Fibonacci Confluence Zones
If you have not first read my article, ‘You’re still misusing Fibonacci retracements,’ please do so before reading this article. This article will continue where we left off in discussing the new and improved way of drawing accurate and efficient Fibonacci retracements using the Brown Method. I am going to use the same Forex pair that we used in the first article. The purpose of this article is to show you how you can create Fibonacci Confluence Zones to create natural price levels that act as future support and resistance. First, I am going to start my first swing using the March 2001 low and then retracing back to the confirmation swing high in March 1997. See below.
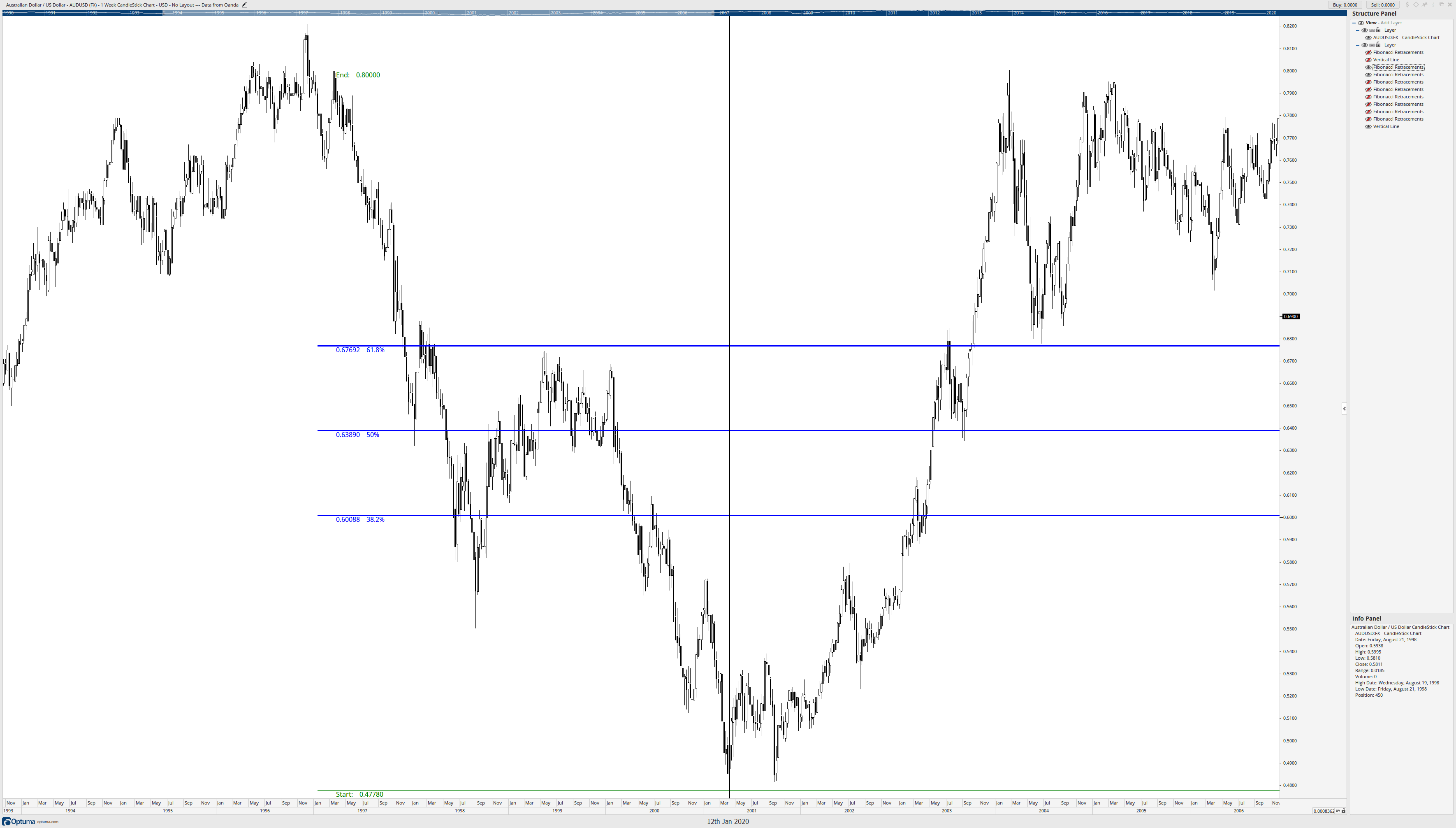
First, I want to know if this retracement is appropriate given how much time has passed – we’re 23 years from the March 1997 high and 19 years from the March 2001 low. Do these Fibonacci retracement levels still work? Do they remain valid? The black vertical line is the start of the retracement, so anything before the retracement is not used, it’s the data afterward that matters. Let’s look.
