If you are trying with any kind of financial market for a significant period of time, you will start testing and forming some kind of system. Then, inevitably, you will begin to focus on technical or fundamental analysis, or maybe a little of both. The perfect understanding of the difference between the two types of analysis is the most important issue you should focus on when trying to make a decision about what kind of trader you want to be.
First, a bit of a disclaimer…
No matter what type of analysis you decide to use, it can be cost-effective. However, none of these types of analysis is 100% guaranteed. The fact that you become a good analyst from a technical or fundamental point of view does not mean you will inevitably earn money. As traders, what we’re looking for is the most likely scenario, not working with certainty. The long-term look is what you should focus on, which really means that you make transactions focused on what is most likely to happen, knowing that will not always work.
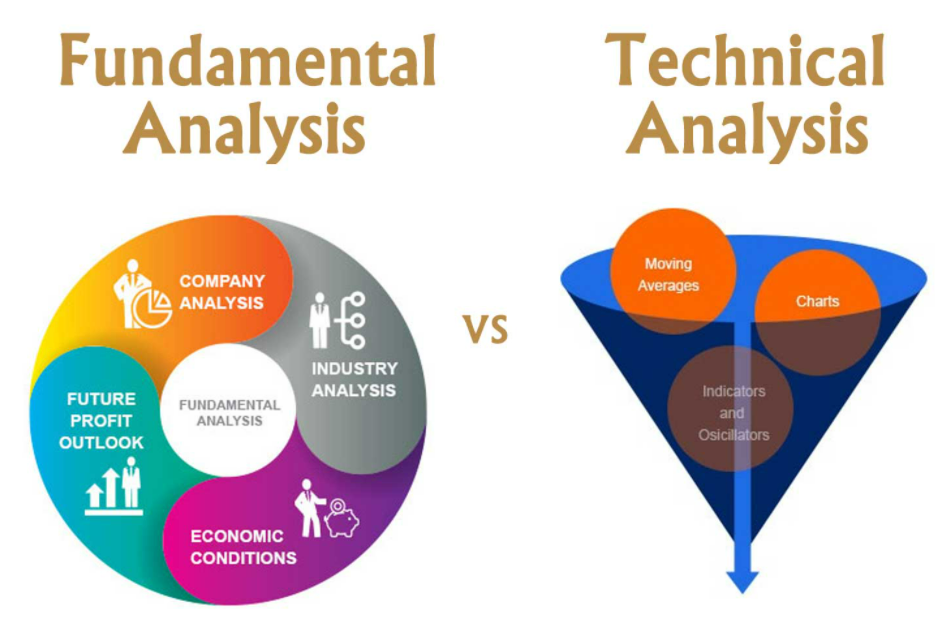
Technical Analysis
Most retail traders focus on technical analysis as it can be defined with some ease. What I mean by this is that it looks for things like support, endurance, trending lines, moving average crosses, and the like. For example, a trader who is using technical analysis to trade in the markets will observe the full share price.
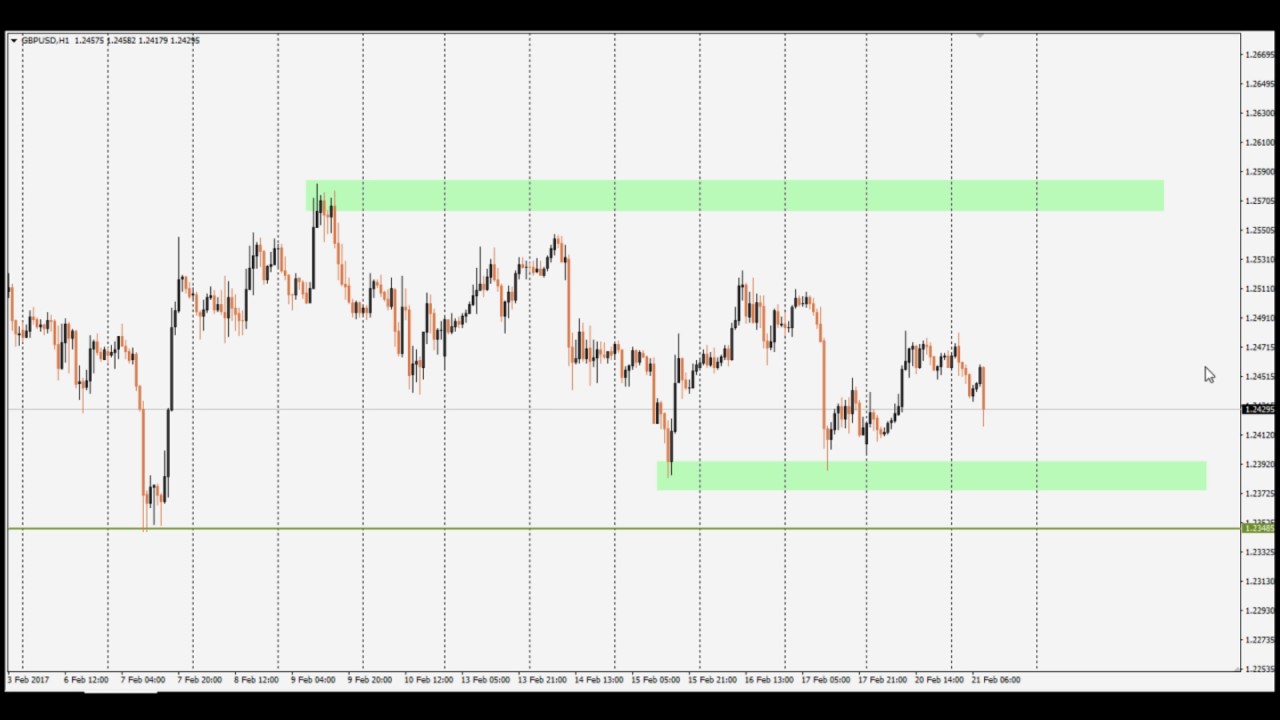
With technical analysis, you can get a configuration like the following:
The EUR/USD pair has been removed from the upward movement. By using your Fibonacci recoil tool, you acknowledge that we have withdrawn 50% of the maxima, which is an area in which most traders related to Fibonacci would be interested in going long. Beyond that, we have the exponential moving average of 200 days just below the candle on the daily graph, which of course shows support. Finally, the candle formed a hammer, which is also bullish.
