To understand how each meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is conducted and who is in charge of monetary policy we should understand how the Federal Reserve is composed, who are its members and how they are elected. In addition, we should know what the tasks are of each entity of the reserve to determine how they will act in the meetings they have throughout the year. The Federal Reserve is not like other central banks as there is some independence between the banks in each district, so it is important to understand how the bank is made up.
The Federal Reserve System is the central bank of the United States. It develops five main functions to promote the efficient operation of the economy of the United States and thus achieve a better welfare of the public in general. The five main functions are:
Control the monetary policy of the country: The objective of the monetary policy is to promote maximum employment, stable prices and moderate interest rates in the United States economy.
Promote the stability of the financial system: It seeks to minimise and contain systematic risk through the activity of monitoring local and foreign financial activity.
Promote the safety and soundness of individual financial institutions: Monitor the activity of each bank individually to analyse its impact on the banking system as a whole.
Promote the security and efficiency of the payment and settlement system: Through services to the banking industry and the US government that facilitate transactions and payments in US dollars.
Promote consumer protection and community development: Through consumer-centred monitoring and review, research and analysis of emerging consumer issues and trends, community economic development activities and administration of consumer laws and regulations.
The structure of the central bank is decentralised so the Federal Reserve is divided into 12 districts. The boundaries of each district were based on the commercial regions that existed in 1913 and other economic variables, so each district of the central bank does not necessarily coincide with the geographical lines of each state. In addition, each district is identified by a number, which makes it easier to identify which district is being analysed in the bank’s reports. In the following graph, you can see the 12 districts of the banks of the reserve.

Graph 43. Federal Reserve Banks. Retrieved 13th January 2017, from https://www.federalreserve.gov/aboutthefed/structure-federal-reserve-system.htm
The twelve districts of the Federal Reserve operate independently, but under the supervision of the board of governors of the reserve. In principle, it was determined that each district will work independently and make its monetary policy decisions separately, but when the national economy became more complex and more integrated, the districts had to cooperate more with each other and coordinate their policies. In 1935 the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) was created, showing a unification of the concepts of each district.
In the mid-1980s, the Federal Reserve centralised and consolidated its financial services as well as creating support channels between the different districts. Reserve banks have become more efficient through the conclusion of service agreements within the system that assign responsibilities for services and functions of national scope between each of the 12 banks.
The drafters of the Federal Reserve Act initially rejected the concept of a single central bank. Instead, a bank was formulated with a system of three fundamental pillars. First, a board of governors of the central bank that would have the task of supervising the work of others. Second, a decentralised structure in its operation of 12 banks in the reserve. And third, a combination of public and private characteristics in its management. Although some central bank entities share characteristics with private sector entities, the Federal Reserve was established to serve public interests. In the following graphs, you can see the composition of the Federal Reserve and its main tasks (graph 44), and how the Federal Reserve was organised (graph 45).

Graph 44. Purposes and Functions. Retrieved 13th January 2017, from https://www.federalreserve.gov/aboutthefed/structure-federal-reserve-system.htm

Graph 45. Purposes and Functions. Retrieved 13th January 2017, from https://www.federalreserve.gov/aboutthefed/structure-federal-reserve-system.htm
In summary, there are three key entities in the Federal Reserve system:
- The Board of Governors of the reserve.
- The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC).
- The Federal Reserve banks.
The board of governors is a federal government agency that reports directly to the Congress, provides general guidance to the system and oversees the 12 reserve banks.
Within the system, there are certain responsibilities that are shared between the Board of Governors in Washington D.C. (whose members are set by the president with the consent of the Senate) and the banks and branches the federal reserve. While the Federal Reserve has frequent communication with the executive branch and congressional officials, its decisions are made independently.
In addition to these key parts in the Federal Reserve, there are two other significant entities that contribute to the functions of the reserve.
- Depository Institutions (banks, credit unions and savings banks): Depository Institutions offer transaction and check accounts to the public, and they can maintain their own accounts in their local Federal Reserve banks. The depository institutions must comply with the reservation requirements, that is, keep a certain amount of cash, either in cash or in an account in a Reserve Bank based on the total balances in the current accounts they hold.