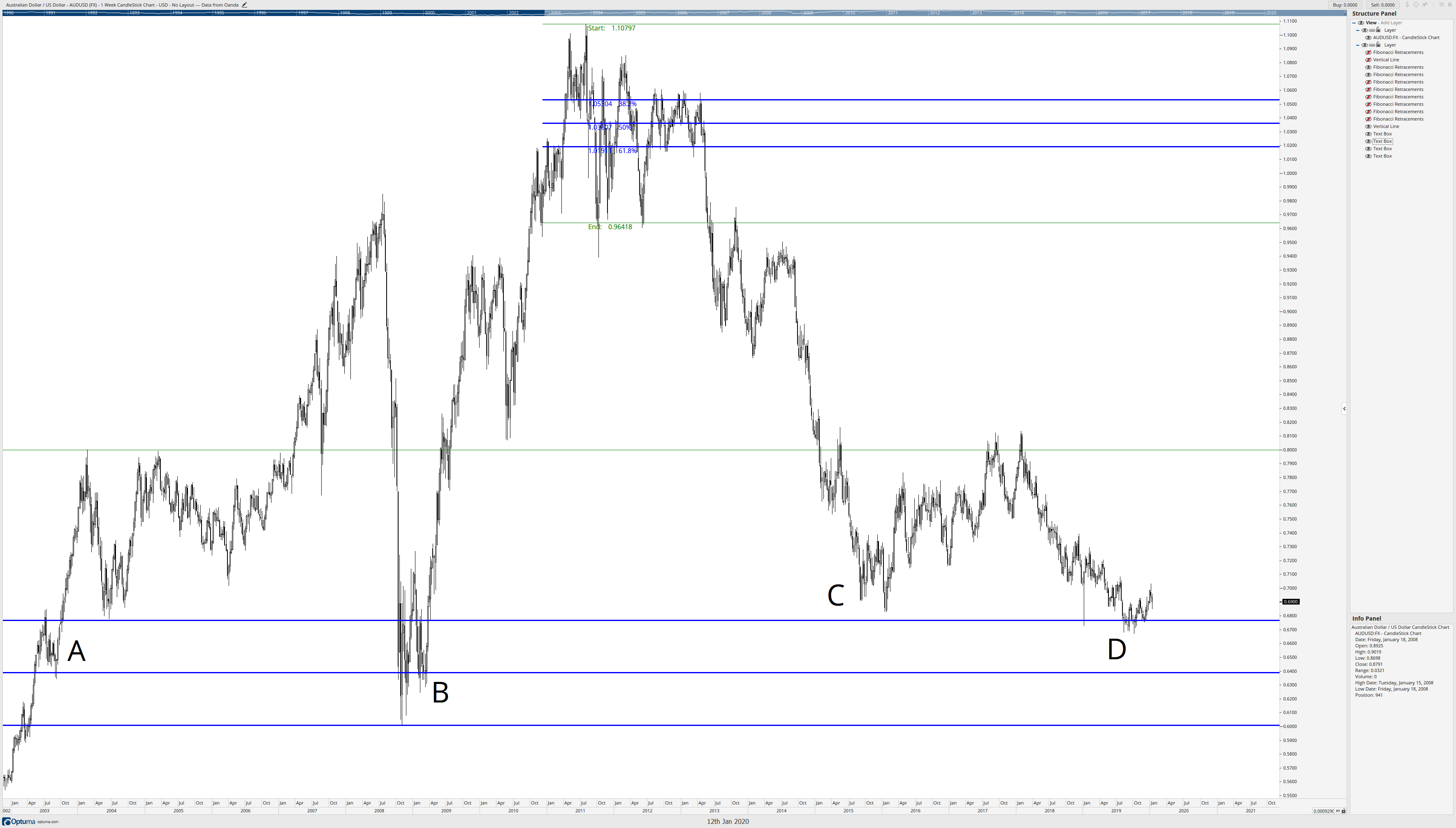
Are these Fibonacci retracement levels we drew still relevant? I would say so. A quick look at A, B, C, and D prove it. Especially for the most recent data at D on the AUDUSD weekly chart – seven-year lows bounce off of the 61.8% Fibonacci retracement level from 20+ years ago! But let’s look at some more Fibonacci retracements made off of other significant swings. Fair warning: there’s going to be several images here.
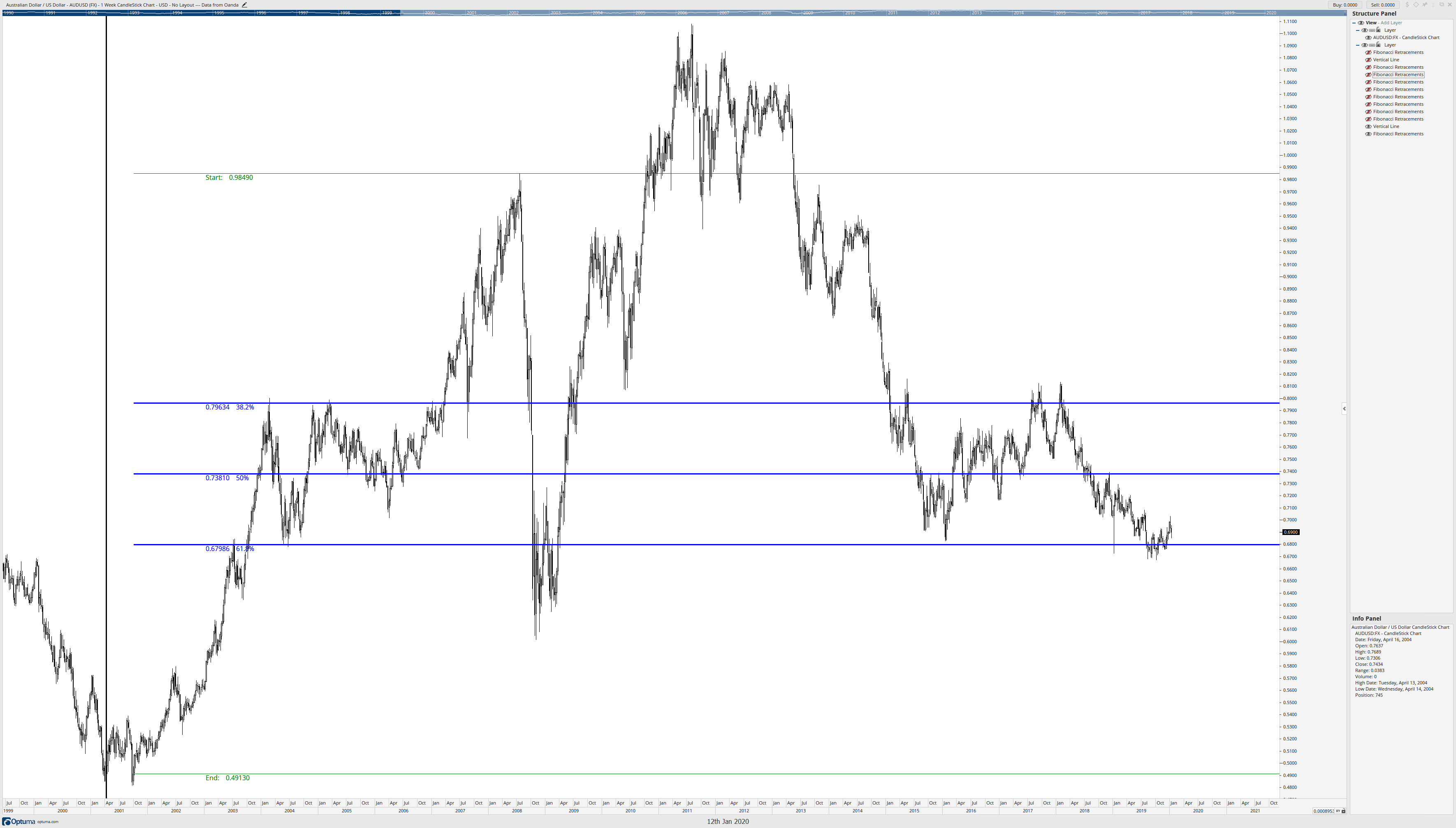
The Fibonacci retracement above is from the swing high in July 2018 to the confirmation swing low in October 2001. Like the previous Fibonacci image, we can see that prices have respected the retracement levels even a decade after the retracements were established. But we’re not done.
