The future of online storage is decentralized. With idle space on your hard drive, and with a reliable internet connection, you can store files for someone from the other end of the world and get paid for it. This is possible because of blockchain, the tech that was brought to life by Satoshi Nakamoto, and one that powers thousands of cryptocurrencies.
With blockchain, it’s now possible to create a decentralized, peer-to-peer, and cryptographically secured storage platform that incentivizes users with crypto.
Storj, a product of Storj Labs, is one such project. And it has received a stamp of approval from Ethereum’s Vitalik Buterin, who has praised the project, saying, “Distributed file storage systems like Storj have the potential to eliminate high mark up costs and market inefficiencies and provide a much higher level of privacy reliability and quality of service than we see today.”
What is Storj all About?
Storj is a decentralized and peer-to-peer, file storage that uses encrypted shards and blockchain-powered hash tables to secure and store files. Storj aims to make cloud file storage more accessible and secure.
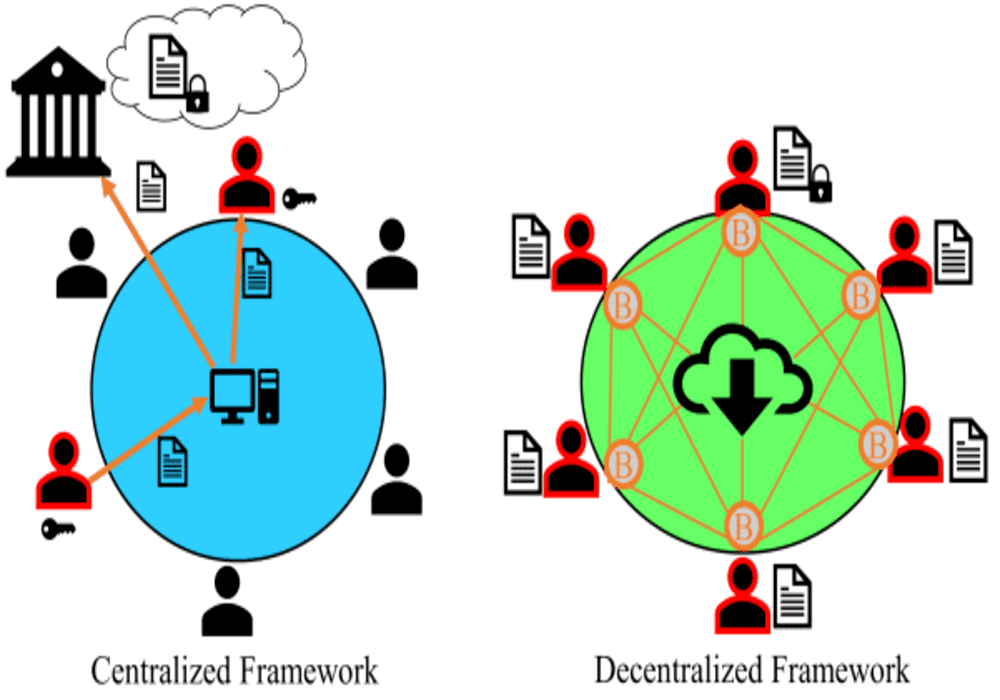
Current file storage solutions such as Dropbox, Google Drive, and so on have limitations. Events such as internet connectivity outages mean that you cannot access your files. Also, the service is centralized, meaning the companies have access and control over your data.
Storj proposes to solve these problems via a blockchain-based, peer-to-peer, private, and distributed file storage solution.
Storj and Torrents
Before we dive into Storj, we need to do a refresher on torrents. At the start of the last decade, torrents became the go-to way for internet users to download content – from movies to TV shows to videos. Torrents operate on a peer-to-peer fashion, as detailed below:
- Many users store copies of a particular file in the peer-to-peer network
- When you want a copy of the file, you send a request to the network
- Users who have a copy of the file (these users are known as seeds) send you fragments of the file
- You (the requester) receives many fragments from many different copyholders, and the torrent software rearranges the fragments to form a complete file
The advantage of using a torrent to download content is you can receive fragments of the file from multiple sources simultaneously. This means you get the file quicker than you would if you were downloading the whole thing at once from just one source.
Now, these torrents were (and still are) an illegal way to acquire content. But since they are operating on a decentralized model, no one can shut them down.
Storj works the same way, except not in an illegal way, or for pirated videos. With that, let’s look at how Storj works.
Functionalities of Storj
#1. File Sharding
Storj’s shard-based storage is much like the fragments of torrents. When a user wants to store a file on Storj, they first divide it into many smaller chunks (sharding). The benefit of this is when you want to download the file, you can do it in parallel, which makes the process quicker. Also, it’s only you who knows where the pieces are located, meaning it’s a completely private affair with you in total control.
The location of shards is one of the major differentiators between Storj and torrents. With torrents, anyone can access the shards. On the other hand, Storj, as a cloud storage service provider, prioritizes user privacy. And it does this by utilizing blockchain and cryptography.
