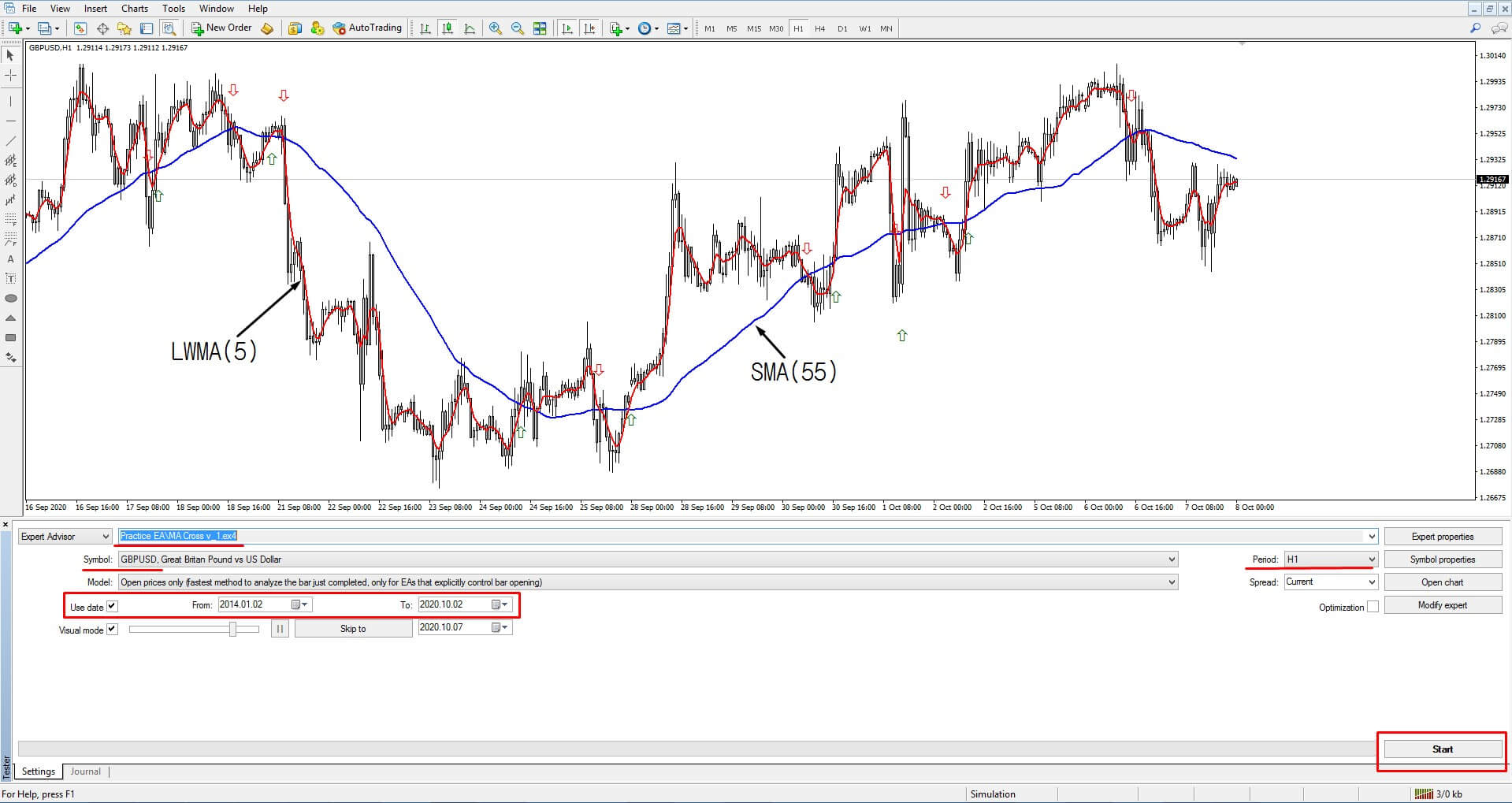
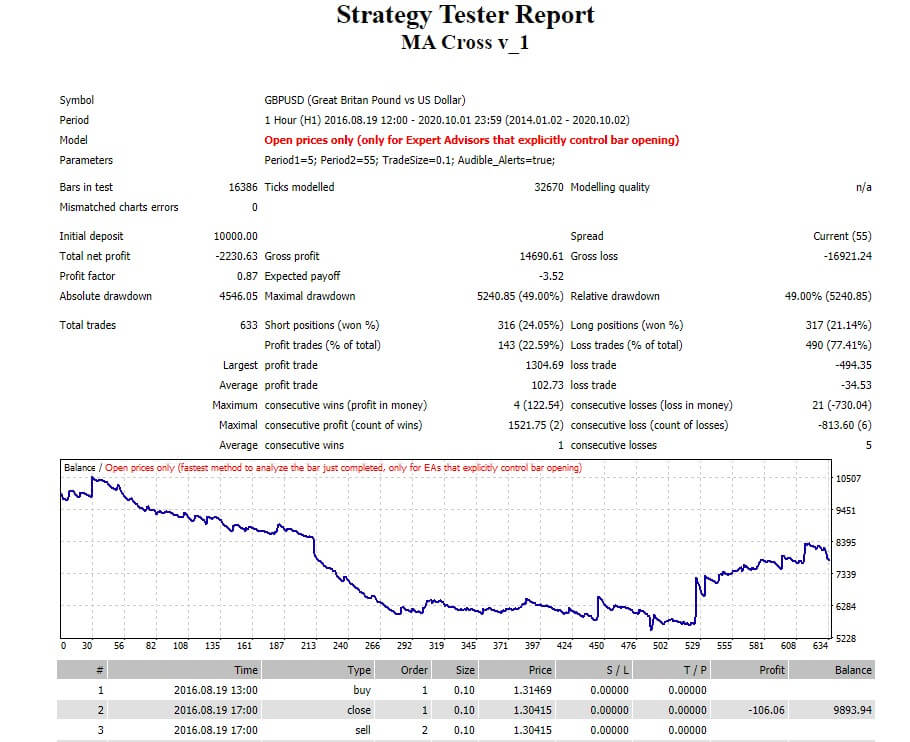
In previous articles, we explained the importance of a plan to succeed in Forex and described its general features. In this article, we will describe the concepts that need to be considered when designing a trading system.
A trading strategy is what most traders call a trading system, but it is not. A trading strategy is just a set of loose rules discretionary traders use to trade. A trading system is a set of closed rules used to systematically trade the market, usually through a computer EA, although a disciplined trader could also use it.
 Traders, especially novice traders, get emotional and lose money because their emotions interfere and stop making rational decisions in the battle’s heat. Thus, the first thing to avoid is discretionary trading. Please read the article Know the Two Systems Operating inside Your Head. That’s why what we aim to create is a trading system that should be systematically traded.