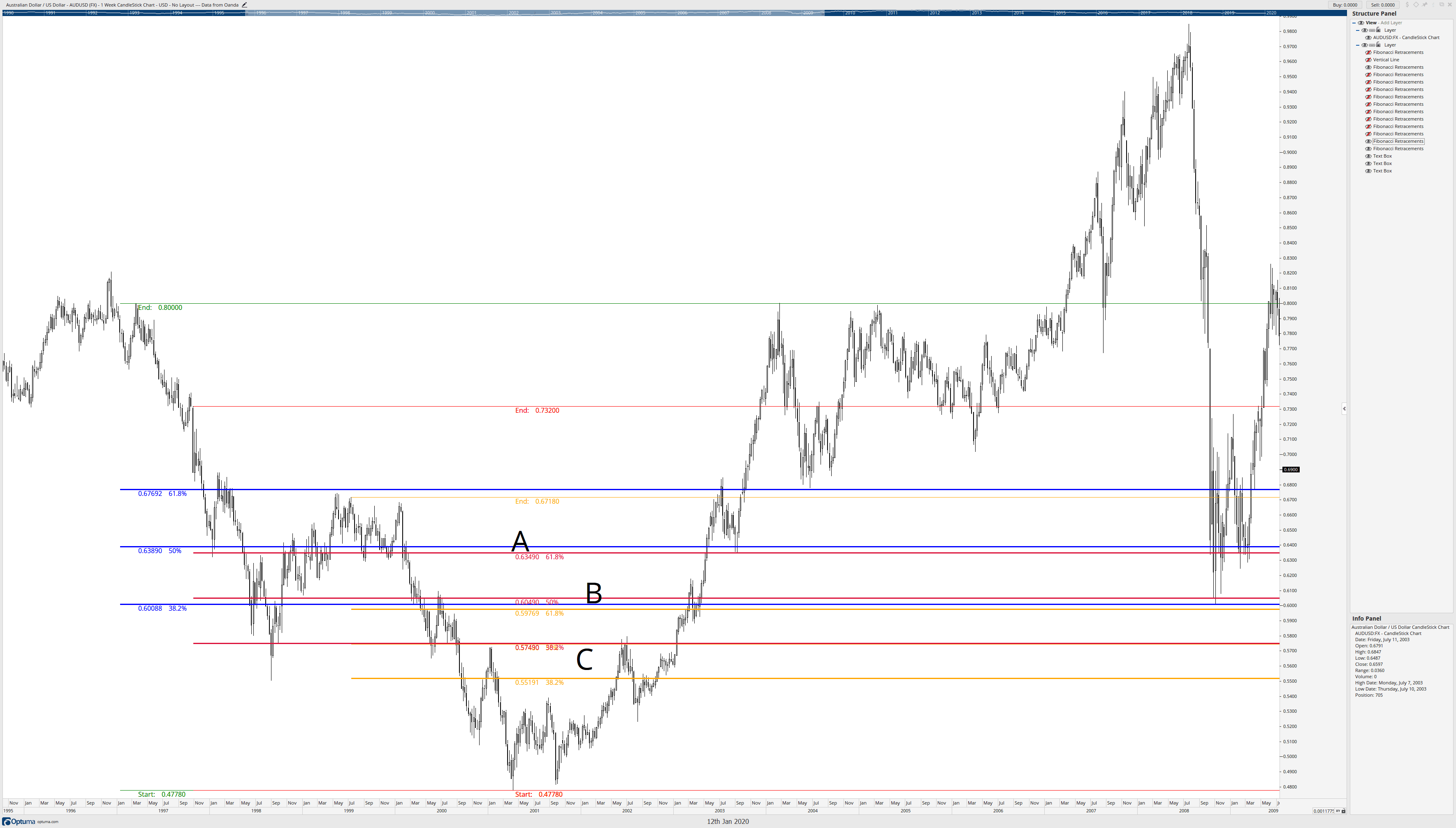
The above image is the first retracement we looked in this article (the same swing low in March 2001) using the same swing low; we draw more retracements to the next confirmation swing lower highs. I’ve drawn two additional Fibonacci retracements in Red and Orange. Notice how some of the Fibonacci retracements occur within proximity of one another. Letter A is shared retracement zones of the 50% and 61.8% of two different retracements. B has a confluence zone of three Fibonacci retracement levels, 50%, 61.8%, and 38.2%. And C has two overlapping retracements of 50% and 38.2%. Now let’s get to the fun part.
The previous image showed three Fibonacci retracement confluence zones at A, B, and C. Those confluence zones were just three of many that will appear on any chart on any time frame. What happens if we draw a series of retracements using major swings as the start point of the Fibonacci retracements and then retrace to the next confirmation swing highs and lows? We’ll get a chart that looks like the one below.
