When the first cryptocurrency – Bitcoin, came into existence, it brought with it more than a digital medium of exchange. Blockchain, the technology underlying it, has brought with it more possibilities that can revolutionize entire industries and even society itself.
Smart contracts are one of the most interesting and explored applications of blockchain technology. Today, Ethereum is almost synonymous with smart contracts – and that’s because it’s the most successful blockchain in providing a platform for people to create smart contacts. In this article, we discover what exactly smart contracts are, their current standing in today’s world, their strong and weak points, and more. But first, where did this whole concept of smart contracts emanate from?
The History of Smart Contracts
The concept of “smart contracts” originated in 1996 with Nick Szabo, a computer scientist, legal scholar, and cryptographer. He defined smart contracts as “a set of promises, specified in digital form, including protocols within which the parties perform on these promises.” As for why “smart,” he explained: “I call these new contracts “smart” because they are far more functional than their inanimate paper-based ancestors.”
Szabo went on and refined the concept over several years – releasing new literature on the subject. He described the concept of establishing contract laws via e-commerce protocols between strangers on the internet.
But the idea of smart contracts remained that – just an idea, until 2009, when Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency emerged, along with blockchain technology. Blockchain provided the environment where smart contracts could now be implemented.
Nowadays, smart contracts are mostly associated with cryptocurrencies, whose underlying technology is blockchain. And although Bitcoin broke the ground for smart contracts, it has limited support for the function. Today, the Ethereum blockchain is the most popular platform for creating smart contracts.
What Are Smart Contracts?
A smart contract is a protocol that allows you to exchange anything of value in a transparent, self-executing, and undeniable way without the need for a middle man. Smart contracts are indeed the reason why the blockchain is referred to as decentralized because they allow us to execute trackable, unalterable, and safe transactions without the involvement of a central authority.
Smart contracts have all the information about a transaction, and they self-verify and self-execute once all the conditions have been met. Unlike traditional contracts, smart contracts are purely computer-generated. A programmed code delineates the obligations, rules, and penalties of the involved parties – the parties involved can even be people who have never met but who are nevertheless bound by the agreement.
With smart contracts, a party cannot deny their involvement at a later date.
Jeff Garzik, the owner of blockchain technology company Bloq, describes smart contracts as such: “Smart contracts guarantee a very, very specific set of outcomes. There’s never any confusion, and there’s never any need for litigation.”
Objects of Smart Contracts
Any smart contract has three integral parts to it. Also known as objects, the three integral parties are as follows:
- Signatories – who are parties subject to the contract and who agree or disagree with the terms set out – using digital signatures
- Subject of agreement – this object has to exist within the smart contract’s environment.
- Specific terms – these are the obligations expected of all parties and the rules, rewards, and penalties associated with those terms. The terms must be mathematically described using a programming language suitable for the particular contract’s environment.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
Smart contracts are essentially deterministic processes – which means their end behavior is entirely dependent on initial input. They execute agreements if and when certain conditions are fulfilled. As such, smart contracts work on the “if…then” premise. It’s important to note that smart contracts are not legal contracts, but pieces of code running on a blockchain.
Smart contracts running on the majority of blockchains are akin to a vending machine. You simply input your cryptocoin into the vending machine (in this case, the blockchain ledger). If your input satisfies the code within the smart contract, the smart contract executes the terms of the agreements set out in it.
