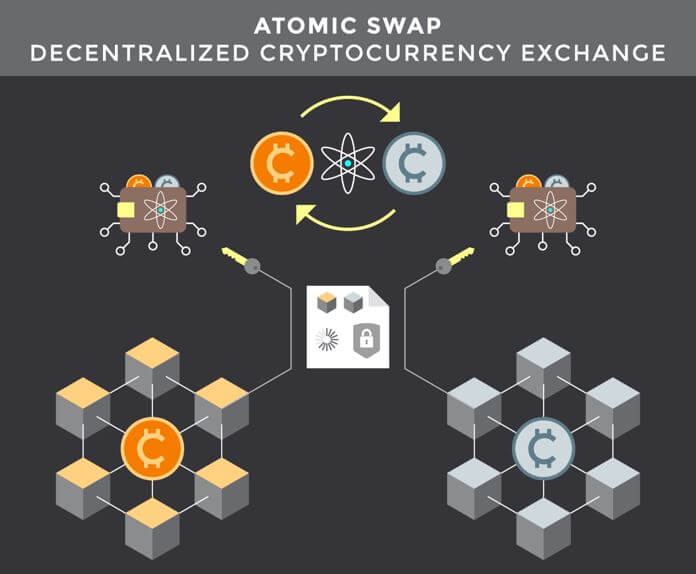
Cryptocurrencies were invented so that we could have deregulated, decentralized and peer-to-peer finance. What perhaps was not factored in was how we could trade one currency for another in the same kind of environment. Centralized exchanges – which are platforms through which individuals can trade one crypto to another, fill this gap. But these exchanges are not the most ideal crypto exchange platforms – because of issues that are inherent to them, and also because they do not live up to the tenets of cryptocurrency.
Enter atomic swaps – a technology that could be the solution to this problem. Atomic swaps is a technique that lets you trade crypto coins directly with other crypto holders. Also known as atomic cross-chain trading, this technology relies on smart contracts to automatically execute trades between two parties when both parties meet their end of the bargain.
Atomic swaps have the potential to revolutionize how we transfer crypto value.
History of Atomic Swaps
The concept of a trustless, decentralized, and peer-to-peer method of exchanging crypto was being floated since 2012 when cryptos were beginning to pick up and become a force in the trading arena. In July of that year, Sergio Demian Lerner created what was the first draft of such a protocol. The idea was a good one, but it was never really worked on.
There wasn’t a breakthrough until May 2013 when Tler Nolan created the first full account of how such a protocol can work – through atomic swaps. Though many other developers have come up with their own iterations of trustless and decentralized exchange protocols, Nolan is credited as the inventor of the technology.
The Problem with Centralized Crypto Exchanges
Centralized exchanges always have the possibility of getting hacked hanging over them. This is because cryptocurrency is a very appealing asset to fraudsters. (Isn’t it to all of us?) And these fraudsters are always devising new ways to get around security settings.
- Subject to Bad Management
Centralized exchanges are managed by people, and people are fallible. Simple mistakes or seemingly harmless loopholes could undo a centralized exchange – and with it investor funds – very fast.
- Inability to handle high demand
Centralized exchanges can simply not handle high volumes of demand, especially a sudden increase.
- Subject to Censorship and Regulation
Centralized exchanges are much like other businesses. Since they operate in jurisdictions, they are subject to the arbitrary whims of such jurisdictions. Cryptocurrency exists to avoid this very issue.
How Atomic Swaps Work
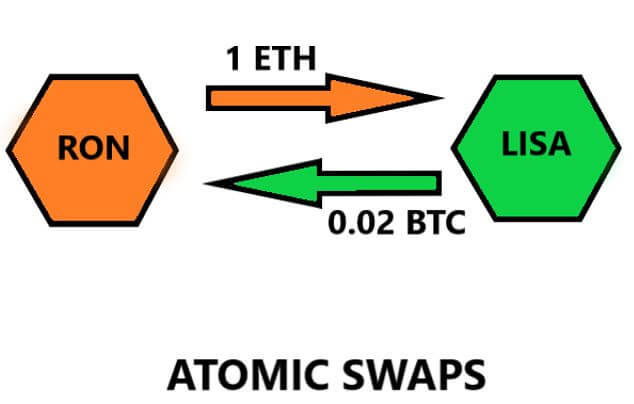
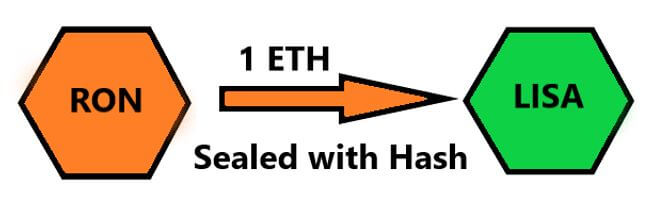
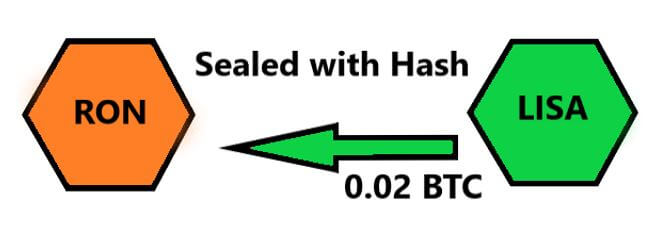
Atomic swaps work by letting the two transacting parties make a shared “secret.” The parties will swap the agreed cryptos if and only if their secrets are an exact match. This way, if a third party happens to barge in on the transaction, they have no way of meddling with the transaction since they don’t know the secret.