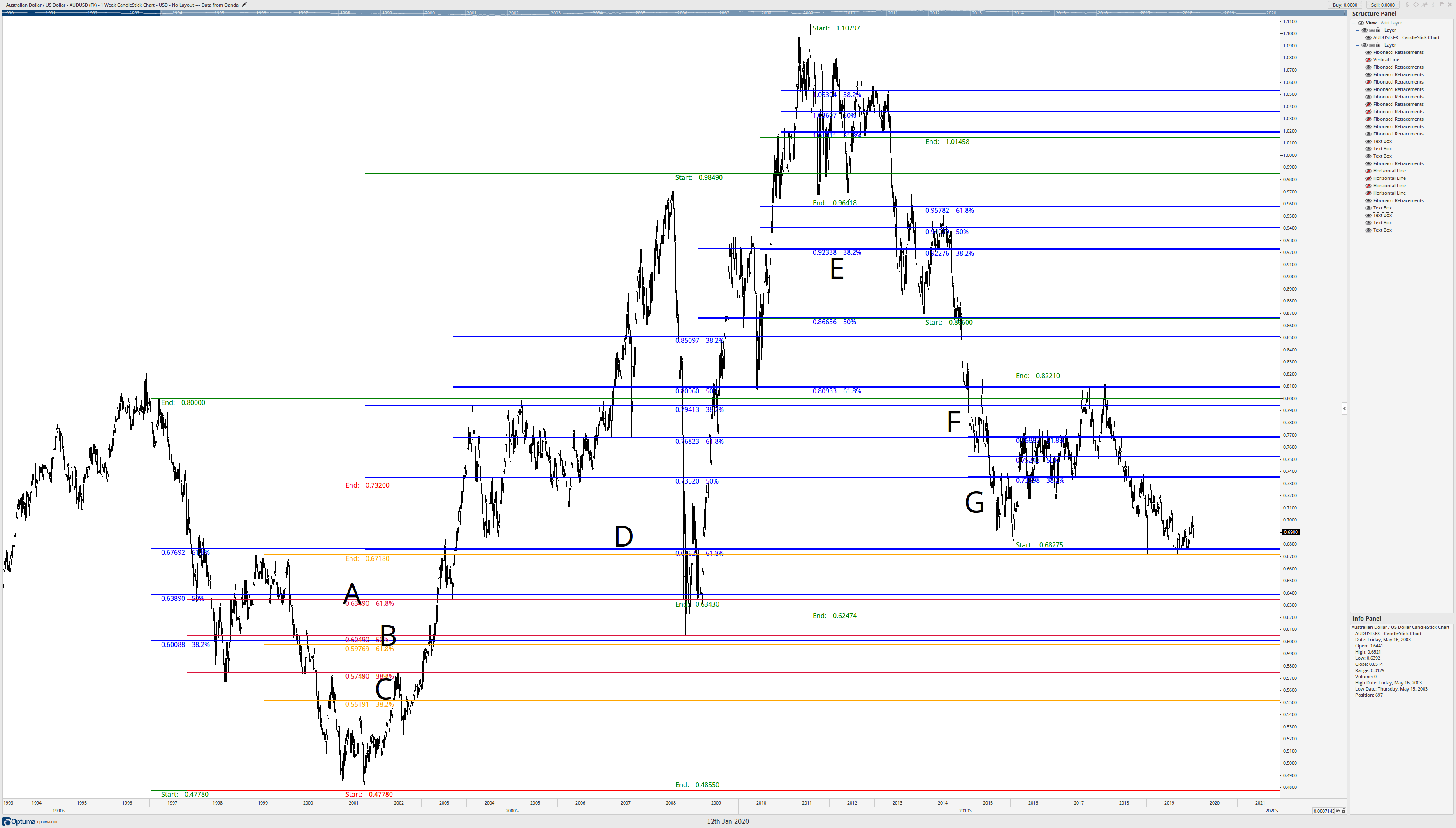
I’ve added some other letters to identify more confluence zones. I admit the chart does look like a mess. And it should. Not every Fibonacci retracement to a new confirmation swing high or low will coincide with shared Fibonacci levels, but they frequently do. Once we’ve drawn out a series of retracements, we should see a set of these confluence zones. Now begins the cleanup phase. We’re going to place horizontal lines where there are confluence zones of Fibonacci retracement levels.
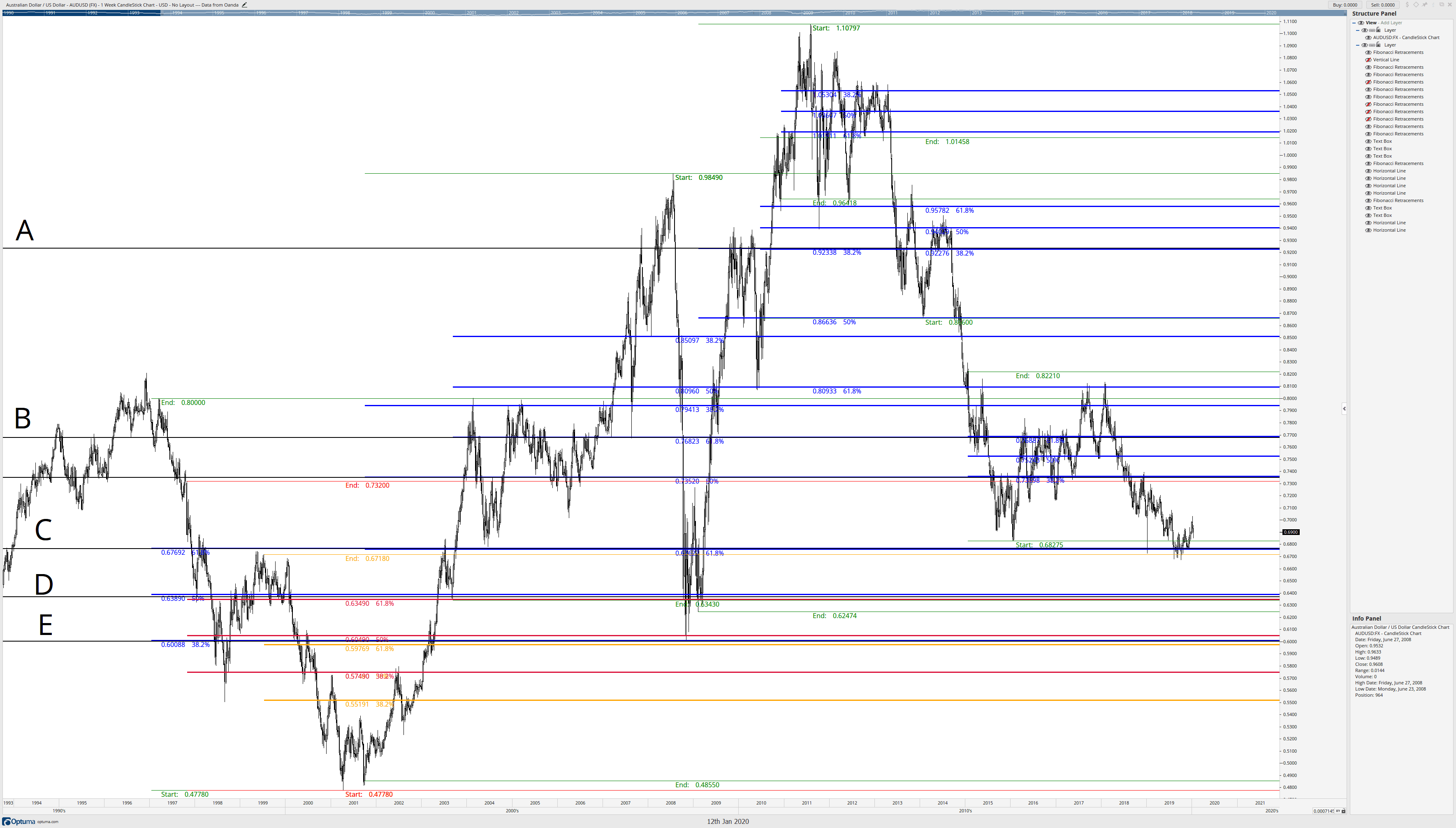
