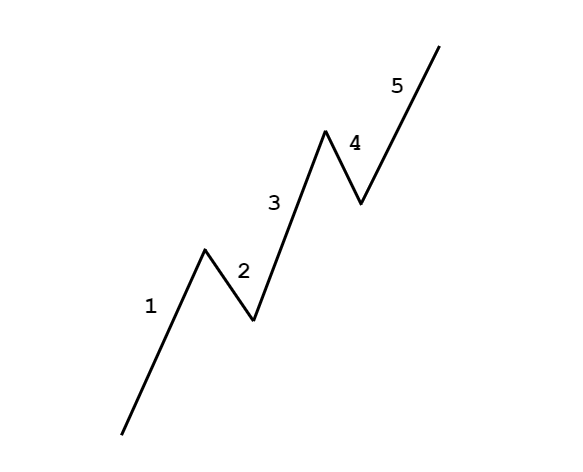Introduction
Over the last six lessons, we discussed the Elliot Wave Theory from understanding the basics of applying it in the financial markets. In this article, we shall have a quick summary of the previous learnings.
The Elliot wave theory was discovered by a professional accountant named Ralph Nelson, who claimed that markets don’t move in random directions, but recurring swings called waves. Most importantly, Elliott stated that the waves are fractals. That is, each swing or wave in the market can be broken into smaller and smaller waves of the same type.
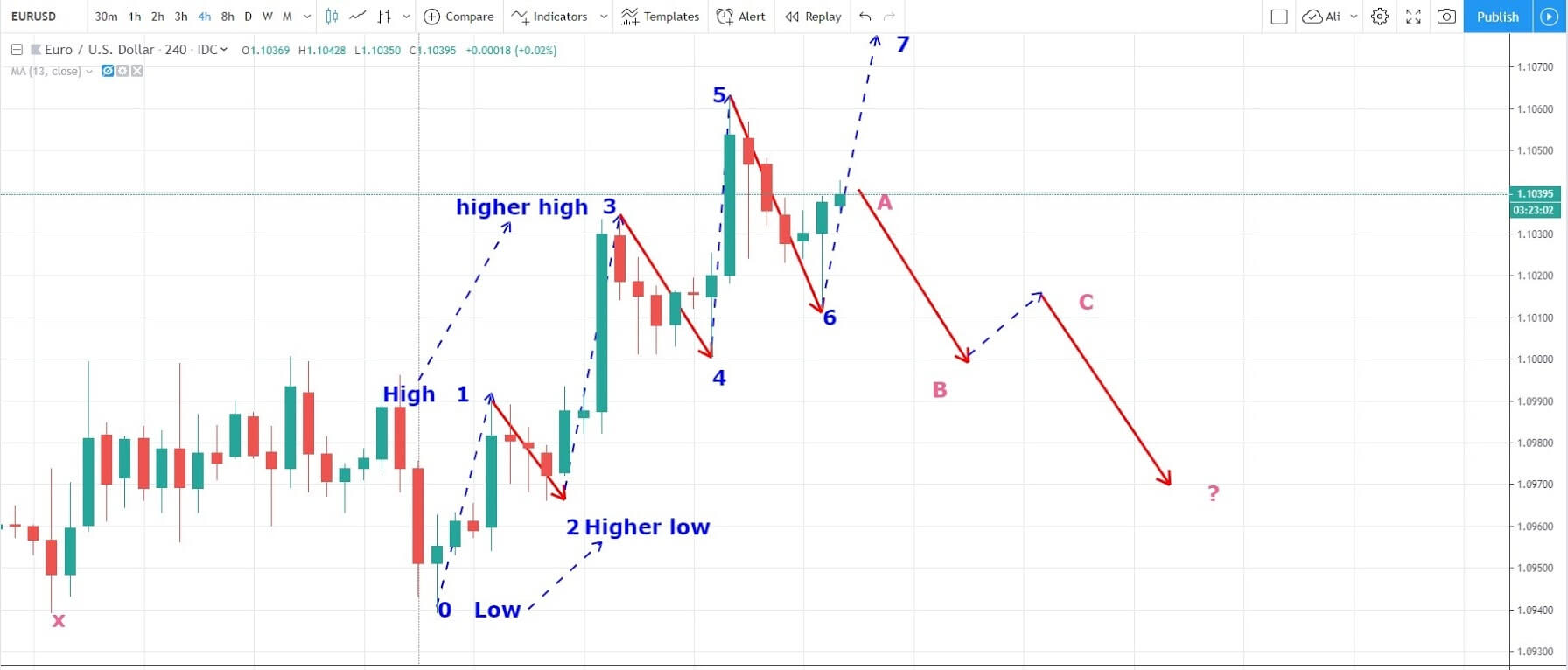
The market moves in the 5-3 Elliot pattern. This pattern is appliable on uptrend and downtrend. Also, it occurs in every timeframe.