This whole process is executed by something known as Hashed Timelock Contracts (HTLCs).
HTLCs are a type of payment channels that ensure both parties to the transaction hold up their end of the bargain for the swap to be successful. A hashlock uses a cryptographic algorithm that allows either party to access the funds when and only when they have signed up their side of the transaction.
The timelock is a sort of insurance policy that will see to it that both parties get back their funds in the event the transaction has not gone through during a specified time frame.
The HTLC is made to create an environment where both parties rely on each other for the exchange to be successful. If, for whatever reason, the transaction is unsuccessful (e.g., network failure or one party not meeting their end of the deal), the timelock returns the funds to the rightful owners.
On-chain and Off-Chain Atomic Swaps
Atomic swaps can take place either on-chain or off-chain.
An on-chain atomic swap takes place on either currency’s blockchain. For an on-chain swap to be successful, both currencies must share the same hashing algorithm, and they both must also support HTLC. The first-ever on-chain swap was executed by Litecoin and Decred in September of 2017.
An off-chain swap takes place outside of the blockchain – in what is called a “layer 2.” Bitcoin and Litecoin were the first to conduct an off-chain swap in November of 2017.
Advantages of Atomic Swaps
- Atomic swaps will help users of different cryptocurrency networks interact with each other. This contributes to the interoperability of these networks.
- Atomic swaps facilitate “currency agnosticism” of the crypto ecosystem. This means the crypto market will be open to everyone rather than having a segmented market where people are holding to just one of a few coins. In other words, no matter which coin you use, you can transfer it to anyone, and anyone can do the same for you.
- Atomic swaps facilitate trustless, fee-less and peer-to-peer, uncensorable currency exchanges
- They remove the need for third-party intermediaries hence making the swap as direct as possible.
- Atomic swaps give users complete control over their money, instead of entrusting it to centralized exchanges that are prone to governance issues and corruption. Moreover, the issue of banned withdrawals, account deactivation, or wallet maintenance problems is gone.
- Direct wallet-wallet crypto trading is the epitome of decentralization finance. Centralized exchanges are prone to state regulation – which renders them centralized platforms.
- Atomic swaps are faster, period. The whole Know Your Customer procedures and other confirmation steps required by centralized exchanges slow down the trading process.
- In an atomic swap, the need for an intermediary token is removed. E.g., if you want to buy Decred and you have LTC, you may need to trade that LTC for BTC – which you’ll then trade for Decred. Atomic swaps remove this long process by allowing you to trade at a go.
- Trading at an exchange means you’ll be charged a lot of fees. And these exchanges set these fees and can increase them at will.
Limitations of Atomic Swaps
Atomic swaps look like the ideal way to swap cryptocurrencies among users, but unfortunately, we’re yet to reach the point where its adoption is a straightforward process. This is why:
i) Adoption
The current iteration of the technology needs the involved cryptocurrencies to meet three conditions:
Both must share a hash algorithm
Both cryptos must be able to initiate timelock contracts
Both cryptos must have certain programming functionalities
These prerequisite characteristics lock out so many cryptocurrencies, as well as companies and users, that can give the technology a try as of now.
ii) Speed
Atomic swaps have the ability to get swaps done in an instant – but right now, it still needs a ton of work before it can get to the point of handling large volumes of data.
iii) Lack of Compatibility
Right now, a lot of existing wallets do not support atomic swaps. This impedes the wide-scale adoption of the technology.
Final Thoughts
Atomic swaps will help solve the problems of interoperability and lack of scalability in the current crypto space. The technology also has the potential to expand the growth of the crypto industry, as well as open up new avenues for truly decentralized and peer-to-peer transactions – which is the way it’s supposed to be. We can only hope that the technology will be enhanced and refined to be better positioned for this worthy task.