The letters A, B, C, D, and E show where the Fibonacci confluence zones have formed, and are represented by horizontal lines (black) on the chart. Now, you can either delete or hide all of the Fibonacci retracements so that we are left with only the horizontal lines at A, B, C, D, and E.
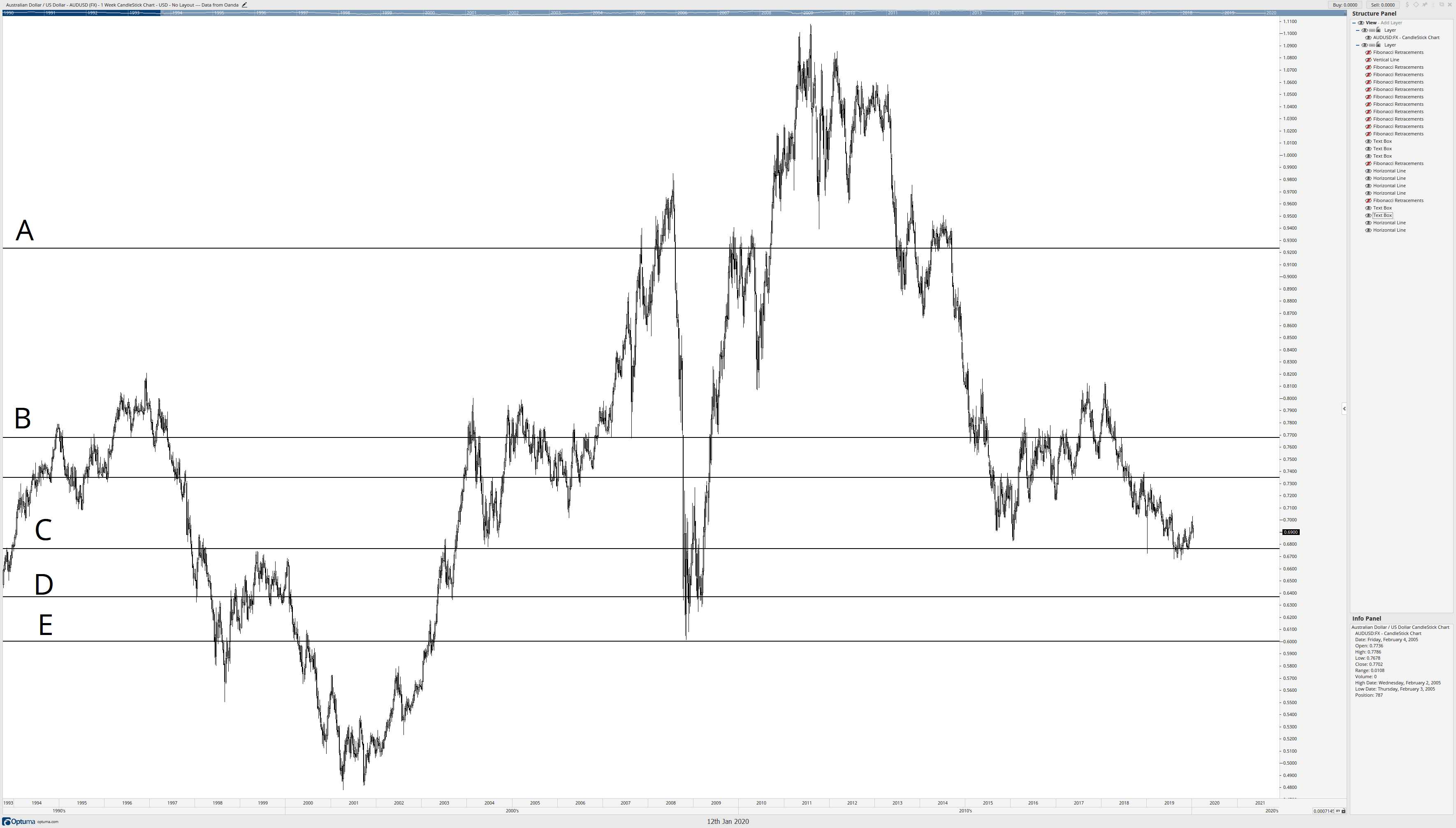
I know that the horizontal line at D represented the most confluence zones on the AUDUSD weekly chart, but it also represented some of the longest-lasting and respected Fibonacci retracement levels. Starting at the horizontal level at D, I draw a box from D down to the major low on the AUDUSD chart. Now, the width of this box doesn’t matter – just the range.