Impulse Waves
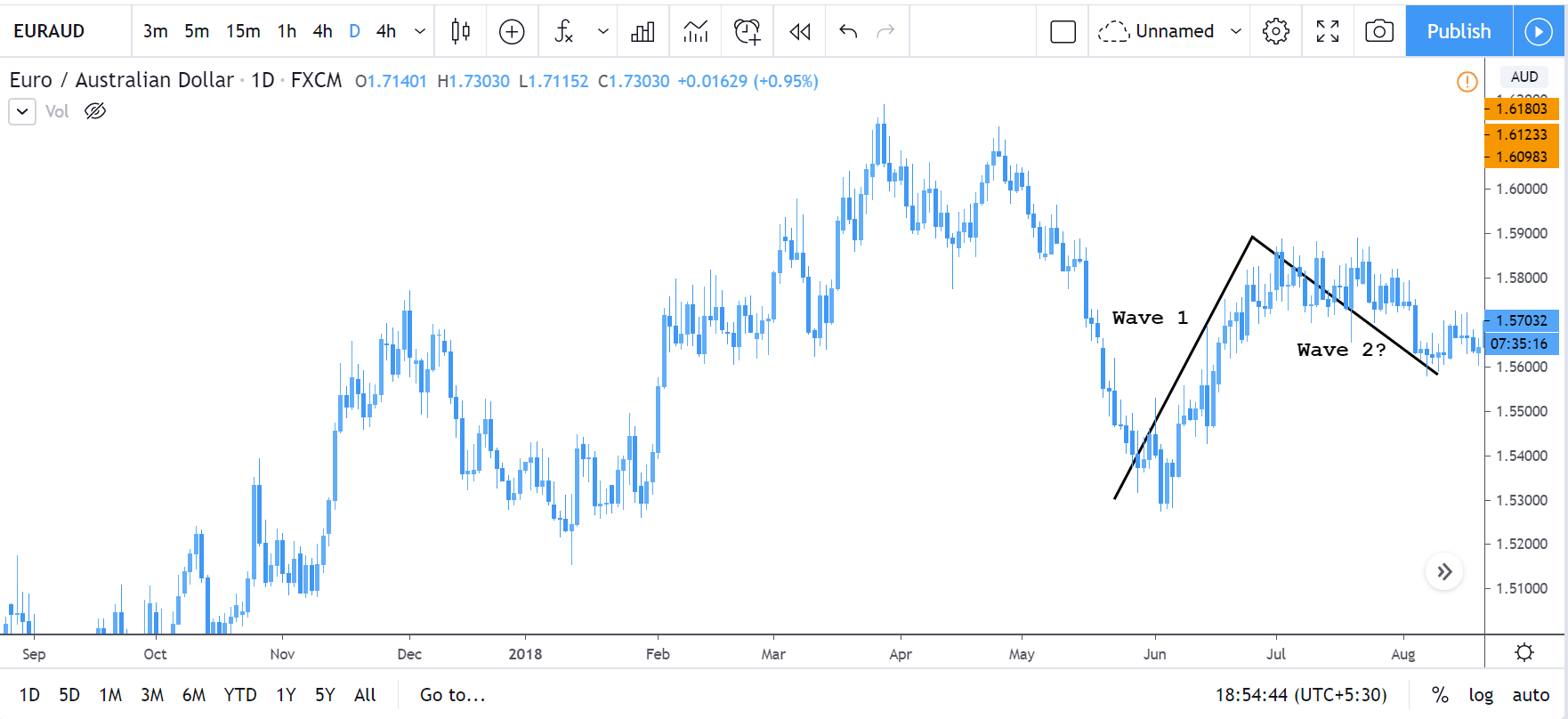
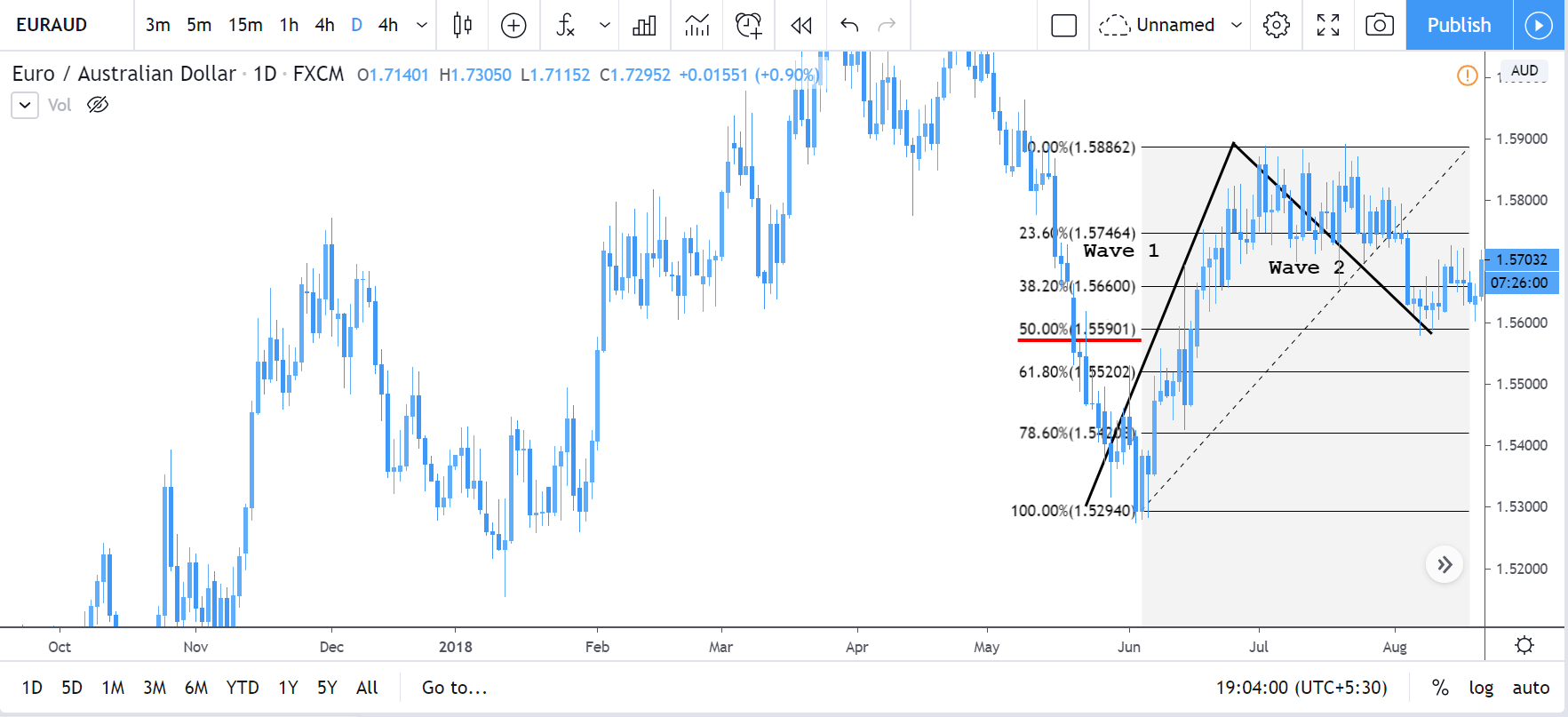
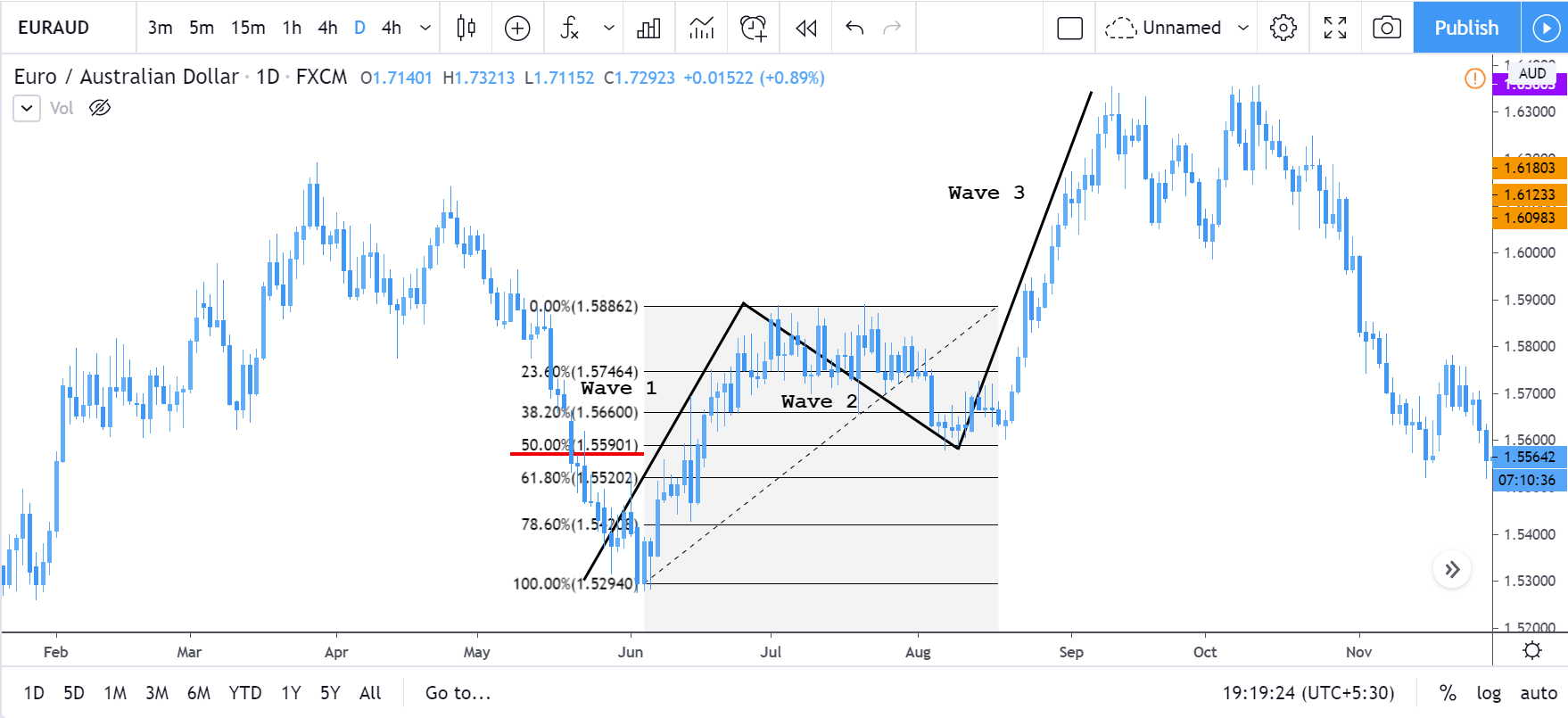
