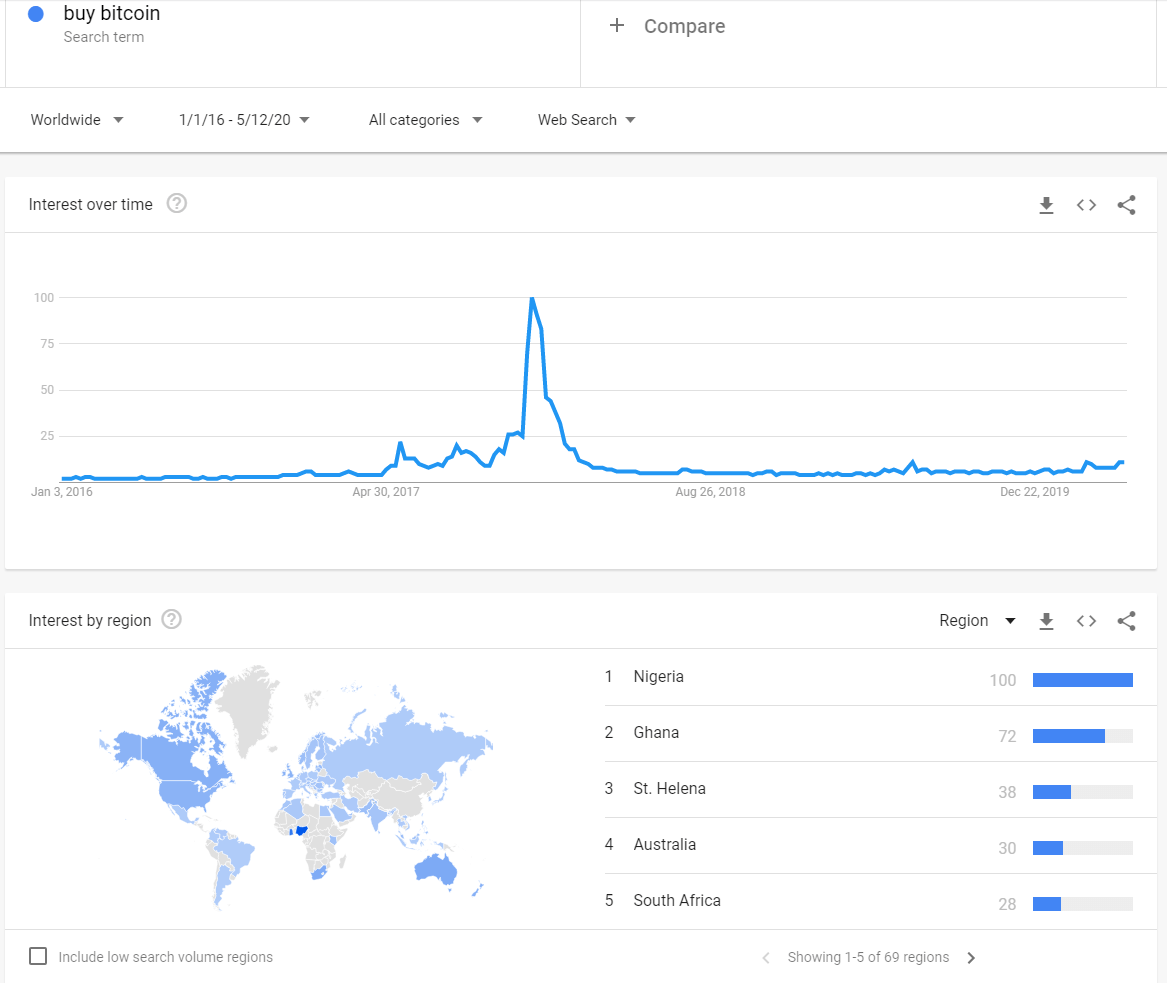
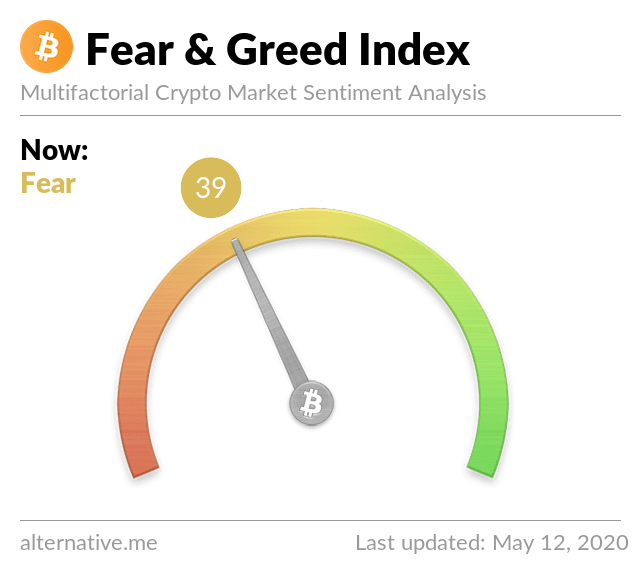
About eleven years since we had the first cryptocurrency, the asset class is more popular than ever. Millions of people are using cryptocurrencies as a store of value, as a trading instrument, and still, others are using the asset class as an exchange of value.
