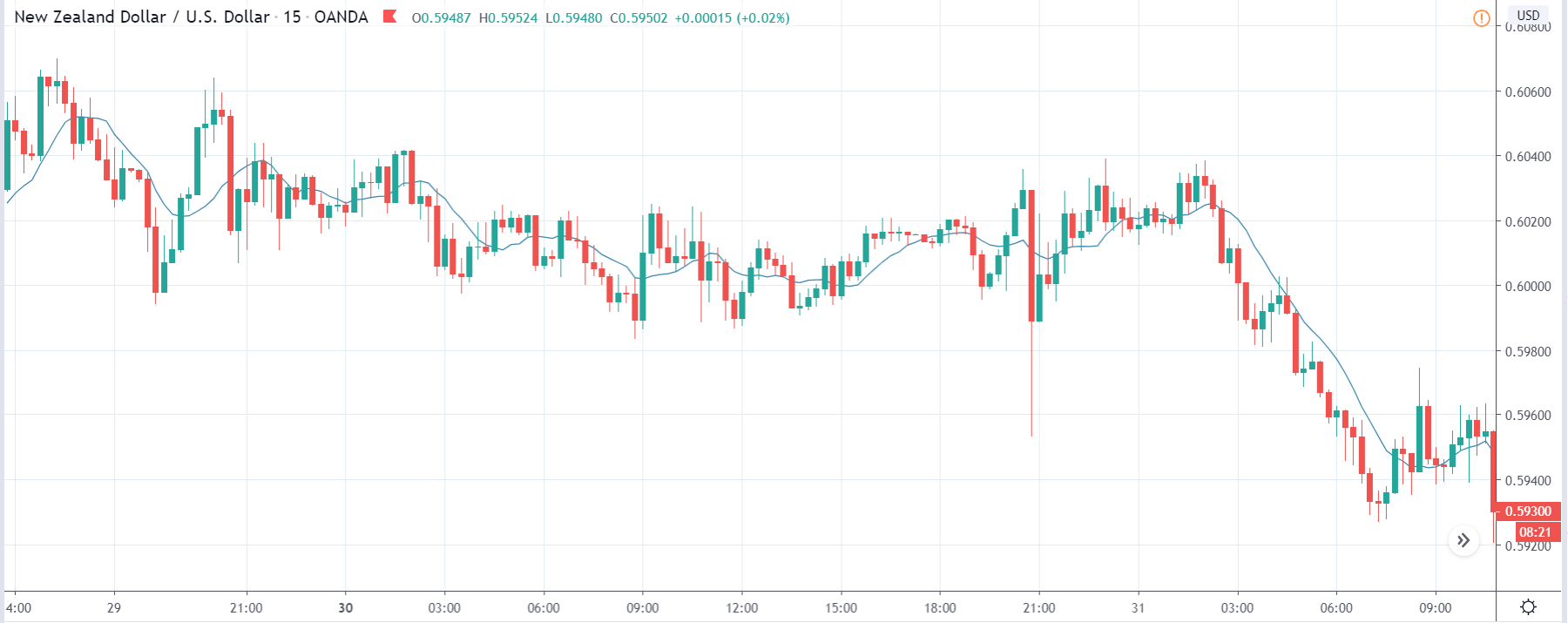
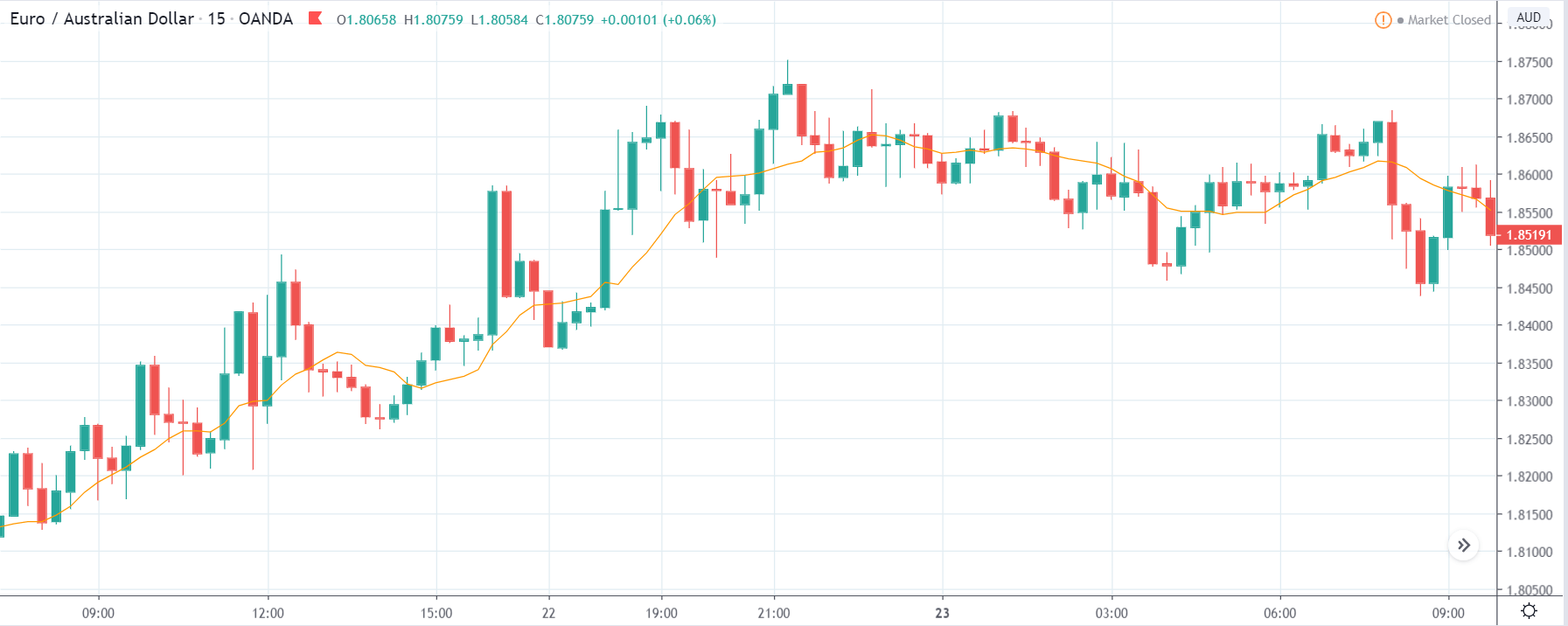
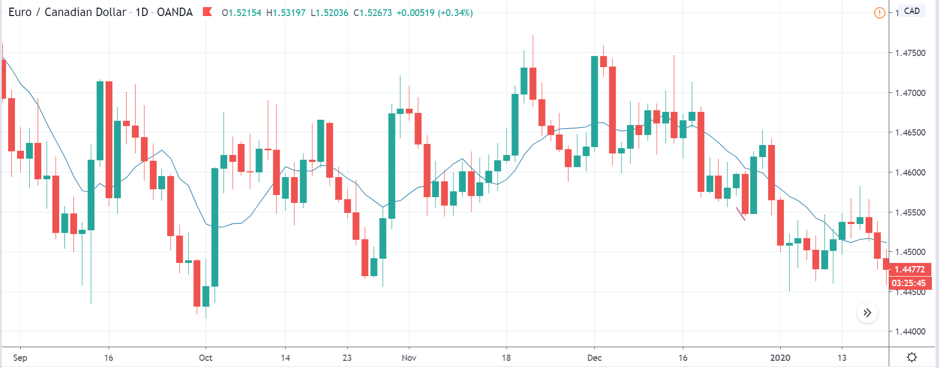
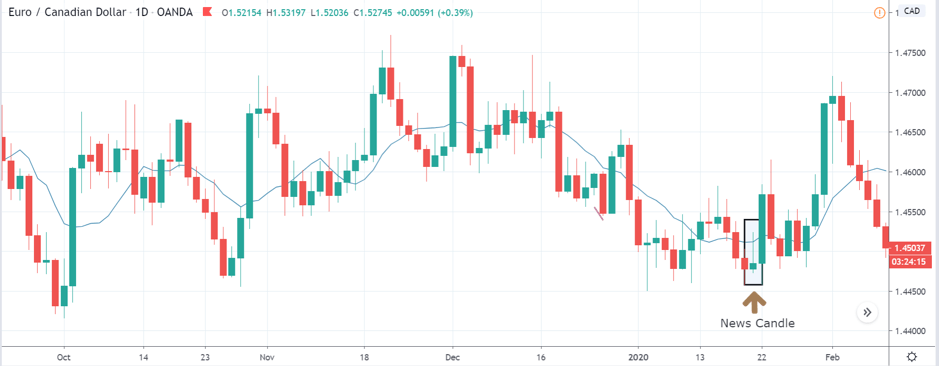
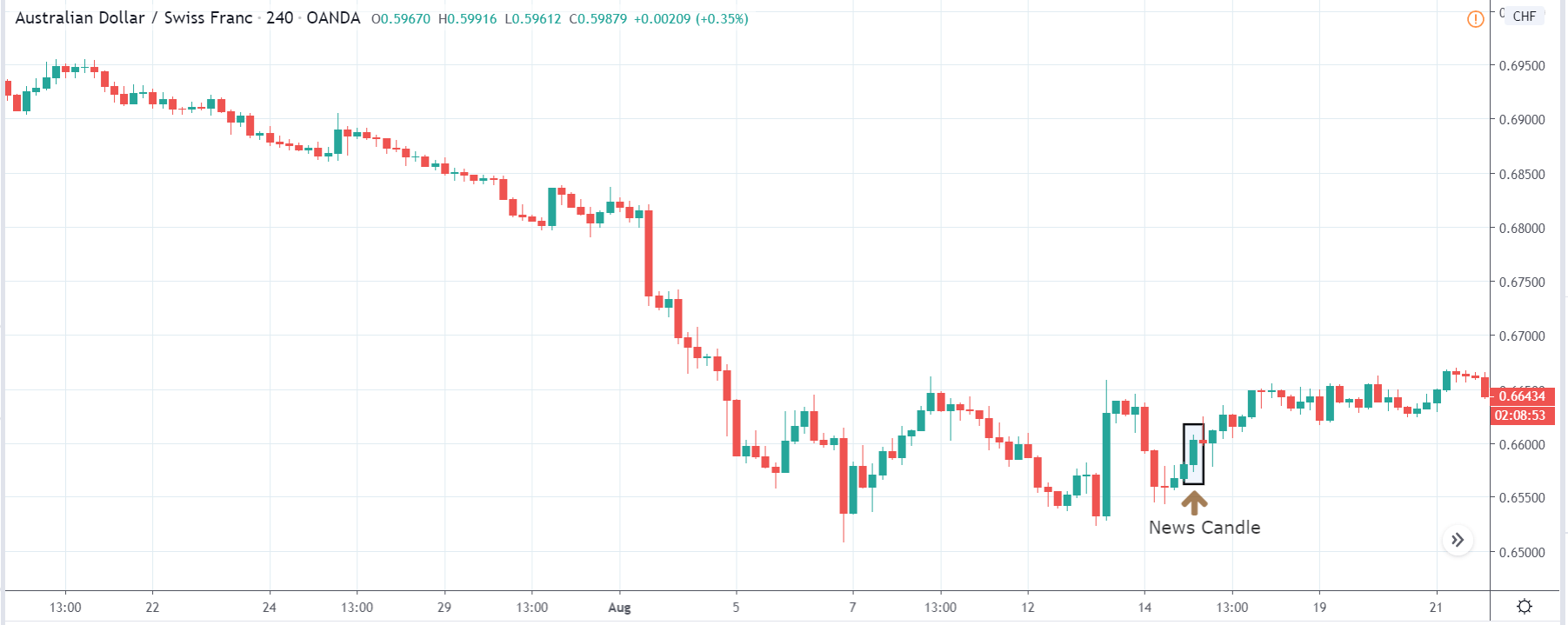