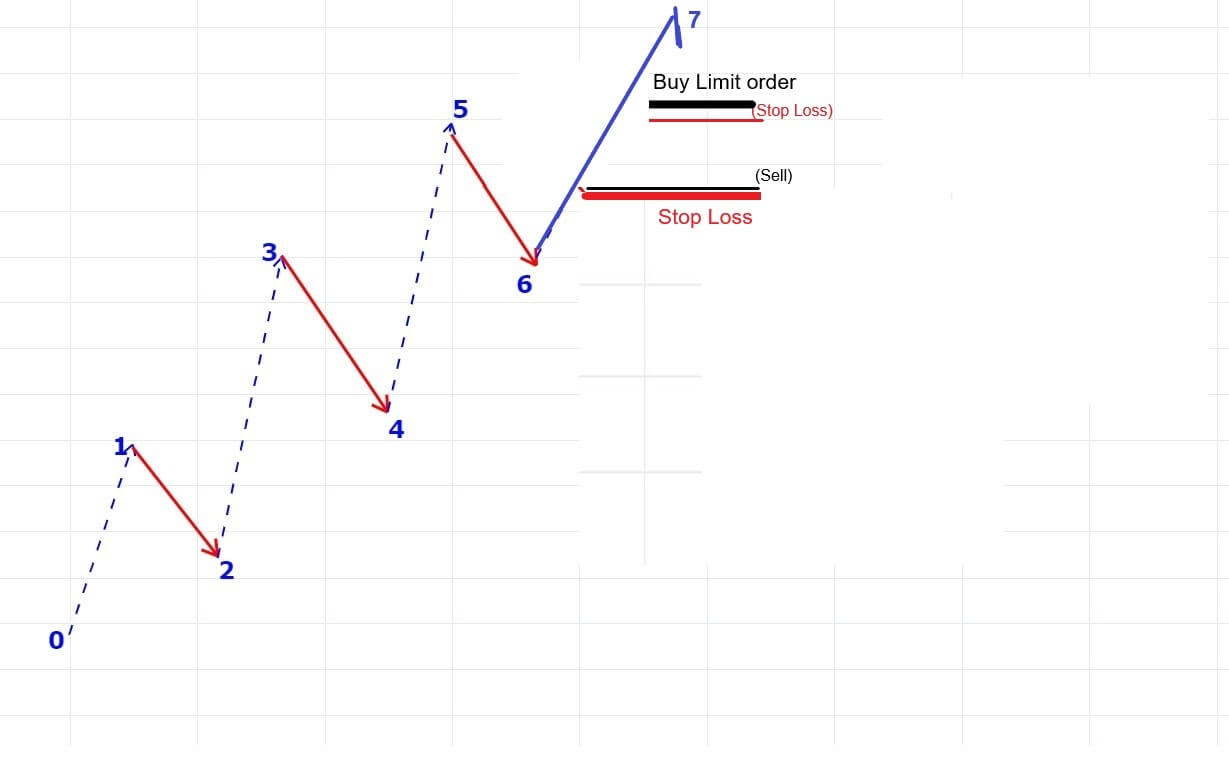
In the 5-3 wave pattern, 5 refers to the impulse waves. The 5-wave pattern is a trending wave pattern that moves along the overall trend. It is made up of 5 waves where Wave 1, 3, and 5 are impulse waves towards the trend, while waves 2 and 4 are retracements to the impulse waves. Out of the three impulse waves, wave 3 is usually the strongest and the longest and is ideal for trading.
- Wave 1 is where only a small number of people take positions.
