Around security in blockchain some interesting myths have been created that make this technology look like a total panacea and something almost surreal, for that reason, we dedicate this article to break these myths and make see the truth about this technology.
Safety is certainly one of the main, or perhaps the main, requirement for blockchain technology. In fact, in a way, security has become the first bastion of defense of this technology that now conquers more and more spaces. And it is not for less, the security in the blockchain is excellent, but reaching it takes a lot of work. In addition, it is not a magic solution, because as in any computer system always reigns the premise of cybersecurity:
“There is no 100% secure computer system.”
That is the harsh reality of the computer world, and blockchain, being a computer technology, is not exempt from this rule. So why our confidence in your safety? Why have so many myths been created around this technology? What is the truth? Let’s try to show that several of the myths that have been created around blockchain technology.
Myth 1: Blockchain is unhackable.
One of the first myths we see in the blockchain world is about the inability of blockchain technology. The truth is that this is not 100% true. Certainly, blockchain technology presents a high level of security, and more if we compare it with any type of sector that is based on centralized technologies.
Bitcoin, the world’s first cryptocurrency, has shown us several times that it has errors that can be dangerous for everyone. So what protects us from the blockchain catastrophe? Simple, the assurance that the community will detect and correct those errors, as it has always done. And in the worst-case scenario, in the event of an error that has not been detected early, the network can always agree to return to a block where that has not happened.
This is in addition to the continuous work to develop security measures that avoid serious problems, and the always reliable decentralization, which will allow us to rebuild everything in case the worst comes to pass. But we can also be sure of something, that a project like Bitcoin has accumulated 46 serious errors, is an incredible achievement, because in contrast Windows 10 (developed by one of the corporations that dominate the world) in just a period of 4 years accumulates more than 8100 errors.
Myth 2: Blockchain is absolutely immutable.
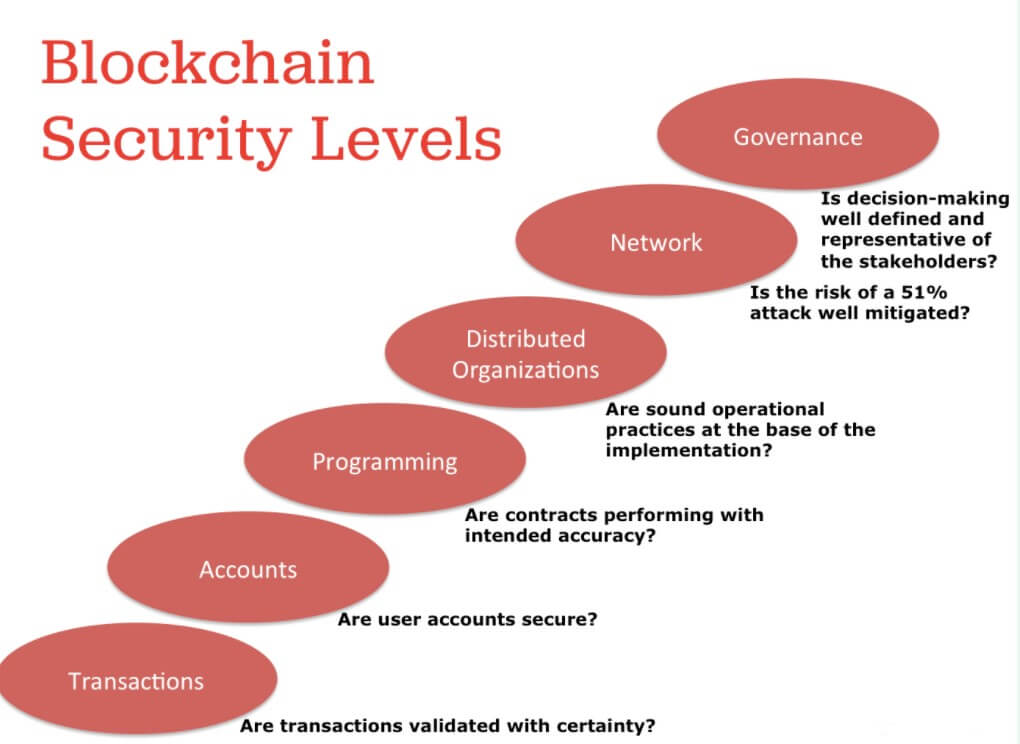
Another common myth in the blockchain world is the “absolute immutability” of the blockchain. Something that is not true. The truth is that the blockchain can be rectified or modified under very specific conditions, and we know that from those who have read about the 51% Attack. This attack has the ability to modify the blockchain significantly despite the attempts we make to avoid it, and all within the parameters allowed by the protocol because after all, most of the nodes (51%) have decided to do so.
