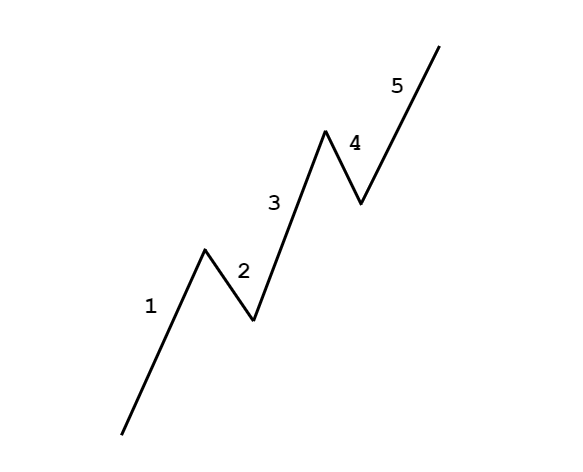Introduction
The 5-3 wave pattern is made up of the combination of 5-wave impulsive pattern and a 3-wave corrective pattern. The 5-wave pattern is inclined towards the predominant trend, while the 3-wave pattern is always against the trend. It is basically a pullback to the overall trend.
However, it does not end there. Within each wave in the impulsive and corrective waves, there is a set of other impulsive and corrective waves. And in that each smaller set of impulsive and corrective waves, there exists another miniature set of impulsive and corrective waves. This top-down approach goes on and on, forever.
The Top-down Approach
The Top-down approach can be considered as a synonym for fractals. In the Elliot wave theory, each wave is made of sub-waves and so on. In an uptrend, the 5-wave impulsive pattern faces upside. In these five waves, waves 1, 3, and 5 are towards the overall trend, while waves 2 and 4 against the trend.
In the same uptrend, the corrective wave pattern faces against the trend, where waves A and C face against the trend (downwards), and wave B faces towards the trend (upwards). In this sequence, there are five waves towards the overall trend (with two minor pullbacks) and three against the trend (with one minor pullback).
According to the fractal theory, each push up and push down has the above sequence. For instance, if we extract wave 1 and wave 2, then wave 1 will be made up of a 5-wave impulsive pattern, and wave 2 will be made up of a 3-wave corrective pattern. In conclusion, the combination of two waves (1 and 2) results in a set of 5-3 wave pattern. Refer to the below figure to get a clear understanding.
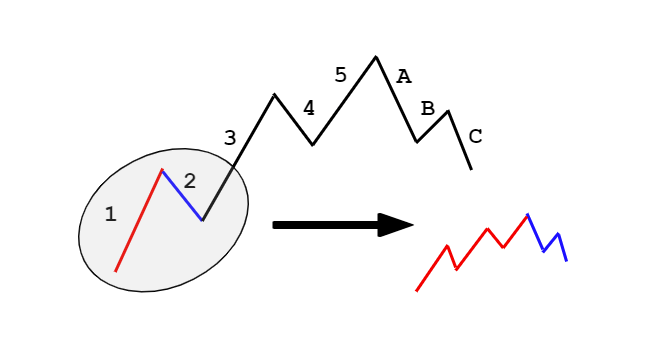
The Ordering and Labelling of Elliot Waves
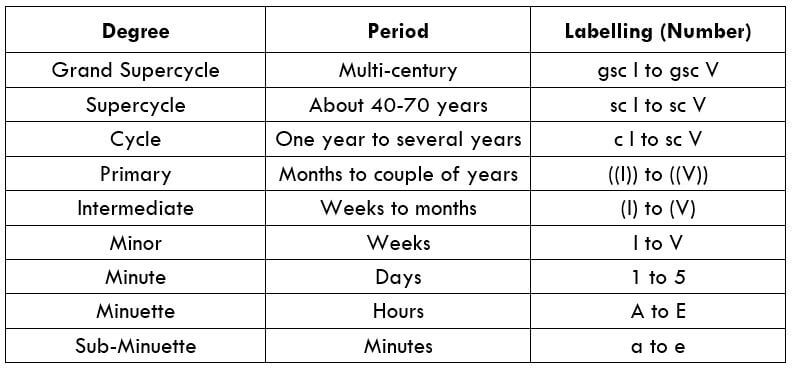
We know that every wave can be broken into smaller waves and so on. But referring to these waves becomes the challenging part. So, to make simplify the labeling of these waves, Elliot has assigned a series of categories to the waves in terms of its size (from largest to the smallest).
Conclusion
We saw that every Elliot wave is made up of another miniature Elliot wave, and this break-down goes forever. But, according to Elliot, the degree identification is not a necessary factor in Elliot wave analysis. As a trader, our goal is not to assign the right degree to the wave pattern but to just understand the timeframe in which it is occurring. In the end, all that matters is the basic analysis of the wave theory. The identification of degree always remains secondary. Cheers.
[wp_quiz id=”71844″]