Litecoin is one of the most popular cryptocurrencies today. The currency is a clone of Bitcoin and appears to ride on the popularity of the pioneer cryptocurrency. However, the crypto has its own merits – like being a ‘lighter’ version of Bitcoin and thus being used in day-to-day transactions. Litecoin is faster than Bitcoin – having a block time of 2.5 minutes compared to Bitcoin’s 10 minutes, meaning it’s quicker and easier for Litecoin miners to make money.
Litecoin was created in 2011 by Charlie Lee, a former Google engineer. He modeled it after Bitcoin but with certain modifications intended to help it scale compared to Bitcoin. At the time of writing, the currency has a per-token value of $69.54 and a market rank of #7 with a market capitalization of 4.59 billion.
In this piece, we’ll take a look into the nitty gritties of mining Litecoin.
#1. Mining equipment
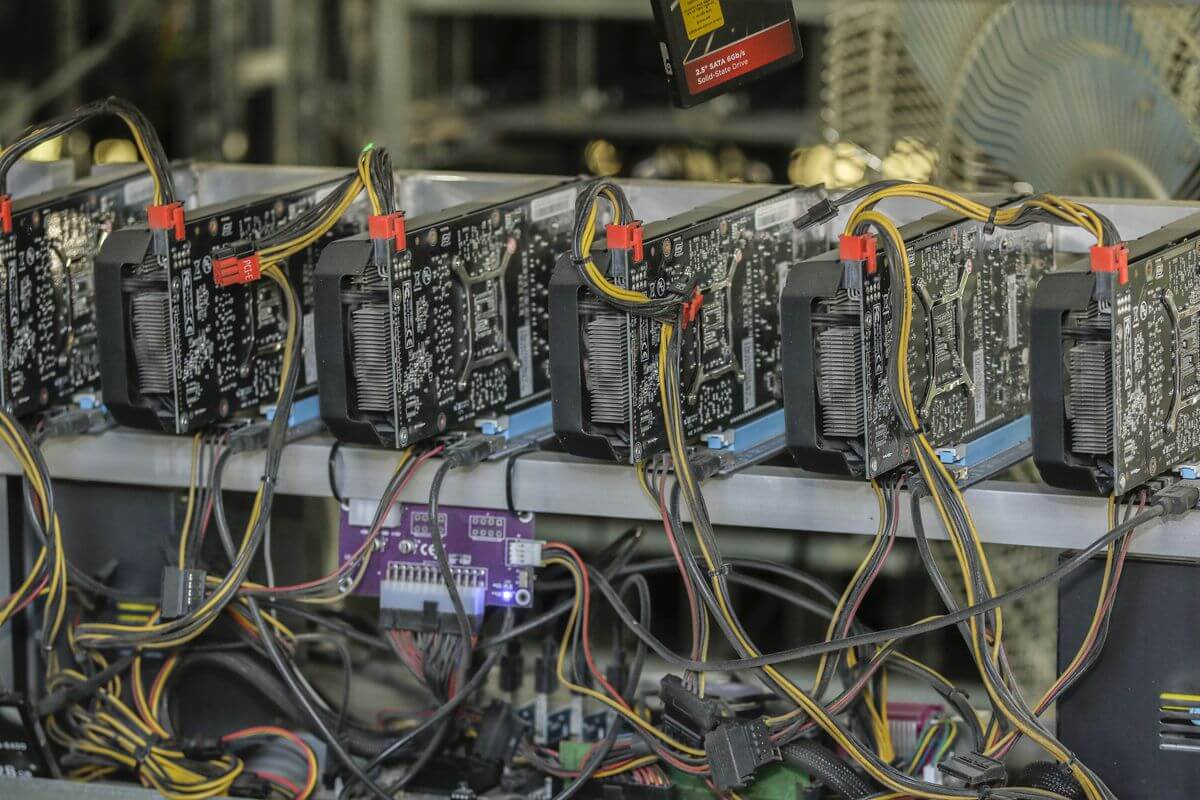
In the early days of Litecoin, the cryptocurrency could be mined using CPUs and GPUs. Litecoin uses the Scrypt hashing protocol – the first successful cryptocurrency to use it. Lee opted for Scrypt instead of Bitcoin’s SHA-256 due to the former being lighter and also because”using Scrypt allows one to mine Litecoin while also mining Bitcoin.”