Unlike traditional money, cryptocurrency does not exist on a physical medium; neither is it regulated or overseen by a central authority. Transactions are peer-to-peer, control is solely the owner’s, and the safety of your crypto is in your hands.
There’s also another caveat. Crypto transactions are irreversible, meaning once you hit the send button, the funds are gone for good. There’s also the not-so-small matter of digital currencies being a high target for hacking and other types of fraud.
Hence, potential crypto users need to find a reliable wallet that’s secure enough to guard their digital assets against these attacks. Other features to look for in a sturdy wallet are flexibility and the number of cryptocurrencies it supports.
However, it can be a tasking exercise rummaging through the web to look for a wallet that fits these and other relevant needs.
In this piece, we came up with a list of the best wallets in the market for iPhone and iPad users. Looking for an iOS crypto wallet? Read on.
1. Bread Wallet
Launched in 2013, the Bread wallet is a crypto wallet app. The app is one of the most popular crypto wallets and one of the easiest to use. Bread features a minimalist yet functional interface that allows you to send and receive crypto without much hassle.
You can purchase Bitcoin via the app using a variety of methods, including credit card, in-person at Bitcoin ATMs, or at the convenience store. Bread also allows you to convert Bitcoin into cash, Ethereum, or to any of multiple ERC-20 tokens.
Bread also runs a loyalty program called BRD rewards. When you hold tokens at BRD, you get a 50% waiver on all your in-app crypto trading fees.
2. Green Wallet
Launched in 2019, Green is a wallet that puts security at the forefront so that you don’t have to choose between security and convenience.
When setting up a Green wallet, you will be required to undergo a two-factor authentication process via SMS or Google Authenticator, and/or email. A two-step authentication process is also required for every transaction you carry out.
The wallet also does not store your private keys, encrypted or not. This gives you utter control over your crypto funds. Green also ensures complete anonymity for users by allowing them to sign up without KYC procedures and proceed to trade right away.
3. Coinomi
Coinomi is a crypto wallet that lets you safely store, manage, and interact with Bitcoin and other 1770+ crypto assets. Funds are secured with private keys and state-of-the-art cryptography, ensuring your crypto is always under water-tight security.
Coinomi also ensures user anonymity by not having KYC or due diligence procedures or transaction tracking. Also, it doesn’t link your identity to transactions or traces your IP address.
For those users willing to fork out a bit more cash, Coinomi offers more options such as multi-seed support, unspent transaction output (UXTO) control, and cold storage.
4. Jazz Liberty
Jazz Liberty allows you to send and receive Bitcoin, Ethereum, and 90 other cryptocurrencies. On Jazz, you can check your crypto balance anytime as well as track individual coins and their price changes over the last month up to the latest hour. This also includes updates on the performance of the top 100 coins and markets and market trends. You also get access to the latest crypto news and updates from the app’s news module.
Jazz also provides a 12-word mnemonic phrase that you can use to recover your private key, so you never lose your funds. The phrase also allows you to access your funds anywhere in the world, ensuring utter convenience.
5. Abra Wallet
Launched in 2014, Abra prides itself of simplicity, instant investment, and accessibility – with support available in more than 150 countries.