The attack we have already seen in action, Ethereum Classic (ETC) recently suffered another attack of this type. Bitcoin Gold was another recent victim of such attacks, and other cryptocurrencies are constantly suffering it today. But isn’t Blockchain supposed to be immutable? The answer to this is: It is under certain circumstances. If a blockchain network has its power distributed among its nodes so that none of them has the most power in their hands, then that network will be secure. Otherwise, it’s a recipe for disaster.
Myth 3: All blockchain is highly decentralized.
Decentralization may be the worst myth of all, and it is because decentralization in blockchain projects is misunderstood (or misused). And many projects, and companies, use the word “Blockchain” to confuse, trying to convey that they are a decentralized network when they are not.
For example, Bitcoin is a fairly decentralized network, but there’s still a long way to reach a “safe zone of decentralization”, that area where Bitcoin users turn to their own nodes instead of third parties to perform their operations. The latter may sound utopian, but it would be the perfect example of absolute decentralization. Still, Bitcoin is a good example of decentralization.
However, if we choose other projects such as Ripple, Stellar, Tether, Bitcoin SV, Tron, UNUS, IOTA, Compound, BAT, Theta,… that decentralization is lost. Yes, these projects are blockchain, some with great renown and great economic level, but each and every one of them have of decentralized what of decentralized has a Bank.
In short, they are projects that use the words “blockchain” and “decentralization” to disguise an almost absolute centralization existing over their systems. And we are not talking about centralization at the level of development, but also at the level of nodes, miners, and other structures that make it possible to function. In this sense, this myth falls for the clear evidence that a “blockchain project” is not automatically decentralized because it is blockchain.
Myth 4: Cryptography makes Blockchain secure.
This myth, surely, is one of the most difficult of all to understand. The reason for this is because it is a half-truth. Cryptography is certainly the basis of blockchain security, but cryptography is constantly broken.
An example that breaks this myth can be seen in IOTA. This cryptocurrency is based on DAG (Directed Acyclic Graphs) technology and uses a cryptographic function that was considered secure. However, a hacker managed to break that algorithm and as a result, thousands of users were affected, with theft of funds and access to the seeds of their purses. A serious problem where cryptography was not enough to maintain security. As a negative result, the IOTA network was out of service for 14 days until the problem was fixed.
However, the operating model of Bitcoin, the management of its development, and its active community is a successful formula to combat the problems that could come along this line.
Myth 5: Smart contracts are the ultimate programming tool.
Smart contracts are often seen as the biggest breakthrough achieved thanks to blockchain, and that vision is correct. However, smart contracts are not inherently secure by running on a blockchain, as many show, on the contrary, a public smart contract is subject to public scrutiny, and if there are malicious actors in that audience who can see a vulnerability, they’ll exploit it for a profit.
Yes, smart contracts are very powerful, but their security is far from perfect, in fact, we could say that it is still a work in progress, as we can see to platforms like Ethereum, where they seek to constantly improve their language to enable the most secure development of such tools.
Computer security has always been a space where the impossible always ends up being possible. There are many systems that claim to be “ineligible” and always end up giving in to some error in their systems sooner or later. It is something that reaches even the big ones, such as OpenBSD, the most secure operating system in the world, and that in all its history (23 years) has only had two errors in its installation by default.
That being said, blockchain although it is a very secure system, perhaps one of the safest to handle our money, is not an all-powerful and perfect solution. We are certainly far from that, and that, however illogical, is a good thing.
In this sense, the future of blockchain security will always be positive, it will always go in the interest of being able to improve what we currently have, to face the challenges of the future. That way we can stay calm, blockchain security will improve, and with it, our impression of a technology that is changing the world.