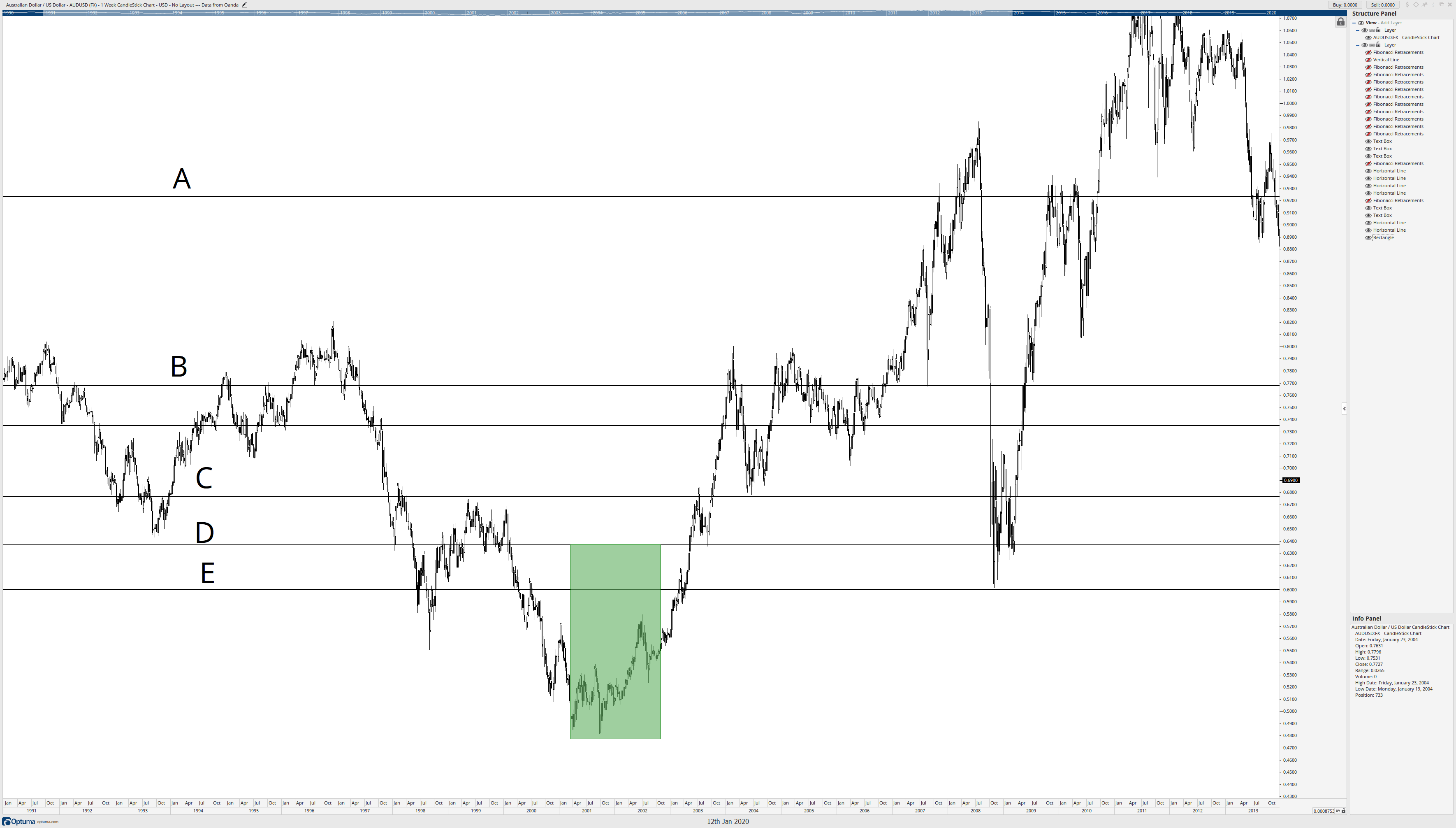
After I’ve established that box from D down to the major low, I can remove the horizontal lines. Then I start to copy the box all the way to the top of the range. All I’m doing here is copying and pasting the box so they ‘stack.’
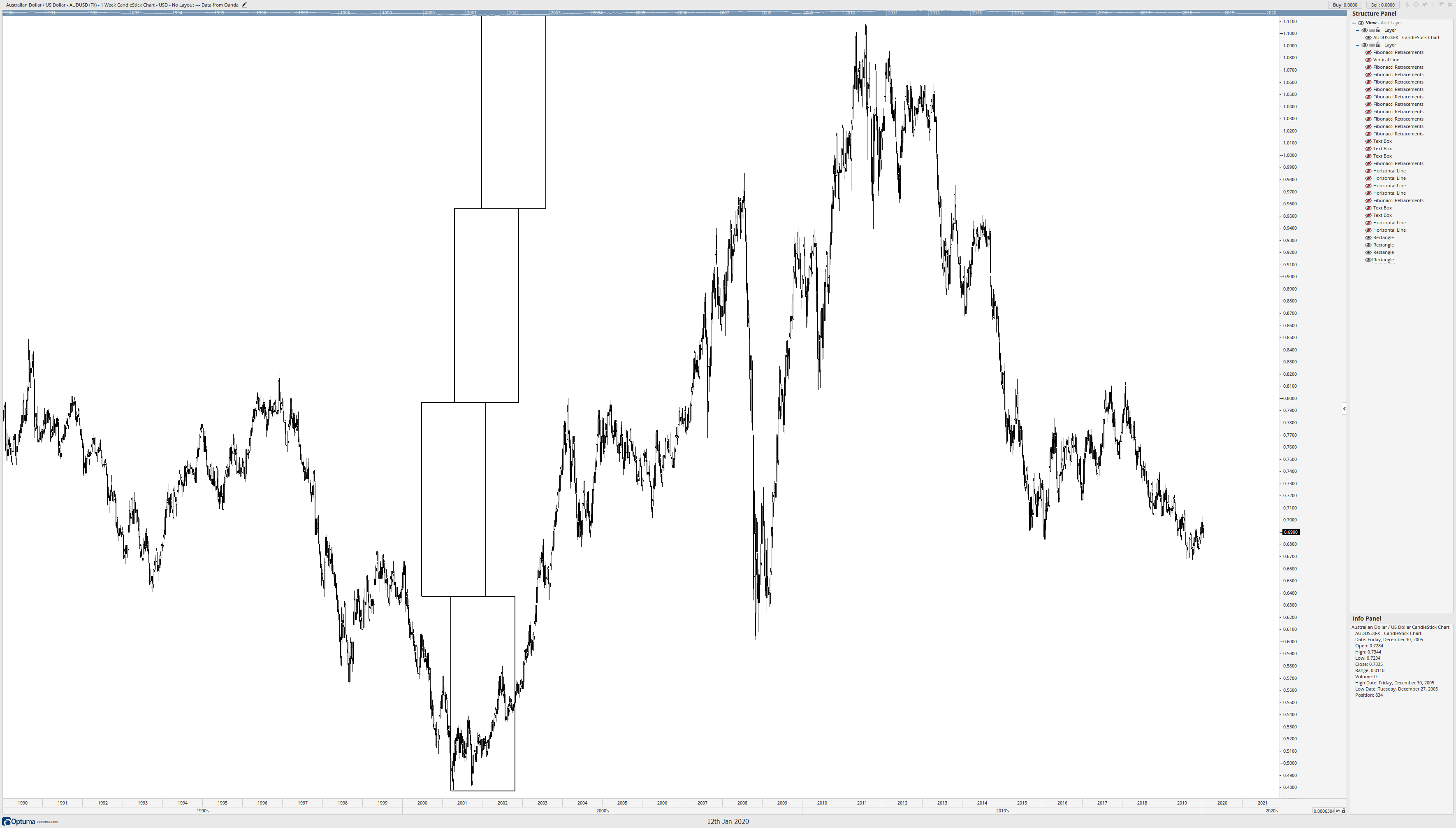
Now comes the cool part. I’m going to treat each box like its own range and place Fibonacci retracements inside each box, moving from bottom to top.
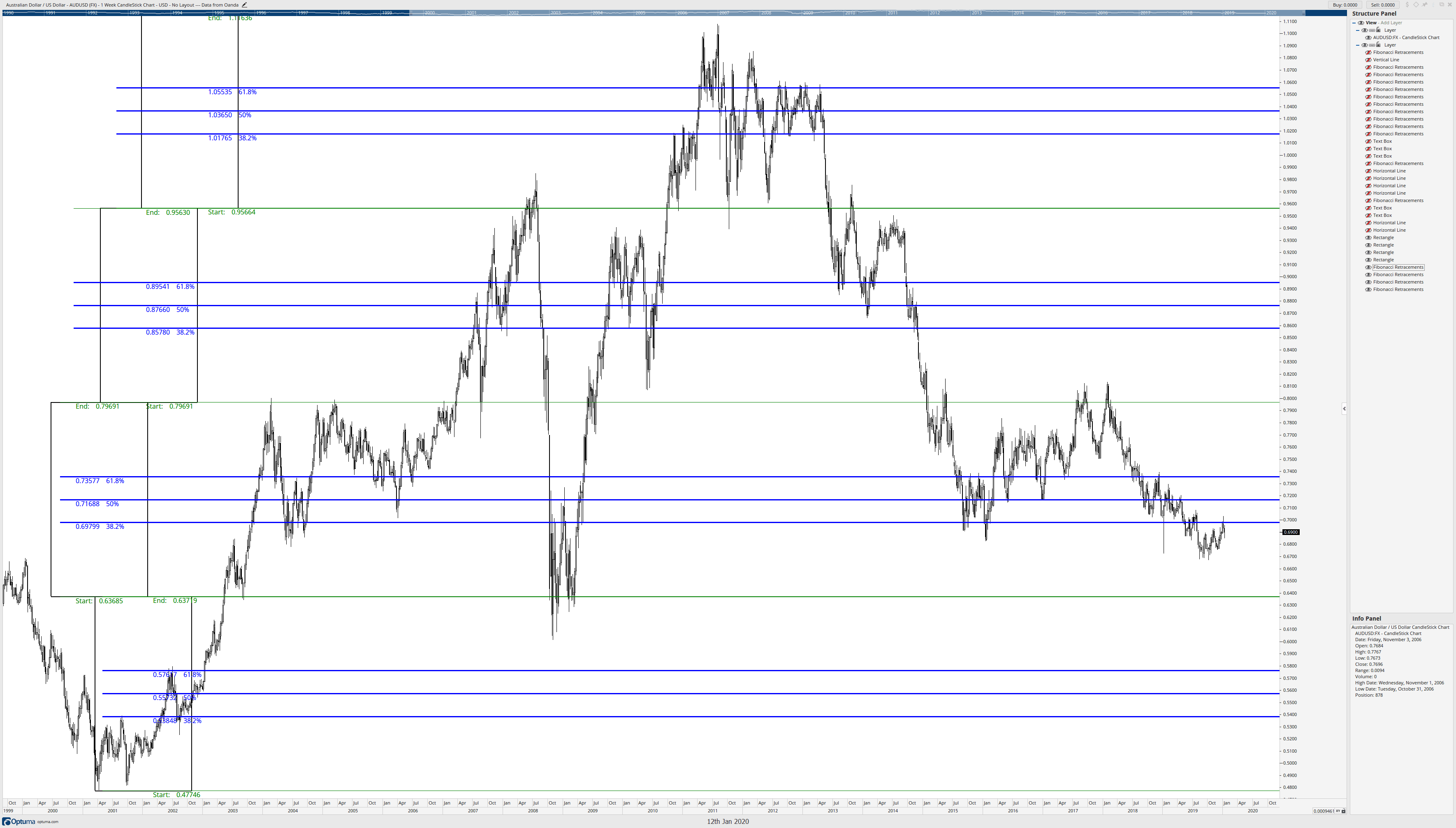
No matter how many times I’ve done this, it still blows my mind. But there is probably a lingering question. You’re probably looking at the chart and saying, ok, cool, but there are some massive gaps between these Fibonacci levels. You are correct if you are thinking about this. Now, Connie Brown never wrote about this next part; it’s something I discovered and developed on my own. The approach comes from the idea that markets are fractalized and proportional, so we should be able to break down like zones into smaller ranges. This is especially important and useful for traders who prefer to trade on faster time frames like four-hour or one-hour charts. Using price action that is more recent and relevant, I can draw a Fibonacci retracement from the 50% level at 0.71688 to the start/end of the box at 0.6368.