Abra allows you to buy, sell and exchange over 100 cryptocurrencies, including big hitters such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Bitcoin Cash, Bitcoin SV, as well as other less known ones like Aeon, Ardor, BURSTcoin, and Blackcoin. To get started, simply deposit crypto or Fiat via MasterCard, Visa, or bank transfer.
Abra users can also move between various coins and tokens as well as withdraw to an external wallet at any time.
6. DropBit
DropBit allows you to “send and receive Bitcoin as easy as sending a text or tweet.” It calls itself the “Venmo for Bitcoin” – allowing you to send Bitcoin to friends via text message or Twitter, even if they don’t have DropBit or any crypto wallet at the moment.
DropBit also allows you to maintain anonymity in your transactions by ensuring server requests for sending addresses are signed by your wallet at a ‘derivative path’ unassociated with your Bitcoin address. DropBit also does not keep your contact(s) on their servers. Instead, it uses a cryptographic hash of your phone number when verifying transactions. And in case you lose your wallet, you just need to input your 12-word recovery phrase to recover your private key.
7. TrustWallet
Trust wallet is a multi-coin wallet that allows you to store Bitcoin, Ethereum, Tron, Binance Coin, XRP, and so on. You can instantly trade cryptocurrencies on Trust wallet, thanks to its seamless integration with both Binance Dex and the Kyber Network protocol.
Trust wallet also protects your privacy by keeping your private key only locally and surrounded by many layers of security.
The wallet also supports ERC20 tokens and BEP2 tokens for the Binance Chain. It also allows you to interact with decentralized applications (DApps) on its Web3 browser.
8. Edge Wallet
Formerly known as Airbitz, the Edge wallet allows you to store, trade, and buy dozens of cryptocurrencies. This includes the ability to swap one crypto for another, as well as buy crypto with Fiat.
Edge has also partnered with some of the top blockchain services around the world, e.g., Moonpay, Bitrefill, Wyre, and Safello, to enable you to purchase mobile top-ups, gift-cards, and other services.
Other notable features of Edge include a seed phrase backup feature, PIN code feature for added security, QR code support to allow you to spend funds, an estimation of transaction fees so you can account for every coin, the ability to add ERC-20 tokens and Segwit support for Bitcoin and Litecoin.
9. Copay
Copay wallet is an off-shoot of BitPay, a trusted crypto payment gateway for 10,000+ merchants and businesses around the world. It’s a non-custodial wallet app that’s easy to use, with support for Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash.
Copay facilitates multi-signature use, allowing more than one user to use the wallet. You can also create multiple private keys in the same Copay wallet, e.g., one for you and another for your friend.
Other unique selling points of Copay include: 150+ Fiat currency denominations for conversion, multiple language support, email and push notifications, and QR code support.
10. Ledger Nano X
This is a wallet by industry favorite Ledger. Nano X features remarkable ease-of-use and flexibility while ensuring your crypto is protected with the highest level of security, with your private key tucked away in a certified secure chip. Ledger Nano is a hardware wallet and, thus, a cold storage wallet – the safest option for storing your crypto funds.
The wallet is Bluetooth enabled, which allows smartphone users to sync the device with the Ledger Live Mobile app to safely interact with your crypto from your smartphone.
11. Blockchain Wallet
Blockchain wallet is one of the most popular crypto wallets, available in 140+ countries, and featuring 25 languages. It currently supports Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, Stellar, and USD Digital (USD-D).
Blockchain wallet supports two-factor authentication for maximum security as well as a 12-word recovery phrase that allows you to access your funds even if you lose your wallet.
12. BitPay
BitPay is another wallet app under the purview of crypto-exchange BitPay. The wallet’s apparent simplicity and accessibility, along with its high-level security involving multisig and key encryption, have made it a favorite among crypto users.
BitPay currently supports Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, Ethereum, and other tokens. You can create multiple wallets on the wallet, meaning you can share your wallet with family or friends.
You also get to receive instant email and push notifications for any transaction, helping you stay in control of your funds at all times.
Final Words
When looking for a good crypto wallet, you’re looking for one that does more than hold your funds. You want security, privacy, options, and a good user experience. These wallets offer that, and more. As usual, before settling for any wallet, Do Your Own Research; look for user reviews, check its security history, and so on. As well, choose a wallet that suits your personality.