Introduction
Economic output from the Agriculture Sector is non-negotiable for the economy. The increasing population must be fed and meet the demands of consumption at all times. Hence, the Central Government is committed to making positive growth in the Agriculture Sector. Agriculture Sector is the primary sector where Government Spending goes.
Since food is an essential commodity, it is an ever-green industry that will never run out of demand. Hence, understanding this sector can help us understand dependent industries’ performance and expenses associated with personal consumption.
What is GDP from Agriculture?
Gross Domestic Product
GDP is the measure of a country’s total economic output. It is the total monetary value of all the goods and services produced within the country regardless of citizenship (resident or foreign national).
It is the market value of all the finished goods and services within a nation’s geographical borders for a given period. The period is generally a quarter (3 months) or a year.
Agriculture Sector
Also, it accounts for all the activities associated with crop production called the Primary Sector of an economy. From the point of cultivation to end-marketing of the food products all are accounted under the Agriculture Sector. It primarily includes farming, fishing, and forestry.
The quick increase in the world population has put pressure on the Agriculture sector to bring innovations through science and technology to increase crop yield. Agriculture Sector is the primary source of food for a country’s population.
The Agriculture Sector goes beyond farm business and includes farm-related industries like Food Service and Food Manufacturing (Packaged Foods, Processed Foods).
How can the GDP from Agriculture numbers be used for analysis?
The agriculture sector contributes about 6.4% of the World GDP. The most significant contributor to this being China, followed by India. China accounts for 19.49%, and India accounts for 7.39% of total agricultural output. The United States is in third place.
It is necessary to understand the economic output of Agriculture is a function of population, as China, India, and the USA are ranked in population terms in the same order.
The three sectors of the economy, namely, primary Sector, secondary (Industry) Sector, and tertiary (Service) sector, contribute to the overall GDP. It is common for developed nations to have a high contribution to GDP from the Service Sector. Developing economies like China, Japan would have higher contributions from the Industry Sector. The underdeveloped economies would have Agriculture or Primary Sector as a leading contributor to GDP.
In the United States, the entire Agriculture Sector contributes about 5.4% of the GDP. The farms have only contributed 1% of GDP, and the rest is contributed to by the dependent industries that rely on agricultural input to produce goods. The Food Service, Textiles, Beverages, Processed Foods, Tobacco products, etc. contribute the remaining 4% to the GDP.
11% of the total U.S. employment is accounted for by the Agriculture Sector, which is about 22 million jobs in 2018. Food accounts for 13% expenditure of an average American Household.
It is essential to understand that food is an essential requirement for conducting our livelihood. Hence, Government Spending first prioritizes the Agriculture Sector and releases benefit programs to assist the sector and maintain and grow its economic output. The society and Government will quickly collapse if the Agriculture Sector slows down, and that is why it is called the “Primary Sector.”
The Government Outlays on Food Programs and Nutrition Assistance exceeds that of any other federal program. Improper management and assistance to the Agriculture Sector can lead to price hikes in the food industry. It would trigger a negative response from the public that could cost them in the next elections. Hence, the Government is committed to assisting the Agriculture Sector at all times, good or bad.
Impact on Currency
GDP from Agriculture in itself is not a high impact indicator, as the broader measures like Real GDP and GDP Growth Rates are more important for the Currency Markets.
GDP from Agriculture does not paint the full picture of the economy, but can be an essential tool for the Central Authorities to keep track of Agriculture Sector performance. Businesses dependent on Agriculture input may use this data to understand potential business opportunities amongst different countries. Still, for the International Currency Markets, it does not serve as a useful indicator.
It is a proportional and lagging indicator. Higher GDP from Agriculture is good for the economy and its currency, and vice-versa.
Economic Reports
For the United States, the Bureau of Economic Analysis releases quarterly GDP figures on its official website every quarter. The release schedule is already mentioned on the website and is generally released one month after the quarter ends.
In the full report, we can extract the GDP from Agriculture figures. We can also go through GDP by Industry to get the Construction Industry performance in the report. Major international organizations like the World Bank, CIA World Factbook, etc. actively maintain GDP by Sector figures of most countries on their official website.
Sources of GDP from Agriculture
For the United States, the BEA reports are available in the sources mentioned below.
GDP -BEA | GDP by Industry – BEA | FARM – GDP
The St. Louis FRED keeps track of all the GDP and its related components in one place on its official website here. World Bank also maintains the Agriculture Sector as a percentage of GDP on its official website. We can find GDP sector composition for different countries here. We can find the consolidated list of Agriculture – GDP figures for most countries here.
Impact of the “GDP from Agriculture” news release on the Forex market
The agricultural sector plays an essential role in the process of economic development of a country. It contributes to the economic prosperity of advanced countries, and its role in the economic development of underdeveloped countries is of vital importance. In other words, countries where per capita real income is low, the emphasis is laid on agricultural and other primary industries.
History tells us that agricultural prosperity contributed considerably to the national income and the GDP. When we are talking about the impact of this contribution on the currency, we will have to say that it is least and not of much importance to investors. They look at broader data, which is the GDP, and make decisions based on the reading.

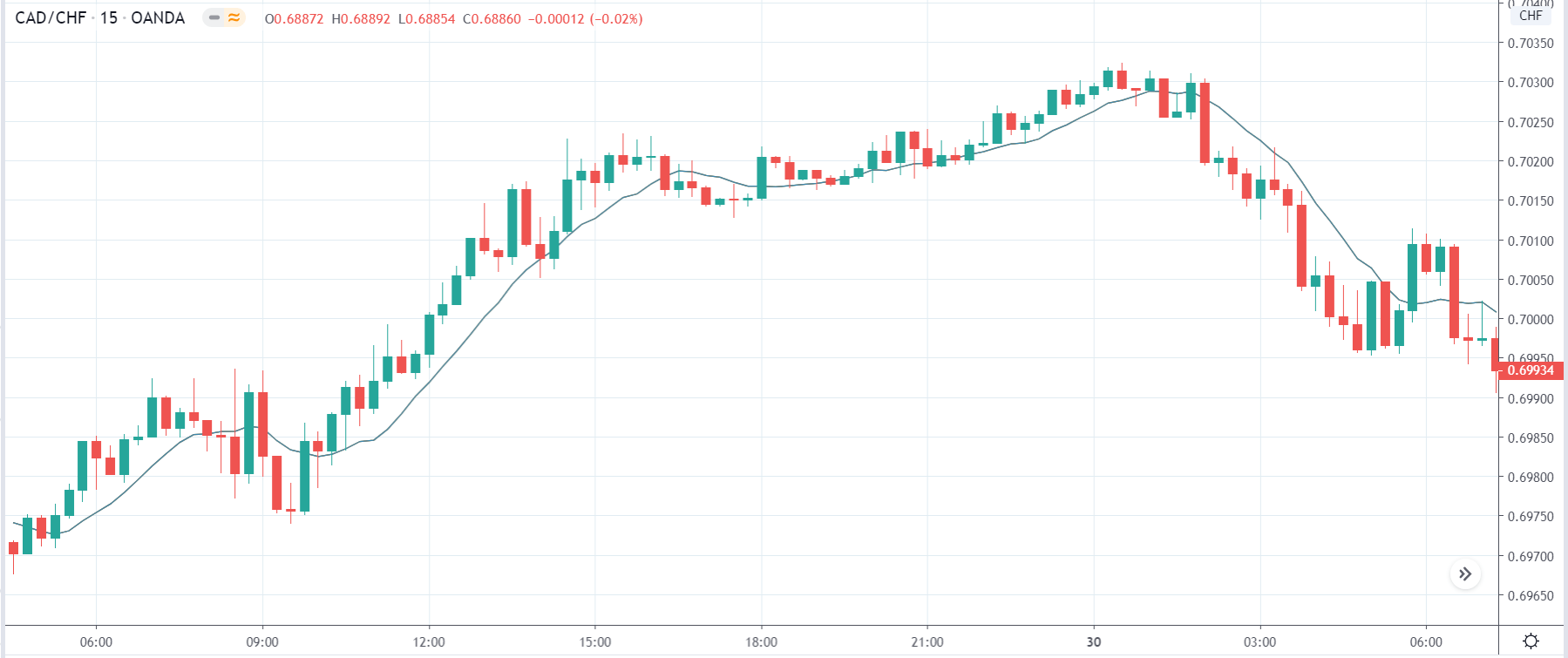
In today’s example, we will examine the impact of GDP on different currency pairs and observe the volatility due to the news announcement. The below image shows the latest quarter GDP data of Australia, where it was more or less the same as in the quarter. Let us find out the reaction of the market to this news release.
