Chainlink – Beginners Guide
During the long and hard crypto winter of late 2018, many projects failed to stay afloat, but during all this, Chainlink managed to actually keep growing and defied the bearish market. At the moment, Chainlink is one of the leading cryptocurrencies in the DeFi sector. How did it manage to grow as consistently, and what sets is apart?

Problem
Blockchains use math–cryptography and practically guarantee security, trust, and decentralization. However, the problem is that each blockchain is its own universe, which means that getting information from and to another blockchain would require a trusted source. To retrieve information about event outcomes or even something as simple as Bitcoin’s price meant that you are required to trust a source to tell the truth.
What is Chainlink?
Chainlink figured out how to get any type of information in and out of a blockchain while remaining secure and decentralized, but also trustless. Sources of data between the blockchain and the “outside” world, known as oracles, are no longer a single point of failure for a smart contract. Chainlink created a network of nodes that can provide information to and from the blockchain, which created a vital part of smart contract infrastructure as a result. This “blockchain middleware” meant that Chainlink oracles could provide essential information without sacrificing on decentralization or security.
Chainlink essentially created a secure bridge to the “outside” world.
To minimize the potential failure of the aforementioned oracles, Chainlink focused on the distribution of data sources, distribution of oracles, as well as the use of trusted hardware.
Origins of Chainlink

Chainlink was founded by the current CEO Sergey Nazarov and the current CTO Steve Ellis. The project started in Sept 2017, when the project raised $32 million in an ICO, thus creating 1 billion LINK tokens. In May 2019, Chainlink launched on the Ethereum mainnet. At the moment, Chainlink is the 7th largest cryptocurrency by market cap, as well as the largest DeFi cryptocurrency by market cap, and is very close to the $4 billion dollar mark.
Use Cases

Chainlink is different from most projects in terms of having real use cases, as it is demonstrated by its list of partners, with most notable being Polkadot and Synthetix from the crypto sector and SWIFT and Google coming from the traditional business world.
As an example, Chainlink could be used to send a real-world money transfer from SWIFT and via Chainlink. The proof the payment could then be sent back via Chainlink to SWIFT. This use of Chainlink by SWIFT has created a seamless interaction between the traditional world and the crypto world, all while minimizing the potential points of failure.
So how does it all work?
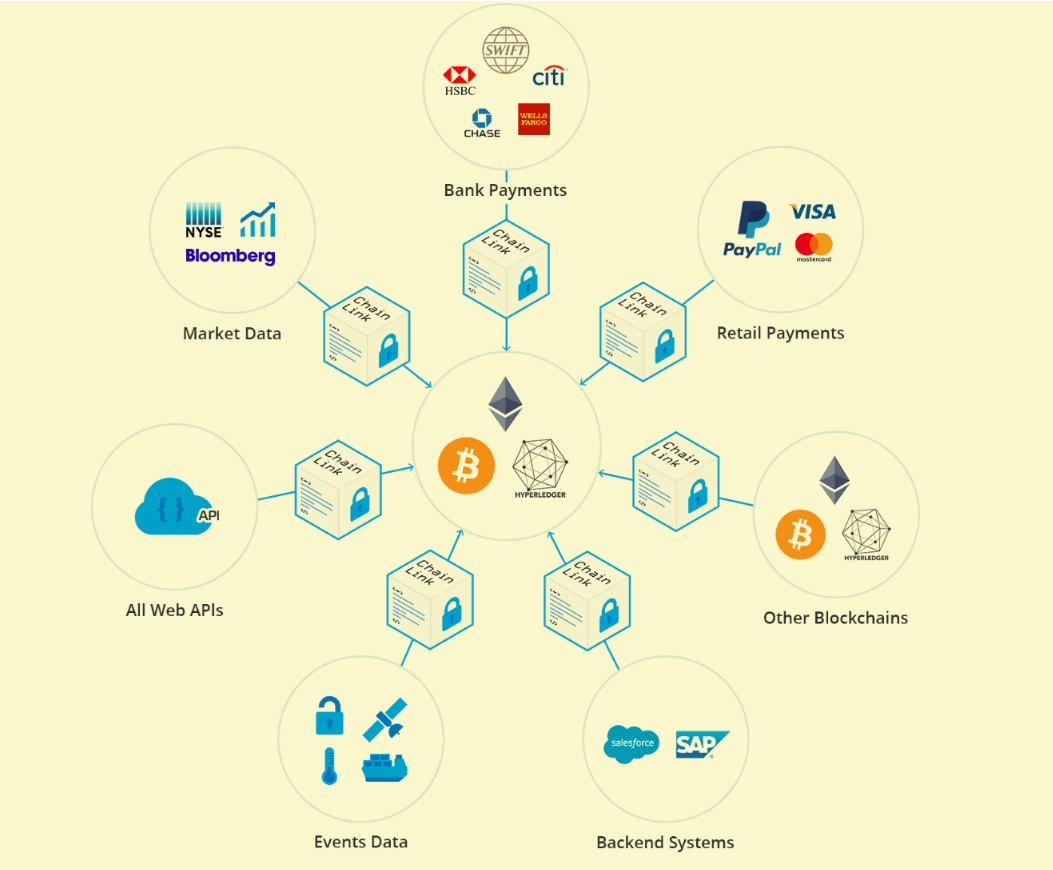
Chainlink can be defined as a decentralized oracle network that consists of purchasers and data providers. Purchasers request data, while providers return it in a secure way.
Purchasers select the data they want to obtain, while providers bid to provide that data. Providers have to commit a stake of LINK tokens when making a bid, which serves as proof that they are honest. Once providers are selected, their job is to bring the correct answers on the chain.
Chainlink uses something called “oracle reputation system” to aggregate as well as weigh the data provided. If everything goes well, providers get paid, and everyone is happy, but if the providers misbehave, they lose their stake.
How do you get Link tokens?
The Chainlink network uses an Ethereum-based ERC-677 token that inherits the ERC-20 token standard’s functionality while allowing token transfers to contain a data payload. This token protocol is also used for payment of data providers who are bringing and translating data into the blockchain.
Besides earning LINK tokens by being a provider, you can also buy LINK tokens on various exchanges, such as Coinbase, Binance, and Huobi.
The Future of Chainlink

Two of the key objectives Chainlink focused on to ensure the security of its network are the distribution of data sources and the distribution of oracles. Like all networks, Chainlink’s main goal is to add more people and operators to become more robust and valuable.