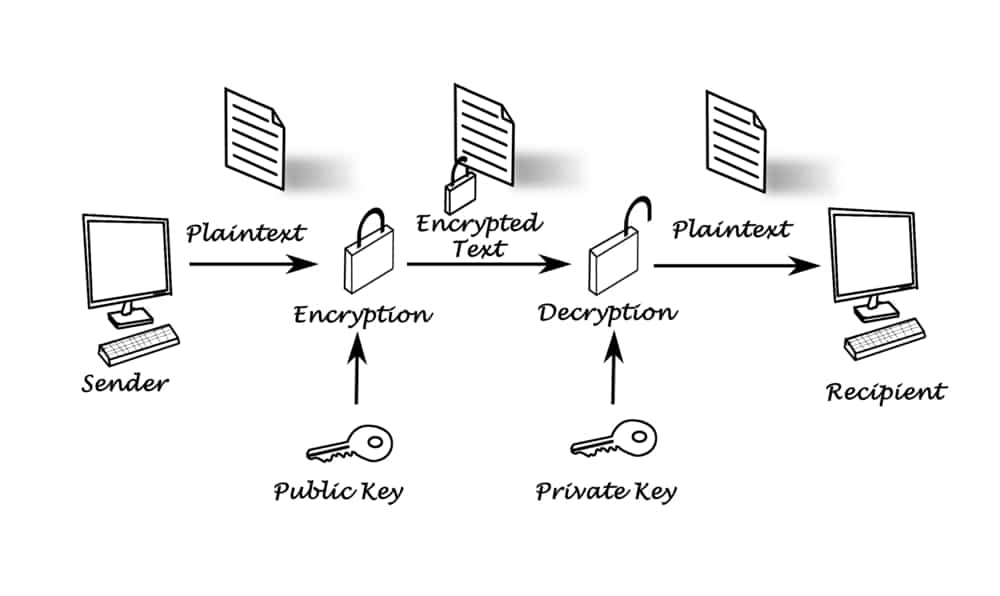
For instance, “If Person A completes task 1, then payment from Person B is delivered to Person A.” Based on this protocol, smart contracts allow for the exchange of any kind of value, with each contract duplicated many times over and stored on publicly distributed ledgers. Once that happens, data encryption is employed to ensure the full anonymity of the participants.
Features of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts have inherent characteristics that are unique to them, and that set them apart from conventional contracts. These characteristics are as follows:
Distributed. Smart contracts are replicated and distributed across all the nodes in a blockchain network
Deterministic. Smart contracts only execute the actions they were instructed to, provided the conditions are met. Also, the outcome is the same, no matter who executes it
Autonomous. Smart contracts self-execute themselves by automating all sorts of tasks
Immutable. Smart contracts are unchangeable after being executed. As such, we can say they’re tamper-proof
Customizable. Before they’re deployed, smart contracts can be coded to suit specific preferences and needs
Trustless. Thanks to their automated process, parties can transact via smart contracts without knowing or trusting each other
Transparent. Smart contracts take place on a publicly available ledger. So, anyone can verify the details of a transaction
Potential Applications of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts can be used to improve and streamline processes across a wide chain of industries. Here are some examples:
☑️ Elections
Since they are publicly verifiable, trackable, and irreversible, smart contracts would provide a fool-proof, secure system, allaying all concerns about elections rigging. Also, smart contracts would enable voters to vote online, allowing them to make their voice heard from whatever location they’re in.
☑️ Management
Today’s business operations are riddled with back-and-forth verification and approval processes that slow down productivity. A blockchain ledger acts as a single source of trust as well as streamlines communication and work processes thanks to its accuracy, transparency, and autonomy.
☑️ Automobile
By using smart contracts, it could be easier to determine whose fault it was in an accident – the sensor or the driver, in self-driving cars. Also, automobile insurers could know how to charge rates depending on where, and under which conditions customers were operating their vehicles.
☑️ Real Estate
Smart contracts would help real estate agents cut on advertising costs. Since the blockchain is publicly available, all you would need to do is pay with cryptocurrency and encode your contract on the ledger. On the ledger, your services are open for everyone can see, helping you cut on advertising costs and so on.
☑️ Healthcare
Smart contracts could improve the healthcare industry in so many ways. Firstly, personal health records could be encoded and stored on the blockchain with a private key available to only the relevant parties. Receipts of delivered services could be stored on the blockchain and sent to insurers as proof of delivery. Smart contracts would also make it inherently easier to perform general healthcare management tasks such as regulation compliance, result testing, and managing health care supply inventories.
☑️ Insurance
With smart contracts, it would be easier to fulfill insurance claims when certain conditions are met as per the client-company terms of agreement. Also, smart contracts would come in useful in times of disaster by allowing people to claim their money in a timely fashion. Details like the degree of damage or loss can be recorded on the blockchain and compensation decided upon accordingly.
☑️ Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT technology enables everyday devices to be connected to the internet in order to improve their usefulness to us. These devices could be connected to the blockchain to track all the products and processes in action.
And in e-commerce, Blockchain technology combined with IoT would enable the location and possession of products so that the right product gets delivered to the right person.
☑️ Mortgaging
Smart contracts would eliminate the need for middlemen and lengthy processing usually involved in mortgage agreements. Also, all details and information could be stored in a location where anyone can verify at all times.