Traders, especially novice traders, get emotional and lose money because their emotions interfere and stop making rational decisions in the battle’s heat. Thus, the first thing to avoid is discretionary trading. Please read the article Know the Two Systems Operating inside Your Head. That’s why what we aim to create is a trading system that should be systematically traded.
Price imbalances
There are plenty of criteria to find these imbalances. There are two visual clues we can think of. The first one is a rubber band. 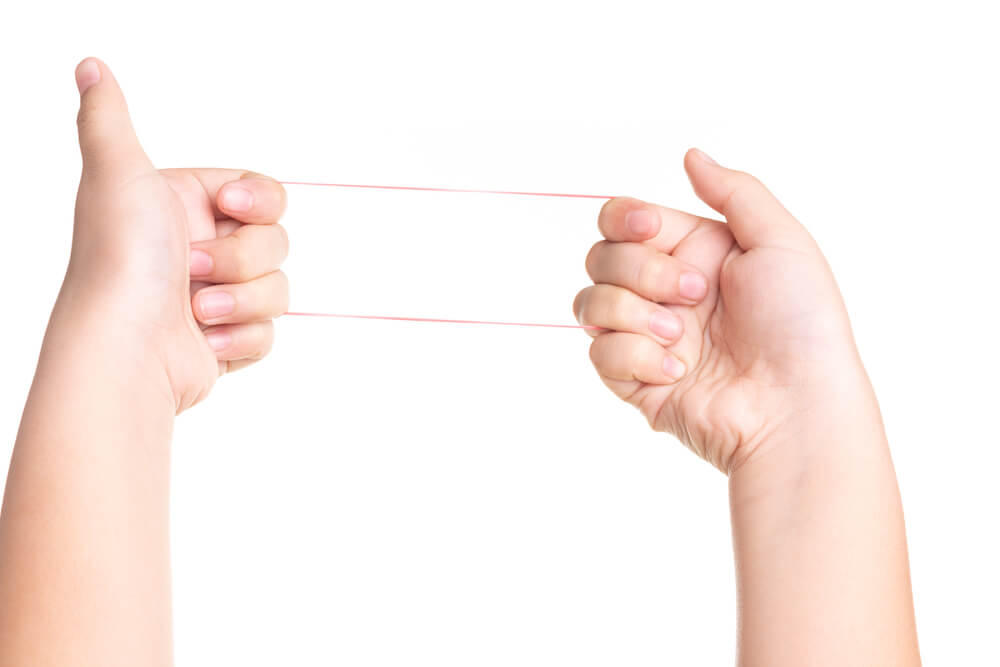 The rubber band idea describes the price as if it was a rubber band or spring. When it moves far away from equilibrium, we expect the force to pull it to its center to increase and eventually drive it back to equilibrium.