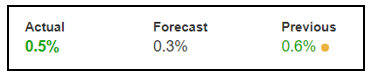
AUD/USD | Before the announcement:
We will first look at the AUD/USD currency pair to observe the impact of GDP on the Australian dollar. In the above image, we see that the market is in an uptrend, and recently the price seems to have retraced the up move. This is an ideal chart pattern for joining the trend, but since a significant news announcement is due, we need to wait to understand the impact it creates on the chart.
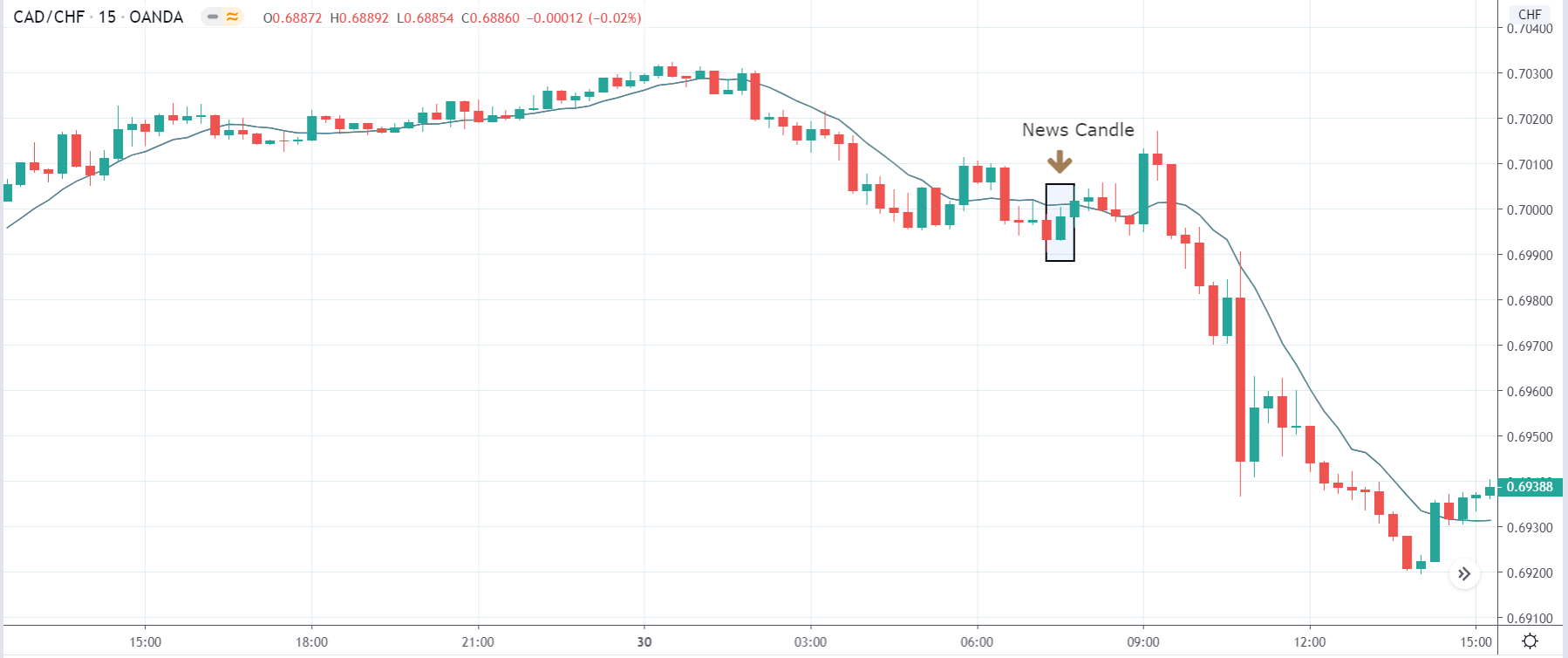
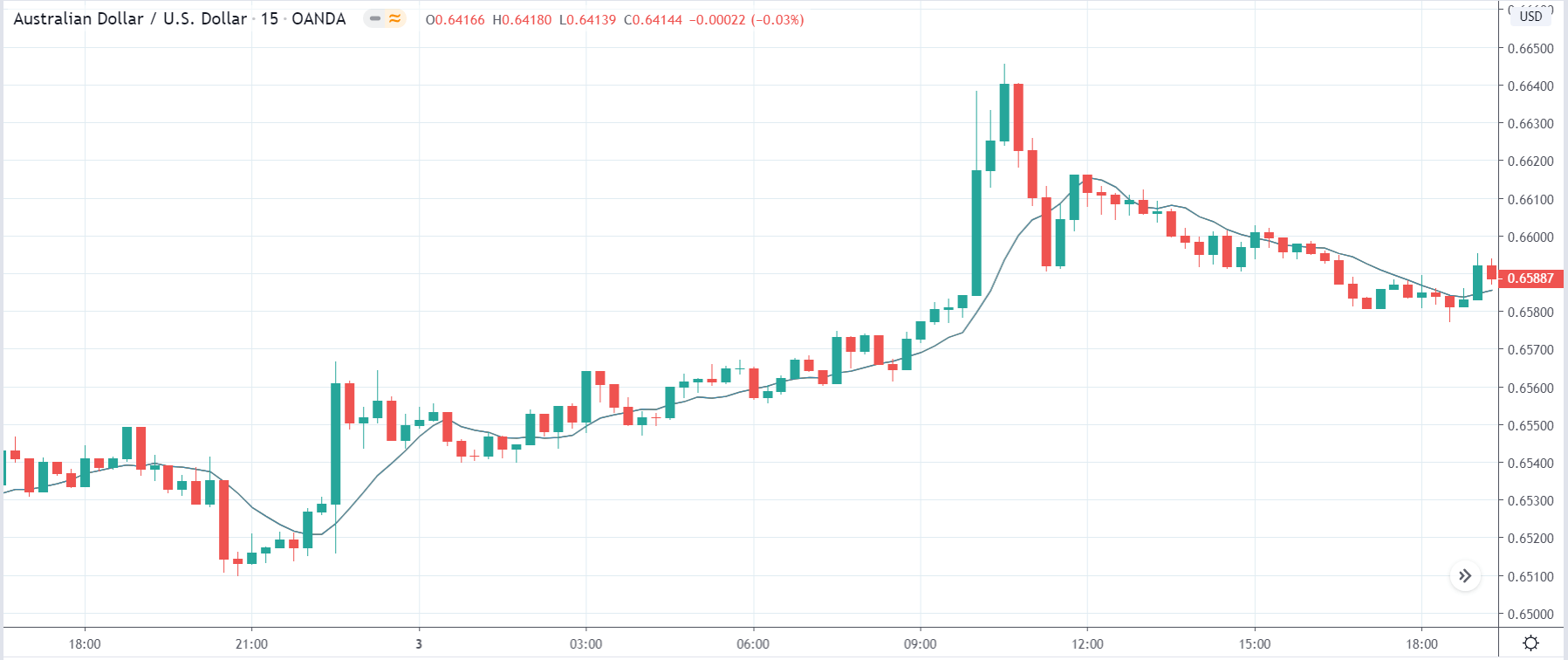
AUD/USD | After the announcement:
After the news announcement, the market moves higher, where the price rises sharply above the moving average. The bullish ‘news candle’ is a consequence of better than expected GDP data, which was higher by 0.2%. Although it was marginally less than the previous quarter, it turned out to be positive for the currency. This is a confirmation sign of trend continuation where one can expect a new ‘higher high.’
