The sole objective of the entire Keynesian economy is to generate inflation. That is what the Keynesian shamans call economic growth, inflation. People often don’t understand what inflation means or why it exists and that makes them fall for the generally false belief that inflation makes debts evaporate.
This is a crucial point where your incorrect analysis leads to a completely erroneous vision and predictions. I will try to clarify this fundamental error because although it is a rather abstruse and technical matter, it is essential to understand it because on this depends everything that is happening and everything that is going to happen.
The fundamental error comes from blind faith in the power of shamans: the shaman, in the fanciful world of Keynesians, can cause rain whenever he wishes and, therefore, whether it is raining or not, or whether it will rain tomorrow depends only on a certain correlation of political forces between a certain group of pro-rain shamans and another group of anti-rain shamans. If it doesn’t rain, it is because for now, the anti-rain shamans are resisting the pressures they are subjected to by those who want it to rain.
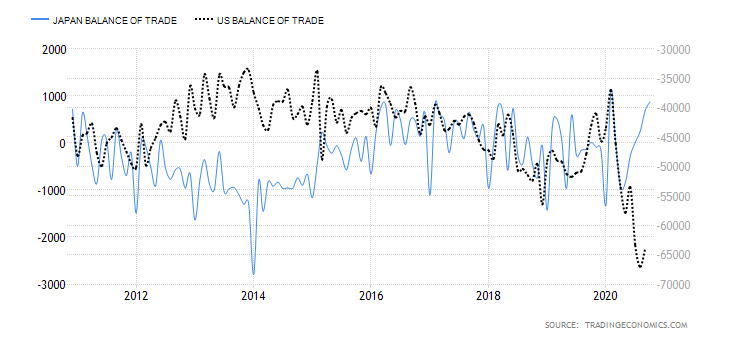
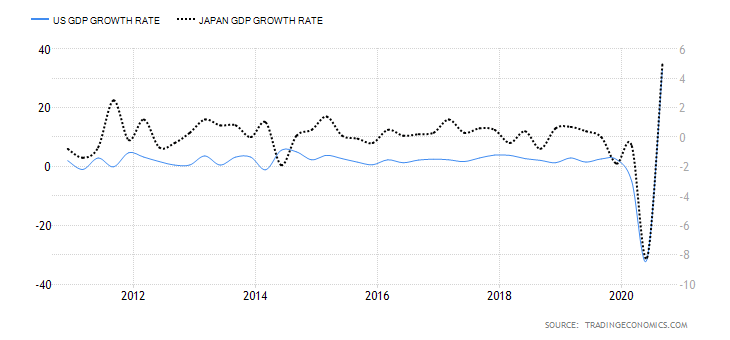
The fact that the yen’s monetary economy has been crushed for 20 years by powerful deflationary forces, incapable of generating any inflation, should, according to the Keynesians, in the face of the group of pro-inflationary shamans, supporters of pressing the red button labeled “INFLATION” There would be certain very powerful groups that have been opposing the push of that button. The problem with this explanation between mythology and gibberish is that these “powerful groups opposed to an inflationary monetary policy in Japan” do not exist.
The explanation is another: if there is no inflation it is because the laws of the economy do not allow it to exist. This button, which allows the Central Bank to trigger inflation “when it is convenient” (when it is convenient for the State), works until it ceases to function and it is precisely this “which stops the inflation button” that marks, as a symptom, the death of a Keynesian economy.
The Keynesian growth model that we have experienced for the past 40 years is an economic farce that simulates creating wealth when what it actually does is consuming (destroying) capital (“capital” in the economic sense). This suicidal escape, analogous to the scene of “more wood, that is war,” in which Marx scrapped the train to feed its wood to the boiler of the locomotive, ends when there is no longer capital that can be consumed. This is what you have to understand, to understand what is happening.
The fact that consumers, businesses, and states appear severely over-indebted is not important, it is only a symptom. The fact that nominal interest rates are capped at their decline with the “zero limits” preventing the big clown from generating negative real rates, is not important, it is just a symptom. The fact that the financial system is deliriously leveraged and severely broken is also only a symptom. The fact that rich countries roll out insane trade deficits with poor countries and rich economies depend on loans from poor countries, that national pension systems are bankrupt and unable to pay pensions, are also symptoms.
All these are just symptoms that the capital that had been progressively consumed has already disappeared. It must be understood that the golden age of wine and roses was not a time of genuine economic prosperity, based on the ability of society to create economic wealth, but was a mirage in which we seemed to be rich because, in an insane orgy of consumption, We were destroying the capital that previous generations took 200 years to accumulate.