The rubber band idea describes the price as if it was a rubber band or spring. When it moves far away from equilibrium, we expect the force to pull it to its center to increase and eventually drive it back to equilibrium.
The second visual clue is looking at the price moving in waves. Since there are numerous traders, their goals set in different timeframes, we can expect waves of different periods and amplitudes. A trend form when the combination of di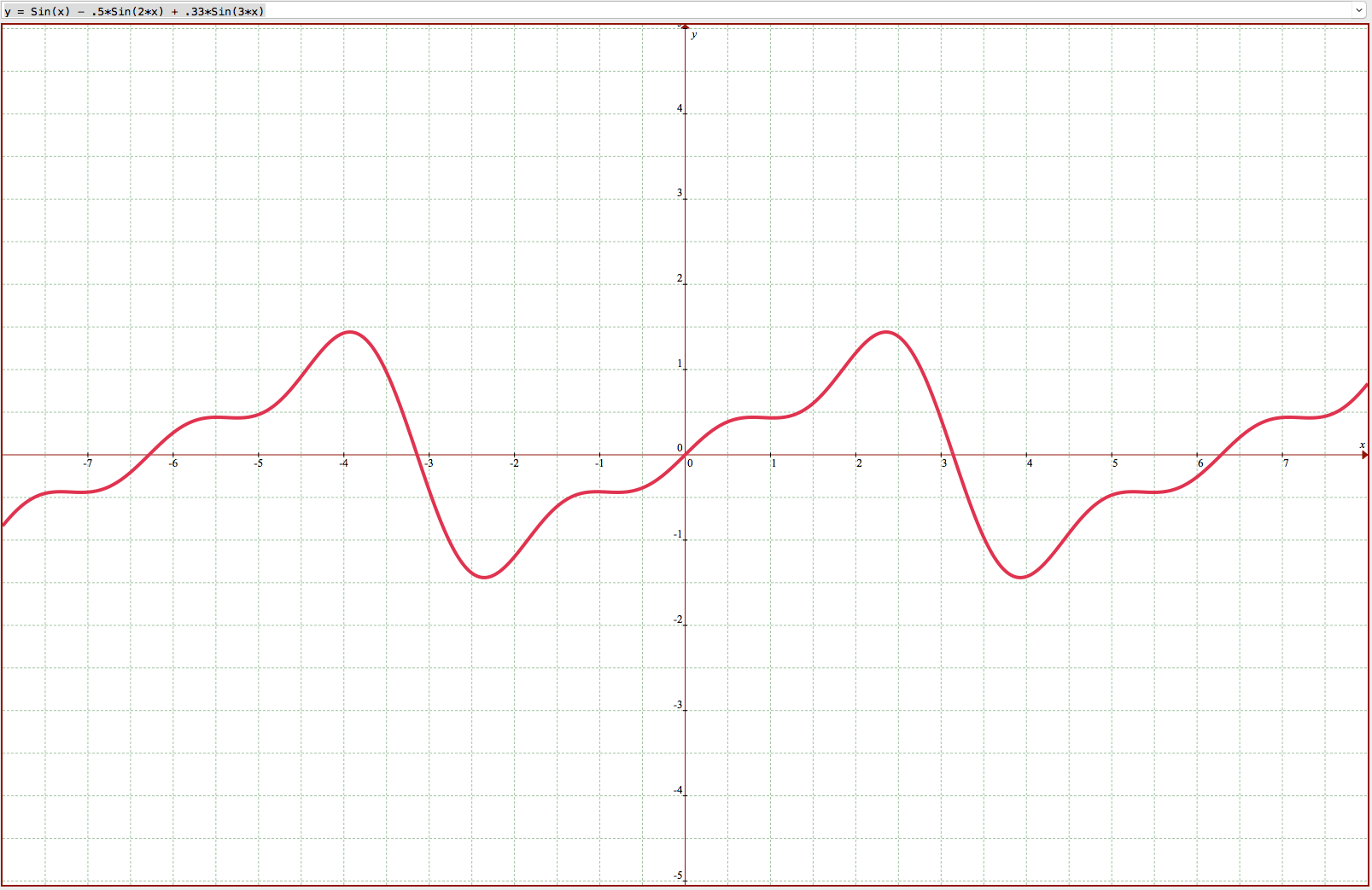 fferent waves are in sync, and chaotic moves occur when waves desync.
fferent waves are in sync, and chaotic moves occur when waves desync.