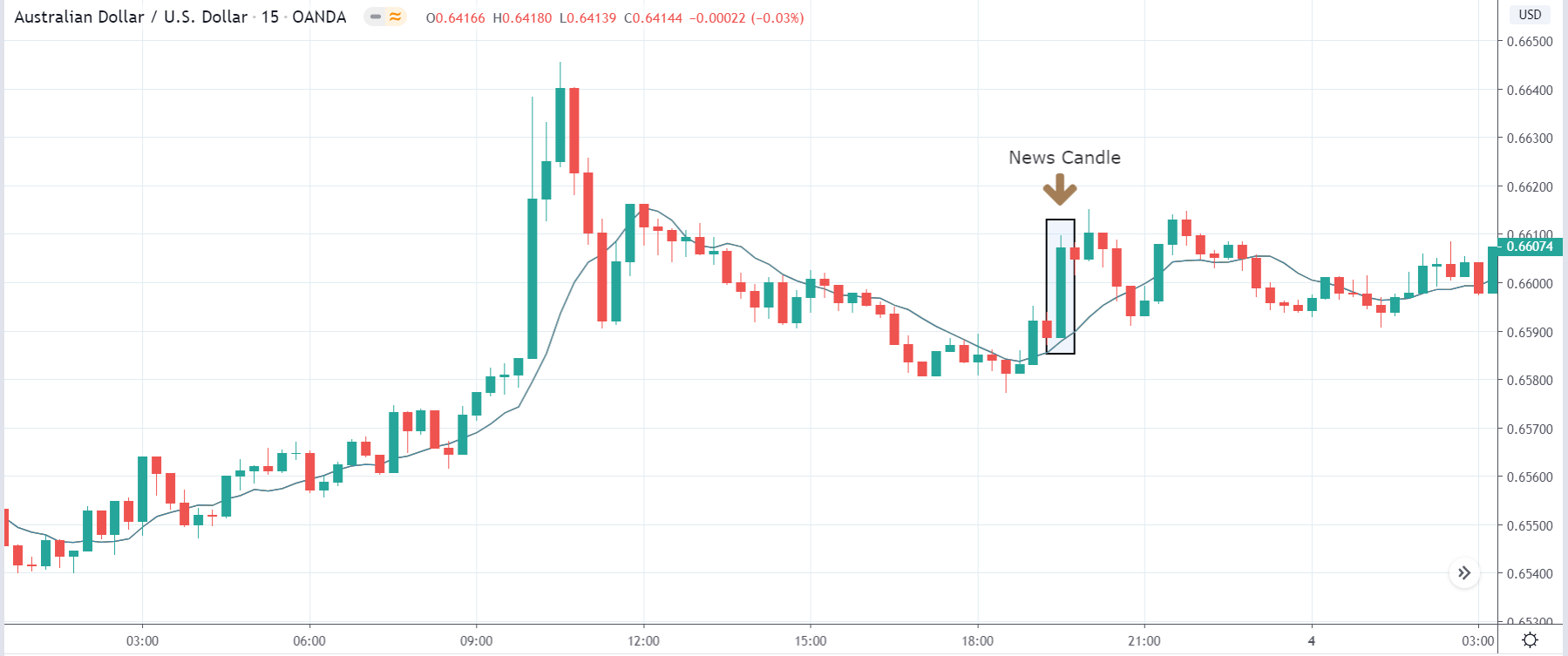
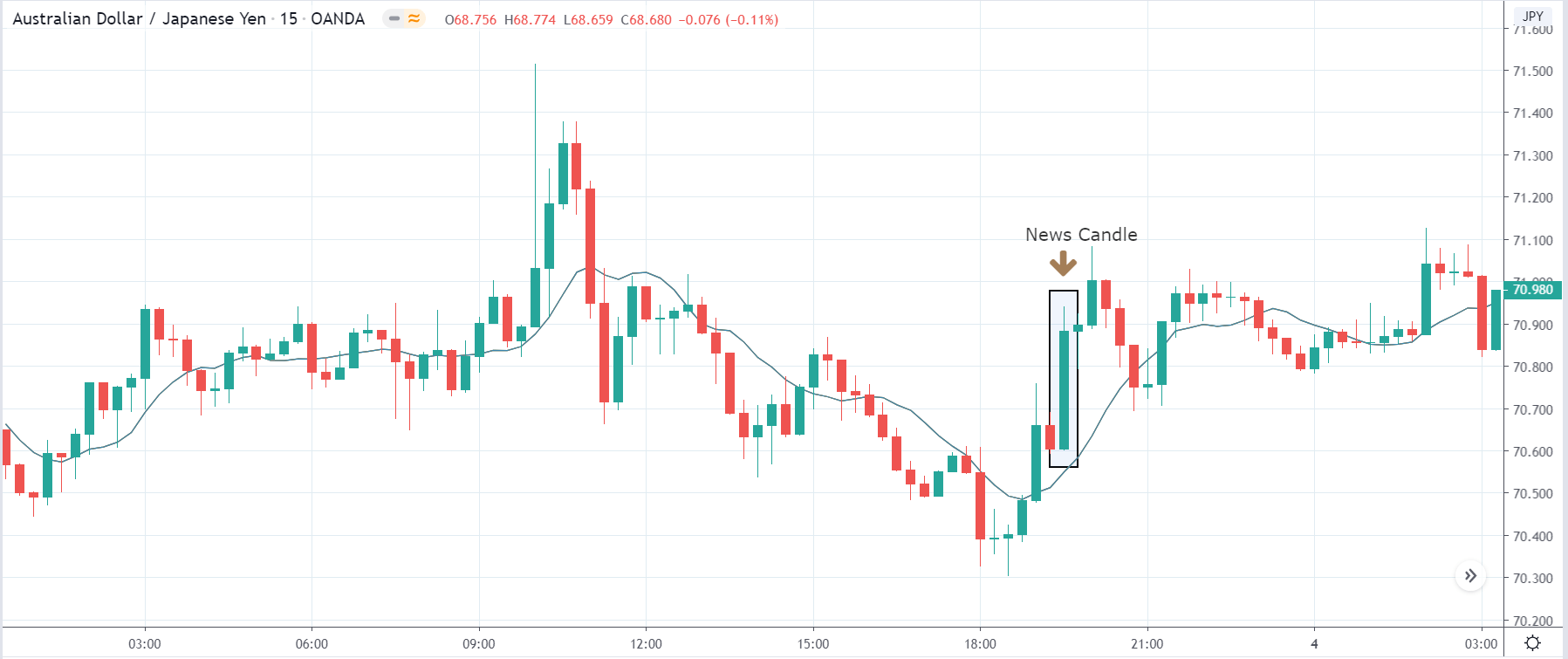
AUD/JPY | Before the announcement:
AUD/JPY | After the announcement:
The above images represent the AUD/JPY currency pair, where the market moves within a ‘range’ before the news announcement. We also notice an initial reaction from the ‘support’ where the price has moved higher from the ‘low.’ Since economists have forecasted a lower GDP estimate in the fourth quarter, it is not recommended to take a ‘long’ position before the news release.
