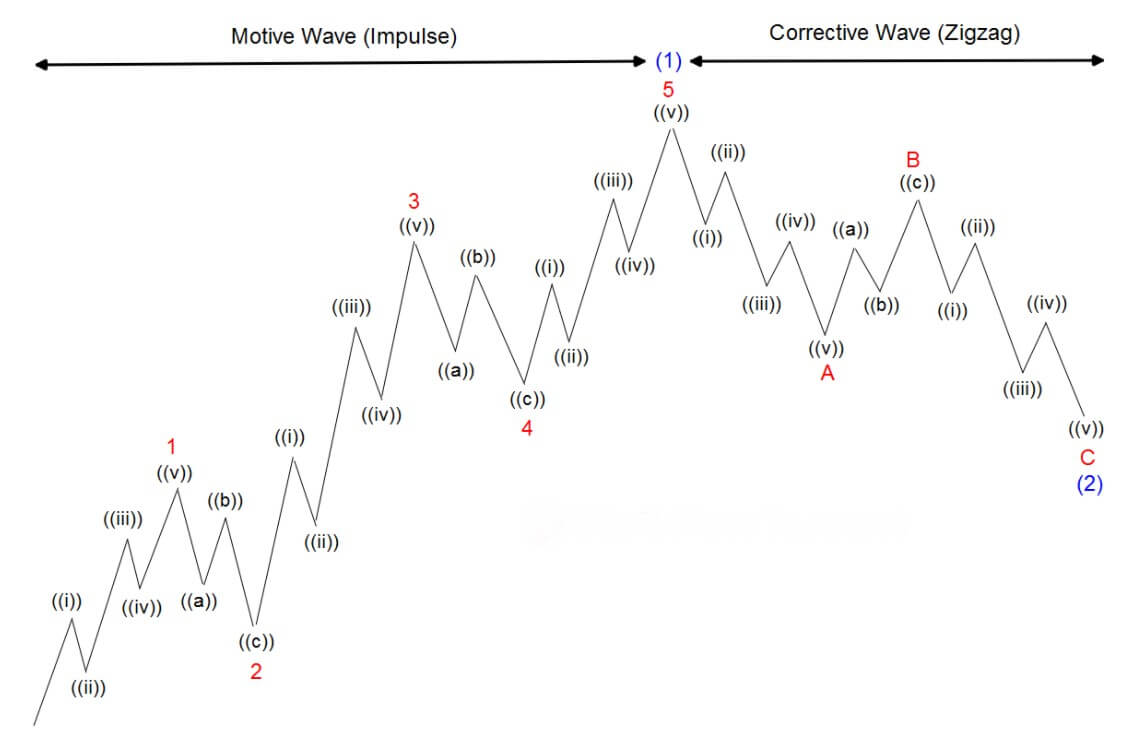
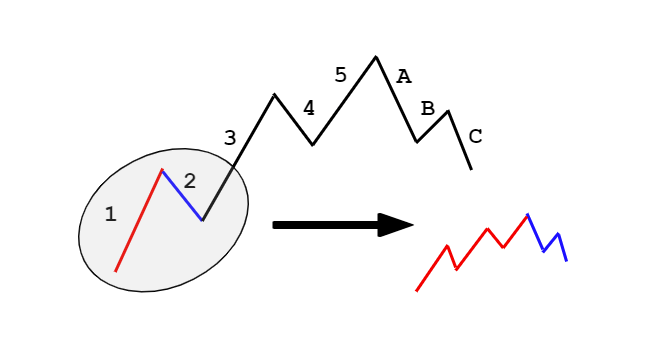
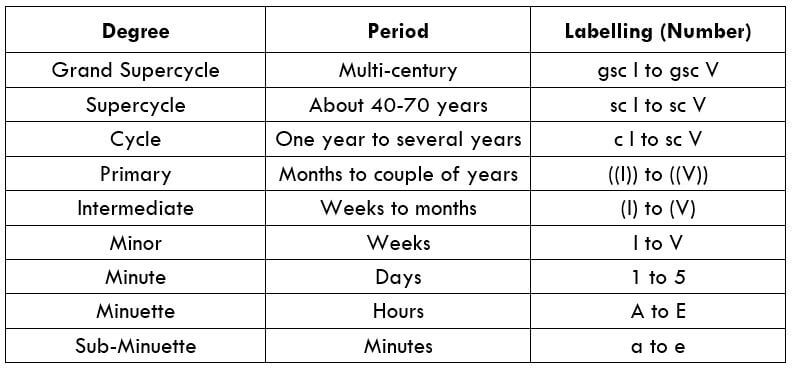
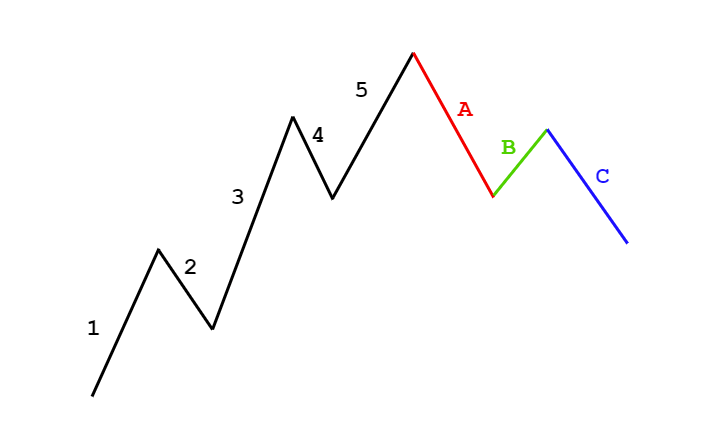
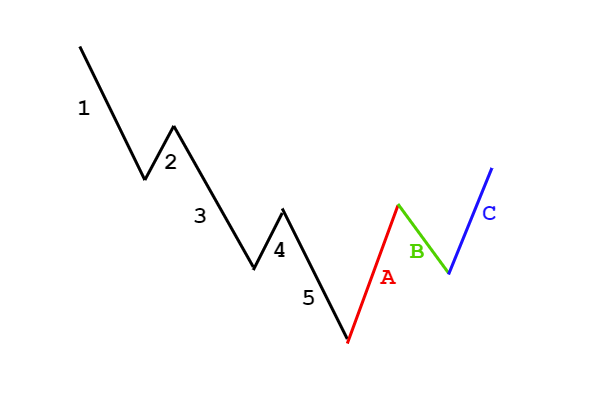
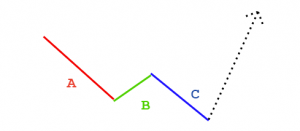
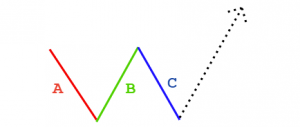
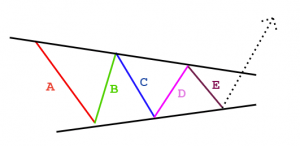
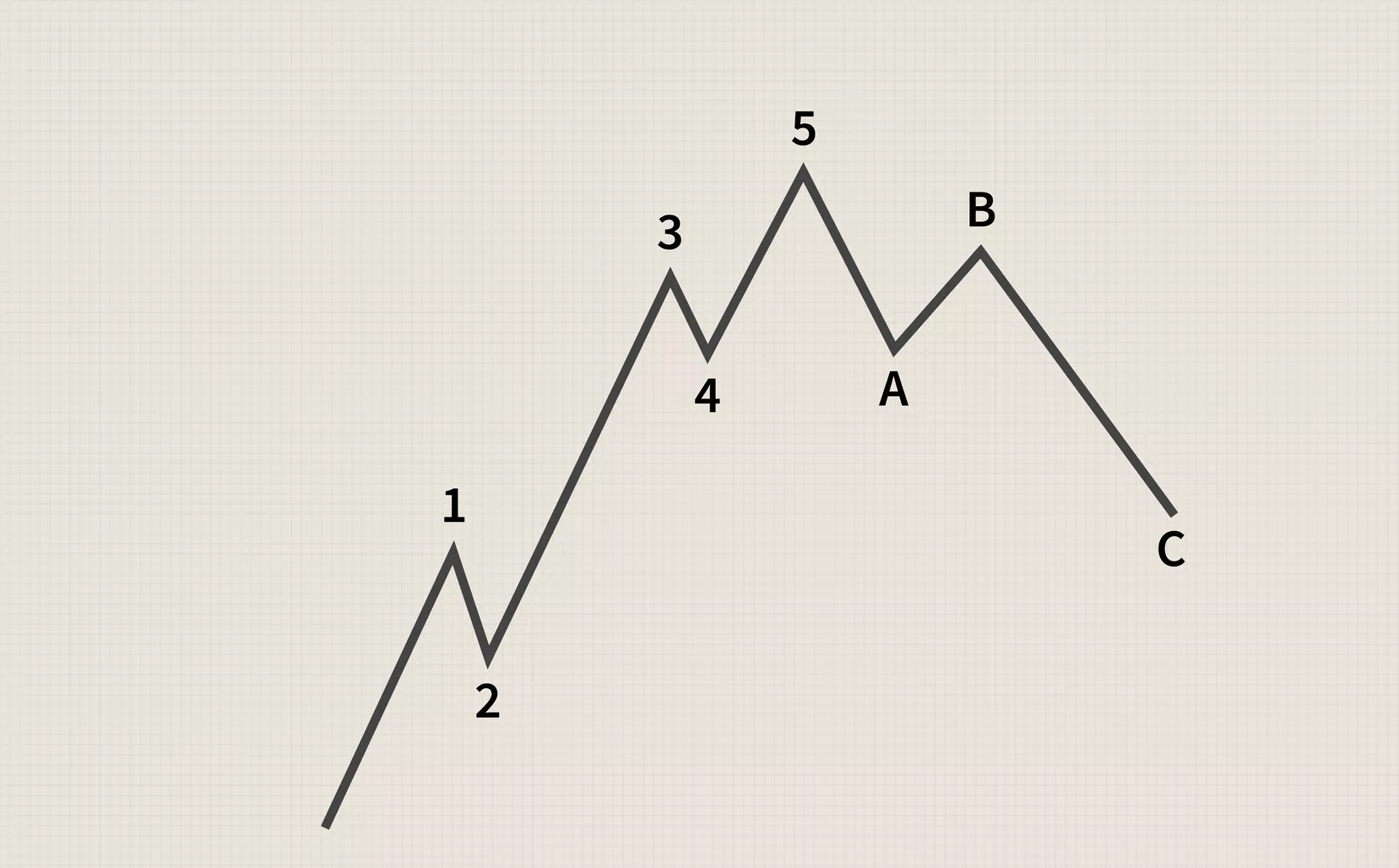
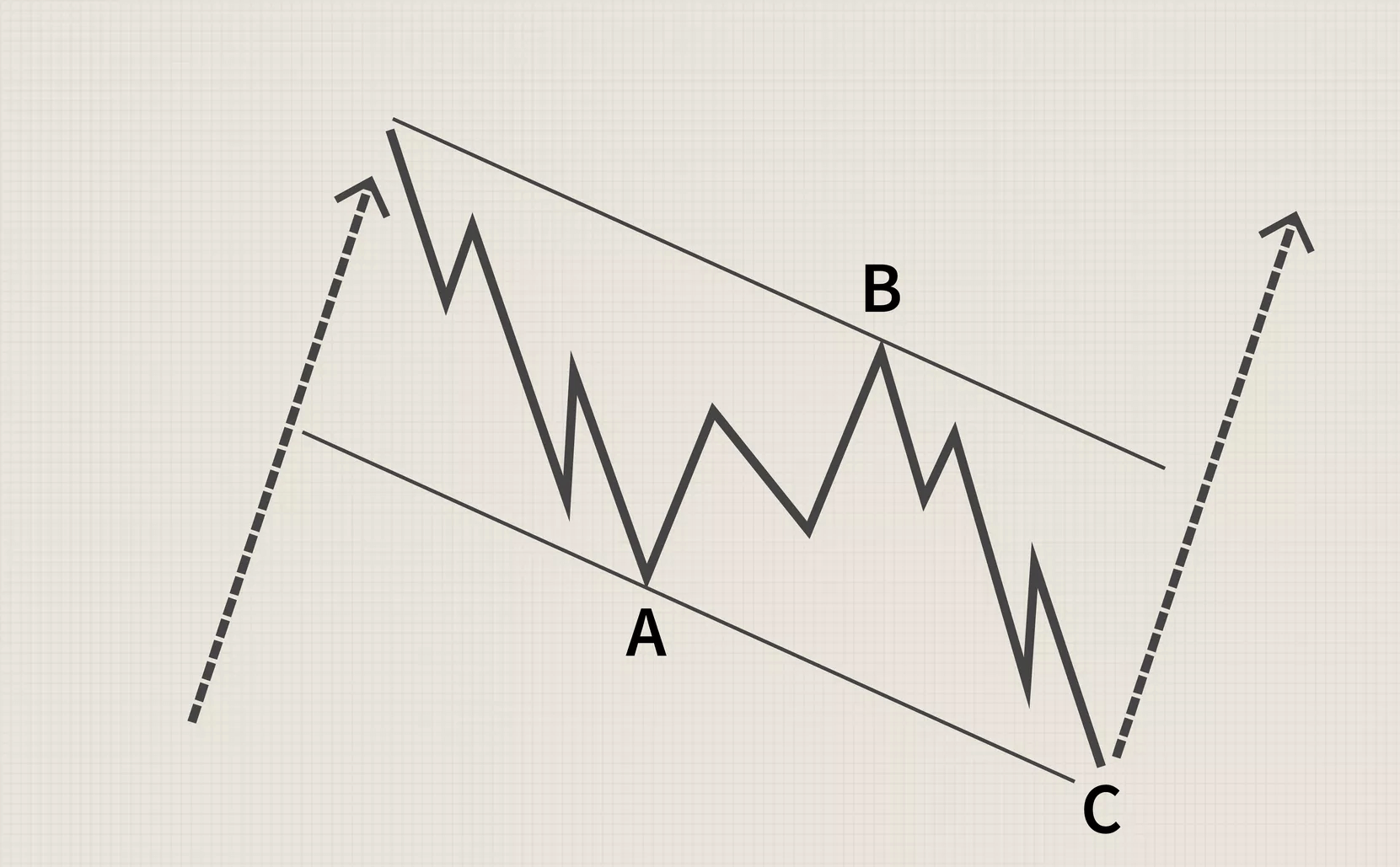
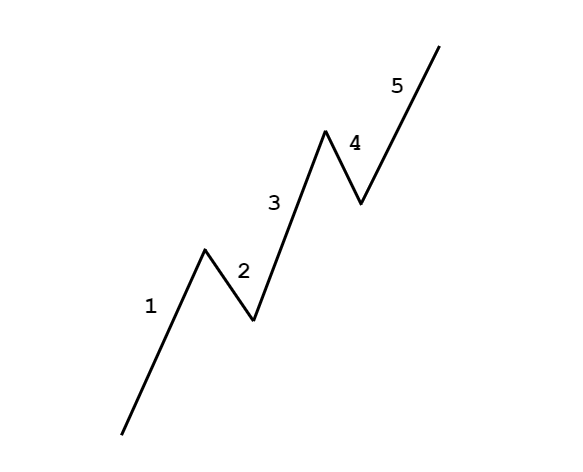There are few technical analysis components that can credit a single person, but Elliott’s wave theory has that distinction. The founder of the theory is Ralph Nelson Elliott, who was born in Marysville, Kansas, in 1871 and then moved to San Antonio, (Texas state).
Elliott began his career as an economist in the middle of 1890. After holding executive positions in private companies and a successful consulting business, the United States State Department wanted Elliott to be the candidate for the post of Chief Accountant of Nicaragua (a country that was then under US control).
