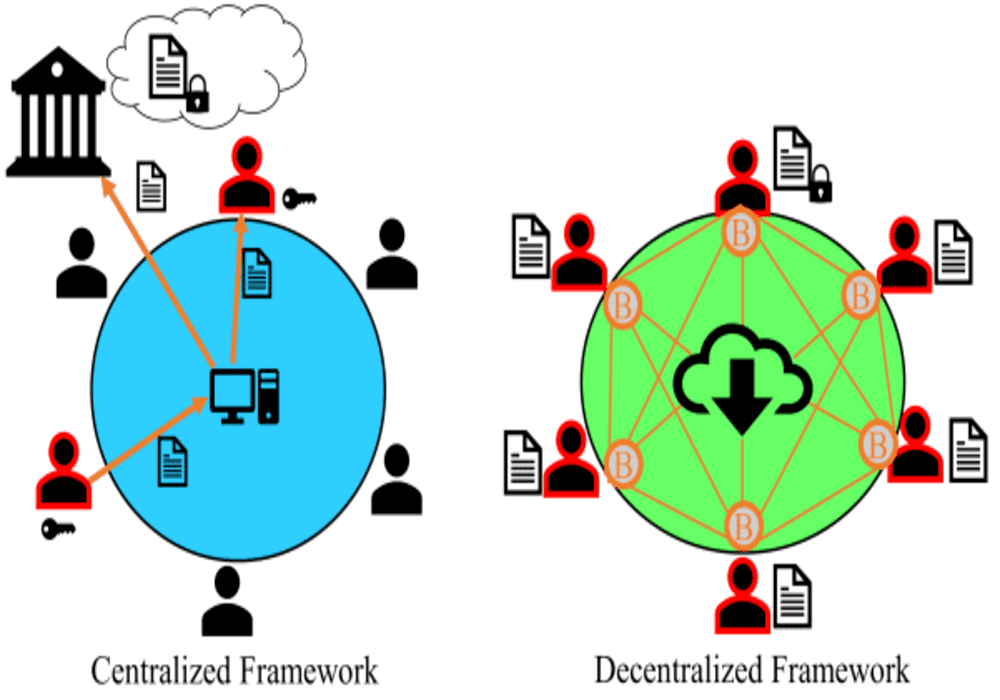
Since time immemorial, the world has run on centralized systems. But centralization has proven to have its own challenges, such as bureaucracy, slow decision-making processes, and single points of failure. On the other hand, a decentralized model offers room for more timely decisions. And it eliminates a single point of attack.
With blockchain, the concept of decentralization is even better. The technology brought to life by Bitcoin’s creator – Satoshi Nakamoto – can facilitate unprecedented speeds, transparency, and security in the way we do things.
Thanks to blockchain, we are now talking about decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) – organizations that (can) run on decentralized platforms and without the need for human input. Such an organization model not only saves money, but it also saves time and packs a ton when it comes to efficiency.
Aragon Network is a platform that aims to empower organizations anywhere to achieve this. Powered by its native token, ANT, Aragon is leading the way towards a decentralized economy.
What is Aragon?
Launched in February 2017, Aragon is an Ethereum-based, open-source project that aims to empower anyone to create their own decentralized applications (DApp). It features a native token, ANT, that gives network participants the right to vote on the future direction of the platform. The ultimate goal for the project is for it to become a decentralized autonomous organization and DApp that’s free for anyone to create their own on the Aragon blockchain.
The project’s Rationale
Traditional organizations spend a ton of money on overhead and administrative costs. And in their interactions with other organizations, there is the undesirable mix of fees, delays, and intermediaries that lead to overall friction and inefficiencies. Aragon seeks to remedy this by providing a platform where organizations can operate in a decentralized model on a shared platform.
Most organizations share what can be called standard functions. Whether it’s providing equity to investors, allowing shareholders to vote on key decisions, fundraising, compensating employees, implementing security access, almost all organizations have similar administrative functions. These functions make up part of the Aragon DApp solution for any organization that’s on-boarded on the network. Aragon hopes to simplify the process of setting up and running these operations on the blockchain.
The Technology Behind Aragon
The Aragon platform is made of Aragon Core, a Solidity decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) framework, and online-based DApps. Aragon focuses on two key principles:
- A decentralized court/jurisdiction for solving disputes on the network and enforcing contracts on the platform
- An upgrade system
Aragon Core, which supports organizational and management logic, is made of four components:
- Bylaws defining user permissions
- A decision-making governance system
- Capital system for token issuance
- A finance accounting system
Aragon’s interface is designed to be friendly and intuitive for non-technical users, yet provides an environment for developers to create applications and contribute to the network.
Also, Aragon’s incorporation of DAO principles is intended to eventually allow the network to give control to users who will govern the system through a voting mechanism incentivized by the ANT token.
In addition, the network hopes to eventually be financially self-reliant by aggregating fees collected from users. The funds will be allocated to maintaining the network and paying service providers such as core contract developers, the jurisdiction of courts, and a bug bounty program.