- Advisory Committees of the Federal Reserve System: They make recommendations to the Board of Governors and reserve banks depending on the functions of each one. There are four advisory councils that assist and advise the board on public policy issues.
The Federal Reserve has its own advisory committees that help in making decisions, but one of the most important committees is the one that advises them on issues of agriculture, small businesses and labour market issues. The board of governors requests committee reports twice a year to assess the state of the economy and national sectors.
As mentioned in the introduction, the goal of the Board of Governors, federal banks and the FOMC is to work together to promote the health of the United States economy and price stability, coupled with the stability of the national financial system.
The way the Federal Reserve works is as follows. The Board of Governors, located in Washington D.C., is the governing body of the federal reserve system. It is made up of seven members who are nominated by the President of the United States and are confirmed in their positions by the Senate. The board guides the operation of the federal reserve system to promote the objectives and complete the responsibilities given to the reserve system.
All board members serve on the FOMC, which is the body within the Federal Reserve that establishes monetary policy. Each member of the Board of Governors is appointed for a period of 14 years; the terms are staggered so that a term expires on January 31 of each even year. After completing a full 14-year term, a Board member cannot be reappointed. The president and vice president of the Board are also appointed by the United States President and confirmed by the Senate, but they only serve for a term of four years, although they can be re-elected for another four years.
Nominees for these positions must already be members of the Board or must be appointed simultaneously to the Board. The Board oversees the operations of the 12 reserve banks and shares with them the responsibility of supervising and regulating certain institutions and financial activities.
The board also provides general guidance, direction and supervision when reserve banks provide loans to deposit institutions, and when reserve banks provide financial services to depository institutions and the federal government. As part of the surveillance, the Board evaluates and approves the budgets of each reserve bank. It also ensures that the concerns of consumers are heard by the central bank to respond to their needs.
The 12 central banks and their 24 branches are the operating arms of the Federal Reserve System. Each reserve bank operates within its particular geographic area or district. Each reserve bank collects data and other information about the business and the needs of the community in each district. Then that information is compiled by the FOMC so that the Board acts based on these studies.
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is the part of the federal reserve that is responsible for setting the national monetary policy. The FOMC makes decisions regarding open market operations that affect the interest rate of federal funds (the interest rates at which financial institutions lend to each other), the size and composition of the assets held by the reserve and communications with the public about the future course of monetary policy.
The FOMC consists of 12 voting members (7 members of the board of governors, the president of the New York Federal Reserve and 4 of the remaining 11 district presidents who rotate in this position annually.) All 12 presidents of the Banks in the districts attend the meetings they have with the FOMC and participate in the discussion about the state of the economy and what steps to follow, but only the presidents who are members of the committee at the time of the meeting can vote in Monetary Policy Decisions. By law, the FOMC determines its own internal organisation and by tradition, the FOMC elects the president of the Board of Governors as its president and the president of the New York Federal Reserve bank as its vice president.
FOMC meetings are usually held eight times a year in Washington D.C. and other times as necessary. This committee is in charge of supervising the open market operations, which are the main tools of the Federal Reserve to execute the monetary policy of the United States.
The monetary policy of the Federal Reserve is the set of actions taken by the central bank to achieve three specific objectives:
- Maximum employment.
- Stable price levels.
- Stable and moderate interest rates in the long term.
The Federal Reserve conducts the national monetary policy by controlling the interest rate in the short term of the economy and by influencing the availability and cost of credits in the economy. Since monetary policy directly affects interest rates, there is an indirect effect on the prices of the goods of the economy, on the wealth of people and on the exchange rates with respect to other currencies. Through these channels, monetary policy influences the level of spending of the economy, investment, production, the level of employment and inflation in the United States.
An effective monetary policy complements the government’s fiscal policy to sustain economic growth in both the short and long term. Although the objectives of the bank with regard to the monetary policy have not changed, it has changed the form and the tools to control the variables of interest. The Federal Reserve was created by Congress in 1913 to provide the nation with more security, flexibility and a more stable financial system.
In the minutes signed in the creation of the Federal Reserve, it was established that the Board of Governors and the FOMC should conduct monetary policy to promote its three main objectives. In this mandate that was given to the federal reserve, the objectives will be considered fulfilled when the majority of people who are looking for work are successful in their search, and when the prices of goods and services on average are relatively stable.