- Wave 2 is where the institutional traders and some smart retail traders enter.
- Wave 3 is where the mass public enter, while smart & professional traders exit their positions.
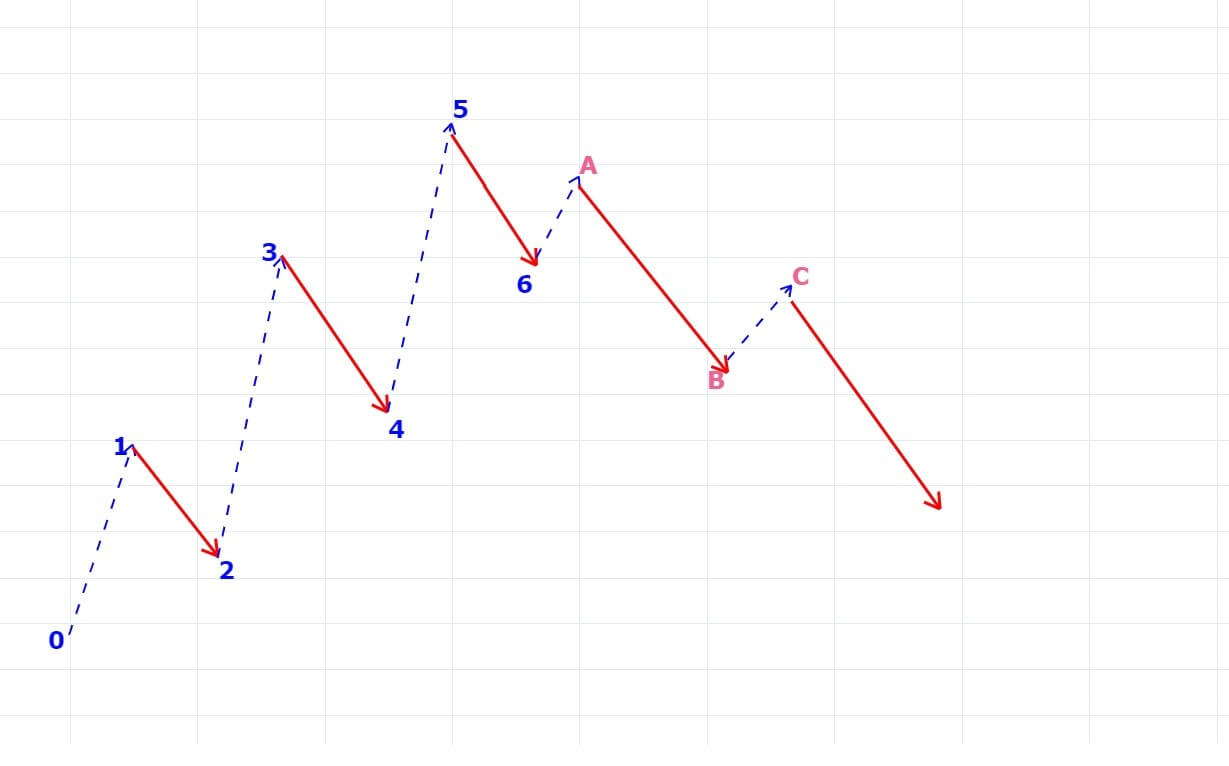
Corrective Waves
For every trending market, there is a pullback. And this retracement corresponds to corrective waves. The corrective waves are a 3-wave pattern that moves against the overall trend. It is denoted as wave ABC or abc, depending on the timeframe. The first corrective wave begins after the end of the impulse wave. Note that, the corrective wave pattern should not go beyond the area of wave 1 impulse wave. If it does happen, the waves must be counted from the beginning.
There are 21 types of corrective patterns based on their design. The three basic ones include
- The Zig-Zag Formation
- The Flat Formation
- The Triangle Formation
Rules in Elliot Wave Theory
There are three rules in the Elliot wave pattern to confirm the legitimacy of the pattern. The strategies will hold true only if the following strategies are satisfied.