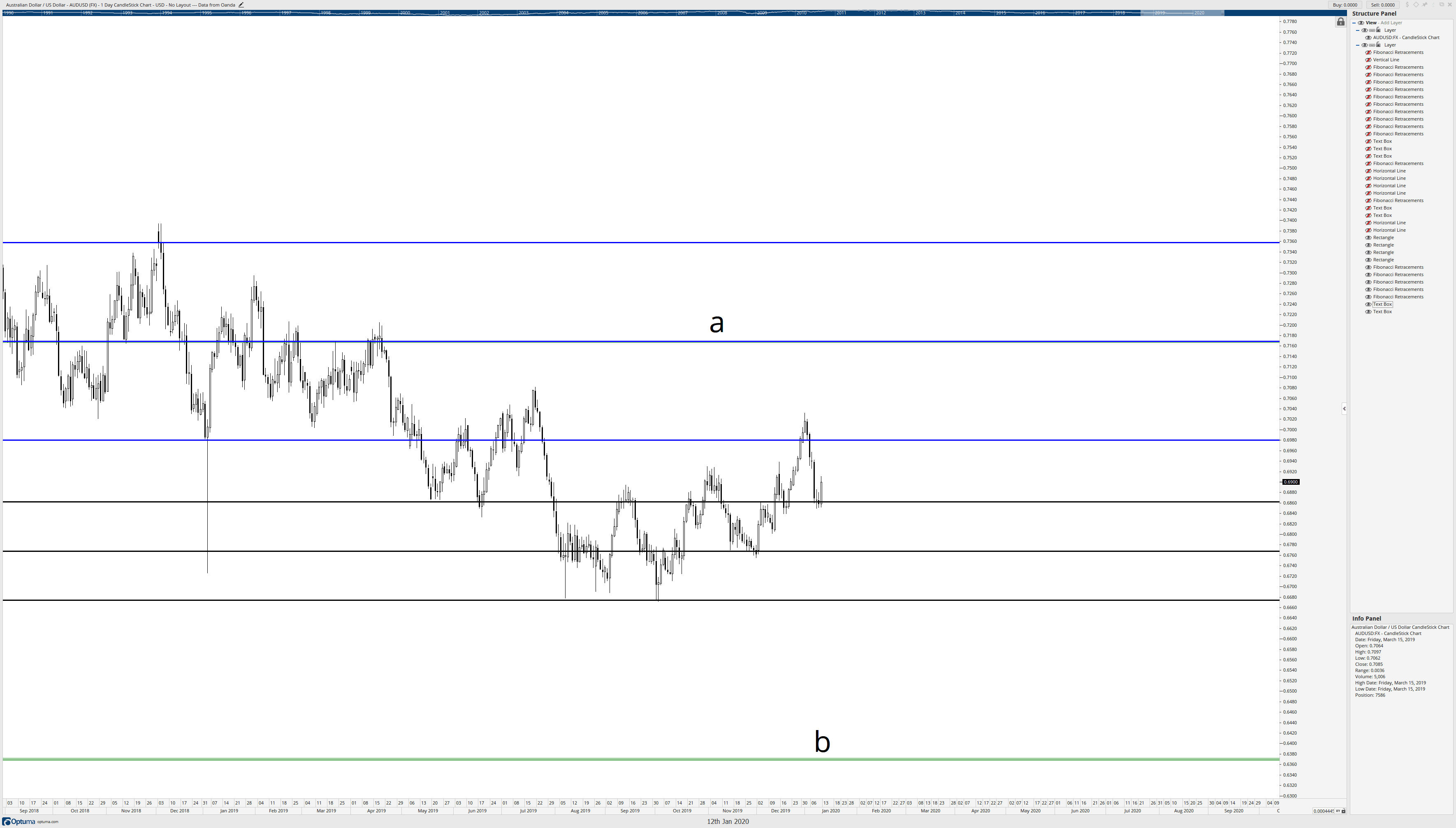
Letters a and b on the chart above identify the 50% Fibonacci level and start/end level described in the prior paragraph. The black horizontal lines represent the Fibonacci retracement drawn from a to b. I’ve also switched the chart from a weekly chart to a daily chart. When we see that daily chart, we get a real idea of how powerful the Brown Method of Fibonacci analysis is and how precise the study of these confluence zones can be.
In summary, to utilize the Brown Method, the followings steps are as follows:
- Create Fibonacci retracements by using a major swing high/low and drawing to the confirmation swing with a strong bar – not the next extreme high/low.
- After identifying Fibonacci confluence zones, place horizontal lines on the major price levels where multiple Fibonacci levels share the same price range.
- Delete or hide the Fibonacci levels so that only the horizontal lines are present – make sure you identify which horizontal line had the most powerful collection of Fibonacci levels.
- After identifying which horizontal line was the most potent and relevant, determine if it is closer to the all-time high or all-time low. Draw a box or a price range from that horizontal line to the all-time high or low – whichever is closest.
- Repeat the boxes by copying the same box and ‘stack’ it to the all-time high/low – the opposite of whichever was used to establish the box/price range.
- Draw Fibonacci retracements in the boxes.
Sources:
Brown, C. (2010). Fibonacci Analysis: Fibonacci Analysis. Hoboken: Wiley.
Brown, C. (2019). The Thirty-Second Jewell: Thirty Years Behind Market Charts From Price To W.D. Gann Time Cycles. Tyton, NC: Aerodynamic Investments Inc.