During his stay in Central America, Elliott contracted a debilitating illness, which forced him to retire early at the age of fifty-eight. Around this time, he decided to devote himself to the study of the American stock market.
When Elliott began his study of markets, it was generally believed that markets were chaotic and random. Elliott, after many studies, was convinced that there was some sort of underlying order in the way they moved and proposed that market prices develop into specific patterns and trends. This was considered a revolutionary idea at the time.
It began its study by studying more than 75 years of historical data from stock markets using annual, monthly, weekly, daily, hourly, and half-hour charts. Remember, this was in the 1930s before there was computing capacity available to help review graphs and keep records. All these analyses were done manually and to carry it out without help was an achievement in itself.
As his research progressed, he began to establish rules that he could apply. The greater his confidence, the more frequently he began to spread his ideas publicly. In March 1935, an ordinary day, he sent a telegram after the closing of the market indicating that the US stock market is coming to an end.
The next day, Thursday, March 14, 1935, the Dow Jones Industrial Average reached its lowest closing price for the whole year. In fact, the market began an increase which lasted nearly two years and doubled the value of the Dow. Elliott, using its own market rules that he himself had developed, had set the bottom of the market within a trading day.
What makes this most notorious was the moment in history that Elliott made the prediction. In 1935, the United States was in the midst of the Great Depression, and the idea that markets could grow seemed unthinkable.
A few months after predicting the decline in March 1935, Elliott wrote “The Elliott Principle” with Charles J. Collins. Collins himself received Elliott’s telegram on Wednesday afternoon, predicting the decline of the market.
With the book, Wave Theory Elliott was officially born.
After Elliott’s death in 1948, many renowned financiers continued to make predictions based on Elliott Wave’s studies. In the early 1970s, a novice analyst at Merrill Lynch, Robert Prechter, was impressed with Elliott’s work and introduced it to the public through his own books.
Prechter won the US Trade Championship in 1984 with Elliott Wave, with a yield of 444% in four months on a real-money options trading account. Prechter also successfully predicted America’s long-term bullish market that began in 1982 and the October 1987 crash. The CNBC in 1989 named him “Guru of the Decade”.
Today, Prechter is considered the world’s best known Elliott The Wave Analyst, and the book, called “The Beginning of the Elliott Wave”, is considered today as the modern Bible for understanding this topic.
There’s a lot of criticism of the Elliott Wave and Prechter himself has made the wrong predictions. That said, Elliott’s wave theory is considered an important part of the technical analysis and is part of the curriculum of the authorized market technician designation.