It must be understood that large monetary bubbles do not appear by chance, as an accident, or as a social pathology consisting of an epidemic of speculative greed. Monetary bubbles are just an exaggerated version of what a Keynesian economy always does, and in the midst of panic, is to consume capital while generating inflation, money, and unpayable debt. A process based on consuming capital is inherently unsustainable and the more advanced the Keynesian pathology, the less real capital remains in the world and the more gigantic the states have become and their appetite to consume capital (The sole purpose of the Keynesian toy is to satisfy the insatiable appetite of the State and to guarantee its unlimited growth).
The succession of large-scale monetary bubbles, which condemn large sections of the population to be crushed by debt, always marks the agonizing end of the Keynesian experiments. They are a last flight forward and are characterized by the glamour and splendor of consumer orgies in which the last real savings available are destroyed. (See the “Happy 20s” that preceded the Great Depression)
Bubbles, and in a particular house or land bubbles, are just a terminal episode of a much broader disease called Keynesianism. When, for example, the leverage of Japanese banks soared, it was perfectly foreseeable that they would suffer a housing bubble and when the housing bubble materialized, it was perfectly foreseeable that their economy would collapse amid desperate and futile attempts to “beat the deflation.” The cliché “inflation ends up wiping out debts” is only true in the early stages of Keynesian disease, when “inflation” can take the form of a “wage-price spiral.”