☑️ Employment Contracts
Smart contracts could help reinforce employer-employee contracts. The terms, conditions, and expectations on either side would be made clear, helping to improve fairness. Moreover, smart contracts can be used to streamline salary processing and avoid delays. They can also be used to improve transparency by preventing companies from altering an employee’s contract once they’re hired.
☑️ Supply chains
The supply chain – the flow of goods from production to the final user is a central part of many industries, and it involves a lot of work verifying and tracking products. Smart contracts can remove the need for this as every detail is available on the blockchain, where everyone can track the location of commodities at any time. And if an item is lost in the process, smart contracts can be used to identify its exact location.
Besides, smart contracts bring transparency to the whole supply chain so that no party can default or breach the contract terms.
Blockchain platforms That Support Smart Contracts
The following blockchains are some of the most popular platforms facilitating the creation of smart contracts. Of course, Ethereum is the most recognized of them all because it was built almost solely as a smart contract platform. NEM, the blockchain supporting the cryptocurrency XEM, is also popular because it allows users to create smart contracts with Java, one of the most widely used programming languages in the world. These are the go-to blockchains for smart contracts in 2019:
Pros and cons of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts provide several benefits to users. From watertight security to saving on costs to accuracy, the following are the advantages of using smart contracts:
Pros of smart contracts:
 Autonomy
Autonomy
Smart contracts allow you to eliminate the need for third parties, e.g., lawyers, facilitators, guarantors, etc. – granting you full control of the agreement process.
 Time-efficient
Time-efficient
Smart contracts remove the need for intermediaries and the lengthy processes involved in traditional contracts. Everything is executed in a timely fashion, which avoids delays.
 Precision
Precision
The code that is the smart contract is written in a detailed manner outlining the obligations, rules, and penalties pertaining to the agreement. As such, the smart contract becomes a comprehensive agreement that accomplishes everything upon execution. This precision helps ensure there can be no room for miscommunication or misinterpretation. And in case of any error, it’s easy to track exactly where it occurred.
 Safety
Safety
Smart contracts are protected with high-level cryptography, which provides the highest safety standards. It’s extremely difficult to hack smart contracts – so users can be sure their documents are safe and secure.
 Efficient
Efficient
Owing to their accuracy, security, and time-saving qualities, smart contracts provide a high level of efficiency that helps the parties involved realize more value-generating transactions.
 Paperless
Paperless
Since smart contracts use computer codes, the use of paper is eradicated. This saves on stationery costs and also helps companies reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to environmental protection.
 Storage and Backup
Storage and Backup
Smart contracts are accurate to the tiniest of details. All the details of any transaction are stored on a public ledger, and any of the signees can access them at any time. And in case of any dispute regarding the terms of agreement, the parties can refer to the public ledger.
 Saves money
Saves money
As smart contracts only involve the signatories to the agreement, there’s no need for intermediaries and third parties like lawyers, witnesses, etc. Thus, the money that would have been used to pay these third parties is removed from the equation.
 Trust
Trust
The properties of transparency, autonomy, and security of smart contracts generate confidence in their execution. They eliminate any chance for manipulation, bias, or manual errors. Also, their undeniable nature significantly removes the need for litigations since every detail is clear on the blockchain.
 Speed
Speed
Smart contracts run on computer codes and exist on the internet. There is no need to process or verify documents manually or correct every little detail. As a result, they can complete transactions very fast.
Cons of Smart Contracts:
Smart contracts also have their own share of challenges. Most of these challenges arise from the fact that they are still an evolving technology. Some of the challenges are:
 They Are Vulnerable
They Are Vulnerable
Smart contracts are still a young technology. For example, the code that makes up the contract has to be perfect and bug-free. However, mistakes can still be made that would allow bugs into the network – which would be exploited by scammers.
 Government Regulation
Government Regulation
The novelty of smart contract technology leaves a lot of questions unanswered. How will governments regulate these contracts? How will they be taxed? What happens when the contract can’t get to the subject of agreement?
 Immutability
Immutability
The unchangeable nature of smart contracts can be advantageous in some situations, but not so much in others. For instance, hackers made away with millions of ether (ETH) after they hacked a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) in 2016. This was possible partly because developers were unable to fix the code. This is what eventually led a hard fork that gave rise to a second Ethereum chain – Ethereum Classic. Had it been possible to fix the code, this situation would have been mitigated.
 Uncertain Legal Status
Uncertain Legal Status
Smart contracts do not fit into the current legal framework in many countries. Most contracts today require parties to be at least a certain age and be properly identified. The anonymity and lack of intermediaries make those requirements a challenge.
