Many trading strategies or systems that we are familiar with, are based or based on technical analysis or indicators. Unlike these strategies, Carry Trade is a fundamentally based strategy. Carry trade, also sometimes known as a financial bicycle, is a strategy that allows you to take advantage of the existing differential in interest rates of two different currencies.
Although it is a fairly short and simple definition we must have very clear a very important concept of fundamental analysis in Forex such as interest rates. As you know, each currency represents the economy of a country as a whole. All right, interest rates are one of the most important fundamental indicators for analyzing the state of a country’s economy and, therefore, the strength or weakness of its currency.
Interest rates generally set the cost of money, that is, the price we pay for using a certain amount of capital for a certain amount of time. It’s very important for you to know, one of the most important economic news stories that are usually published and affect the price of the currency in question is interest rates.
You should not confuse carry trade with financial arbitration. Arbitrage is a strategy that consists of obtaining an economic benefit by taking advantage of the price difference of a financial asset in different markets. And unlike carry trading, in arbitration, the risk is very low.
Foundations of a Carry Trade
As mentioned above, the spread in interest rates between two currencies offers traders and investors the opportunity to win over the long term. The main idea of any carry trade strategy is very simple: the investor finances or borrows a currency with a low-interest rate (weak economy), sells this currency, and buys another with a higher interest rate (strong economy).
Now, how do we know if an economy is strong or weak? There are several factors that affect interest rates, but inflation or inflation prospects is one of the most important. A strong or solid economy has good GDP growth (Gross Domestic Product) and good employment data, if people consume more goods and services, there is greater demand and inflation increases. To control the increase in inflation and keep it within the target range, the Central Bank of that country has to raise interest rates to limit inflation. By raising the interest rate, the country becomes more attractive for attracting foreign investment and this results in the revaluation or strengthening of that country’s currency.
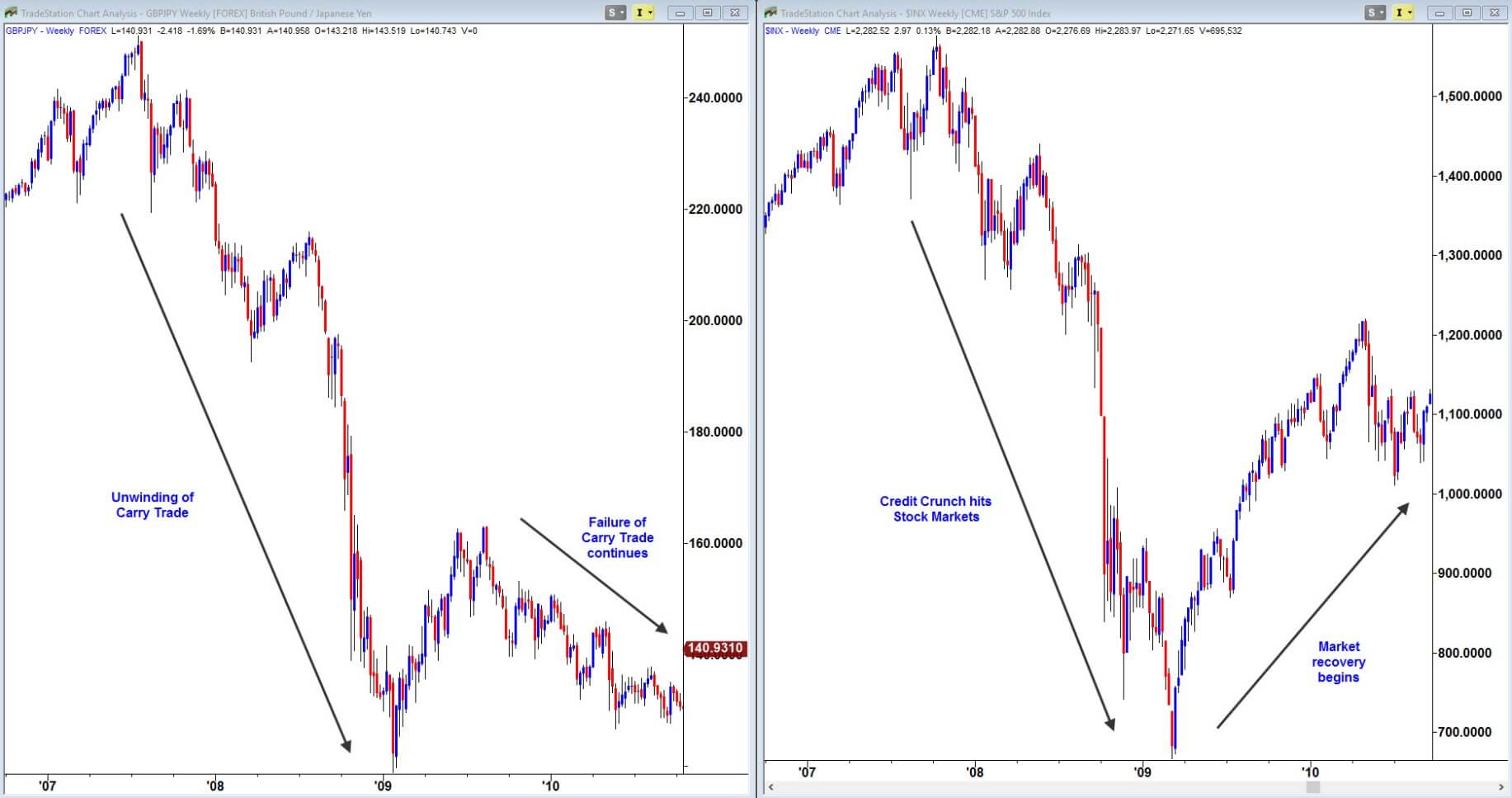
On the contrary, if an economy is weak or grows very little, has poor data on GDP and employment, consumption of goods or services is low and that country cannot afford to have such a strong currency. The central bank must reduce or keep interest rates very low, thus incentivizing credit since it is cheaper for companies to borrow. As a result, investors will want to take their money to another country with better interest rates by making the local currency devalue or weaker.