The importance of stable prices for the economy is given because when there is stability in this variable, there is a stable growth in the long term of the economy, the level of employability is higher and more stable and helps the bank’s third objective since with stable inflation and within certain ranges, the interest rate in the long term will be moderate and in line with the expectations of the agents in the economy. In addition, they generate stability in the wealth of the population so stable prices over time will help improve the quality of life of American citizens.
Stable prices will also encourage savings and capital formation since when there is a low risk that inflation is outside of its target ranges, the risk of erosion in the value of assets is reduced, which is very evident when there is high inflation. For example, if a consumer wants to buy a machine for his factory and there is very high inflation, in the future, that acquired asset will lose its value which will also affect the confidence of people, who could postpone their consumption and investment decisions.
One of the objectives of the Federal Reserve that on some occasions has not been achieved is to control and promote the stability of the financial system by reviewing and regulating financial institutions and their activities. A financial system is considered stable when all institutions of the system such as banks, savings banks and cooperatives can provide resources to households, businesses and the community in general, to invest and participate actively in the economy which will generate long-term growth term.
The resources and services that a stable financial system should have are lines of credit for business, loans to students, savings accounts, retirement accounts among others. That is, there is an effective connection between lenders and borrowers where both parties are benefited by certain returns of their money and in other cases by the money supply that cannot be obtained otherwise. A healthy system must face low transaction costs that do not affect the distribution of resources because if the costs of lending are very high, the function of banks will not be fulfilled and there will be no relationship between people with money to invest and those who do not. They have the necessary resources.
With the task of the Federal Reserve to monitor the health of the financial system, it is supposed that there should be some regulations for banks to be able to face adverse conditions in times of crisis or possible bank runs that would affect the liquidity of banks. Monitoring risk through the financial system is the task of the Federal Reserve and other regulatory entities which should ensure that banks do not take excessive risks which have sometimes failed since private banks manage to bypass those regulations.
In conclusion, the federal reserve is a system composed of three key entities such as the board of governors, the banks of the 12 districts and the FOMC. Each of these entities has its own responsibilities, but they are under the authority of the Board of Governors. Within the board members, there are some members who are chosen by the president of the republic and confirmed by the Senate. The Federal Reserve is responsible for maintaining the good performance of the economy with stable price variables that allow interest rates without greater volatility. It is also a mandate of the reserve to monitor the financial system of the United States, but private banks have managed to bypass these regulations. For investor decision-making, it is important to analyse in each meeting who are the presidents of the banks with votes and the situation in their district to project what will be the decision of each one regarding monetary policy.
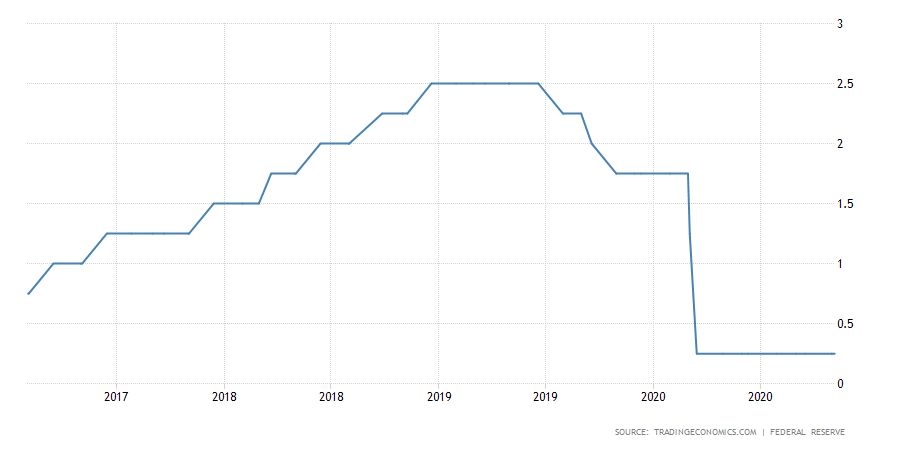 Source: TradingEconomics.com
Source: TradingEconomics.com