 Limited Use
Limited Use
For now, smart contracts can only be used to agree on assets of digital value. This poses a challenge when it comes to transacting in real-life assets.
Examples of Real-life Uses of Smart Contracts
While most governments and the banking establishment have an ambivalent attitude to cryptocurrencies, the technology behind – blockchain, and smart contracts have had a more welcoming reception. Smart contracts are now being implemented across various industries. The following are examples of real-life applications of smart contracts:
Inmusik is a streaming platform that uses smart contracts to decentralize revenues and properly allocate revenues to the rightful contributors. Powered by blockchain technology, the company can facilitate fair and lucrative payouts for artists, collaborators, labels, and also incentivize music listeners by offering rewards to music listeners.
Ascribe is a digital platform that uses smart contracts to facilitate secure ownership of digital work by the rightful artists. The blockchain technology enabling this allows artists to track where their work is published on the web so that they can claim their rightful publication fee.
Tracr is a blockchain-based project that helps improve the diamond industry’s supply chain by monitoring the production and traceability of diamonds, reducing compliance costs, and improving visibility in the chain. It also helps to enhance privacy and security in regards to handling sensitive data in the chain.
Applicature is an agency that uses smart contracts to protect patients’ privacy, reduce healthcare transaction costs, and improve healthcare protocols. Patients have access to a secure and transparent record of their health information, and practitioners get rid of go-betweens and red tape in data conservation and compliance procedures.
The Future of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are still an evolving technology. Their future lies in detangling some of the issues that have held smart contracts from achieving mainstream acceptance. Some of these are the question of their legal status, regulation, and the ‘final’ nature of their transactions.
Still, blockchain enthusiasts see the technology making a significant impact on law, the merchant industry, credit, accounting, etc. It’s possible that we’ll begin seeing smart contract templates – which are legally enforceable smart contracts. We’ll also start seeing accountants utilize smart contracts for real-time auditing as well as the merging of smart contracts into a hybrid of paper and digital content where transactions are verified on the blockchain and corroborated by physical copy.
Conclusion
Smart contracts have the potential to change how we carry out daily transactions. They can help increase trust, save money, and revolutionize entire industries by introducing more transparency and facilitating accountability. For now, crypto and blockchain enthusiasts are keenly watching smart contract technology evolve further, and if after all, the technology will manage to transcend the current barriers to its full-scale adoption across different facets of businesses and society.











 IoT stands for the Internet of things. It is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital devices. These devices are provided with unique identifiers that can transfer data in the network without human-to-human or human-to-machine interaction. This is possible as the devices are extended with internet connectivity and sensors so that the transfer of data is possible.
IoT stands for the Internet of things. It is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital devices. These devices are provided with unique identifiers that can transfer data in the network without human-to-human or human-to-machine interaction. This is possible as the devices are extended with internet connectivity and sensors so that the transfer of data is possible. The concept of IoT enables smart homes. Most of the devices we use at home can be embedded with sensors, and with the help of IoT, we can control them remotely using our smartphones. When at home, they can easily be controlled using Alexa, Google Home, with the help of voice recognition. To enable all these functionalities, sensitive data such as voice and facial recognition should be stored. This data can be stored securely in the blockchain, which allows strict access restrictions. It can be accessed by anyone else if required only through individual permissions using smart contracts.
The concept of IoT enables smart homes. Most of the devices we use at home can be embedded with sensors, and with the help of IoT, we can control them remotely using our smartphones. When at home, they can easily be controlled using Alexa, Google Home, with the help of voice recognition. To enable all these functionalities, sensitive data such as voice and facial recognition should be stored. This data can be stored securely in the blockchain, which allows strict access restrictions. It can be accessed by anyone else if required only through individual permissions using smart contracts. IoT plays a very crucial role in health care these days. Remote health care can be achieved using IoT. Elderly care is essential to most of the countries these days as the elderly population is increasing in countries like China, Japan, and the US. Since there are fewer people to take care of the elderly, IoT can come to our rescue.