Watch this because now countries with the current situation have started to lower rates and print money for free and even the US. that can be considered a strong economy has very low-interest rates. Same situation in Europe with the policies of the European Central Bank.
The Objective of the Carry Trade Strategy
The carry trade has a clear objective: to obtain benefits from the spread of interest rates and not from the variation of prices that can be given during the execution of this strategy. Therefore, benefits can be derived from this strategy, although the price of the currencies involved does not vary by a single pip.
However, as traders, we hope that the currency in which we invest will be strengthened so that by exchanging it for the currency we borrow (we finance) the profit obtained will be greater.
Some Disadvantages of the Carry Trade
One of the disadvantages of this strategy, as you may have already thought, is the risk that the currency in which you buy will be devalued. This is largely due to the fact that the most common practice of a carry trade is to finance or borrow from developed countries with strong economies to invest in debt securities (bond market) of emerging countries with higher yields.
Another disadvantage of this strategy is that there is uncertainty about the maintenance of current interest rates in the future. As a long-term strategy, interest rates tend to vary over the course of the year (in fact we are seeing it recently) and although these variations are small the final benefit will depend on these small variations that can be made by the central bank of each country.
A Practical Example of a Carry Trade
One of the main currencies that traders used to enhance carry trade is the Japanese yen because of its very low (near zero or even negative) interest rates. This has changed because currencies with the euro or the dollar already have very low-interest rates as well. Previously, they borrowed the Japanese yen and then bought or invested in assets denominated in dollars, euros, or other currencies of emerging economies.
Let’s imagine now that we want to carry trade and provide the differential between the interest rates of Japan’s economy (with interest rates of 0%) and the economy of an emerging country like Brazil (with interest rates of 7%). The process would be roughly like described below:
-We borrowed 10,000,000 yen at an interest rate of 0%, which means that within a year we would have to pay back 10,000,000 yen.
-We sell the 10,000,000 yen and buy dollars at an exchange rate of 100 yen to the dollar and in this way we get 100,000 dollars.
-We sell the dollars obtained and buy Brazilian real at an exchange rate of R$ 3 per dollar, obtaining R$ 300,000.
-With the Brazilian real we buy bonds or bills of the Brazilian central bank with an annual maturity and an annual yield of 7%. Within a year we will receive 321,000 reais (capital plus interest).
-Now we must pay the initial credit by returning the 10,000,000 Japanese yen we borrowed. Assuming the exchange rates have not changed, we exchange real to dollars and get $107,000. Then we change the dollars into yen and get 10,700,000 yen.
-Finally, we return the 10,000,000 yen of the initial credit and we have 700,000 yen (equivalent to 7,000 dollars) of benefit.
In this way, we have obtained a profit-based exclusively on the deference of interest rates. In this example, we assume that exchange rates remain constant, but what would happen if, for example: does the Japanese yen revalue and after a year go from 100 yen to the dollar to 90 yen to the dollar?
In this case, by exchanging the $107,000 obtained to yen we will receive 9,630,000 yen. We must pay the initial loan of 10,000,000 yen, therefore, we would have a loss of 370,000 Japanese yen that would be equivalent to a loss of 3.7% in the carry trade operation.
