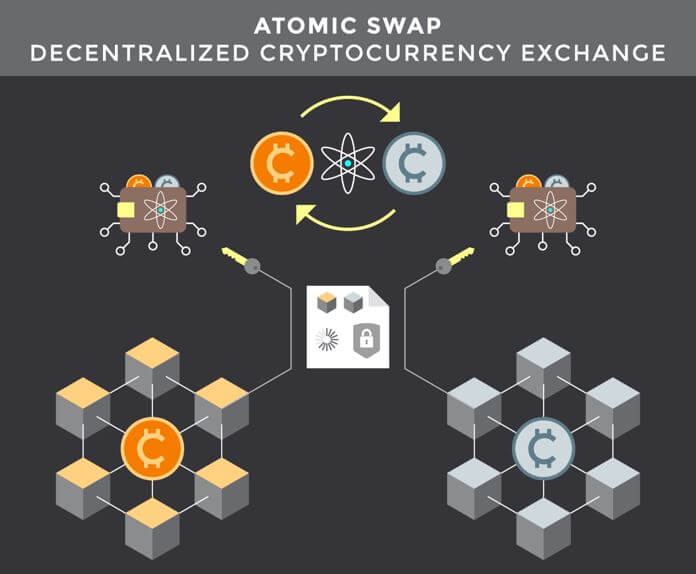
Introduction
One of the features of cryptocurrencies is that they are decentralized. However, in reality, it is not completely decentralized. For the buying and selling of cryptocurrencies, the most popular option is to use a centralized exchange. Hence, adding an element of centralization in them.
Though this seems to be the best way to exchange cryptocurrencies, there are other better ways as well. This is because centralized exchanges sometimes possess big problems. There have cases where new exchanges have been hacked, which has caused losses for exchange and their clients. Moreover, the common issue with all exchanges is high withdrawal and trade fees. So, trading cryptos turns out to be expensive for clients with small capital.
Thus, the irony here is that cryptos that are known to be a peer-to-peer payment system requires users to go to a third party to exchange the coins. However, crypto analysts have taken this concern as a priority and have been able to come with something called “Atomic Swap.”
What is an Atomic Swap?
Atomic swaps are a solution to the above-discussed problem. Atomic Swap is a peer-to-peer exchange of cryptocurrency without the involvement of a middleman. If you are wondering what “atomic” means, it is a terminology used in computer science, meaning something would either completely happen or completely not.
Understanding Atomic Swaps
The main goal is to send someone cryptocurrency without the involvement of a third party. Let’s understand how the atomic swap makes this possible, with an example.
Assume Ron wants to send 1 Ether in exchange for 0.02 Bitcoins from Lisa. In atomic swap terms, we say that Ron has 1 ETH and wants to swap with Lisa for 0.02 BTC.
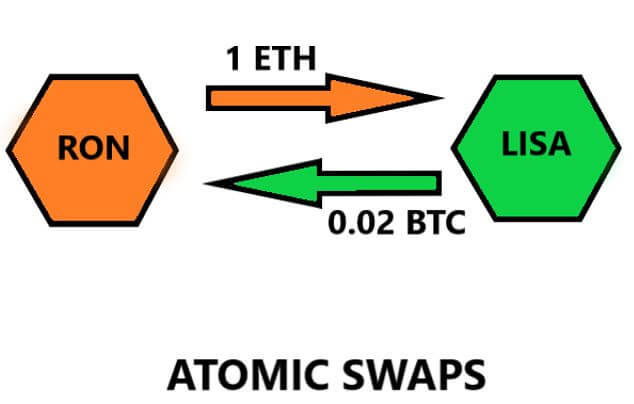
The key ingredient here is to create a smart contract called a hashlock. You may relate this to a container where the money is placed and is locked with a secret password.
How is the Hashlock made?
The hashlock, which is a smart contract that remains locked until the key is revealed, is made by Ron.
The hashlock is made using the following steps:
- A big random number is picked. It is called the primate. This is nothing but a secret password.
- This number is used to create another number called the A smart contract is created to send Lisa 1 ETH, locked with a hashlock created by him. This coin is accessible only when Lisa is able to figure out the preimage to the hash.
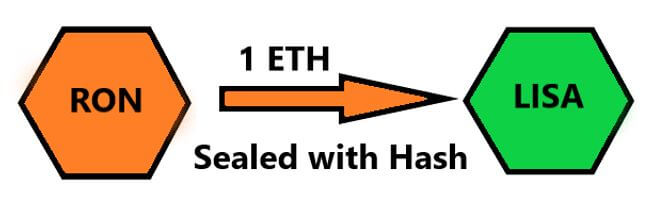
Note that calculating the hash from the preimage is easy, but determining the preimage from the hash is extremely challenging. In other words, Lisa cannot unlock the coins until she gets the preimage from Ron himself.
Role of Lisa
Now Lisa checks if she has received coins from Ron. This can be easily verified by checking on the public blockchain. After verification, Lisa creates a smart contract for 0.02 BTC with the same hash used by Ron.
Unlocking the coins
Now when Ron goes on to unlock the coins sent by Lisa, he uses the preimage he had created. But, in doing so, the preimage is recorded on the blockchain and becomes public information. Hence, Lisa can now use that preimage to unlock the coins sent by Ron.
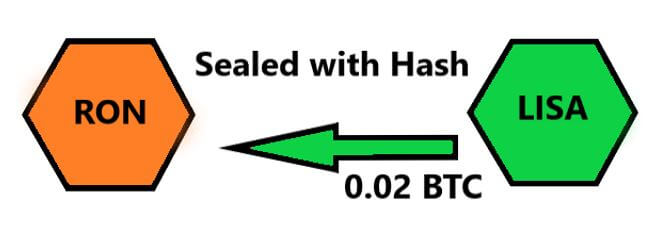
Therefore, this completes the transaction without the involvement of a middleman.
This is a solution to the problem that exists in crypto exchanges. Since most users are still into exchanges, the idea of atomic swaps must be inculcated into exchanges and make them truly decentralized.