The main idea of a trading system is to find imbalances in the price and profit from it. Essentially, it takes the form of “buy low and sell high,” “sell high to buy back low,” or its variants “buy high sell higher,” “sell low, sell lower.”
The Effect of timeframes and a portfolio in the trading results
In their book Active portfolio management, Grinold and Kahn described the fundamental law of active management. The formula has two variables: The manager’s skill (IC) and the number of investments performed (N).

We could think of IR ( Information Coefficient) as a quality index of the results.
If we analyze the equation, we see that IC measures a trader’s ability to produce profits, since if N is constant, IR grows if IC grows.
But, if we keep the IC constant, we see that IR grows with the number of trades (N).
This explains that a portfolio of assets will be more profitable than only one asset. It also explains why shorter trading timeframes would produce higher results. Of course, with very short timeframes, the trading costs would eat a growing portion of the profits, so there is a limit to how short we could go.
Diversification
Diversification is a key concept to reduce the overall risk in trading. The idea is simple. Let’s say we have a long position the EURUSD with an overall dollar risk of 10 pips. If the dollar moves up and drives the pair southwards, we lose $100 on every lot. If we have an equivalent long position on the USDJPY, we will cover the risk on the EURUSD with the gains on the USDJPY, driving it to zero or, even, being positive overall.
If the assets are uncorrelated and the risk on each trade is similar on all trades, the overall basket’s risk will less than 50% of the sum of all open trades risk.
The profitability rule
Two parameters define the profitability of a system: the percent winners and the reward risk ratio.
The formula that tells the minimum percent winners (P) required with a determined reward/risk ratio (Rwr) for the system to be profitable is:
P > 1 / (1+Rwr)
Conversely, below is the formula of the minimum reward/risk ratio needed with a determined percent winners figure on a profitable system:
Rwr > (1-P)/P
If you play with the second formula, you will see that at reward/risk ratios below one, the system should grant winners higher than 50 percent. Furthermore, Systems with high reward risk ratios would need less than 50% winners to be profitable.

The conclusion is we must look for systems with high reward/risk ratios to protect us from periods of low winner’s percent.
Assessing the quality of a trading system
There are several methods to measure the quality of a trading system. We propose the use of Van Tharp’s SQN, which is a variation of the chi-square test, a well-known method to evaluate the goodness of a sample against a random distribution. The SQN test is a Chi-square test that is capped to 100 samples so that the length of the sample does not modify its value.
SQN = 10 x E / STD(E)
Where E is the expected profit on each trade, which is the sum of all profits divided by the number of trades, and the denominator is the standard deviation of E.
But if the sample is less than 100 instead of 10, the multiplier is the square root of N, the number of trades.
SQN = √N x E / STD(E)
Systems below 1 are bad. systems of 1.5 to 2 average, and from 2 to 3 good and over 3 excellent.

Elements of a Trading System
We can decompose a trading system into its several elements, although not all of them need to be present. We have already discussed this, but let’s describe its basic elements.
A Setup: The setup is a market state where we think there is an imbalance in the price, or a condition we expect can be resolved with a price move, for example, the price reaching a top or a bottom of a channel.
A permissioning filter: This forbids trading under specific market conditions: Low volume, extreme volatility, particular hours or days.
Entries: This the stage that times the market. It can be a breakout, a candlestick pattern, or an indicator signal.
Stop-loss: This defined an invalidation level, under which the trade is likely no longer profitable. This level will limit our losses and save our capital for further trades.
Take-profit: It defines our planned profit. It may be set using support/resistance levels or any other sign the current trade movement is over, such as a reversal signal or the crossover of averages.
Re-entry rule: You may also consider this rule in your findings. For instance, a market failing to do something, for example, continue moving up, may signify it will move down. Thus, you could stop and reverse instead of close the position. Also, if you got out of a position, you could consider re-entry if the market flags a continuation of the previous movement. That way, you could tight your stops keeping most of your profits and reenter instead of loose stops, which may eat a large portion of your hard-earned profits if the market does not recover.