What comes to your mind when you hear the word cryptocurrency?
Probably it’s the distributed and consensus ledger technology that forms the basis of the whole crypto universe.
As such, it would seem counter-intuitive if other solutions built around this ledger technology end up diluting its decentralized aspect. Yet, the ratio of centralized exchanges’ trading volume to that of decentralized exchanges suggests that traders prefer the former to the latter.
Well, there are many halftones between the two concepts – decentralized and centralized – with an arguable belief that not everything is always black and white. Besides, if the power of decentralization was to transverse all aspects of our everyday life, wouldn’t it send us into disarray? So, the real question here should be, to what extent should an exchange be decentralized?
Decentralized Exchanges Explained
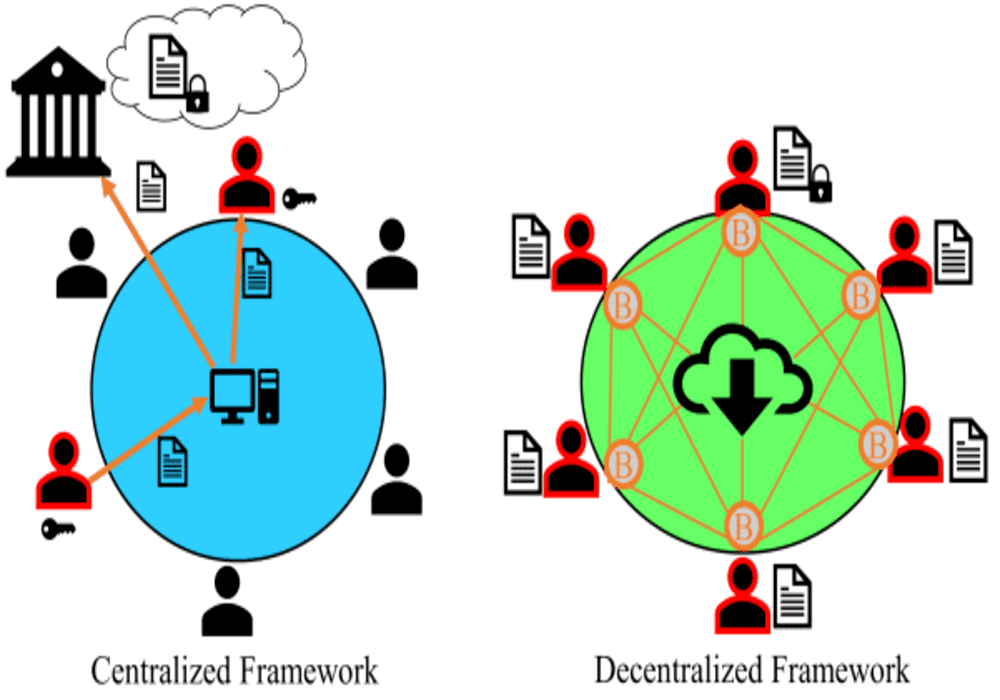
Much like cryptocurrencies, decentralized crypto exchanges (DEXs), seek to create a trustless environment where buyers and sellers can transact freely. Instead of using matching buy and sell orders in a central book, DEXs utilize smart contracts to link traders directly to each other, eliminating the need for a third-party. In this way, these types of exchanges don’t hold users’ assets or any other personal data. They only serve as a matching and routing layer for trade orders.

Generally, there are two types of decentralized crypto exchanges: currency-centric and currency-neutral. Currency-centric exchanges are tied down to one specific blockchain network escrowing its native currency, e.g., Ethereum, Waves, Tron, and any other blockchain that has smart contract capabilities. Currency-neutral exchanges, on the other hand, tend to be more versatile. This means that they can be built on various blockchain networks and are therefore not tied to one specific digital coin ecosystem.
How Decentralized Exchanges Work
Regardless of their differences, all decentralized exchanges work pretty much the same way. A client brings their funds like ETH, which are stored in the exchange’s network in the form of proxy tokens, in this case, DEX-ETH. Ideally, these tokens serve as collateral for the actual coins stored by the exchange.
To execute a trade, the client sends an order to sell their tokens in exchange for, say DEX-BTC tokens, which also represent the actual BTC owned by the other party. The smart contract then matches and processes the orders, after which the proxy tokens are exchanged between the two parties. The seller gets the DEX-BTC while the buyer receives the DEX-ETH tokens. After receiving tokens, both parties can convert them to the actual currency, ETH and BTC, using the same trading channel or a different one.
Advantages and disadvantages of Decentralized Exchanges
Given their architecture, one of the biggest advantages that rises to the forefront is security. The exchanges don’t hold customers’ funds in a central reserve and are thus not vulnerable to hacks or theft. At the same time, decentralized exchanges don’t require a user’s personal information, which also goes a long way in improving security and anonymity in line with the purpose of crypto.
A DEX eliminates the need for a middleman between traders, helping reduce the trading fees. Additionally, traders who like keeping up with crypto market trends, you might consider using decentralized exchanges. This is especially true if you invest in an Initial Coin Offering (ICO). Often, ICOs find their way into DEXs prior to centralized exchanges.
Despite their numerous advantages, decentralized exchanges have their shortcomings. To start with, they require a higher degree of technical know-how to use efficiently. They also lack essential trading features, which makes them intimidating to new crypto traders.
Due to the small number of users on DEXs, they have a relatively low trading volume. This translates to limited liquidity in addition to difficulties in finding a matching order since there’s a limited number of traders on the platform.
Decentralized exchanges also suffer from slow transactions. The slow speed of transactions may not be a big deal to small-scale traders, but it can be detrimental to trading giants with high-volume transactions.
Also, by their very nature, DEXs have no physical location or proof of existence. Therefore it would be difficult to launch a complaint should an issue arise.
Centralized Exchanges Explained
Unlike their counterparts, centralized exchanges, also known as CEXs, function similarly to traditional stock exchanges. Essentially, they act as a middle-party between crypto traders and, in exchange, collect a small fee on every successful trade.
These exchanges are structured in such a way that they own their users’ private keys (or wallets), meaning that all transactions have to be executed in the mechanisms laid out by the central authority. Their having access to users’ wallets is a double-edged sword.
First, in case of a lost password, a user can easily recover their funds by simply contacting the exchange’s support team. At the same time, centralized exchanges are prone to hacks and thefts since they store client funds in a centralized database. But even with this downside, CEXs continue to attract a higher number of users than decentralized exchanges.
Such popularity can be attributed to the seamless fiat to cryptocurrency trades carried out on the centralized exchanges. As such, it is easier for a new crypto trader to enter the market. Moreover, centralized exchanges boast of useful trading features like the stop losses, margin trading, and lending, which are not available on decentralized exchanges.
Thanks to their high number of users, centralized exchanges have higher liquidity than DEXs. The liquidity is further enhanced by the fact that most CEXs accept fiat currencies and can even be linked to debit cards or bank accounts.
To Centralize or Not to Centralize?
Currently, centralized exchanges control the lion’s share of the global cryptocurrency trading volume. Although they deserve it due to the convenience they offer, they have watered down the idea of decentralization in the blockchain and crypto industry. Perhaps as decentralized exchanges continue to grow, there will be a major shift to these platforms since they maintain users’ privacy and security, which is becoming increasingly important as more centralized exchanges fall victim to hacks.