Modular Custom Features
Organizations will be able to edit existing modules, incorporate more functionalities, or develop completely new ones as they wish. The Aragon team envisions the Aragon core technology finding users that extend beyond operating traditional businesses. Among others, the following use cases could emerge:
- Political elections and national polls: smart contracts could be employed to create a prediction model that holds elected officials to their promises
- Contractor payment module: on-boarding subcontractors and compensating them based on milestones or whichever model they prefer
- Enhanced analytics and accounting: employ advanced visualization techniques to accounting and auditing data for your organization
The ANT Token
The ANT token is the native cryptocurrency of the Aragon network. The token is critical to the governing system and incentivizing mechanism of the platform. The token was sold in a successful initial coin offering (ICO) in May 2017, raising $24 million.
The token is at the center of the running of the platform. Individuals with a stake in ANT can vote on key decisions, participate in the decentralized court system, play a role in the Aragon Foundation and contribute to research and development for the network through the Aragon Nest program.
Who is Behind Aragon?
The Aragon team comprises diverse talents with diverse backgrounds, both geographically and experience-wise.
Luis Cuende is the founder and project lead and holder of accolades, including “The Best Underage European Programmer” in 2011 and “Forbes 30 Under 30” and “MIT Innovators Under 35”. He has also been an advisor to the Vice President of the European Commission in charge of the EU’s Digital Agenda.
Jorge Izquierdo is the Tech Lead. He has several projects under his belt and is also a recipient of the Thiel Fellowship and Apple’s WWDC scholarship.
The ultimate goal of the project, however, is for Aragon to no longer need a team. The developers hope community involvement and support will drive future initiatives, with the Foundation only playing a minor role in coordinating contributions.
What’s the Market Look Like for ANT?
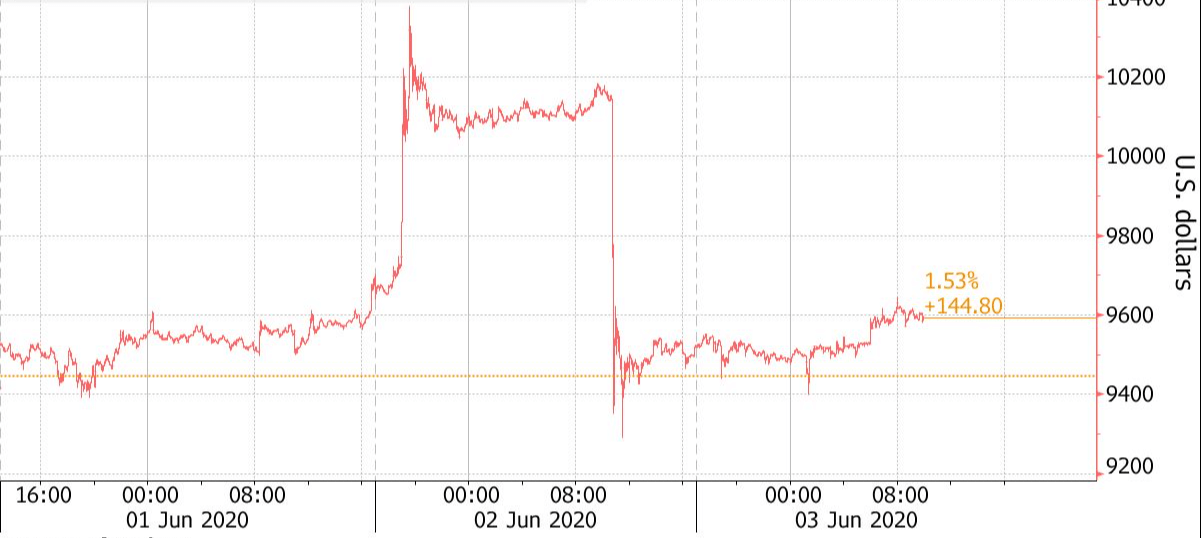
At the time of writing, ANT is trading at $1.12 while ranking at #126 in the crypto market. It has a market cap of $35, 983, 594, a 24-hour volume of $259, 021, a circulating supply of 32,100, 881, and a total supply of 39, 609,534. The token’s highest price ever was $7.76( Jan 07, 2018), while it’s lowest was $0.285450 (No 25, 2018).
Where to Buy and Store ANT
ANT is available on several popular exchanges, including Bittrex, Liqui, Changelly, Livecoin, IDEX, EtherDelta, Novaexchange, HitBTC, and ShapeShift. You will need to first purchase BTC or ETH, then exchange it for ANT.
ANT is Ethereum-based, meaning you can store it on any Ethereum-compatible wallet. Some options include MyEtherWallet, MetaMask, ethaddress, Atomic Wallet, Guarda Wallet, Ledger Nano, and Trezor. Ledger and Trezor are particularly superior options in terms of security.
Final Words
Aragon can help usher in a radical shift in the structure and operations of organizations. By helping them integrate blockchain technology, we can start seeing the revolutionary features of transparency, immutability, and decentralization – taking form in actual day-to-day functions in organizations.
Aragon has created a friendly and intuitive interface so that both non-technical and developers can derive and create value, optimize processes, and participate in the blockchain revolution. Aragon could very well be the next-gen solution for a decentralized economy.