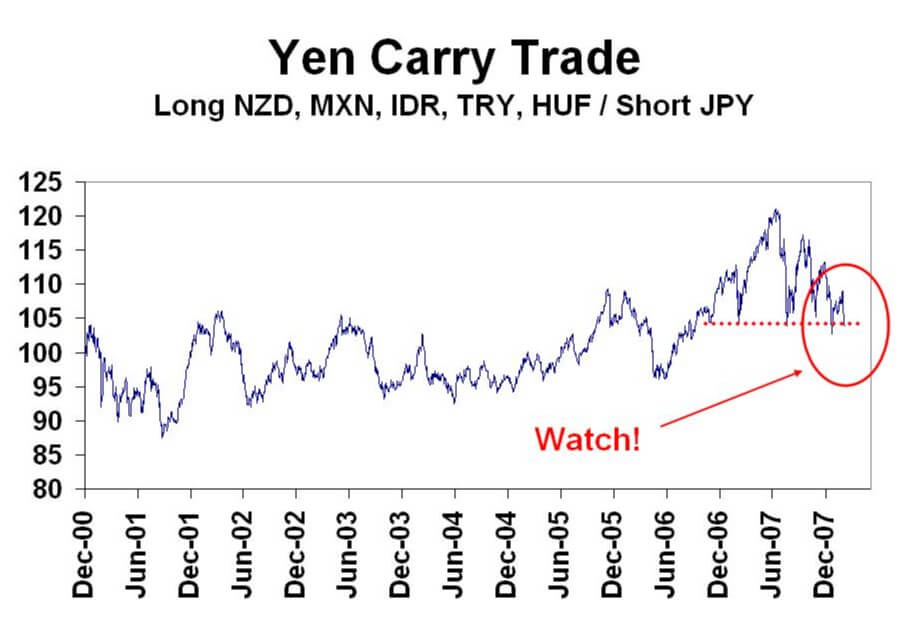
Risks Associated with a Carry Trade
As we saw in the example above one of the most important risks for the foreign exchange trader or investor arises when exchange rates do not move in their favor, that is, the currency you borrowed is revalued or the currency is devalued in the money you borrowed was invested.
There is another risk, which is associated with the choice of the asset to invest in since we can invest in the bond market, equity market, or real estate market. In the case of shares or the real estate market, we do not have a guaranteed return and in the case of the fixed income market, there is always the risk of default by the issuer of the bonds.
How to Use Carry Trade in the Forex market to Maximize Profits
In the Forex market when we open a position, we’re basically borrowing one currency, trading it for another, and depositing it. All this happens on a daily basis, so if a trade remains open from 5 pm, New York time, the trader will be paying the overnight interest rate on the borrowed currency and at the same time earning the interest rate on the held currency.
Because each currency pair is made up of two currencies representing two economies with two different interest rates, most of the time there will be a spread in the interest rates of the pair. This difference will result in a net gain or interest payment. Interest is paid in the currency borrowed (sold) and paid in the currency purchased. In this way, each currency pair has an interest payment and an interest charge associated with maintaining the position.
This means that if we buy a currency with a higher interest rate than the borrowed currency (sale), and keep it open after 5 pm, New York time (23:00h Spain), the net interest rate differential will be positive and we will make money with this. Otherwise, if the currency we buy has a lower interest rate than the borrowed currency, the net spread will be negative and we will pay interest to keep that transaction open after 5 pm (New York time).
This interest rate differential that we earn or must pay, you can find it on your trading platform under the name of Swap or Rollover. In the specifications of each currency, we will have a long position swap (buy) and a short position swap (sell).
In order to use this strategy in practice we must take into account the following:
1. Find currency pairs with a positive swap
You can see this information on the website or on your broker’s platform. If you use Metatrader you have it easy, you can see it by right-clicking on the asset in question in “contract specification”.
2. Conducting a favourable swap transaction
Once we have located an opportunity (this is easy) you should not do an operation for no reason. The idea is to make a transaction through a profitable system and also that the swap is favorable to you. The swap will generate a daily plus and in the event that the transaction leaves by stop loss (loss) will be less. And if the operation is profitable it will be greater. It is a plus in our operation.
3. More medium-term long-term vision
Keep in mind that the time in this type of operation is in your favor so keep in mind that these operations are not short-term and are raised to get the juice from them during their duration.
4. Sound risk assessment and capital management
As with any other type of trading system and trades, before you open a trade make sure you know what percentage of the account you can lose. Do not be optimistic because the swap is favorable, the operation can go against you shortly after opening it, and if you have not measured the risk well you can have a bad time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tell you that carry trade is a strategy based on fundamentals that try to profit from the difference between currency pairs and the interest rates. Therefore, you should be very clear that interest rates are and what fundamental factors affect them.
It is a long-term lake strategy so patience is key to getting the desired results. Despite being a long-term operation, this doesn’t mean you can open an operation and forget about it. It is necessary to monitor interest rates and possible changes in the rates and monetary policies of the central banks of the disputed currencies in such a pair.
Exchange rate risk is a critical factor in the carry trade, which is why this strategy works well in periods of low volatility. On the contrary, you should always bear in mind that carry trade is a high-risk trading strategy in periods of instability such as the current one. However, if the swap significantly affects your operation you can consider the operation to exploit only the positive swap part.