A trading system based on a technical analysis tells the trader to prolong.
The trader based on technical analysis is paying attention to what the price does, not necessarily to what it should do. Just follow what the market tells you in terms of price, and this makes trading in financial markets a little easier. This is why you don’t have to think about many other variables other than what the price is making and whether or not it comes close to your technical configuration concept. If you choose any other factors to participate in trade, such as fundamental analysis, something we’ll get to in a moment, things can get a little more complicated.
Fundamental Analysis
The fundamental analysis focuses on economic factors and what a market “should do”. What I want to express with that is that you will take the figures and the economic announcements and try to find out where the price is going. On an equal footing, if interest rates rise in one country over another, then that currency should rebound over the other. For example, interest rates are expected to continue to rise in the United States at the same time as the ECB remains quiet for the foreseeable future. If that is the case, the EUR / USD pair should eventually fall based on interest rate spreads. There is a multitude of announcements that could be looking at, perhaps, GDP figures, employment, and, of course, the prospects for interest rates.
Ultimately, Forex tends to move in the direction of expected interest rate movements. However, there are other problems that may arise, such as geopolitical situations. For example, Brexit has wreaked havoc on the price of sterling for some time. This is because there are many doubts and not necessarily due to the prospect of the interest rate. In a sense, however, even that route will lead to interest rates, at least in the long term. The idea, of course, is that there is a lot of uncertainty about the British economy when they leave the European Union, and we do not know what they will do with EU-related trading.
The EU is, of course, the UK’s largest trading partner, so this could obviously have a significant negative effect on the UK economy. People are essentially fleeing the British pound because of fear, or the fact that they believe that the Bank of the UK will have to keep interest rates extraordinarily low as the economy slows down. In the end, even the most opaque reasons eventually lead to interest rates, although it may not necessarily be immediately apparent.
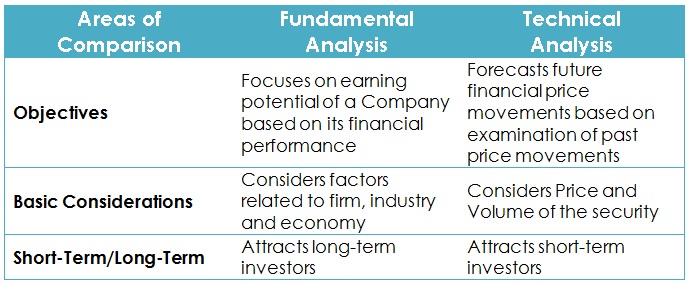
Fundamental Vs. Technical
The most typical way traders get involved in the market is a combination of both types. For example, by using Brexit as a backdrop, we know that the British pound has fought for some time. A technical trader will understand the basics of that situation and recognize that selling the British pound makes more sense in general.
They understand the fundamentals of the negative for the British pound, although they don’t get too involved with all the nuances of economic advertisements. They just know the feeling is negative. With that information, they then begin to look for patterns of the sale in chandeliers, failures in resistance, or some other type of scenario in which we break down the support as examples.
With the use of both types of analysis, although most traders using a mixture probably use technical analysis of about 80%, the reality is that it gives you a bias in which to trade with the market. After all, fundamental long-term biases determine exactly what determines the trend, while the technical analyst simply looks for signals to get involved.
There is no right way to operate in the currency market, although it must be borne in mind that technical analysis is much simpler than fundamental because, at the end of the day, fundamental analysis suggests what “should happen,” ignoring what appears on the chart. So, I think most people use a little of both to make their trading decisions.