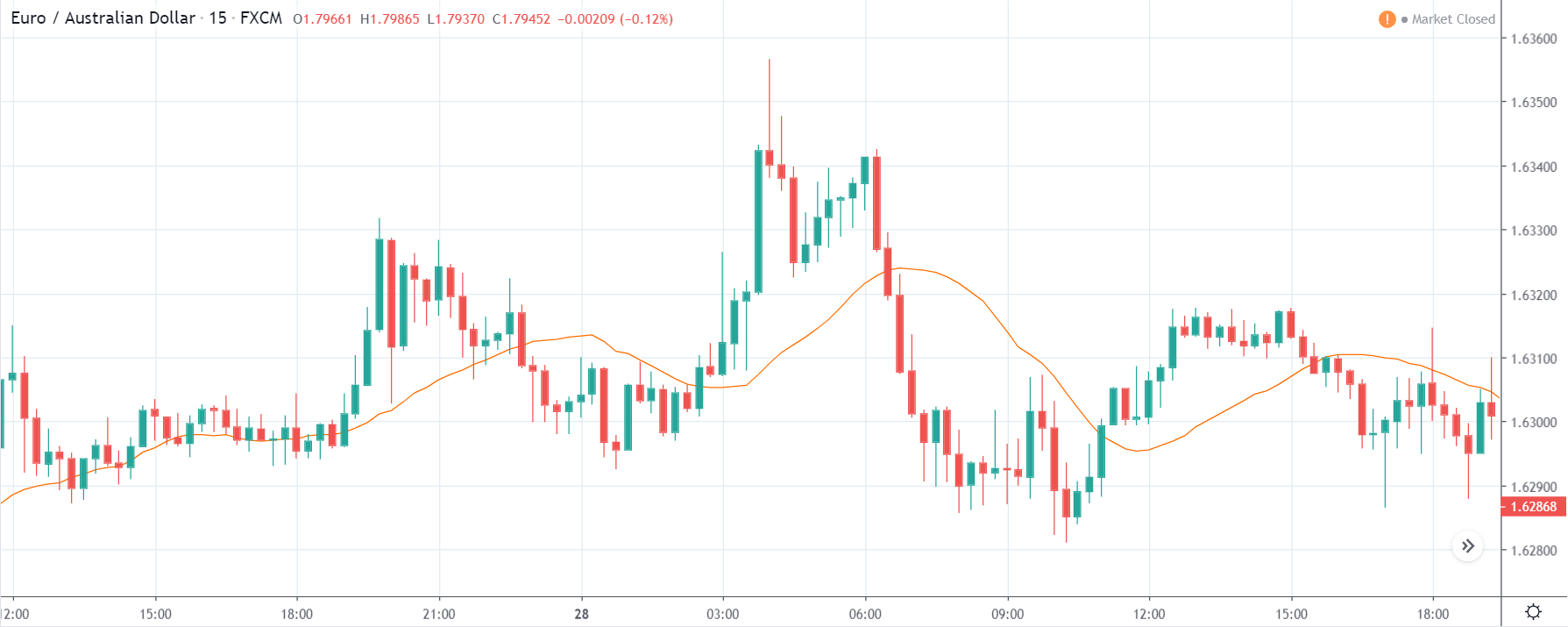
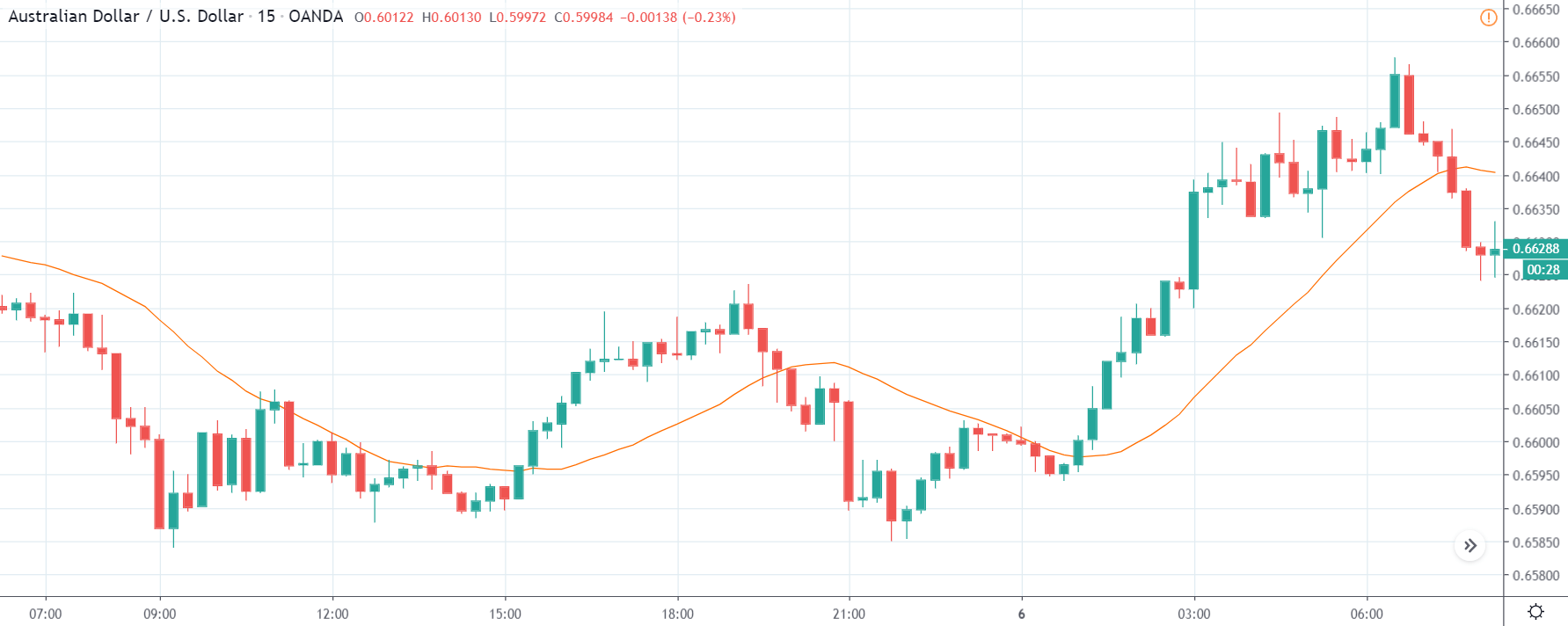
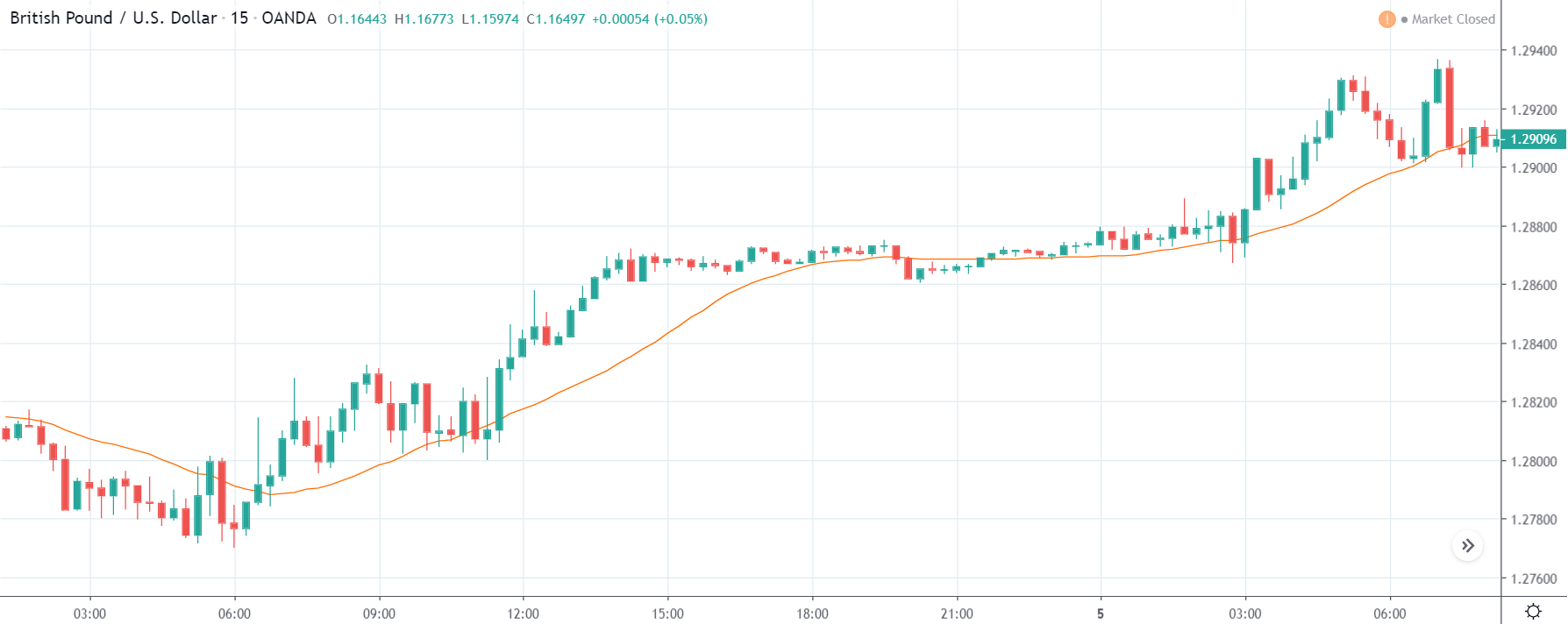
EUR/ZAR | Before the announcement:
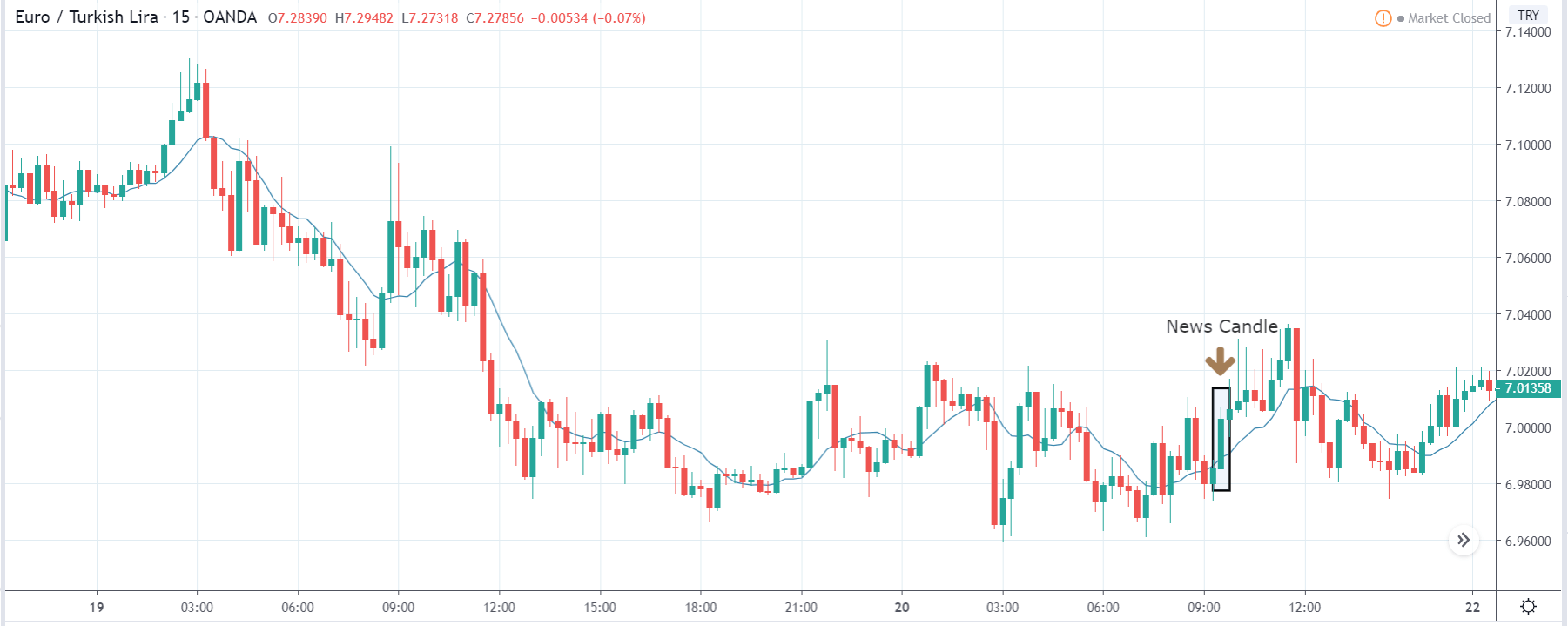