Debtors, whether States, consumers or corporations, have a fixed-rate debt, which means that both the value of that debt and the value of the debt service are fixed in nominal terms. Also, the savings of savers is fixed nominally. A price-wage spiral is a change in the scale of the nominal value of the currency. As the value of the currency shrinks, debts and savings shrink to the same extent. Debtors see their debts evaporate because savers see their savings evaporate. It is a transfer of income from savers to debtors and is part of the general scheme of making the economy present some joy by consuming existing capital. (The real savings are transferred by the State to the debtors who consume it. Then the debts are erased and a new lot of savings can be transferred for consumption)
In the current situation, where wages are falling, and variable mortgage rates and prices are rising, it is obvious that “inflation” will not evaporate any debt. The one who made 1,000, paid a mortgage of 600 and bought a shopping basket for 400. If the mortgage rises to 700, the shopping basket to 450, and the salary is lowered to 900, this wage earner will not have the slightest feeling that “inflation” is helping him pay off his debts.
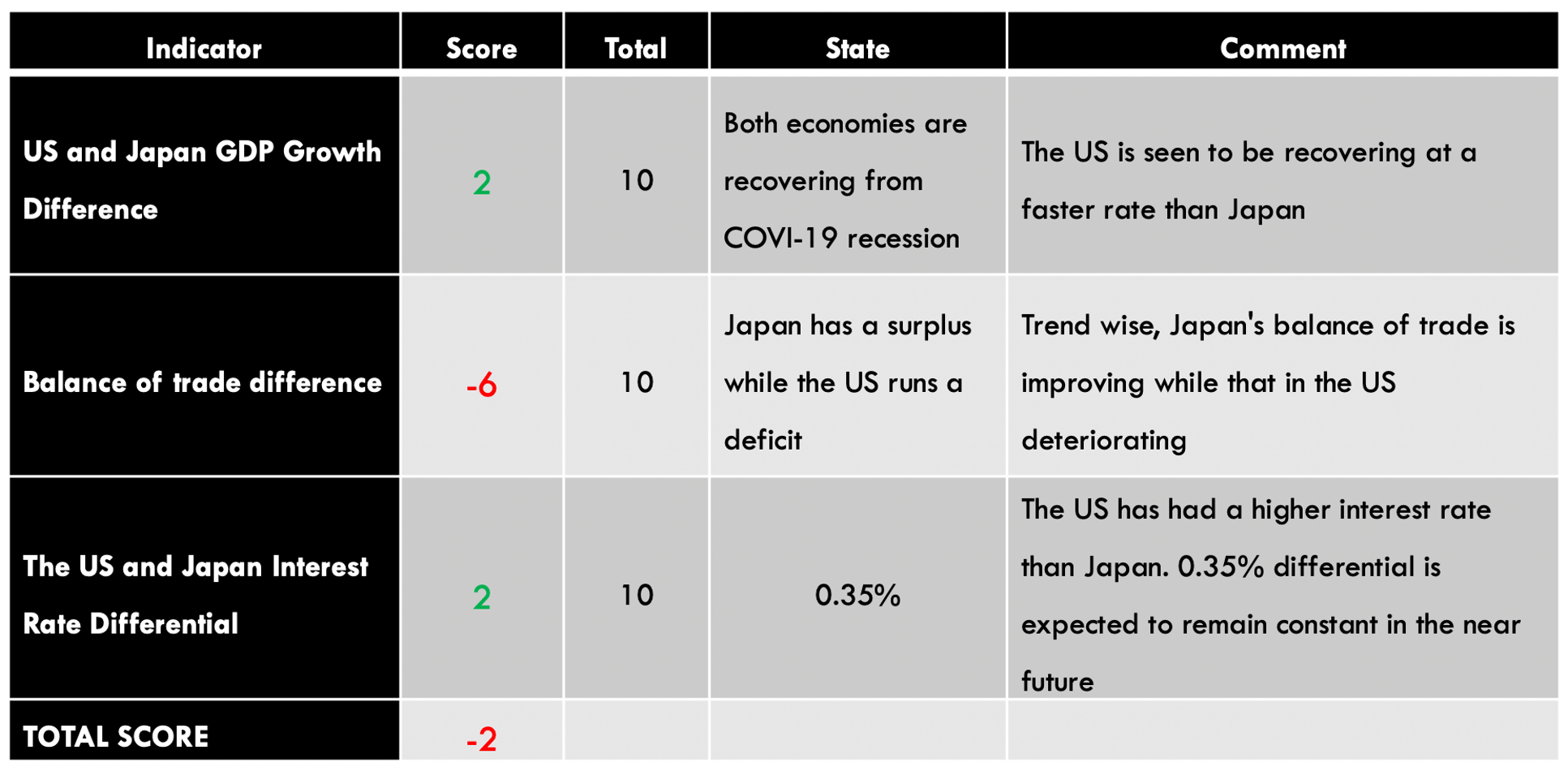
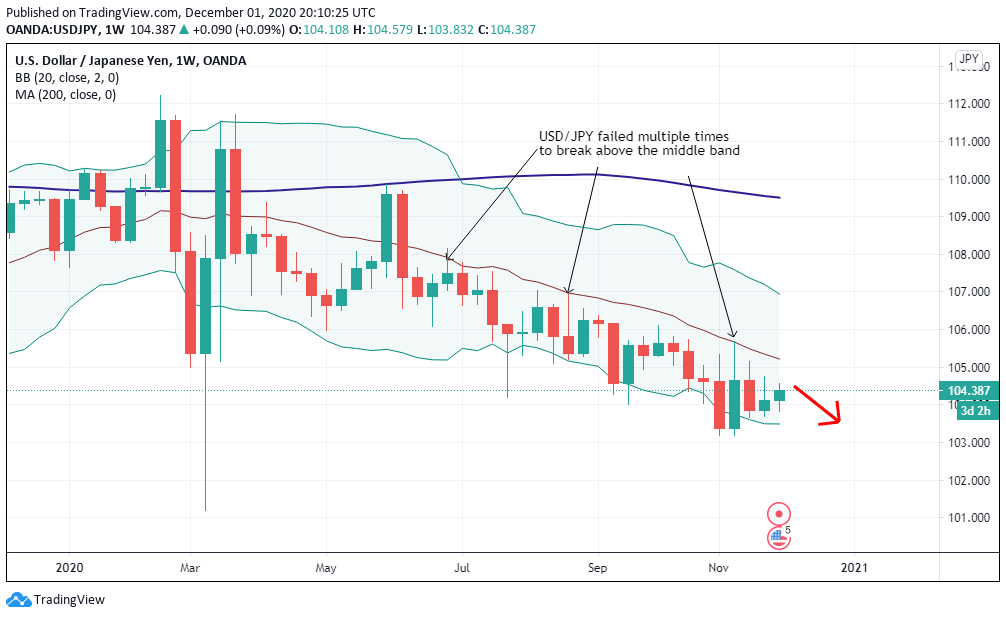
That these debtors have loans at variable and not fixed rates, that the installments of these mortgages are 60% of wages even when the rates are at 1.25% and that these loans have been granted by banks with leverage of x60, that they obtain a gross margin of 0.4% of those loans that they finance with the saving of some investors in fixed income willing to lend their saving for the 1.25% minus a differential of 0.35%, is not a set of misfortunes that have coincided accidentally. They are all features of the same phenomenon and express the terminal phase of a Keynesian economy based on capital consumption. The various “Band-Aids” that try to alleviate some of these superficial symptoms will not cure the disease because the cause is deeper: it is an explosive growing state that literally devours its subjects.