If you’ve heard of cryptocurrency, you’ve probably also heard of private and public keys, or at least private and public address. You’ve also probably wondered about the concept behind them. This simple guide is all you need to understand the concept and secure your coins.
Private and public keys are important components of blockchain – the technology behind cryptocurrencies. To understand cryptocurrencies better and stay safe while interacting with them, it’s essential to know the meaning of private and public keys and their role in cryptocurrency.
Public and private keys are based on cryptography, which simply means the science and art of encrypting information so that third parties can’t understand it. In other words, cryptography enables data to be stored and communicated in a manner that unauthorized parties cannot understand. It’s employed today in private and public keys to make blockchain- and hence cryptocurrency, a safe environment for users.
Cryptography is mostly famous for being used in wartime, especially by Julius Caesar, the Roman military general who sent encrypted messages to his generals to ensure the enemy couldn’t understand them. Known today as Caesar’s cipher, his cryptography involved shifting each letter of a word three times to the left of the alphabet.
Today, encryption is all around us, even if we don’t realize it. From our phone apps to our phone screens to our credit cards – all these are encrypted to protect our personal information.
Symmetric Key Cryptography and Asymmetric Key Cryptography
Cryptography exists in two forms: asymmetric key cryptography and symmetric key cryptography.
In symmetric cryptography, the same key is used to both encrypt and decrypt the message. A good example is Julius Caesar’s encrypted messages. The same key, i.e., using three letters to the left of the alphabet, can be used to decrypt or decode the message. Another example is today’s door lock, in which the same key is used to lock and unlock the door.
The drawback to symmetric key cryptography is somebody can figure it out soon enough. Using the above examples, for instance, it’s easy for someone to steal a key to a door lock. And Julius Caesar’s opponents could figure out the cipher, eventually.
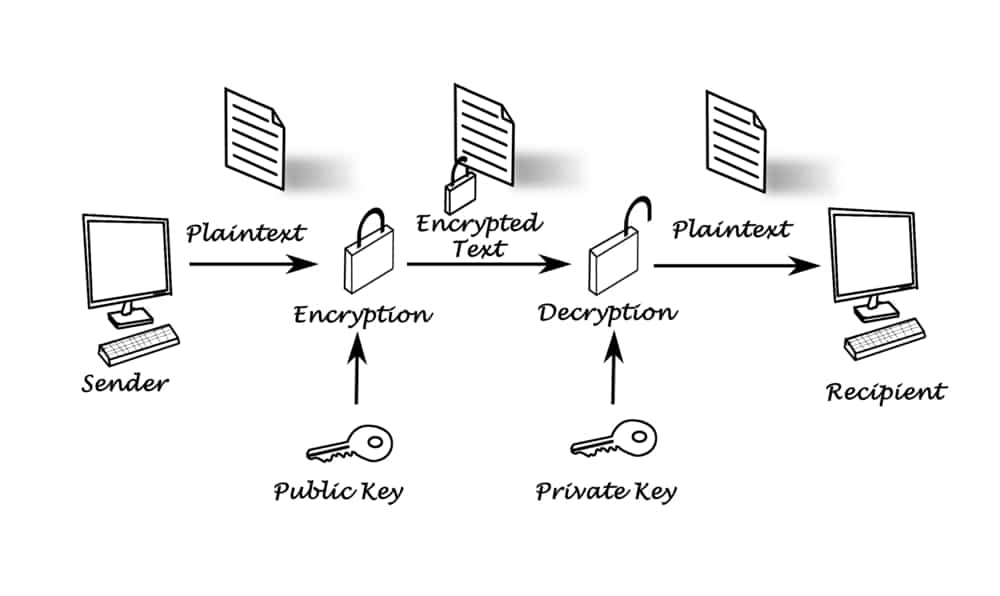
Asymmetric cryptography, on the other hand, is more complex. Two keys are used to decrypt information. In the case of blockchain, one key – the public key, is used to encrypt data and a second key – the private key, is used to decrypt it.
Asymmetric cryptography adds an extra layer of security to a transaction by securing both the item transacted and the recipient’s ability to access it.
Public Key Cryptography and Blockchain
The idea behind blockchain technology is to create a network where people can securely carry out transactions without the possibility for a third party or a central authority interfering. The security of the network, transactions, and parties involved is crucial to this process. In a traditional model, the third party, or the authority, usually provides the security – like the bank overseeing transactions, or protecting money in general.
But the blockchain model has no overseeing authority. So how will security be ensured? The answer is in public and private keys – which are based on cryptography.
Public and private keys are digital assets that, when combined, form a digital signature, allowing the secure sharing and unlocking of information or data.
What’s the Difference between Public and Private Key?

Since the blockchain model uses cryptography to facilitate transactions, and public cryptography uses both public and private keys, every user on a blockchain network has a public and private key.
Now, the keys are usually randomly generated alphanumeric sequences that are unique to every user.
A blockchain network, e.g., Bitcoin, usually generates a private key when a user creates a wallet. This key uses 256-bit encryption. This encryption makes use of really large numbers that unauthorized parties can’t guess or calculate. After the key is generated, it’s incredibly important that it’s kept private and secure. Nobody other than the owner is to see or have access to it.
The private key confirms a person’s identity when carrying out a transaction on the blockchain.
By contrast, the public key is exactly that – the key that an individual shares with the public, or in this case, the blockchain network. The public key is also generated by the blockchain network based on the private key. This means it’s only that private key in the world that can decrypt a message attached to that public key.
It helps to think of the public and private keys in real-world terms. Think of the public key as your bank account number – people who know it can send you money through it. The private key is like your pin code – it’s only known to you, and you use it to access the money in your bank account.
How Public and Private Keys Work
An individual’s private and public keys combine to create a digital signature that proves their ownership of funds and allows them access to those funds. To carry out a transaction on the blockchain, a person must use both keys together.
The following is an illustration of how public and private keys work. Person A wants to send, let’s say, Bitcoin to Person B. They can do this by obtaining Person B’s public key, and attaching the relevant information – in this case, the number of coins, to that public key, and then send it to Person B.
As the information is attached to person B’s public key, and it’s only their private key than can decrypt the information on their public key, Person A is sure that it’s only Person B who can see that information on the blockchain network. So, Person A will use Person B’s key to encrypt the information, because only Person B’s private key can decipher it.
Person B receives the information from Person A, and using their private key, creates a digital signature which will unlock the information and access it.
The role of a digital signature is central to this process. On the blockchain network, it serves these three purposes:
☑️ It proves that the owner of a private key has authorized a transaction
☑️ It proves that a transaction is undeniable – i.e., there’s no doubt that the owner and they alone authorized the transaction, and they cannot repudiate their involvement in it in future
☑️ It proves that the transaction has been authorized by that signature and has not been altered or modified by anyone after it was signed
How does Blockchain Use Cryptography?
The blockchain model uses cryptography in these ways:
Protects the identity of users – It enables every individual to keep their identity private, so they can securely transact on the network
Secures blocks –It allows people to execute transactions on the blockchain, which then adds blocks which no one can modify, sealing them permanently
Validate transactions – It enables individuals on the network to confirm transactions are indeed initiated by who they say they’ve been initiated by, and they can thus be added on the blockchain
Conclusion
It’s exciting to see how cryptography – the technology behind public and private keys, has evolved from being used during medieval wars to become the technology that enables people to transact on the futuristic blockchain world. And as blockchain technology continues to become accepted by other industries outside of finance, cryptography will continue to be central. It will be exciting to see how art and science will play a role in blockchain-based processes in the future.