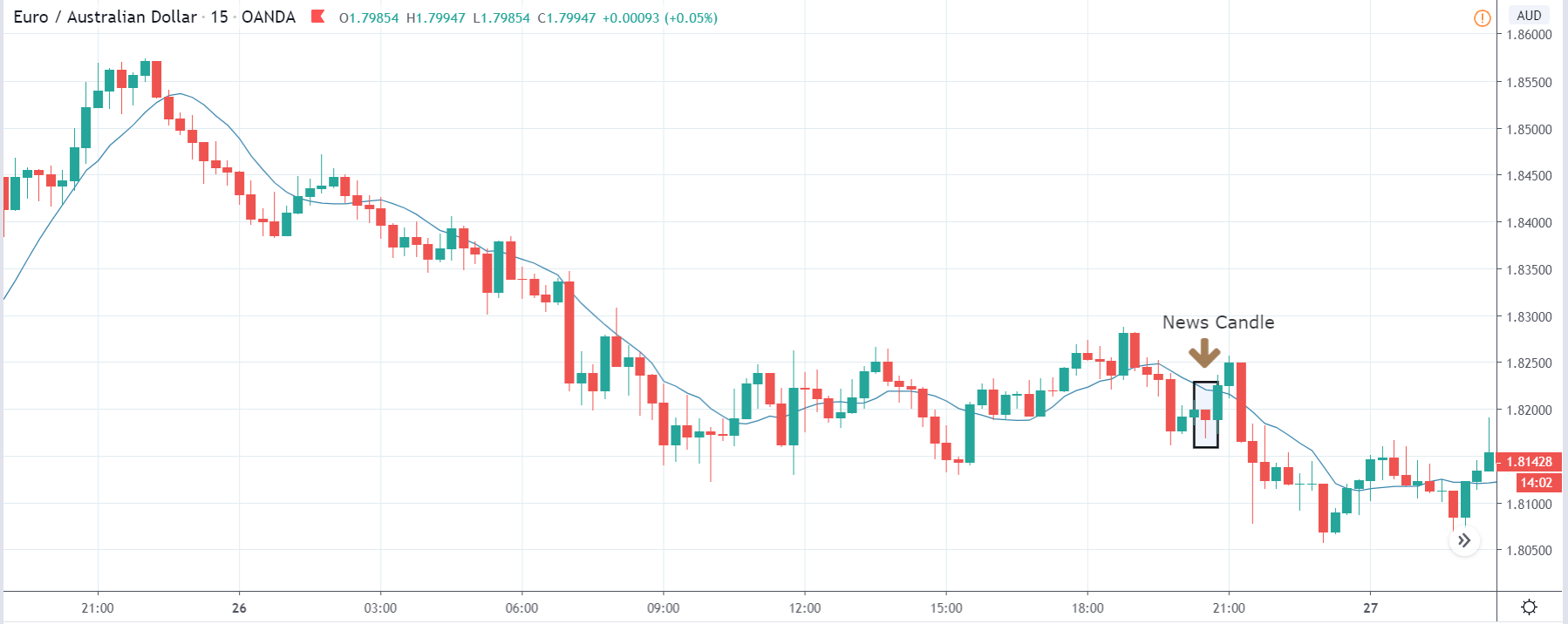
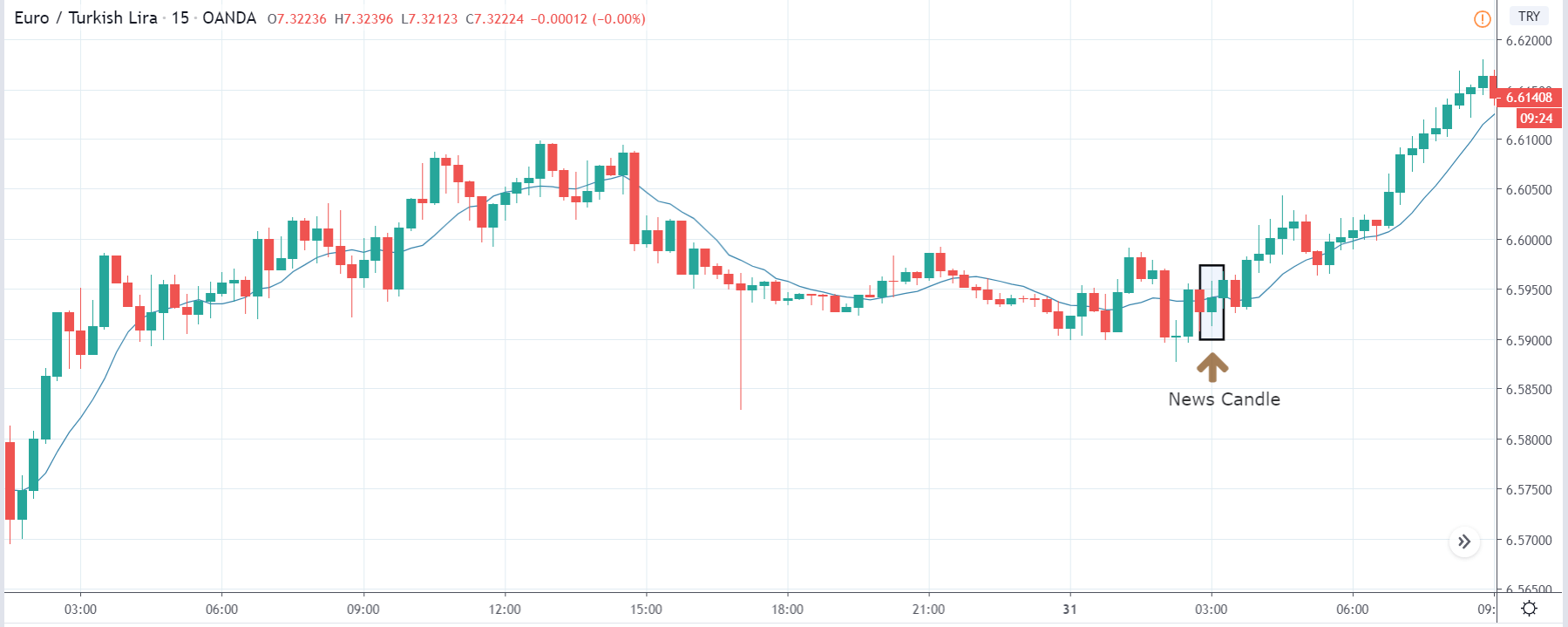
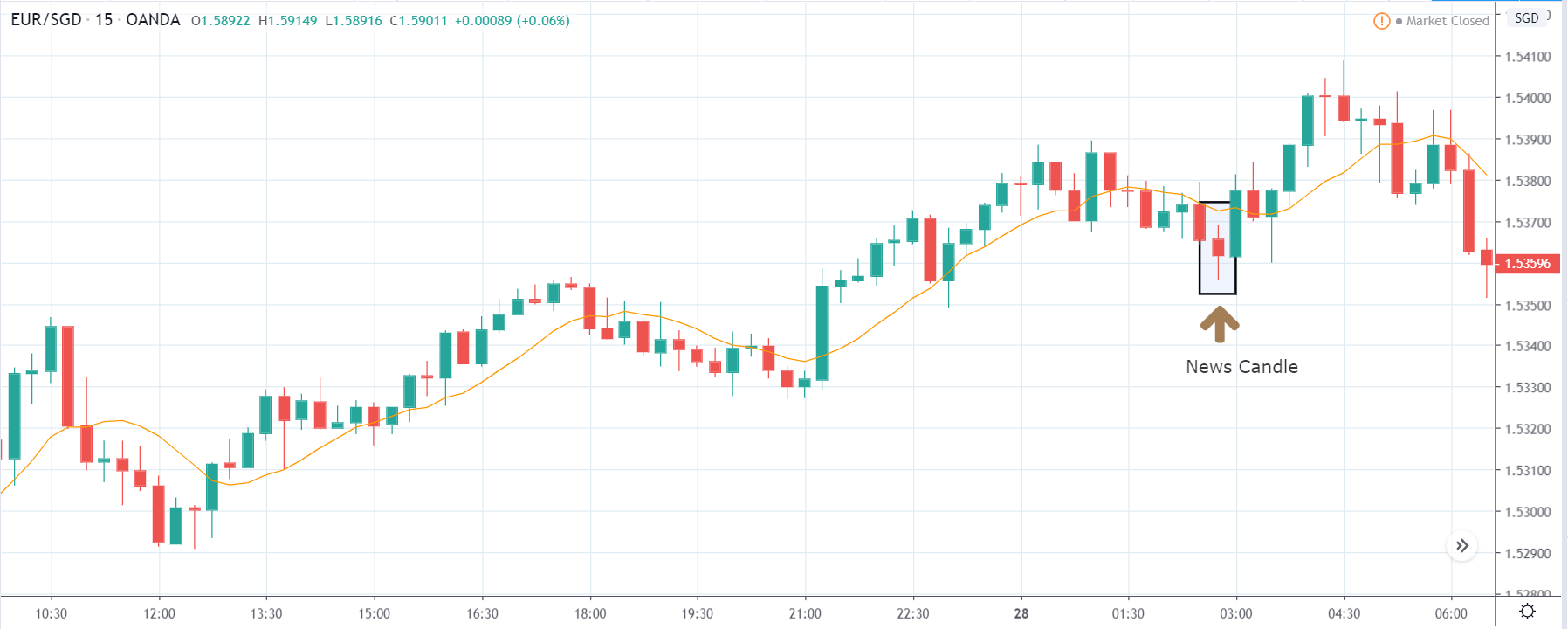
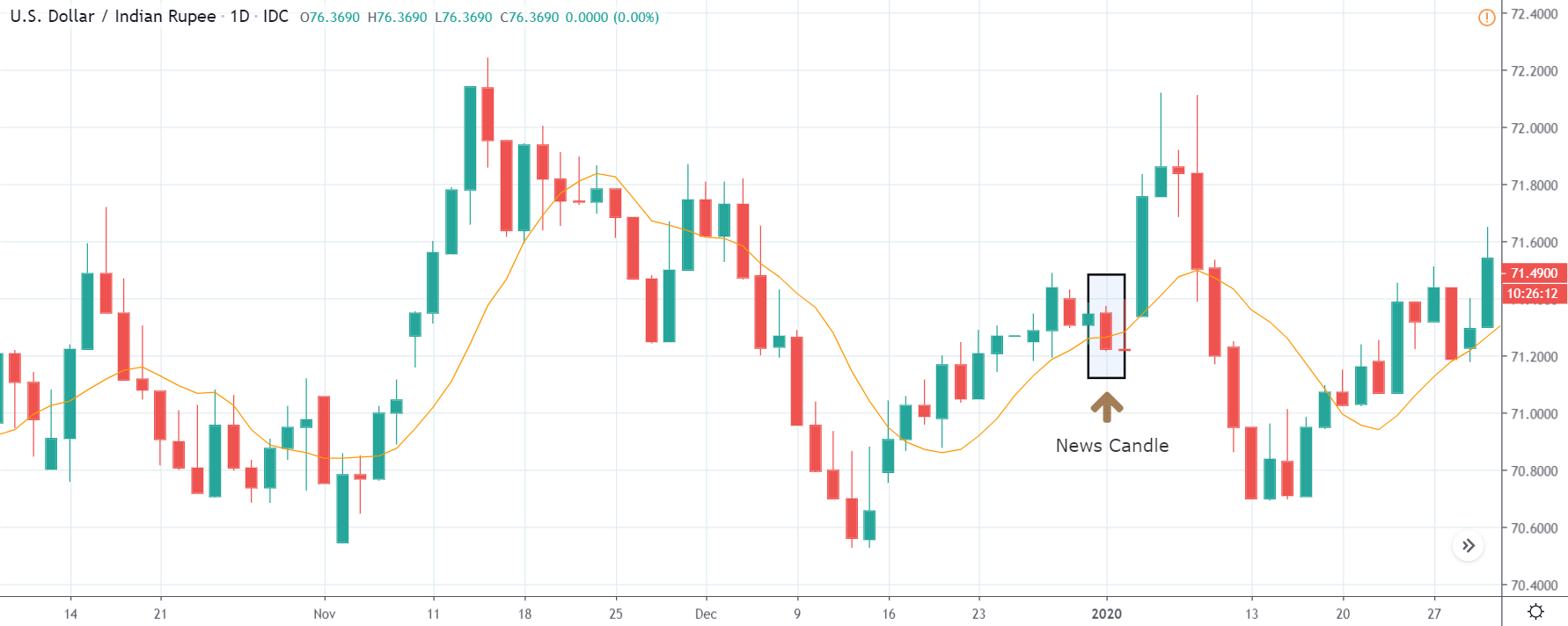
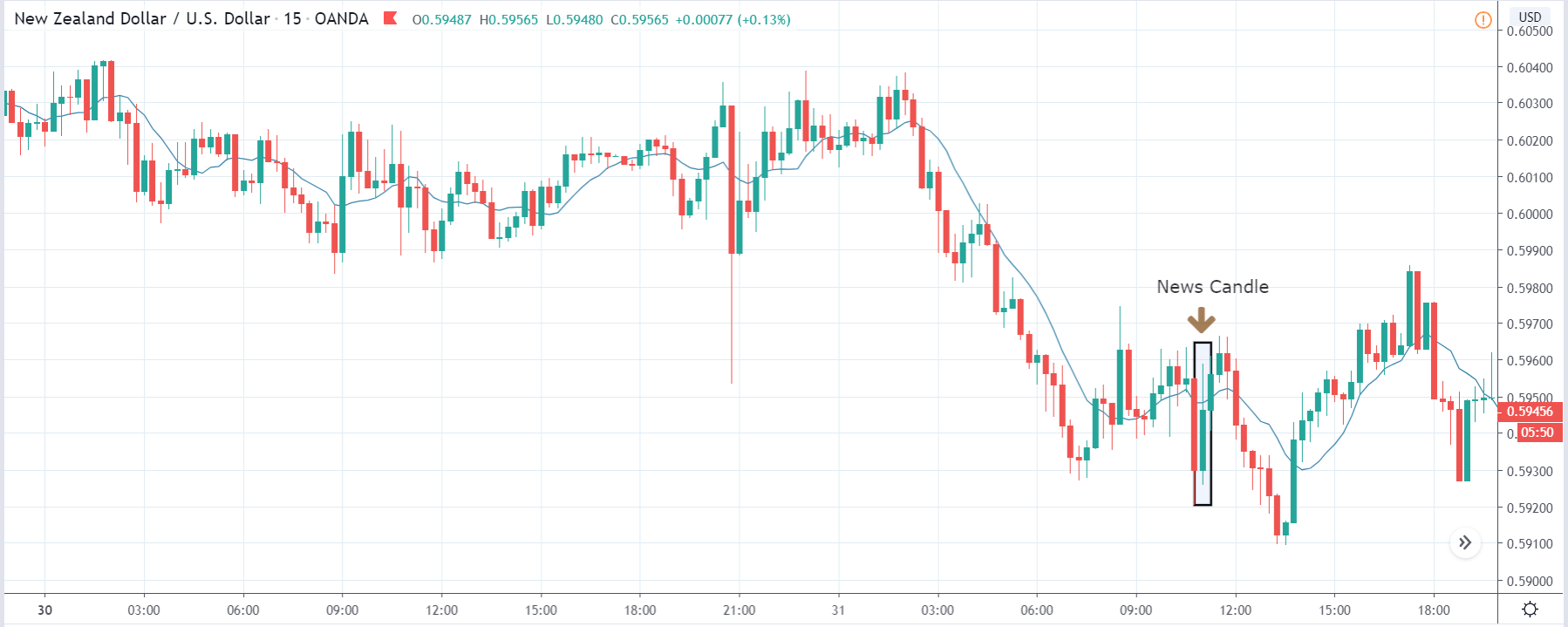
