Solving the Bitcoin scalability problem is no easy task. This problem has taken a long time of research and development, but the solution could already be among us. Its name is Lightning Network and could lead Bitcoin to the apex of scalability to deal with the massification of cryptocurrencies.
The Lightning Network protocol is a protocol designed to improve the scalability of Bitcoin. This is possible because Lightning Network works as a second layer on Bitcoin. One that allows this cryptocurrency to perform things that it normally could not and more specifically; instant transactions with very low commissions. The development and creation of this protocol began with the work of Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja. But at present, it is companies such as Blockstream, Lightning Labs, and ACINQ that drive the development of it. The whitepaper of this development can be found at that link on their main website.
To understand a little of the potential of this technology, we need to keep two things in mind. The first is that Bitcoin was created as a digital money solution. Second, that goal is impossible to achieve in the current state of the Bitcoin network and software. The reason for this is very simple: Bitcoin has trouble scaling.
Currently, Bitcoin can only process 7 to 8 transactions per second. This is a very small capacity and it cannot cope with the massive use of cryptocurrency. As a result, the Bitcoin network becomes slow and very expensive when it comes to paying commissions. For this reason, a new way of performing transactions quickly was needed, which was simple to use and compatible with Bitcoin without making major modifications. The answer to these needs and more is Lightning Network, a protocol from which we will learn a little more below.
Why is needed to improve the scalability of Bitcoin?
Surely you are asking yourself this very question and it is your right. You will think that if Bitcoin has such a powerful and extensive network then why it should improve its scalability. The short answer is; because by improving scalability, transactions are done faster and less expensive.
To explain the answer at length let’s do this little exercise. Imagine you do a transaction in Bitcoin. At that time the Bitcoin network has very little use and the commission cost of each transaction is very small.
However, the cost of fees may increase as network usage increases. This is because a queue or excess of transactions is generated in the mempool. It is there that miners tend to prioritize transactions with higher commission payments for more profits. That way, if you want a transaction to be processed quickly, then you will have to pay more in commissions.
But the latter case also tells us that commission costs will increase to the point where we will not be able to make micro-payments. For example, sending 1 dollar may result in more than 1 dollar for the cost of the commission. This is a meaningless situation and one that scalability improvement can solve, hence the need to improve this feature.
How Lightning Network works
The operation of the Lightning Network depends on several technical factors and a process to make it safe to use. First, Lightning Network depends on the non-malleability of the cryptocurrency being secured. In this way, it would be impossible for a third party to change the information about the transactions or cryptocurrencies during the verification or generation process.
In Bitcoin and Litecoin the non-malleability property of the transactions was introduced thanks to the arrival of SegWit (Segregated Witness). With this soft fork, Bitcoin solved this problem and put the first building blocks for a new way to scale its capabilities.
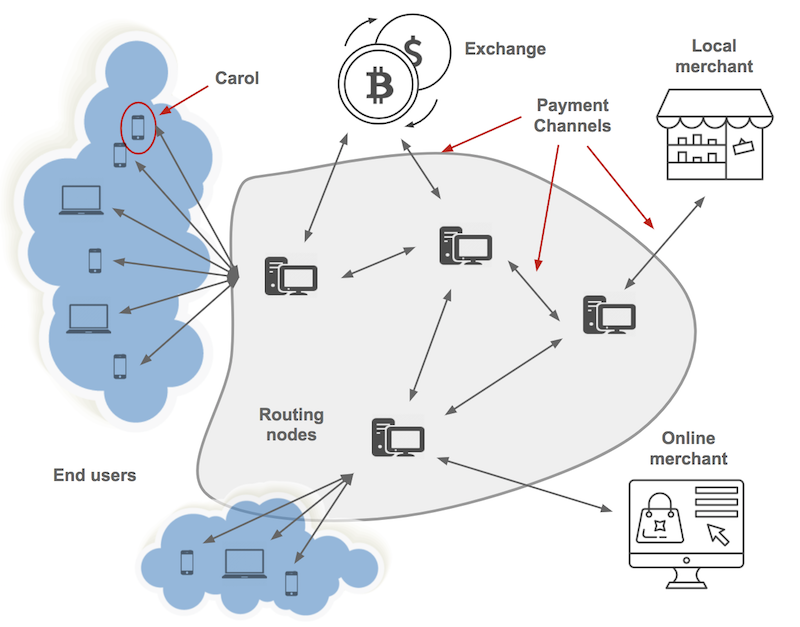
That’s how the development of Lightning Network and its so-called pay channels began. These payment channels are the cornerstone of Lightning Network operation and the key to enabling unprecedented scalability in Bitcoin.
What are paid channels?
Payment channels are the basis of the Lightning Network. A payment channel is actually a multi-signature transaction in the blockchain with at least one of them sending funds. In this channel, each person has a private key and each future transaction can be made only if the keys of the two parties sign. This is a means of consensus that the compromise has been approved to be executed by both parties.
In addition, payment channels may be open for a certain period of time. Normally this is about 10 minutes or what it takes to mine the next block on the blockchain. But once the channel is opened, channel participants can instantly exchange assets between themselves using the funds stored in that channel. In a nutshell, this means that parties that are part of a Lightning Network payment channel can make payments to each other instantly.
Despite this behavior, the transactions made in said payment channel are completely valid in the blockchain. This is because once the channel is closed, the transactions made are transmitted to the network, verified, and included in a Bitcoin block.
Explaining how Lightning Network works
To understand how Lightning Network works, it’s best to break down your entire operating process step by step. For that reason, we will explain to you a simple exercise on how to perform this process along with other points of interest to clear all your doubts.
First, within Lightning, we will have two participants who will create an initial transaction in the $20 blockchain. Of that $20, $10 will be from Carmen and $10 from Aitor. This deal could be different and can vary within the channel we mentioned earlier, so Carmen could have $15 and Aitor $5 at the end of all exchanges.
What Lightning does is take the technology behind the paid channels and create a network that shapes them using smart contracts to make sure the network can run on a decentralized basis.
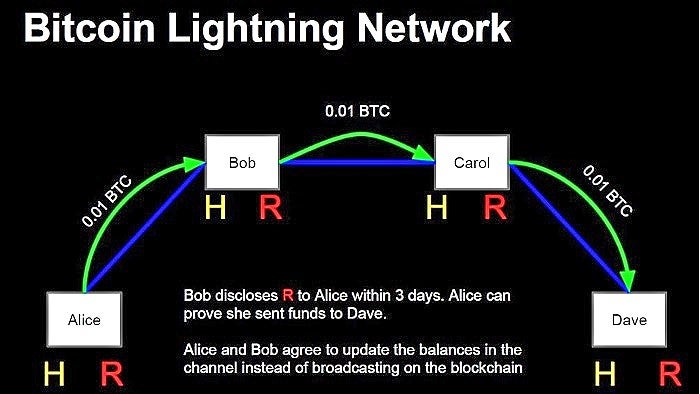
In this regard, we would have the following breakdown of the process:
- Carmen opens a pay channel with Aitor that in turn has a channel with Laura, which in turn has an open channel with David.
- Right now we have 4 parties participating in different payment channels or payment channels.
- Carmen wants to exchange assets with David, so she can send funds through Aitor and Laura to ultimately reach David, the recipient.
Due to the nature of the Lightning Network, Carmen would not have to rely on Aitor and Laura within the process as cryptography is used to ensure that the funds David will receive will be exactly the same as Carmen has sent. Otherwise, they’ll be automatically returned to Carmen.