After the news announcement, we see that the price quickly moves up, and market surges to the upside. As the GDP data was beyond expectations, traders bought Australian dollars and strengthened the currency. Therefore, the news release has a hugely positive impact on the currency pair. In this pair, once needs to be cautious before taking buy trade as the price is at the top of the ‘range.’
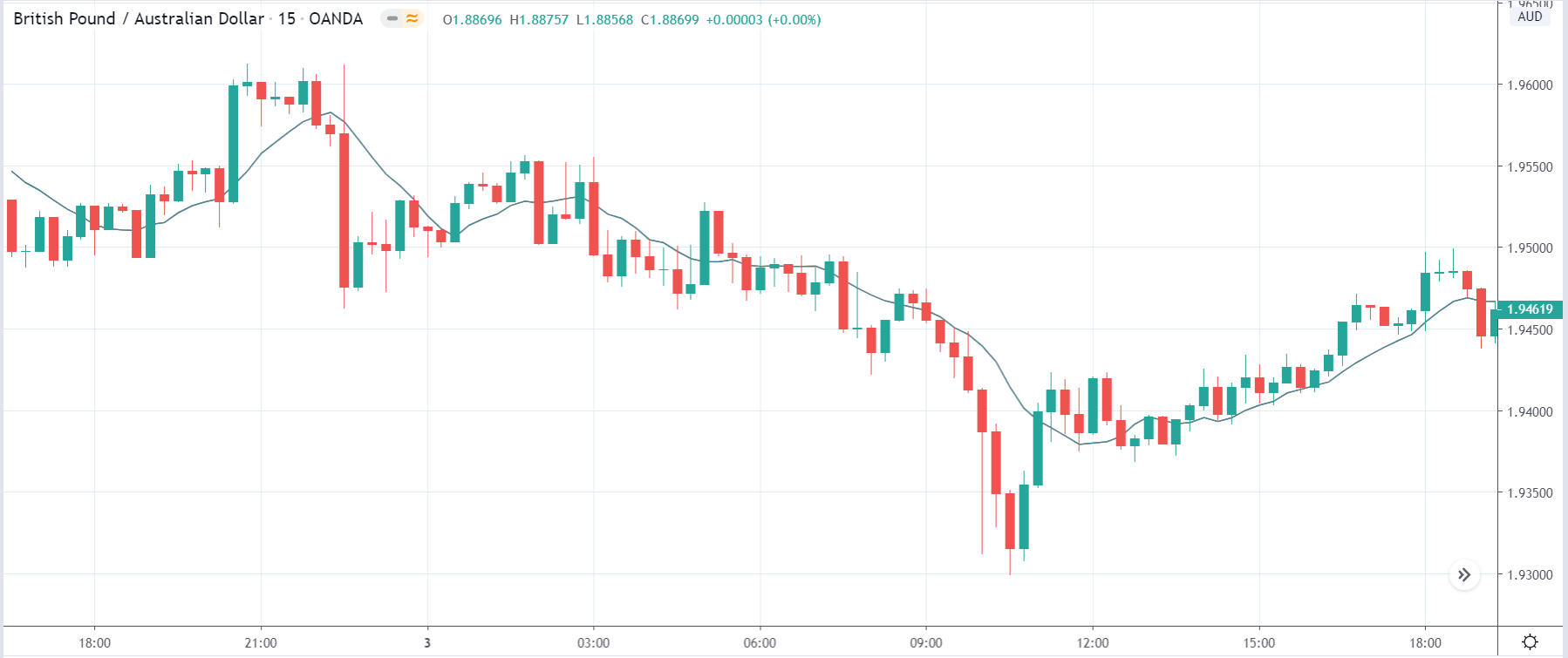
GBP/AUD | Before the announcement:
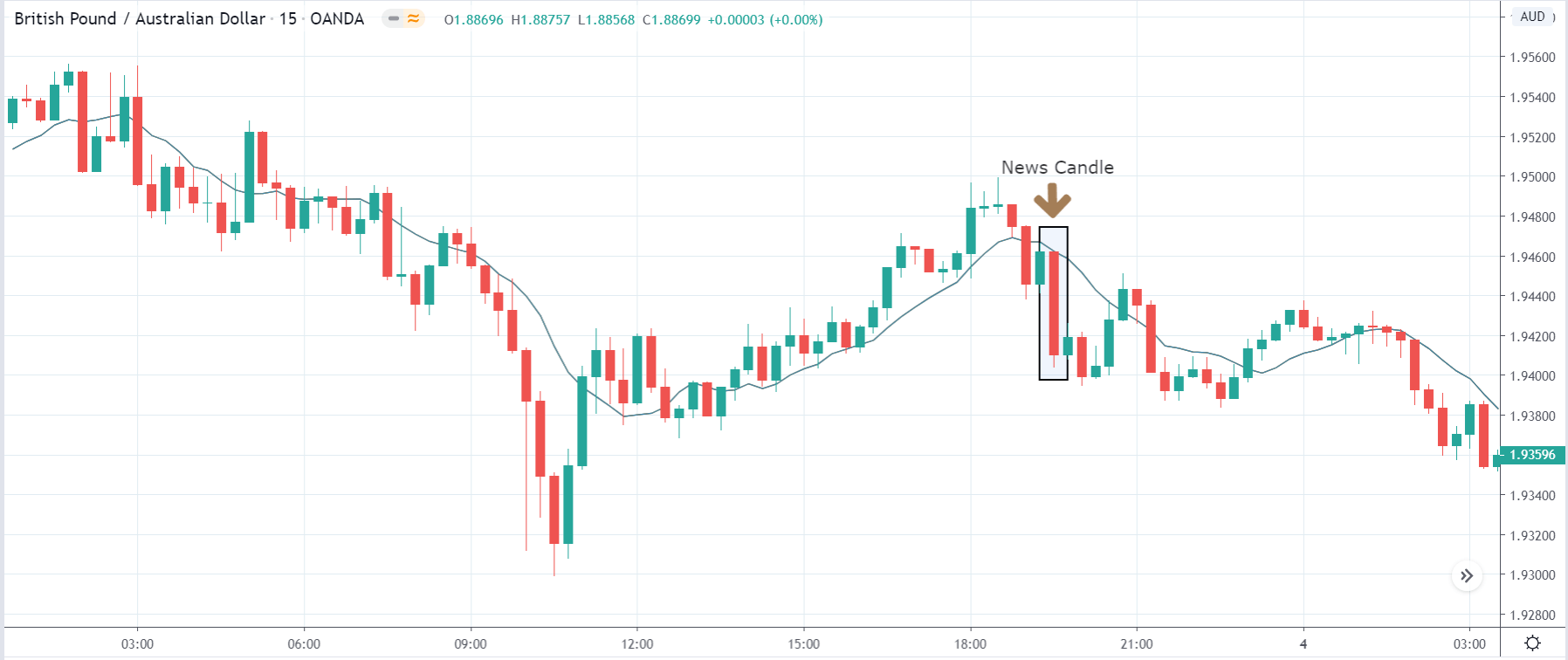
GBP/AUD | After the announcement:
The above images are that of GBP/AUD currency pair, where we see that before the news announcement, the market has retraced the downtrend by more than half, indicating that the Australian dollar has gained strength newly. After the occurrence of trend continuation candlestick patterns, it could result in a flawless sell trade. However, there is also a probability that the news release could change the dynamics of the chart.