IoT plays a very crucial role in health care these days. Remote health care can be achieved using IoT. Elderly care is essential to most of the countries these days as the elderly population is increasing in countries like China, Japan, and the US. Since there are fewer people to take care of the elderly, IoT can come to our rescue. Agriculture can be widely improved by deploying IIOT (Industrial IOT) sensors and satellite imagery to monitor the millions of acres of land. With IoT used in the supply chain, provenance tracking can be enabled. Crops can be sold by using smart contracts even before harvesting them as all this data ensures the buyer of the quality of the product from the fields to their floor. This makes a profitable trade for all the parties involved.
Agriculture can be widely improved by deploying IIOT (Industrial IOT) sensors and satellite imagery to monitor the millions of acres of land. With IoT used in the supply chain, provenance tracking can be enabled. Crops can be sold by using smart contracts even before harvesting them as all this data ensures the buyer of the quality of the product from the fields to their floor. This makes a profitable trade for all the parties involved.
 One primary application of smart contracts lies in the healthcare industry. Transferring and sharing patients’ electronic medical records (EMR) should be done in the most secure way. We are not saying that the current technology is not secure at all. We are just saying that using this technology will enhance the existing security.
One primary application of smart contracts lies in the healthcare industry. Transferring and sharing patients’ electronic medical records (EMR) should be done in the most secure way. We are not saying that the current technology is not secure at all. We are just saying that using this technology will enhance the existing security. Banking systems have undergone a lot of changes proportional to technology adoption by the people. Smart contracts can play a crucial role in the mortgages provided by banks or any non-banking financial institutions. Banks spend a lot of money to check if the property that is being mortgaged currently is already mortgaged or not. To check if the property does indeed belong to the person applying for the mortgage or not. If the documents of the property are placed in blockchain with the help of smart contracts, this can be verified in a click. This saves a lot of money to both consumers and banking, reportedly in billions.
Banking systems have undergone a lot of changes proportional to technology adoption by the people. Smart contracts can play a crucial role in the mortgages provided by banks or any non-banking financial institutions. Banks spend a lot of money to check if the property that is being mortgaged currently is already mortgaged or not. To check if the property does indeed belong to the person applying for the mortgage or not. If the documents of the property are placed in blockchain with the help of smart contracts, this can be verified in a click. This saves a lot of money to both consumers and banking, reportedly in billions. These days we have to provide our KYC documents at various places like to open a bank account, to take a sim card, driving license, registering property to name some. If the KYC documents are stored in a blockchain, with the help of smart contracts, the right people can be given proper authority to access them. Also, if any changes required from our side, we need to make a change at one single repository instead of making changes at every entity where we have given the documents.
These days we have to provide our KYC documents at various places like to open a bank account, to take a sim card, driving license, registering property to name some. If the KYC documents are stored in a blockchain, with the help of smart contracts, the right people can be given proper authority to access them. Also, if any changes required from our side, we need to make a change at one single repository instead of making changes at every entity where we have given the documents. Supply Chain is one major area that can benefit hugely using blockchain adaptability and thereby using smart contracts. There are various documents throughout the supply chain cycle which can be misplaced and tough to authenticate at and every area required. If smart contracts are used to share and verify these documents, a lot of time and money can be saved to clear the goods at national highways, significant seaports, etc. Provenance tracking can also be done, thus increasing the bar of trust among consumers.
Supply Chain is one major area that can benefit hugely using blockchain adaptability and thereby using smart contracts. There are various documents throughout the supply chain cycle which can be misplaced and tough to authenticate at and every area required. If smart contracts are used to share and verify these documents, a lot of time and money can be saved to clear the goods at national highways, significant seaports, etc. Provenance tracking can also be done, thus increasing the bar of trust among consumers. Voting can be achieved relatively and transparently using blockchain and smart contracts. With blockchain involved, no one can tamper with the election process, and with the smart contracts, it is possible to ensure the correct person is voting instead of the duplicity of votes.
Voting can be achieved relatively and transparently using blockchain and smart contracts. With blockchain involved, no one can tamper with the election process, and with the smart contracts, it is possible to ensure the correct person is voting instead of the duplicity of votes. We all know it takes time for the insurance industries to clear the claims as it takes time to check the claims for its authenticity. With the adoption of smart contracts, the respective authorities can easily fact check the claims. For example, for travel insurance, we can easily verify whether the flight is a delay or canceled, thus passing the request.
We all know it takes time for the insurance industries to clear the claims as it takes time to check the claims for its authenticity. With the adoption of smart contracts, the respective authorities can easily fact check the claims. For example, for travel insurance, we can easily verify whether the flight is a delay or canceled, thus passing the request.