To achieve utter privacy, Storj implements a distributed hash table (DHT) through which a user locates all the shards of the original file. To access the shards, you need a private key. Without the key, it’s next to impossible to track down the locations of the various shards. Storj’s hash table is known as Kademlia, and it’s one of the network’s core technologies.
#2. Parity Shards and Erasure Coding
On Storj, shards are distributed across computers all over the network. But what would happen if one of the computers went down or stopped running the network? What would happen to the shards on that particular computer?
Such a scenario necessitates that Storj implements some sort of redundancy. (In computer science, redundancy is the duplication of components so that there will be a backup in case of system failure). Storj achieves redundancy via ‘parity shards.’ When a user uploads a file, they can choose how much redundancy they want for the file. With enough parity shards, you can significantly reduce the chances of losing pieces of your data.
However, with time, the likelihood of losing shards increases. To counter this, Storj performs regular audits. But as a user of the platform, the best practice would be periodically recalling and then reuploading your files.
At the same time, too much redundancy would slow down the network. Storj combats this by implementing coding rules that reduce redundancy by erasing shards that have been overly duplicated. Through this process, Storj also identifies data whose redundancy should be increased.
#3. End-to-end encryption
Apart from sharding, Storj ensures high-level privacy by implementing end-to-end encryption. Sharding already ensures that no one, not even data hosts (called farmers), can access the whole file. But this is not enough since even for one to be able to access and read a shard would be problematic.
To prevent this, Storj facilitates data owners (known as tenants) to encrypt their files before sharding. The encrypted file has only one key that you keep on your computer (or in the bridge – more of that in a moment).
As the only owner of a private key, you’re the only person who can read the file. Therefore, farmers store not just encrypted files, but ones that are a part of a whole original file. This makes your data secure since the data kept by a farmer is useless as just a shard – and an encrypted one at that – that’s part of a larger file.
For an entity to hack the Storj network and locate a file, they would first need to find all the shards that make the whole of the file. This is next to impossible without the private key. Again, they would need to convince farmers to send them the shards. And lastly, they would need to access the encryption key (either by guessing (impossible) or stealing). As you can see, for one to access data stored on Storj, they’d need to jump through so many hoops, but even those wouldn’t get them very far.
#4. File Verification
Anyone entrusting their data with Storj would naturally ask themselves the following questions from time to time: “How can I know my files are still there?” “What if a farmer has deleted them or turned their computer off?”
Storj deals with this concern by carrying out hourly audits, together with other verification processes. For farmers to receive their payments, they must first provide proof of having the shards they’ve been assigned. For this to happen, farmers receive a request from Storj. If they have changed or deleted the shard, it will not be possible for them to respond to the request. But if they currently have the file, they are able to respond to the request correctly.
They will then receive a reward for storing and maintaining the file. As you can see, farmers have an incentive to store and protect files accurately.
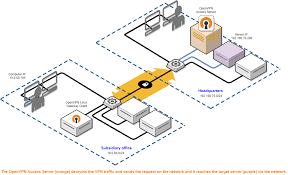
#5. Bridge
Bridge is the name of the server or protocol that allows you to access your encryption keys across a range of multiple devices. Initially, tenants could only store their keys locally on their computer. However, this was limiting because it meant you could not switch devices.
Bridge decentralizes your access – all you need to do is to verify your identity and access your files from any device.
Storj’s Token (STORJ)
STORJ is the Storj network’s native token. It acts as a means of payment on the network. Tenants pay fees for having their files stored on the network, while farmers are compensated for sharing their storage space and bandwidth.
The token runs on top of Ethereum’s blockchain, and it uses a proof-of-work consensus mechanism. Storj has a maximum supply of 500 million.
What’s the Market Look Like for STORJ?
As of June 11, 2020, STORJ’s price was $0.160915, and it ranked at #158, with a market cap of $26, 082, 246, the 24-hour volume of $114, 759, 728, a circulating supply of 162, 086, 753, and a total supply of 424, 999, 998. The token’s all-time high was $3.13 (Jan 09, 2018), while its all-time low was $0.048353 (March 13, 2020).
Where to Buy and Store STORJ
Currently, you can buy STORJ tokens from any of these exchanges: Binance, Coindirect, eToro, and Poloniex.
As an ERC20-compliant token, STORJ can be stored at any Ethereum-compatible wallet. Popular choices include MyEtherWallet, MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Atomic Wallet, Trezor, and Ledger Nano.
Who’s on the Storj Team?
Storj is the brainchild of Shawn Wilkinson, who’s also the CEO of Storj Labs, the company behind the project. The rest of the team includes professionals in software engineering, business, marketing, graphic design, and more.
Final Words
Storj provides a compelling product: decentralized, peer-to-peer, and cloud-based storage with two formidable layers of security. Its working model is robust, yet simple, file owners upload their content, and farmers secure them with their extra storage space and bandwidth resources. If Storj catches on, it could very well give traditional online storage services a run for their money.