After the news announcement, market crashes and the price significantly moves lower. As the GDP data was positive for the economy, it leads to bullishness in the Australian dollar resulting in the price fall. One could take a risk-free ‘short’ position at this point, expecting the market to move much lower.
That’s about ‘GDP from Agriculture’ and its impact on the Forex market after its news release. If you have any questions, please let us know in the comments below. Good luck!
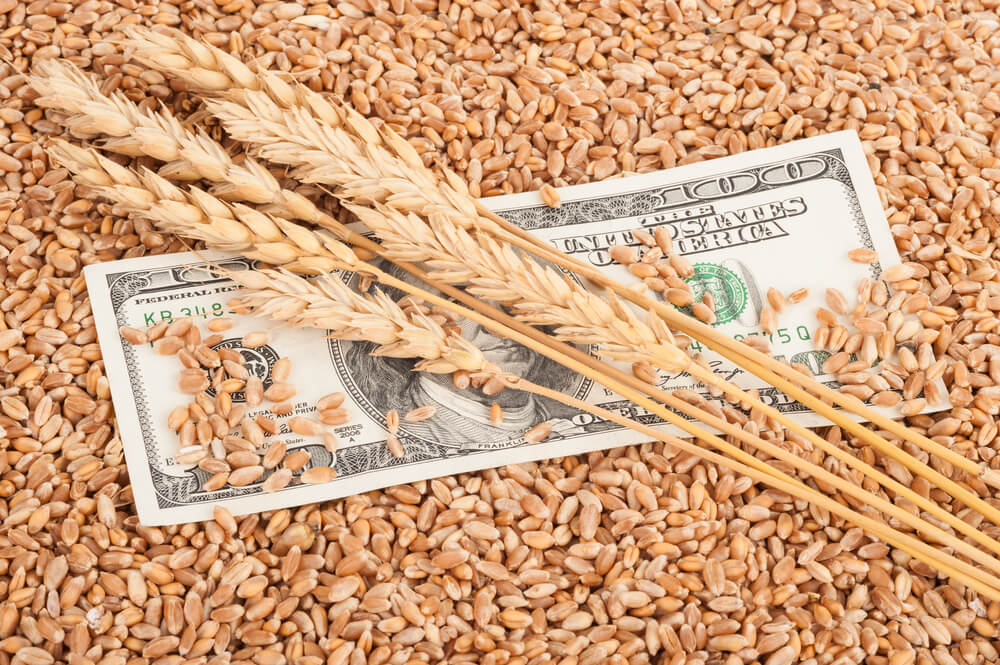



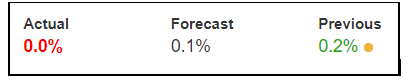
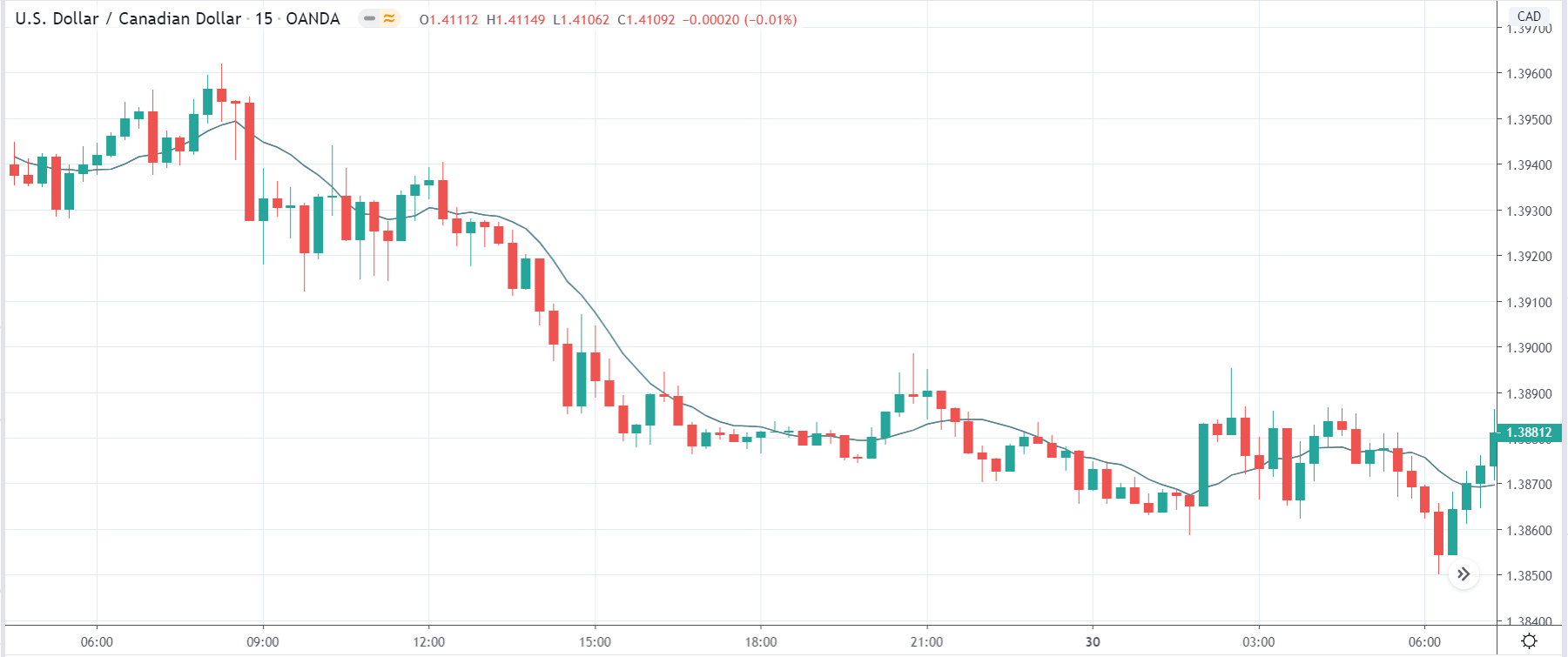
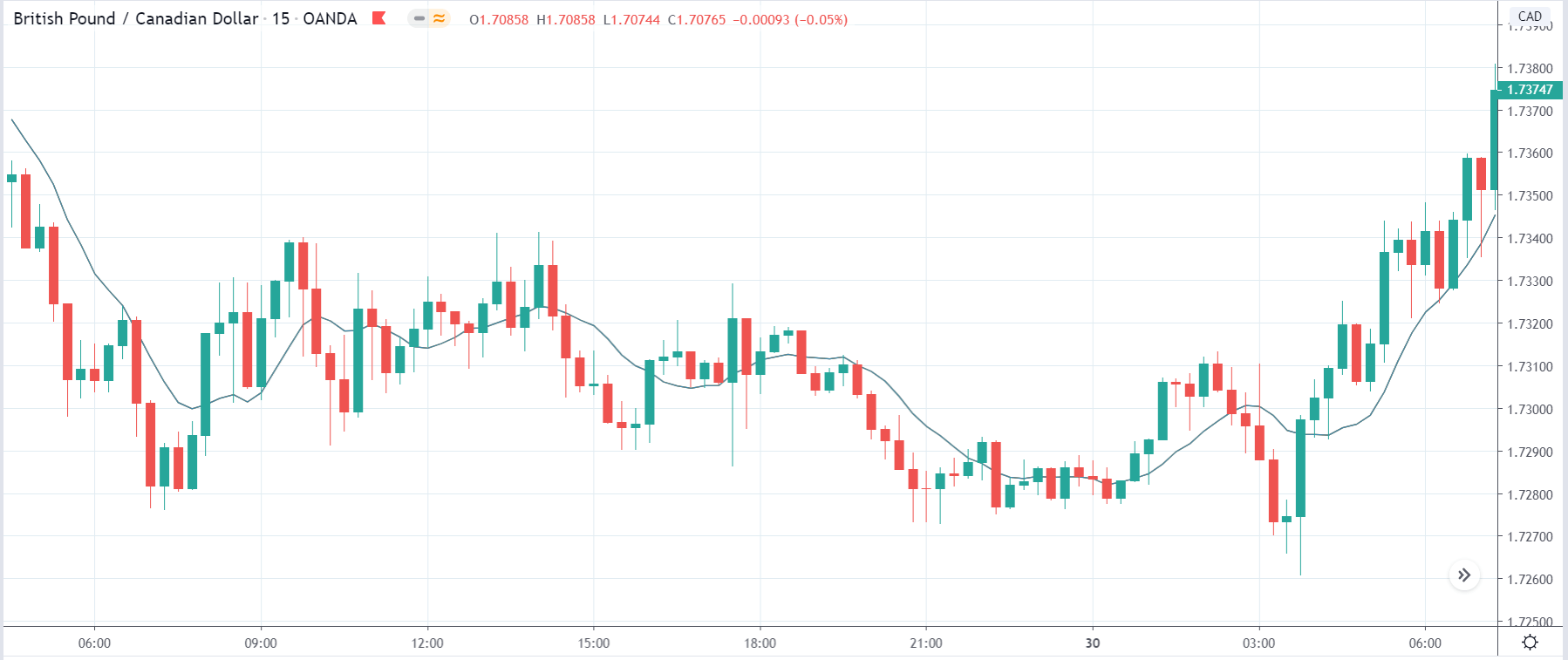
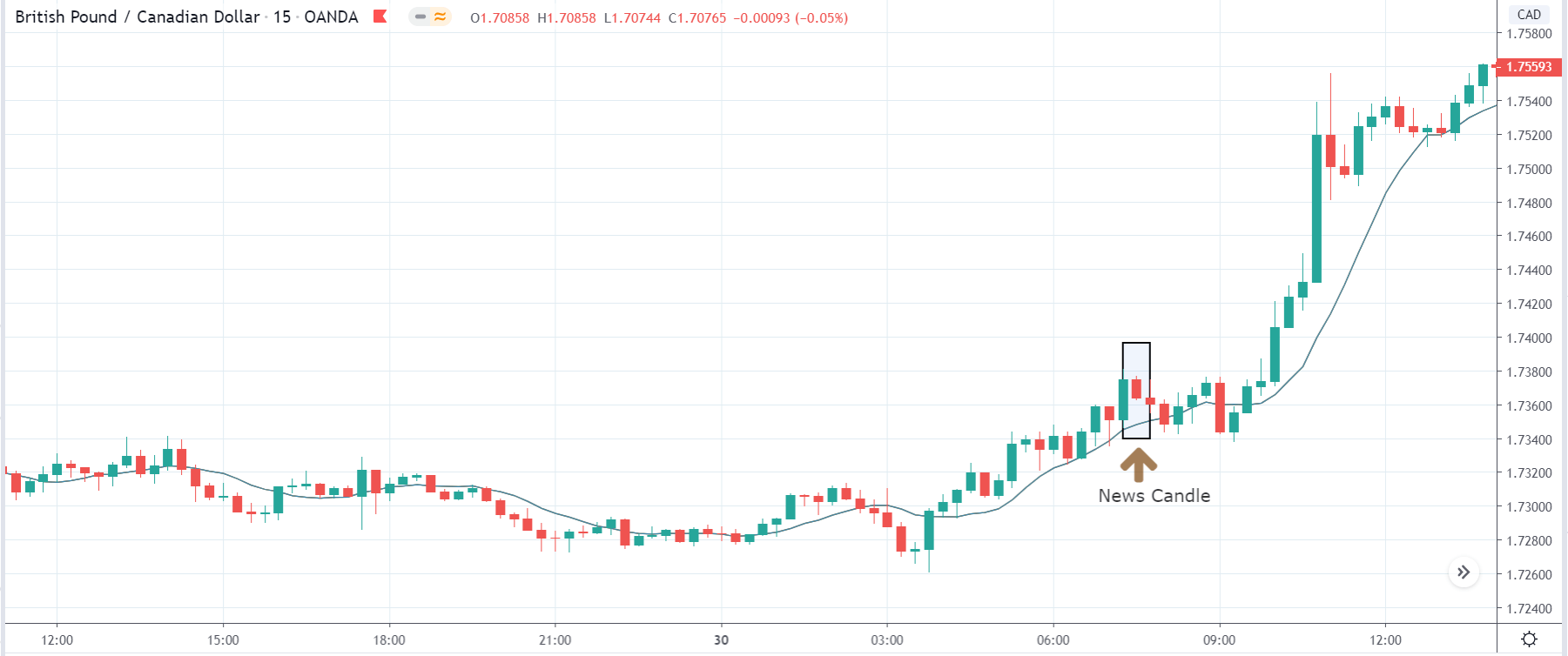
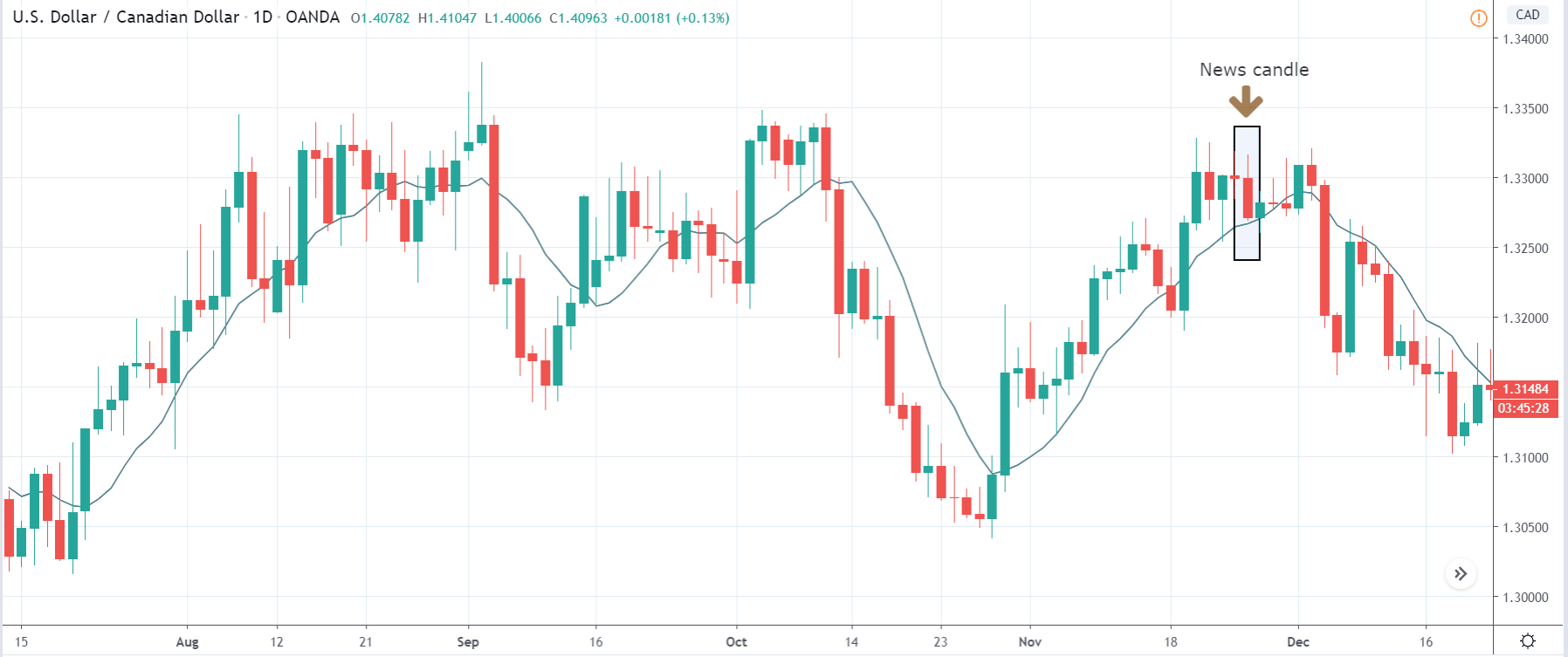
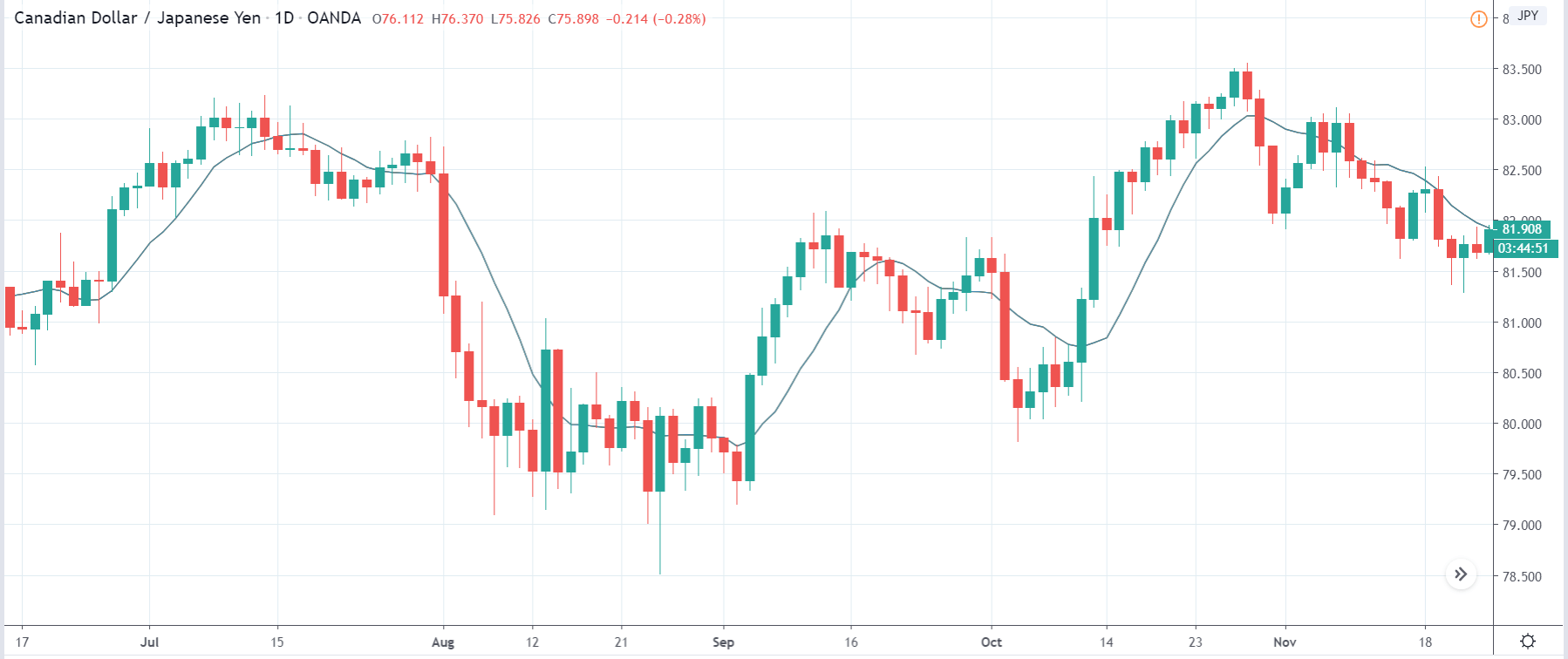