- Rule 1: Wave 3 must never be the shortest impulse wave.
- Rule 2: The Wave 2 must hold above Wave 1.
- Rule 3: Wave 4 must never cross in the price area of Wave 1.
Even if one of the rules is not satisfied, waves must be recounted from the start.
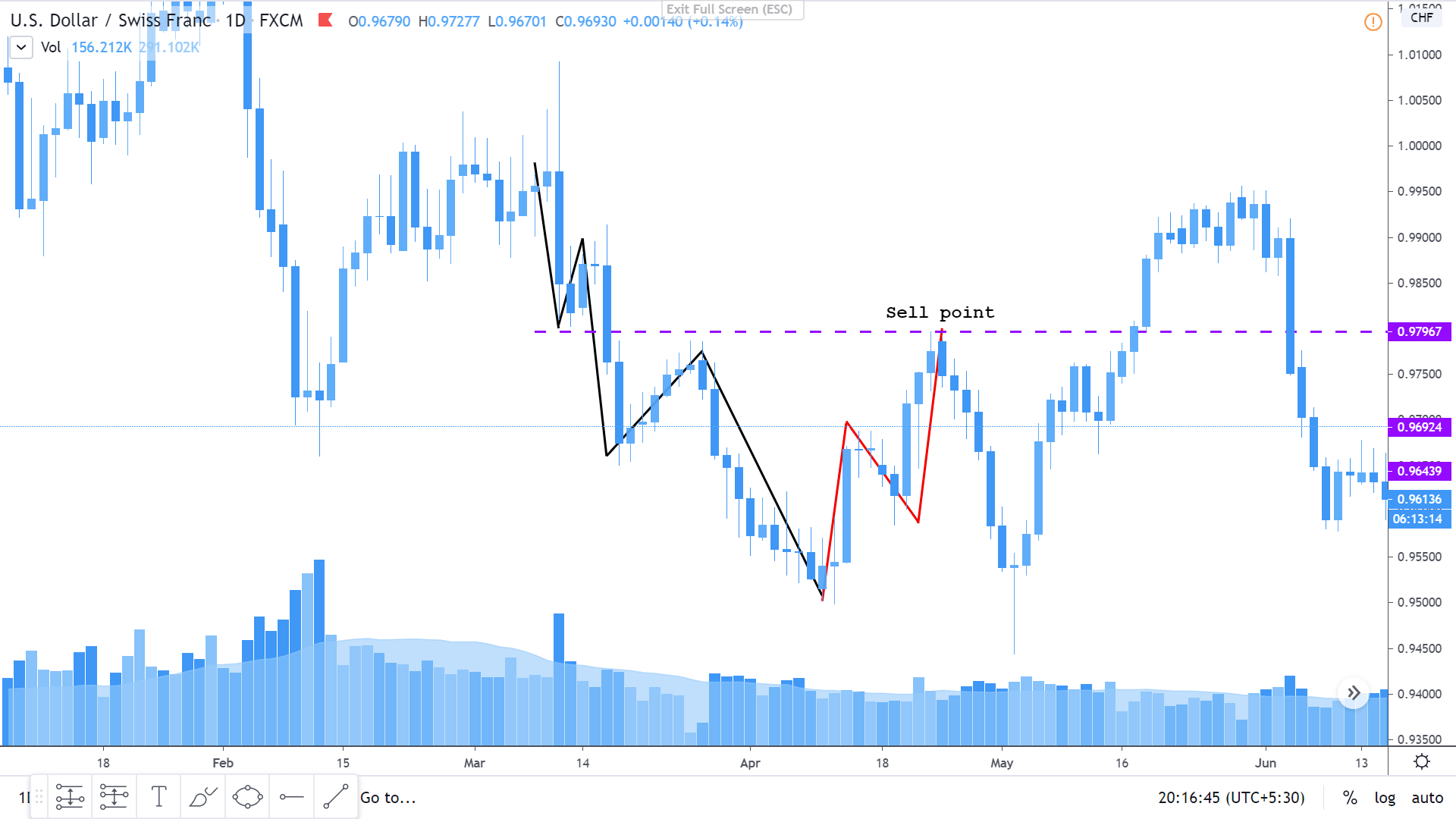
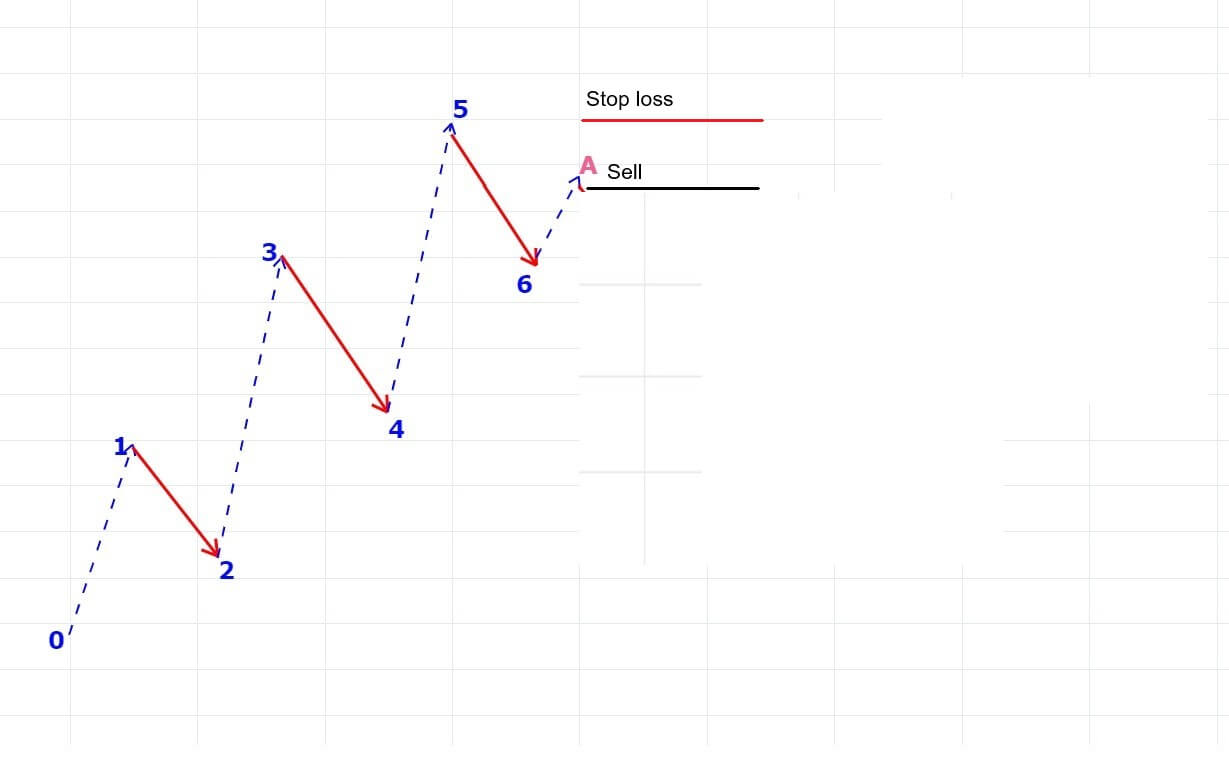
We have also discussed different ways of trading the Forex market using the Elliot wave theory, and that lesson can be found here.
Final words
The Elliot Waves are a great tool in determining the direction of the market. One can get a clear understanding of if the market is trending or retracing. Accordingly, one can take a trading decision by adding other tools which will help in precise entries.
We hope you found the Elliot Wave theory course informative and useful. Do try this out for yourselves as well. Happy trading!