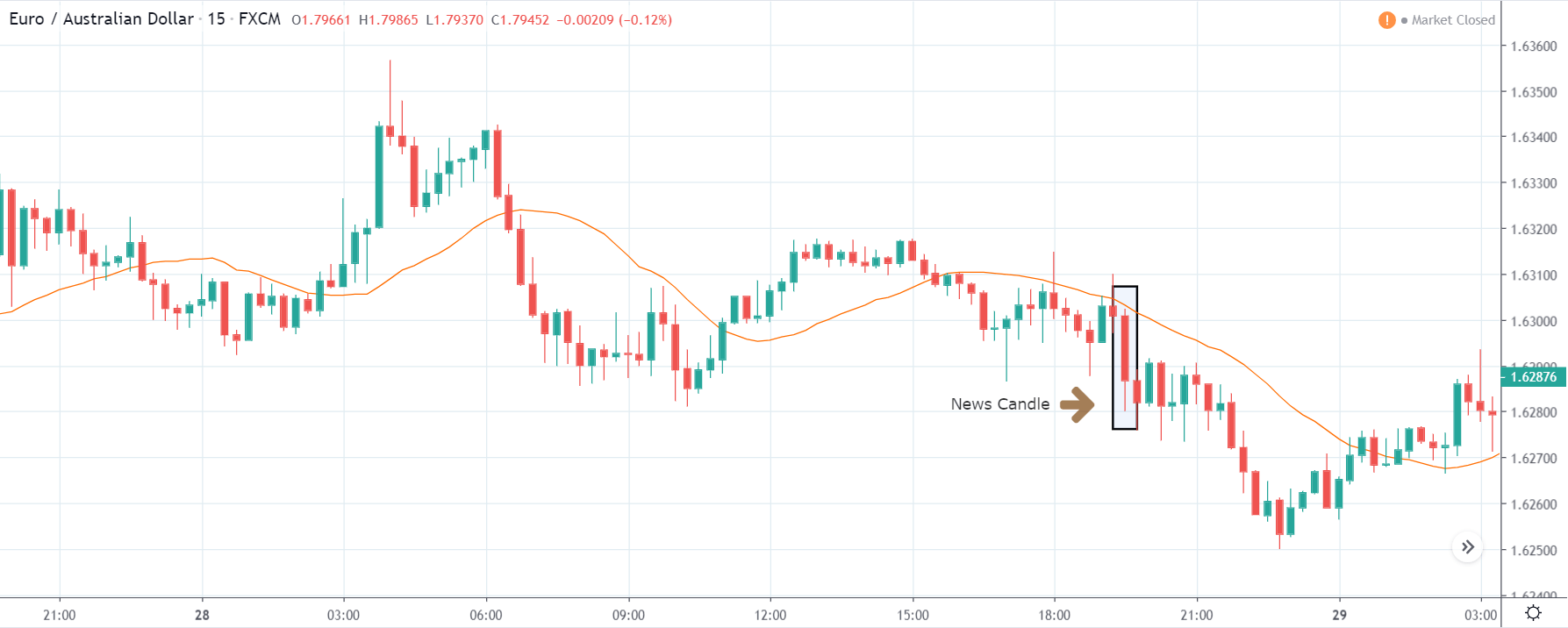
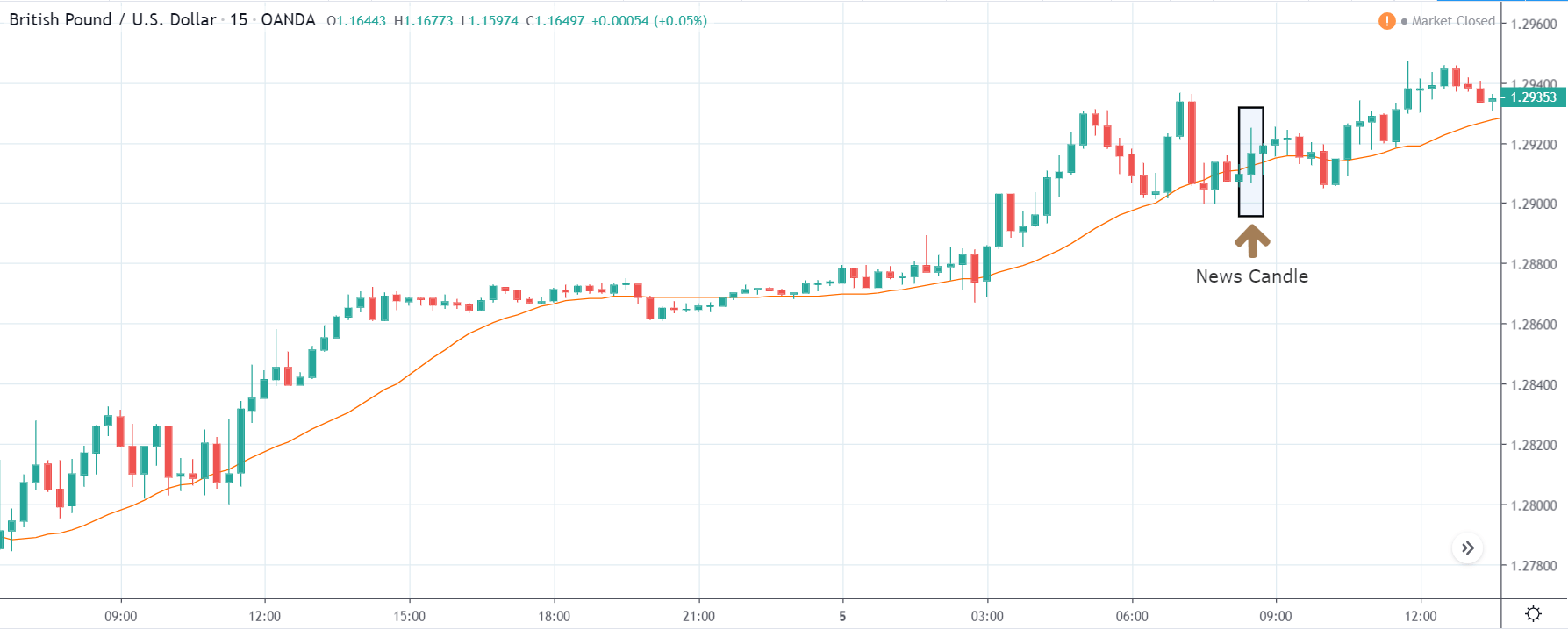
EUR/ZAR | After the announcement:
The above images are that of EUR/ZAR currency pair, where we see that the market is in an uptrend, and recently the price is within a ‘range.’ Here as well, the South African Rand is showing weakness with no signs of strength at all. Technically, we will be looking to buy the currency pair once the price ‘pullbacks’ to a key ‘support’ or ‘demand’ area.
After the news announcement, the price stays at the same level as before and closes, forming a ‘Doji’ pattern. A bullish reaction to the Mining Production data can be witnessed after the close of the ‘news candle,’ which showed an increase in volatility to the downside and thereby strengthening of the South African Rand.
That’s about ‘Mining Production’ and its impact on the Forex market after its news release. If you have any questions, please let us know in the comments below. Good luck!