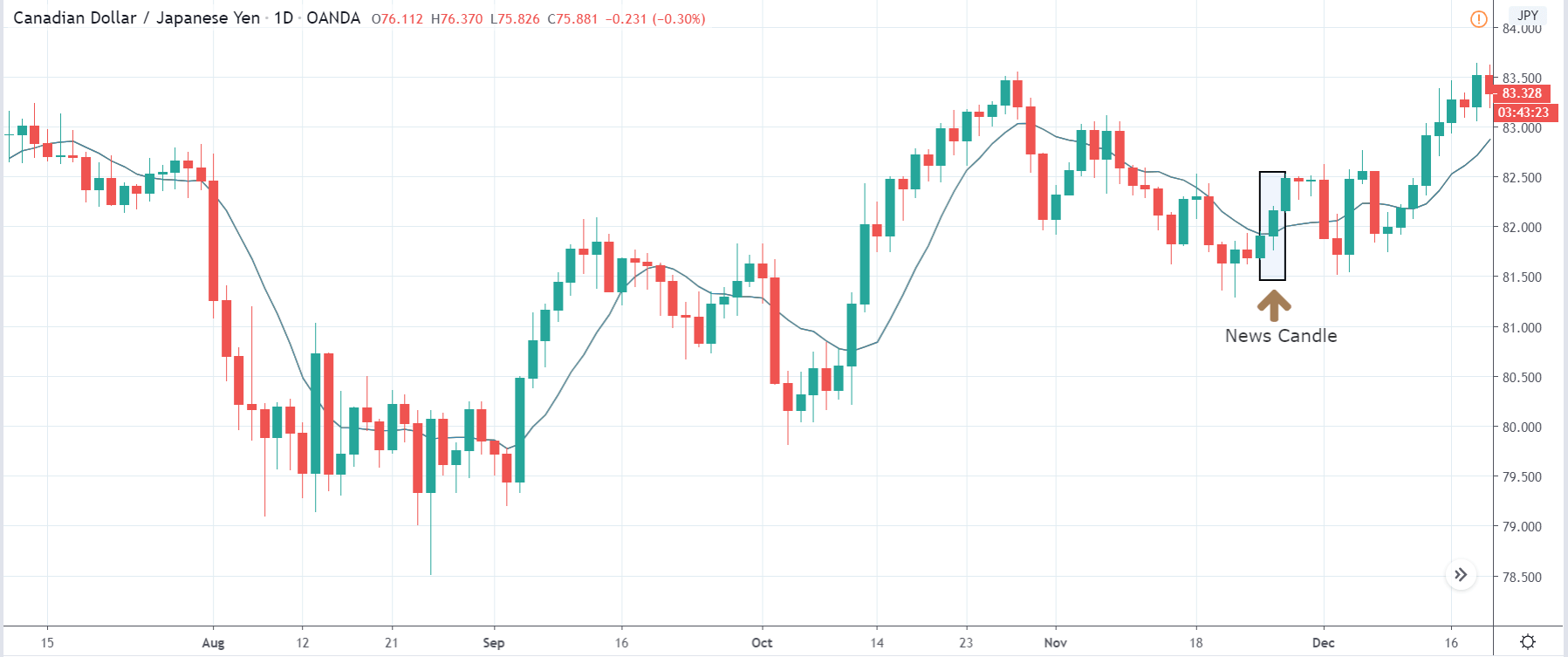
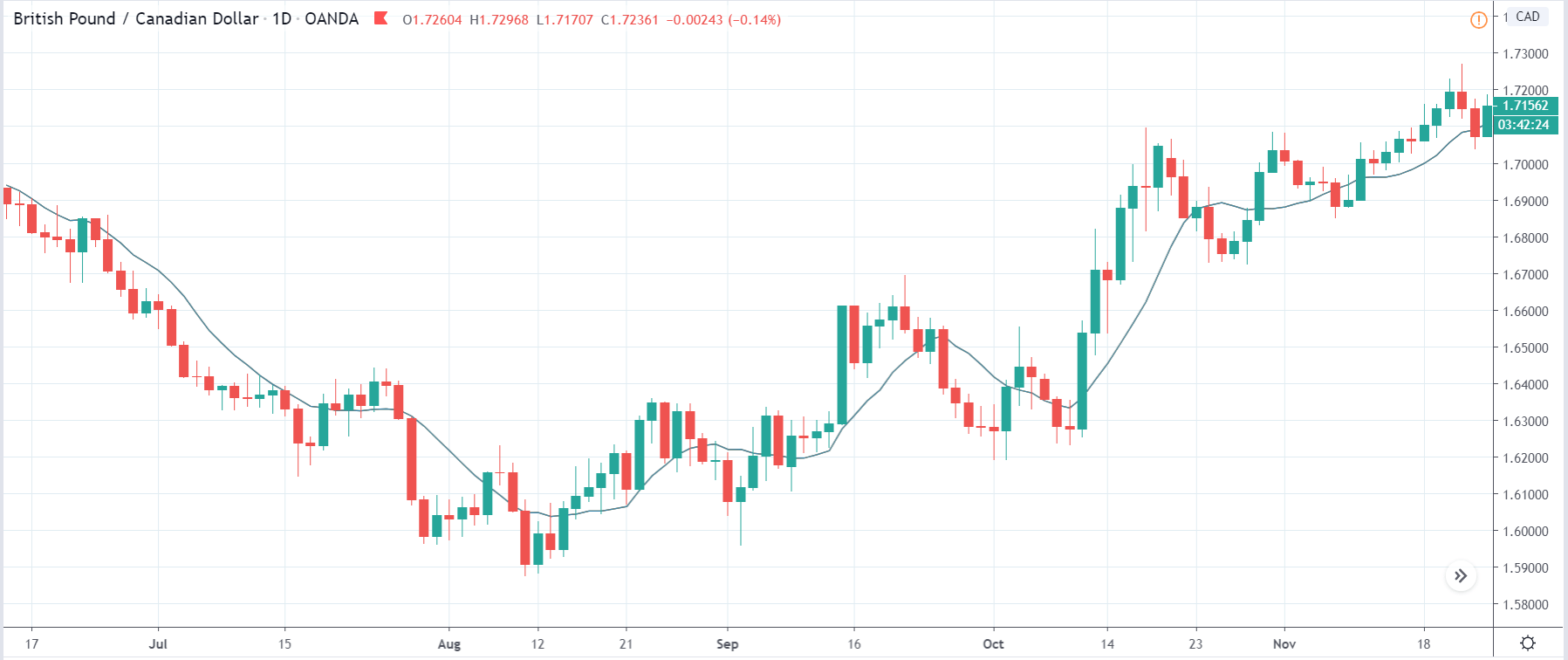
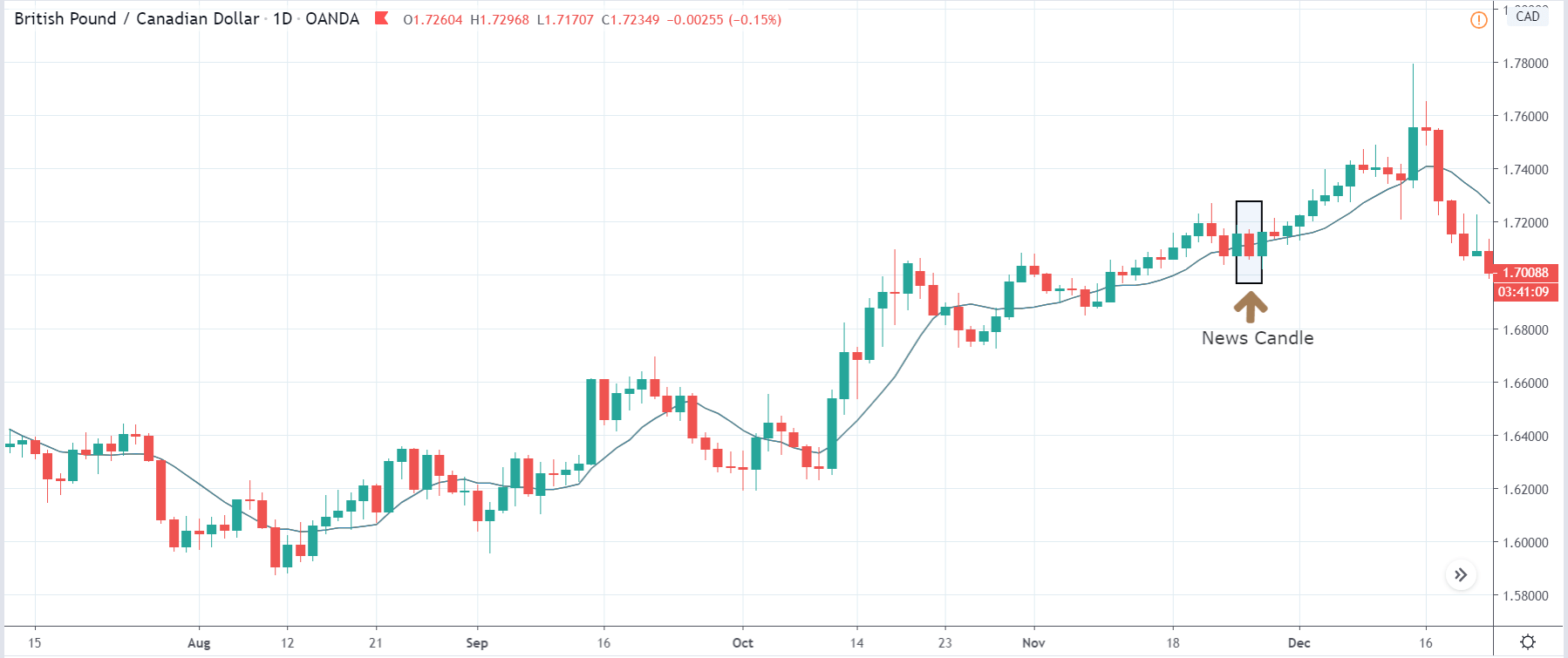
 In today’s lesson, we will analyze the impact of GDP on various currency pairs by observing the change in volatility before and after the news announcement. For that purpose, we have collected the GDP data of Canada, where the below image shows the month-on-month GDP data released recently. Let us find out the market’s reaction to this data.
In today’s lesson, we will analyze the impact of GDP on various currency pairs by observing the change in volatility before and after the news announcement. For that purpose, we have collected the GDP data of Canada, where the below image shows the month-on-month GDP data released recently. Let us find out the market’s reaction to this data.