However, it’s no longer possible to turn a profit when mining Litecoin with CPUs and GPUs. This is because as competition has ramped up for the currency, mining difficulty has increased, requiring miners to use application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) developed specifically for the currency. One of the most popular ASICs for Litecoin include Bitmain’s Antminer and LTCMaster. ASICs tend to go for around $1,000 for older models and around $2,000 for newer models. It’s best to go for the newer models, which are more effective.
#2. Should you join a mining pool?
Once you’ve identified which hardware to use, the next decision will be to mine solo or join a mining pool. A mining pool is a group of miners who share computing power to multiply the chances of finding a block and earn mining rewards. Mining alone means you will get to keep all the mining rewards plus a fraction of the transaction fees. (The current mining rewards are 12.5 LTC per block. This will be halved in the next Litecoin halving, which will happen in 2023). And even then, this will require that you have massive hash power (multiple ASIC machines). Mining with a single ASIC is almost guaranteed never to turn a profit.
By contrast, concentrated computing power in pool mining makes it many times easier for the pool to discover new blocks and attain a reward. The reward is then distributed according to the contribution of each miner. Bear in mind pool mining itself is not guaranteed to turn a profit since it depends on chance, but earnings via a pool are more steady than solo mining.
Before you join a mining pool, make sure to investigate it thoroughly. Some pools out there are outright scams, while others are just plain shady. Also, it’s not uncommon for a mining pool to fall victim to hacks. So always check a pool’s security history and how they handled any breaches, reputation, member reviews, and management team. Also, try not to keep large amounts of your proceeds with the pool. It’s good practice to transfer proceeds to your wallet as soon as possible.
Some of the most trusted and popular Litecoin pools out there include F2Pool, LitecoinPool.org, ViaBTC, and ProHashing.
Litecoin: Cloud Mining
ASICs and pools are not for everyone. Maybe you want to mine Litecoin and don’t have the means or desire to splurge on expensive hardware. Well, you’re in luck because there’s an option of cloud mining that allows you to pay a remote data center to do the mining for you.
With this option, you will be required to put up a certain amount of money – but not nearly as much as you would for an ASIC – to get access to the cloud mining platform. The more you invest, the more you stand to gain from the platform.
We can’t stress this enough – cloud mining is even more susceptible to scams than mining pools. There are individuals out there who are happy enough to take strangers’ money without an actual mining operation going on on their side. This behooves you to do serious research before getting entangled with any cloud miner. One of the most reputable cloud mining sites is Scotland-based Hashflare, which also has data centers in Estonia and Iceland. Hashflare has been around since 2014 – demonstrating its credibility and staying power.
Wallets
The last thing you need to consider is where to store your Litecoin. You have a variety of options starting with the Litecoin Core Client. This is a wallet by the Litecoin Foundation and is open-source, feature-packed, and updated regularly to make it more robust and easier to use. With the Litecoin Core Client, you can store, send, and receive Litecoin as well as view the transaction history of the blockchain. To use this wallet, you have to download the full blockchain on your computer. Of course, it will take up a lot of space, but it pays a lot of security dividends in the long run. The wallet supports Windows, MacOS, and Linux. By using Litecoin Core, you also contribute to the network’s security and decentralization since you’re running a ‘full node.’
You also have the option of a cold storage wallet. A cold wallet is one that’s not connected to the internet. This means it is unhackable, and hence very safe. If you have a large sum of Litecoin, a cold storage wallet is your best go-to option. There are also paper wallets that constitute a physical paper in the form of a QR code or a string of alphanumerics. A paper wallet is safer than an online wallet, but it’s vulnerable to theft and damage through fire, water, and wear and tear. You can increase your paper wallet security by laminating it and putting it in a safe place that only you know about. These days, people even strongly advocate for ‘brain wallets,’ which constitute memorizing a seed phrase that you can use to recreate your private key. Obviously, a brain wallet is the most secure of all these options.
Other people choose to keep their crypto funds on exchanges. Exchanges have the advantage of quickly swapping your crypto for fiat. However, this option is not recommended. That’s because exchanges are famously the target of hacking, and you can lose your money in the case of a security breach. Also, you have limited control over your Litecoin in such a wallet.
Final Thoughts
Litecoin is one of the most relevant cryptocurrencies, and investing in it through mining is a savvy move. Of course, there are risks to every profitable endeavor, so make sure to do your due diligence before you go all in.